The Effect of Kinematic Conditions and Synovial Fluid Composition on the Frictional Behaviour of Materials for Artificial Joints
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
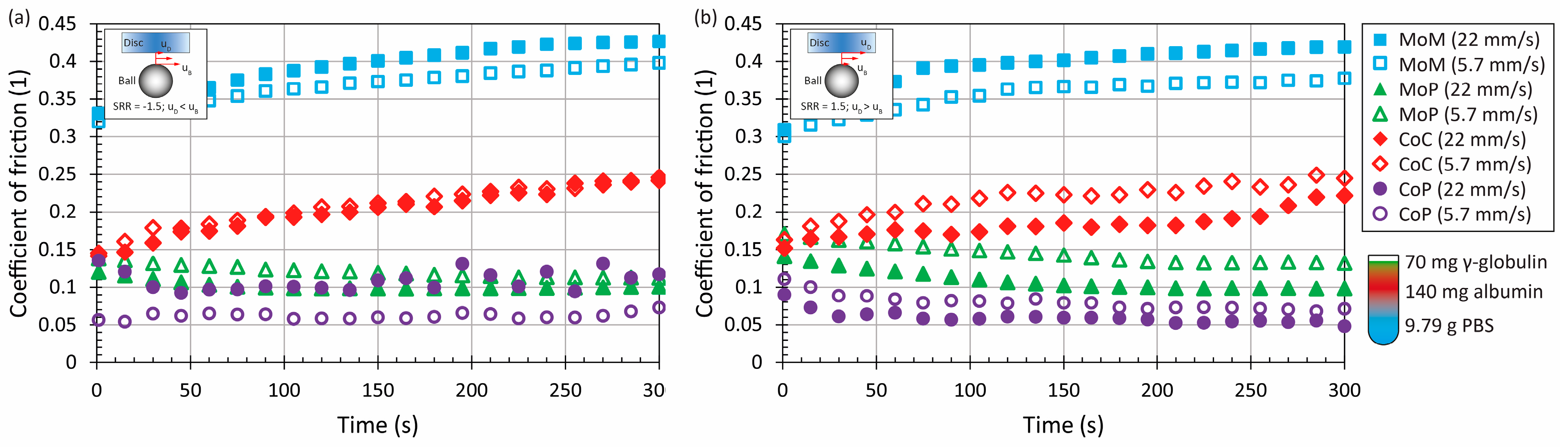
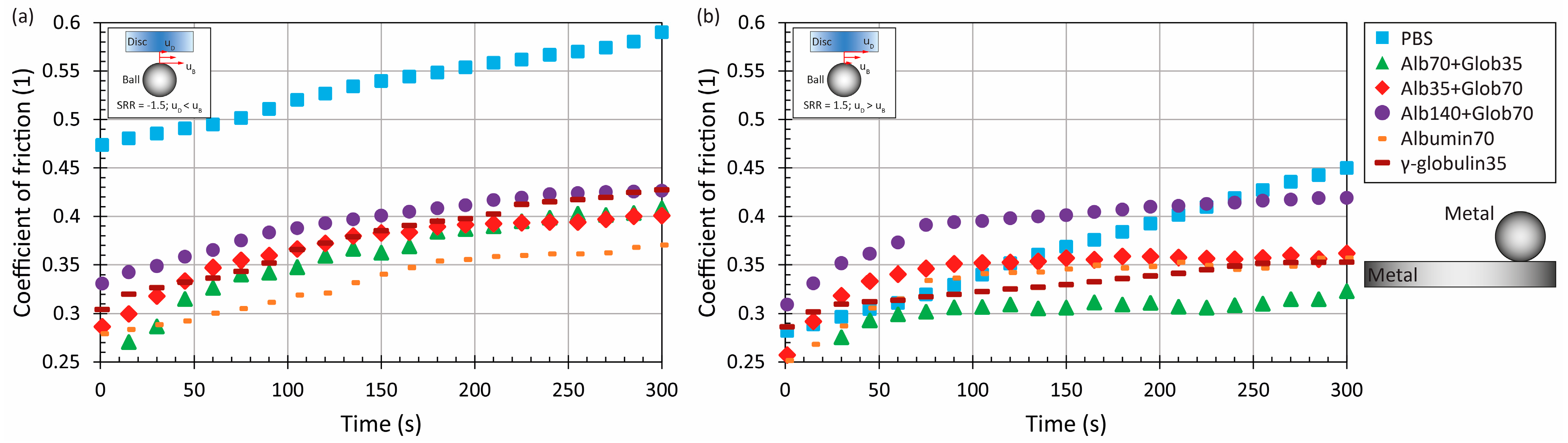
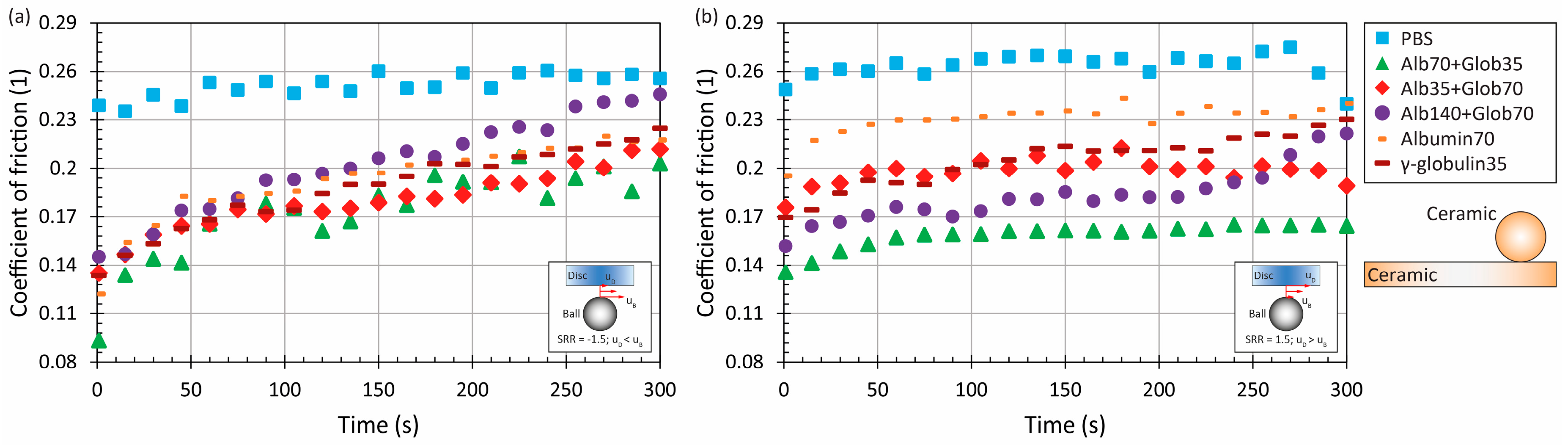
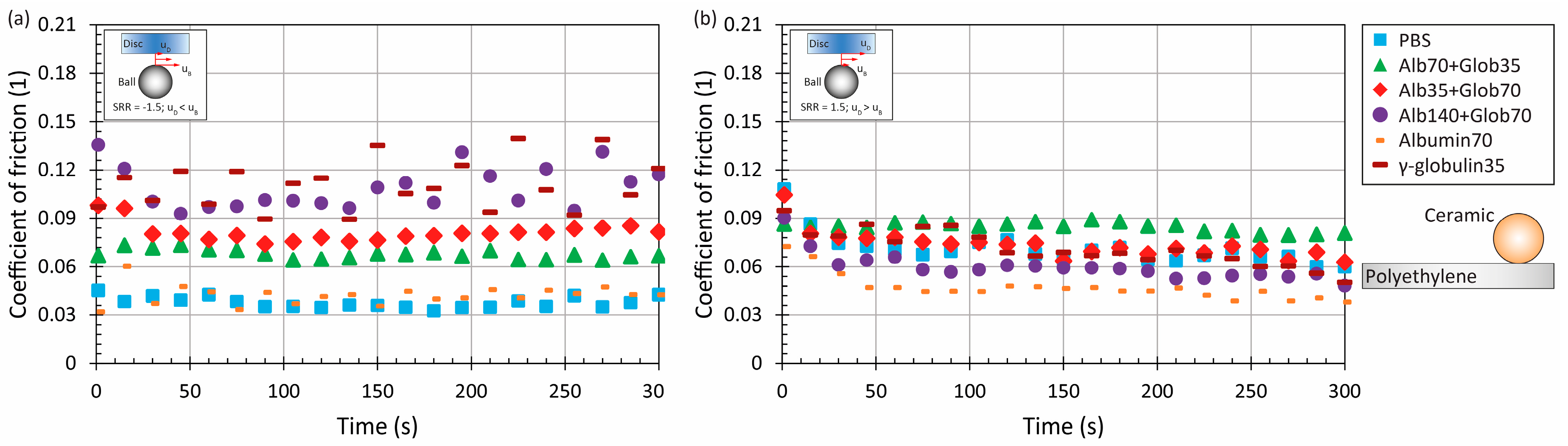
3.1. The Effect of Material and Kinematic Conditions
3.2. The Effect of Model Synovial Fluid Composition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Health at a Glance 2015: OECD Indicators; OECD: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pramanik, S.; Agarwal, A.K.; Rai, K.N. Chronology of total hip joint replacement and materials development. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs 2005, 19, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Huch, K.; Müller, K.A.C.; Stürmer, T.; Brenner, H.; Puhl, W.; Günther, K.-P. Efficacy of prednisone 1–4 mg/day in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled withdrawal clinical trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.B.; Porter, M.L.; Trail, I.A.; Hunt, L.P.; Murphy, J.C.; Hardinge, K. Long-term results of Charnley low-friction arthroplasty in young patients. Bone Jt. J. 1993, 75, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavraki, A.; Cann, P.M. Friction and lubricant film thickness measurements on simulated synovial fluids. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2009, 223, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.Q.; Laurent, M.P.; Johnson, T.S.; Blanchard, C.R.; Crowninshield, R.D. The influences of lubricant and material on polymer/CoCr sliding friction. Wear 2003, 255, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, S.C.; Unsworth, A. The Effects of Proteins on the Friction and Lubrication of Artificial Joints. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2006, 220, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawae, Y.; Murakami, T.; Chen, J. Effect of synovia constituents on friction and wear of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene sliding against prosthetic joint materials. Wear 1997, 216, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, M.R.; Heuberger, M.; Vörös, J.; Spencer, N.D. Influence of polymer surface chemistry on frictional properties under protein-lubrication conditions: implications for hip-implant design. Tribol. Lett. 2001, 10, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuberger, M.P.; Widmer, M.R.; Zobeley, E.; Glockshuber, R.; Spencer, N.D. Protein-mediated boundary lubrication in arthroplasty. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nečas, D.; Sawae, Y.; Fujisawa, T.; Nakashima, K.; Morita, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Vrbka, M.; Křupka, I.; Hartl, M. The Influence of Proteins and Speed on Friction and Adsorption of Metal/UHMWPE Contact Pair. Biotribology 2017, 11, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.B.; Fang, H.W.; Liu, H.L.; Chang, C.-H.; Hsieh, M.-C.; Lee, W.-M.; Huang, H.-T. Frictional characteristics of the tribological unfolding albumin for polyethylene and cartilage. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 431, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Essner, A.; Polineni, V.K.; Stark, C.; Dumbleton, J.H. Lubrication and wear of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene in total joint replacements. Tribol. Int. 1998, 31, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowson, D.; Wang, F.C.; Wang, W.Z.; Jin, Z.M. A predictive analysis of long-term friction and wear characteristics of metal-on-metal total hip replacement. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2007, 221, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockett, C.L.; Harper, P.; Williams, S.; Isaac, G.H.; Dwyer-Joyce, R.S.; Jin, Z.; Fisher, J. The influence of clearance on friction, lubrication and squeaking in large diameter metal-on-metal hip replacements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 1575–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrbka, M.; Nečas, D.; Bartošík, J.; Hartl, M.; Křupka, I.; Galandáková, A.; Gallo, J. Determination of a Friction Coefficient for THA Bearing Couples. Acta Chirurgiae Orthopaedicae et Traumatologiae Cechoslovaca 2015, 82, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brostow, W.; Hagg Lobland, H.E. Materials: Introduction and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mavraki, A.; Cann, P.M. Lubricating film thickness measurements with bovine serum. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gispert, M.P.; Serro, A.P.; Colaço, R.; Saramago, B. Friction and wear mechanisms in hip prosthesis: Comparison of joint materials behaviour in several lubricants. Wear 2006, 260, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guezmil, M.; Bensalah, W.; Mezlini, S. Tribological behavior of UHMWPE against TiAl6V4 and CoCr28Mo alloys under dry and lubricated conditions. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 63, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morillo, C.; Sawae, Y.; Murakami, T. Effect of bovine serum constituents on the surface of the tribological pair alumina/alumina nanocomposites for total hip replacement. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nečas, D.; Vrbka, M.; Urban, F. The effect of lubricant constituents on lubrication mechanisms in hip joint replacements. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 55, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guezmil, M.; Bensalah, W.; Mezlini, S. Effect of bio-lubrication on the tribological behavior of UHMWPE against M30NW stainless steel. Tribol. Int. 2016, 94, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nečas, D.; Vrbka, M.; Křupka, I.; Hartl, M.; Galandáková, A. Lubrication within hip replacements—Implication for ceramic-on-hard bearing couples. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 61, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Myant, C.W.; Underwood, R.; Hart, A. Inlet protein aggregation: A new mechanism for lubricating film formation with model synovial fluids. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2011, 225, 696–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myant, C.; Underwood, R.; Fan, J. Lubrication of metal-on-metal hip joints: The effect of protein content and load on film formation and wear. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 6, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkes, M.; Myant, C.; Cann, P.M.; Wong, J.S.S. The effect of buffer solution choice on protein adsorption and lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2014, 72, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nečas, D.; Vrbka, M.; Rebenda, D.; Gallo, J.; Galandákovác, A.; Wolfovád, L.; Křupkaae, I.; Hartla, M. In situ observation of lubricant film formation in THR considering real conformity: The effect of model synovial fluid composition. Tribol. Int. 2018, 117, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nečas, D.; Vrbka, M.; Urban, F.; Gallo, J.; Křupka, I.; Hartl, M. In situ observation of lubricant film formation in THR considering real conformity: The effect of diameter, clearance and material. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 69, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawae, Y.; Yamamoto, A.; Murakami, T. Influence of protein and lipid concentration of the test lubricant on the wear of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene. Tribol. Int. 2008, 41, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
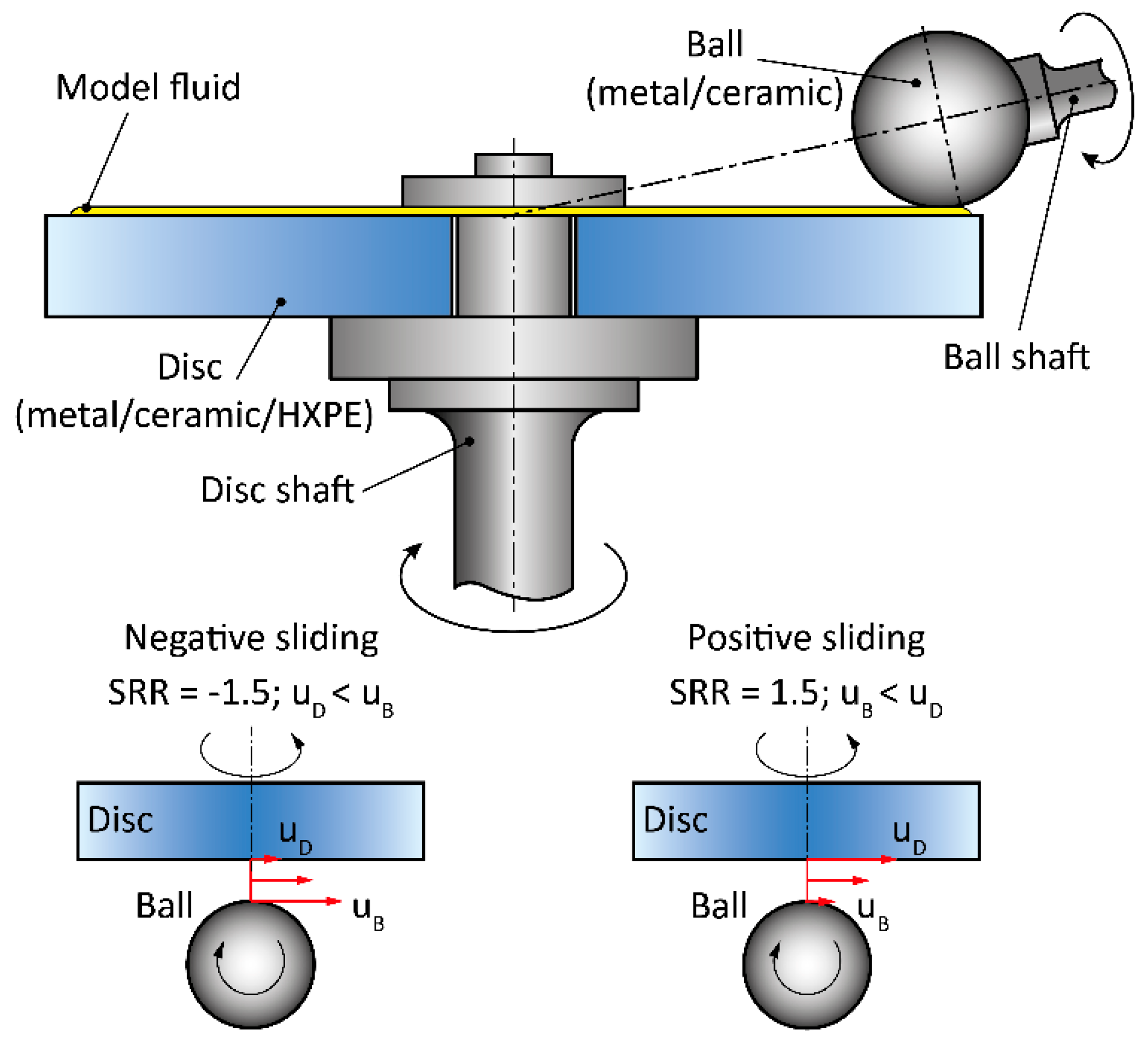
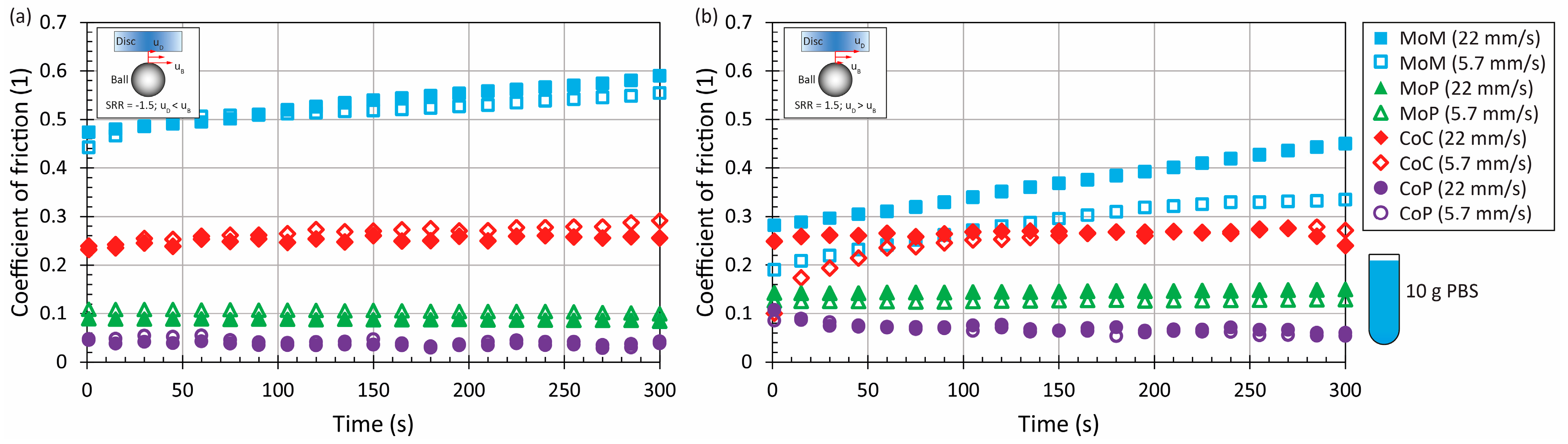
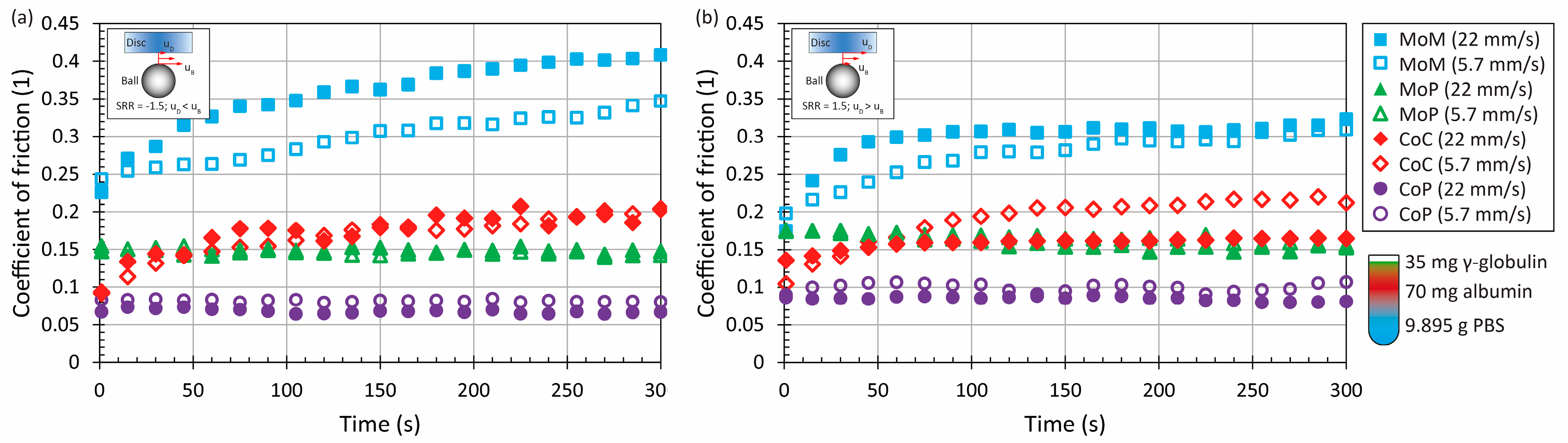
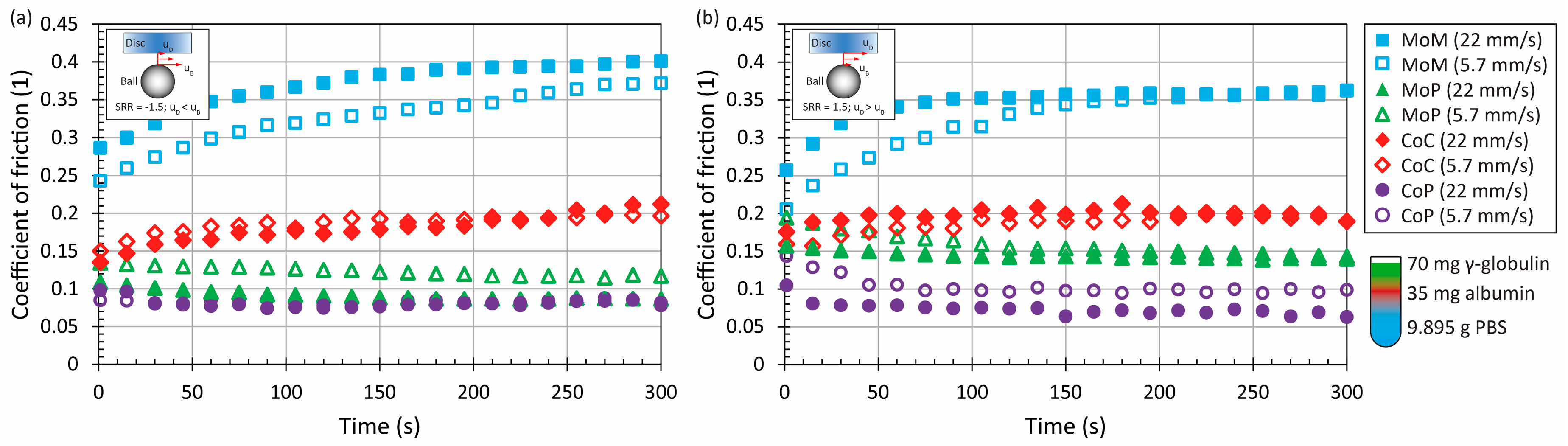

| Parameter | Ball | Disc | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Metal | Ceramic | Metal | Ceramic | HXPE |
| Average surface roughness Ra (μm) | 0.087 | 0.035 | 0.008 | 0.998 | 0.841 |
| Standard deviation SD (μm) | ±0.00587 | ±0.00414 | ±0.00039 | ±0.10707 | ±0.13631 |
| Model Synovial Fluid (MSF) | Volume (mL) | Protein Content (mg/mL) | Total Protein Concentration (mg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | Albumin | γ-globulin | - |
| Alb70+Glob35 | 10 | 7 | 3.5 | 10.5 |
| Alb35+Glob70 | 10 | 3.5 | 7 | 10.5 |
| Alb140+Glob70 | 10 | 14 | 7 | 21 |
| Albumin70 | 10 | 7 | - | 7 |
| γ-globulin35 | 10 | - | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| PBS | 10 | - | - | - |
| Experiment Set | Material Combination | Mean Speed (mm/s) | Slide-To-Roll Ratio (%) | Model Synovial Fluid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Metal-on-Metal (MoM) | 5.7; 22 | 150; −150 | Alb70+Glob35; Alb35+Glob70; Alb140+Glob70; PBS |
| 2 | Metal-on-highly crosslinked polyethylene (HXPE) (MoP) | 5.7; 22 | 150; −150 | Alb70+Glob35; Alb35+Glob70; Alb140+Glob70; PBS |
| 3 | Ceramic-on-Ceramic (CoC) | 5.7; 22 | 150; −150 | Alb70+Glob35; Alb35+Glob70; Alb140+Glob70; PBS |
| 4 | Ceramic-on-HXPE (CoP) | 5.7; 22 | 150; −150 | Alb70+Glob35; Alb35+Glob70; Alb140+Glob70; PBS |
| 5 | MoM | 22 | 150; −150 | Albumin70; γ-globulin35 |
| 6 | MoP | 22 | 150; −150 | Albumin70; γ-globulin35 |
| 7 | CoC | 22 | 150; −150 | Albumin70; γ-globulin35 |
| 8 | CoP | 22 | 150; −150 | Albumin70; γ-globulin35 |
| Slide-To-Roll Ratio (%) | Mean Speed (mm/s) | Ball Speed (mm/s) | Disc Speed (mm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| −150 | 5.7 | 9.975 | 1.425 |
| −150 | 22 | 38.5 | 5.5 |
| 150 | 5.7 | 1.425 | 9.975 |
| 150 | 22 | 5.5 | 38.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nečas, D.; Vrbka, M.; Křupka, I.; Hartl, M. The Effect of Kinematic Conditions and Synovial Fluid Composition on the Frictional Behaviour of Materials for Artificial Joints. Materials 2018, 11, 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050767
Nečas D, Vrbka M, Křupka I, Hartl M. The Effect of Kinematic Conditions and Synovial Fluid Composition on the Frictional Behaviour of Materials for Artificial Joints. Materials. 2018; 11(5):767. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050767
Chicago/Turabian StyleNečas, David, Martin Vrbka, Ivan Křupka, and Martin Hartl. 2018. "The Effect of Kinematic Conditions and Synovial Fluid Composition on the Frictional Behaviour of Materials for Artificial Joints" Materials 11, no. 5: 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050767
APA StyleNečas, D., Vrbka, M., Křupka, I., & Hartl, M. (2018). The Effect of Kinematic Conditions and Synovial Fluid Composition on the Frictional Behaviour of Materials for Artificial Joints. Materials, 11(5), 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050767





