New Insights into Sensitization Mechanism of the Doped Ce (IV) into Strontium Titanate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Preparation of Pure SrTiO3
2.2. Preparation of Ce-Doped SrTiO3
2.3. Materials Characterizations
2.4. Photocatalytic Activity Tests
2.4.1. Effect of Initial Concentration of Methylene Blue on Photocatalytic Activity
2.4.2. Effect of Ce Doping Amount on Photocatalytic Activity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Synthesis Conditions
3.1.1. Effect of Tartaric Acid Dosage
3.1.2. Effect of Distilled Water Amount
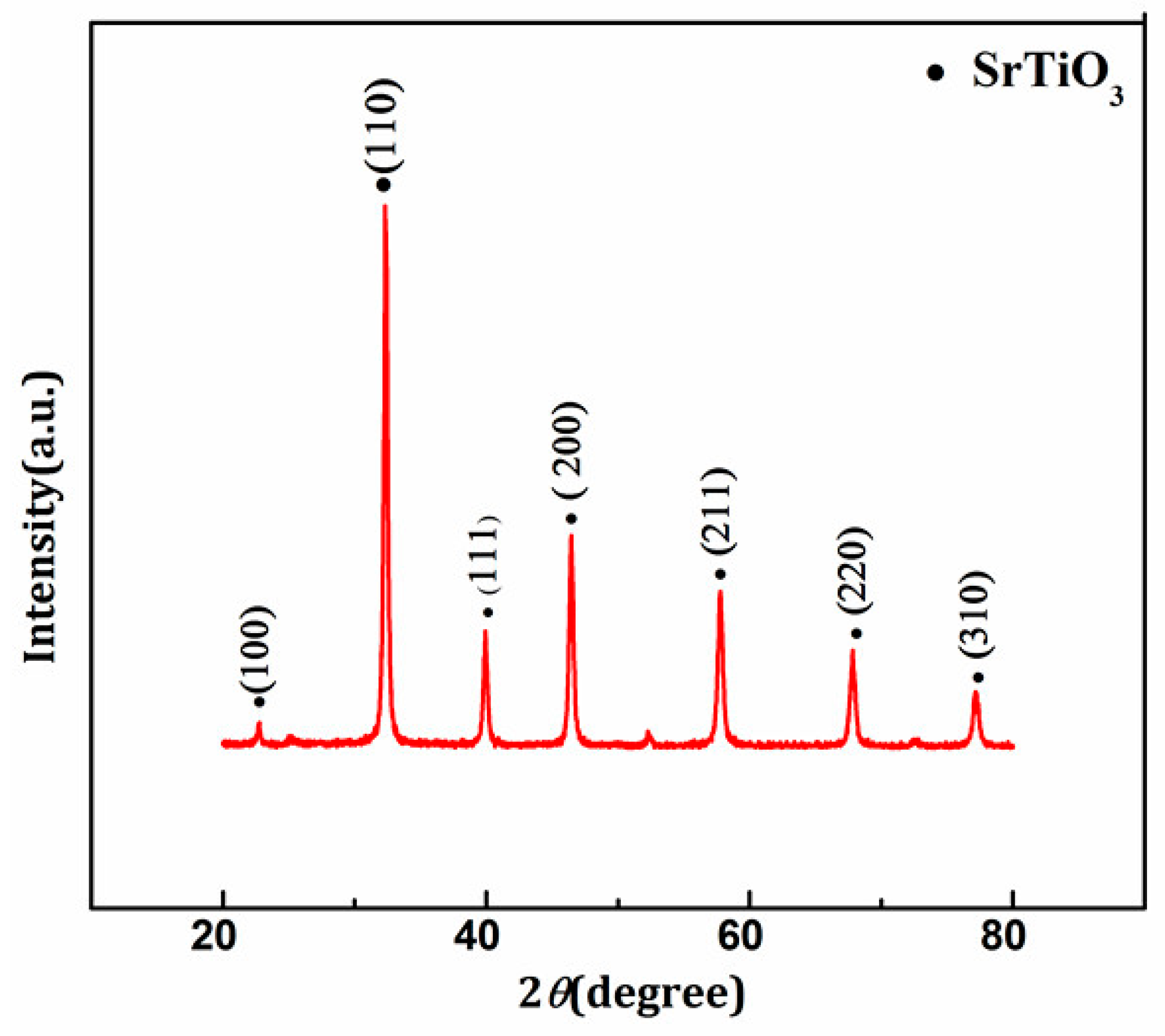
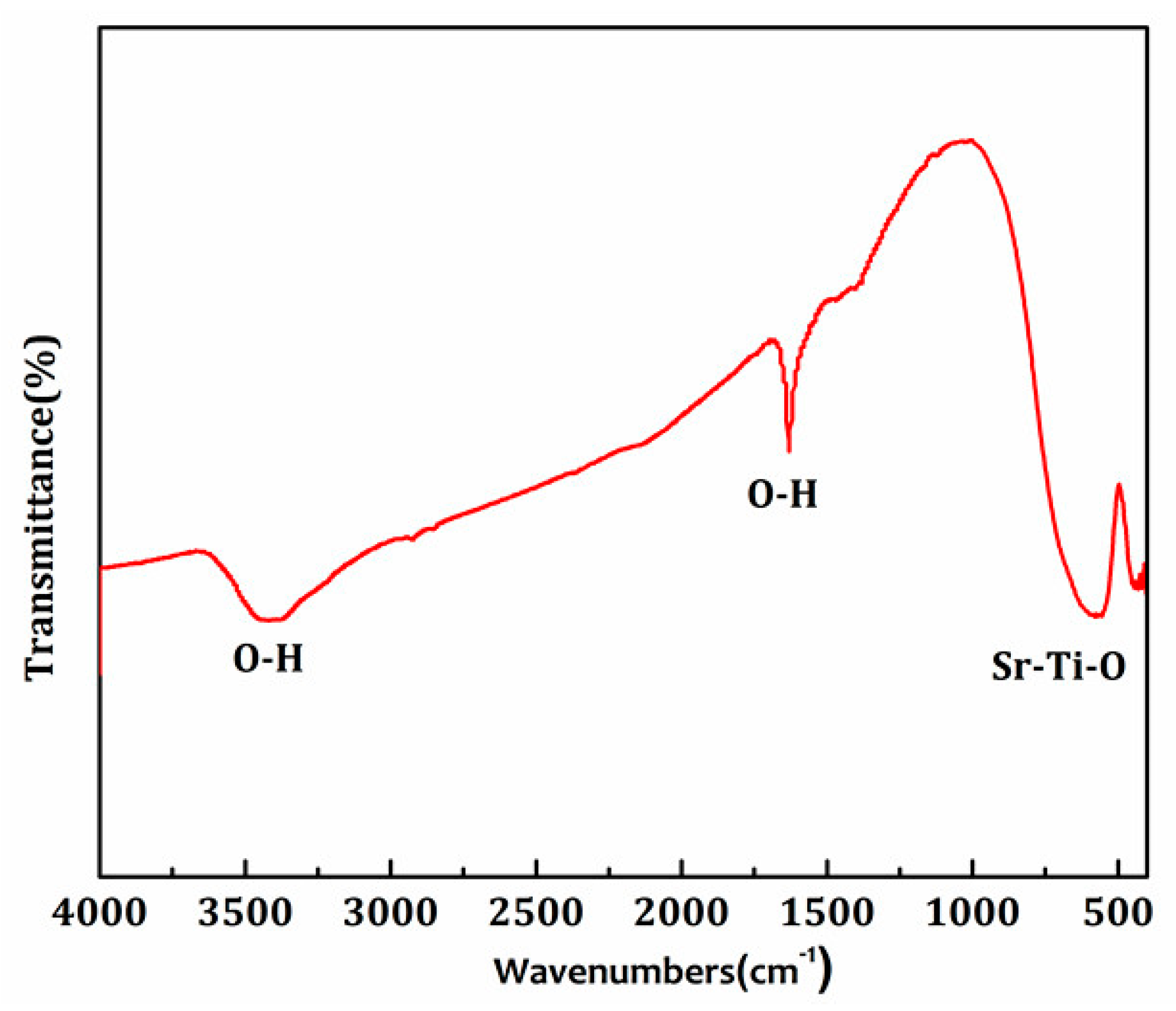
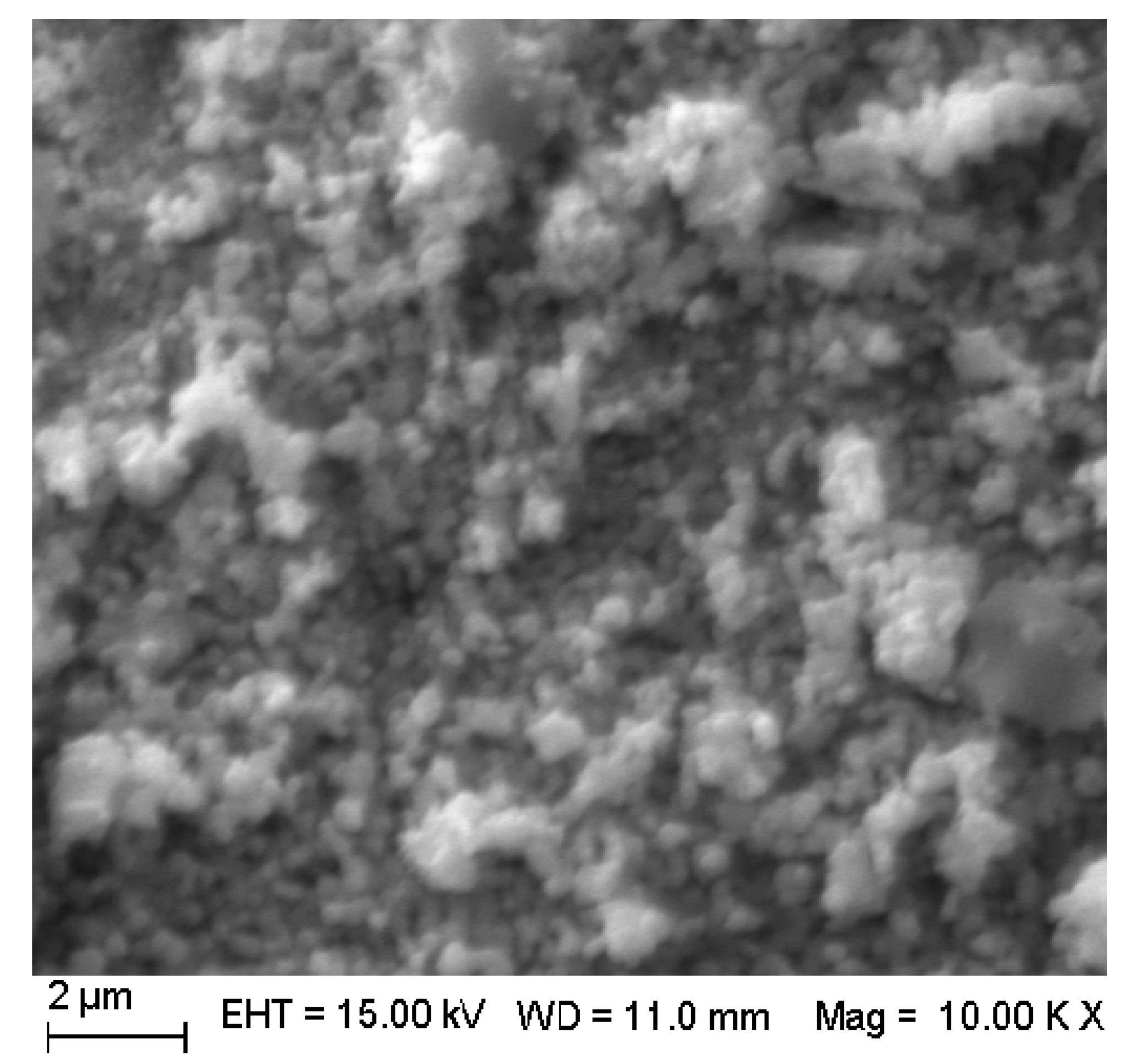
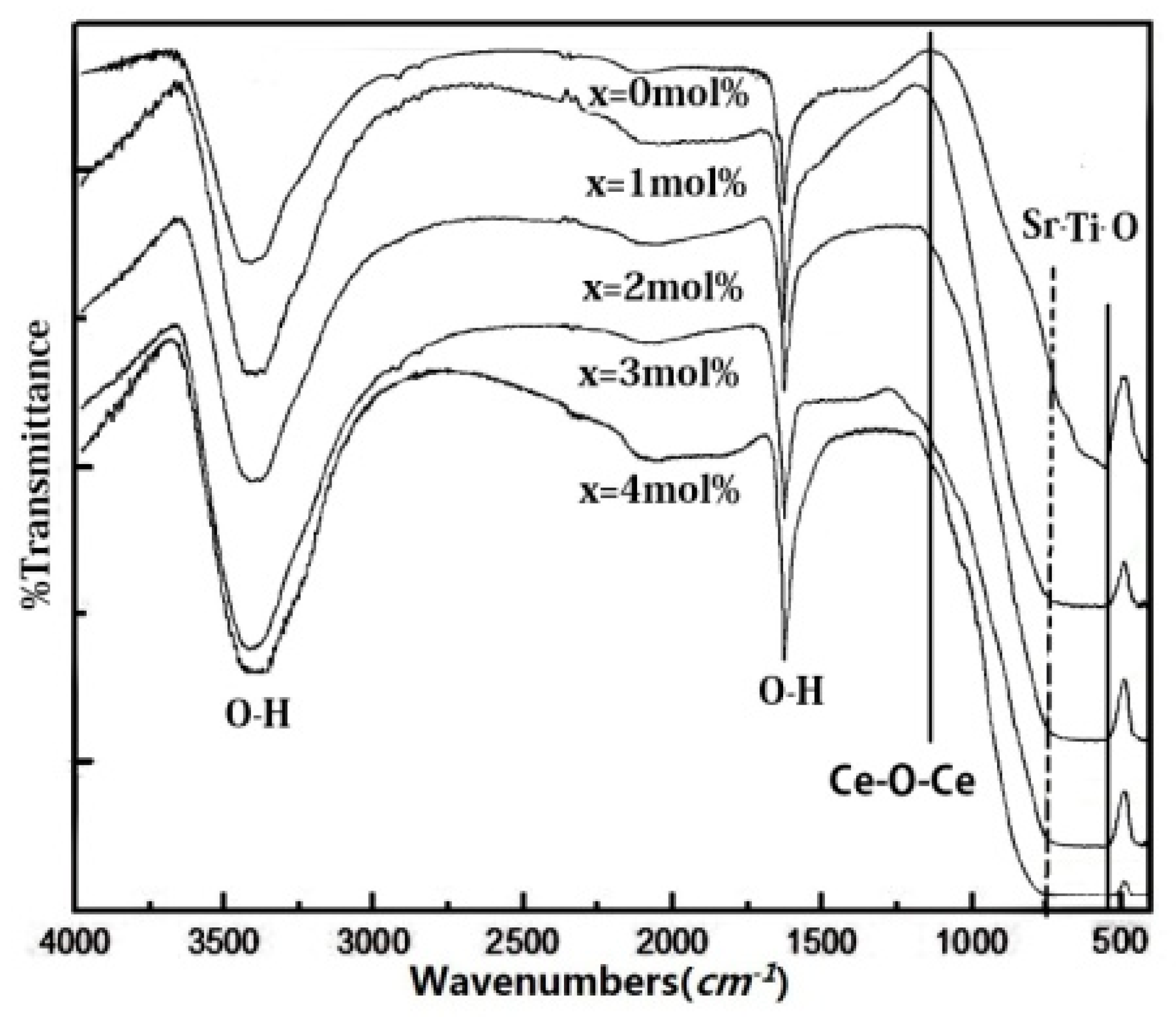
3.2. XRD, IR, and SEM Analysis of SrTiO3
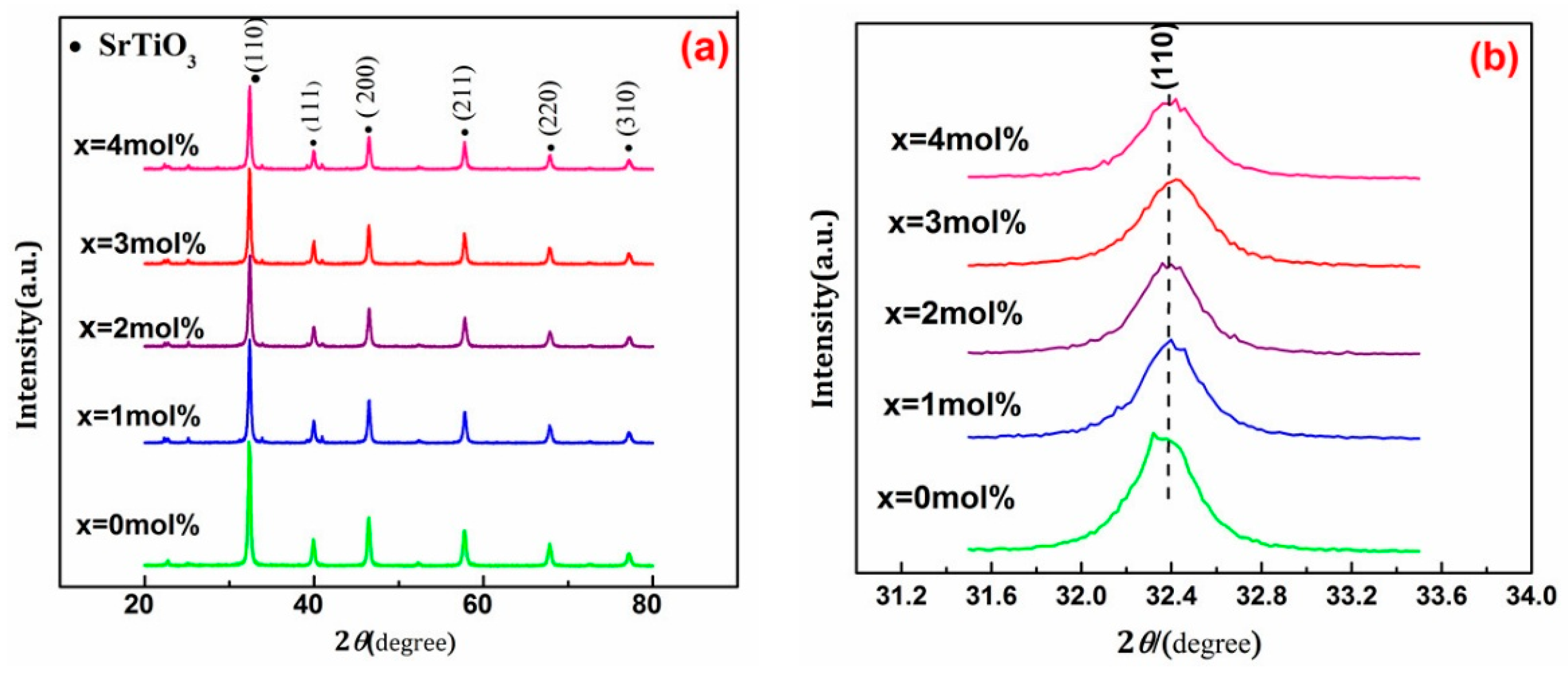
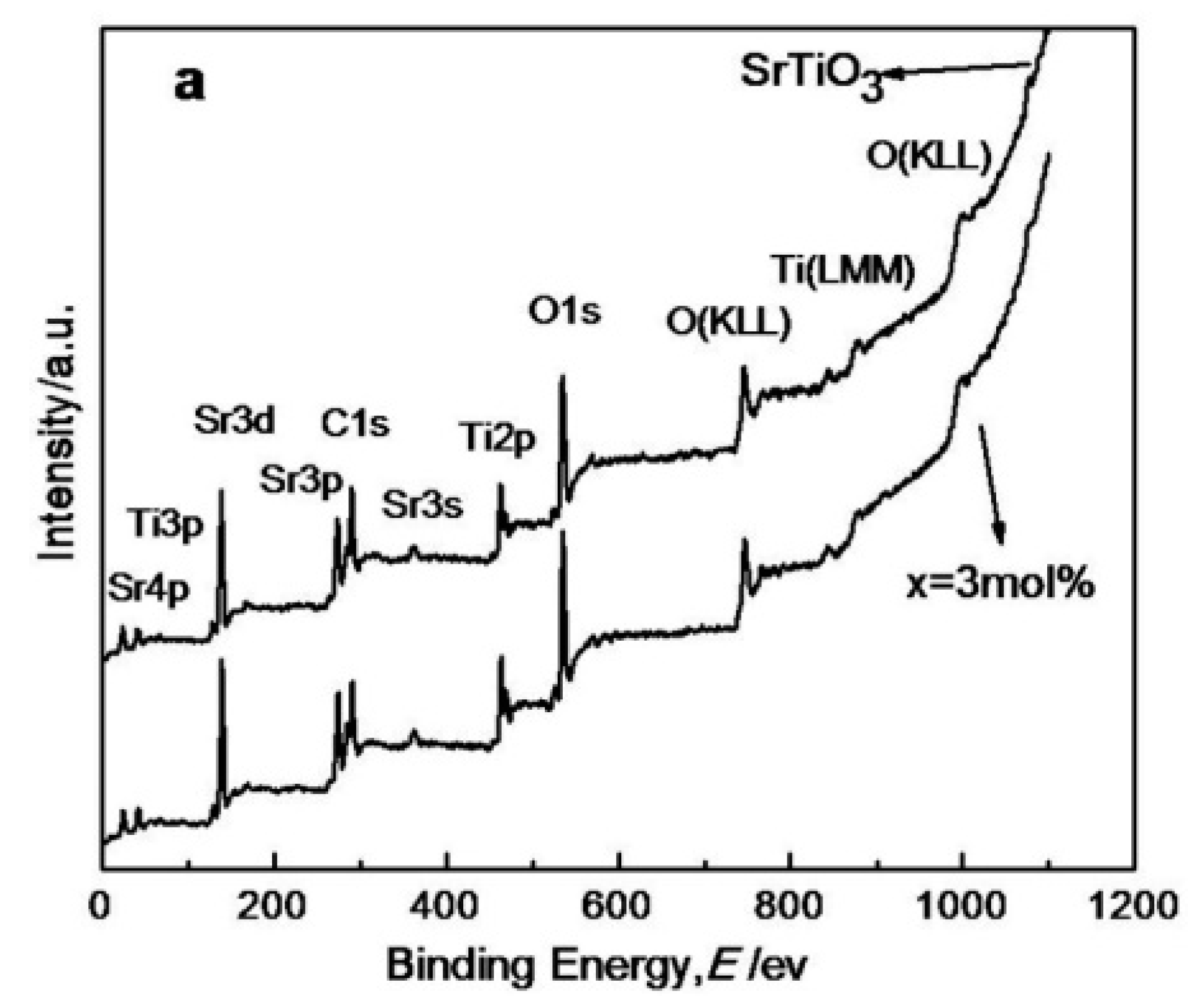
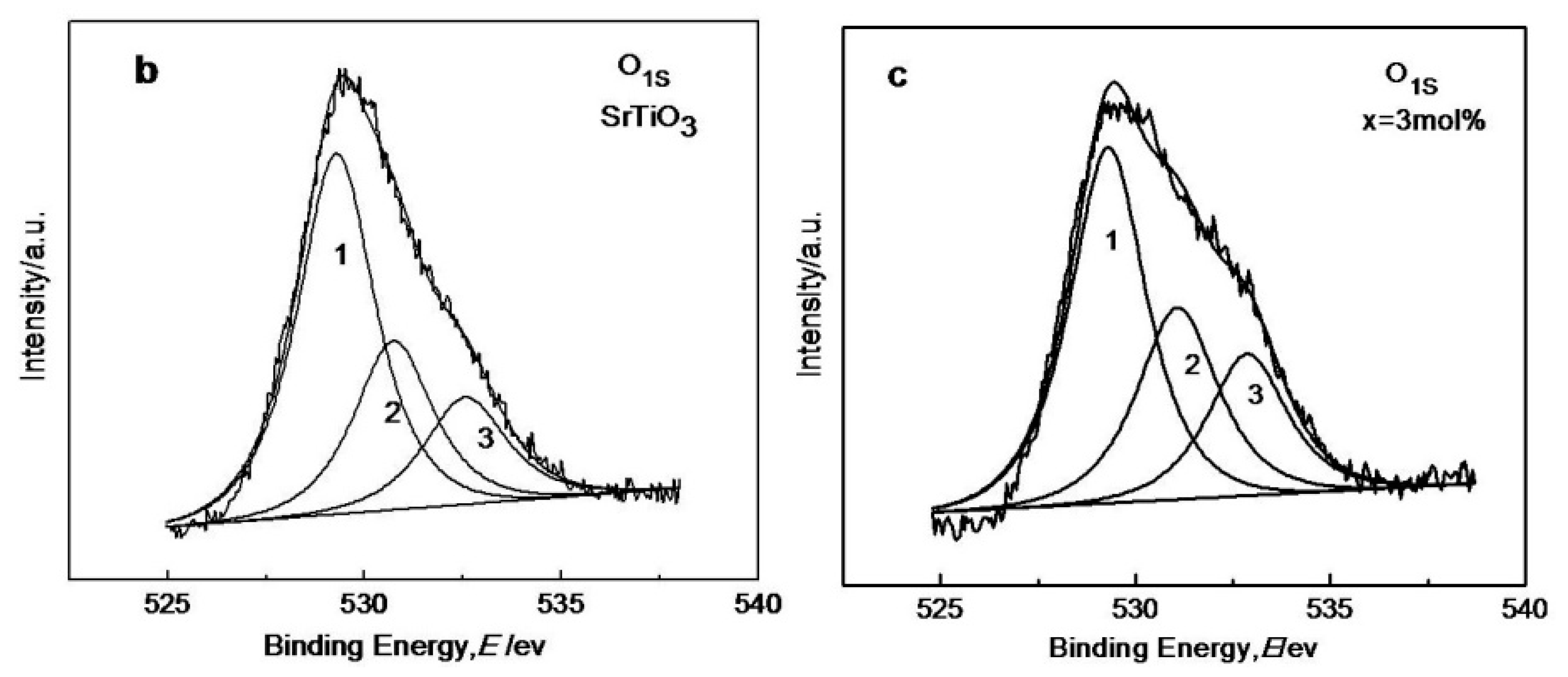
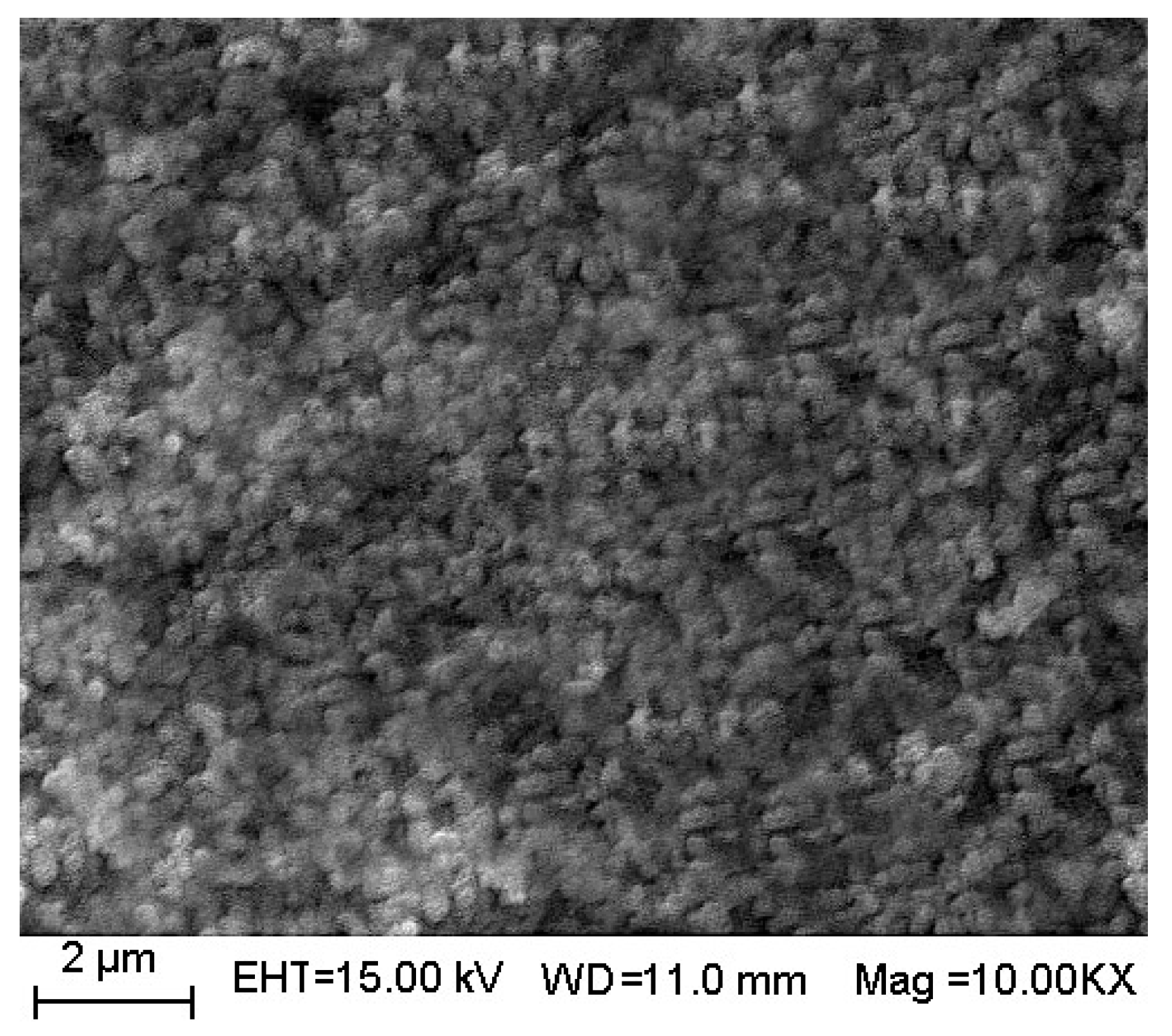
3.3. XRD, BET, IR, XPS, and SEM Analysis of Ce4+ Doped SrTiO3
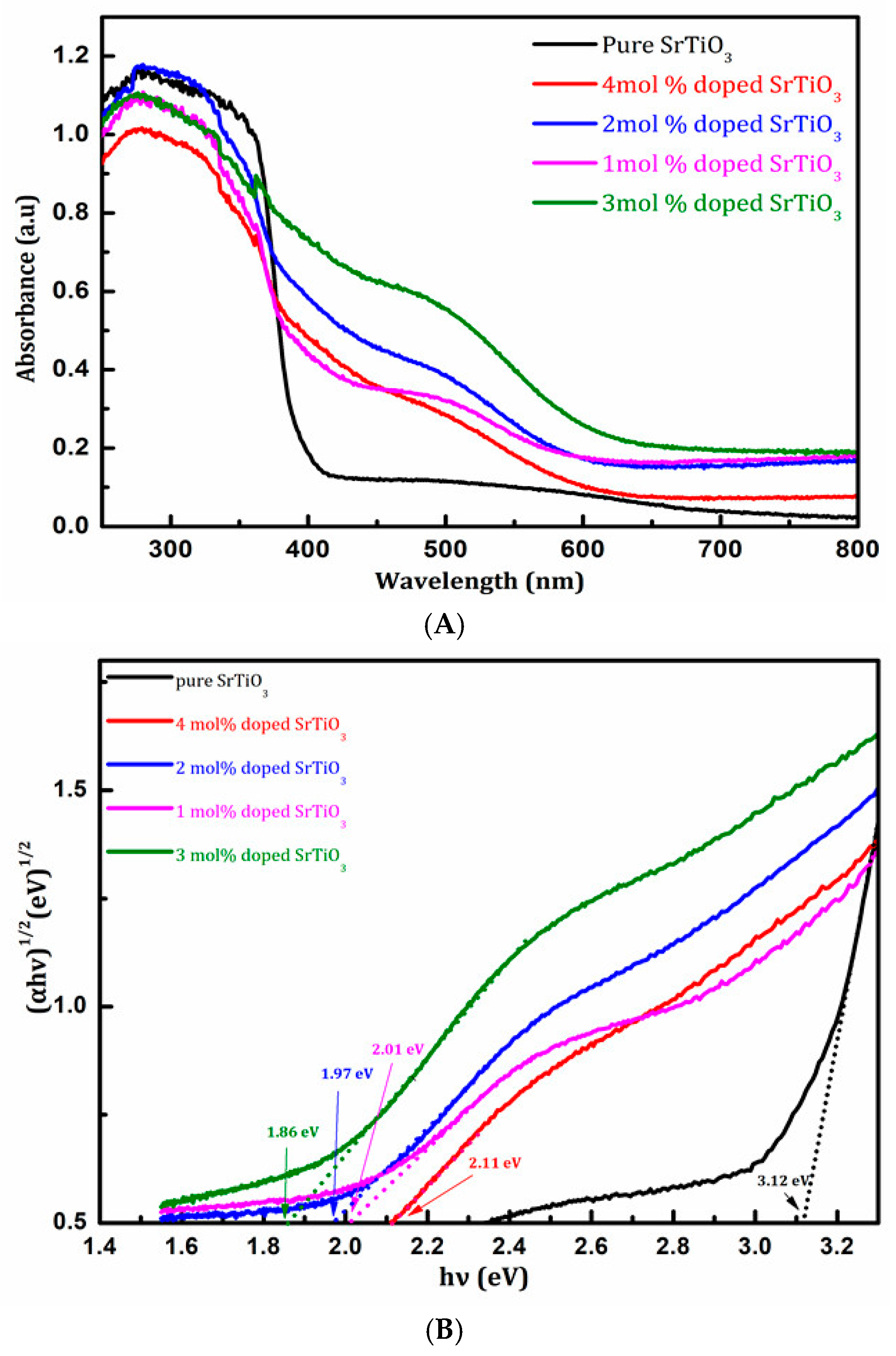
3.4. Optical Properties and Photocatalytic Activity
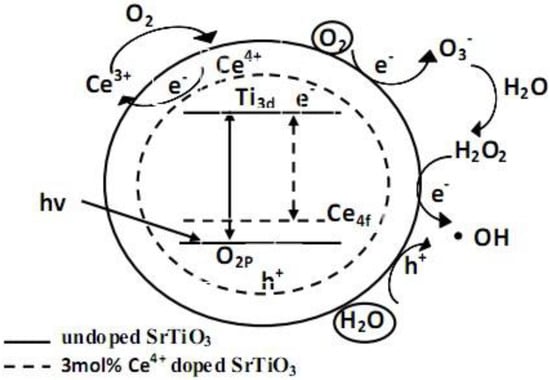
3.5. Photocatalytic Activity and Corresponding Mechanism
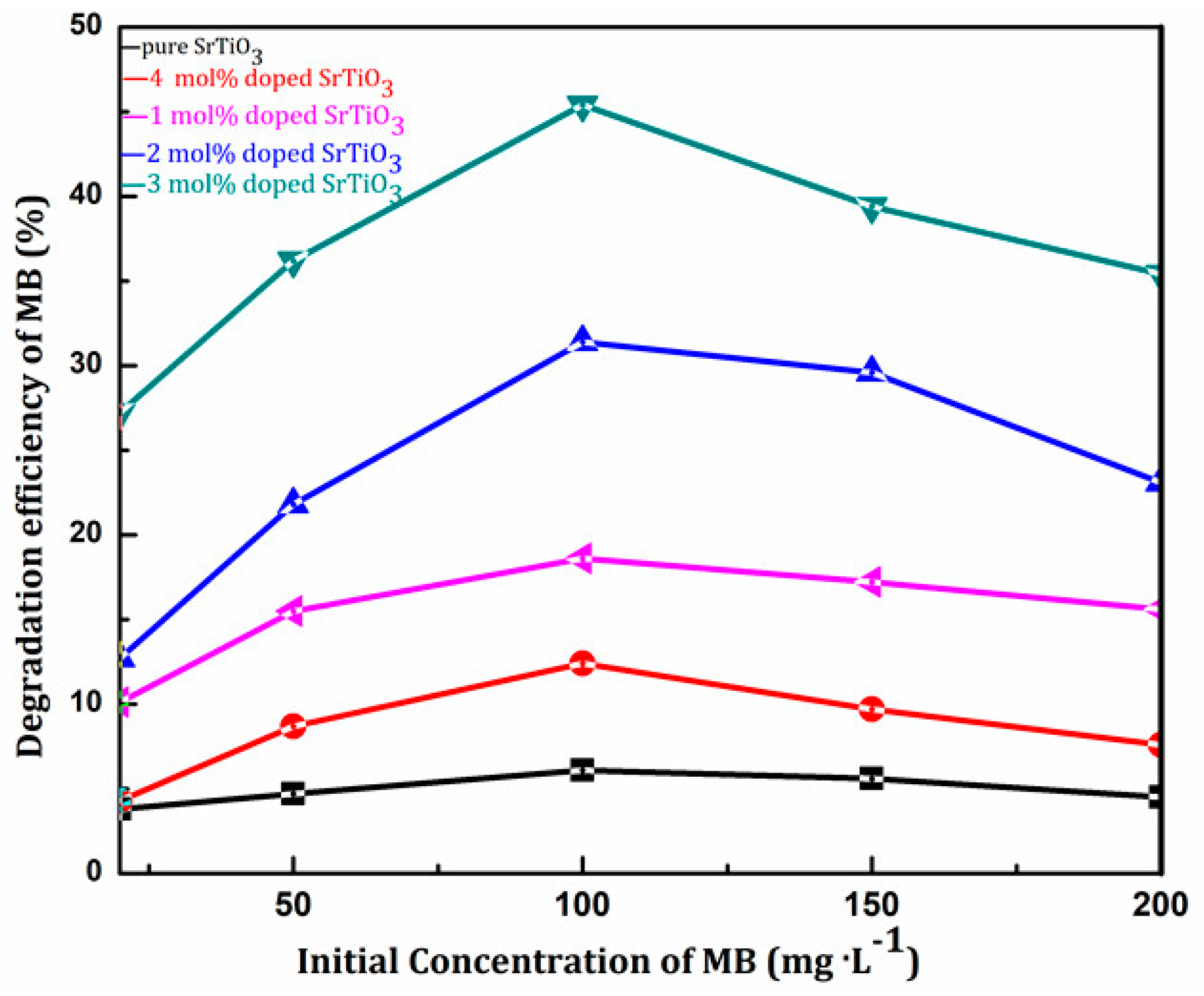
3.5.1. Effect of Initial Concentration of Methylene Blue on Photocatalytic Activity
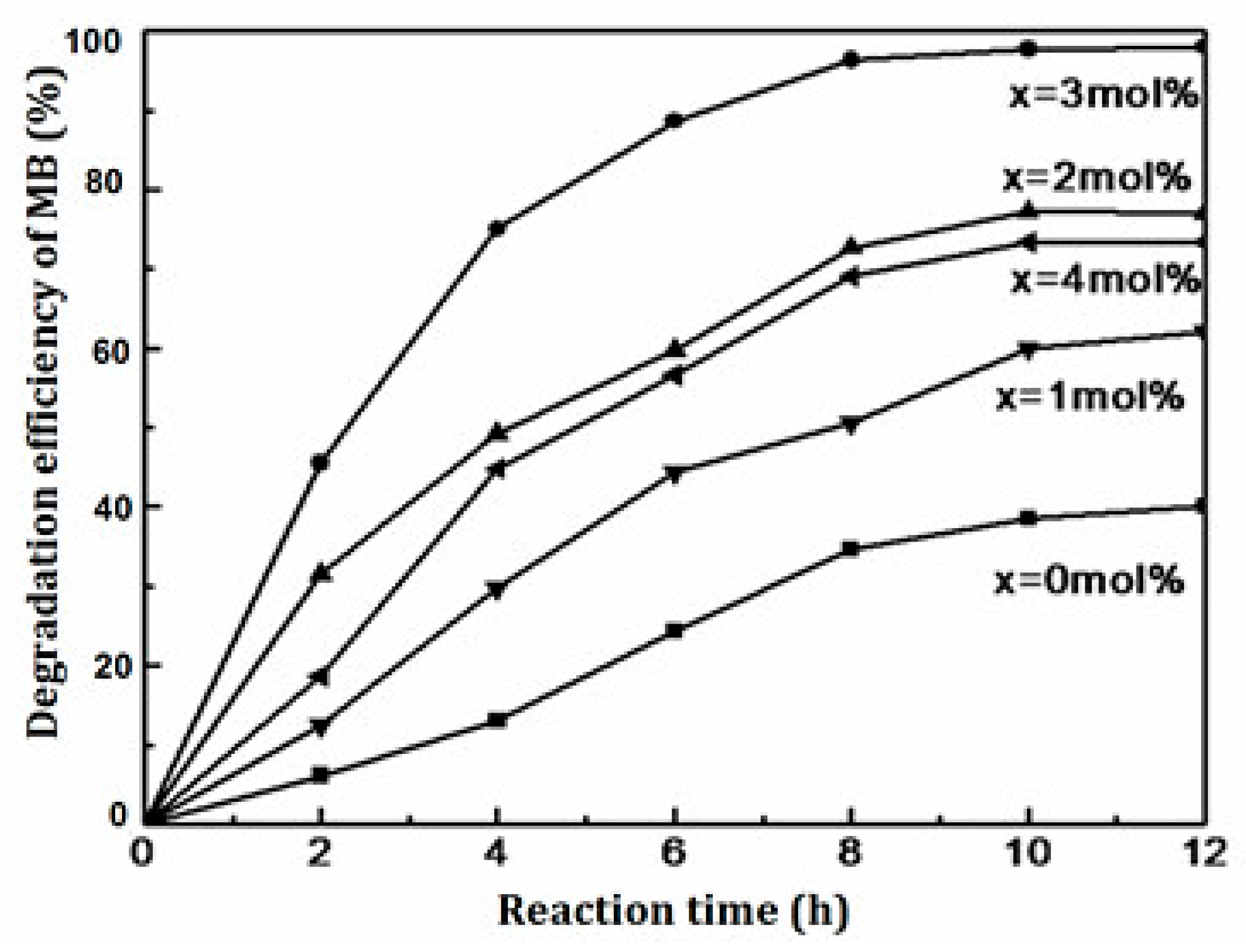
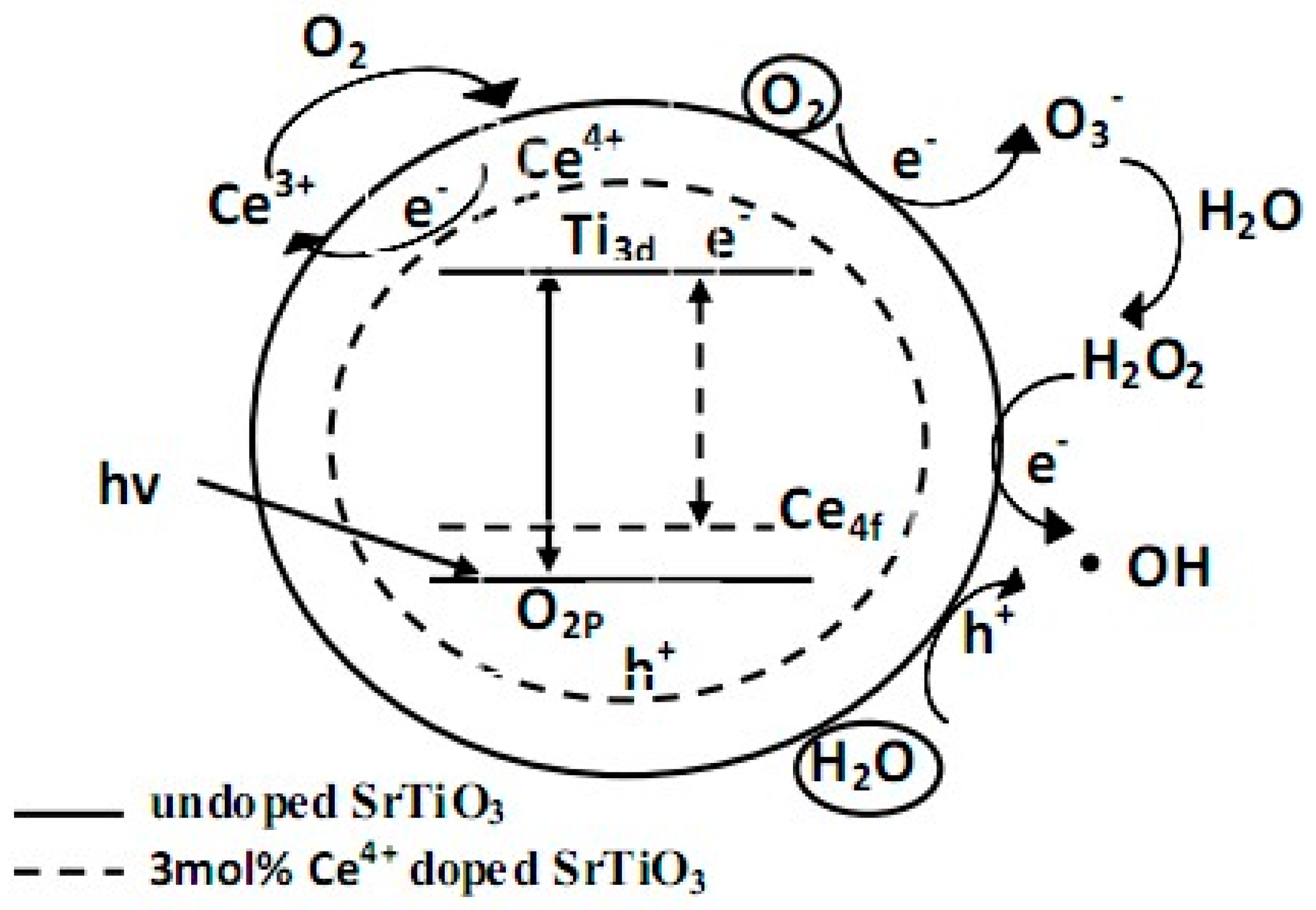
3.5.2. Photocatalytic Activity and Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, T.P.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, C.H.; Shao, C.L.; Liu, Y.C. A Facile in Situ Hydrothermal Method to SrTiO3/TiO2 Nanofiber Heterostructures with High Photocatalytic Activity. Langmuir 2011, 27, 2946–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, M.Y.; Li, Y.Z.; Hou, J.T.; Zeng, M.; Zhao, X.J. Extremely efficient full solar spectrum light driven thermocatalyticactivity for the oxidation of VOCs on OMS-2 nanorod catalyst. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 174, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.P.; Xu, L.J.; Liu, C.L. Magnetic composite BiOCl-SrFe12O19: A novel p-n type heterojunction with its enhanced photocatalytic activity. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 2211–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, R.M.; Alvarez-Galvan, M.C.; de la Mano, J.A.V. A framework for visible-light water splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 1865–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ji, Z.Y.; Lin, J.J.; Li, P. Preparation and optical and photocatalytic properties of Ce-doped ZnO microstructures by simple solution method. Mater. Sci. Semicon. Proc. 2017, 71, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A. Simple and large scale refluxing method for preparation of Ce-doped ZnO nanostructures as highly efficient photocatalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 265, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, M.F.; Ahmed, A.I.; Ibrahim, A.; Bouzid, H.; Al-Sayari, S.A. Highly efficient photocatalyst based on Ce doped ZnO nanorods: Controllable synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 229, 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- Piña-Pérez, Y.; Tzompantzi-Morales, F.; Pérez-Hernández, R.; Arroyo-Murillo, R.; Acevedo-Peña, P.; Gómez-Romero, R. Photocatalytic activity of Al2O3 improved by the addition of Ce3+/Ce4+ synthesized by the sol-gel method. Photodegradation of phenolic compounds using UV light. Fuel 2017, 198, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharatvaj, J.; Preethi, V.; Kanmani, S. Hydrogen production from sulphide wastewater using Ce3+ TiO2 photocatalysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 3935–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.B.; Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W. A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: Synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.F.; Hu, X.L.; Ho, W.K.; Hu, P.; Huang, Y.H. Facile fabrication of porous Cr-doped SrTiO3 nanotubes by electrospinning and their enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 3935–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehuta, K.A.; Kittilstved, K.R. Speciation of Cr(III) in intermediate phases during the sol–gel processing of Cr-doped SrTiO3 powders. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 6138–6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canu, G.; Buscaglia, V. Hydrothermal synthesis of strontium titanate: Thermodynamic considerations, morphology control and crystallisation mechanisms. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2017, 19, 3867–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.N.; Zhu, F.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; LU, G.; Zhao, Z. Morphology-Controlled Synthesis SrTiO3/TiO2 Heterostructures and Their Photocatalytic Performance for Water Splitting. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 21111–21118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.P.; Liu, C.L.; Xu, L.J. Novel heterojunction Bi2O3/SrFe12O19 magnetic photocatalyst with highly enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 24601–24610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.M.; Xie, Y.; Yu, C.L.; Liu, X.M.; Dai, Y.H.; Liu, L.J. Novel hybrid Sr-doped TiO2/magnetic Ni0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4 for enhanced separation and photodegradation of organics under visible light. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24056–24063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutty, T.R.N.; Nag, A. Role of interface states associated with transitional nanophase precipitates in the photoluminescence enhancement of SrTiO3:Pr3+, Al3+. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 2271–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadetnejad, D.; Yildirim, R. Photocatalytic hydrogen production by water splitting over Au/Al-SrTiO3. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Z.H.; Ge, Y.Z.; Ye, W.Y. Visible light activation of SrTiO3 by loading Ag/AgX (X = Cl, Br) for highly efficient plasmon-enhanced photocatalysis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 198, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.D.; Qiu, H.; Inoue, T.; Yao, Q.W. Band gap engineering of SrTiO3 for water splitting under visible light irradiation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 12507–12514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, Y.; Miyoshi, Y.; Maeda, T.; Ishikiriyama, K. Photocatalytic property of metal ion added SrTiO3 to Overall H2O splitting. Appl. Catal. A 2016, 521, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Lia, L.Y.; Dong, Z.F.; Xu, R.; Wu, Y. Fabrication of CeO2 nanorods for enhanced solar photocatalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 5275–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Number | n(Sr2+)/n(tartaric acid) | Sol State | Relative Crystallinity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2:1 | white precipitation | 23 |
| 2 | 1:1 | white precipitation | 27 |
| 3 | 1:2 | transparent | 78 |
| 4 | 1:3 | transparent | 85 |
| 5 | 1:4 | transparent | 89 |
| 6 | 1:5 | transparent | 89 |
| Sample Number | H2O (mL) | Sol State | Drying Time (h) | Relative Crystallinity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | white precipitation | 5 | 13 |
| 2 | 10 | white precipitation | 6 | 20 |
| 3 | 15 | transparent | 8 | 80 |
| 4 | 20 | transparent | 10 | 89 |
| 5 | 25 | white precipitation | 15 | 89 |
| Catalysts | Surface Area/(m2·g−1) | Pore Volume/(cm3·g−1) | Mean Pore Size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| SrTiO3 | 11.8 | 0.040 | 13.6 |
| 1 mol % Ce4+ doped SrTiO3 | 13.5 | 0.047 | 14.2 |
| 2 mol % Ce4+ doped SrTiO3 | 25.9 | 0.052 | 8.1 |
| 3 mol % Ce4+ doped SrTiO3 | 48.7 | 0.132 | 7.7 |
| 4 mol % Ce4+ doped SrTiO3 | 12.7 | 0.048 | 15.2 |
| Catalysts | Surface Atomic Composition | Surface Atomic Ratio | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr | Ti | O | n(Sr)/n(Ti) | |
| SrTiO3 | 24.18% | 13.77% | 55.44% | 0.96 |
| 3 mol %Ce4+ doped SrTiO3 | 25.02% | 13.01% | 57.19% | 1.05 |
| Samples | Degradation Efficiency (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 mg/L | 50 mg/L | 100 mg/L | 150 mg/L | 200 mg/L | |
| SrTiO3 | 3.8 | 4.7 | 6.1 | 5.6 | 4.5 |
| 1 mol % Ce4+ doped SrTiO3 | 10.1 | 15.5 | 18.6 | 17.2 | 15.6 |
| 2 mol % Ce4+ doped SrTiO3 | 12.7 | 21.8 | 31.4 | 29.6 | 23.1 |
| 3 mol % Ce4+ doped SrTiO3 | 27.2 | 36.2 | 45.4 | 39.4 | 35.4 |
| 4 mol % Ce4+ doped SrTiO3 | 4.3 | 8.7 | 12.4 | 9.7 | 7.6 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, L. New Insights into Sensitization Mechanism of the Doped Ce (IV) into Strontium Titanate. Materials 2018, 11, 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040646
Xie T, Wang Y, Liu C, Xu L. New Insights into Sensitization Mechanism of the Doped Ce (IV) into Strontium Titanate. Materials. 2018; 11(4):646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040646
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Taiping, Yuan Wang, Chenglun Liu, and Longjun Xu. 2018. "New Insights into Sensitization Mechanism of the Doped Ce (IV) into Strontium Titanate" Materials 11, no. 4: 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040646
APA StyleXie, T., Wang, Y., Liu, C., & Xu, L. (2018). New Insights into Sensitization Mechanism of the Doped Ce (IV) into Strontium Titanate. Materials, 11(4), 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040646