Stress Evolution of Amorphous Thermoplastic Plate during Forming Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theory
2.1. Polyetherimide
2.2. Thermal Analysis
2.3. Mechanical Analysis
3. Finite Element Analysis
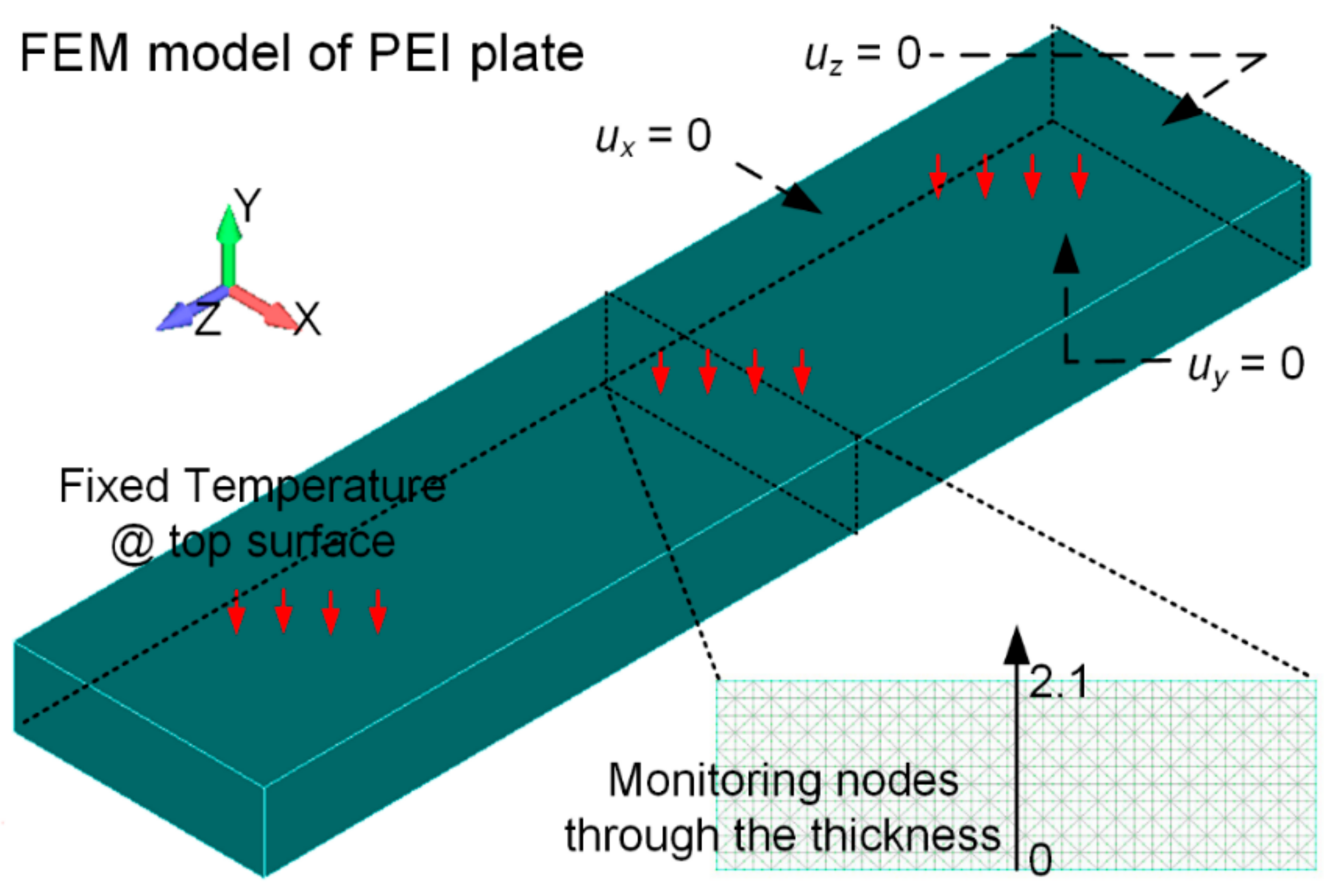
3.1. Model
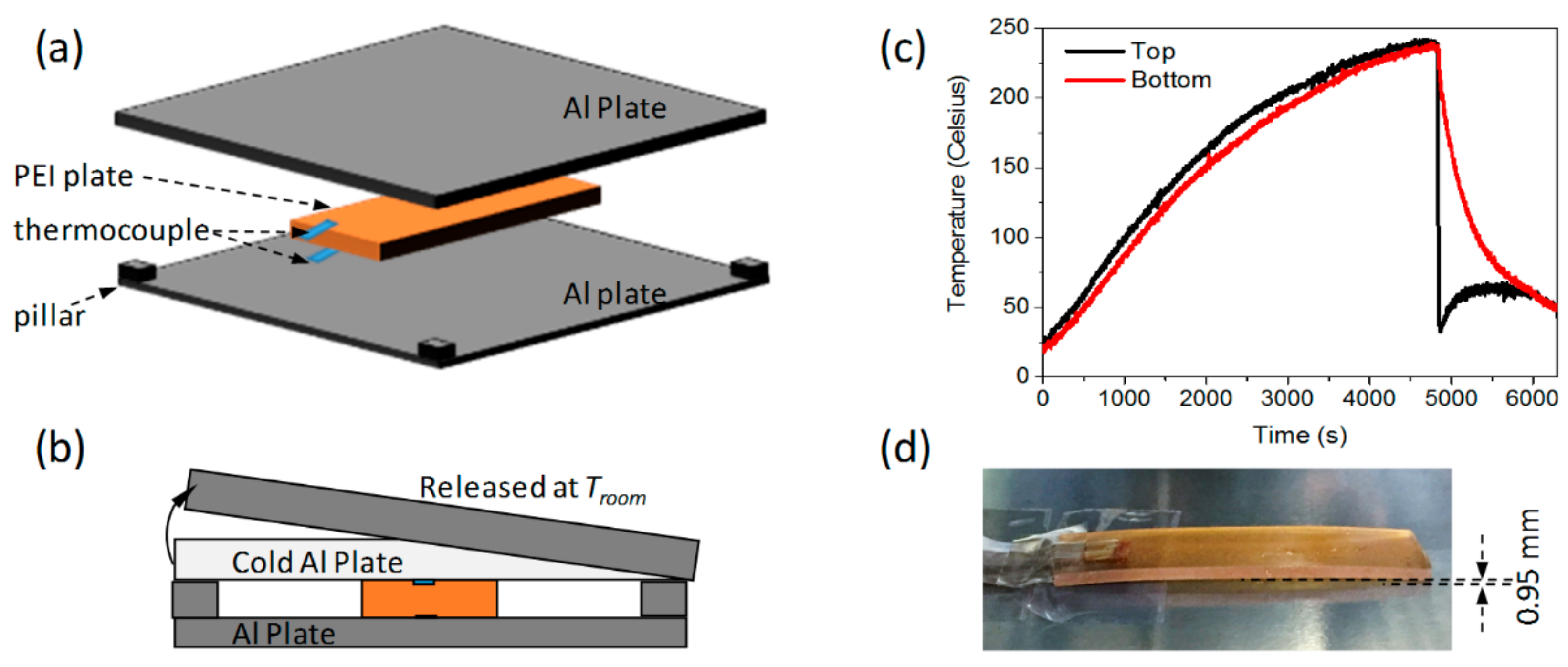
3.2. Program Validation
4. Thermally-Induced Mechanical Change
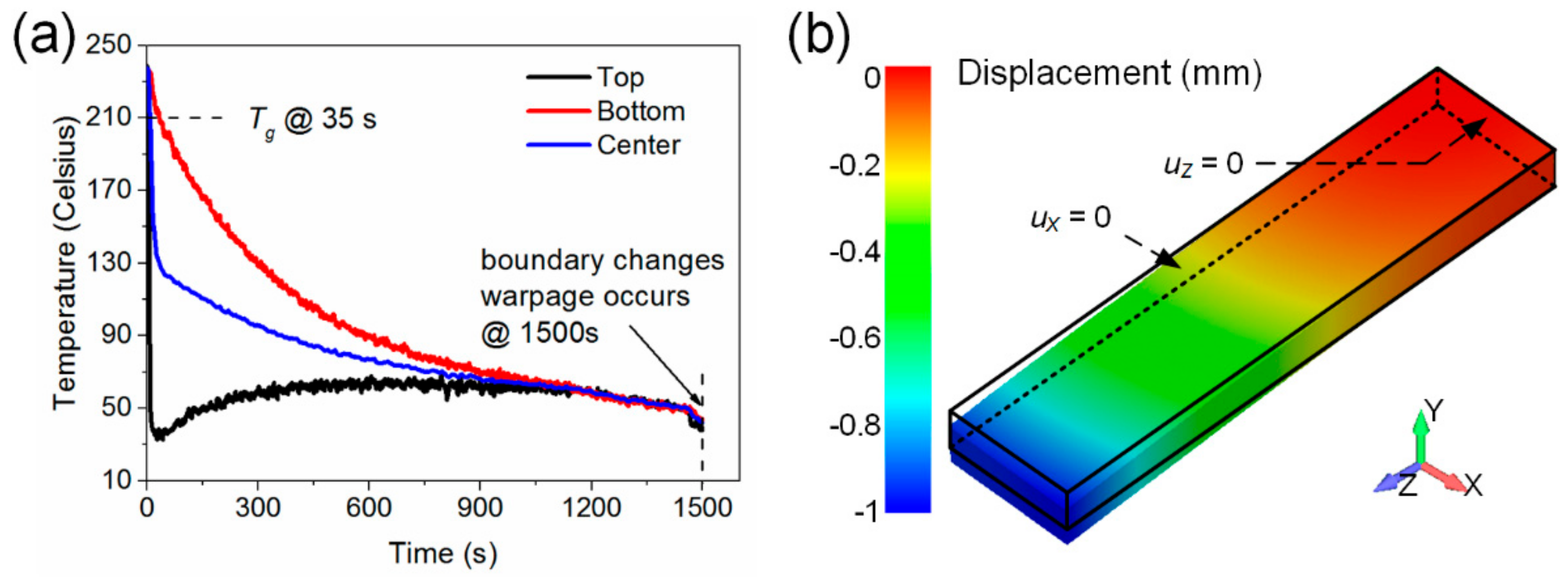
4.1. Temperature Profile
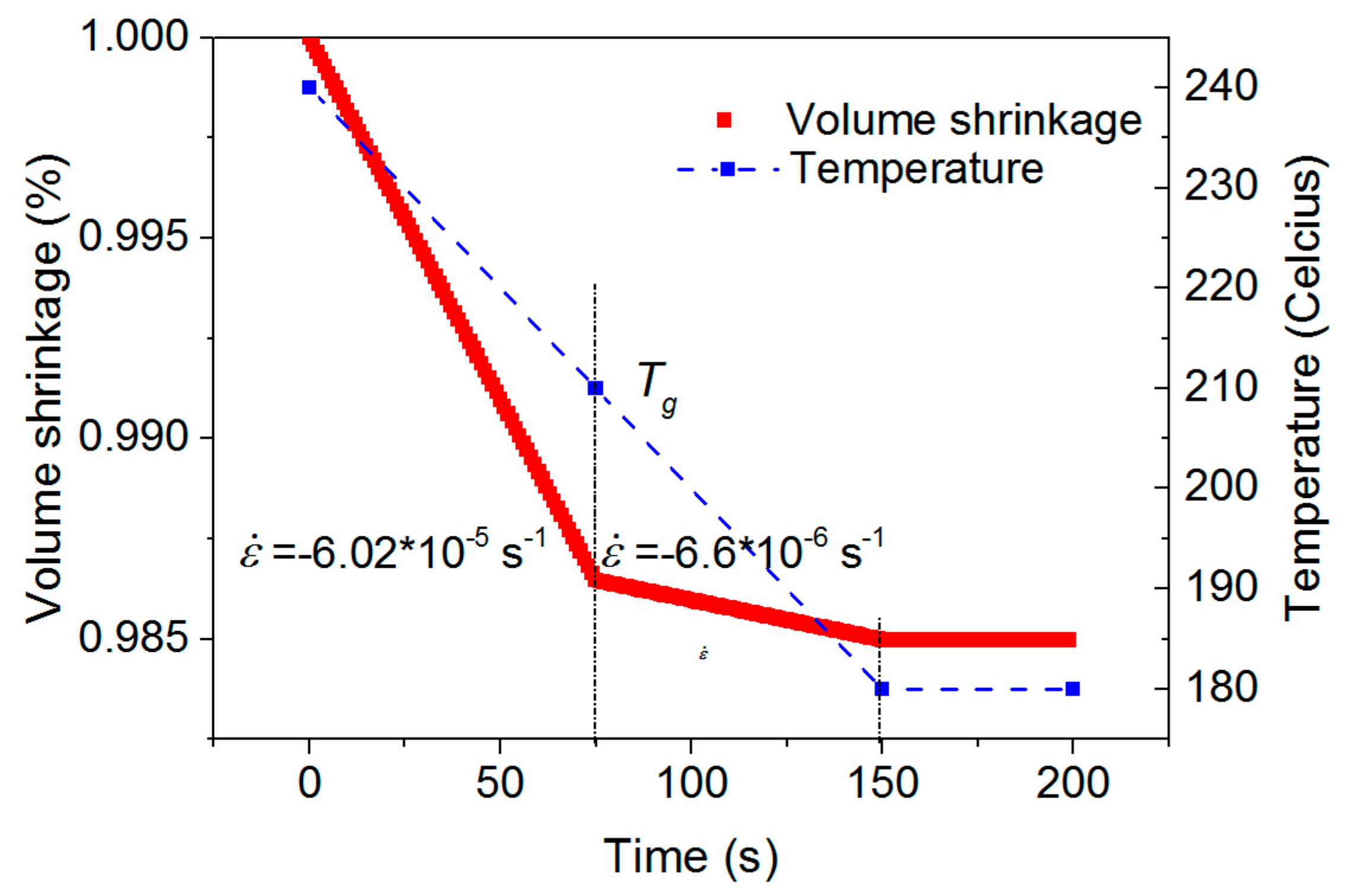
4.2. Volume Shrinkage
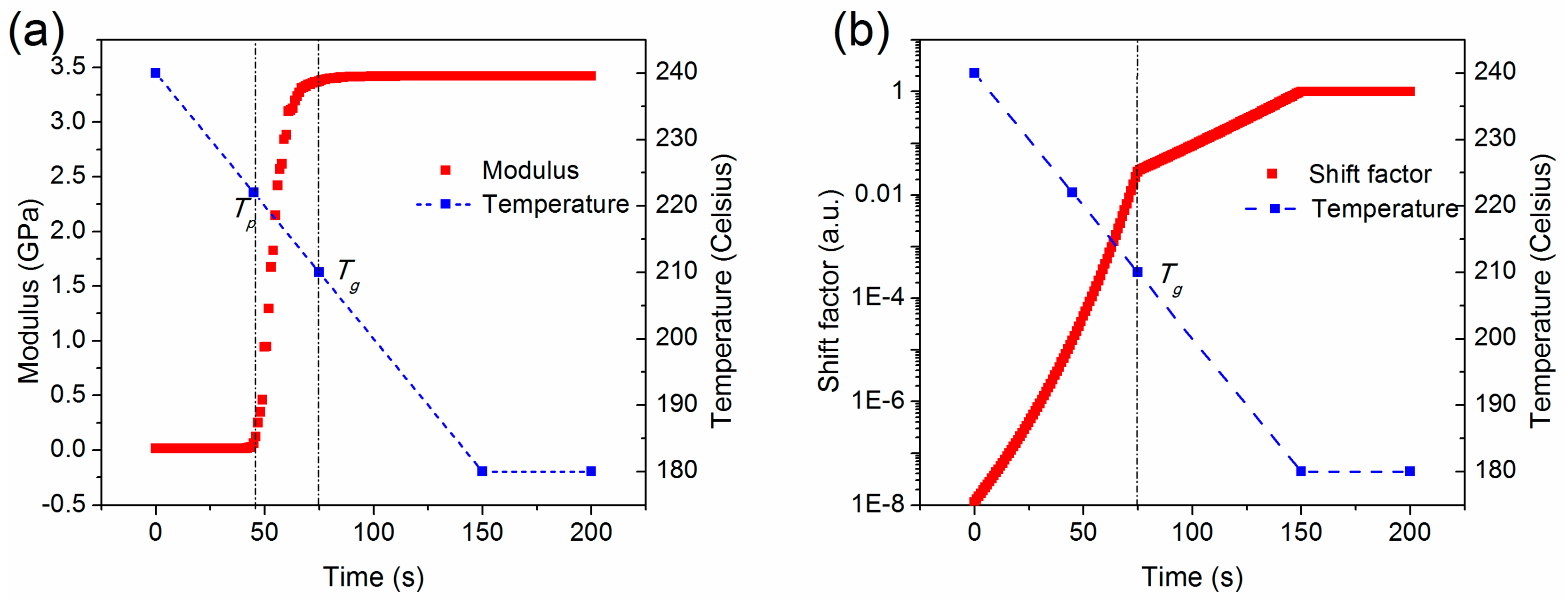
4.3. Modulus and Shift Factor
5. Stress Evolution
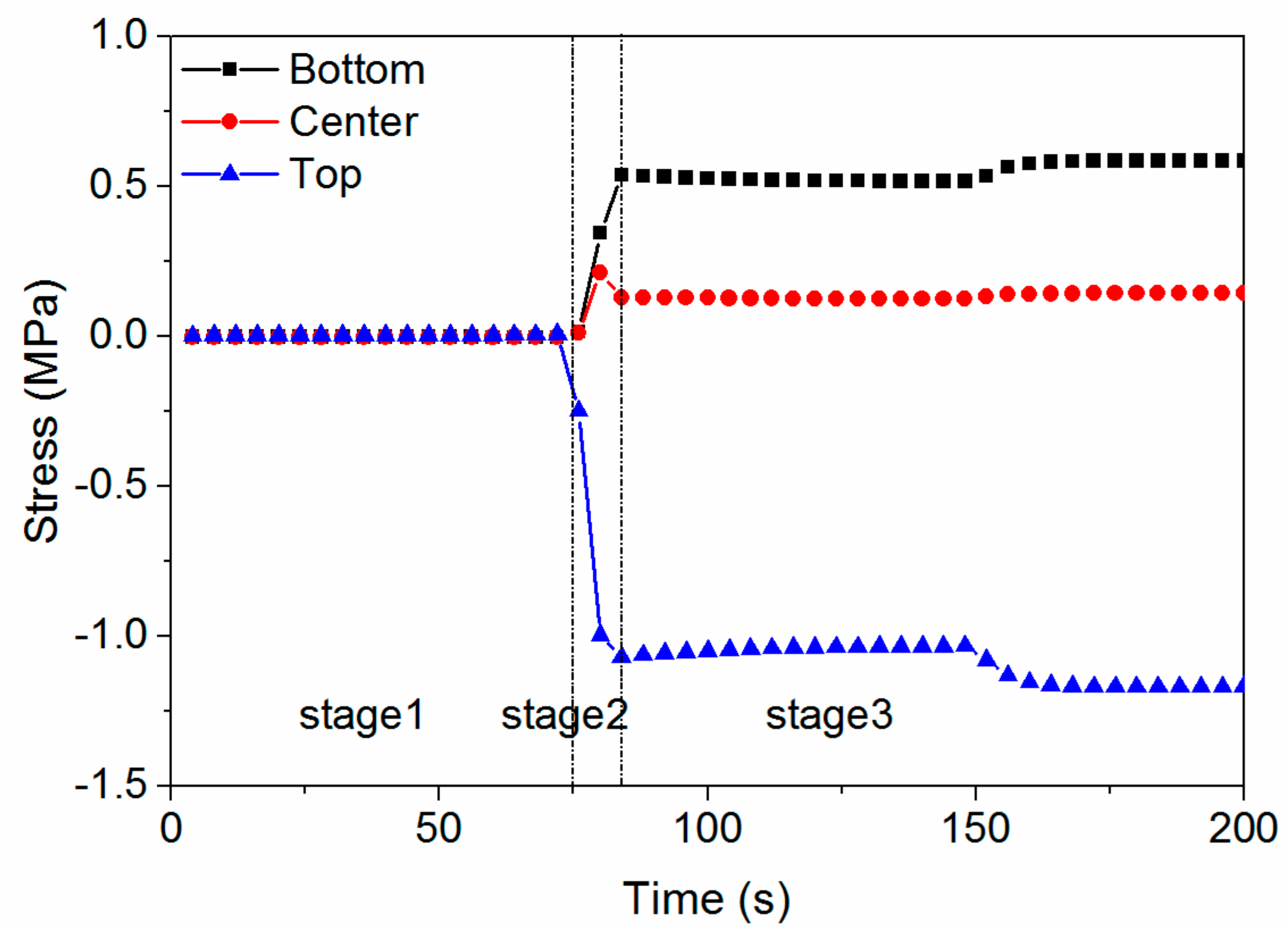
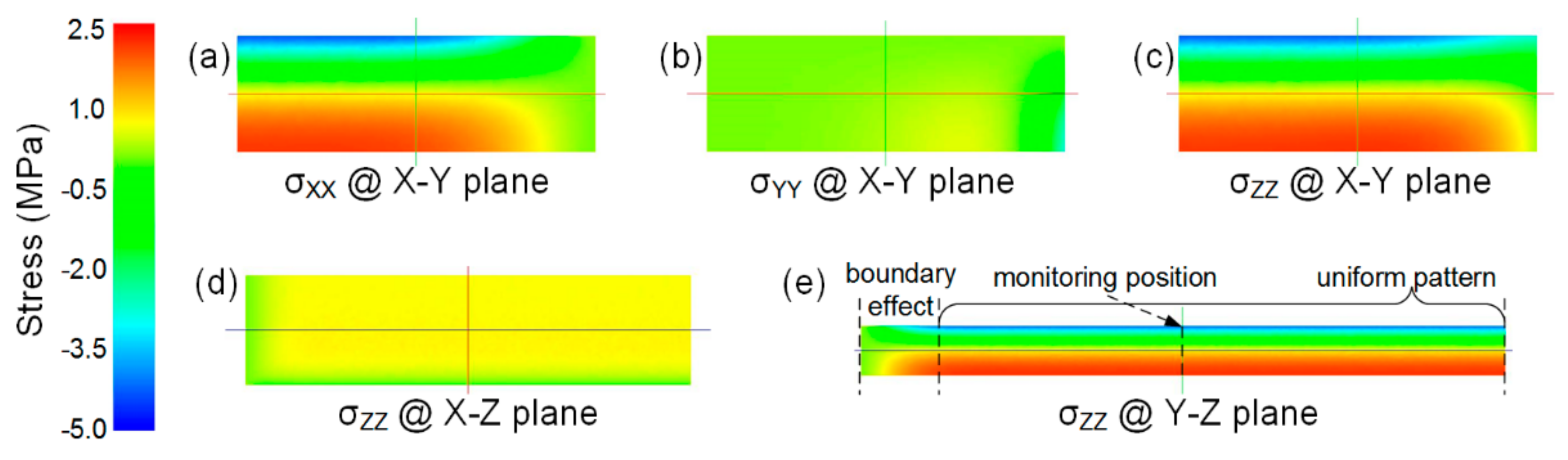
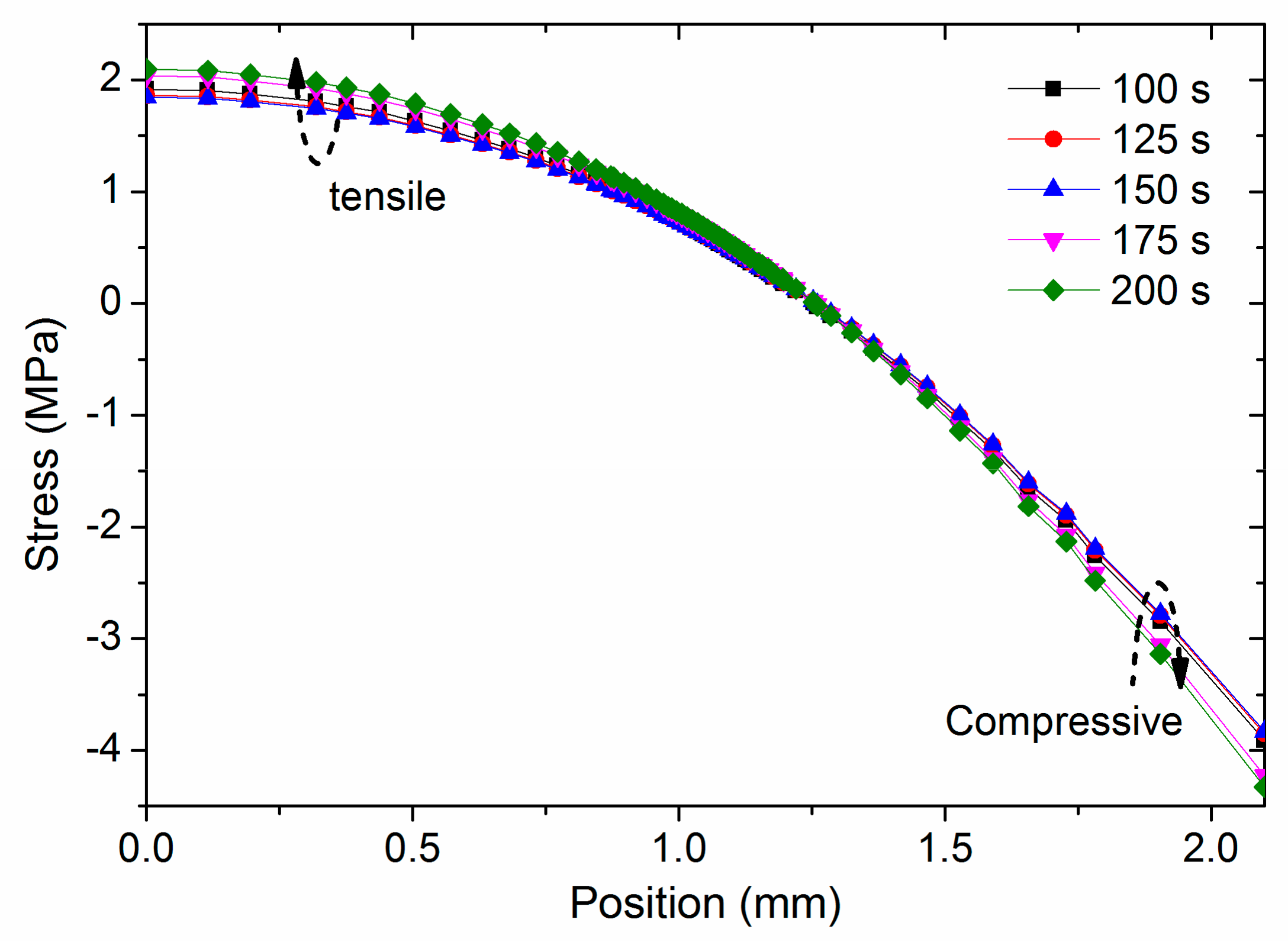
5.1. Residual Stress Distribution
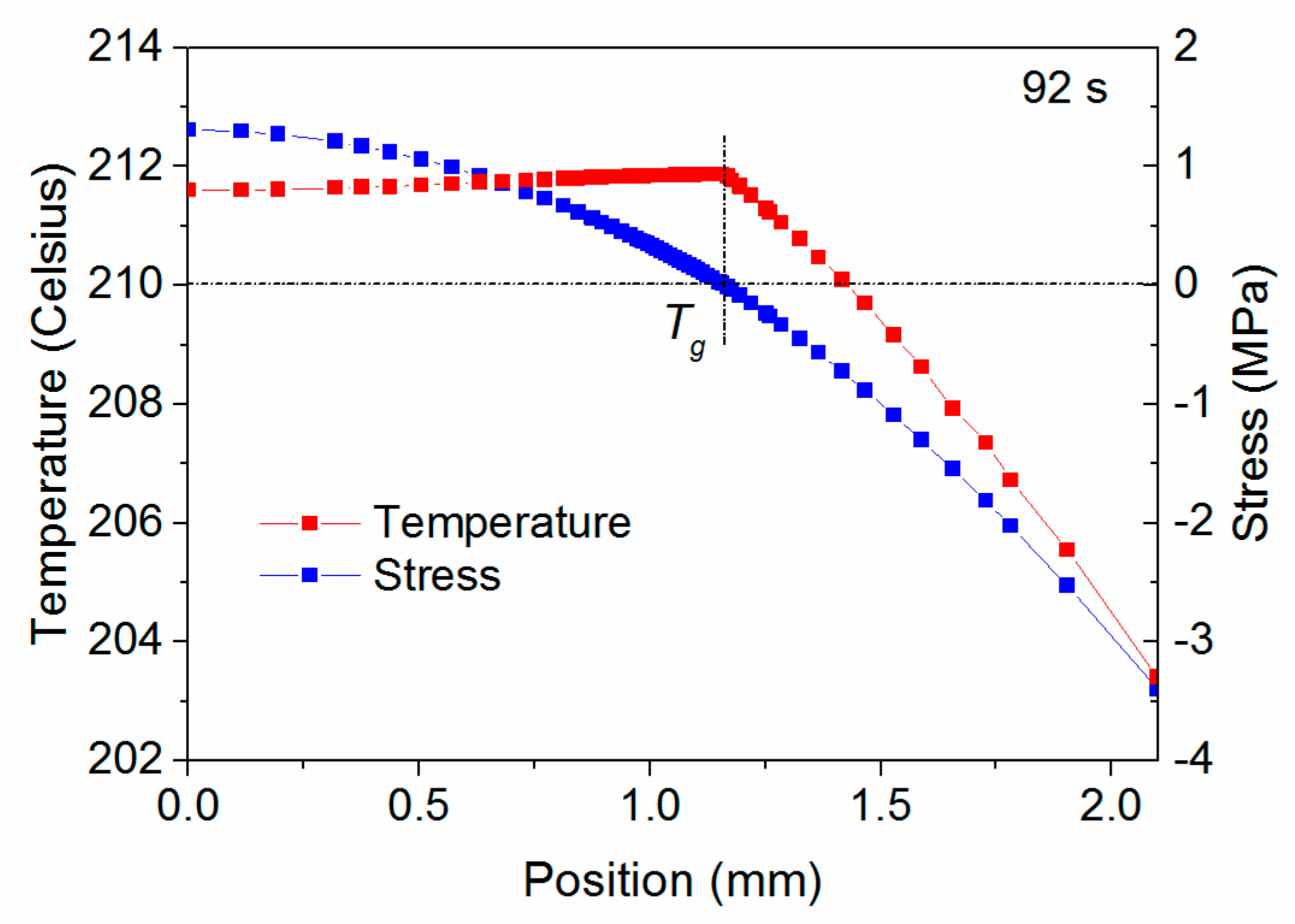
5.2. Temperature Distribution Through Plate Thickness
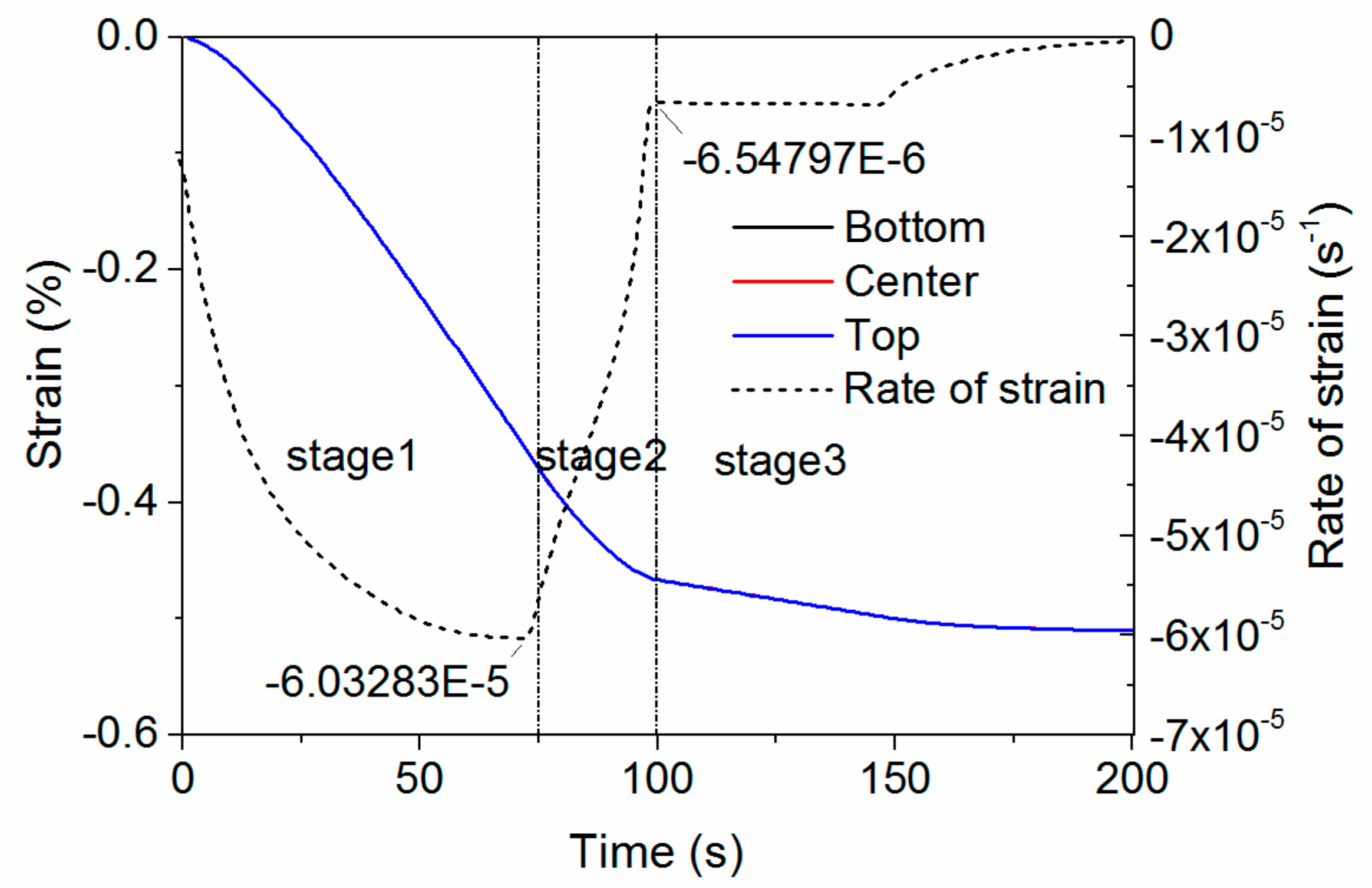
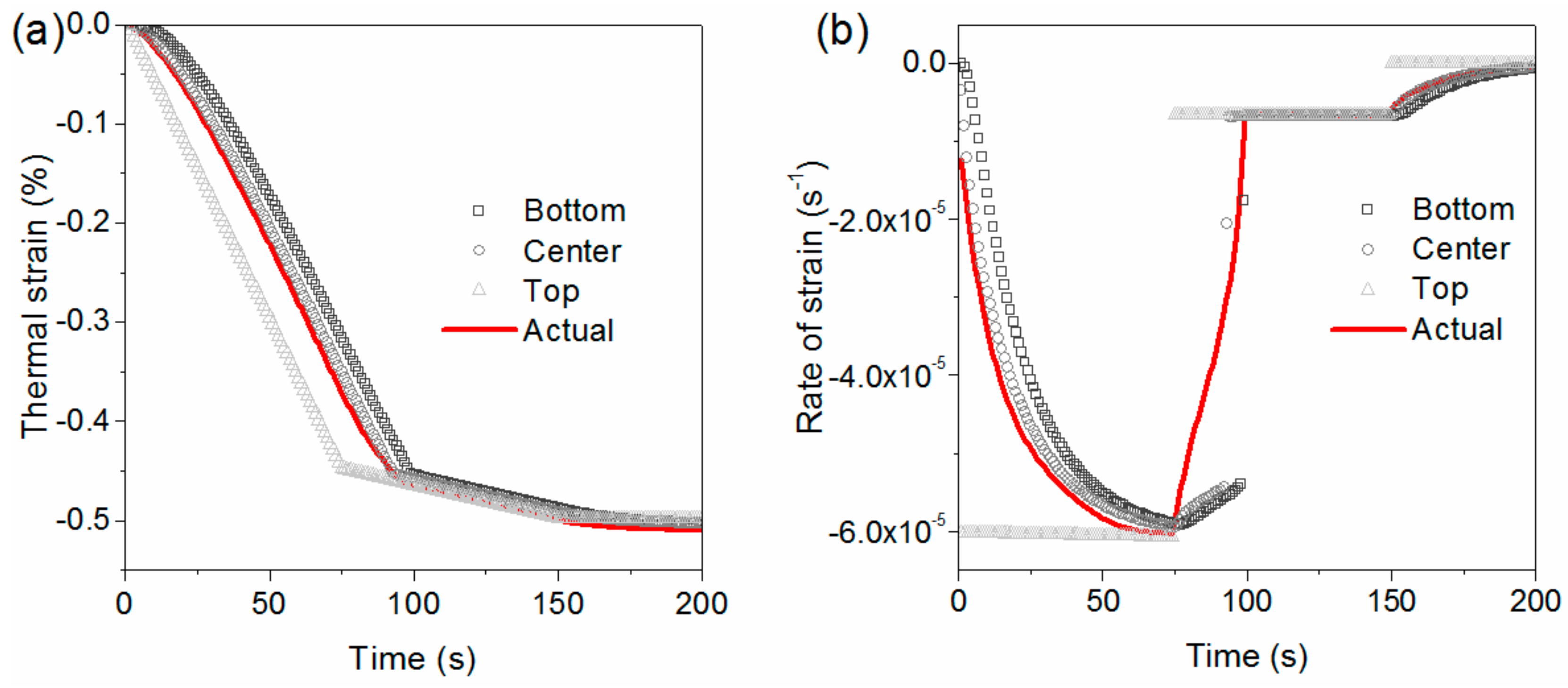
5.3. Thermal Strain and Rate of Strain
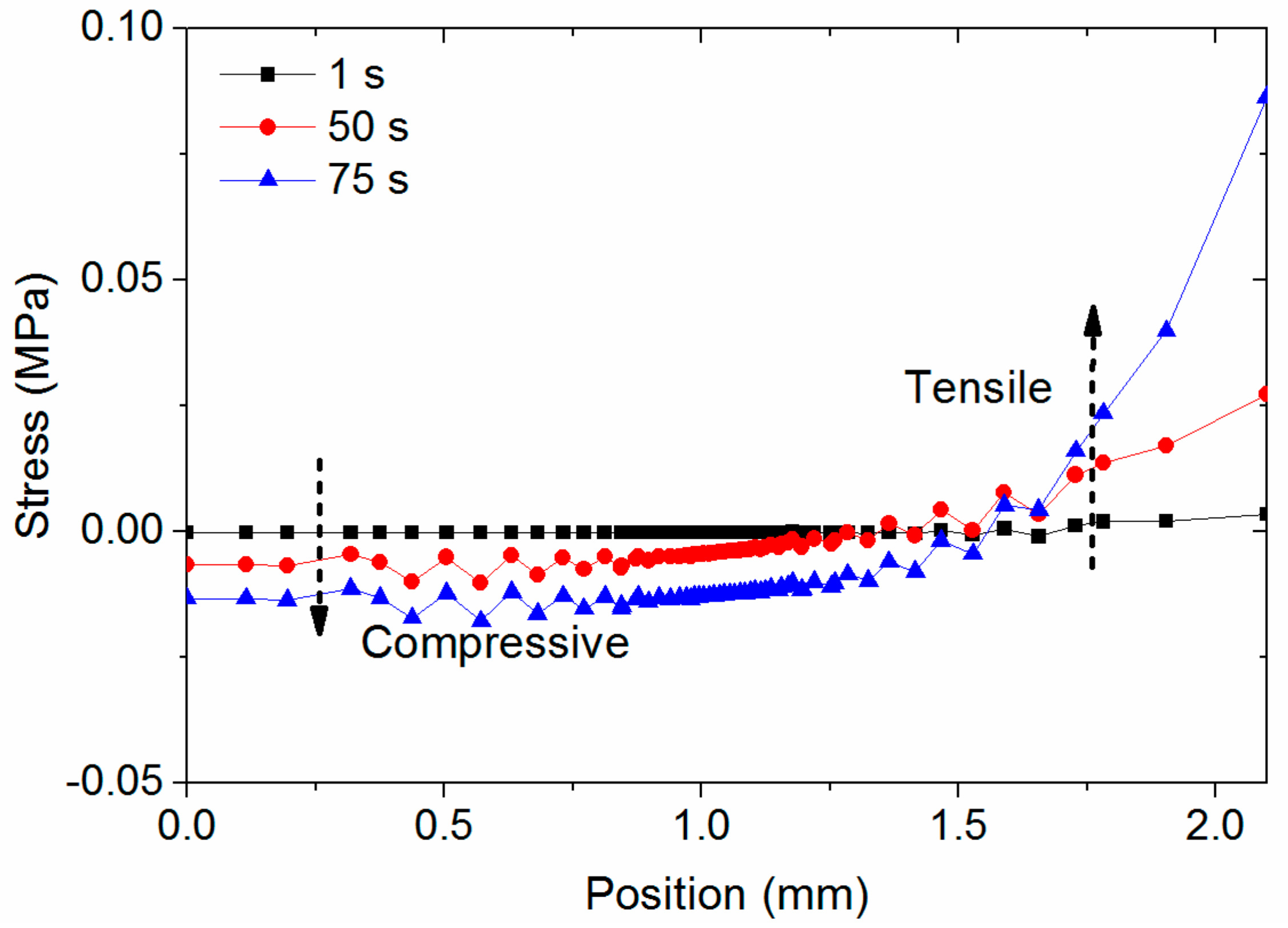
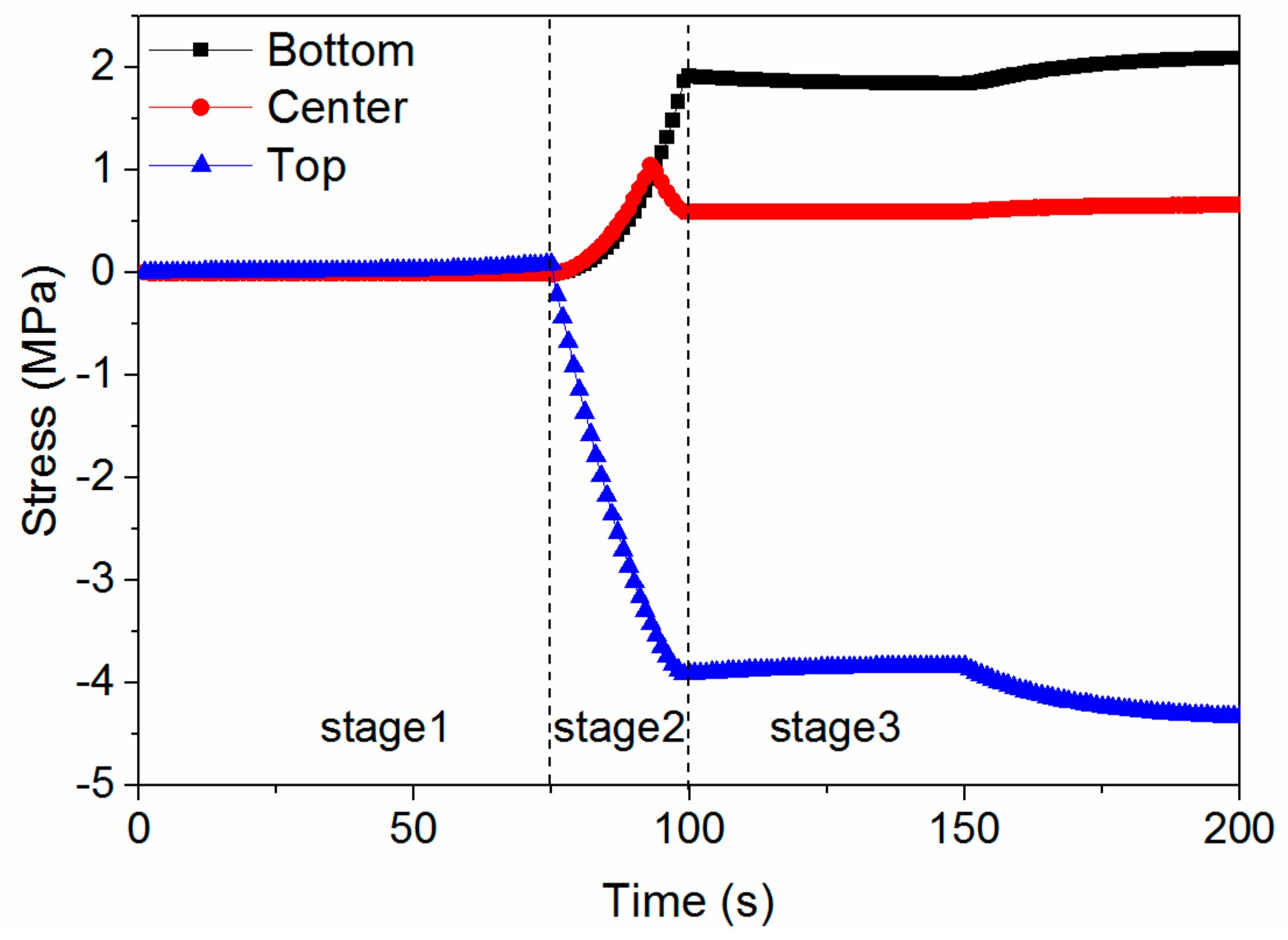
5.4. Stress in Stage 1
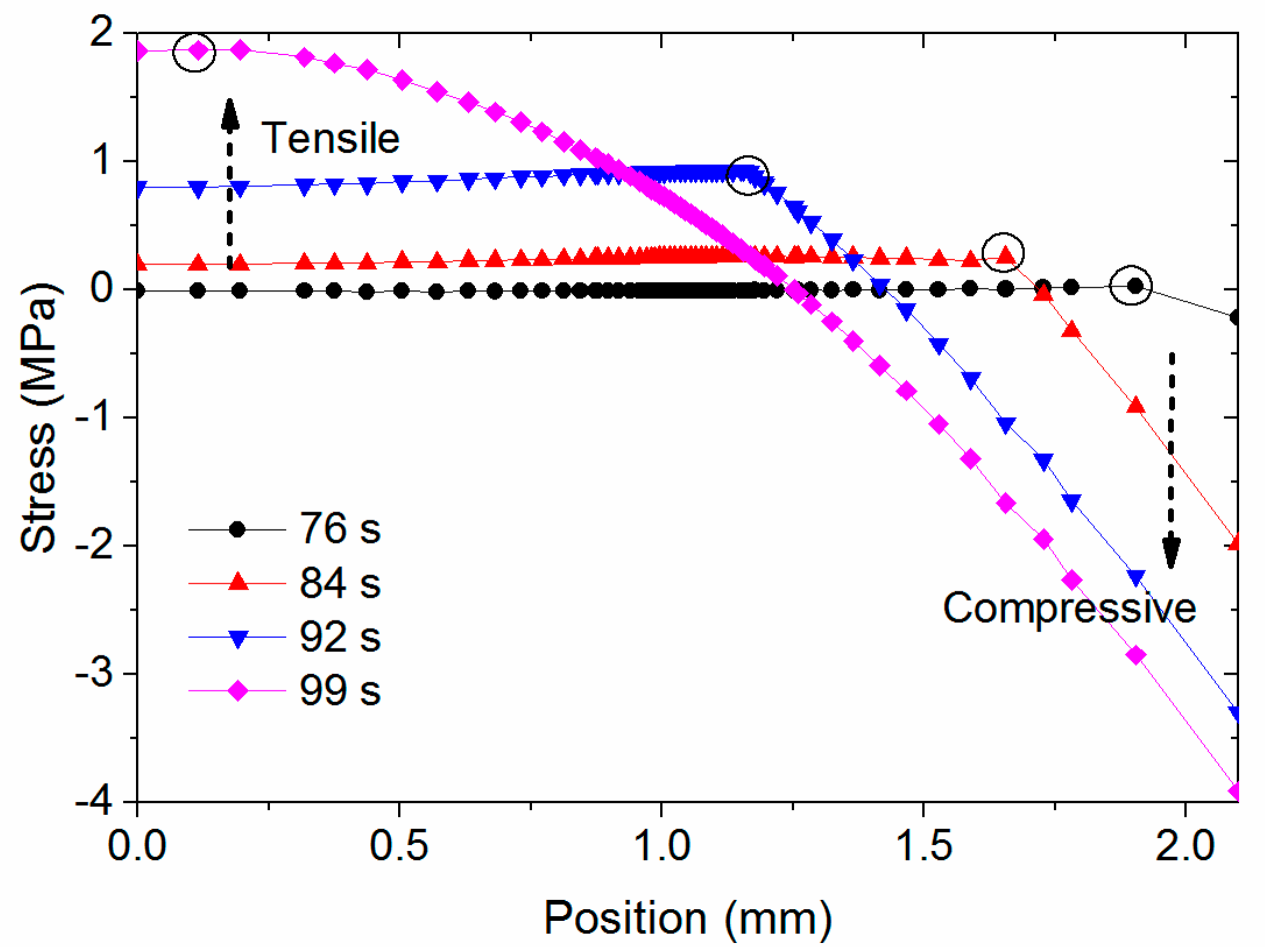
5.5. Stress in Stage 2
5.6. Stress in Stage 3
5.7. Stress Evolution Process
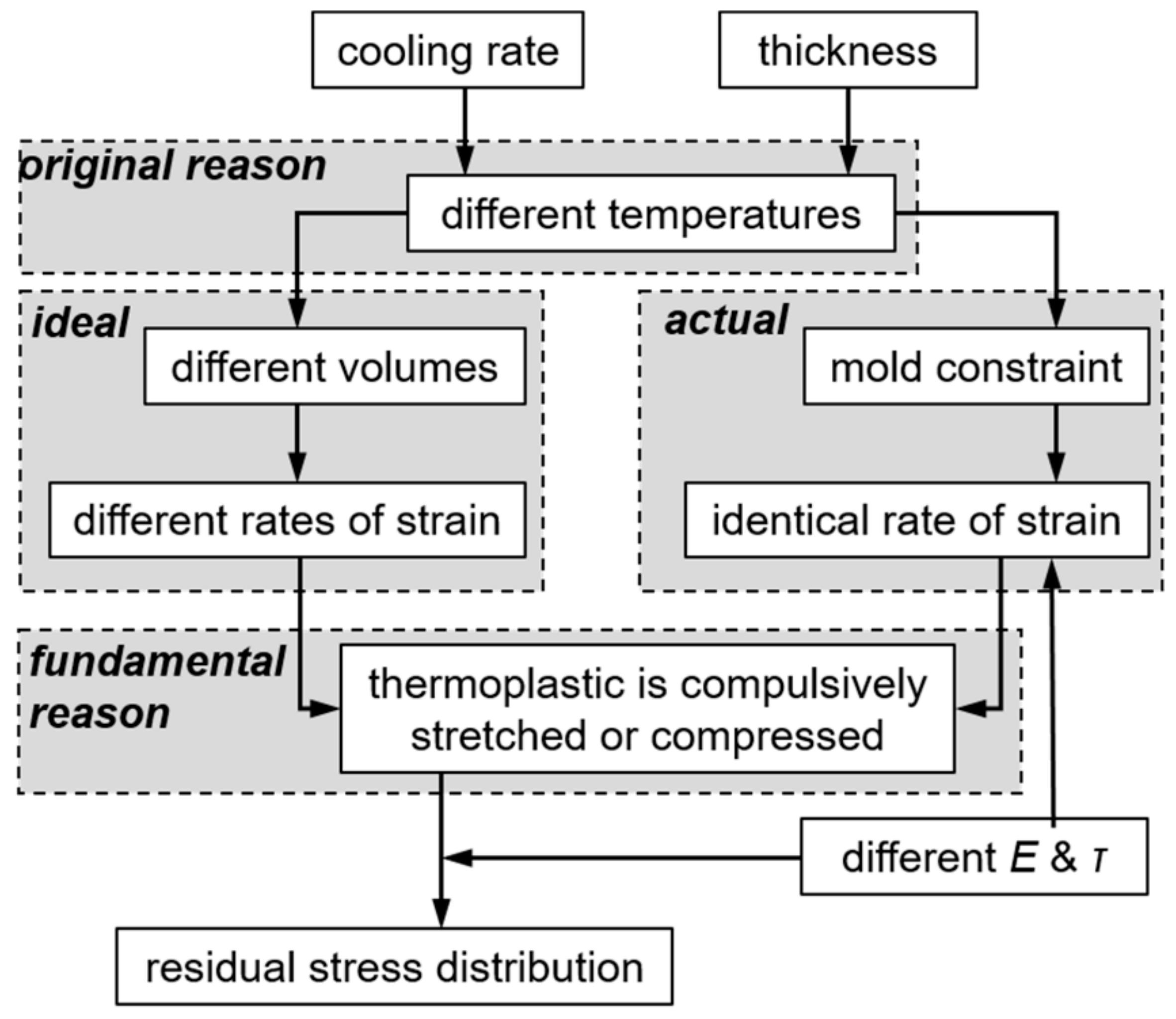
6. Forming Mechanism of Residuals Stress
7. Conclusions
- Stage 1:
- When the temperature of the whole plate is greater than Tg, stress barely forms.
- Stage 2:
- When the plate cools to Tg from one side to the other side, a large portion of the residual stress forms in a relatively short time, although the duration of this stage is typically short.
- Stage 3:
- Until the whole plate cools to room temperature, the residual stress changes further, and finally a parabolic-shaped residual stress forms.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| T | Temperature, K |
| Tg | Glass transition temperature, 483 K |
| Troom | Room temperature, 298 K |
| Tt | Pressure-dependent Tg |
| T | Time, s |
| V | Volume, m3 |
| V0 | Reference volume, m3 |
| P | Pressure, MPa |
| ρ | Density, kg/m3 |
| Cp | Specific heat, kJ/(kg·K) |
| k | Thermal conductivity, W/(m·K) |
| B | Material coefficients |
| C | Constant in Tait equation, 0.0894 |
| AT | Shift factor |
| E | Young’s modulus, MPa |
| τ | Stress relaxation time, s |
| ε | Strain |
| σ | Stress, MPa |
| b | Fitting parameter |
Appendix A. Cooling Rate
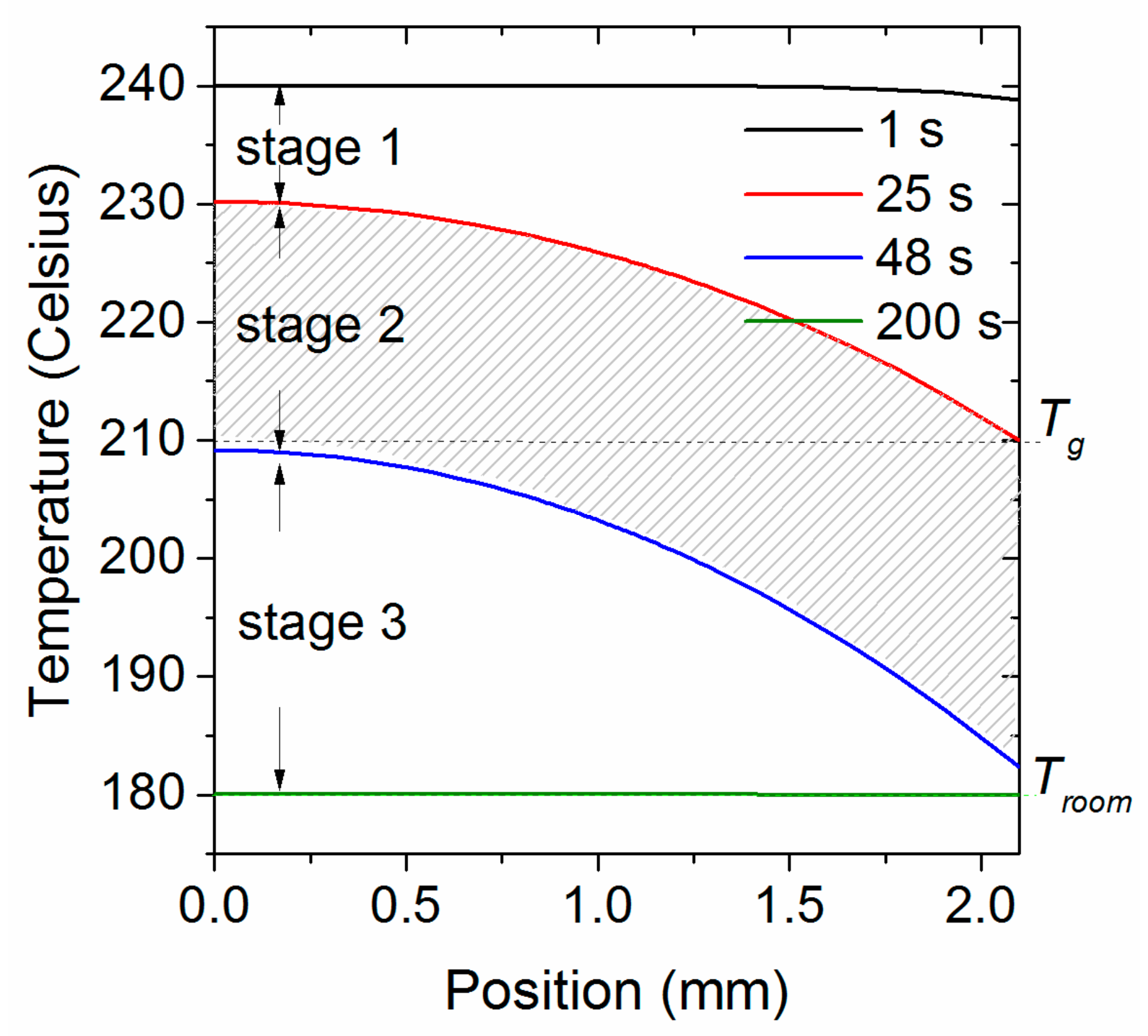
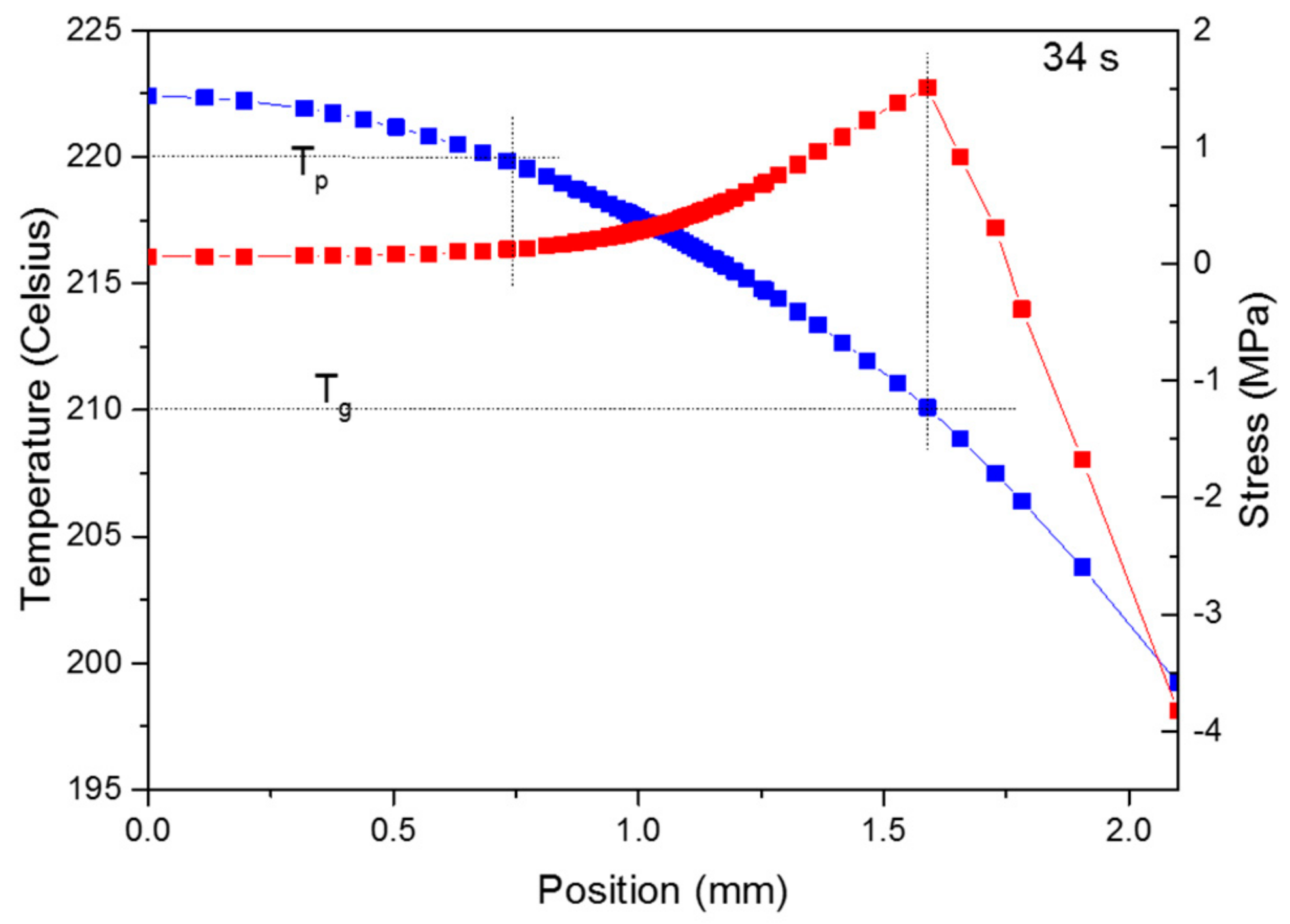
Appendix B. Plate Thickness
References
- Nohara, L.B.; Cândido, G.M.; Nohara, E.L.; Rezende, M.C. Processing of Carbon Fiber/PEI Composites Based on Aqueous Polymeric Suspension of Polyimide. In Thermoplastic-Composite Materials, 1st ed.; Slavka Krautzeka 83/A; Adel El-Sonbat; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; Volume 5, pp. 91–112. ISBN 978-953-51-0310-3. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Zhou, H. Modelling and simulation of residual stress and warpage in injection moulding. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2004, 218, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J. Modeling and simulation of thermally induced stress and warpage in injection molded thermoplastics. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1996, 36, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, C. Numerical simulation of thermally induced stress and warpage in injection-molded thermoplastics. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2001, 20, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.; Lai-Fook, R.; Hernandez-Aguilar, J. Residual thermal stresses in injection moldings of thermoplastics: A theoretical and experimental study. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2002, 42, 1098–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Morales, A.; Figueroa-López, U. Residual stresses in injection molded products. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 4399–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlevliet, P.P.; Bersee, H.E.; Beukers, A. Residual stresses in thermoplastic composites—A study of the literature. Part III: Effects of thermal residual stresses. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. 2007, 38, 1581–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, T.; Gillespie, J.; Pipes, R.; Manson, J.A.; Seferis, J. Prediction of process-induced residual stresses in thermoplastic composites. J. Compos. Mater. 1990, 24, 616–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trende, A.; Åström, B.; Nilsson, G. Modelling of residual stresses in compression moulded glass-mat reinforced thermoplastics. Compos. Part A Appl. Sic. 2000, 31, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Krevelen, D.W.; Te Nijenhuis, K. Properties of Polymers: Their Correlation with Chemical Structure; Their Numerical Estimation and Prediction from Additive Group Contributions, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.I.; Kang, T.J.; Chung, K.; Youn, J.R. Prediction and measurement of residual stresses in injection molded parts. Fibers Polym. 2001, 2, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.; Chen, X.; Lam, Y.; Yue, C. Effects of polymer melt compressibility on mold filling in micro-injection molding. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 095019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonan, S.A.; Soyarslan, C.; Haupt, P.; Kwiatkowski, L.; Tekkaya, A.E. A simple finite strain non-linear visco-plastic model for thermoplastics. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2013, 66, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, C.T. Experimental Characterization of Constitutive models for PEEK Thermoplastic Composite at Heating Stage During Forming. J. Compos. Mater. 1997, 31, 1480–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, C.T. Thermoelastic Behavior of PEEK Thermoplastic Composite during Cooling from Forming Temperatures. J. Compos. Mater. 1997, 31, 2230–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Ogasawara, T.; Yoshikawa, N.; Zhai, H.Z. Modeling the Viscoelasticity of Polyetherimide. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Q.; Ogasawara, T.; Yoshikawa, N.; Zhai, H. Stress Evolution of Amorphous Thermoplastic Plate during Forming Process. Materials 2018, 11, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040464
Wu Q, Ogasawara T, Yoshikawa N, Zhai H. Stress Evolution of Amorphous Thermoplastic Plate during Forming Process. Materials. 2018; 11(4):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040464
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Qi, Tomotaka Ogasawara, Nobuhiro Yoshikawa, and Hongzhou Zhai. 2018. "Stress Evolution of Amorphous Thermoplastic Plate during Forming Process" Materials 11, no. 4: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040464
APA StyleWu, Q., Ogasawara, T., Yoshikawa, N., & Zhai, H. (2018). Stress Evolution of Amorphous Thermoplastic Plate during Forming Process. Materials, 11(4), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040464




