A Novel Design Framework for Structures/Materials with Enhanced Mechanical Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
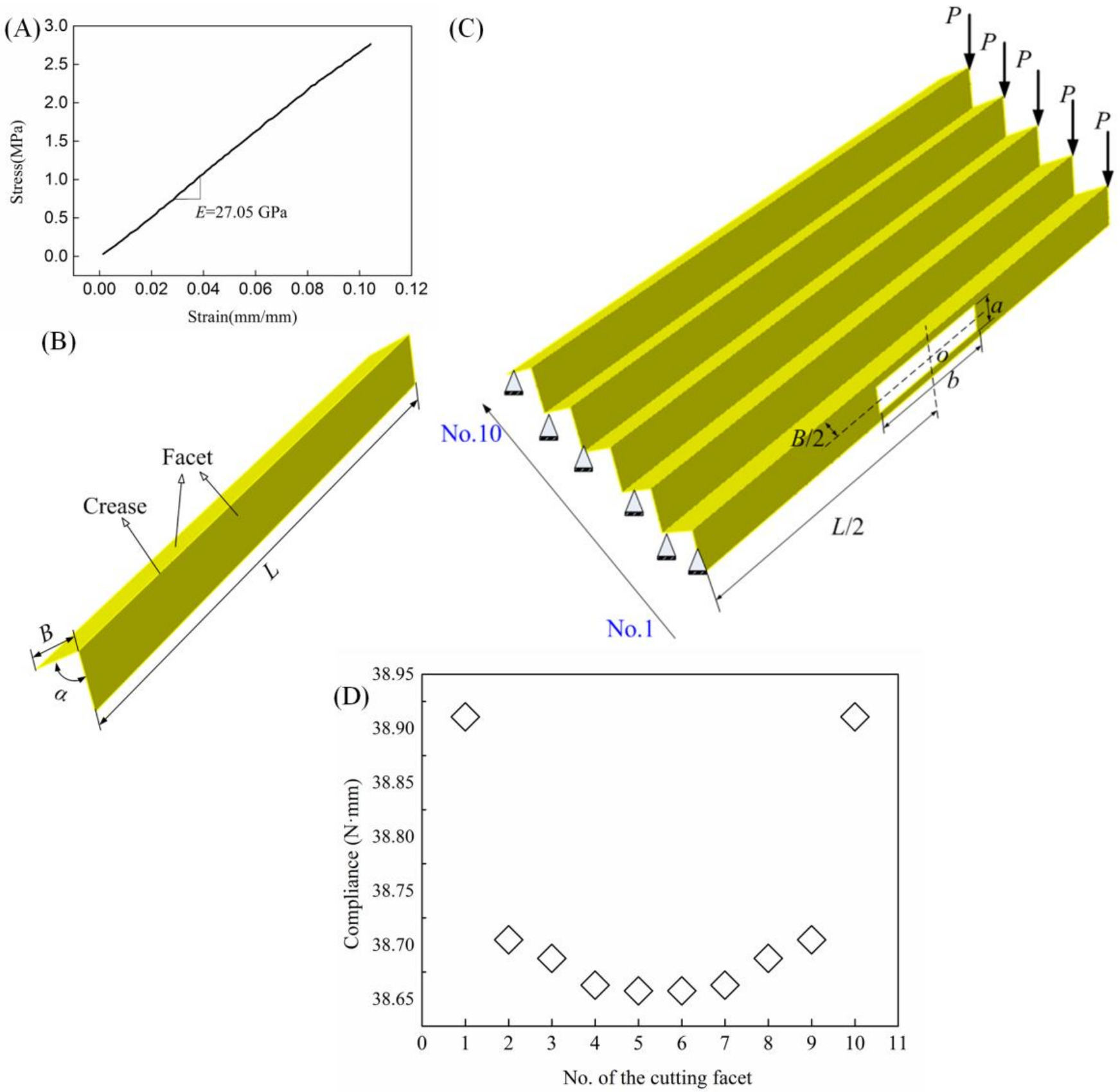
2.1. Testing
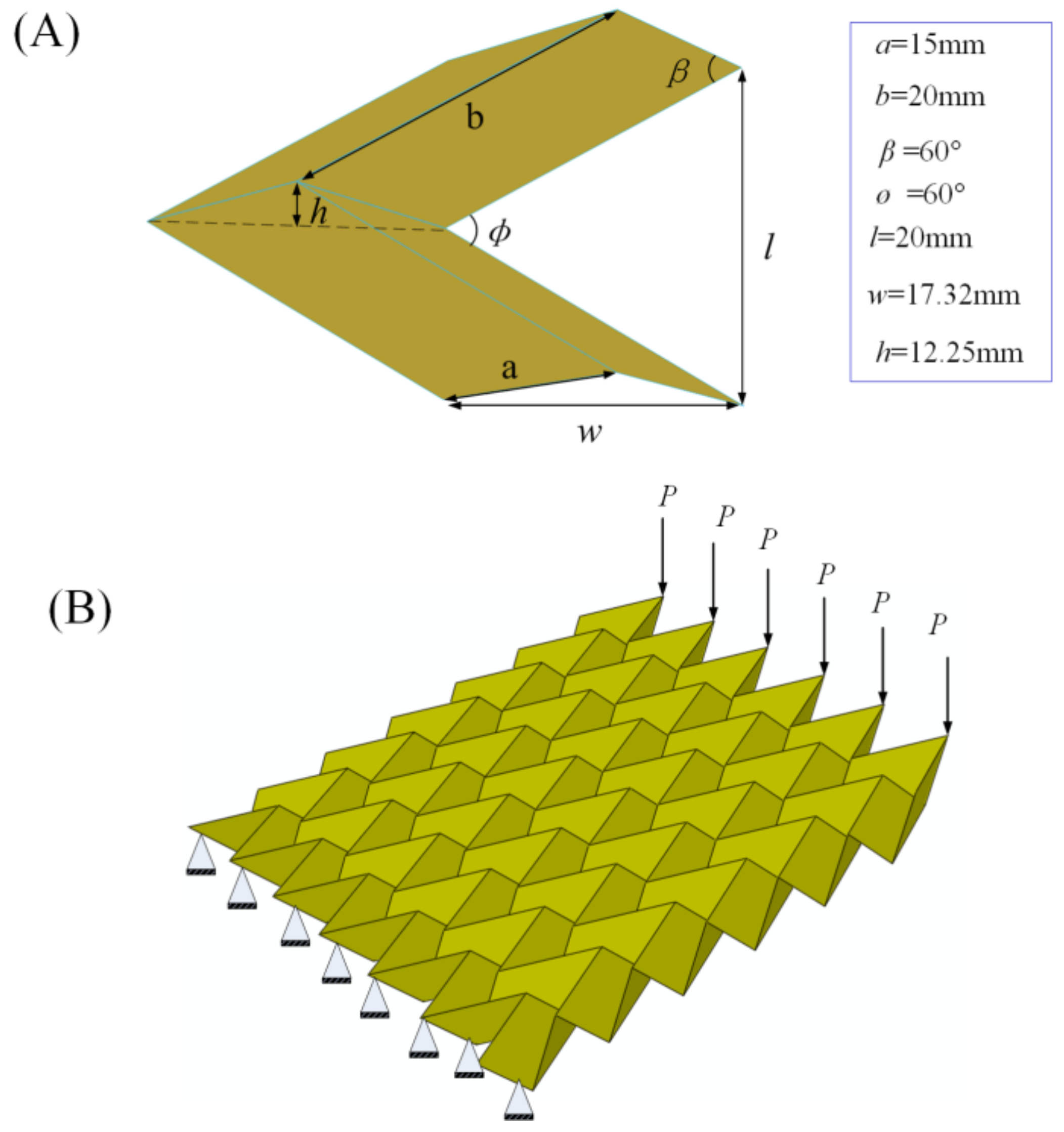
2.2. Geometrical Dimensions
2.3. Finite Element (FE) Simulations
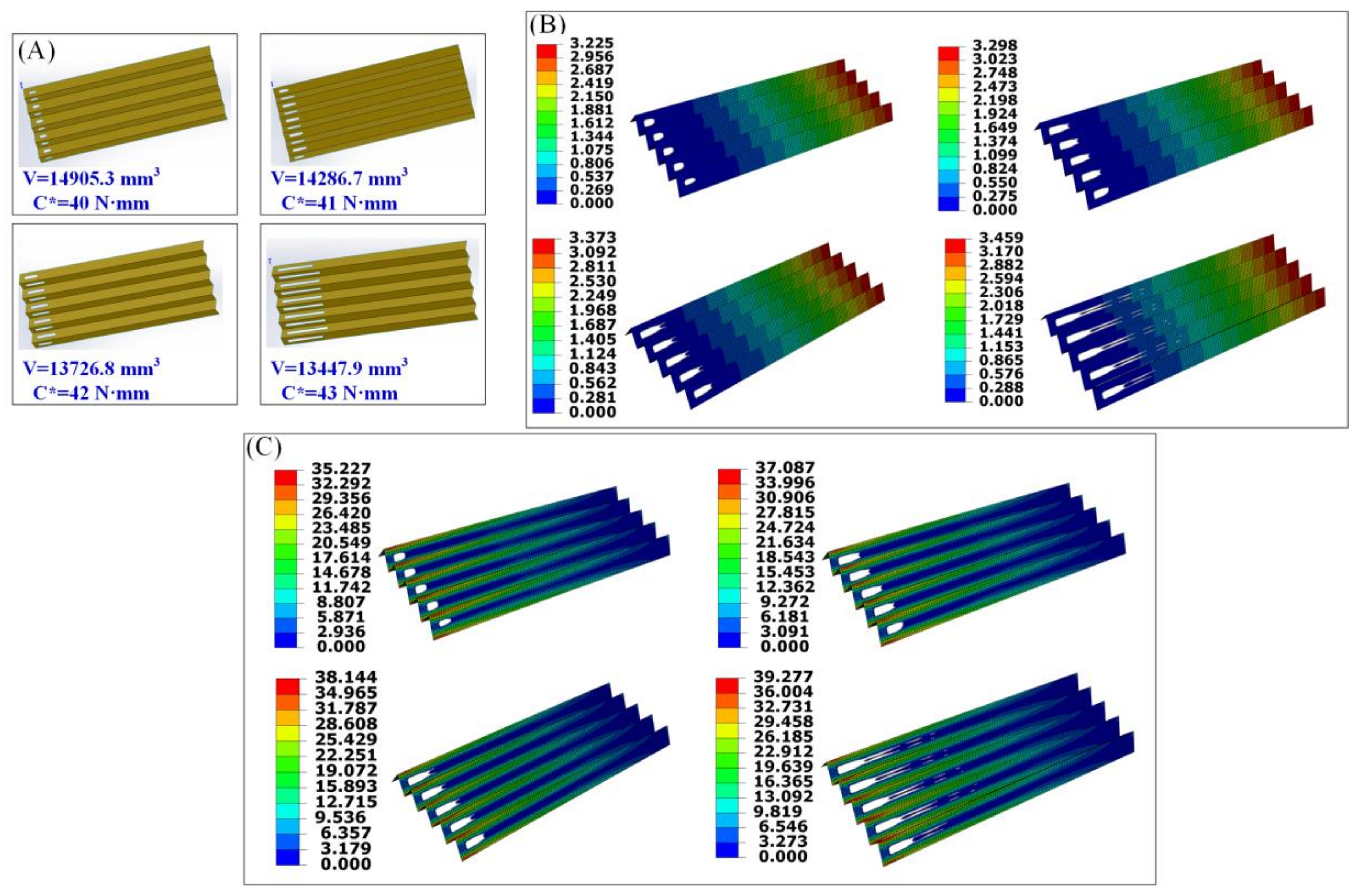
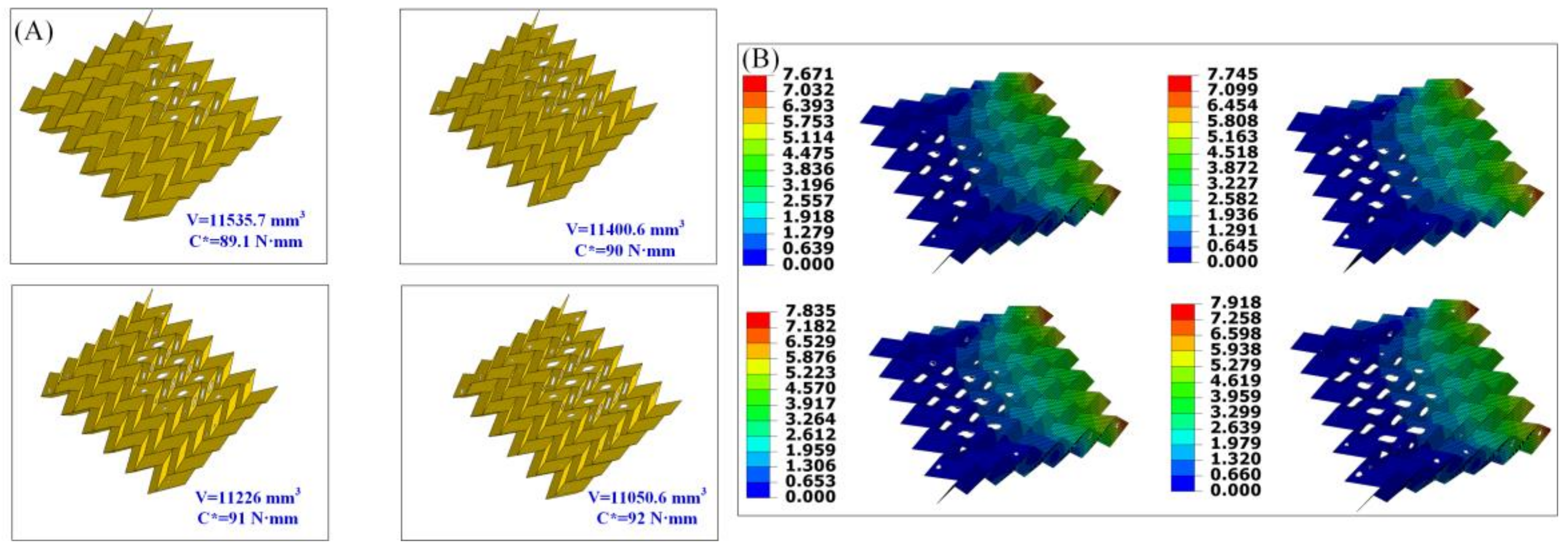
2.4. Topology Optimization
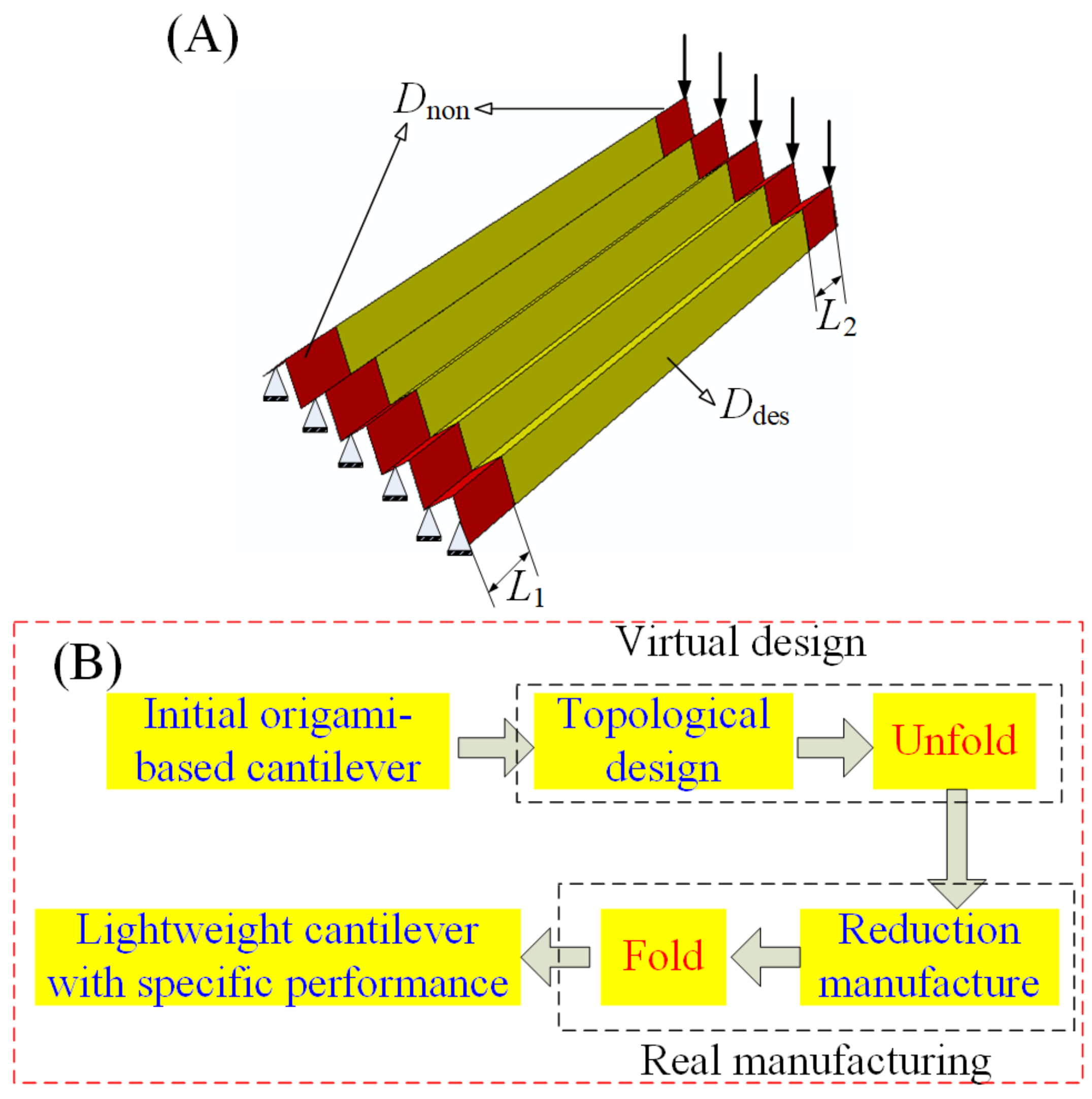
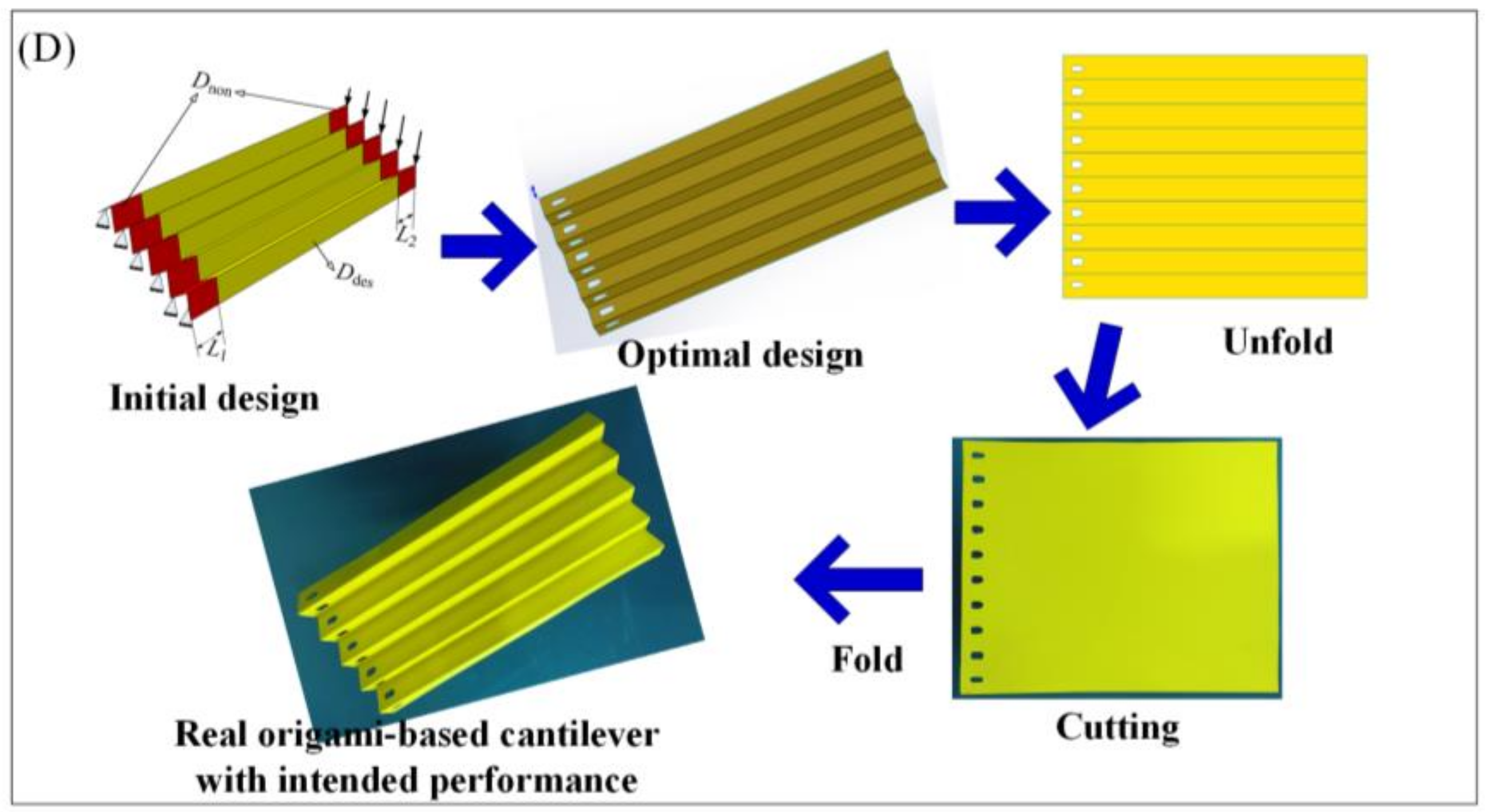
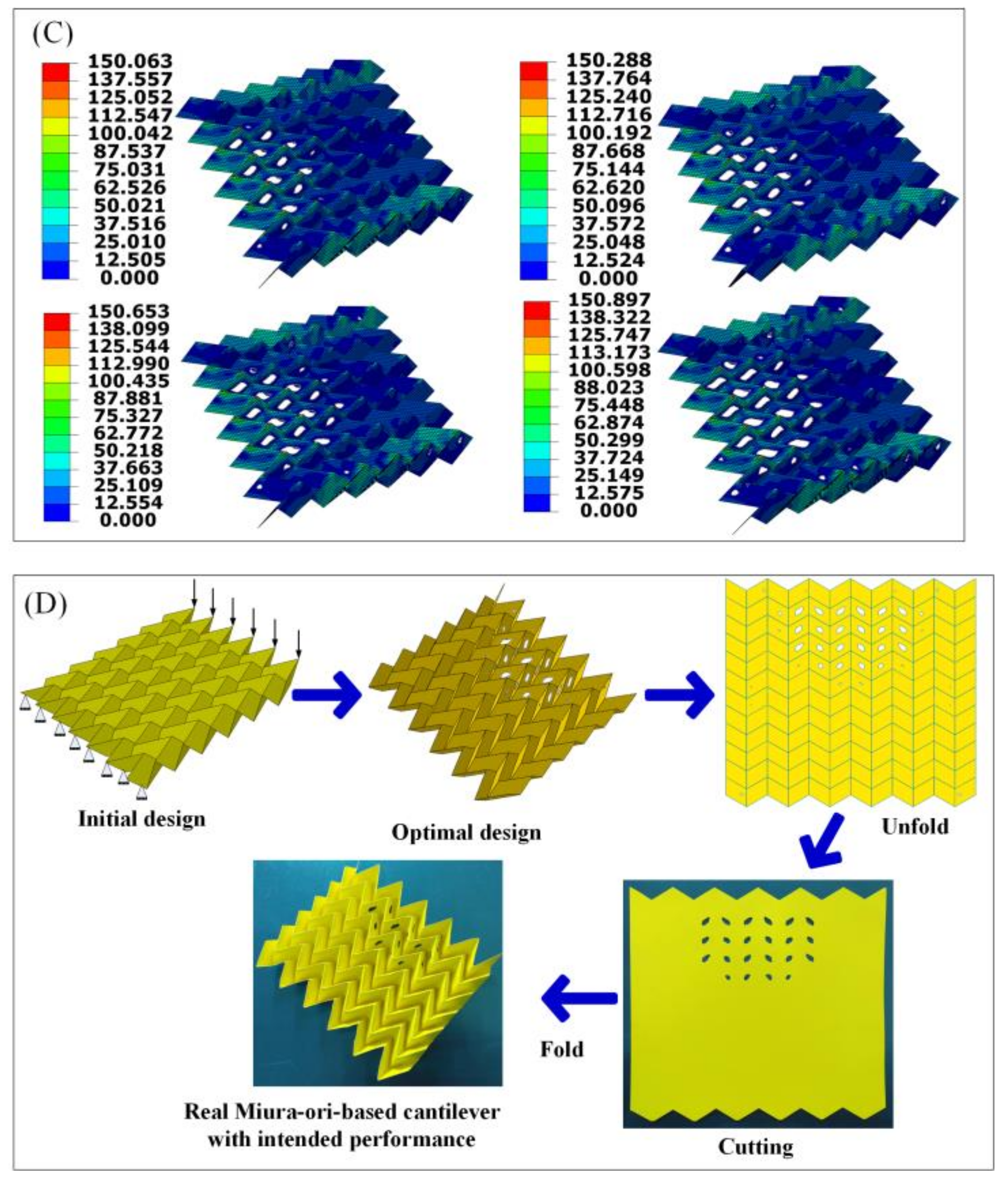
2.5. Design and Fabrication Framework
3. Results
3.1. Deflection Behavior of the Origami-Based Cantilever
3.2. Design and Fabrication of the Origami-Based Cantilevers
3.3. Design of Miura-Ori-Based Structures
4. Discussion and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haftka, R.T.; Zafer, G. Elements of Structural Optimization; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Anindyajati, A.; Boughton, P.; Ruys, A.J. Modelling and optimization of Polycaprolactone ultrafine-fibres electrospinning process using response surface methodology. Materials 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolowski, J.; Zolesio, J.P. Introduction to Shape Optimization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Noël, L.; Duysinx, P. Shape optimization of microstructural designs subject to local stress constraints within an XFEM-level set framework. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2017, 55, 2323–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendsøe, M.P.; Sigmund, O. Material interpolation schemes in topology optimization. Arch. Appl. Mech. 1999, 69, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendsøe, M.P.; Kikuchi, N. Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1988, 71, 197–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.M.; Steven, G.P. A simple evolutionary procedure for structural optimization. Comput. Struct. 1993, 49, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, D. A level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2003, 192, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. A new topology optimization approach based on Moving Morphable Components (MMC) and the ersatz material model. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2016, 53, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Wang, Y. Structural topology optimization based on non-local Shepard interpolation of density field. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2011, 200, 3515–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, J.H.; Liang, Q.Q. A level set method for topology optimization of continuum structures with bounded design domains. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2008, 197, 1447–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendsøe, M.P.; Sigmund, O. Topology Optimization: Theory, Methods, and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Xie, Y.M. Convergent and mesh-independent solutions for the bi-directional evolutionary structural optimization method. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2007, 43, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, J.H.; Jiang, J.S.; Xie, Y.M. Evolutionary structural topology optimization for continuum structures with structural size and topology variables. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2007, 10, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.H.; Zhang, W.H.; Xia, L. Topology optimization in aircraft and aerospace structures design. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2016, 23, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, J.K.; Prévost, J.H. Optimizing multifunctional materials: Design of microstructures for maximized stiffness and fluid permeability. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2016, 43, 7028–7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osanov, M.; Guest, J.K. Topology optimization for architected materials design. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2016, 46, 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.H.; Huang, X.; Rong, J.H.; Xie, Y.M. Multi-scale design of composite materials and structures for maximum natural frequencies. Mater. Des. 2013, 51, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutradhar, A.; Park, J.; Carrau, D.; Nguyen, T.H.; Miller, M.J.; Paulino, G.H. Designing patient-specific 3D printed craniofacial implants using a novel topology optimization method. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2016, 54, 1123–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, S.; Zhou, S.; Xu, W.; Leary, M.; Choong, P.; Xie, Y.M. Topological design and additive manufacturing of porous metals for bone scaffolds and orthopaedic implants: A review. Biomaterials 2016, 83, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wen, G.; Xie, Y.M. Layout optimization of continuum structures considering the probabilistic and fuzzy directional uncertainty of applied loads based on the cloud model. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2016, 53, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Qiu, Z. A novel method of non-probabilistic reliability-based topology optimization corresponding to continuum structures with unknown but bounded uncertainties. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 326, 573–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csébfalvi, A.; Lógó, J. A critical analysis of expected-compliance model in volume-constrained robust topology optimization with normally distributed loading directions, using a minimax-compliance approach alternatively. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y. 3D printing of shape memory polymer for functional part fabrication. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 84, 2079–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengier, F.; Mehndiratta, A.; von Tengg-Kobligk, H.; Zechmann, C.M.; Unterhinninghofen, R.; Kauczor, H.U.; Giesel, F.L. 3D printing based on imaging data: Review of medical applications. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2010, 5, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, S.; Vahabzadeh, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Bone tissue engineering using 3D printing. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Caspers, M. An overview of additive manufacturing (3D printing) for microfabrication. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Peng, R.; You, Z. Origami of thick panels. Science 2015, 349, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teoh, J.E.M.; An, J.; Feng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chua, C.K.; Liu, Y. Design and 4D Printing of Cross-Folded Origami Structures: A Preliminary Investigation. Materials 2018, 11, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xu, S.; Wen, G.; Xie, Y.M. Mechanical behaviour of a creased thin strip. Mech. Sci. 2018, 9, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.L.; Evans, A.A.; McLeod, L.; Hayward, R.C.; Hull, T.; Santangelo, C.D.; Cohen, I. Using origami design principles to fold reprogrammable mechanical metamaterials. Science 2014, 345, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, C.; Krishnaraju, D.; Konjevod, G.; Yu, H.; Jiang, H. Origami based mechanical metamaterials. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felton, S.; Tolley, M.; Demaine, E.; Rus, D.; Wood, R. A method for building self-folding machines. Science 2014, 345, 644–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranger, E.; Guidault, P.A.; Cluzel, C. Numerical modeling of the geometrical defects of an origami-like sandwich core. Compos. Struct. 2011, 93, 2504–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, B.H.; Lund, J.M.; Lang, R.J.; Magleby, S.P.; Howell, L.L. Waterbomb base: A symmetric single-vertex bistable origami mechanism. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 094009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, G. Axial crushing of thin-walled structures with origami patterns. Thin Walled Struct. 2012, 54, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Xu, S.; Shen, J.; Zhou, S.; Xie, Y.M. Energy absorption of thin-walled tubes with pre-folded origami patterns: Numerical simulation and experimental verification. Thin Walled Struct. 2016, 103, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchi, K.; Diaz, A.R. Origami design by topology optimization. J. Mech. Des. 2013, 135, 111003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchi, K.; Buskohl, P.R.; Bazzan, G.; Durstock, M.F.; Reich, G.W.; Vaia, R.A.; Joo, J.J. Origami actuator design and networking through crease topology optimization. J. Mech. Des. 2015, 137, 091401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, O.; Petersson, J. Numerical instabilities in topology optimization: A survey on procedures dealing with checkerboards, mesh-dependencies and local minima. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 1998, 16, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, M.; Guest, S.D. Geometry of Miura-folded metamaterials. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3276–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Wen, G.; Qing, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhao, G. A Novel Design Framework for Structures/Materials with Enhanced Mechanical Performance. Materials 2018, 11, 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040576
Liu J, Fan X, Wen G, Qing Q, Wang H, Zhao G. A Novel Design Framework for Structures/Materials with Enhanced Mechanical Performance. Materials. 2018; 11(4):576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040576
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jie, Xiaonan Fan, Guilin Wen, Qixiang Qing, Hongxin Wang, and Gang Zhao. 2018. "A Novel Design Framework for Structures/Materials with Enhanced Mechanical Performance" Materials 11, no. 4: 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040576
APA StyleLiu, J., Fan, X., Wen, G., Qing, Q., Wang, H., & Zhao, G. (2018). A Novel Design Framework for Structures/Materials with Enhanced Mechanical Performance. Materials, 11(4), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040576




