A Facile Method to Prepare a Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Metal Surface by Peptide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
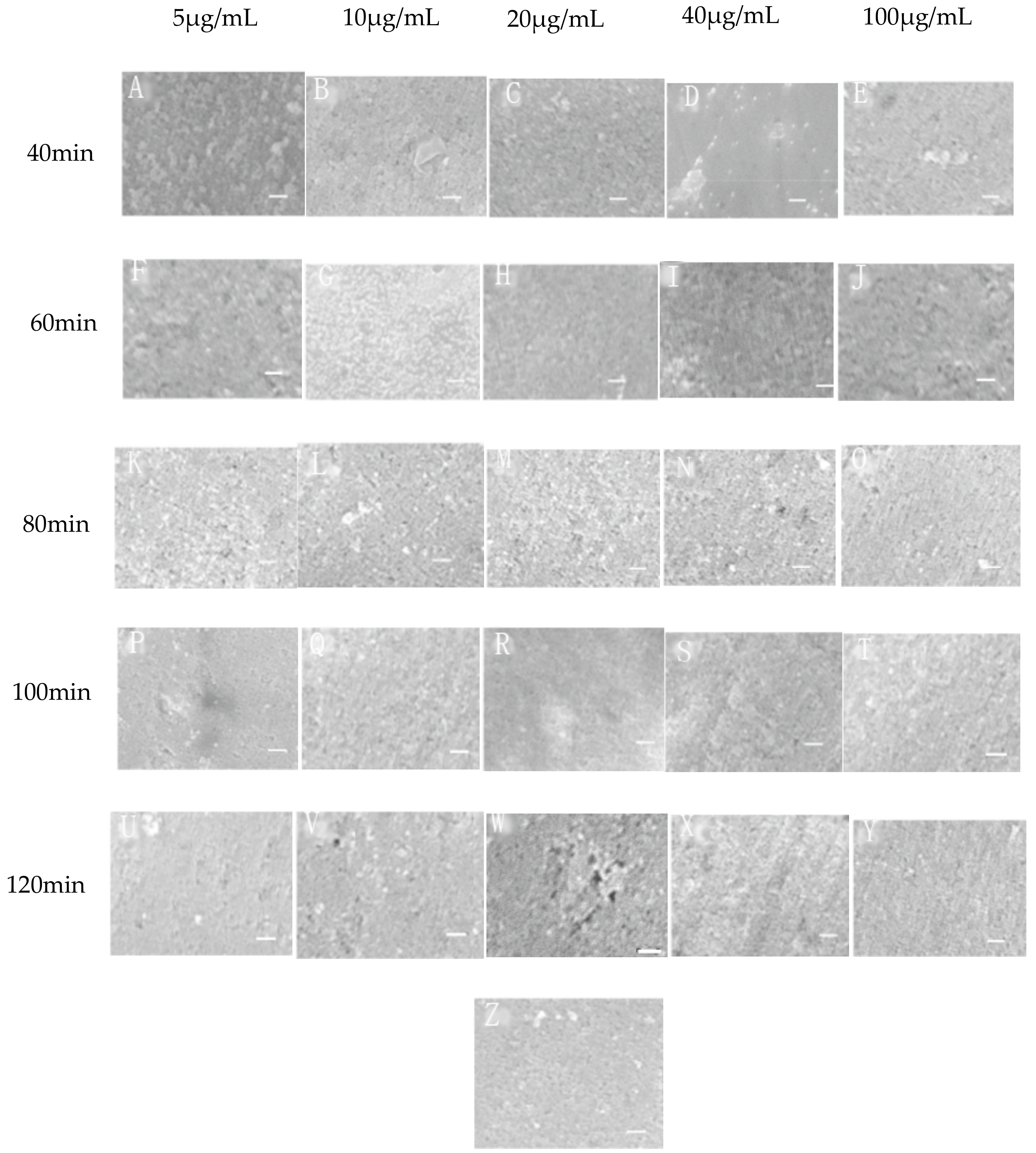
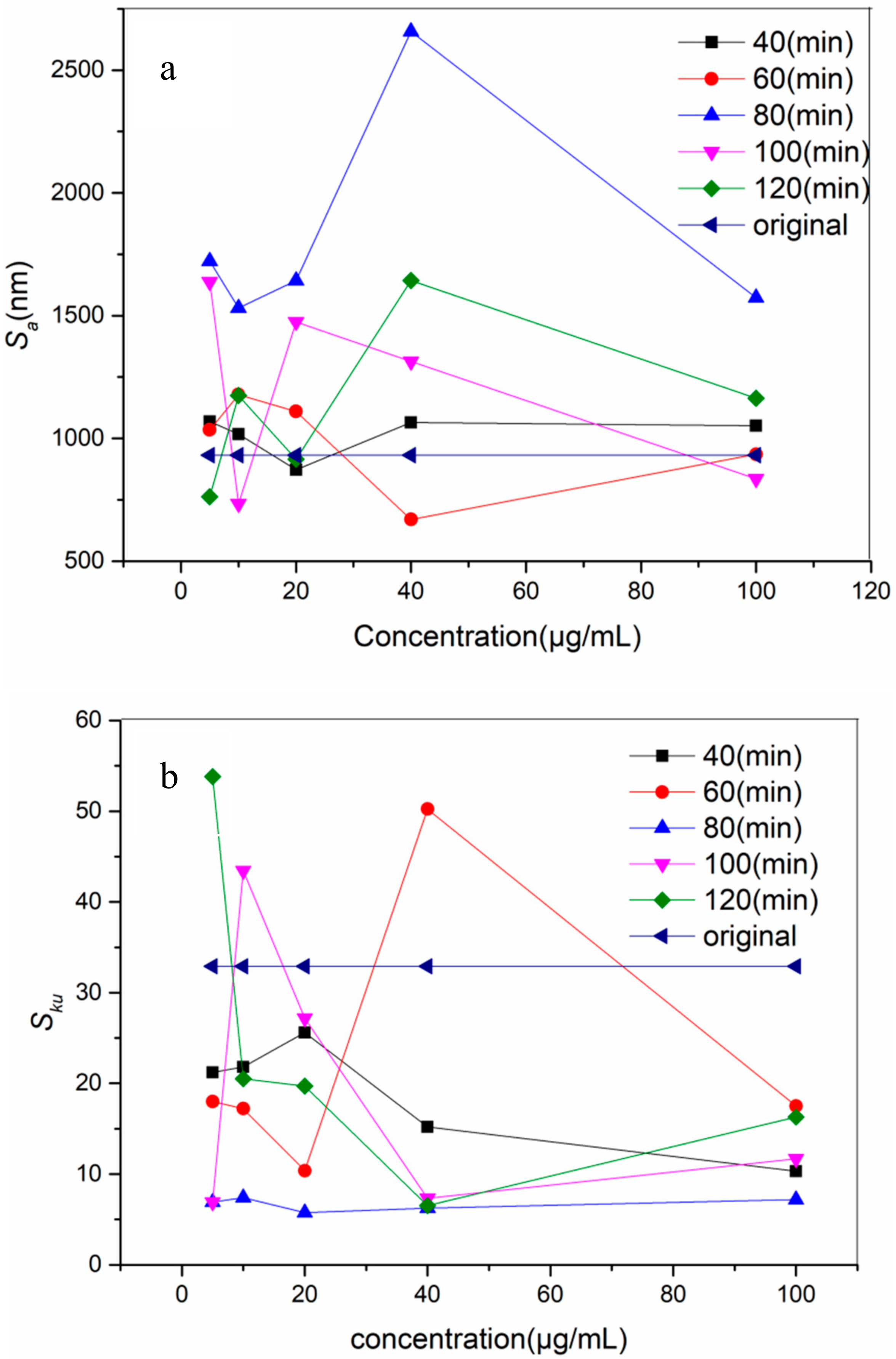
3.1. Surface Topography and Roughness
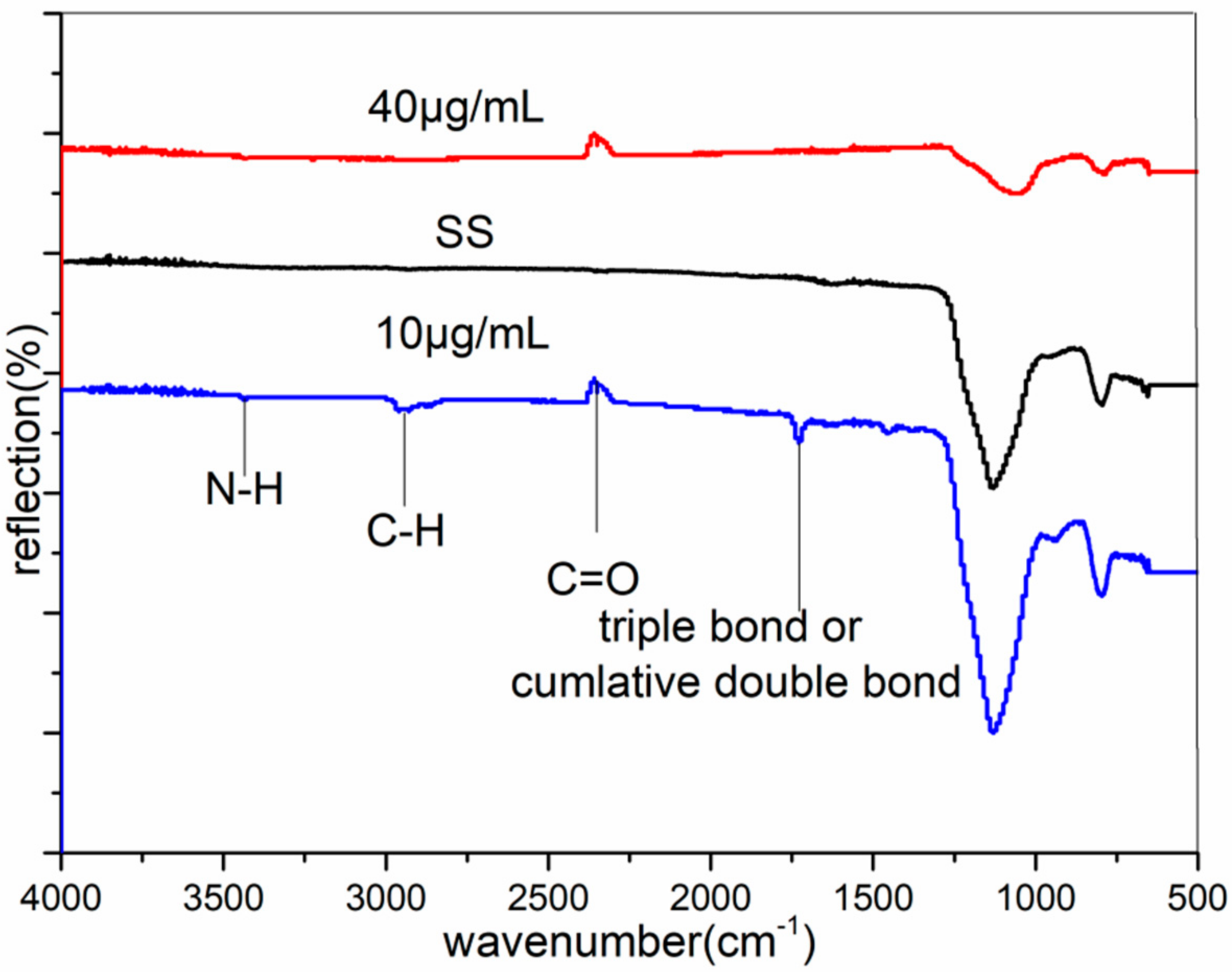
3.2. FTIR Analysis
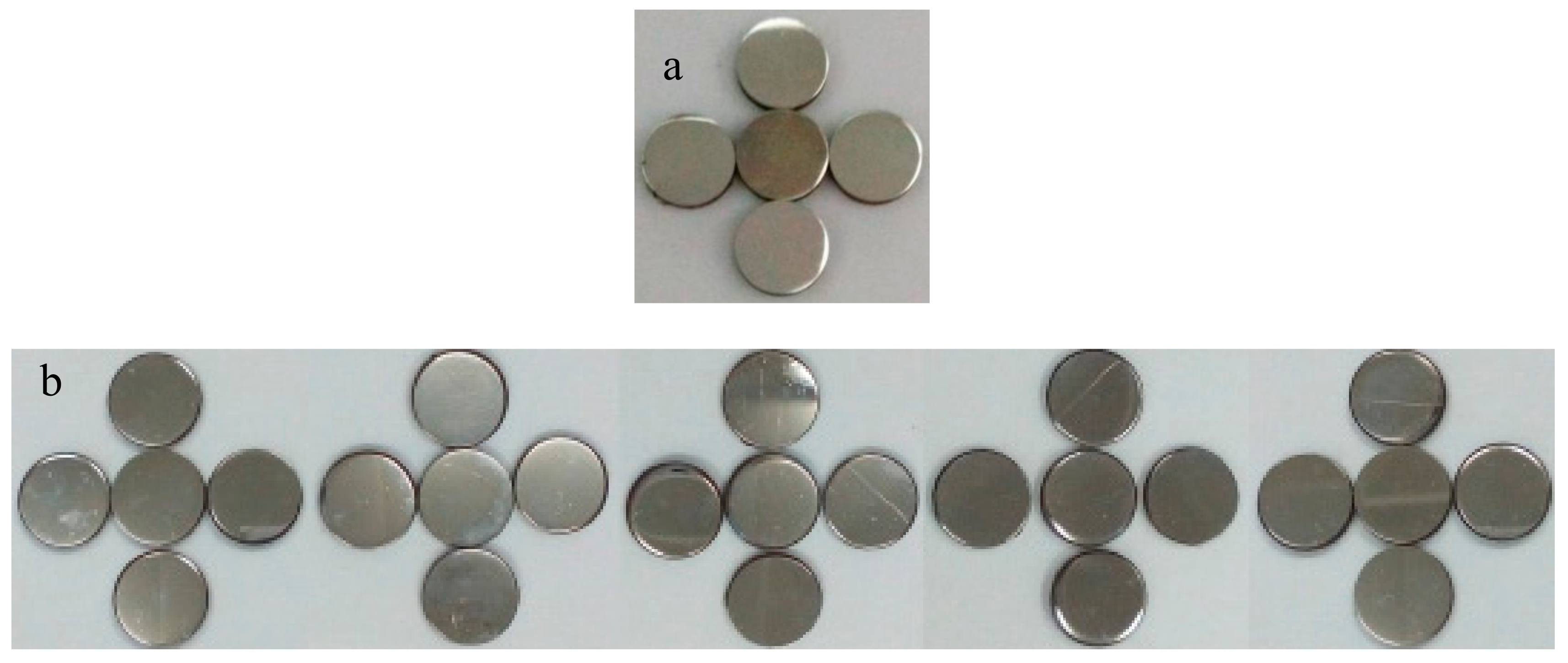
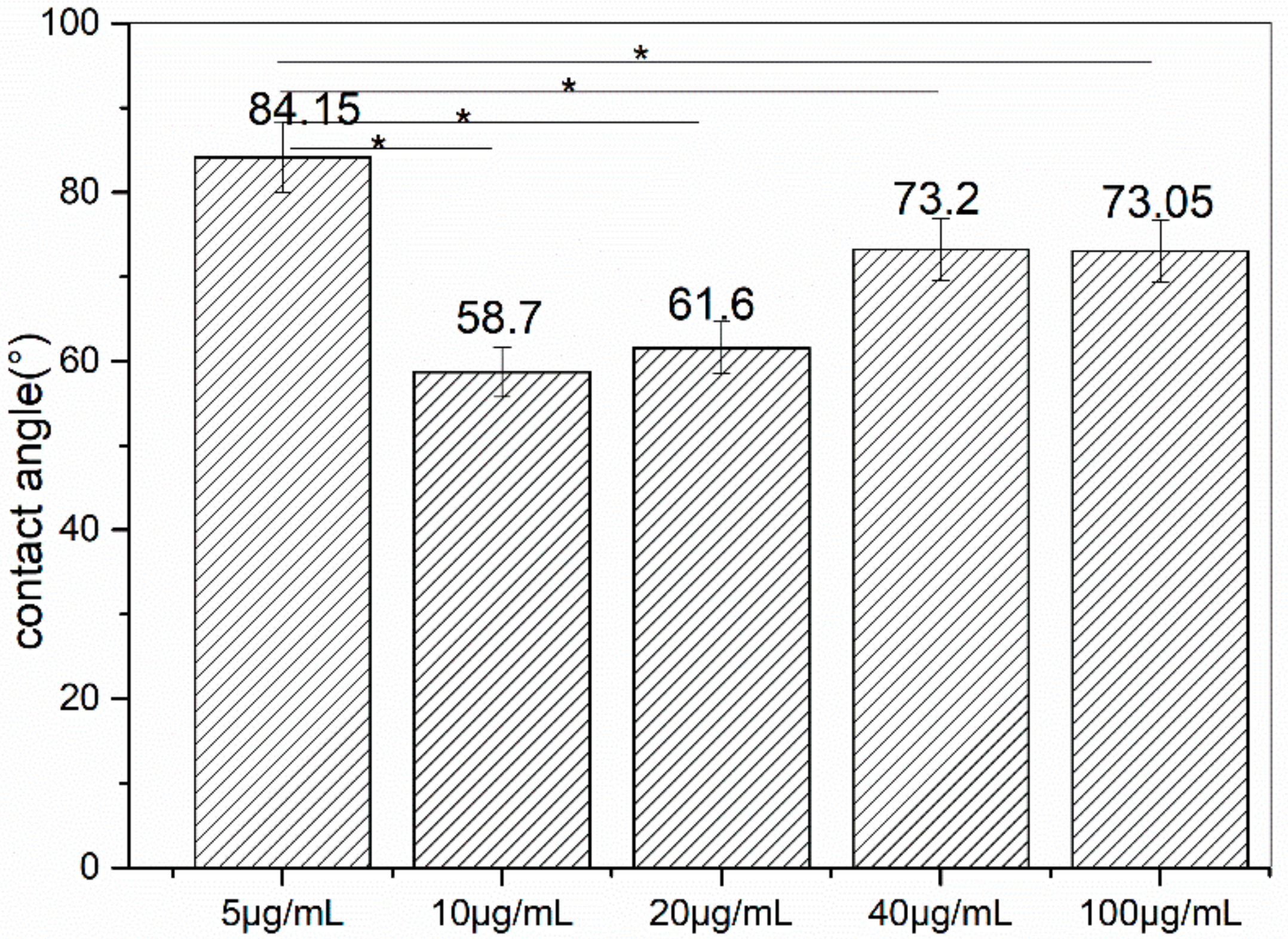
3.3. Measurement of Water Contact Angle
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- A metal binding-peptide could modify the metal surface properties.
- (2)
- The optimal incubating time and concentration was 80 min and 10 μg/mL.
- (3)
- The modified metal has the same hydrophobicity with the metal binding-peptide.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnold, J.W.; Bailey, G.W. Surface Finishes on Stainless Steel Reduce Bacterial Attachment and Early Biofilm Formation: Scanning Electron and Atomic Force Microscopy Study. Poult. Sci. 2000, 79, 1839–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, R.J. Biofilms: Strategies for metal corrosion inhibition employing microorganisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 76, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowski, Z.; Beyenal, H. Fundamentals of Biofilm Research, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 3–4. ISBN 978-1-4665-5960-8. [Google Scholar]
- Kanematsu, H.; Barry, D.M. Biofilm and Materials Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 147–169. ISBN 978-3-319-14564-8. [Google Scholar]
- Buskens, P.; Wouters, M.; Rentrop, C.; Vroon, Z. A brief review of environmentally benign antifouling and foul-release coatings for marine applications. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2013, 10, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briand, J.F. Marine antifouling laboratory bioassays: An overview of their diversity. Biofouling 2009, 25, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, S.; Müller-Steinhagen, H. Tailored surface free energy of membrane diffusers to minimize microbial adhesion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 230, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, E.; Diamantino, T.C.; Sousa, O. Marine paints: The particular case of antifouling paints. Prog. Org. Coat. 2007, 59, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, N.; Zeng, H.B.; Wu, J.P. Marine mussel adhesion: Biochemistry, mechanisms, and biomimetics. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 2139–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, M.S.; Shenashen, M.A.; El-Safty, S.A.; Higazy, S.A.; Selim, M.M.; Isago, H.; Elmarakbi, A. Recent progress in marine foul-release polymeric. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 87, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, R.J.; Ornek, D.; Wood, T.K. Aluminium- and mild steel-binding peptides from phage display. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 68, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seker, U.O.; Demir, H.V. Material Binding Peptides for Nanotechnology. Molecules 2011, 16, 1426–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Cao, P. Research status of anti-biofouling metal material modified by peptides. Mater. Mechan. Eng. 2014, 38, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, M.P.; Bendick, J.A.; Holm, E.R.; Hertel, W.M. Economic impact of biofouling on a naval surface ship. Biofouling 2011, 27, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, L.D.; Stokes, K.R.; Walsh, F.C.; Wood, R.J.K. Modern approaches to marine antifouling coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 3642–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanematsu, H.; Barry, D.M. Corrosion Control and Surface Finishing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Diego, M.Y.; Søren, K.; Kim, D.J. Antifouling technology—Past, present and future steps towards efficient and environmentally friendly antifouling coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 50, 75–104. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.J.; Song, J.L.; Sun, J. Progress in Fabrication and Application of Superhydrophobic Surfaces on Metal Substrates. Mater. Eng. 2011, 5, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S.; Sarikaya, M.; Johnson, E. A genetic analysis of crystal growth. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 299, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slocik, J.M.; Stone, M.O.; Naik, R.R. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles using multifunctional peptides. Small 2005, 1, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Rheem, Y.; Yoo, B.; Chong, Y.; Bozhilov, K.N.; Kim, D.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Hur, H.G.; Myung, N.V. Peptide-mediated shape- and size-tunable synthesis of gold nanostructures. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2681–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, R.R.; Stringer, S.J.; Agarwal, G.; Jones, S.E.; Stone, M.O. Biomimetic synthesis and patterning of silver nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 2002, 1, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, K.T.; Lee, Y.J.; Krauland, E.M.; Kottmann, S.T.; Belcher, A.M. Peptide-mediated reduction of silver ions on engineered biological scaffolds. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 1480–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Whyburn, G.; Huang, Y. Specific peptide regulated synthesis of ultrasmall platinum nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 15998–15999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Mao, J.; Zhou, B.; Wei, W.; Gong, S. Peptide aptamers against titanium-based implants identified through phage display. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umetsu, M.; Mizuta, M.; Tsumoto, K.; Ohara, S.; Takami, S.; Watanabe, H.; Kumagai, I.; Adschiri, T. Bioassisted room-temperature immobilization and mineralization of zinc oxide—The structural ordering of ZnO nanoparticles into a flower-type morphology. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 2571–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togashi, T.; Yokoo, N.; Umetsu, M.; Ohara, S.; Naka, T.; Takami, S.; Abe, H.; Kumagai, I.; Adschiri, T. Material-binding peptide application-ZnO crystal structure control by means of a ZnO-binding peptide. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 111, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolpert, M.; Hellwig, P. Infrared spectra and molar absorption coefficients of the 20 alpha amino acids in aqueous solutions in the spectral range from 1800 to 500 cm−1. Spectrodchim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2006, 64, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, A. Infrared spectroscopy of proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1767, 1073–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vreuls, C.; Zocchi, G.; Genin, A.; Archambeau, C.; Martial, J.; Van de Weerdt, C. Inorganic-binding peptides as tools for surface quality control. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2010, 104, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, E.M.; Li, D.Y.; Irvin, R.T. A peptide- stainless steel reaction that yields a new bioorganic e metal state of matter. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 5311–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Y.H.; Li, X.S.; Yang, J.Y.; Que, G.H. Influence of surface free energy on the adhesion of marine benthic diatonm Nitzscha closterium MMDL533. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Amino acid sequence and number | NLNPNTASAMHV 12 |
| Aliphatic index | 73.33 |
| Isoelectric point (pI) | 6.74 |
| Molecular Weight | 1268.4 |
| GRAVY | −0.275 |
| formula | C52H85N17O18S1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, C.; Yuan, C.; Cao, P. A Facile Method to Prepare a Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Metal Surface by Peptide. Materials 2018, 11, 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081289
Ma C, Yuan C, Cao P. A Facile Method to Prepare a Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Metal Surface by Peptide. Materials. 2018; 11(8):1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081289
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Chunying, Chengqing Yuan, and Pan Cao. 2018. "A Facile Method to Prepare a Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Metal Surface by Peptide" Materials 11, no. 8: 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081289
APA StyleMa, C., Yuan, C., & Cao, P. (2018). A Facile Method to Prepare a Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Metal Surface by Peptide. Materials, 11(8), 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081289





