Novel Sustainable Composites Based on Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) and Seagrass Beach-CAST Fibers: Performance and Degradability in Marine Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Composite Preparation
2.3. Composite Characterization
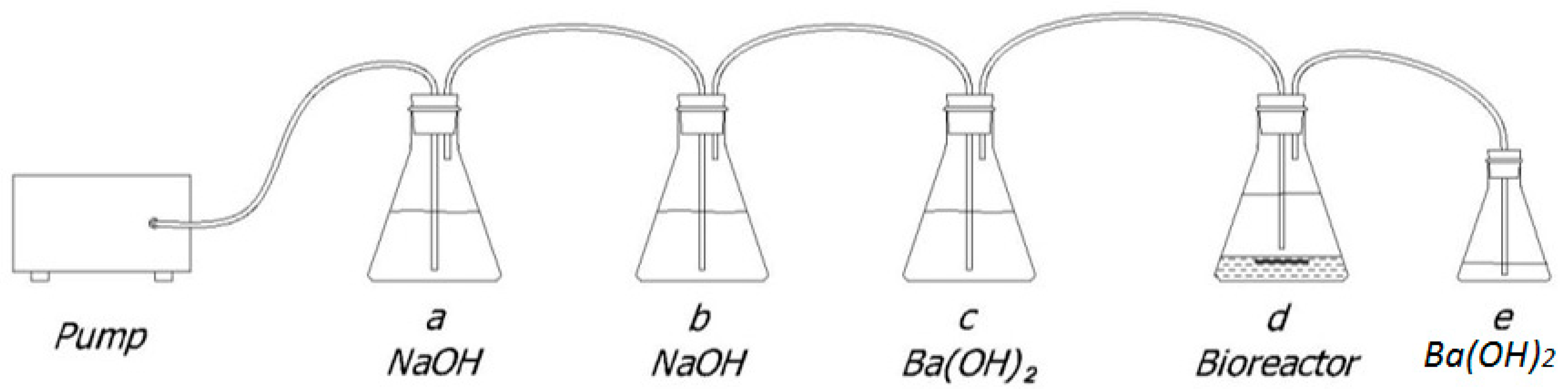
2.4. Biodegradation/Degradation Tests in Marine Environmental Conditions
2.4.1. Lab-Scale Aerobic Biodegradation Test
2.4.2. Degradation Test in Marine Mesocosms
3. Results and Discussion
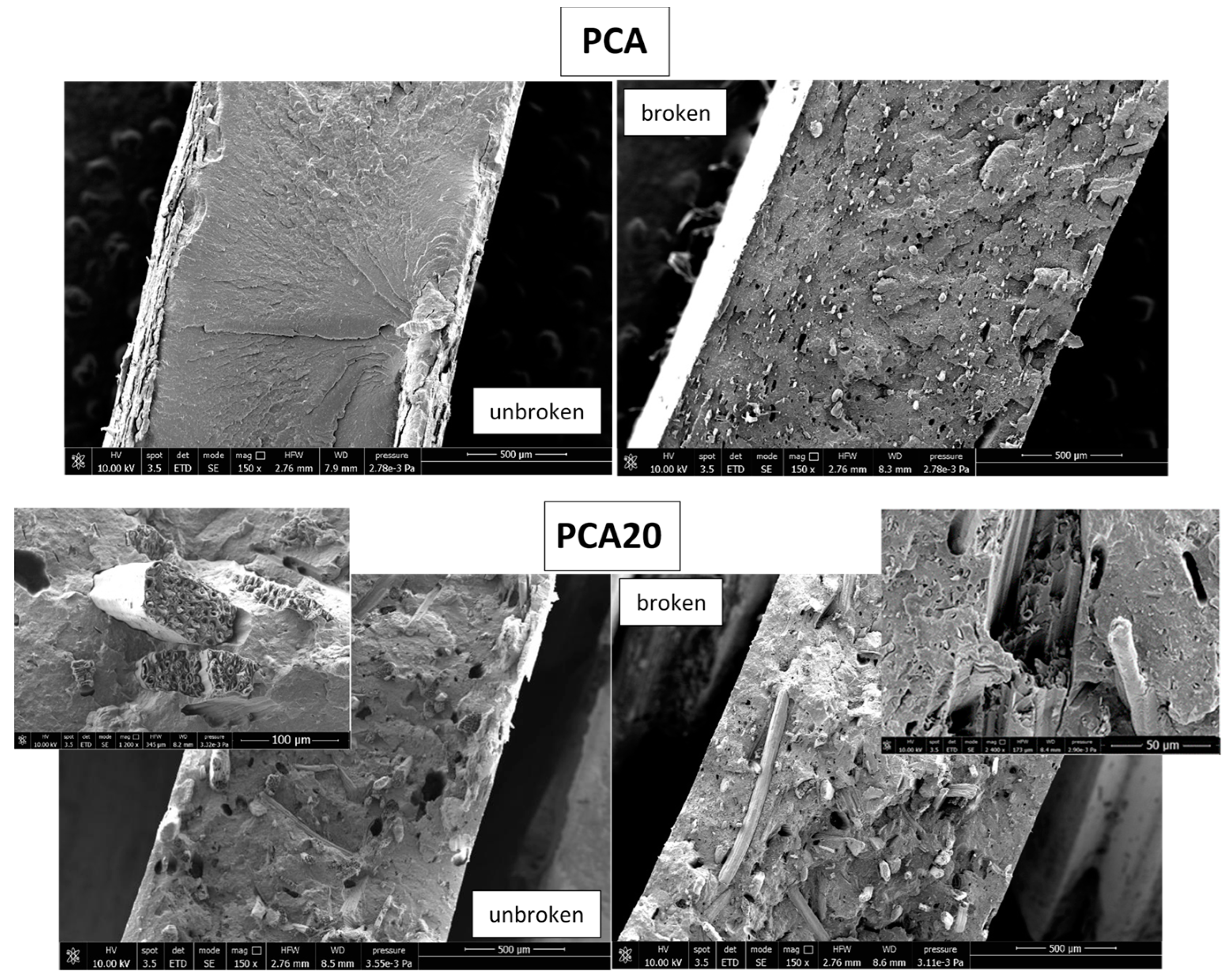
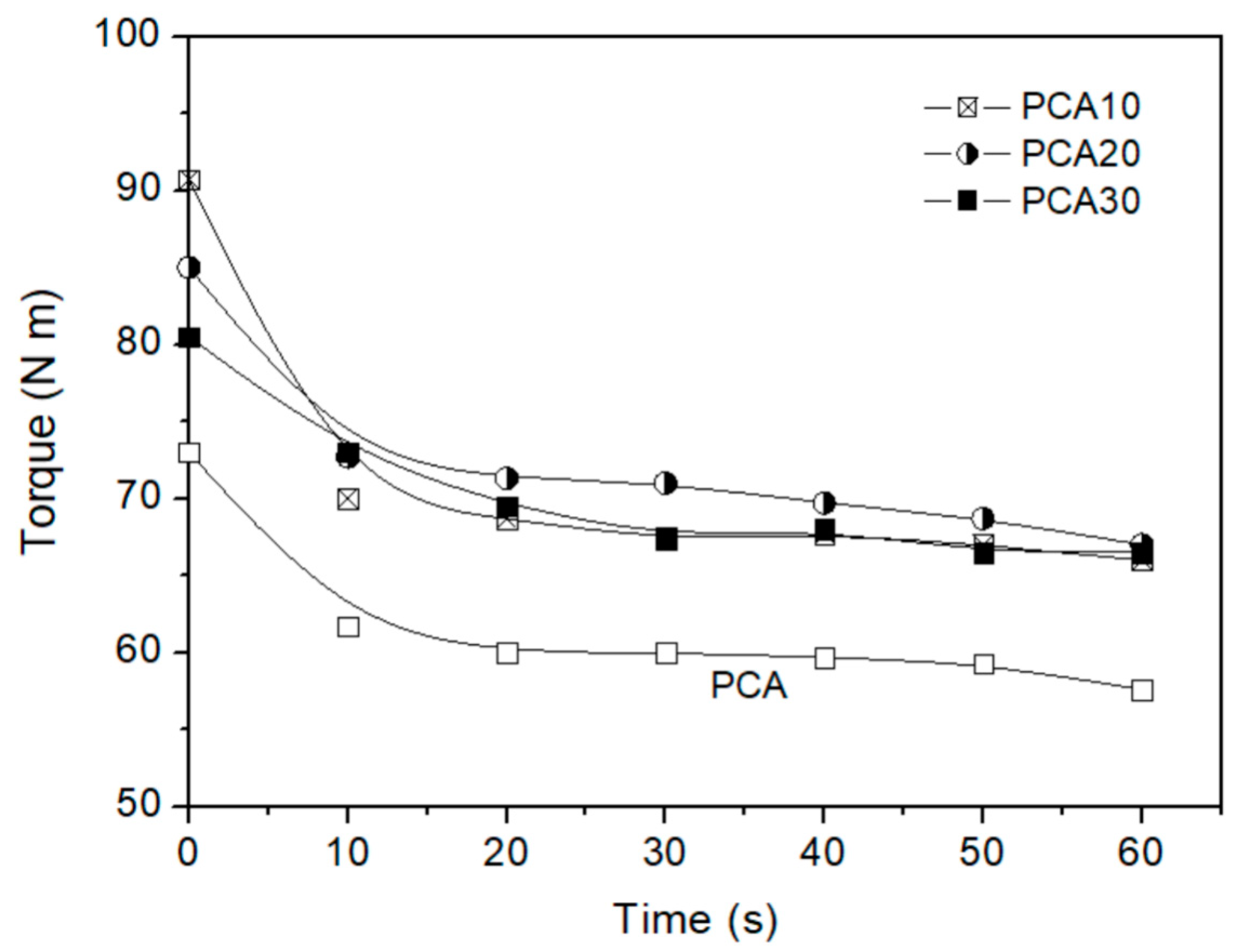
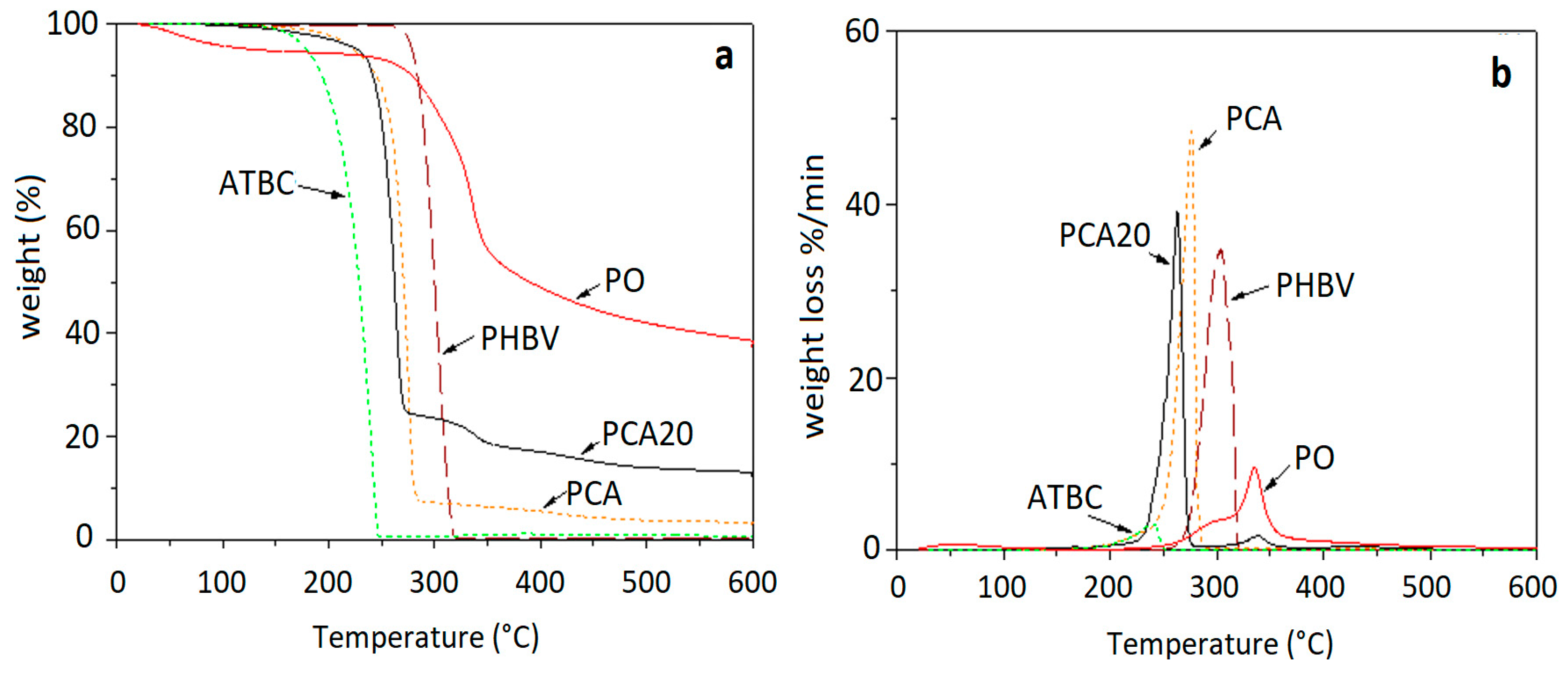
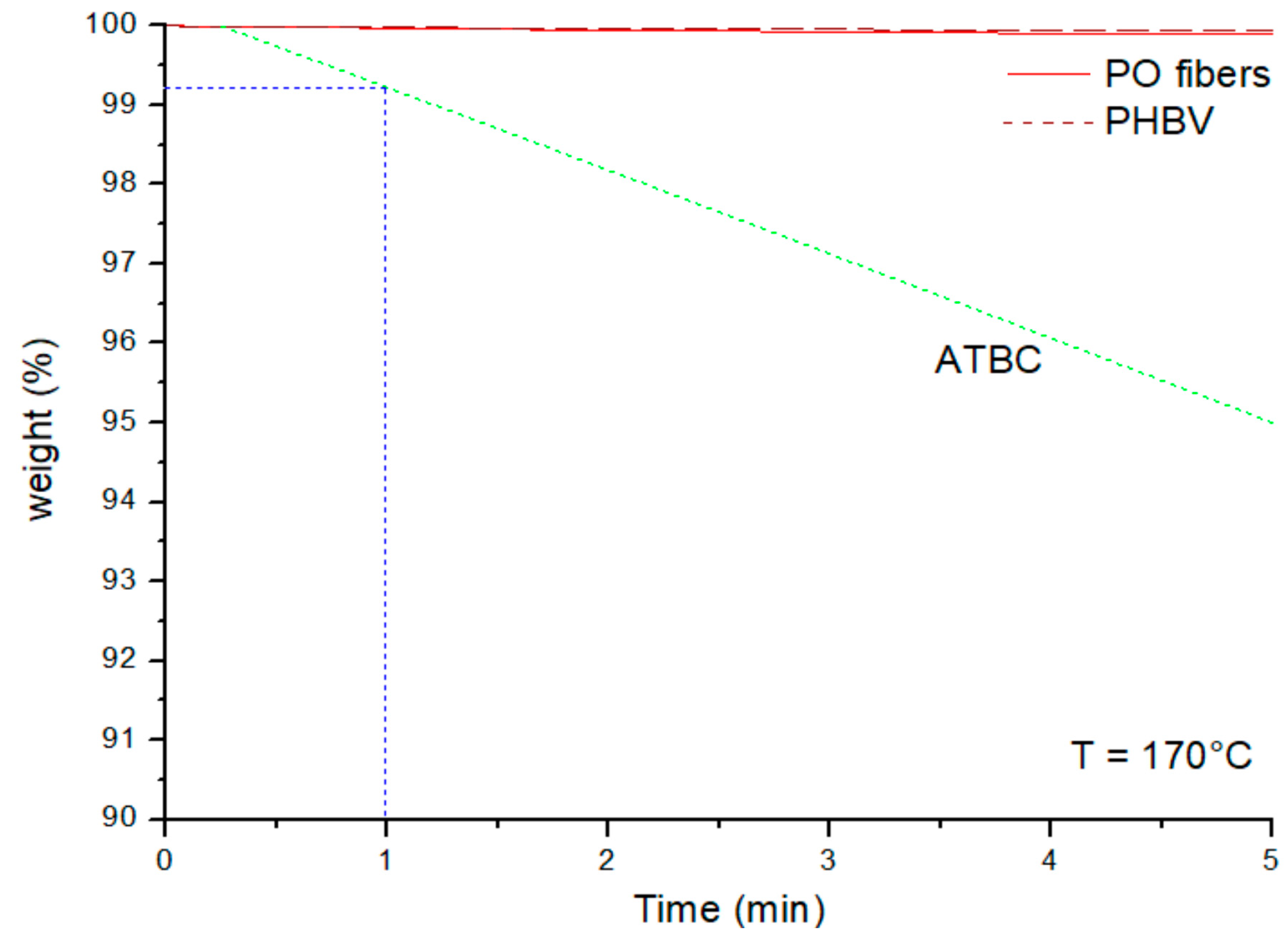
3.1. Composite Processing and Characterization
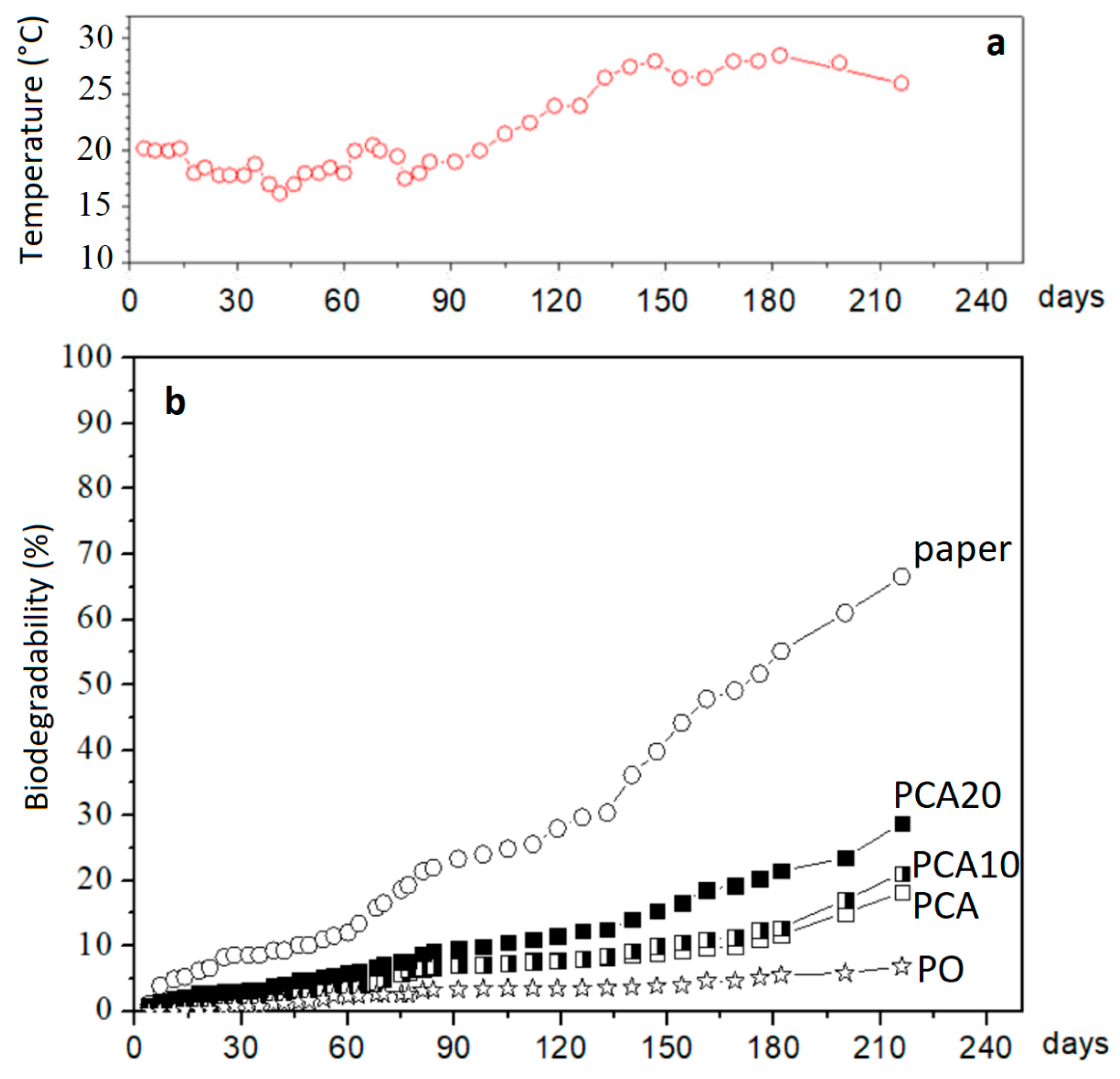
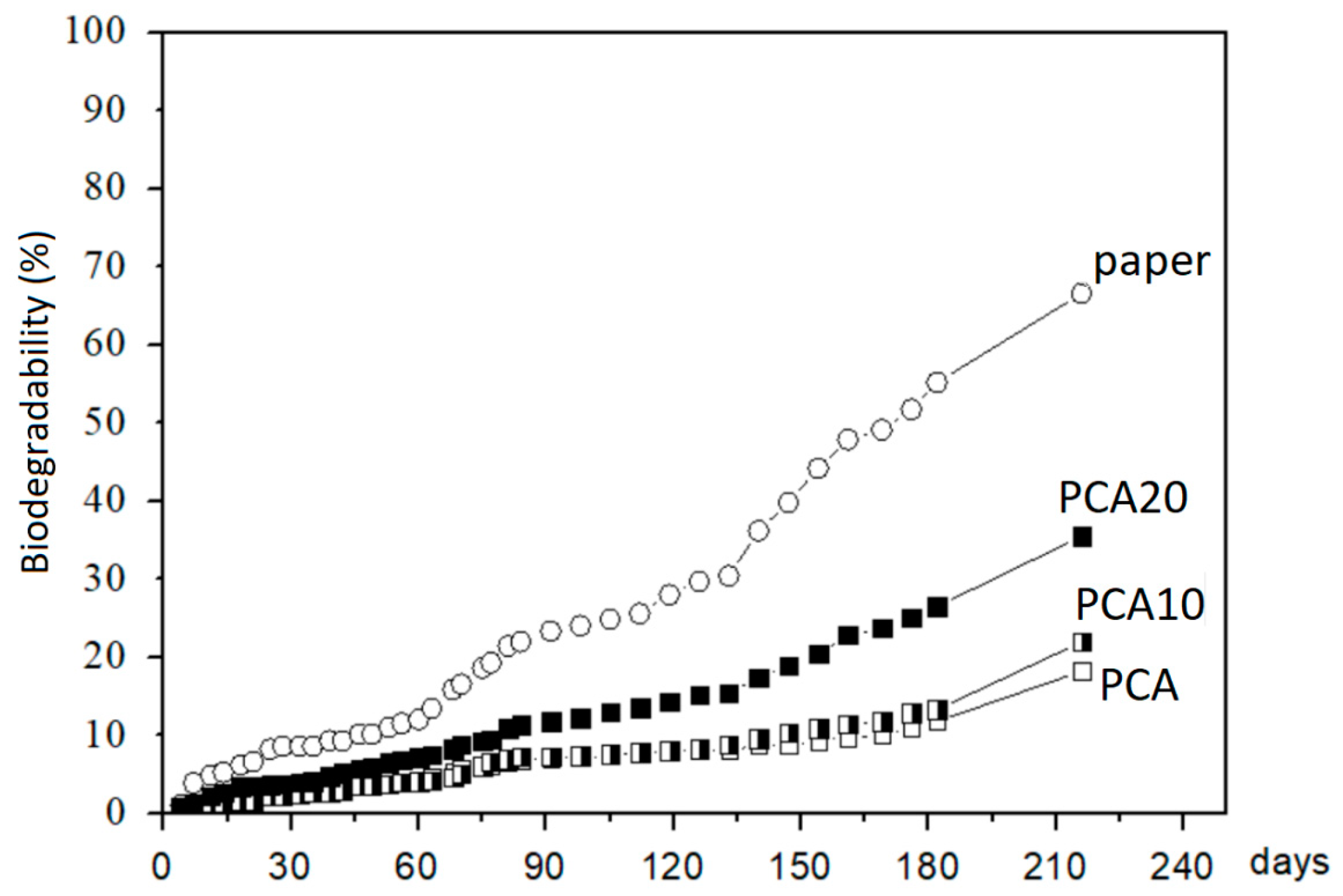
3.2. Lab-Scale Biodegradation Test
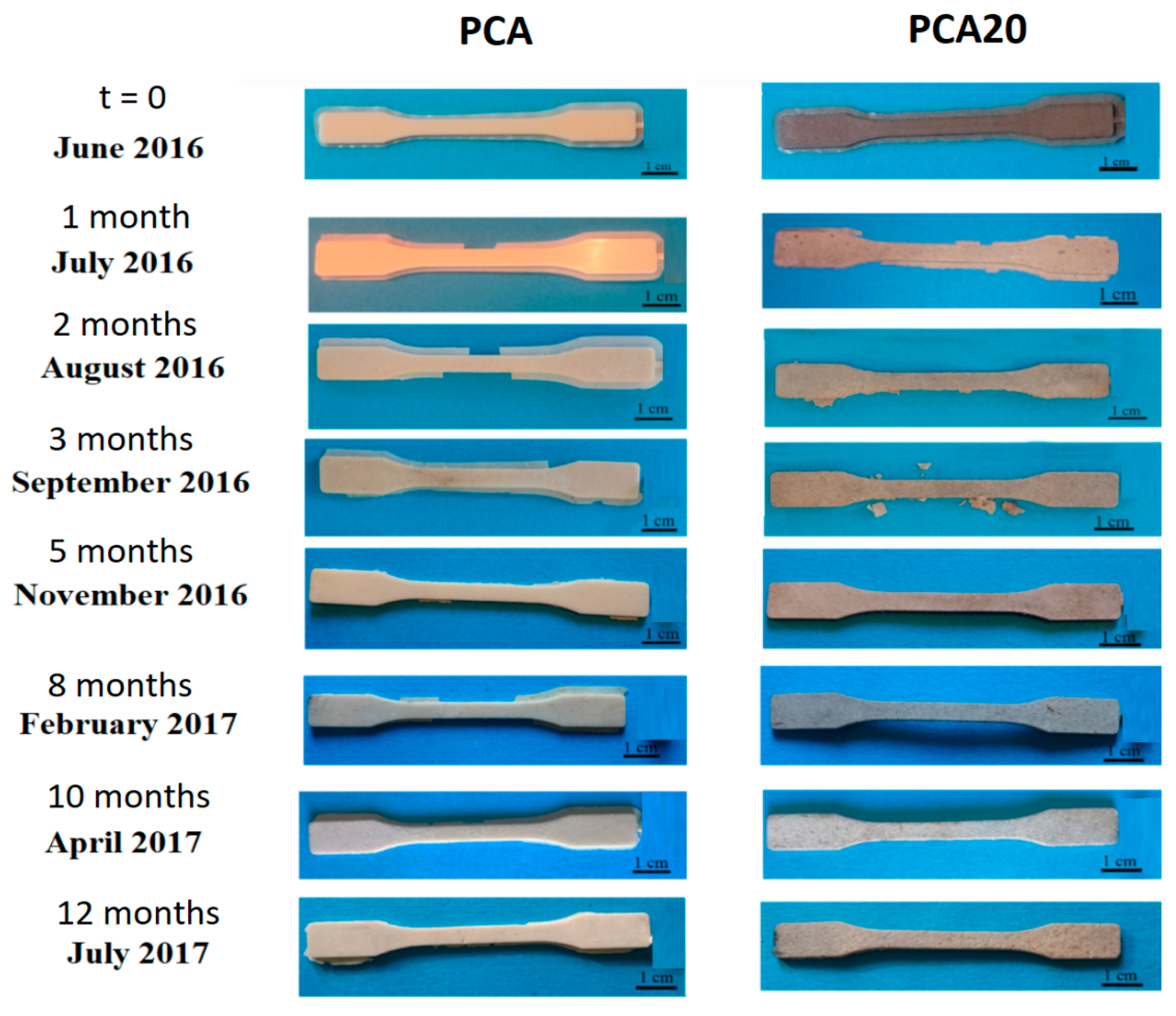
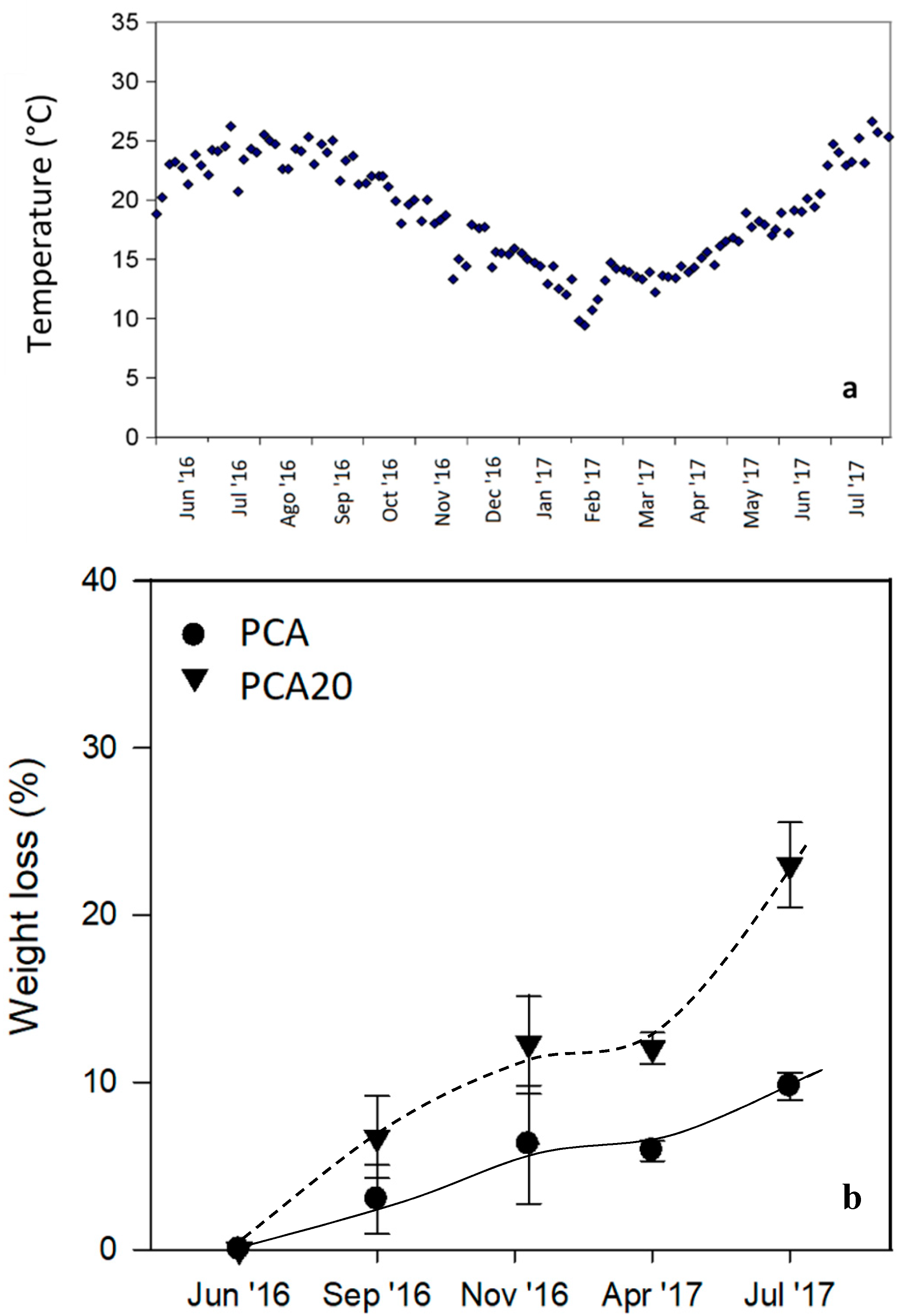
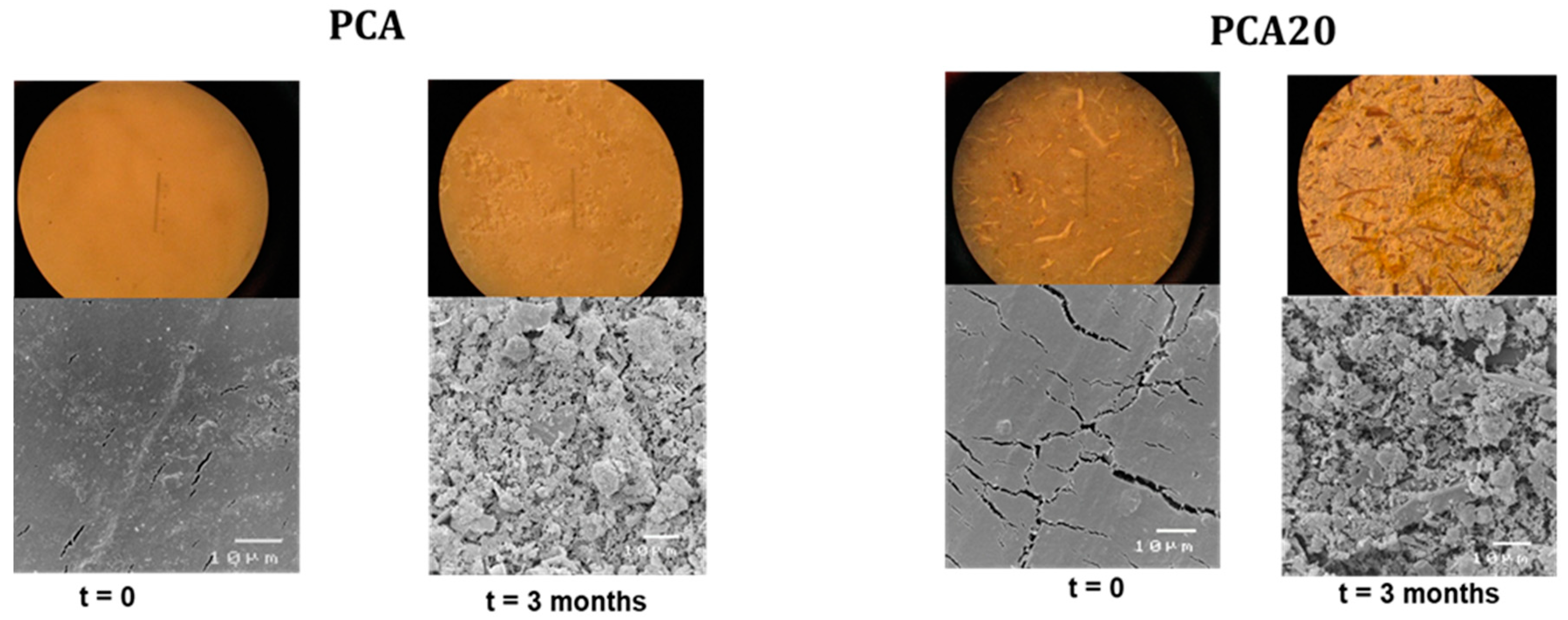
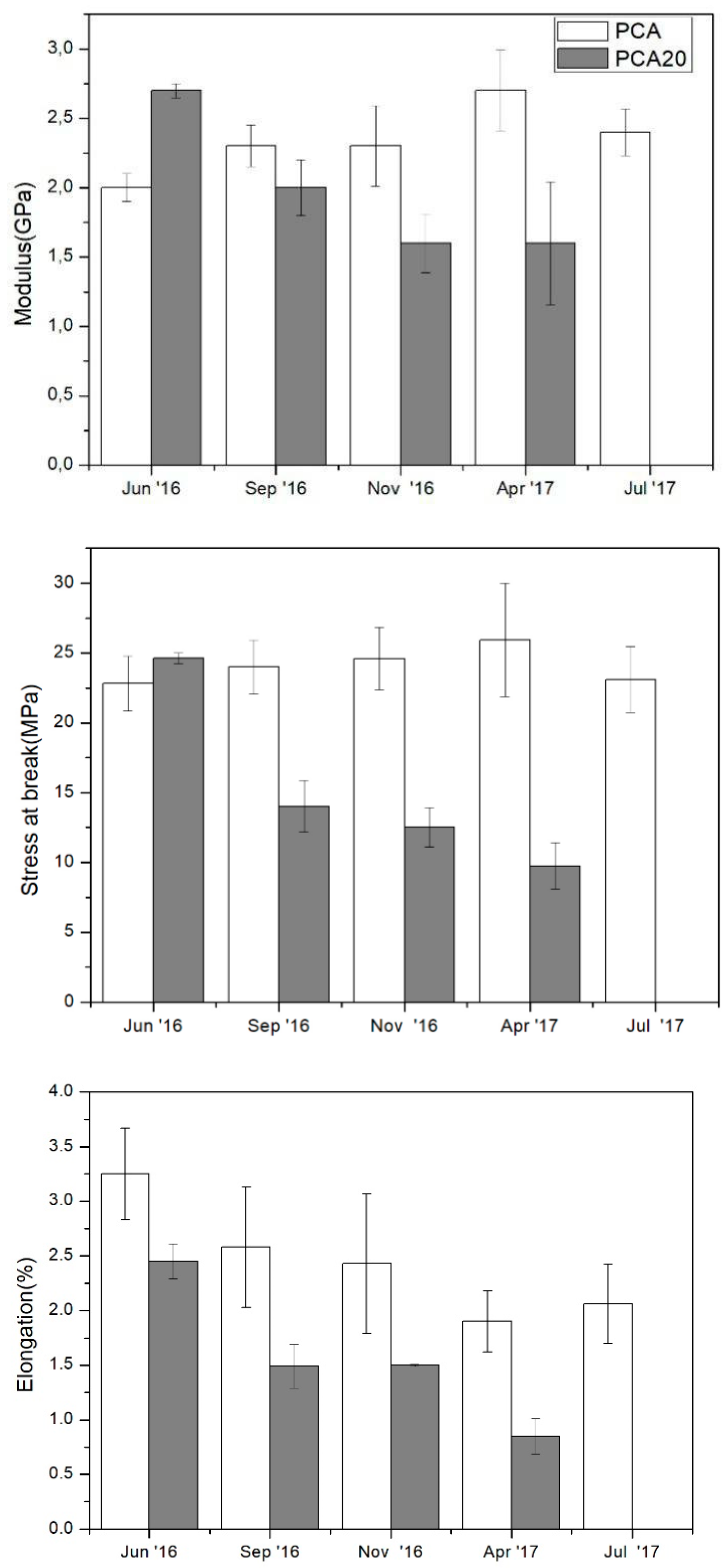
3.3. Degradation Test in Marine Mesocosms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- COM (2018) 28. A European Strategy for Plastics in a Circular Economy. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/transparency/regdoc/rep/1/2018/EN/COM-2018-28-F1-EN-MAIN-PART-1.PDF (accessed on 8 May 2018).
- Valavanidis, A. Global Plastic Waste and Oceans Pollution Million tons of Plastic Waste Have Gone Missing in the World Oceans? Athens, Greece, May 2016. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/303549578 (accessed on 8 May 2018).
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestri, E.; Menicagli, V.; Vallerini, F.; Lardicci, C. Biodegradable plastic bags on the seafloor: A future threat for seagrass meadows? Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605–606, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.S.; Boots, B.; Blockley, D.J.; Rocha, C.; Thompson, R. Impacts of discarded plastic bags on marine assemblages and ecosystem functioning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5380–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padovani, G.; Carlozzi, P.; Seggiani, M.; Cinelli, P.; Vitolo, S.; Lazzeri, A. PHB-rich biomass and BioH2 production by means of photosynthetic microorganisms. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 49, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugnicourt, E.; Cinelli, P.; Lazzeri, A.; Alvarez, V. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): Review of synthesis, Characteristics, processing and potential applications in packaging. eXPRESS Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshman, K.; Shamala, T.R. Enhanced biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates in a mutant strain of Rhizobium Meliloti. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudesh, K.; Abe, H.; Doi, Y. Synthesis, structure and properties of polyhydroxyalkanoates: Biological polyesters. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2000, 25, 1503–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroiné, M.; Le Duigou, A.; Corre, Y.M.; Le Gac, P.Y.; Davies, P.; César, G.; Bruzaud, S. Seawater accelerated ageing of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 105, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volova, T.G.; Boyandin, A.N.; Vasiliev, A.D.; Karpov, V.A.; Prudnikova, S.V.; Mishukova, O.V.; Boyarskikh, U.A.; Filipenko, M.L.; Rudnev, V.P.; Xuân, B.B.; et al. Biodegradation of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) in tropical coastal waters and identification of PHA-degrading bacteria. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, M.; Krasowska, K.; Heimowska, A.; Adamus, G.; Sobota, M.; Musioł, M.; Janeczek, H.; Sikorska, W.; Krzan, A.; Žagar, E.; et al. Environmental degradation of blends of atactic poly[(R,S)-3-hydroxybutyrate] with natural PHBV in Baltic sea water and compost with activated sludge. J. Polym. Environ. 2008, 16, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Suzuyoshi, K. Environmental degradation of biodegradable polyesters 2. Poly(ε-caprolactone), poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], and poly(l-lactide) films in natural dynamic seawater. Polym. Degrad. Stabl. 2002, 75, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, S.H.; Gordon, S.H.; Shogren, R.L.; Tosteson, T.R.; Govind, N.S.; Greene, R.V. Degradation of starch–poly(β-hydroxybutyrate-co-β-hydroxyvalerate) bioplastic in tropical coastal waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Thomas, N.L. Preparation and properties of polyhydroxybutyrate blended with different types of starch. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, K.C.; Pereira, J.; Smith, A.C.; Carvalho, C.W.P.; Wellner, N.; Yakimets, I. Characterization of polyhydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate (PHB-HV)/maize starch blend films. J. Food Eng. 2008, 89, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbole, S.; Gote, S.; Latkar, M.; Chakrabarti, T. Preparation and characterization of biodegradable poly-3-hydroxybutyrate-starch blend films. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 86, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seggiani, M.; Cinelli, P.; Verstichel, S.; Puccini, M.; Vitolo, S.; Anguillesi, I.; Lazzeri, A. Development of fibres-reinforced biodegradable composites. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2015, 43, 1813–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, T.; Kao, N. PLA Based biopolymer reinforced with natural fibre: A Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiellini, E.; Cinelli, P.; Chiellini, F.; Imam, S.H. Environmentally degradable biobased polymeric blends composites. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiellini, E.; Cinelli, P.; Imam, S.H.; Mao, L. Composite films based on biorelated agro-industrial waste and poly(vinyl alcohol). Preparation and mechanical properties characterization. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Hinrichsen, G. Biofibres, biodegradable polymers and biocomposites: An overview. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2000, 276, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Lopresti, F.; Botta, L. PLA based biocomposites reinforced with Posidonia oceanica leaves. Compos. Part B 2018, 139, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, B.; Boronat, T.; Moriana, R.; Fenollar, O.; Balart, R. Development of natural fiber-reinforced plastics (NFRP) based on biobased polyethylene and waste fibers from Posidonia oceanica seaweed. Polym. Compos. 2015, 36, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, B.; Boronat, T.; Moriana, R.; Fenollar, O.; Balart, R. Green composites based on wheat gluten matrix and Posidonia oceanica waste fibers as reinforcements. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglia, D.; Petrucci, R.; Fortunati, E.; Luzi, F.; Kenny, J.M.; Torre, L. Revalorisation of Posidonia oceanica as reinforcement in polyethylene/maleic anhydride grafted polyethylene composites. J. Renew. Mater. 2014, 2, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiari, R.; Marrakchi, Z.; Belgacem, M.N.; Mauret, E.; Mhenni, F. New lignocellulosic fibres-reinforced composite materials: A stepforward in the valorization of the Posidonia oceanica balls. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 1867–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seggiani, M.; Cinelli, P.; Mallegni, N.; Balestri, E.; Puccini, M.; Vitolo, S.; Lardicci, C.; Lazzeri, A. New bio-composites based on polyhydroxyalkanoates and Posidonia oceanica fibres for Applications ina Marine Environment. Materials 2017, 10, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Hartog, C.; Kuo, J. Taxonomy and biogeography of seagrasses. In Seagrasses Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Larkum, A.W.D., Orth, R.J., Duarte, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestri, E.; Vallerini, F.; Lardicci, C. A qualitative and quantitative assessment of the reproductive litter from Posidonia oceanica accumulated on a sand beach following a storm. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 66, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erceg, M.; Kovačić, T.; Klarić, I. Thermal degradation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) plasticized with acetyl tributyl citrate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 90, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, M.P.; Castro-Lopez, M.D.; Rayón, E.; Barral-Losada, L.F.; López-Vilariño, J.M.; López, J.; González-Rodríguez, M.V. Plasticized poly(lactic acid)–poly(hydroxybutyrate) (PLA–PHB) blends incorporated with catechin intended for active food-packaging applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10170–10180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrieta, M.P.; López, J.; Rayón, E.; Jiménez, A. Disintegrability under composting conditions of plasticized PLA–PHB blends. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 108, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, M.P.; López, J.; López, D.; Kenny, J.M.; Peponi, L. Development of flexible materials based on plasticized electrospun PLA–PHB blends: Structural, thermal, mechanical and disintegration properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 73, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, R.; Persenaire, O.; Lemmouchi, Y.; Sampson, J.; Martin, S.; Bonnaud, L.; Dubois, P. Enhancement of cellulose acetate degradation under accelerated weathering by plasticization with eco-friendly plasticizers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on Flavouring Group Evaluation 10, Revision 3 (FGE.10Rev3): Aliphatic primary and secondary saturated and unsaturated alcohols, aldehydes, acetals, carboxylic acids and esters containing an additional oxygenated functional group and lactones from chemical groups 9, 13 and 30. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 25–63. [Google Scholar]
- Balestri, E.; Lardicci, C. Nursery-propagated plants from seed: A tool to improve the effectiveness and sustainability of seagrass restoration. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, M.P.; Samper, M.D.; Lopez, J.; Jimenez, A. Combined effect of poly(hydroxybutyrate) and plasticizers on polylactic acid properties for film intended for food packaging. J. Polym. Environ. 2014, 22, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Gassan, J. Composite reinforced with cellulose based fibers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1999, 24, 221–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fombuena, V.; Sanchez-Nacher, L.; Samper, M.D.; Juarez, D.; Balart, R. Study of the properties of thermoset materials derived from epoxidized soybean oil and protein fillers. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2013, 90, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieck, K.P.; Reußmann, T.; Hauspurg, C. Correlations for the fracture work and falling weight impact properties of thermoplastic natural/long fibre composites. Mater. Werkst. 2000, 31, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graupner, N.; Müssig, J. A comparison of the mechanical characteristics of kenaf and lyocell fibre reinforced poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 2010–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganster, J.; Fink, K.P. Novel cellulose fibre reinforced thermoplastic materials. Cellulos. 2006, 13, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, Y.; Kanesawa, Y.; Tanahashi, N.; Kumagai, Y. Biodegradation of microbial polyesters in the marine environment. Polym. Degrad. Stabl. 1992, 36, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestri, E.; Vallerini, F.; Lardicci, C. Recruitment and patch establishment by seed in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica: Importance and conservation implications. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestri, E.; Lardicci, C. Stimulation of root formation in Posidonia oceanica cuttings by application of auxins (NAA and IBA). Mar. Biol. 2006, 149, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Katwijk, M.M.; Thorhaug, A.; Marbà, N.; Orth, R.J.; Duarte, C.M.; Kendrick, G.A.; Althuizen, I.H.J.; Balestri, E.; Bernard, G.; Cambridge, M.L.; et al. Global analysis of seagrass restoration: The importance of large-scale planting. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 53, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Extrusion Temperature (°C) | Screw Speed (rpm) | Cycle Time (s) | Injection Temperature (°C) | Injection Pressure (bar) | Molding Time (s) | Mold Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 170 | 100 | 60 | 170 | 210 | 15 | 60 |
| Sample | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Stress at Break (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Charpy’s Impact Energy (kJ/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCA | 2.01 ± 0.10 | 23.60 ± 1.97 | 3.25 ± 0.42 | 3.61 ± 0.36 |
| PCA10 | 2.37 ± 0.18 | 23.42 ± 1.87 | 2.63 ± 0.17 | 3.83 ± 0.26 |
| PCA20 | 2.72 ± 0.05 | 24.62 ± 0.39 | 2.45 ± 0.16 | 4.14 ± 0.52 |
| PCA30 | 2.38 ± 0.15 | 21.45 ± 1.63 | 1.92 ± 0.16 | 4.37 ± 0.24 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seggiani, M.; Cinelli, P.; Balestri, E.; Mallegni, N.; Stefanelli, E.; Rossi, A.; Lardicci, C.; Lazzeri, A. Novel Sustainable Composites Based on Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) and Seagrass Beach-CAST Fibers: Performance and Degradability in Marine Environments. Materials 2018, 11, 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050772
Seggiani M, Cinelli P, Balestri E, Mallegni N, Stefanelli E, Rossi A, Lardicci C, Lazzeri A. Novel Sustainable Composites Based on Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) and Seagrass Beach-CAST Fibers: Performance and Degradability in Marine Environments. Materials. 2018; 11(5):772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050772
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeggiani, Maurizia, Patrizia Cinelli, Elena Balestri, Norma Mallegni, Eleonora Stefanelli, Alessia Rossi, Claudio Lardicci, and Andrea Lazzeri. 2018. "Novel Sustainable Composites Based on Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) and Seagrass Beach-CAST Fibers: Performance and Degradability in Marine Environments" Materials 11, no. 5: 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050772
APA StyleSeggiani, M., Cinelli, P., Balestri, E., Mallegni, N., Stefanelli, E., Rossi, A., Lardicci, C., & Lazzeri, A. (2018). Novel Sustainable Composites Based on Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) and Seagrass Beach-CAST Fibers: Performance and Degradability in Marine Environments. Materials, 11(5), 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050772









