Carboxylic Terminated Thermo-Responsive Copolymer Hydrogel and Improvement in Peptide Release Profile
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
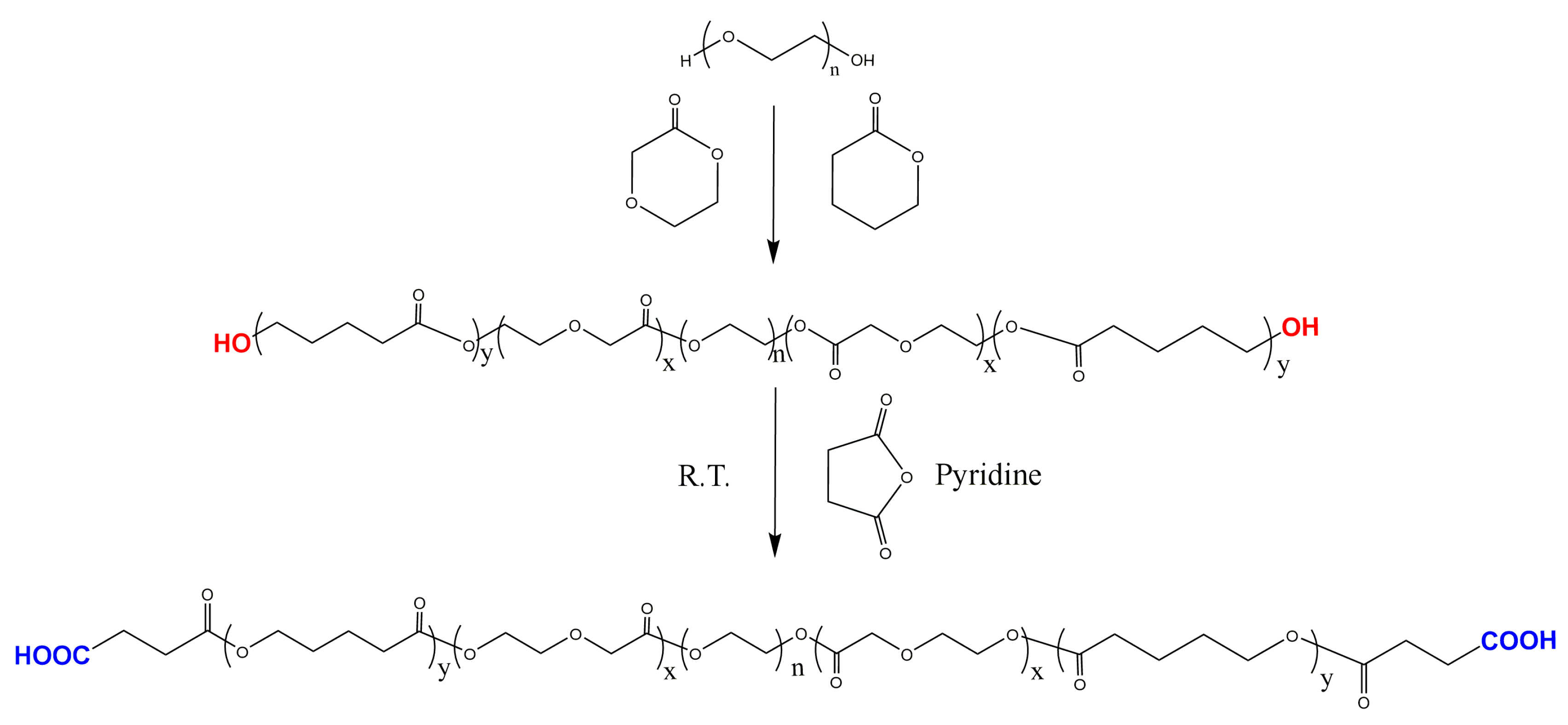
2.2. Synthesis of P(CL–PDO)–PEG–P(CL–PDO) Triblock Copolymer
2.3. Synthesis of Carboxyl Group Terminated PECP
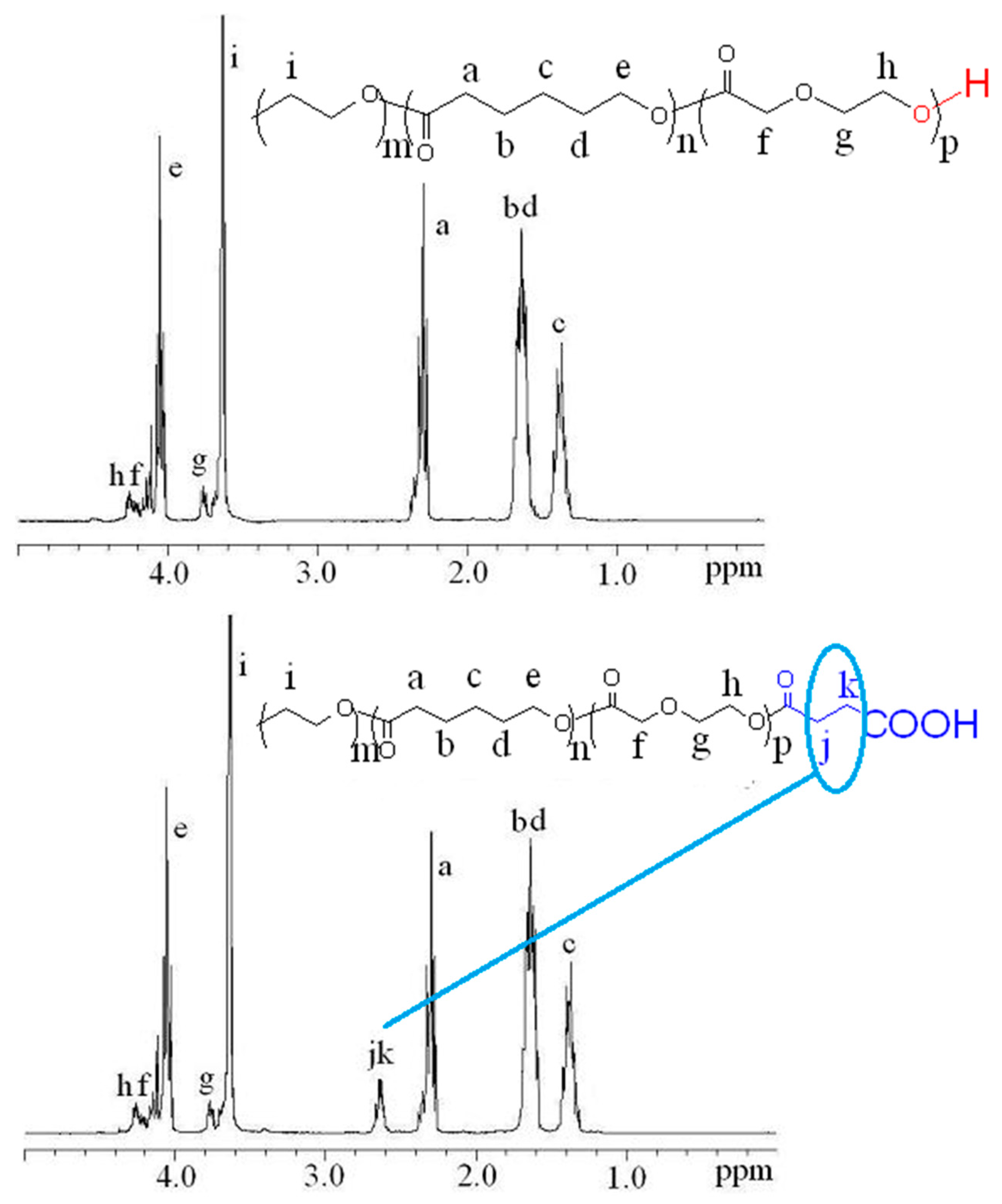
2.4. 1H NMR Study
2.5. Gel Permeation Chromatography
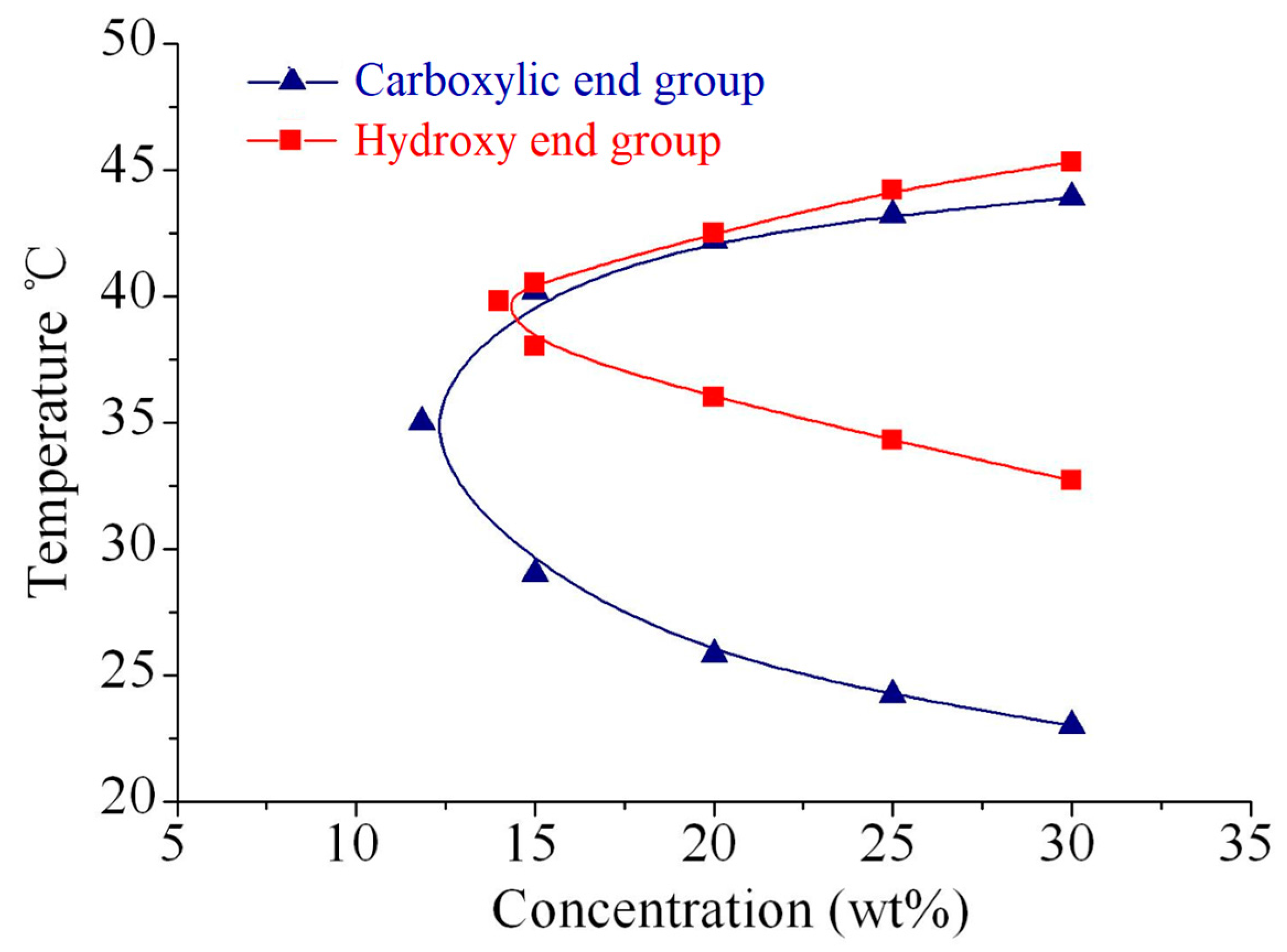
2.6. Sol–Gel Transition
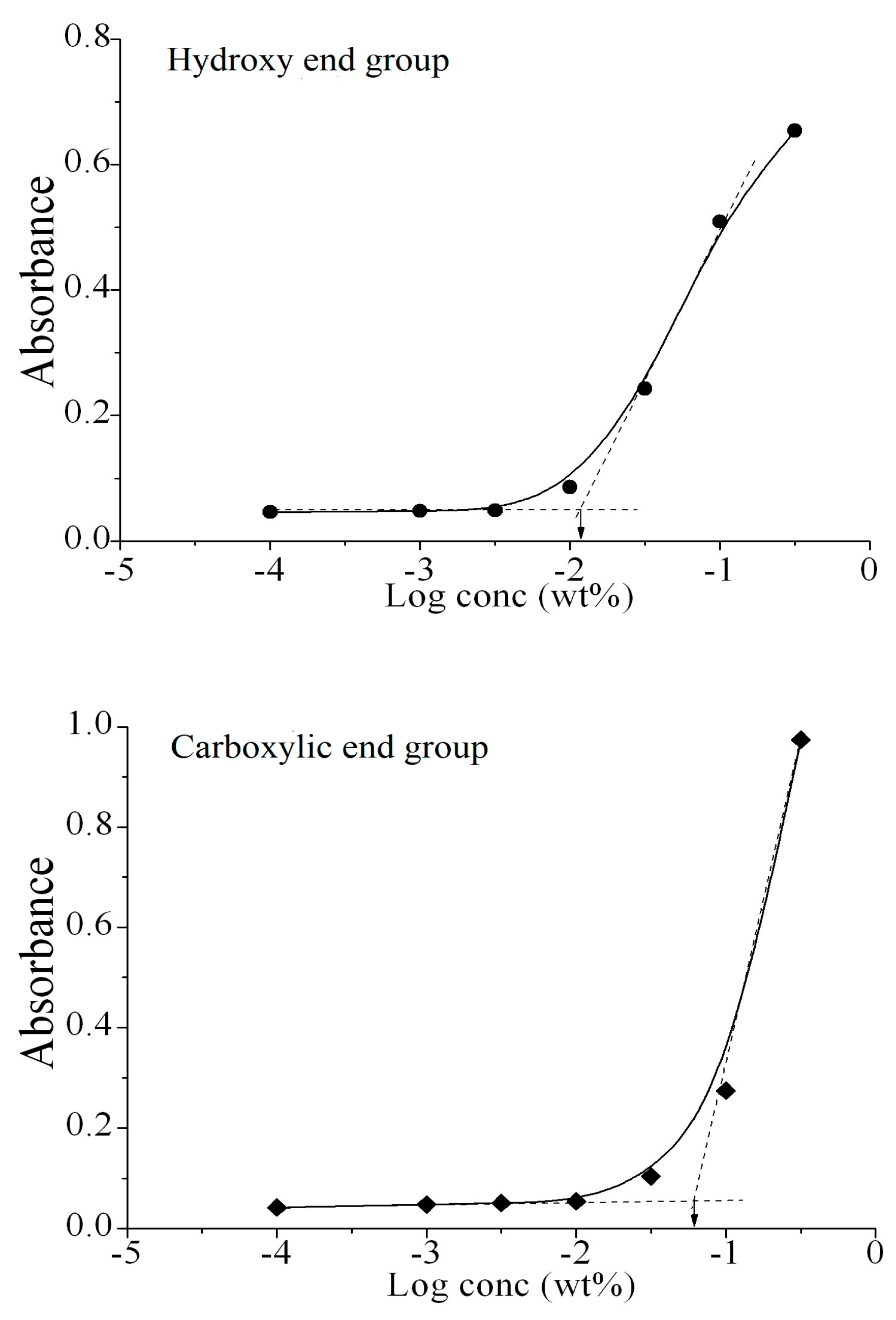
2.7. Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC)
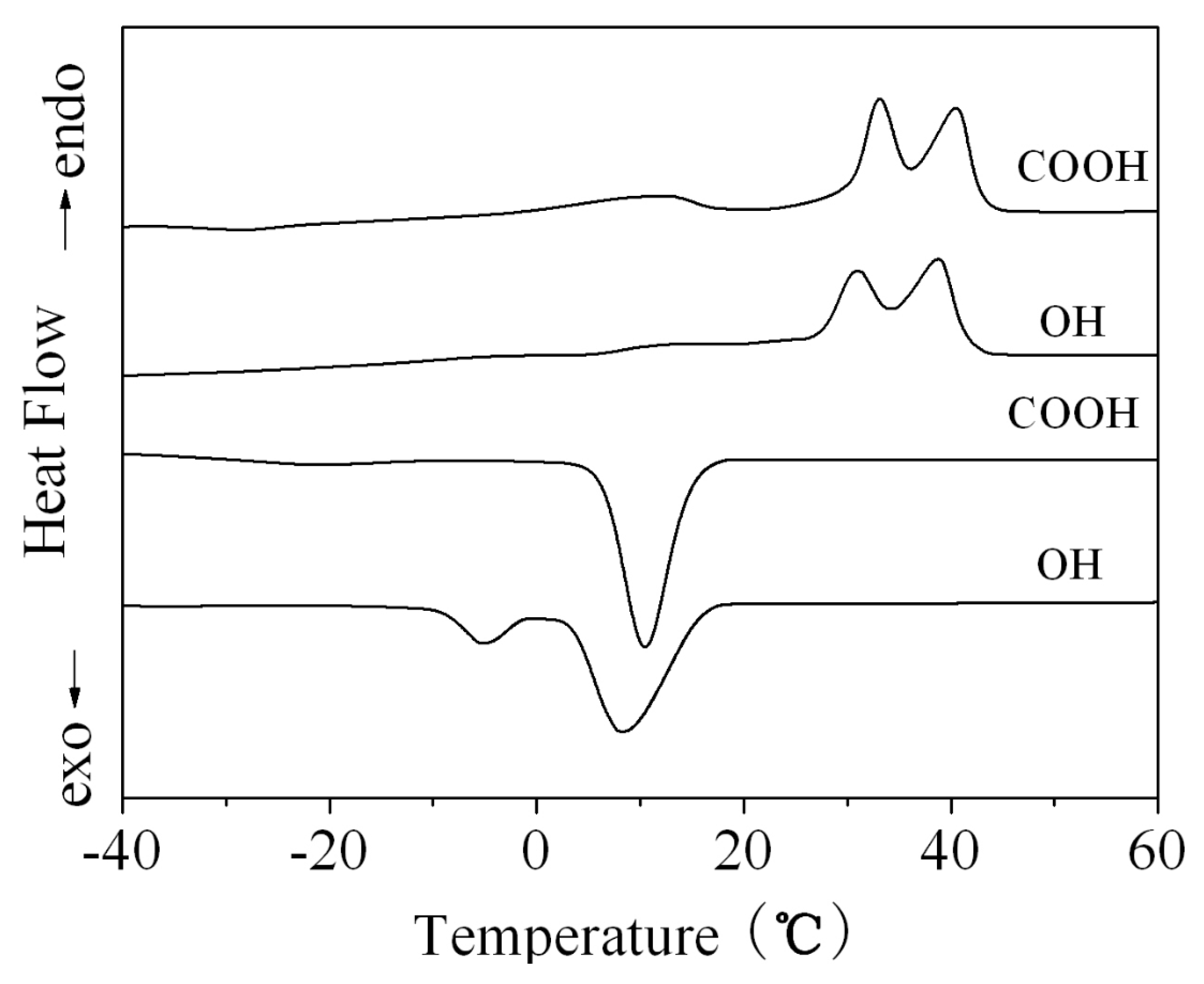
2.8. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
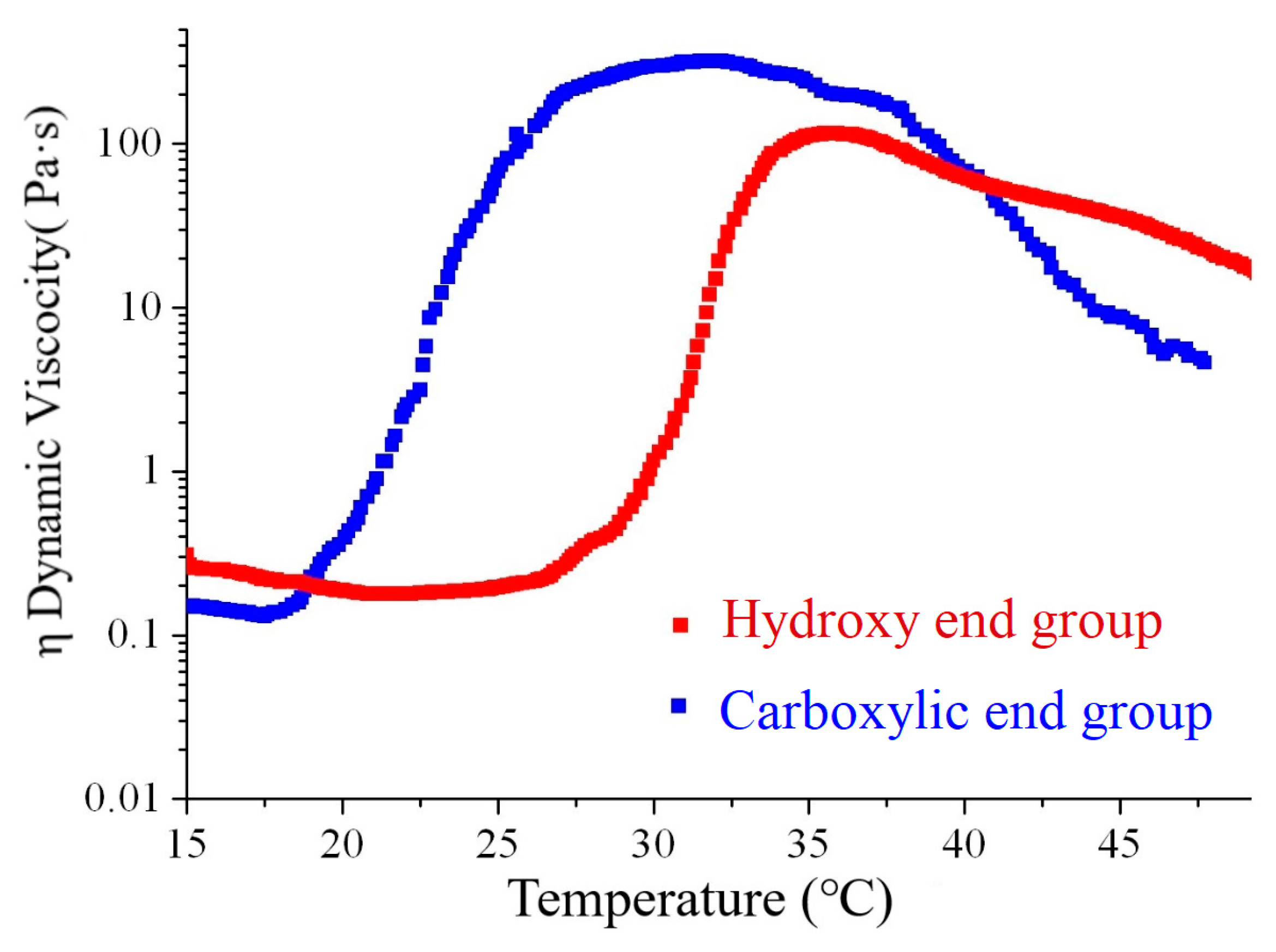
2.9. Dynamic Rheological Analysis
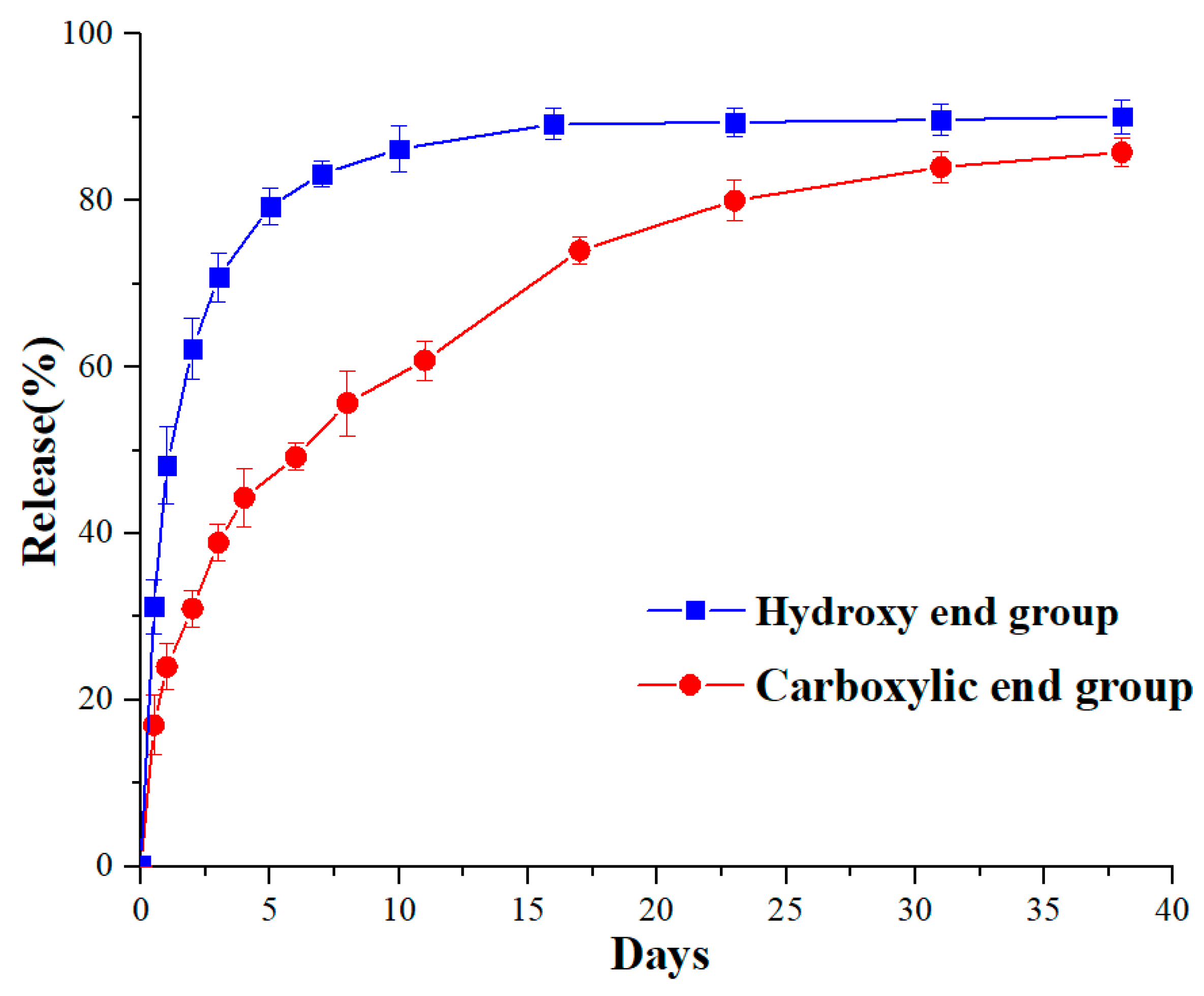
2.10. Release of Peptide Drug
2.11. UV–Vis Spectroscopy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of PECP Triblock Copolymers
3.2. Sol-Gel Transition Behaviors of PECP Copolymer Aqueous Solutions
3.3. Self-Assembly of Micelles
3.4. Crystallization Behaviors of PECP Copolymers
3.5. Dynamic Mechanic Analysis
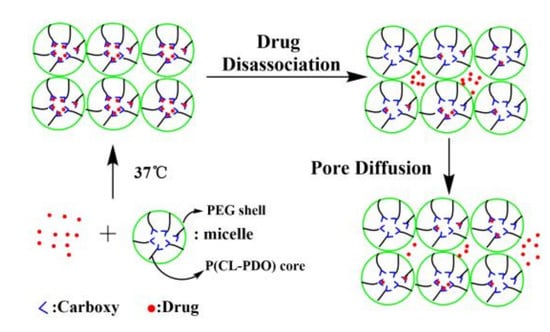
3.6. Drug Release Behaviours In Vitro
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, L.; Zhou, S.B.; Wang, W.; Li, X.H.; Wang, J.X.; Weng, J. Preparation and characterization of porous biodegradable microspheres used for controlled protein delivery. Colloids Surf. A 2009, 345, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Liu, J.; Luo, Z.; Li, M.; Cai, K.Y. Tumor therapy: Targeted drug delivery systems. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 6758–6772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, S.; Bhattacharyya, A.J. Ultrasound-triggered controlled drug delivery and biosensing using silica nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 7155–7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Szoka, F.C. Chemical approaches to triggerable lipid vesicles for drug and gene delivery. Acc. Chem. Res. 2003, 36, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tang, Q.; Yang, D.; Zhang, J.Z.; Zhang, F.; Hu, J. Preparation of pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their application in controlled drug delivery. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 9926–9932. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, P.Y.; Ding, Q.X.; Fan, M.; Liao, J.F.; Qian, Z.Y.; Luo, J.C.; Li, X.Q.; Luo, F.; Yang, Z.M.; Wei, Y.Q. Injectable thermosensitive PEG-PCL-PEG hydrogel/acellular bone matrix composite for bone regeneration in cranial defects. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.Y.; Wu, Q.J.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, D.D.; Luo, F.; Zhao, X.; Wei, Y.Q.; Qian, Z.Y. A biodegradable hydrogel system containing curcumin encapsulated in micelles for cutaneous wound healing. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 6377–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Chen, L.J.; Tan, L.W.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, F.; Wei, Y.Q.; Qian, Z.Y. PEG-PCL based micelle hydrogels as oral docetaxel delivery systems for breast cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6972–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Pickard, S.; Deng, N.J.; Barlow, R.J.; Attwood, D.; Booth, C. Effect of block structure on the micellization and gelation of aqueous solutions of copolymers of ethylene oxide and butylene oxide. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 2371–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatefi, A.; Amsden, B. Biodegradable injectable in situ forming drug delivery systems. J. Controlled Release 2002, 80, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Park, K. Environment-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 53, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.; Bae, Y.H.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, S.W. Biodegradable block copolymers as injectable drug-delivery systems. Nature 1997, 388, 860–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, M.S.; Lee, H.T.; Shim, W.S.; Park, I.S.; Lee, H.J.; Chang, T.H. Poly(D,L-lactic acid-co-glycolic acid)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly (D,L-lactic acid-co-glycolic acid) triblock copolymer and thermoreversible phase transition in water. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 61, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, M.; Chen, D.; Ma, X.; Liu, Y. Injectable biodegradable temperature-responsive PLGA–PEG–PLGA copolymers: Synthesis and effect of copolymer composition on the drug release from the copolymer-based hydrogels. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 294, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, M.; Chen, D.; Hao, T.; Zhao, X.; Hu, H.; Ma, X. Effect of bee venom peptide–copolymer interactions on thermosensitive hydrogel delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 345, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, D.P.; Nguyen, M.K.; Pi, B.S.; Kim, M.S.; Chae, S.Y.; Lee, K.C.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, D.S. Functionalized injectable hydrogels for controlled insulin delivery. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2527–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, H.; Ding, J. A subtle end-group effect on macroscopic physical gelation of triblock copolymer aqueous solutions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2232–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michlovská, L.; Vojtová, L.; Mravcová, L.; Hermanová, S.; Kučerík, J.; Jančář, J. Functionalization conditions of plga-peg-plga copolymer with itaconic anhydride. Macromol. Symp. 2010, 295, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michlovská, L.; Vojtová, L.; Humpac, O.; Kučeríkd, J.; Žídeka, J.; Jančářab, J. Hydrolytic stability of end-linked hydrogels from PLGA–PEG–PLGA macromonomers terminated by α,ω-itaconyl groups. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 16808–16816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oborná, J.; Mravcová, L.; Michlovská, L.; Vojtová, L.; Vávrová, M. The effect of PLGA-PEG-PLGA modification on the sol-gel transition and degradation properties. Express Polym. Lett. 2016, 10, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Ding, J.D. Synthesis of a chemically-crosslinked thermo-sensitive hydrogel film and in situ encapsulation of model protein drugs. React. Funct. Polym. 2006, 66, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.; Wu, D.Q.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Huang, F.W.; Cheng, S.X.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhuo, R.X. Peptide-functionalized thermo-sensitive hydrogels for sustained drug delivery. Macromol. Biosci. 2009, 9, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Dong, J.H.; Qiu, K.Y. Synthesis and characterization of poly (styrene co maleic anhydride) titania hybrid materials by the in-situ sol-gel process. Acta Polym. Sin. 1998, 3, 344–349. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Hao, J. Sol stability of crystalline thermogelling poly(ε-caprolactone-co-p-dioxanone)–poly(ethylene glycol)–poly(ε-caprolactone-co-p-dioxanone) copolymers. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrisdis, P.; Holzwarth, J.F.; Hatton, T.A. Micellization of Poly(ethy1ene oxide)-Poly(propy1ene oxide)-Poly(ethy1ene oxide) triblock copolymers in aqueous solutions: Thermodynamics of copolymer association. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 2414–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, C.; Attwood, D. Effects of block architecture and composition on the association properties of poly(oxyalkylene) copolymers in aqueous solution. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2000, 21, 501–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.J.; Suh, J.M.; Sohn, Y.S.; Bae, Y.H.; Kim, S.W.; Jeong, B. Thermogelling Poly (caprolactone-b-ethylene glycol-b-caprolactone) aqueous solutions. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 5260–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Q.; Den, X.M.; Hao, J.Y. Thermogelling Hydrogels of Poly(e-caprolactone-co-D,Llactide)–Poly(ethylene glycol)–Poly(e-caprolactone-co-D,Llactide) and Poly(e-caprolactone-co-L-lactide)–Poly(ethylene glycol)–Poly(e-caprolactone-co-L-lactide) aqueous solutions. Polymer 2007, 48, 4786–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, M.H.; Lim, J.L.; Ko, J.Y.; Park, S.H.; Kim, J.E.; Cho, H.J.; Park, E.S.; Kim, D.D. A new injectable liquid crystal system for one-month delivery of leuprolide. J. Control. Release 2014, 185, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, Z.-K.; Chen, R.; Zhu, H.-Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hao, J.-Y. Carboxylic Terminated Thermo-Responsive Copolymer Hydrogel and Improvement in Peptide Release Profile. Materials 2018, 11, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11030338
Rao Z-K, Chen R, Zhu H-Y, Li Y, Liu Y, Hao J-Y. Carboxylic Terminated Thermo-Responsive Copolymer Hydrogel and Improvement in Peptide Release Profile. Materials. 2018; 11(3):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11030338
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, Zi-Kun, Rui Chen, Hong-Yu Zhu, Yang Li, Yu Liu, and Jian-Yuan Hao. 2018. "Carboxylic Terminated Thermo-Responsive Copolymer Hydrogel and Improvement in Peptide Release Profile" Materials 11, no. 3: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11030338
APA StyleRao, Z.-K., Chen, R., Zhu, H.-Y., Li, Y., Liu, Y., & Hao, J.-Y. (2018). Carboxylic Terminated Thermo-Responsive Copolymer Hydrogel and Improvement in Peptide Release Profile. Materials, 11(3), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11030338