Debinding and Sintering of an Injection-Moulded Hypereutectic Al–Si Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
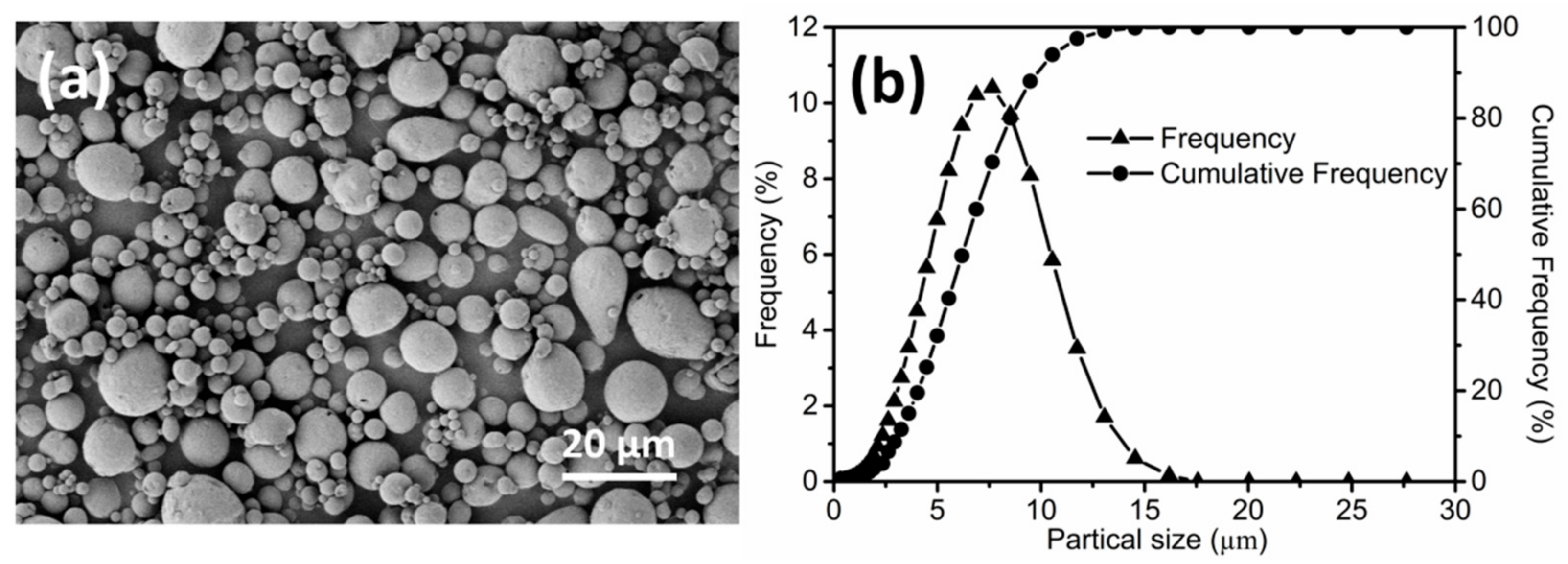
3. Results and Discussion
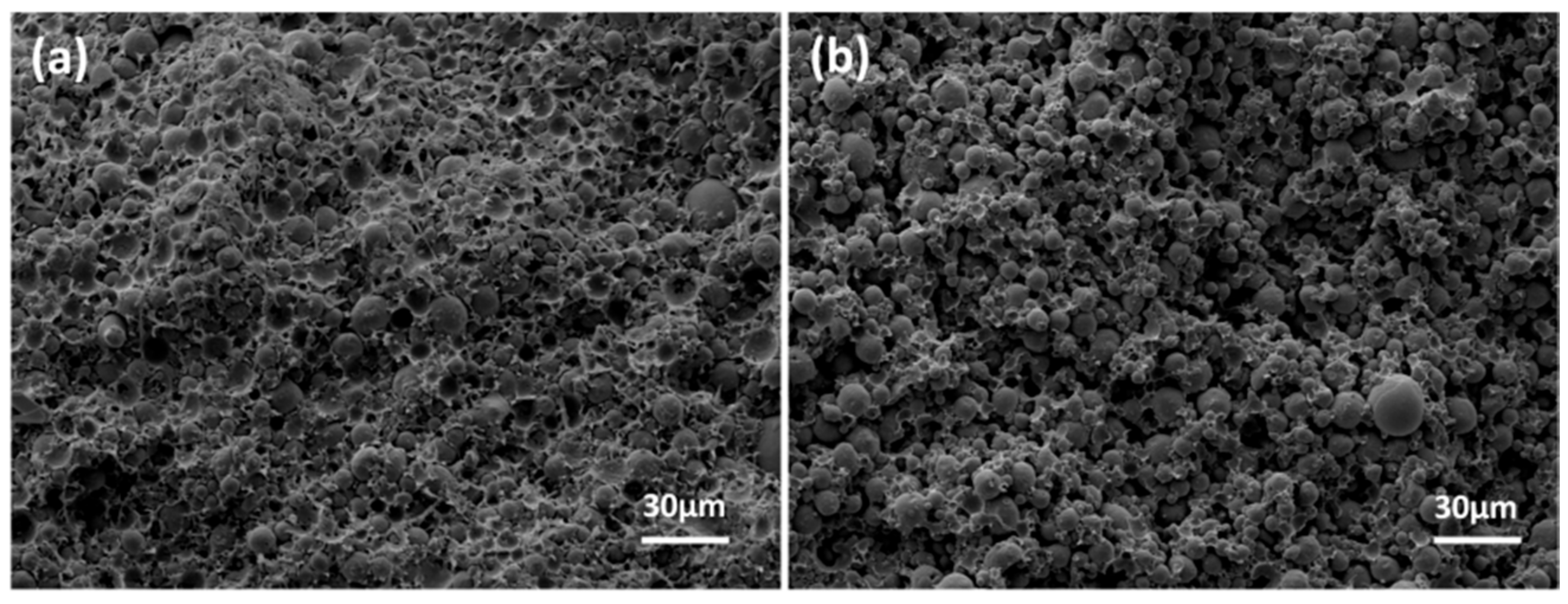
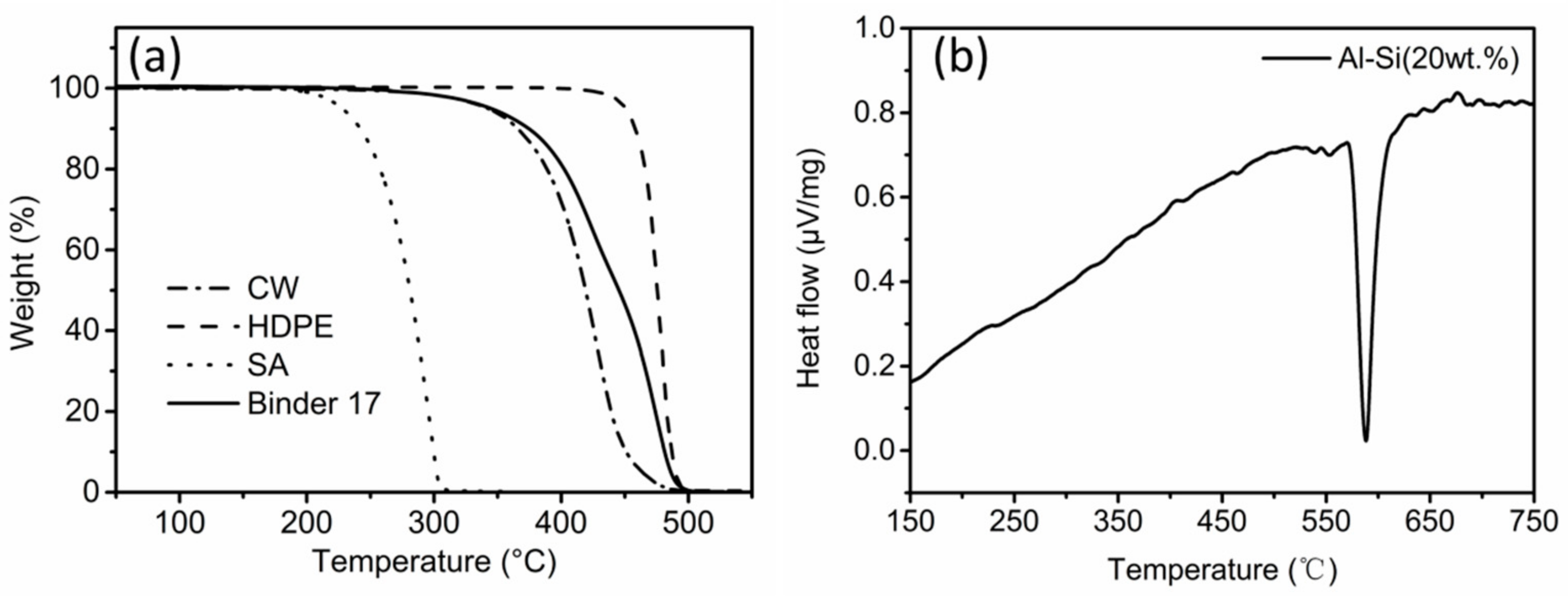
3.1. Solvent Debinding
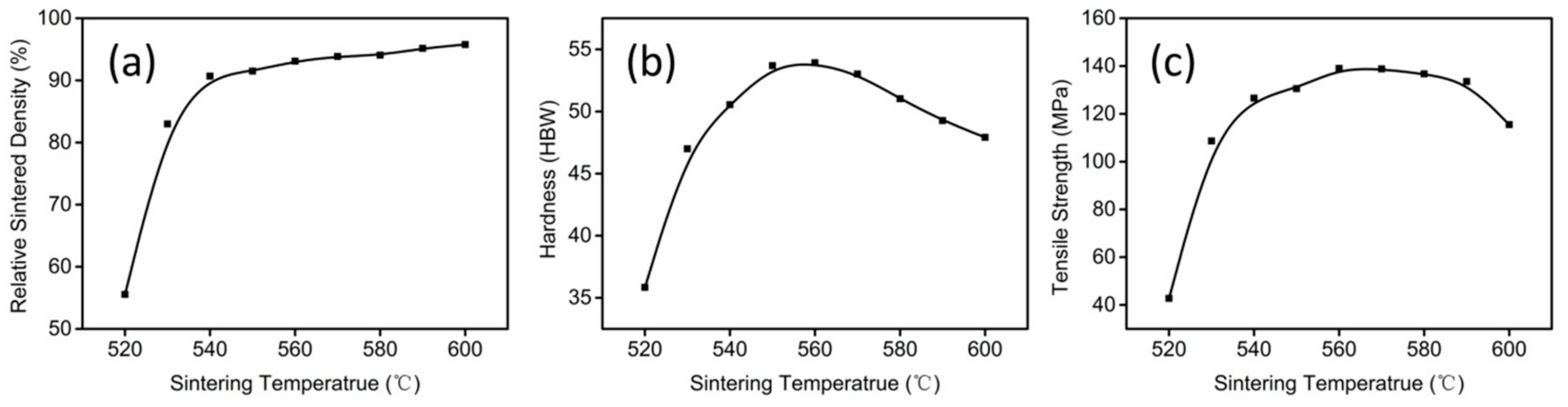
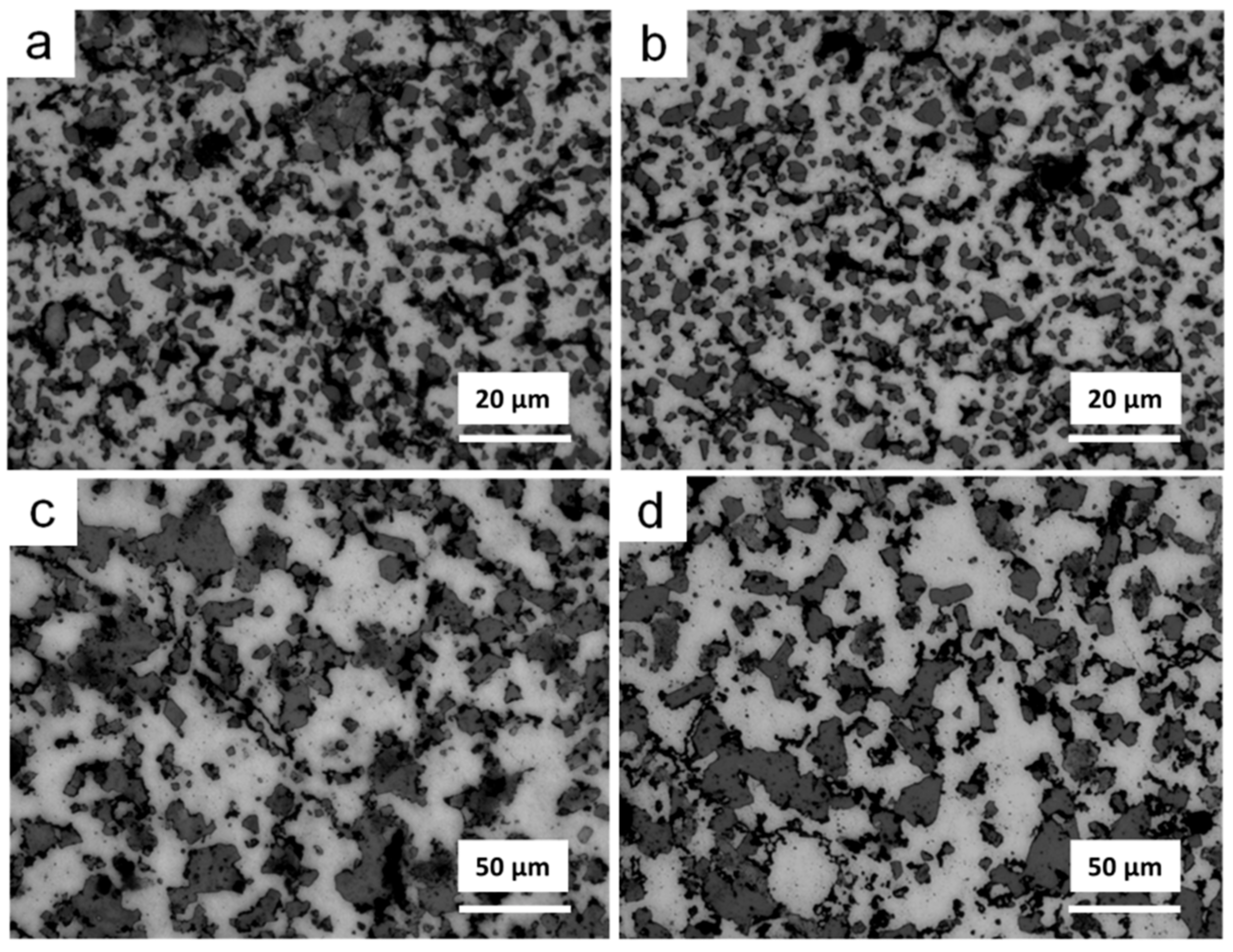
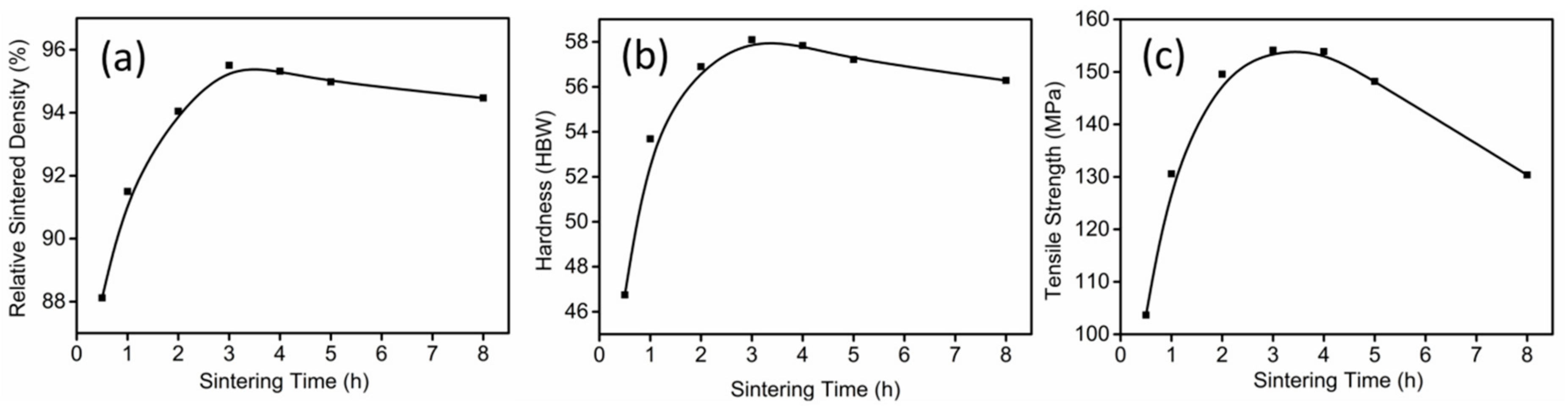
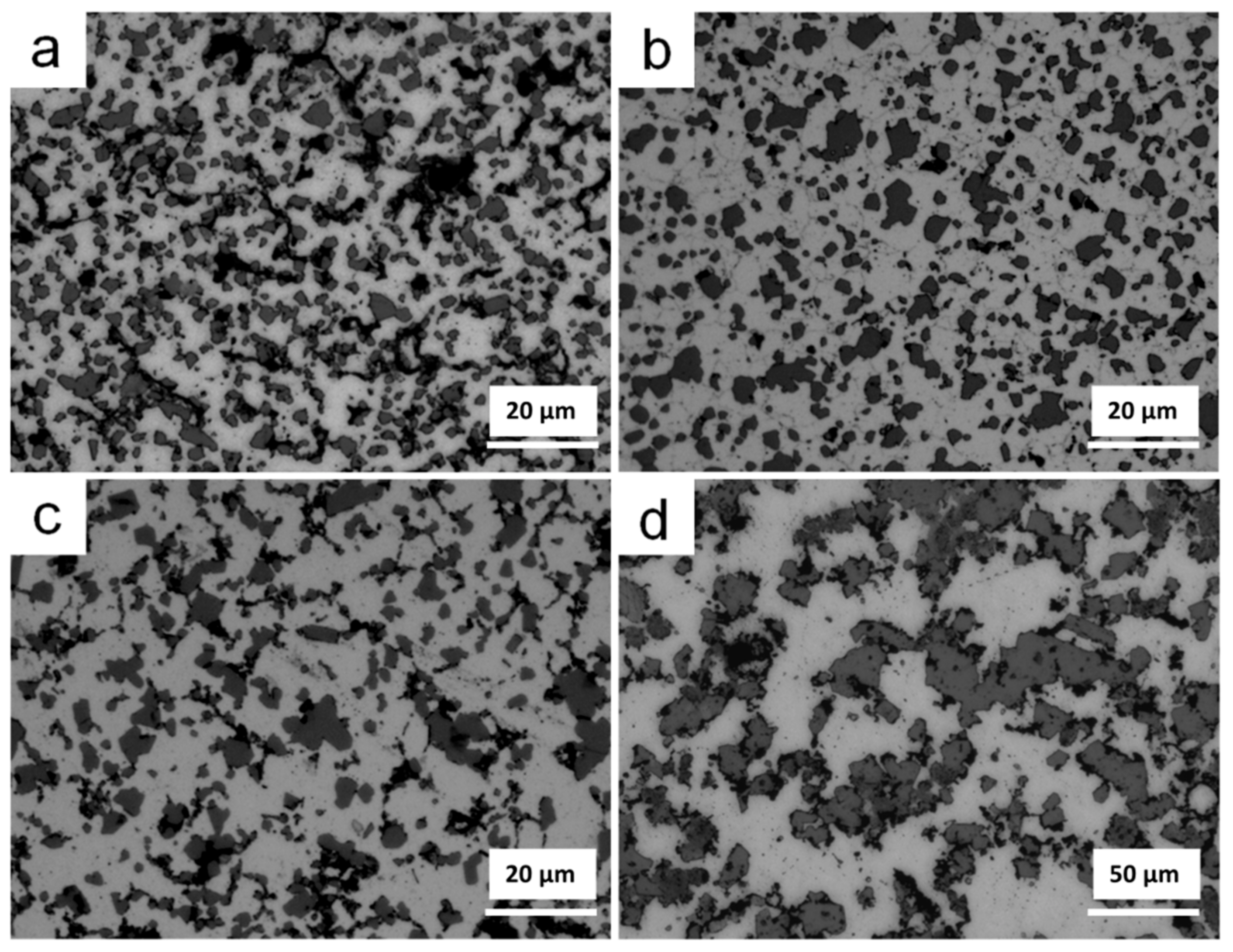
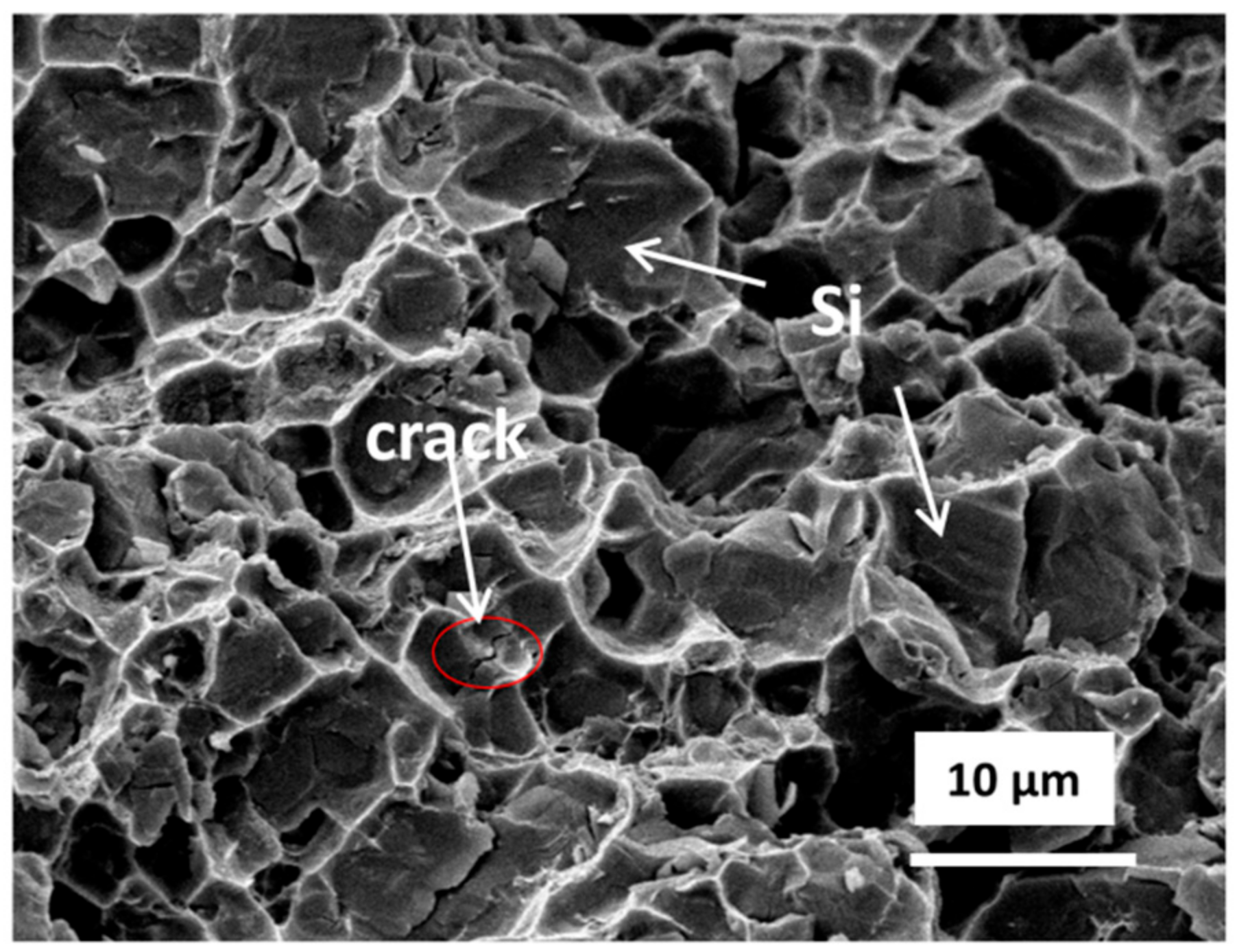
3.2. Thermal Debinding and Sintering
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jung, J.G.; Ahn, T.Y.; Cho, Y.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.M. Synergistic effect of ultrasonic melt treatment and fast cooling on the refinement of primary Si in a hypereutectic Al–Si alloy. Acta Mater. 2018, 144, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-D.; Sun, C.-H.; Si, W.-Q.; Zhao, M.; Lu, M.-M.; Zhang, L. Effects of ZnS modification on primary Si in hypereutectic Al–Si alloy. China Foundry 2017, 14, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chung, D. Silicon-aluminium network composites fabricated by liquid metal infiltration. J. Mater. Sci. 1994, 29, 6069–6075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, S.; Lambourne, A.; Ogilvy, A.; Grant, P. Microstructural characterisation of spray formed Si–30Al for thermal management applications. Scr. Mater. 2006, 55, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiu, Z.Y.; Song, M.H.; Wu, G.H. Microstructure and properties of a 70 vol.% SiCp/Al-12Si composite for electronic packaging. Mater. Sci. Forum 2005, 475, 881–884. [Google Scholar]
- Saidin, H.; Azuddin, M. Preparation of Aluminum Feedstock for Green Part Specimen Using Metal Injection Molding. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 465–466, 1250–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; Ahmad, F.; Altaf, K.; Omar, M.A.; German, R.M. Powder injection molding of biocompatible stainless steel biodevices. Powder Technol. 2016, 295, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdoos, H.; Khorsand, H.; Yousefi, A.A. Torque rheometry and rheological analysis of powder–polymer mixture for aluminum powder injection molding. Iran. Polym. J. 2014, 23, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, K.S.; Nyberg, E.; Simmons, K. A new binder for powder injection molding titanium and other reactive metals. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2006, 176, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enneti, R.K.; Shivashankar, T.S.; Park, S.J.; German, R.M.; Atre, S.V. Master debinding curves for solvent extraction of binders in powder injection molding. Powder Technol. 2012, 228, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wen, J.; Xie, Z.; Yang, X. Powder modification mechanism, effects of binder compositions on the thermal behavior, and the mechanical properties of the ceramic injection molded system. Ceram. Int. 2017, 44, 5646–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez-Pavón, A.; Jiménez-Morales, A.; Santos, T.G.; Quintino, L.; Torralba, J.M. Influence of thermal debinding on the final properties of Fe–Si soft magnetic alloys for metal injection molding (MIM). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 416, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ani, S.M.; Muchtar, A.; Muhamad, N.; Ghani, J.A. Binder removal via a two-stage debinding process for ceramic injection molding parts. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 2819–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotter, V. Powder Injection Molding; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, M.; Sauti, R.; Abdullah, N. Debinding and sintering characteristic of injection moulding CoCrMo alloy powder for biomedical applications. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. Eng. 2015, 1, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, A.; Shibata, M.; Kondoh, K.; Takeda, Y.; Katayama, M.; Kanie, T.; Takada, H. Reduction mechanism of surface oxide in aluminum alloy powders containing magnesium studied by. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 70, 3615–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaskill, I.A.; Donaldson, I.W.; Bishop, D.P. On development of press and sinter Al–Ni–Mg powder metallurgy alloys. Powder Metall. 2013, 49, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieczonka, T.; Schubert, T.; Baunack, S.; Kieback, B. Dimensional behaviour of aluminium sintered in different atmospheres. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 478, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, G.B.; Hall, B.J.; Bonner, S.J.; Huo, S.H.; Sercombe, T.B. The effect of the atmosphere and the role of pore filling on the sintering of aluminium. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Sercombe, T.B.; Schaffer, G.B. Metal injection moulding of aluminium alloy 6061 with tin. Powder Metall. 2008, 51, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, G.B.; Sercombe, T.B.; Lumley, R.N. Liquid phase sintering of aluminium alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2001, 67, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas-Vielma, P.; Cervera, A.; Levenfeld, B.; Várez, A. Production of alumina parts by powder injection molding with a binder system based on high density polyethylene. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Stage | Heating Rate (°C/min) | Debinding/Sintering Temperature (°C) | Hold Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | ambient temperature to 200 | 0 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 200 to 500 | 1 |
| 3 | 0.8 | 500 to sintering temperature | Sintering time |
| 4 | furnace cooling | ambient temperature | 0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, J.; Yu, M.; Han, K. Debinding and Sintering of an Injection-Moulded Hypereutectic Al–Si Alloy. Materials 2018, 11, 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050807
Ni J, Yu M, Han K. Debinding and Sintering of an Injection-Moulded Hypereutectic Al–Si Alloy. Materials. 2018; 11(5):807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050807
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Jiaqi, Muhuo Yu, and Keqing Han. 2018. "Debinding and Sintering of an Injection-Moulded Hypereutectic Al–Si Alloy" Materials 11, no. 5: 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050807
APA StyleNi, J., Yu, M., & Han, K. (2018). Debinding and Sintering of an Injection-Moulded Hypereutectic Al–Si Alloy. Materials, 11(5), 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050807





