Abstract
In this study, Fe3O4/ZnO core–shell nanocomposites were synthesized through a chemical method of coating the magnetic core (Fe3O4) with ZnO by co-precipitation of Fe3O4 with zinc acetate in a basic medium of ammonium hydroxide. The phase structure, morphology and electromagnetic parameters of the Fe3O4/ZnO core–shell nanocomposites were investigated. The results indicated that the concentration of the solvent was responsible for controlling the morphology of the composites, which further influenced their impedance matching and microwave absorption properties. Moreover, Fe3O4/ZnO nanocomposites exhibited an enhanced absorption capacity in comparison with the naked Fe3O4 nanospheres. Specifically, the minimum reflection loss value reached −50.79 dB at 4.38 GHz when the thickness was 4.5 mm. It is expected that the Fe3O4/ZnO core–shell structured nanocomposites could be a promising candidate as high-performance microwave absorbers.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, advanced electromagnetic (EM) applications have taken on a fundamental role in areas such as satellite communication, radar systems, and wireless networks [1,2,3,4,5]. However, the problem of powerful electromagnetic interference (EMI) is becoming serious. EMI pollution certainly hinders the extensive utilization of electromagnetic wave (EMW) devices and has many negative effects on the environment and human health. Many efforts have been devoted to investigating efficient solutions for eliminating EMI pollution. Microwave absorption materials (MAMs) are a kind of functional material that can effectively absorb the energy of EMW on their surface and then transform that EMW energy into thermal energy [6,7,8,9]. The development of efficient MAMs is being pursued with high demand, and a considerable number of concepts have been actively investigated in order to develop MAMs with properties including light weight, low price, low thickness, wide absorption bandwidth capability, strong absorption intensity, and anti-oxidation [10,11,12].
Traditional MAMs, including ferrite [13], inorganic metal salts [14], carbonyl iron [15], graphene [16], and conducting polymers [17], have been widely employed in various applications. However, these materials are hardly able to satisfy all of the requirements of qualified MAMs. Typically, permittivity (dielectric property) and permeability (magnetic property) are the key factors influence the absorption property of MAMs. Much research has focused on the synthesis and complementation of different components in order to avoid poor impedance matching [18,19]. According to the EMW absorption mechanism, the microwaves can be absorbed on a large scale and dissipated into thermal energy through magnetic losses and dielectric losses if the characteristic impedance of the absorber is well matched [20]. The composition of magnetic and dielectric materials is significant in improving the impedance matching between permeability and permittivity. Additionally, the employment of different micro-structures in the absorbers could influence their properties. Among the many existing micro-structures, core–shell structures, designed with magnetic components and dielectric components, have attracted a great deal of attention due to their superior microwave absorption properties, which benefit from induced interfacial polarization, as well as improved impedance matching [21].
One-dimensional (1D) zinc oxide (ZnO)-related nanomaterials have attracted enormous attention in recent decades as dielectric absorbents because of their light weight and dielectric semiconductive properties [22]. To date, many types of ZnO-based materials have been reported that confirm that the absorption property can be modified by compositing ZnO with magnetic materials [22,23,24]. Additionally, employing ordinary magnetic-dielectric materials as surrogates for rare metals is cost-effective and utilitarian. Considering the composite synthetic technique of ZnO, many progressive methods have been reported in previous works, such as Zn/ZnO [25], Cu/ZnO [25], and reduced graphene oxide/ZnO [26].
Previous studies have confirmed that good EM impedance matching and the efficient complementarity between relative permittivity and permeability can be realized by the synergistic effect of the magnetic and the dielectric compositions. In the present work, taking this principle into consideration, we chose ferroferric oxide as the magnetic counterpart and synthesized Fe3O4/ZnO core–shell structured nanocomposites with Fe3O4 cores and ZnO shells. The morphologies and EMW absorption properties were investigated in detail. This work provides a lead for designing dielectric-magnetic absorbers via a facile method. Moreover, the as-synthesized Fe3O4/ZnO core–shell structured nanocomposites exhibited an enhanced absorption property, which may be expected to be useful in building a novel platform in advanced EMW absorbers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Ferric chloride (FeCl3·6H2O), sodium citrate (Na3C6H5O7·2H2O), sodium acetate (NaOAc), and zinc acetate (Zn(OAc)2) were commercially obtained from Aladdin Chemical Reagent, China. Ammonium Hydroxide (NH3·H2O), ethylene glycol (EG), and absolute ethanol were purchased from Xilong Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd. (Guangzhou, China). All the reagents were used without further purification. Deionized water was produced in our laboratory and used for all experiments.
2.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
Fe3O4 nanoparticles (NPs) were prepared by a solvothermal method as reported previously [27]. FeCl3·6H2O (0.016 mol) and Na3C6H5O7·2H2O (0.004 mol) were dissolved in EG (70 mL) under magnetic stirring. Then, NaOAc (0.005 mol) was slowly introduced into the mixture solution, generating a transparent suspension. The resulting solution was then transferred into a Teflon-lined stainless-steel autoclave (100 mL capacity). Subsequently, upon sealing, the autoclave was maintained at 200 °C for 10 h. After cooling down to room temperature, the precipitate was collected by the magnet and washed with absolute ethanol and deionized water several times, then dried in a vacuum oven at 50 °C for 12 h.
2.3. Synthesis of Fe3O4/ZnO Nanocomposites
Fe3O4/ZnO nanocomposites were prepared through the chemical method of coating the magnetic core (Fe3O4) with ZnO by co-precipitation of Fe3O4 with Zn(OAc)2 in a basic medium of NH3·H2O. Briefly, the as-prepared Fe3O4 NPs (0.25 mmol) were dissolved in deionized water (50 mL), Zn(OAc)2 (2 mmol) was dissolved in deionized water (20 mL), then the solutions were mixed together by ultrasonic dispersal for 15 min. Subsequently, the mixed solution was mechanically stirred for 0.5 h. In the meantime, a certain amount of NH3·H2O was added to the suspension. Then the resultant solution was loaded into a 100 mL Teflon-lined stainless-steel autoclave and kept at 120 °C for 15 h. The resulting bronzing product was collected, washed with absolute ethanol and deionized water several times by centrifugation, and then dried in a vacuum oven at 50 °C overnight. the convenience of discussion, the Fe3O4/ZnO nanocomposites prepared in 3 mL NH3·H2O and 2 mL NH3·H2O will be denoted as sample A and sample B, respectively.
2.4. Characterization
The crystalline structure and phases of the samples were performed by X-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku Denki Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) using a Cu Kα radiation (λ = 0.15418 nm) in a scattering range (2θ) of 10–80° at an accelerating voltage of 40 kV. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) studies were performed using the ESCALAB 250Xi (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The morphologies of the as-synthesized samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, JSM-7500F, JEOL, Beijing, China) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEM-2100 microscope with an accelerating voltage of 200 kV, JEOL, Beijing, China). The EM parameters of complex relative permeability (μr = μ′ − jμ″) and permittivity (εr = ε′ − jε″) in the frequency range of 2–18 GHz were performed by vector network analyzer, Agilent, N5230A (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA, as shown in Figure 1a). The as-prepared samples were mixed with paraffin (different mass percentages) and pressed into toroidal-shaped samples (inner diameter φin = 3.04 mm, outer diameter φout = 7.00 mm, as shown in Figure 1b).
Figure 1.
The coaxial waveguide instrumentation (a) and the toroidal–shaped sample (b).
3. Results and Discussion
To confirm the phases and structures of the as-prepared samples, the corresponding XRD pattern of Fe3O4/ZnO composites is shown in Figure 2. As for Fe3O4/ZnO composites, the existence of major diffraction peaks corresponding to the (220), (311), (400), (422), (511), and (440) planes can be observed. These planes can be readily indexed to standard cards of JCPDS No.88-0866, revealing that the crystallinity of Fe3O4 remains unchanged after coating. Six diffraction peaks were assigned to the (100), (101), (102), (110), (103), and (112) planes, which is consistent with ZnO (JCPDS No.36-1451). Therefore, the XRD patterns confirmed the coexistence of Fe3O4 and ZnO. The surface elemental states of Fe3O4/ZnO nanocomposites were further analyzed by XPS, and the results are presented in Figure 3. From the typical survey spectrum, the existence of Fe, Zn, C and O elements can be found. In Figure 3b, the high-resolution spectrum of Fe is given; two peaks appeared at 710.9 and 724.3 eV, corresponding to the band energies of Fe 2p3/2 and Fe 2p1/2, respectively [28]. This indicates the generation of oxide of Fe(II) and Fe(III), which is in good agreement with the literature and is consistent with Fe3O4 [29]. The existence of the Fe element indicates that the shell of ZnO may be in porous condition. Figure 3c displays the high-resolution spectrum of Zn. The peaks at 1021.8 and 1044.8 eV correspond to Zn 2p3/2 and Zn 2p1/2, respectively. Hence, the composites are composed of Fe3O4 and ZnO.
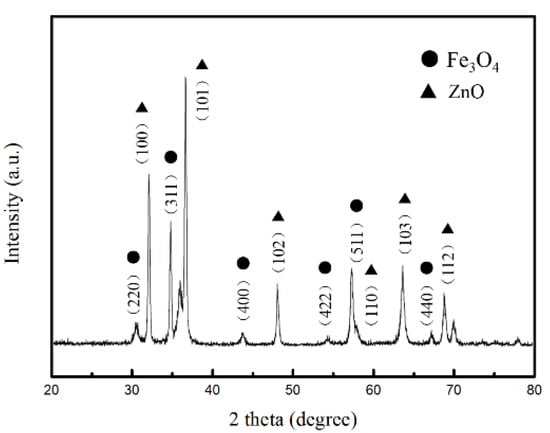
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of and Fe3O4/ZnO composites.
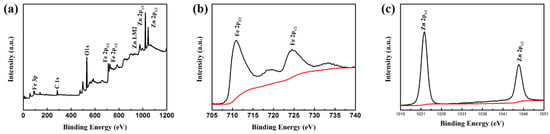
Figure 3.
XPS spectra of Fe3O4/ZnO nanocomposites: (a) survey spectrum; (b) Fe 2p binding energy spectrum; and (c) Zn 2p binding energy spectrum.
The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of Fe3O4 NPs is shown in Figure 4a. It can be seen that Fe3O4 NPs have a relatively uniform spherical shape, and the Fe3O4 NPs with smooth surfaces have diameters in the range of 250–300 nm. Figure 4b,c shows the as-synthesized Fe3O4/ZnO nanocomposites under different experimental conditions. Sample A is shown in Figure 4b; it is visible that the products had a disorderly composition comprising a few scattered Fe3O4 NPs and short ZnO nanorods. The presence of disordered nanorods and NPs suggests that ZnO particles failed to generate chemical bonds with the Fe3O4 NPs and grew into short rod shapes alone with the introduction of a larger amount of ammonium hydroxide (3 mL). When the amount of ammonium hydroxide was reduced to 2 mL (sample B) in the mix solution, the product exhibited a spherical shape (Figure 4c), and the diameters were a bit larger than those of the Fe3O4 NPs in Figure 4a. We deduced that Fe3O4 NPs were uniformly covered by the ZnO shells in a spherical shape. The magnetic NPs are utilized as a seed-mediated growth mechanism to grow a layer of ZnO on their surfaces, thus making the surface much rougher than the naked Fe3O4 NPs. The morphology and distribution of the Fe3O4/ZnO core–shell structured nanocomposites are clearly recognizable from the low-magnification TEM image in Figure 4d. It can be discerned that the nanocomposites are nearly spherical in shape, with a diameter distribution of 280–330 nm, which is consistent with the SEM image in Figure 4c. The high-resolution TEM image of one typical core–shell structured Fe3O4/ZnO composite is demonstrated in Figure 4e. The distinction between the transparent boundary and the dark core confirms the growth of ZnO on the Fe3O4 NP. It can be observed that a thin layer of ZnO is growing on the edge of Fe3O4 NP at a thickness of ~15 nm. Figure 4f also presents the diffraction profile generated by the inserted SAED pattern and confirms the structure of ZnO and Fe3O4. The SEM and TEM results clearly indicate that the nanocomposites possess a core-shell type structure, and that the inner Fe3O4 NPs cores are successfully wrapped with the uniformed ZnO shells.
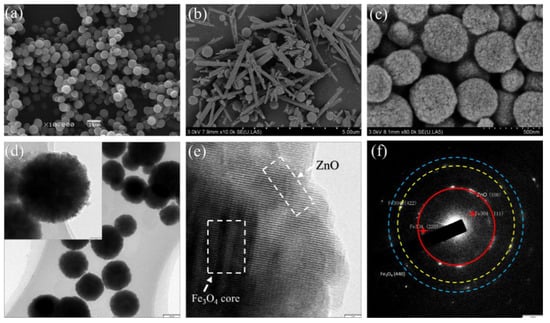
Figure 4.
The SEM images of Fe3O4 (a); sample A (b); and sample B (c); TEM image (d); HRTEM image (e) of sample A and SAED pattern (f) of sample B, respectively.
In order to explore the microwave absorption properties of Fe3O4/ZnO nanocomposites, the relative complex permeability (μr = μ′ − jμ″) and relative permittivity (εr =ε′ − jε″) were measured by a vector network analyzer in the frequency range of 2–18 GHz. The measured samples were prepared by uniformly mixing with paraffin (in mass fractions of 30%, 50%, and 70%) at 85 °C, pressed into toroidal-shaped samples. According to transmission line theory, EM properties can be evaluated based on the relative complex permeability (μr = μ′ − jμ″) and relative permittivity (εr =ε′ − jε″). μ′ and ε′ represent the ability to store EM energy, whereas μ″ and ε″ represent the inner dissipation of EM energy, which originates from the relaxation and resonance mechanisms. The relative complex permittivity (ε′, ε″) and relative complex permeability (μ′, μ″) of Fe3O4, sample A and sample B measured in the frequency range of 2–18 GHz are plotted in Figure 5a–d. From Figure 5a,b, it can be found that ε′ of Fe3O4 is in the range of 4.67–5.03, and ε″ of Fe3O4 is in the range of 0.40–1.02. After being composited with ZnO, the values of ε′ and ε″ show a sharp growth. As for sample A, the values of ε′ and ε″ are in the range of 7.12–8.94 and 0.70–1.67, respectively. Meanwhile, the values of ε′ and ε″ raise to the range of 9.62–16.60 and 1.17–10.23, respectively, after the Fe3O4 NPs were coated with the ZnO shell (sample B). The values of ε′ and ε″ for sample B fluctuate more and exhibit great change in the main measuring frequency region. As shown in Figure 5a, the ε′ of sample B presents a declining trend with increasing frequency, while the trend of ε″ is the contrary, and some peaks appear in the high frequency region. The curves of ε′ and ε″ indicate that the ZnO shell can greatly improve the dielectric properties of the material. Figure 5c,d shows the relative complex permeability of the three materials. As for Fe3O4 NPs, the value of μ′ drops sharply from 1.27 in the frequency range of 2–6 GHz, and then shows a fluctuating trend versus the changing frequency, and the Fe3O4/ZnO (sample A and B) composites display a similar variation trend throughout the entire measured frequency range. This phenomenon may result from the eddy current effect. Compared to the value of μ″, differences in the μ″ values of Fe3O4 and Fe3O4/ZnO composites are distinguished at low frequency. Meanwhile, in the range of 8–18 GHz, the μ″ curves of Fe3O4 and Fe3O4/ZnO composites change to become similar; one μ″ value peak of sample B is observed at ~11 GHz, which may be attributable to the dissipation of EM energy. Furthermore, it is noticed that negative values of μ″ occur in the high frequency range due to calibration or sensitivity issues of the experimental set-up.
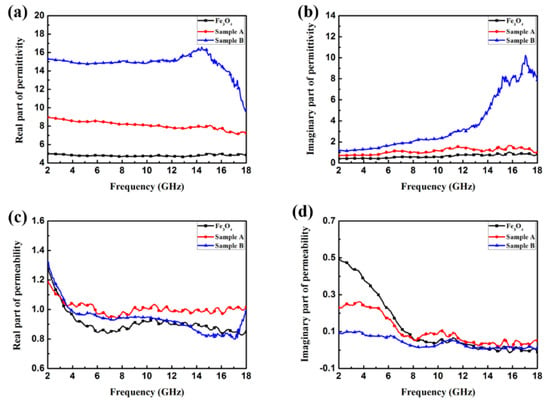
Figure 5.
Frequency dependence on the (a) real part and (b) imaginary part of relative complex permittivity; (c) real part and (d) imaginary part of relative complex permeability.
The theoretical reflection loss (RL) of the composite absorber at different thicknesses was calculated using the following equations [30,31,32]:
Here, Z0 is the impedance of free space, Zin is the normalized input impedance of the absorber, d is the thickness, C is the velocity of EMW in free space, and f is the frequency of the incident wave. RL values of −10 dB and −20 dB correspond to 90% and 99% attenuation of the incident EMW energy, and the frequency range where RL is smaller than −10 dB is defined as the effective absorption bandwidth.
Figure 6a–e shows the plots of RL versus the frequency of the Fe3O4 NPs and two samples of Fe3O4/ZnO composites at different thicknesses. As for Fe3O4 NPs, the minimum RL of −7.28 dB is observed at 15.68 GHz with the thickness of 2.5 mm, which indicates that the naked Fe3O4 NPs have a weak EMW absorption property. Furthermore, with the doping of the dielectric component, the EMW absorption property of sample A can be improved slightly. As shown in Figure 6b, the minimum RL is −13.91 dB at 5.52 GHz with the thickness of 4.5 mm. This is because the ZnO particles failed to generate chemical bonds with the Fe3O4 NPs and grew into short rod shapes alone; therefore, the composites were unable to obtain a good impedance match and interfacial polarization. As for the sample B loaded with 30 wt % (Figure 6c), because of the high dispersion in the paraffin matrix, the Fe3O4/ZnO nanoparticles failed to generate conductive interconnections, so the EMW absorption performance did not show an enhancement in comparison to pure Fe3O4. It is noticed that sample B loaded with 50 wt % shows an enhanced EMW absorption property (Figure 6d). Specifically, the minimum RL value of −50.79 dB can be achieved at 4.38 GHz with the thickness of 4.5 mm. Based on the results of Figure 4d–f, we deduced that the incorporation of the dielectric ZnO into the Fe3O4 NPs may generate a high dielectric constant and loss due to the effective interfaces between the dielectric and magnetic materials, giving them an advantage in terms of matching complex permittivity and permeability. The enhanced EM absorption properties benefit from the uniform core–shell structures, which induce an intensification of interfacial polarization. It is worth noting that the core–shell structured Fe3O4/ZnO composites are able to achieve an enhanced absorption property in both low and high frequency bands; such dual absorption regions are also competitive in comparison to other materials. It can be observed from Figure 6d that the minimum RL values all shift toward the lower frequency region with increasing thickness, which can be explained by the quarter-wavelength match principle [18]:
where tm is the absorber thickness, μr is the complex permeability at fm, and εr is the complex permittivity at fm. The frequency dependence of tm (n = 1, 3) is calculated and plotted on the contour maps in Figure 7. It can be noticed that all the points of RLmin lie on the curves of tm for sample B. Thus, it is demonstrated that the quarter-wavelength match principle is an effective tool that provides a crucial guide in the thickness design of absorbers.
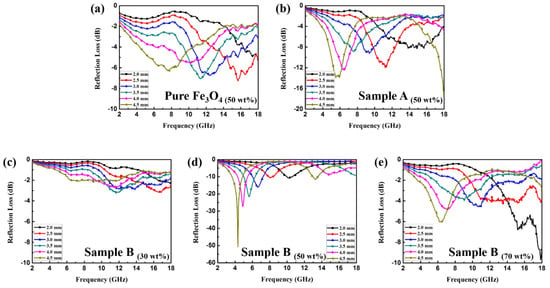
Figure 6.
RL curves of paraffin samples containing 50 wt % Fe3O4 (a) and sample A (b); RL curves of paraffin samples containing 30 wt % (c); 50 wt % (d) and 70 wt % (e) sample B, respectively.
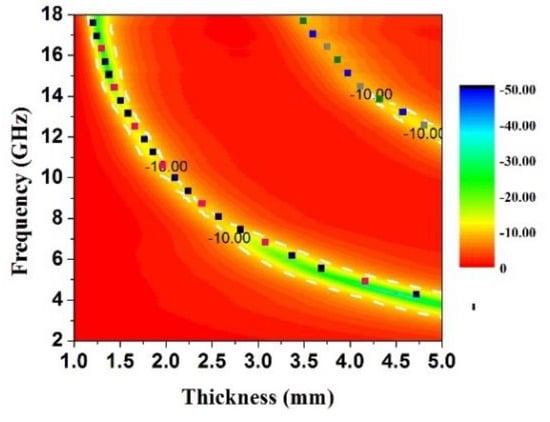
Figure 7.
RL 2-D contour map representations in the frequency range of 2–18 GHz loaded with 50 wt % of sample B.
Typically, the magnetic loss is implied by the imaginary part of permeability and mainly originates from hysteresis loss, domain wall displacement, natural resonance, and eddy current resonance. In general, hysteresis loss is mainly caused by the time lag of the magnetization vector behind the external EM-field vector and will always be negligible in a weak applied field, while domain wall resonance loss takes place in the MHz frequency range. The following equation is used to determine whether eddy currents contribute to the magnetic loss [33]:
If magnetic loss only stems from the eddy current, C0 should be equal to a constant value 2πμ0d2σ (d is the thickness of the MAMs, σ is the electrical conductivity, and μ0 is the permeability in a vacuum) and would be independent of frequency; if not, the magnetic loss is ascribed to natural resonance. From Figure 8a, we find that the value of C0 varies with the frequency and presents a sharp declining tendency in the frequency range of 2–8 GHz. However, when the frequency is in the range of ~8–12 GHz, the value of C0 closes to a constant. Based on this phenomenon, it can be concluded that magnetic loss results from the natural and exchange resonance and the eddy current effect.
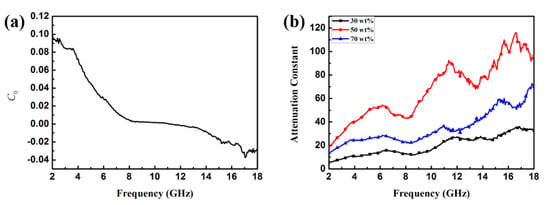
Figure 8.
Frequency dependence of C0 (a) and values of attenuation constant of α (b) of sample B in the range of 2–18 GHz.
According to transmission line theory, EMW absorption properties can be expressed by the attenuation constant of α. The attenuation constants of sample B with 30, 50, and 70 wt % were calculated using the following expression [34,35]:
where c is the velocity of light in a vacuum. Figure 8b shows the plot of the attenuation constant of α versus frequency. It can be seen that the sample with 50 wt % filler loading has the largest value of α; thus, we supposed that the sample with 50 wt % filler loading possesses greater EMW attenuation and impedance matching than the other samples. Figure 9 shows the dielectric loss (tanδε = ε″/ε′) and magnetic tangent loss (tanδμ = μ″/μ′) of Fe3O4/ZnO and Fe3O4 NPs, respectively. tanδε and tanδμ are two possible contributors for EMW absorption, and are commonly used to describe material loss capacity. Therefore, we calculated the tangent loss based on the data in Figure 5. Specifically, sample B has a higher tanδε value than the naked Fe3O4 NPs, indicating that the ZnO shell obviously improves the dielectric properties of the composites. Additionally, Figure 7 clearly shows that the magnetic loss factor (tanδμ) is much higher than the dielectric loss factor (tanδε) in the low frequency range (~2–7 GHz), which indicates that magnetic loss plays a vital role in EMW absorption in this region. Meanwhile, in the high frequency range (~8–12 GHz), the value of tanδε is higher than tanδμ, which indicates that dielectric loss is the main loss in this frequency region. Such a complementarity between dielectric loss and magnetic loss demonstrates the Fe3O4/ZnO composites to possess promising EMW absorption properties.

Figure 9.
Dielectric loss tangent (a) and magnetic loss tangent (b) of the Fe3O4 and Fe3O4/ZnO (sample B), respectively.
In Table 1, the recently reported EMW absorption performances of typical Fe3O4 material-based composites, as well as the Fe3O4/ZnO composites prepared in this work, have been plotted. In comparison with the reported composites in Table 1, it can be observed that the Fe3O4/ZnO composites have a wide effective absorption bandwidth and a promising negative RL value among these composites. It can be concluded that the as-fabricated Fe3O4/ZnO nanocomposites with enhanced EMW absorption properties confirm the presence of an efficient complementarity between magnetic and dielectric loss. The above-mentioned advantages indicate that this special core–shell structured absorber is able to meet the requirements of ideal MAMs.

Table 1.
EMW absorption performances of typical Fe3O4-based composites reported in this work and recent literature.
4. Conclusions
In summary, Fe3O4/ZnO nanocomposites were synthesized via a chemical method of coating magnetic cores (Fe3O4) with ZnO by co-precipitation of Fe3O4 with zinc acetate in a basic medium of ammonium hydroxide, and the morphology and the microwave absorption properties were investigated in detail. It is suggested that the amount of ammonium hydroxide plays a key role in controlling the morphologies of the composites, and the SEM and TEM results further confirmed that ZnO shell generated chemical bonds with the Fe3O4 NPs. Owing to the core–shell structure, an efficient complementary balance was achieved between dielectric loss and magnetic loss. Moreover, the enhanced microwave absorption properties benefitted from the core–shell structure, which induces intensified interfacial polarization. Specifically, the minimum RL value of −50.79 dB can be achieved at 4.38 GHz when the thickness is 4.5 mm. The mechanism of designing neoteric structures with magnetic and dielectric materials in order to broaden the effective absorption bandwidth would open up a promising domain in designing composites with high EM absorption performance. As a result, our Fe3O4/ZnO nanocomposites are expected to form a novel platform for advancing EMW absorbers.
Author Contributions
X.S. conceived and designed the experiments; G.M. and X.L. performed the experiments; M.S. and H.L. analyzed the data; F.W. and J.W. wrote the paper.
Funding
This research was funded by Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20161466).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yuan, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, S.; Lu, Y.; Jin, S.; Li, K.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H. Metal organic framework (MOF)-derived carbonaceous Co3O4/Co microframes anchored on RGO with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances. Synth. Met. 2017, 228, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Qi, X.; Cai, H.; Xie, R.; Long, L.; Bai, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Qin, S.; Zhong, W.; Du, Y. Preparation of porous Fe2O3 nanorods-reduced graphene oxide nanohybrids and their excellent microwave absorption properties. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dom, R.; Subasri, R.; Hebalkar, N.Y.; Chary, A.S.; Borse, P.H. Synthesis of a hydrogen producing nanocrystalline ZnFe2O4 visible light photocatalyst using a rapid microwave irradiation method. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 12782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, X.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, G.; Jiang, M.; Xu, X.; Lu, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Gou, J.; et al. Remarkable improvement in microwave absorption by cloaking a micro-scaled tetrapod hollow with helical carbon nanofibers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 3024–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, R.; Du, Y.; Chen, D.; Ma, W.; Wang, Y.; Xu, P.; Ma, J.; Zhao, H.; Han, X. Electromagnetic functionalized Co/C composites by in situ pyrolysis of metal-organic frameworks (ZIF-67). J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 681, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Li, L. Tunable design of yolk–shell ZnFe2O4@RGO@TiO2 microspheres for enhanced high-frequency microwave absorption. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2017, 4, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.; Wang, G.; Huang, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Yu, L.; Peng, X.; Qin, Y. Uniform Fe3O4 coating on flower-like ZnO nanostructures by atomic layer deposition for electromagnetic wave absorption. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 18804–18809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Tong, G.; Wu, W.; Liu, F.; Qian, H.; Hong, D. Selective preparation and enhanced microwave electromagnetic characteristics of polymorphous ZnO architectures made from a facile one-step ethanediamine-assisted hydrothermal approach. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, E.; Akiba, E. Electromagnetic absorbing materials using nonwoven fabrics coated with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2014, 78, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Huang, Y.; Yan, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Construction of CuS Nanoflakes Vertically Aligned on Magnetically Decorated Graphene and Their Enhanced Microwave Absorption Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5536–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Zhang, H.; Ji, G.; Xu, Z.J. Interface Strategy to Achieve Tunable High Frequency Attenuation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6529–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Dong, X.L.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhu, X.G.; Lei, J.P.; Sun, J.P. Microwave absorption properties of the core/shell-type iron and nickel nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, R.; Du, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Tian, C.; Li, Z.; Han, X.; Xu, P. Metal organic framework-derived Fe/C nanocubes toward efficient microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 13426–13434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, J.; Du, Y.; Bai, J.; Fan, H.; Zhang, H.; Peng, Y.; Li, F. One-pot synthesis of CoFe2O4/graphene oxide hybrids and their conversion into FeCo/graphene hybrids for lightweight and highly efficient microwave absorber. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 5535–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, M.; Lü, X.; Xie, A.; Xu, W.; Rong, X.; Wu, G. The synthesis of three-dimensional (3D) polydopamine-functioned carbonyl iron powder@polypyrrole (CIP@PPy) aerogel composites for excellent microwave absorption. Synth. Met. 2015, 210, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Mou, Z.; Lu, G.; Chen, N.; Dong, Z.; Hu, M.; Qu, L. 3D graphene-Fe3O4 nanocomposites with high-performance microwave absorption. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 13038–13043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Weng, X.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, X.; Gu, G. Synthesis of Fe3O4/polypyrrole/polyaniline nanocomposites by in-situ method and their electromagnetic absorbing properties. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, B.; Liang, X.; Xu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Ji, G.; Du, Y. A permittivity regulating strategy to achieve high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers with compatibility of impedance matching and energy conservation. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y. Electromagnetic and microwave absorption properties of Fe–Sr0.8La0.2Fe11.8Co0.2O19 shell-core composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 2177–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Chen, K.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Jin, Y. Fabrication and microwave absorbing properties of (Z-type barium ferrite/silica)@polypyrrole composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Gao, P.; Yang, P.; Ouyang, Q. Three-dimensional SiO2@Fe3O4 core/shell nanorod array/graphene architecture: Synthesis and electromagnetic absorption properties. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 12296–12303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, R. Facile design of a ZnO nanorod–Ni core–shell composite with dual peaks to tune its microwave absorption properties. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 9294–9302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najim, M.; Modi, G.; Mishra, Y.K.; Adelung, R.; Singh, D.; Agarwala, V. Ultra-wide bandwidth with enhanced microwave absorption of electroless Ni-P coated tetrapod-shaped ZnO nano- and microstructures. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 22923–22933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; Hu, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhang, F.; Wen David Lou, X. A magnetically separable photocatalyst based on nest-like gamma-Fe(2)O(3)/ZnO double-shelled hollow structures with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.-F.; Bi, H.; Wang, C.; Cao, Q.; Jiao, W.; Che, R. Dual-ligand mediated one-pot self-assembly of Cu/ZnO core/shell structures for enhanced microwave absorption. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 41724–41733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, L.; Ouyang, J.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y. Microwave absorbing property optimization of starlike ZnO/reduced graphene oxide doped by ZnO nanocrystal composites. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 14596–14605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xiao, F.; Liu, X.; Feng, C.; Jin, C. Preparation and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of core–shell structured Fe3O4–polyaniline nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 22554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, J.; Ding, L.; Zheng, J.; Xu, J.; Xiong, S. Formation of Fe3O4@SiO2@C/Ni hybrids with enhanced catalytic activity and histidine-rich protein separation. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 15978–15988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Liang, C.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Yuan, K.; Cao, H.; Che, R. Yolk–shell Fe3O4@ZrO2prepared by a tunable polymer surfactant assisted sol–gel method for high temperature stable microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Quan, B.; Liu, W.; Liang, X.; Ji, G.; Du, Y. A facile one-pot strategy for fabrication of carbon-based microwave absorbers: Effects on annealing and paraffin content. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 9097–9102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Guo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Su, T.; Ma, C.; Zhang, R. Constructing hierarchical hollow CuS microspheres via a galvanic replacement reaction and their use as wide-band microwave absorbers. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 2178–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Sun, M.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, W.; Wu, F.; He, M. In situ growth of MoS2 nanosheets on reduced graphene oxide (RGO) surfaces: Interfacial enhancement of absorbing performance against electromagnetic pollution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 24931–24936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, M.; Sun, X.; Lou, H.; Li, X.; Lv, X.; Li, L.; Gu, G. Synthesis of hollow Fe3O4 particles via one-step solvothermal approach for microwave absorption materials: Effect of reactant concentration, reaction temperature and reaction time. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 7539–7550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xie, X.; Pang, Y.; Kobayashi, S. Co/C nanoparticles with low graphitization degree: A high performance microwave-absorbing material. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Nie, X.; Yu, R.; Feng, H. Design of dual-frequency electromagnetic wave absorption by interface modulation strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xing, H.; Liu, Z.; Shen, Z.; Sun, X.; Xu, G. Facile synthesis of net-like Fe3O4/MWCNTs decorated by SnO2nanoparticles as a highly efficient microwave absorber. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 97142–97151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.-F.; Wang, G.-S.; Yue, Y.-H. Fabrication of Fe3O4@SiO2@RGO nanocomposites and their excellent absorption properties with low filler content. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 71718–71723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, N.; Cui, C.; Bi, N.; Sun, Y. One pot synthesis of Fe3O4/MnO2 core–shell structured nanocomposites and their application as microwave absorbers. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24016–24022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lv, B.; Wang, L.; Li, G.; Xu, Y. Fabrication of Fe3O4@C core–shell nanotubes and their application as a lightweight microwave absorbent. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 55738–55744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Meng, F.; Wei, J.; Liu, X. Decoration of basalt fibers with hybrid Fe3O4 microspheres and their microwave absorption application in bisphthalonitrile composites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 2286–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).