Investigating the Mechanism behind ‘Ant Nest’ Corrosion on Copper Tube
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Material
2.2. Test Solution
2.3. Observation Method
2.4. Measurement Method
3. Results
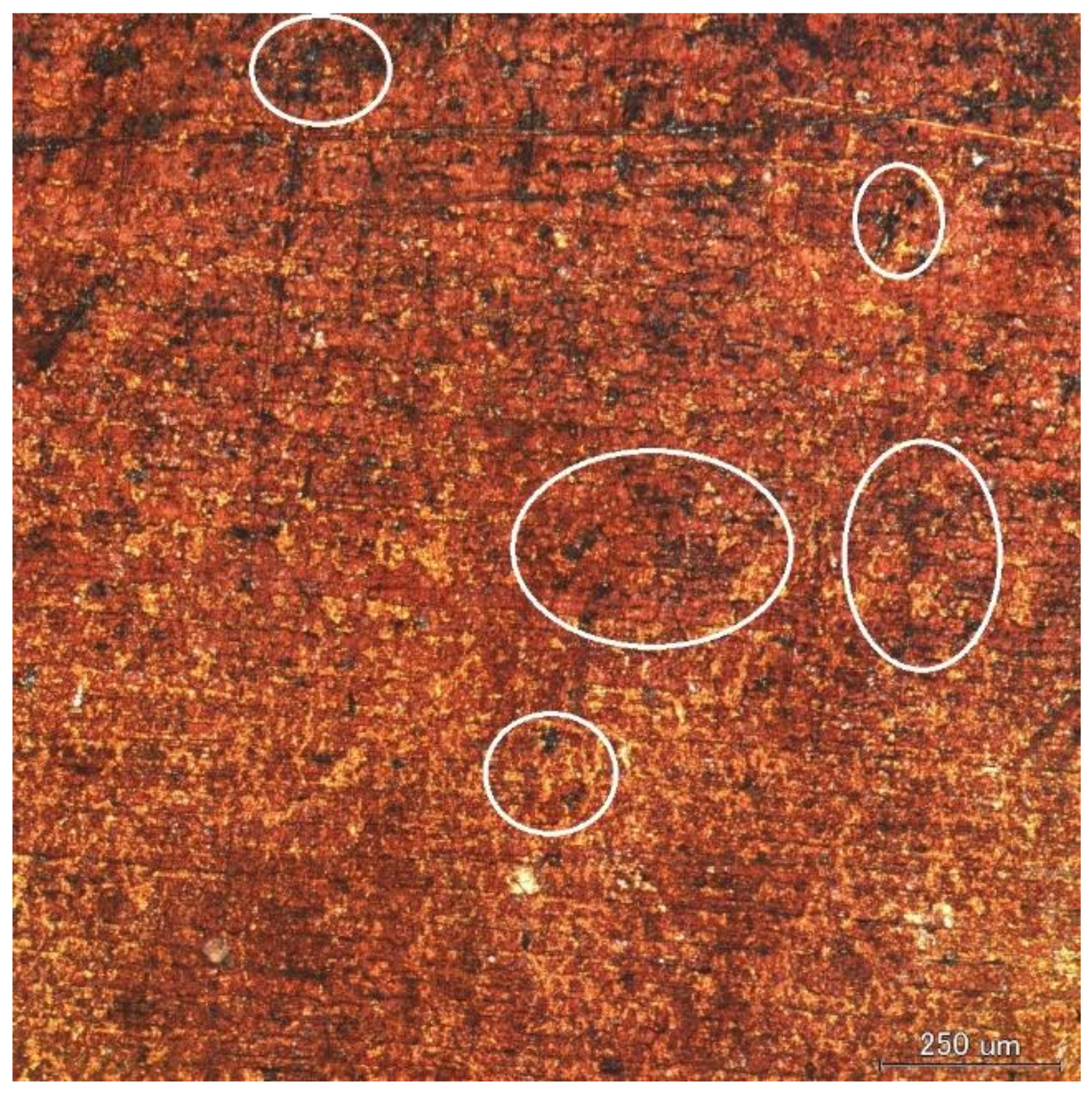
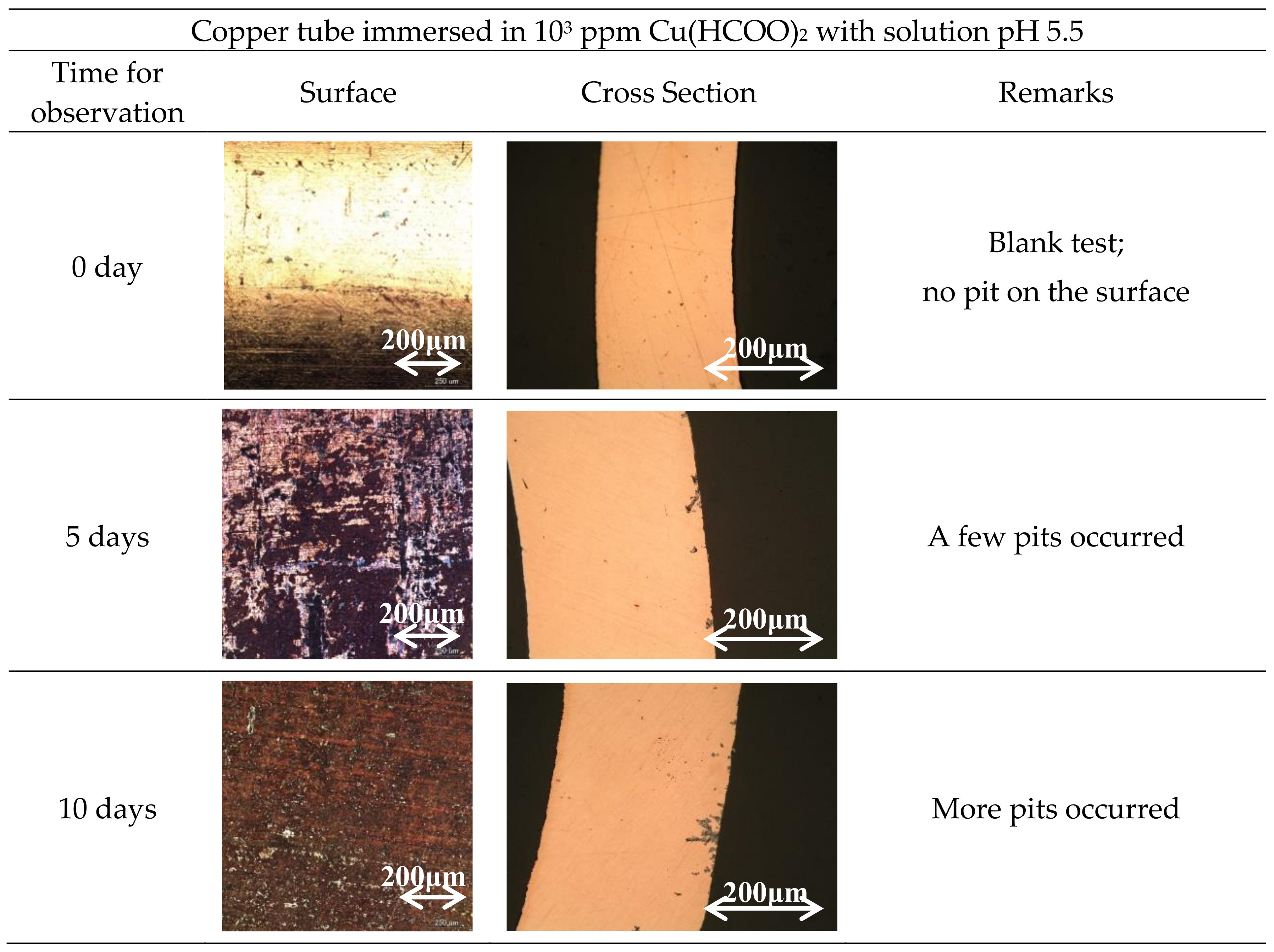
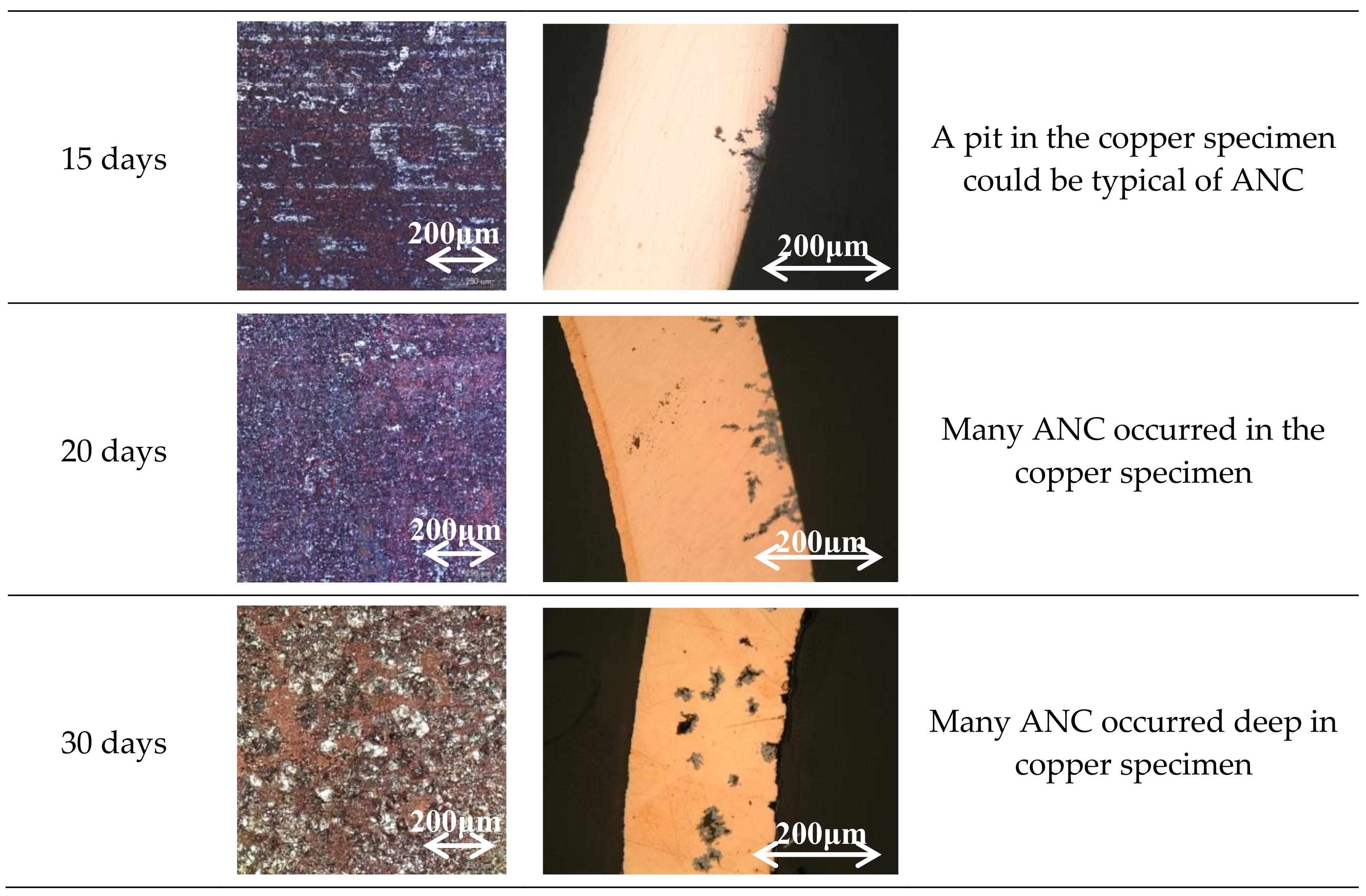
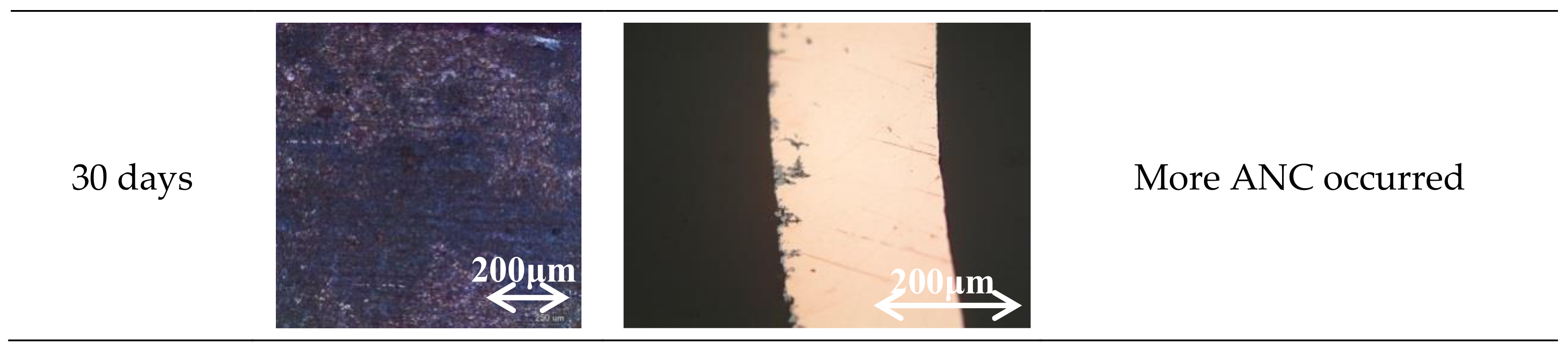
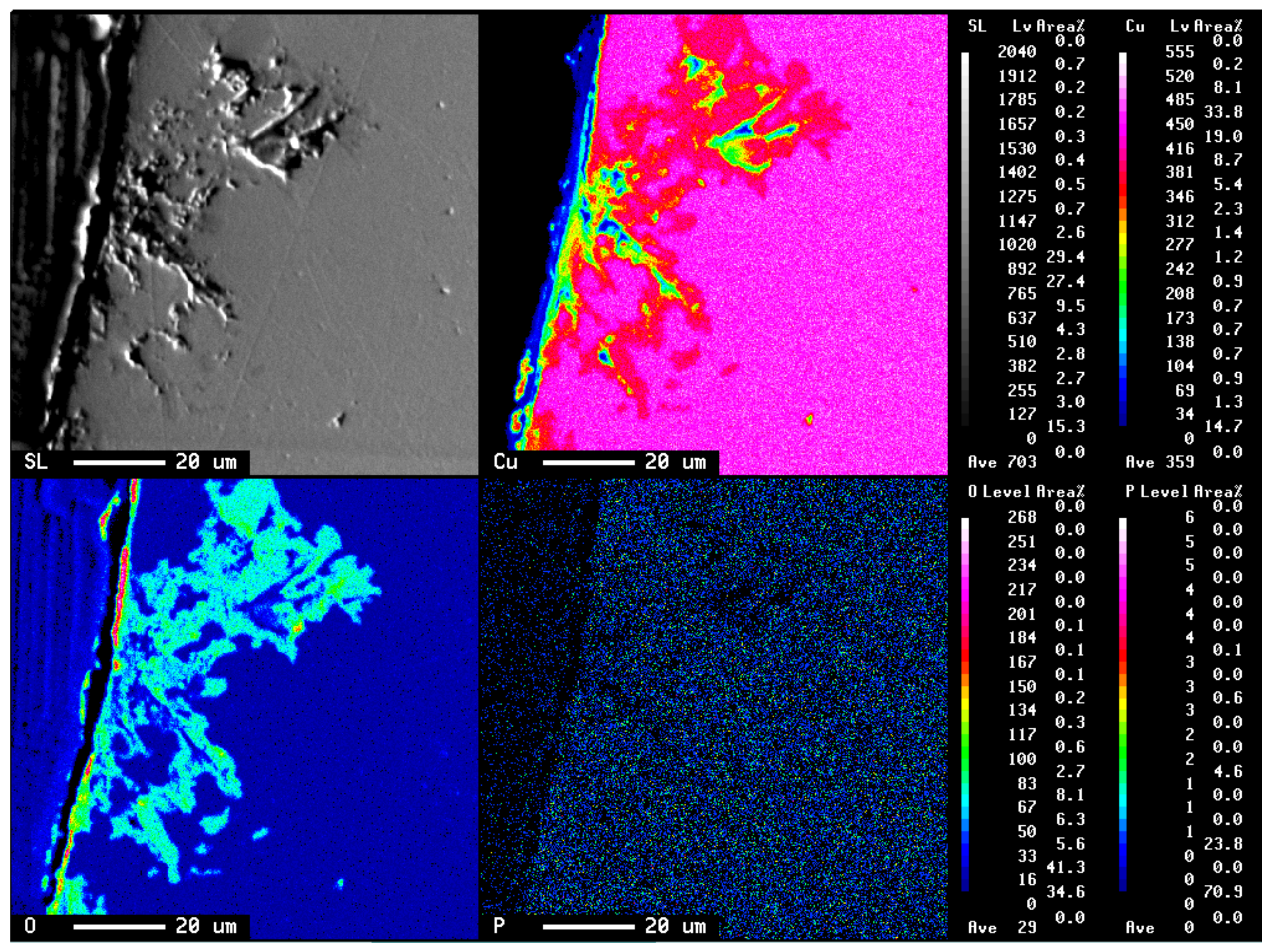
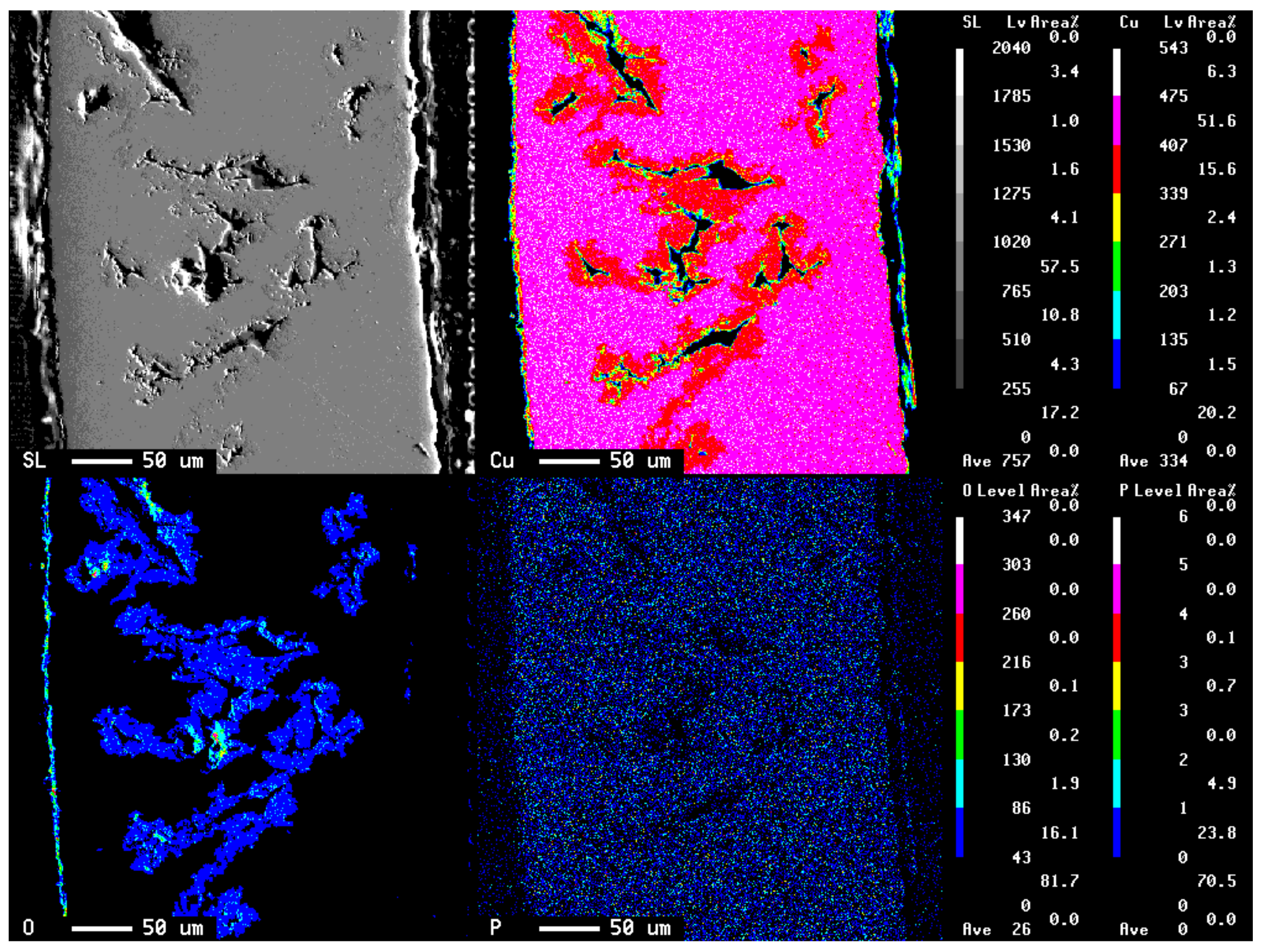
3.1. Specimen Observation
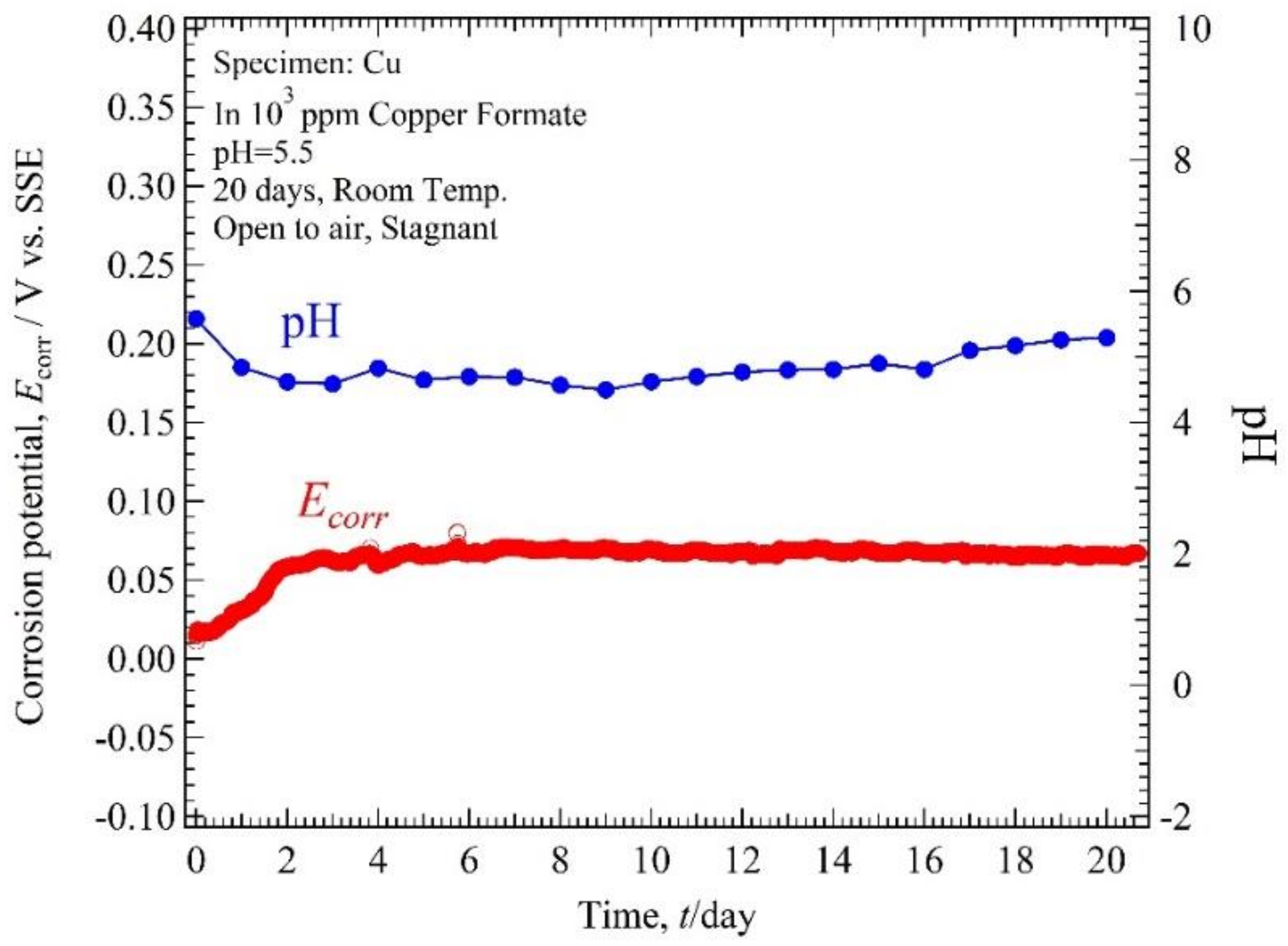
3.2. Ecorr, pH-Time
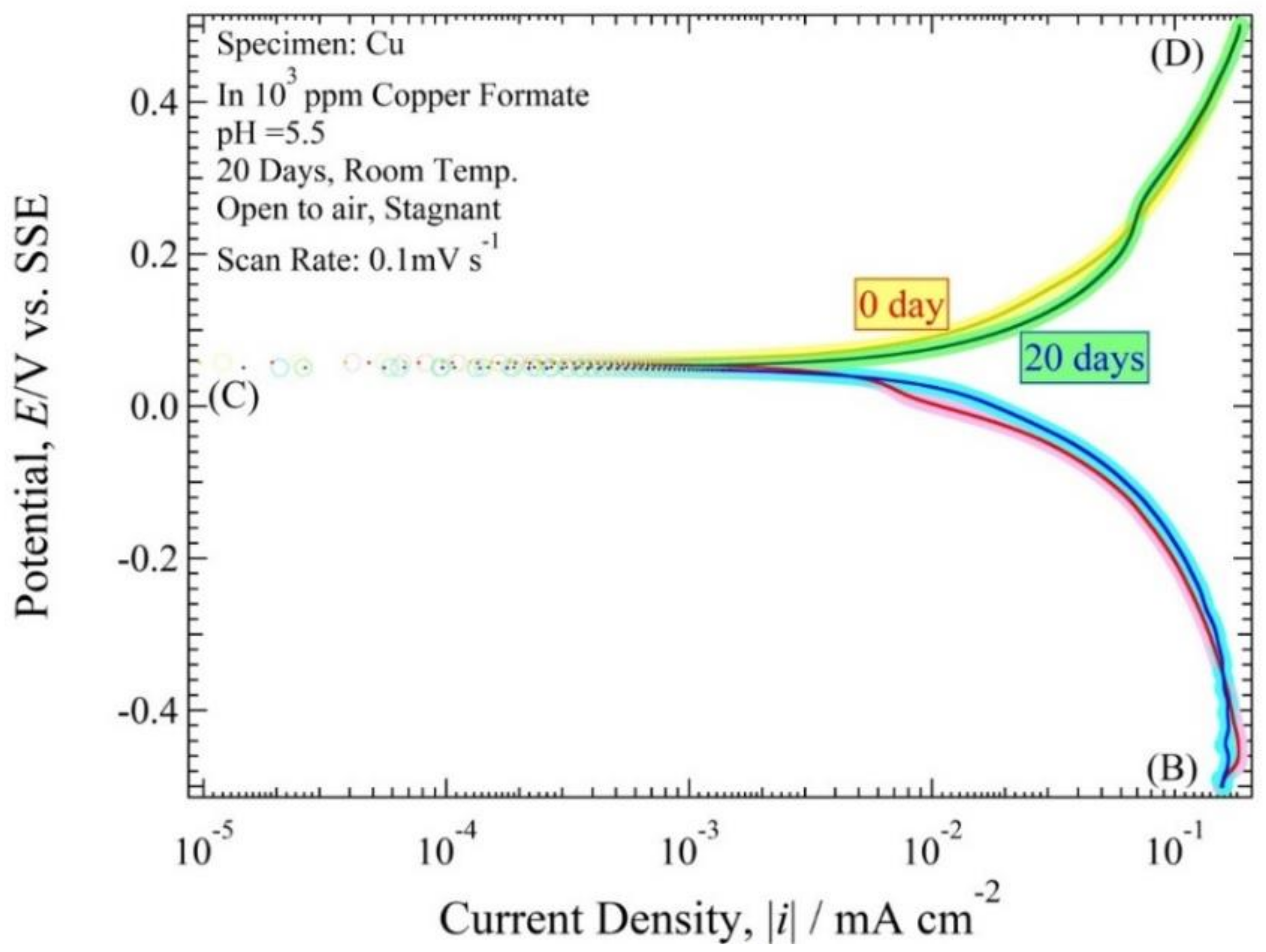
3.3. Polarization Curve
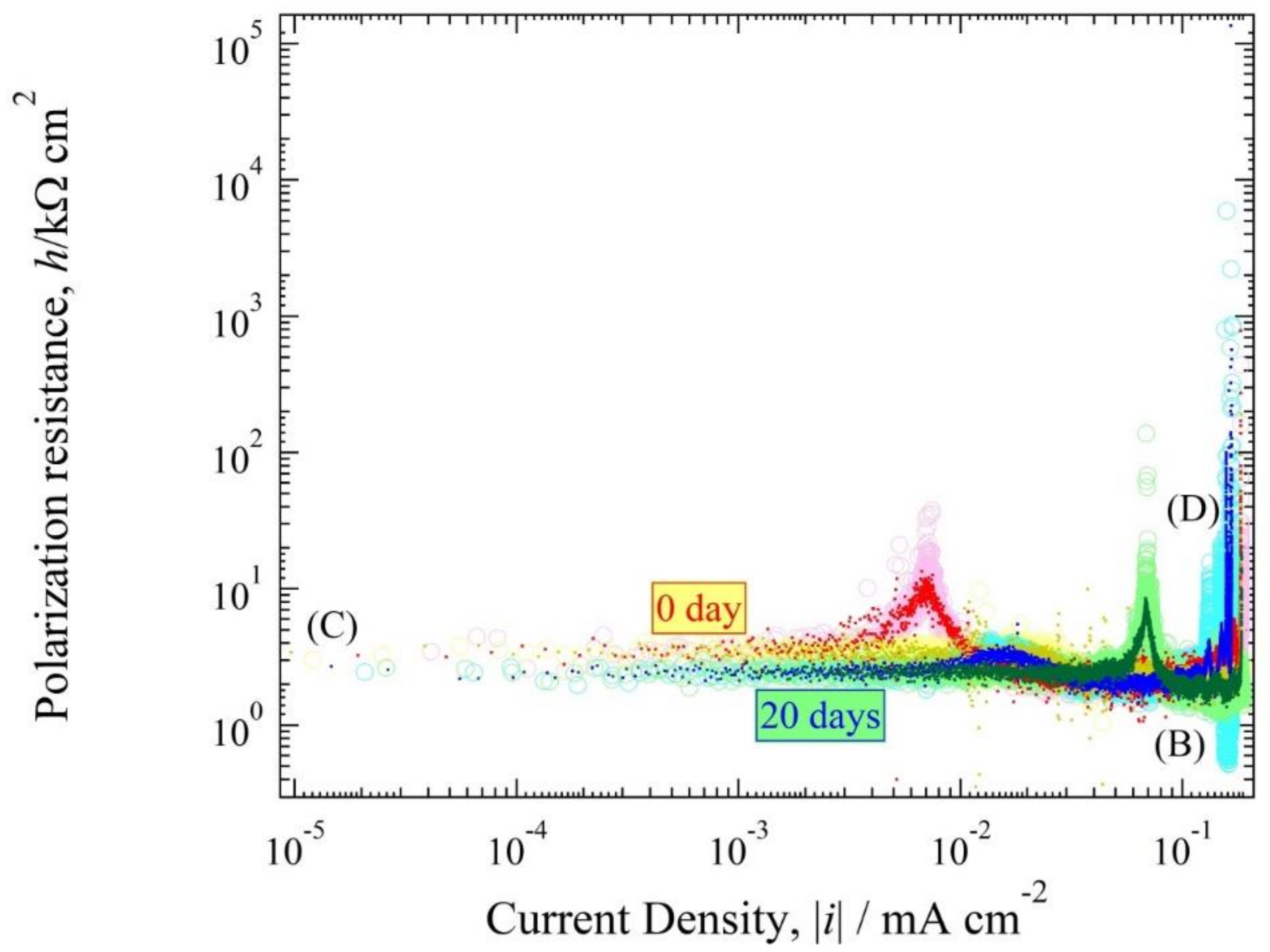
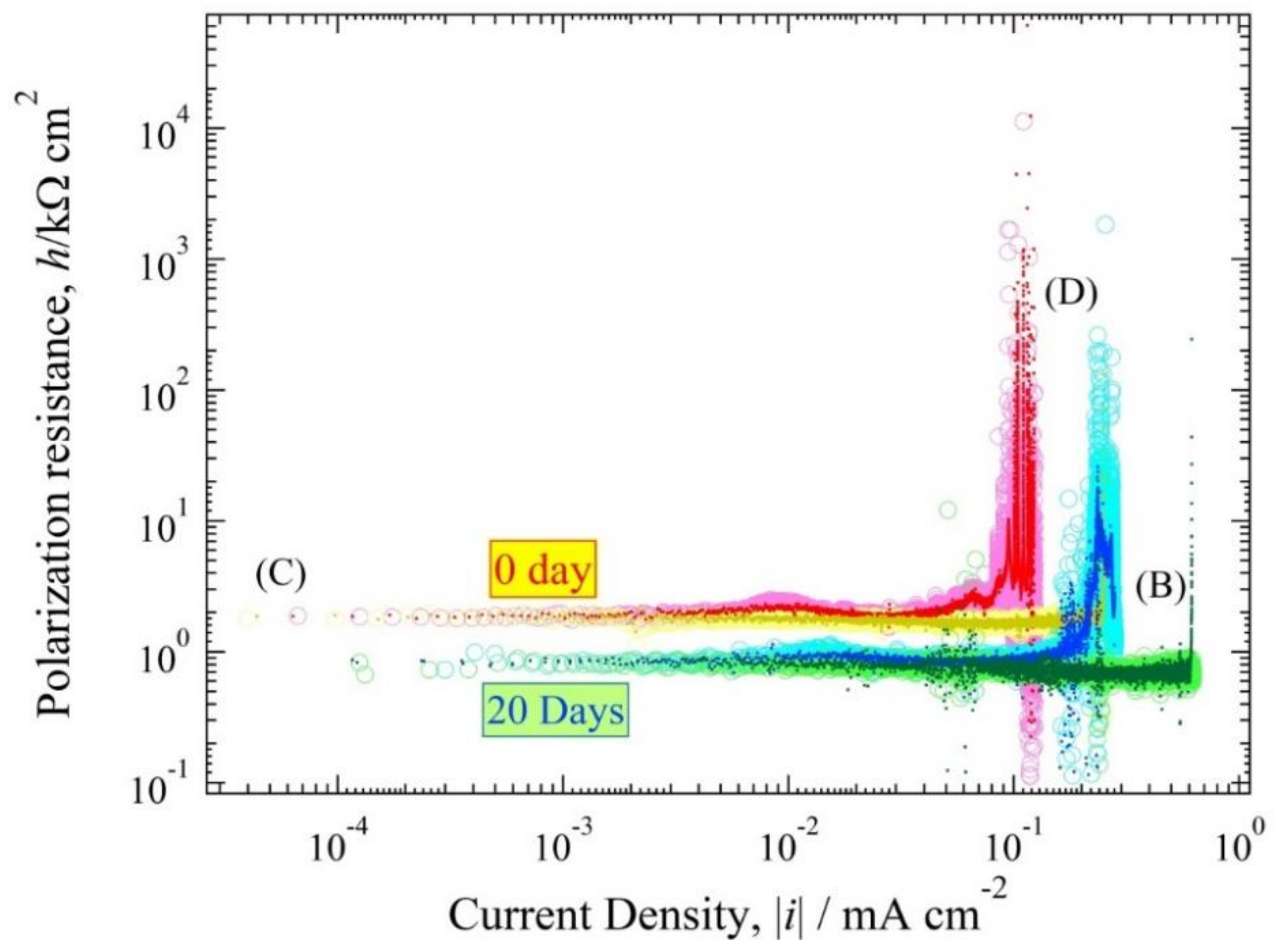
3.4. Polarization Resistance Curve
4. Discussion
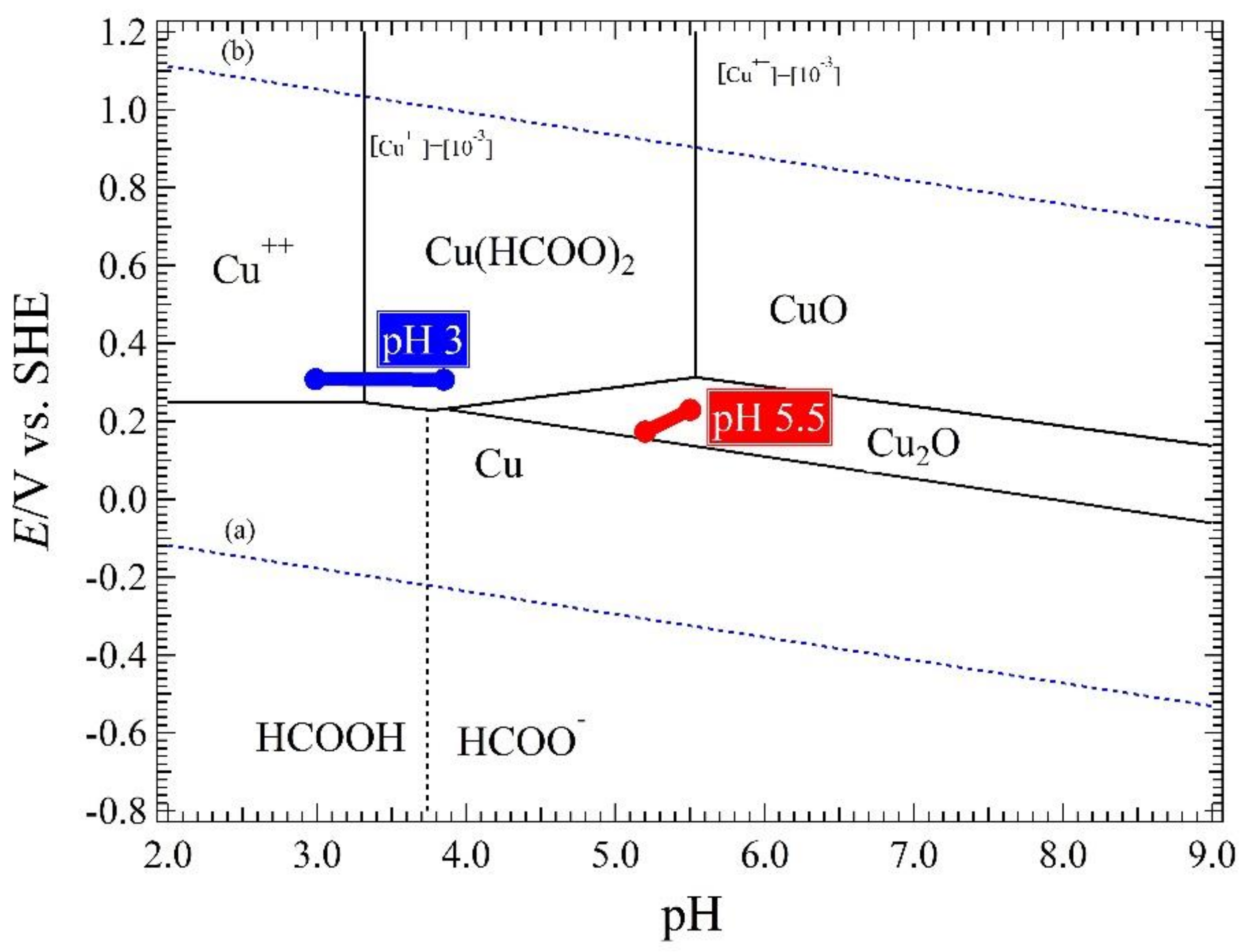
4.1. Relation of Ecorr, pH Solution, and Immersion Time
4.2. The Comproportionation and Disproportionation Reaction in the Corrosion Mechanism
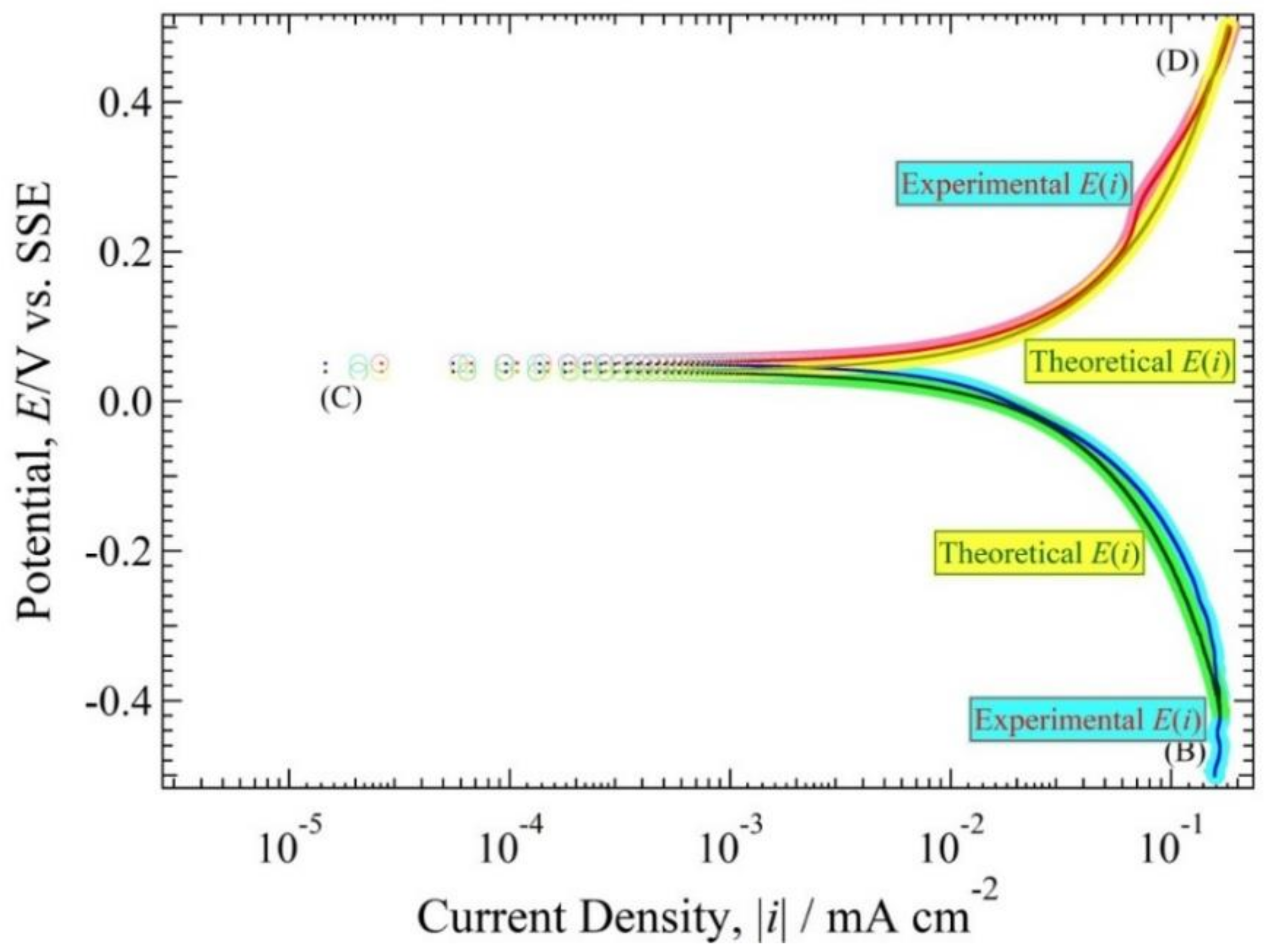
4.3. Polarization Curve and Polarization Resistance Curve Analysis
4.4. The Relationship between h(i) and E(i) Curve
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| i is the net current density (i = ia + ia) (mA cm−2) |
| ia is the anodic branch current density (mA cm−2) |
| ia is the cathodic branch current density (mA cm−2) |
| ha(ia) is the anodic branch polarization resistance (kΩ cm2) |
| hc(ic) is the cathodic branch polarization resistance (kΩ cm2) |
| z is the number of electrons transferred (-) |
| F is the Faraday’s constant (F = 96.5 × 103 A s mol−1) |
| R is the gas constant (R = 8.31 J mol−1 K−1) |
| T is the absolute temperature (K) |
| is the Nernst diffusion layer thickness (cm) |
| is the limiting diffusion current density of (mA cm−2) |
| is the activity of in the bulk solution (-) |
| is the limiting diffusion rate constant of (cm s−1) |
| is the limiting diffusion coefficient of the (cm2 s−1) |
References
- Lundgren, K.; Kjellstrom, T. Sustainability challenges from climate change and air conditioning use in urban areas. Sustainability 2013, 5, 3116–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastidas, D.M.; Cayuela, I.; Bastidas, J.M. Ant-nest corrosion of copper tubing in air-conditioning units. Rev. Metal. 2006, 42, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cano, E.; Polo, J.L.; López-Caballero, A.; Bastidas, J.M. Copper corrosion in air-conditioning systems. Corros. Prev. Control 2005, 52, 56–58. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, P.; Corbett, R.A. CORROSION/99; Paper Number 99342; NACE International: Houston, TX, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Corbett, R.A.; Elliott, P. CORROSION/2000; Paper Number 00646; NACE International: Houston, TX, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, K.; Kain, V.; Shetty, P.S.; Kishan, R. Failure analysis of copper tube used in a refrigerating plant. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2014, 37, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yan, L.; Tang, J.; Sun, Z.; Ma, L. Interactive effect of ant nest corrosion and stress corrosion on the failure of copper tubes. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2018, 83, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltola, H.; Lindgren, M. Failure analysis of a copper tube in a finned heat exchanger. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2015, 51, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.W.; Gertler, P.J. Contribution of air conditioning adoption to future energy use under global warming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5962–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, J.O.; Hamilton, R.I.; Gilmour, J.B. Early Corrosion Failures in Copper Heat Exchanger Tubing. Mater. Perform. 1977, 16, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Miya, K. Quantitative evaluation of progress rate of Ant nest corrosion for Phosphorous deoxidized copper and oxygen-free copper. In Proceeding of the 58th Japan Conference on Materials and Environments (JSCE 2011), Nagoya, Japan, 28–30 September 2011; p. 117. (In Japanese). [Google Scholar]
- López-Delgado, A.; Cano, E.; Bastidas, J.M.; López, F.A. A laboratory study of the effect of acetic acid vapor on atmospheric copper corrosion. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 4140–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, E.; Simancas, J.; Polo, J.L.; Torres, C.L.; Bastidas, J.M.; Alcolea, J. Early corrosion failure of copper tubing used in air-conditioning units. Mater. Corros. 1999, 50, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M.; Watanabe, J. Corrosion Behavior of Phosphorous Deoxidized Copper Tubes in Copper (II) Formate and Copper (II) Acetate Solution. Corros. Eng. Jpn. 2016, 65, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notoya, T.; Atsumi, T.; Kawano, K.; Nagata, K.; Kelly, G.J. Localized “ant’s nest” corrosion in copper tubes and its prevention. In Trends in Electrochemistry and Corrosion at the Beginning of 21st Century; Brillas, E., Ed.; Edicions Universtat de Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 2004; pp. 845–855. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, H.; Kodama, T. Localized corrosion of copper in wet organic acid vapor. Corros. Eng. 1995, 44, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastidas, J.M.; López-Delgado, A.; Cano, E.; Polo, J.L.; López, F.A. Copper corrosion mechanism in the presence of formic acid vapor for short exposure times. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2000, 147, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kameda, Y. Ant’s Nest Corrosion on Copper Tube in Formic Acid Solution. Corros. Eng. Jpn. 2012, 61, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, H.; Saburi, D.; Fujiwara, H. A microstructural aspect of intergranular stress corrosion cracking of semi-hard U-bend tubes of commercially pure copper in cooling systems. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2012, 26, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznicka, B.; Junik, K. Intergranular stress corrosion cracking of copper—A case study. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 3905–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M.; Shirahata, K. Ant Nest Corrosion Developed on Phosphorus Deoxidized and Oxygen-Free Copper Tube. Corros. Eng. Jpn. 2016, 65, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K. Development of Zinc Plating Treatment Copper Tube to Ant’s Nest Corrosion. Corros. Eng. Jpn. 2016, 65, 505–509. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyokawa, K.; Seri, O. Development of Surface Treatment on Copper Tube for Prevention of Ant’s Nest-like Corrosion. J. Jpn. Inst. Copp. Tube 2016, 55, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Notoya, T. Localized corrosion in copper tubes and the effect of anti-tarnishing pretreatment. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1991, 10, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seri, O.; Ichimiya, H.; Sakai, M. Ant’s Nest-Like Pitting Attack on Copper Tubes ans Its Analysis. Corros. Eng. Jpn. 2016, 65, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, P. Fight formicary corrosion. Chem. Process 2005, 68, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Takashi, U.; Situmorang, R.S.; Seri, O. Effect of Copper Formate on Ant’s Nest-like pitting Attacks on Copper Tube. J. Jpn. Inst. Copp. 2017, 56, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Pourbaix, M. Atlas of Electrochemical Equiliberia in Aqueous Solution; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Wagman, D.D.; Evans, W.H.; Parker, V.B.; Schumm, R.H.; Halow, I. The NBS Table of Chemical Thermodynamic properties. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1982, 11 (Suppl. 2), 37, 38, 83, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, M.; Takahashi, H. Effect of Dissolved Oxygen on Corrosion behavior of Phosphorous Deoxidized Copper Tube in Formic Acid Solution. Corros. Eng. Jpn. 2016, 65, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seri, O.; Itoh, Y. Differentiating polarization curve technique for determining the exchange current density of hydrogen electrode reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 218, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seri, O.; Siree, B. The Differentiating Polarization Curve Technique for the Tafel Parameter Estimation. Catalysts 2017, 7, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Substance Formula | State | Chemical Potential, μϕ/kJ mol−1 |
|---|---|---|
| HCHO | aq | −131 |
| HCOOH | aq | −372 |
| HCOO− | aq | −351 |
| H2CO3 | aq | −623 |
| HCO3− | aq | −587 |
| CO2 | aq | −386 |
| H2O | l | −237 |
| OH− | aq | −157 |
| Cu(OH)2 | aq | −249 |
| CuO | cr | −130 |
| Cu2O | cr | −146 |
| Cu2+ | aq | 65 |
| Cu+ | aq | 50 |
| Cu(HCOO)+ | aq | −297 |
| Cu(HCOO)2 | aq | −636 |
| Items | pH 5.5 | pH 3 (Addition HCOOH) | Remarks | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 Day | 20 Days | 0 Day | 20 Days | 20 Days | |
| E(0) | 0.04 V vs. SSE | 0.04 vs. SSE | 0.04 V vs. SSE | 0.04 V vs. SSE | measured |
| h(0) | 3.2 kΩ cm2 | 2.7 kΩ cm2 | 1.8 kΩ cm2 | 0.8 kΩ cm2 | measured |
| αza | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | approximated |
| βzb | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | approximated |
| ired,L | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | unknown |
| iOx,L | −0.17 | −0.15 | −0.11 | −0.2 | approximated |
| ia0 | 8.1 × 10−3 mA cm−2 | 9.6 × 10−3 mA cm−2 | 1.4 × 10−2 mA cm−2 | 3.2 × 10−2 mA cm−2 | corrosion rate |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Situmorang, R.S.; Kawai, H. Investigating the Mechanism behind ‘Ant Nest’ Corrosion on Copper Tube. Materials 2018, 11, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040533
Situmorang RS, Kawai H. Investigating the Mechanism behind ‘Ant Nest’ Corrosion on Copper Tube. Materials. 2018; 11(4):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040533
Chicago/Turabian StyleSitumorang, Riky Stepanus, and Hideki Kawai. 2018. "Investigating the Mechanism behind ‘Ant Nest’ Corrosion on Copper Tube" Materials 11, no. 4: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040533
APA StyleSitumorang, R. S., & Kawai, H. (2018). Investigating the Mechanism behind ‘Ant Nest’ Corrosion on Copper Tube. Materials, 11(4), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040533





