Laser Induced Damage of Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate (KDP) Optical Crystal Machined by Water Dissolution Ultra-Precision Polishing Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
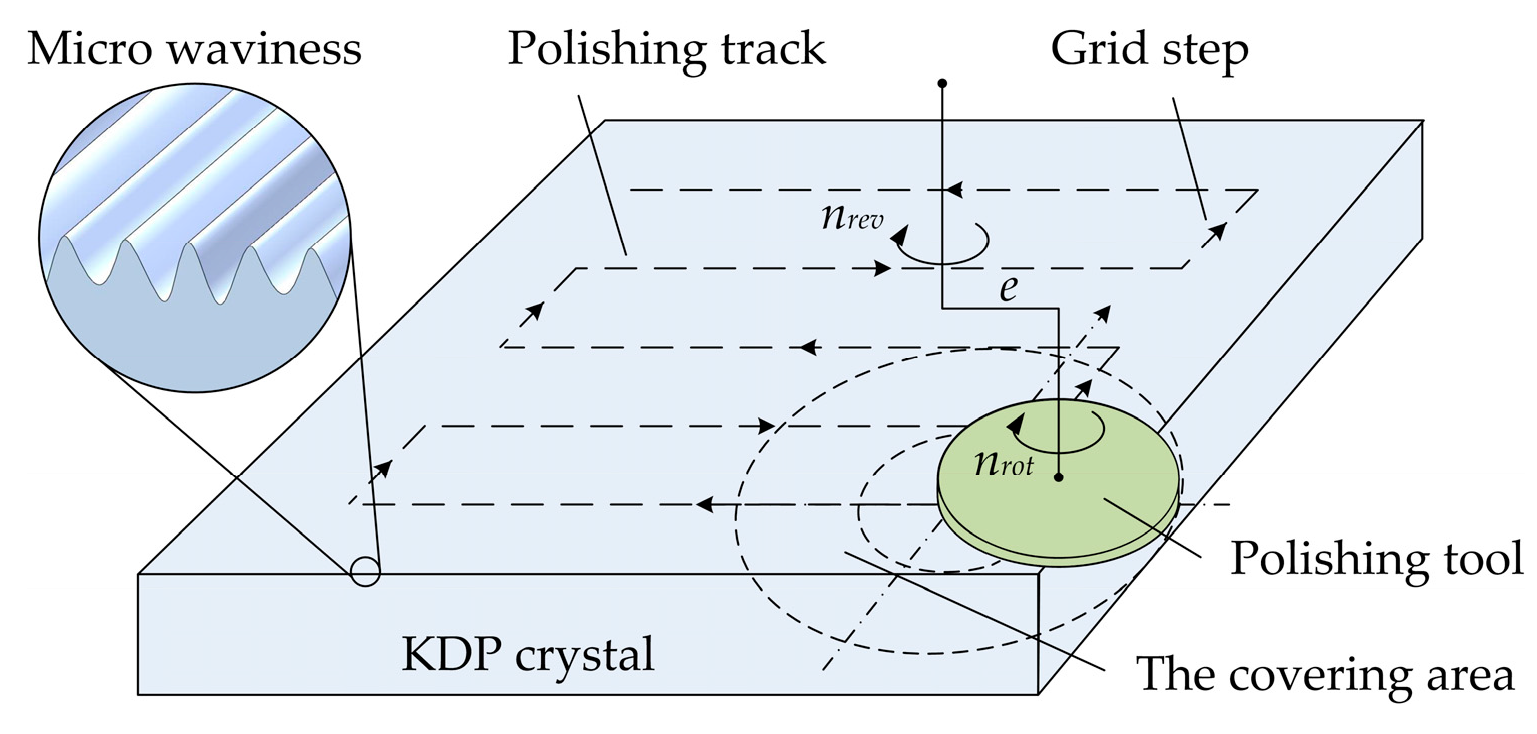
2.1. Samples and Processing
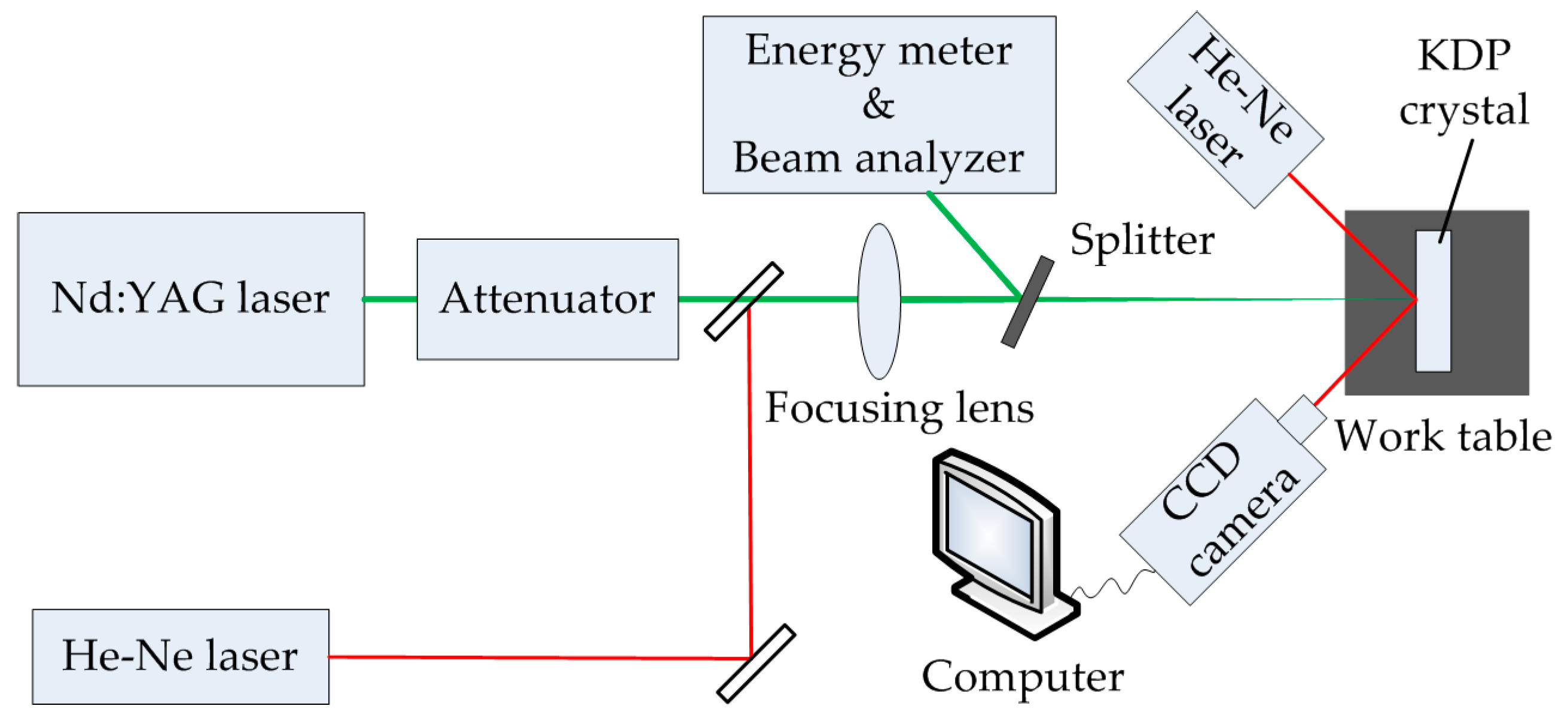
2.2. Laser Damage Test
3. Results and Discussion
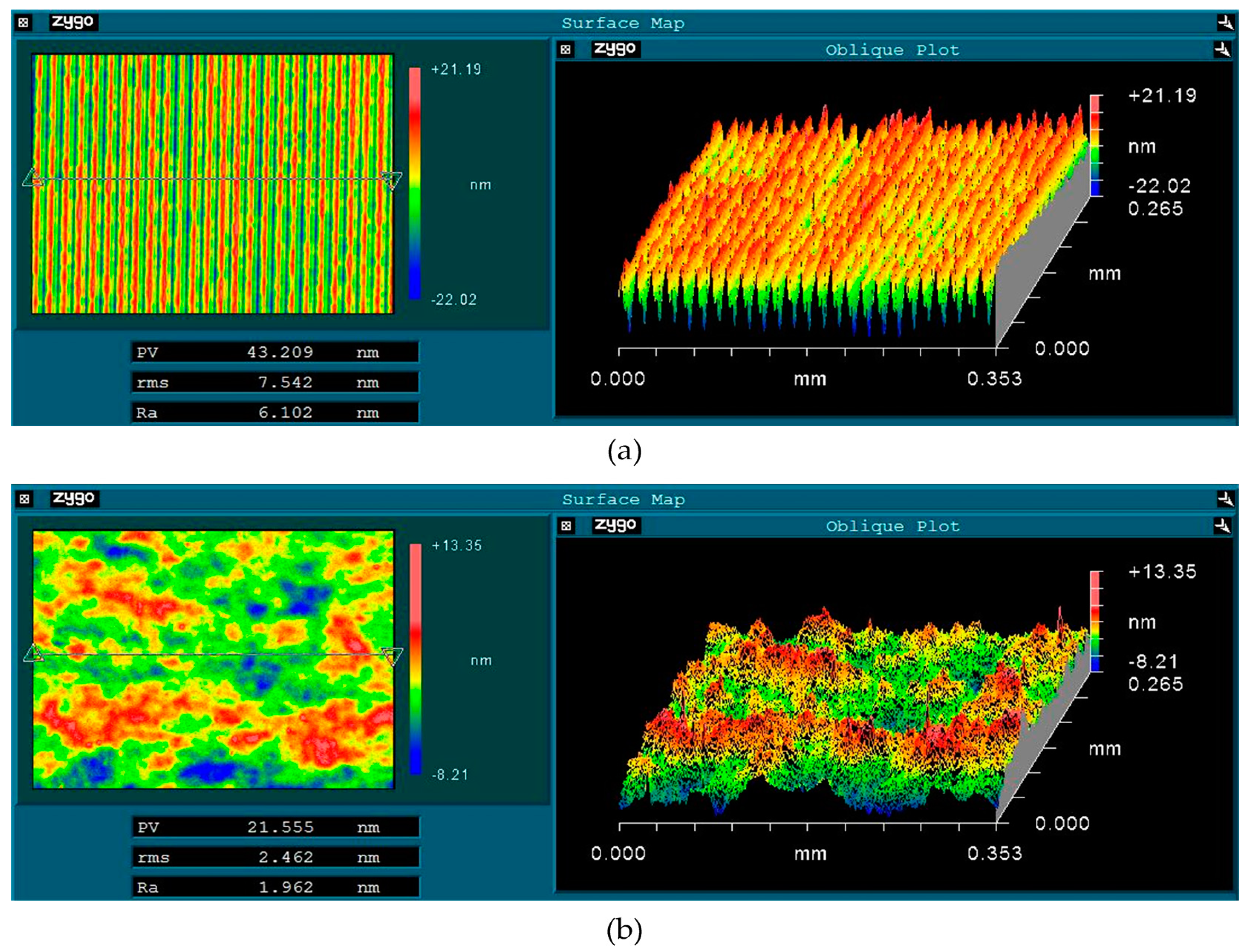
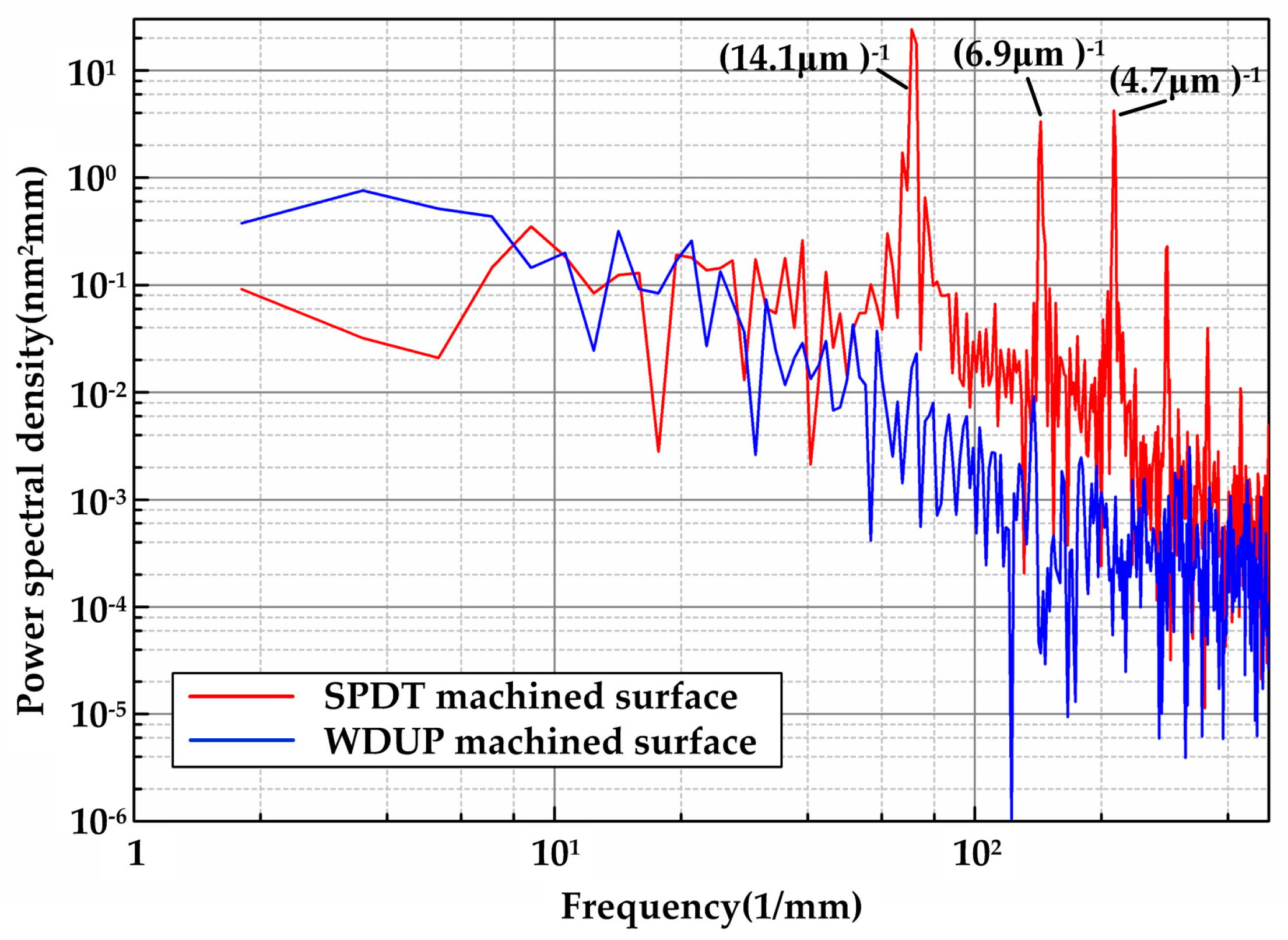
3.1. Surface Quality Analysis
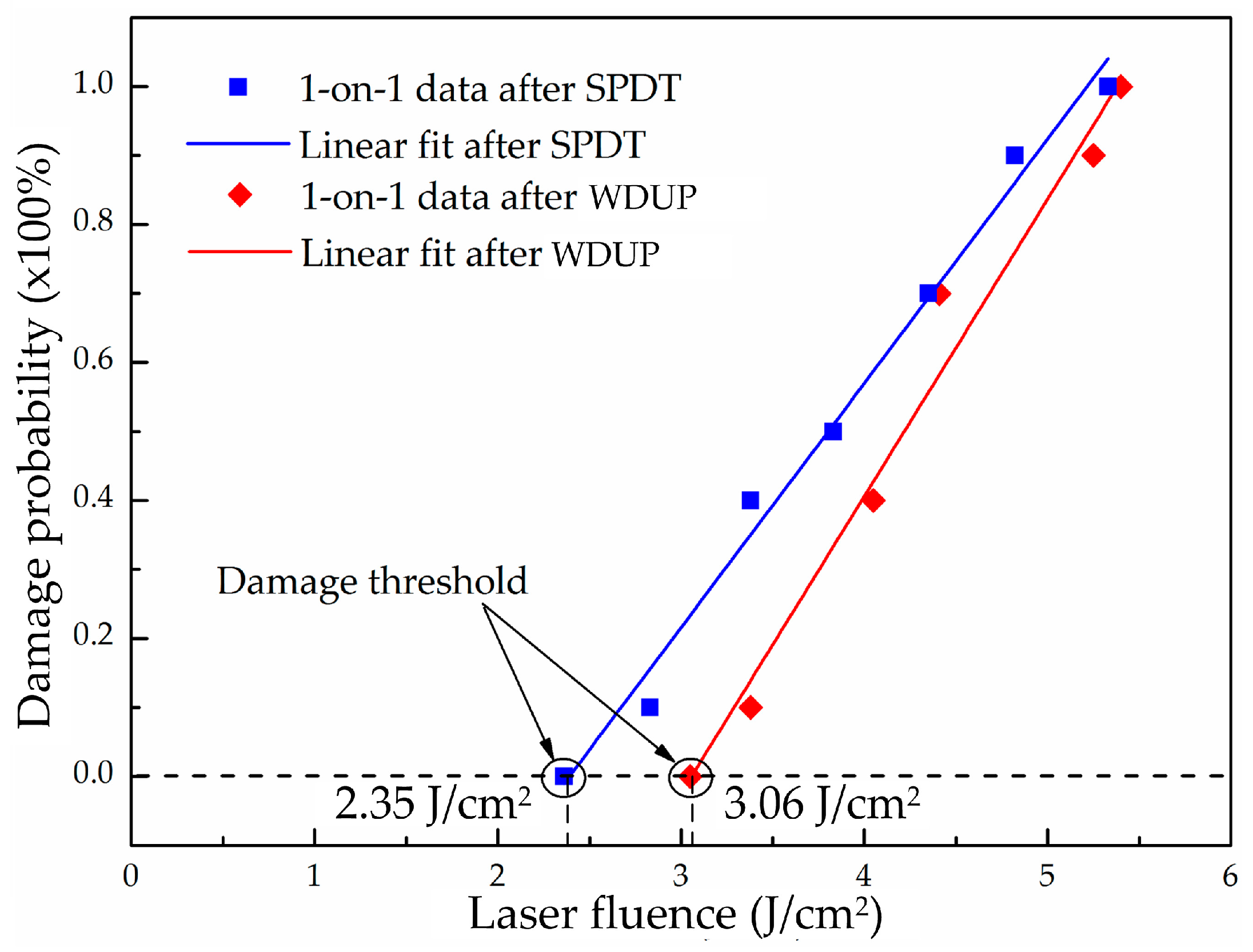
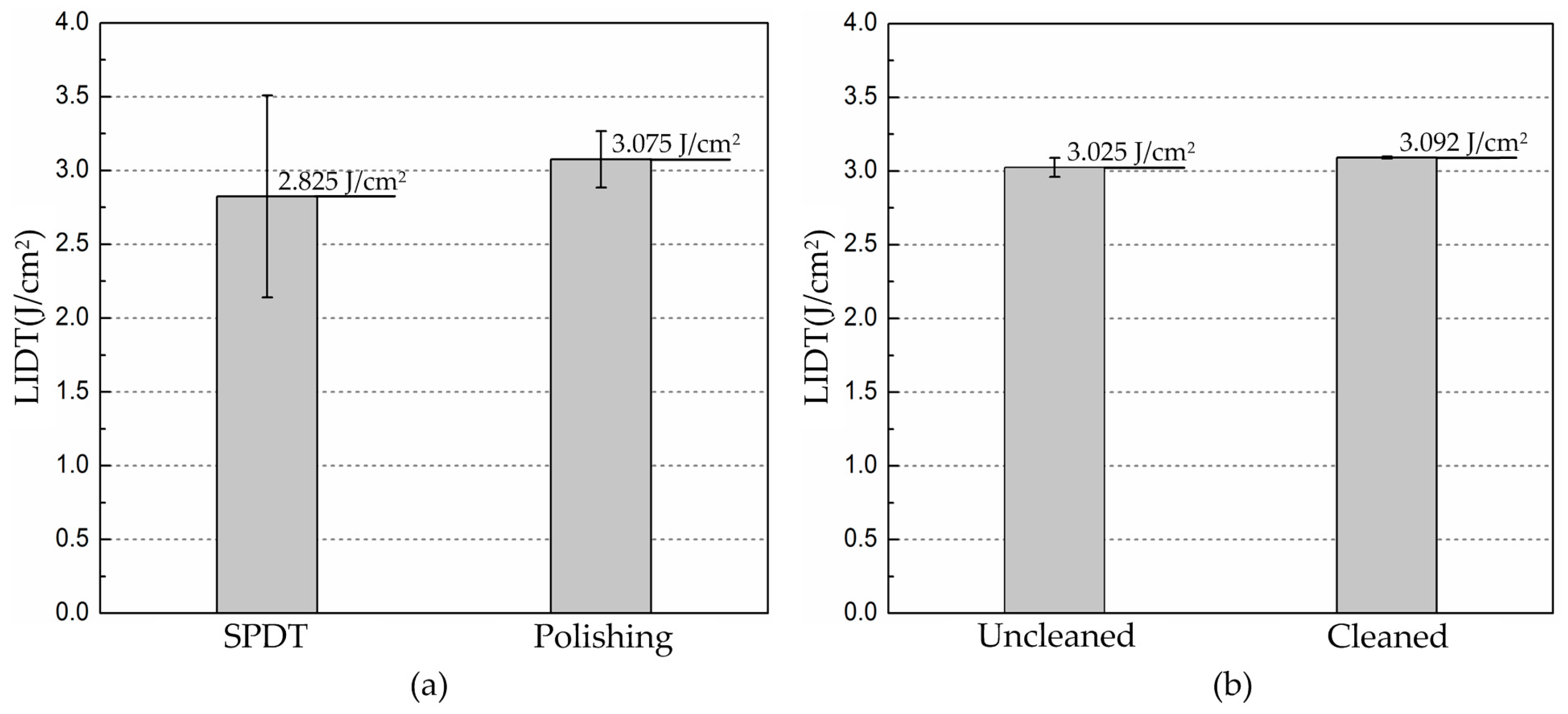
3.2. Laser Induced Damage Threshold Analysis
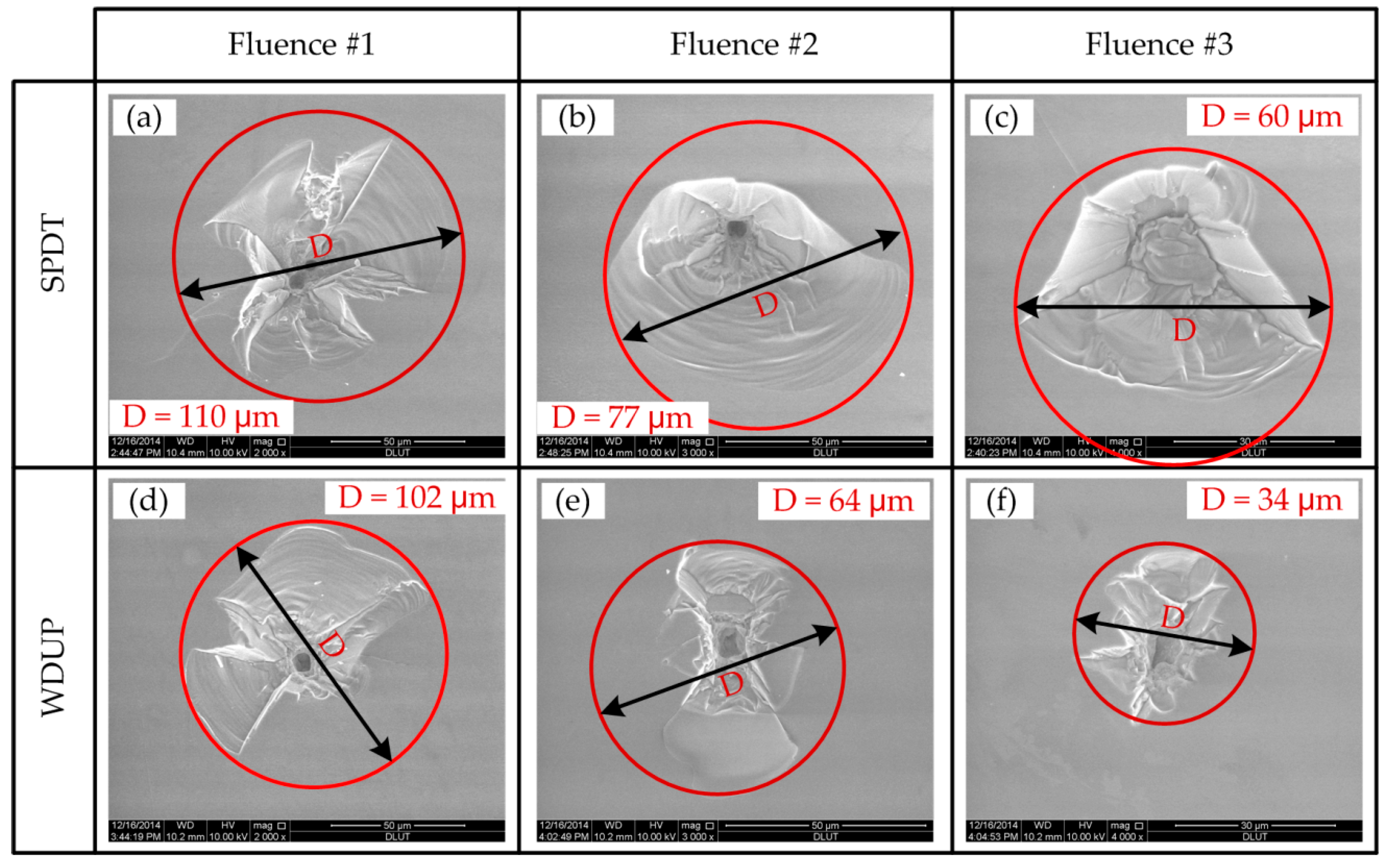
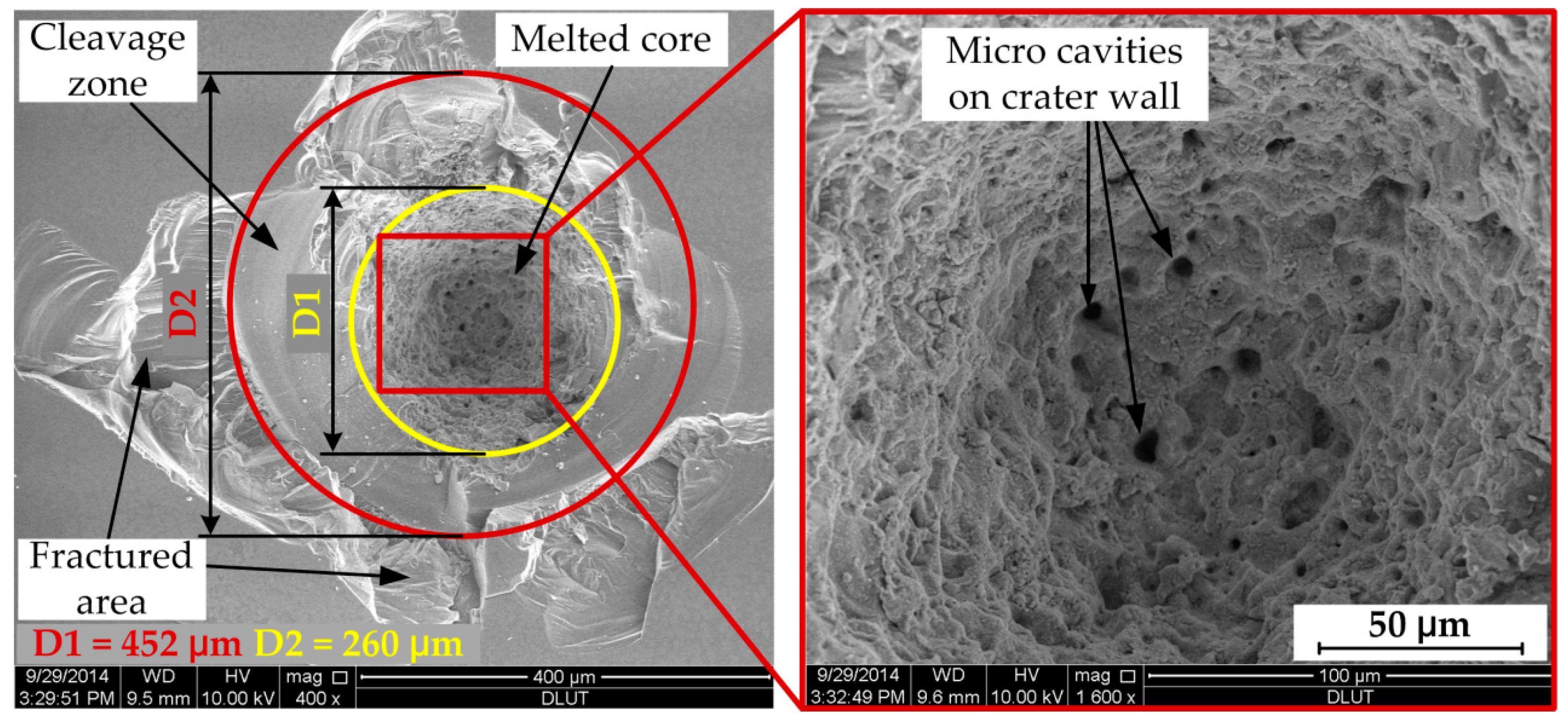
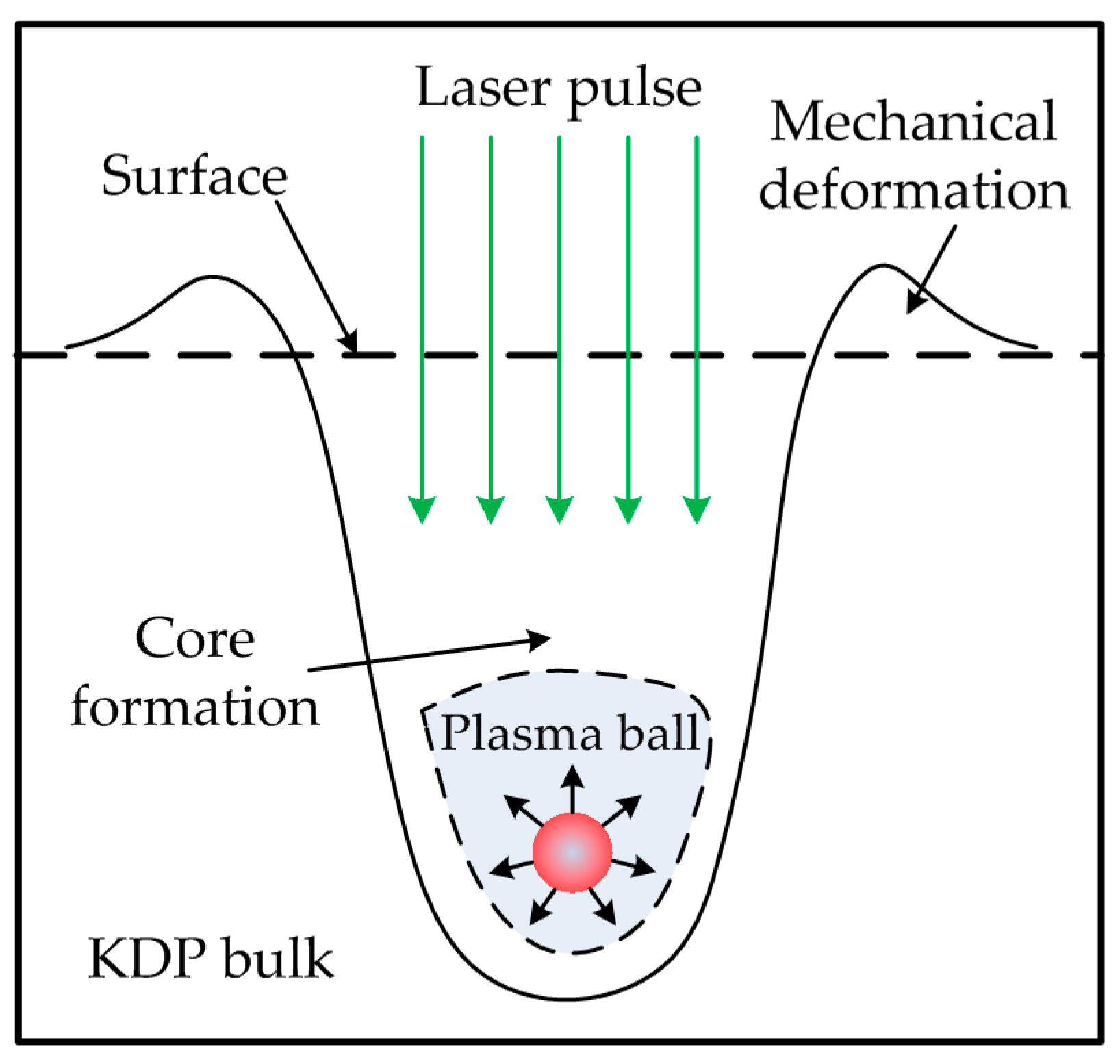
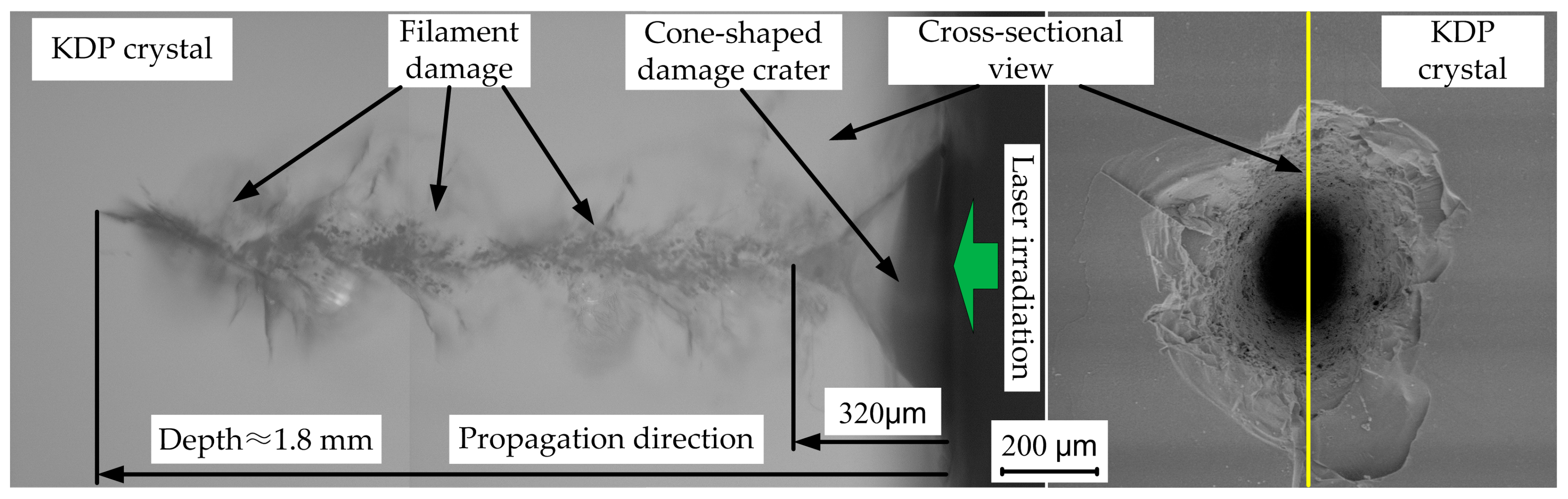
3.3. Laser Damage Sites Observation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Yoreo, J.J.; Burnham, A.K.; Whitman, P.K. Developing KH2PO4 and KD2PO4 crystals for the world’s most power laser. Int. Mater. Rev. 2002, 47, 113–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, S. Overview of the national ignition facility. Health Phys. 2013, 104, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Zheng, W.; Wei, X.; Jing, F.; Hu, D.; Zhou, W.; Feng, B.; Wang, J.; Peng, Z.; Liu, L.; et al. Research and construction progress of SG-III laser facility. Proc. SPIE 2014, 9266, 926607. [Google Scholar]
- Pritula, I.M.; Kolybayeva, M.I.; Salo, V.I.; Puzikov, V.M. Defects of large-size KDP single crystals and their influence on degradation of the optical properties. Opt. Mater. 2007, 30, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenkov, A.A. Fundamental mechanisms of laser-induced damage in optical materials: Today’s state of understanding and problems. Opt. Eng. 2014, 53, 10901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feit, M.D.; Rubenchik, A.M. Implications of nanoabsorber initiators for damage probability curves, pulse length scaling and laser conditioning. Proc. SPIE 2004, 5273, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Ju, X.; Yan, C.; Liu, C. Synchrotron micro-XRF study of metal inclusions distribution in potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) induced by ultraviolet laser pulses. Opt. Mater. Express 2015, 5, 2201–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMange, P.; Negres, R.A.; Zaitseva, N.P.; Radousky, H.B.; Demos, S.G. Correlation of laser-induced damage performance to crystal growth conditions in KDP and DKDP crystals. In Proceedings of the Lasers and Electro-Optics, 2006 and 2006 Quantum Electronics and Laser Science Conference, Long Beach, CA, USA, 21–26 May 2006; IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, X.; Hu, G.; Yang, L.; Xu, Z.; Shao, J. Laser damage dependence on the size and concentration of precursor defects in KDP crystals: View through differently sized filter pores. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 1534–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Li, S.; Peng, X.; Hu, H.; Tie, G. Research of polishing process to control the iron contamination on the magnetorheological finished KDP crystal surface. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papernov, S.; Schmid, A.W. Laser-induced surface damage of optical materials: Absorption sources, initiation, growth and mitigation. Proc. SPIE 2008, 7132, 71321J. [Google Scholar]
- Danileĭko, Y.K.; Manenkov, A.A.; Nechitaĭlo, V.S. The mechanism of laser-induced damage in transparent materials, caused by thermal explosion of absorbing in homogeneities. Quantum Electron. 1978, 8, 116–118. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Chen, M.; Cheng, J.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, W. Two important mechanisms damaging KH2PO4 crystal processed by ultraprecision fly cutting and their relationships with cutting parameters. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 3451–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Q.; Chen, M.J.; An, C.H.; Lian, Z.; Cheng, J.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, W. Mechanism of micro-waviness induced KH2PO4 crystal laser damage and the corresponding vibration source. Chin. Phys. B 2012, 21, 050301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namba, Y.; Katagiri, M. Ultraprecision grinding of potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals for getting optical surfaces. Proc. SPIE 1999, 3578, 692–693. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, K.; Yoshida, H.; Nakai, S.; Katori, Y.; Okamoto, T. Laser damage of optically polished KDP crystal. Proc. SPIE 1992, 1624, 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, B.A.; Hed, P.P.; Baker, P.C. Fine diamond turning of KDP crystals. Appl. Opt. 1986, 25, 1733–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Hu, D. Surface quality of large KDP crystal fabricated by single-point diamond turning. In Proceedings of the 2nd SPIE International Symposium on Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies, Xi’an, China, 2–5 December 2006; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA; p. 61492M. [Google Scholar]
- Tie, G.; Dai, Y.; Guan, C.; Chen, S.; Song, B. Research on subsurface defects of potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals fabricated by single point diamond turning technique. Opt. Eng. 2013, 52, 33401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, M.; Cheng, J.; Xiao, Y.; Pang, Q. Study on the optical performance and characterization method of texture on KH2PO4 surface processed by single point diamond turning. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 279, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menapace, J.A. Developing magnetorheological finishing (MRF) technology for the manufacture of large-aperture optics in megajoule class laser systems. Proceeding of the SPIE Laser Damage Conference, Boulder, CO, USA, 26–29 September 2010; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA; p. 78421W. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Jiao, F.; Chen, H.; Tie, G.; Shi, F.; Hu, H. Novel magnetorheological figuring of KDP crystal. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2011, 9, 102201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Wang, B.; Guo, D.; Li, Y. Experimental study on abrasive-free polishing for KDP crystal. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, H853–H856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Teng, X.; Guo, D. Micro water dissolution machining principle and its application in ultra-precision processing of KDP optical crystal. Sci. China Technol. Sc. 2015, 58, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, L.; Gao, W.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Ji, F.; Pan, J.; Wang, B. KDP aqueous solution-in-oil microemulsion for ultra-precision chemical-mechanical polishing of KDP crystal. Materials 2017, 10, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menapace, J.A.; Ehrmann, P.R.; Bickel, R.C. Magnetorheological finishing (MRF) of potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) crystals: Nonaqueous fluids development, optical finish and laser damage performance at 1064 nm and 532 nm. Proc. SPIE 2009, 7504, 750414. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Gao, H.; Chen, Y.; Guo, D. A water dissolution method for removing micro-waviness caused by SPDT process on KDP crystals. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 85, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electrotechnical Sector Committee. Laser and Laser-Related Equipment Determination of Laser-Induced Damage Threshold of Optical Surfaces, Part 1: 1-on-1 Test; ISO 11254-1; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, D.; Wang, X.; Gao, H. Simulation of large scale KDP crystal polishing by computer controlled micro-nano deliquescence. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 497, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Characterization of Ultra-Precision Machined Surfaces Using Spectral Density and Fractal Analysis. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.H.; Hawley-Fedder, R.A.; Stolz, C.J.; Menapace, J.A.; Borden, M.R.; Whitman, P.K.; Yu, J.; Runkel, M.; Riley, M.O.; Feit, M.D. NIF optical materials and fabrication technologies: An overview. Proc. SPIE 2004, 5341, 84–102. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Guo, D.; Teng, X. Investigation on the cleaning of KDP ultra-precision surface polished with micro water dissolution machining principle. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2017, 60, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, C.W.; Matthews, M.J.; Bude, J.D.; Spaeth, M.L. The effect of laser pulse duration on laser-induced damage in KDP and SiO2. Proc. SPIE 2007, 6403, 64030K. [Google Scholar]
- Duchateau, G.; Hébert, D.; Hallo, L. Modeling of laser-induced damage in KDP crystals by nanosecond pulses: A preliminary hydrodynamic study. Proc. SPIE 2010, 7842, 78420S. [Google Scholar]
- Papernov, S.; Schmid, A.W. Two mechanisms of crater formation in ultraviolet-pulsed-laser irradiated SiO2 thin films with artificial defects. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 114906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negres, R.A.; Feit, M.D.; Demos, S.G. Dynamics of material modifications following laser-breakdown in bulk fused silica. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 10642–10649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, R. Research on the High Power Laser Induced Damage of the Optical Components. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F. Assessing microstructure changes in potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals induced by mechanical stresses. Scr. Mater. 2016, 113, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
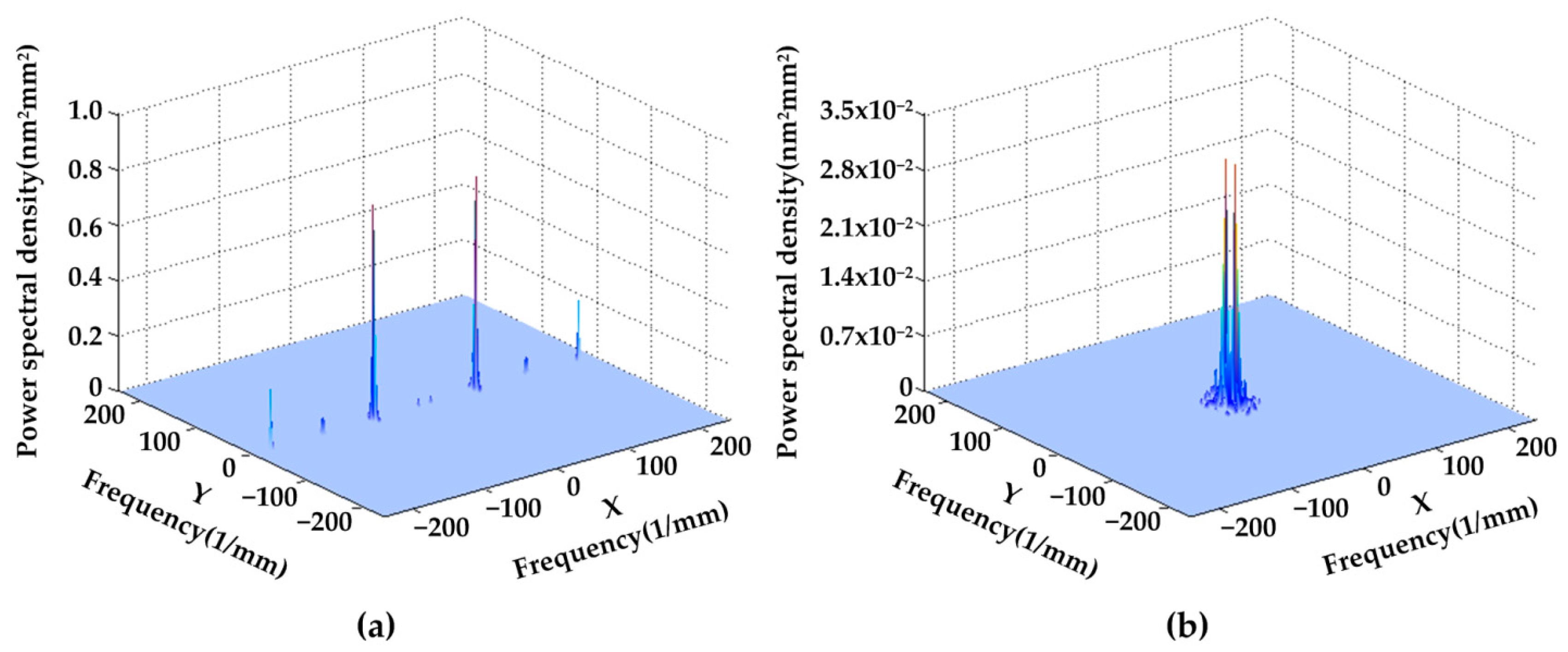


| Processing Method | Surface Feature | RMS Roughness/nm |
|---|---|---|
| SPDT | Micro-waviness | 7.442 |
| WDUP | Smooth | 2.349 |
| Processing Method | Laser Induced Damage Threshold (LIDT) (J/cm2) |
|---|---|
| SPDT | 2.825 ± 0.684 |
| WDUP | 3.075 ± 0.191 |
| WDUP (uncleaned) | 3.025 ± 0.064 |
| WDUP (cleaned) | 3.092 ± 0.007 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Guo, D.; Liu, Z. Laser Induced Damage of Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate (KDP) Optical Crystal Machined by Water Dissolution Ultra-Precision Polishing Method. Materials 2018, 11, 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11030419
Chen Y, Gao H, Wang X, Guo D, Liu Z. Laser Induced Damage of Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate (KDP) Optical Crystal Machined by Water Dissolution Ultra-Precision Polishing Method. Materials. 2018; 11(3):419. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11030419
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yuchuan, Hang Gao, Xu Wang, Dongming Guo, and Ziyuan Liu. 2018. "Laser Induced Damage of Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate (KDP) Optical Crystal Machined by Water Dissolution Ultra-Precision Polishing Method" Materials 11, no. 3: 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11030419
APA StyleChen, Y., Gao, H., Wang, X., Guo, D., & Liu, Z. (2018). Laser Induced Damage of Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate (KDP) Optical Crystal Machined by Water Dissolution Ultra-Precision Polishing Method. Materials, 11(3), 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11030419





