Tribological Behavior of Copper–Graphite Composites Reinforced with Cu-Coated or Uncoated SiO2 Particles
Abstract
1. Introduction
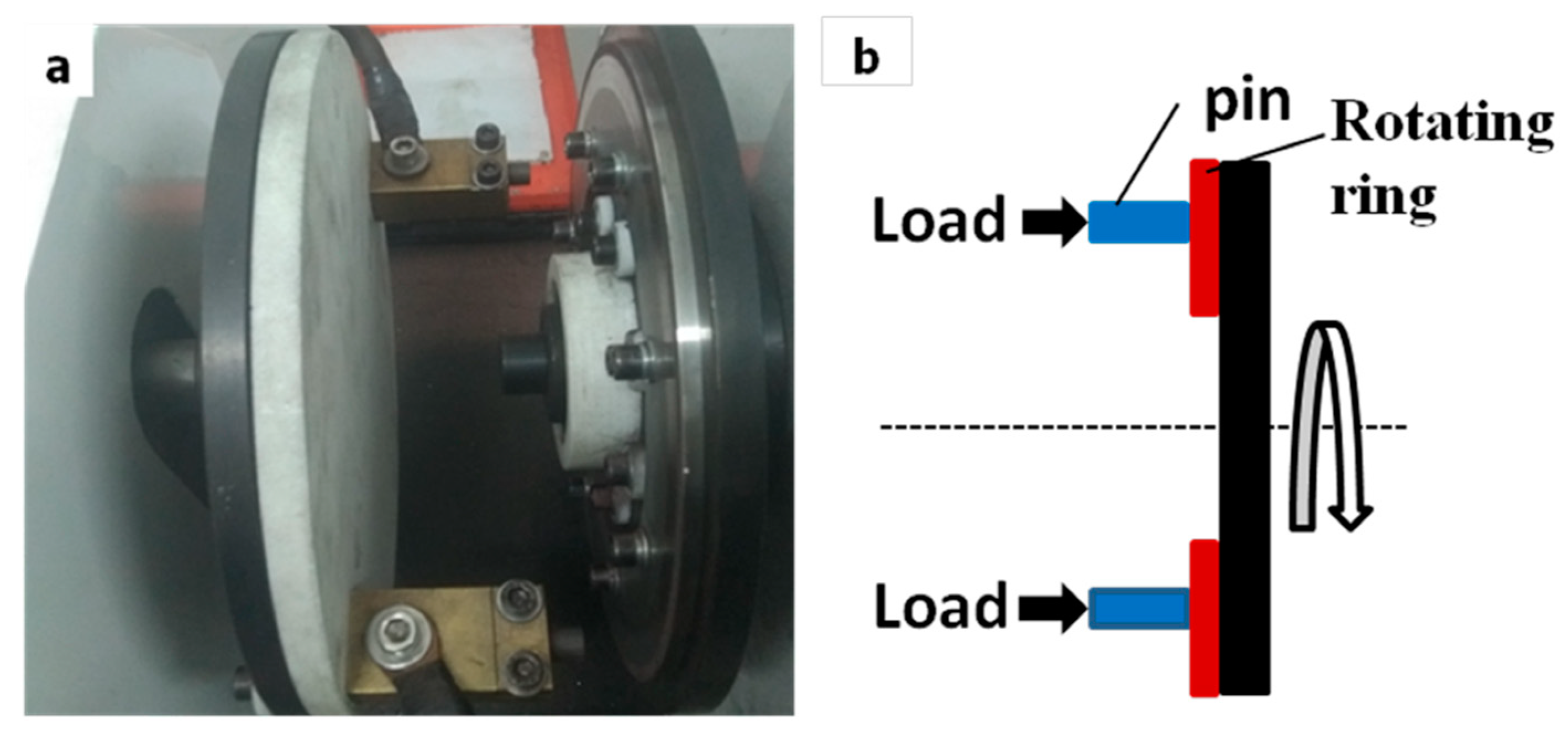
2. Experimental
3. Results
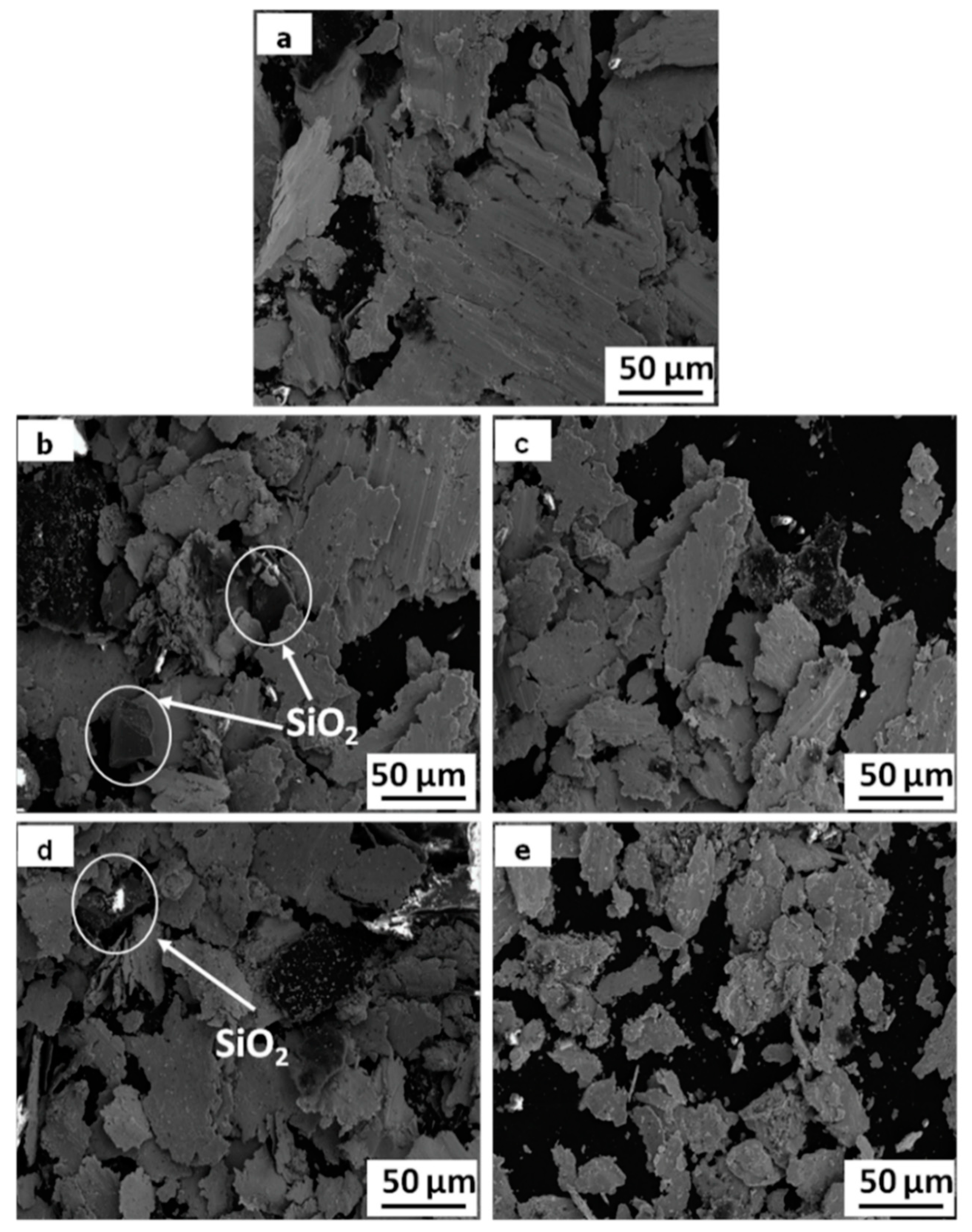
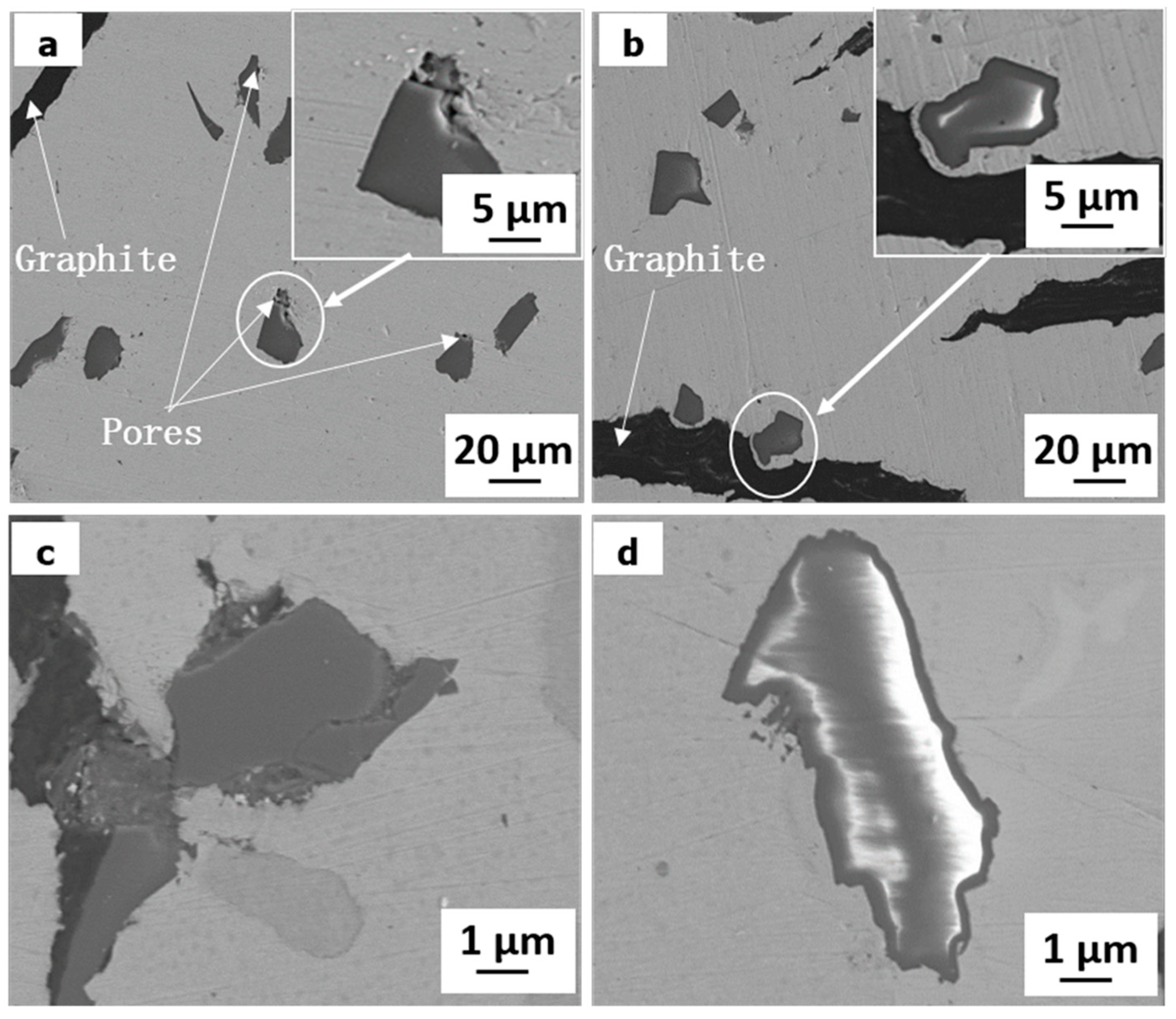
3.1. Microstructure, Density, and Hardness of Composites
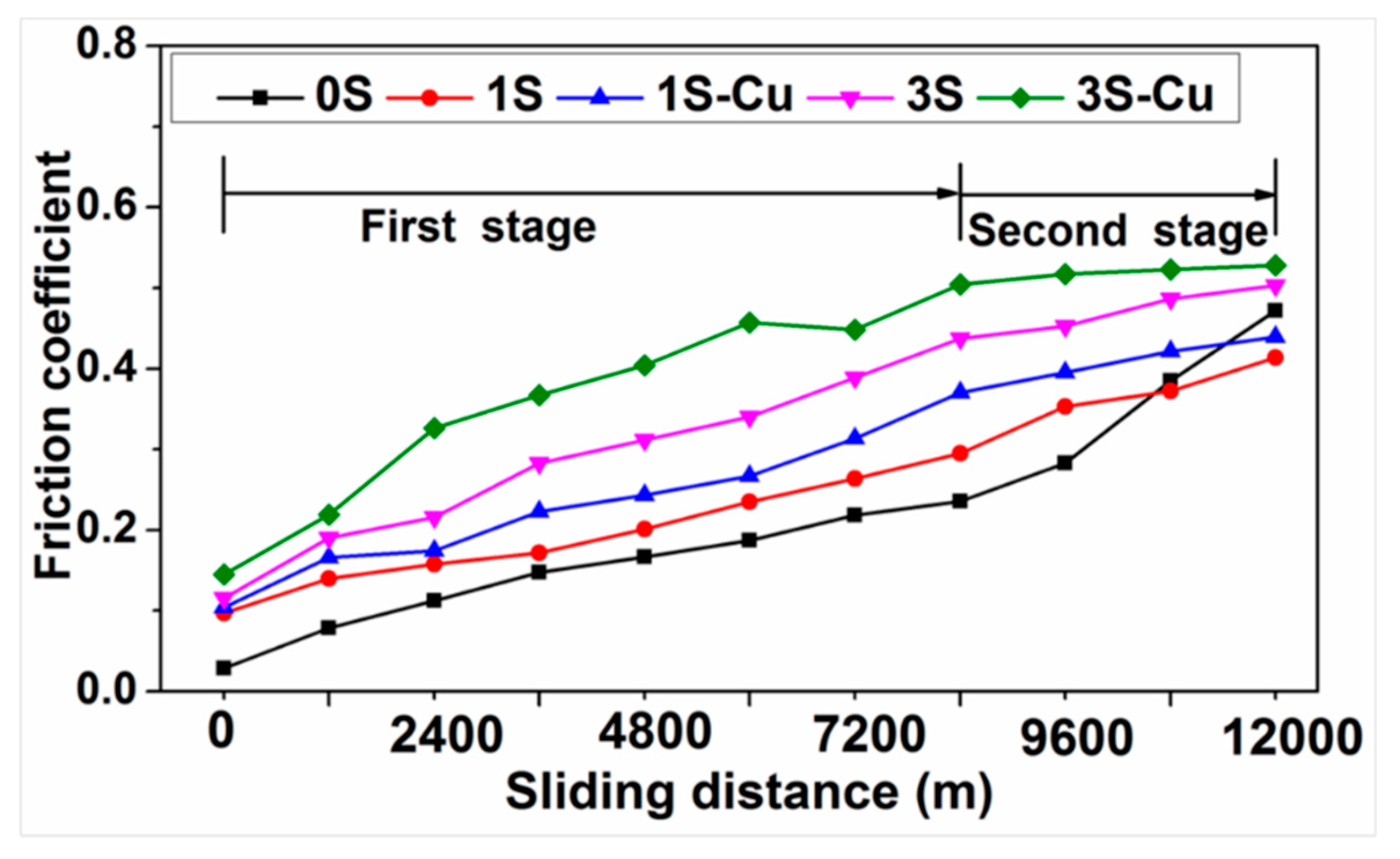
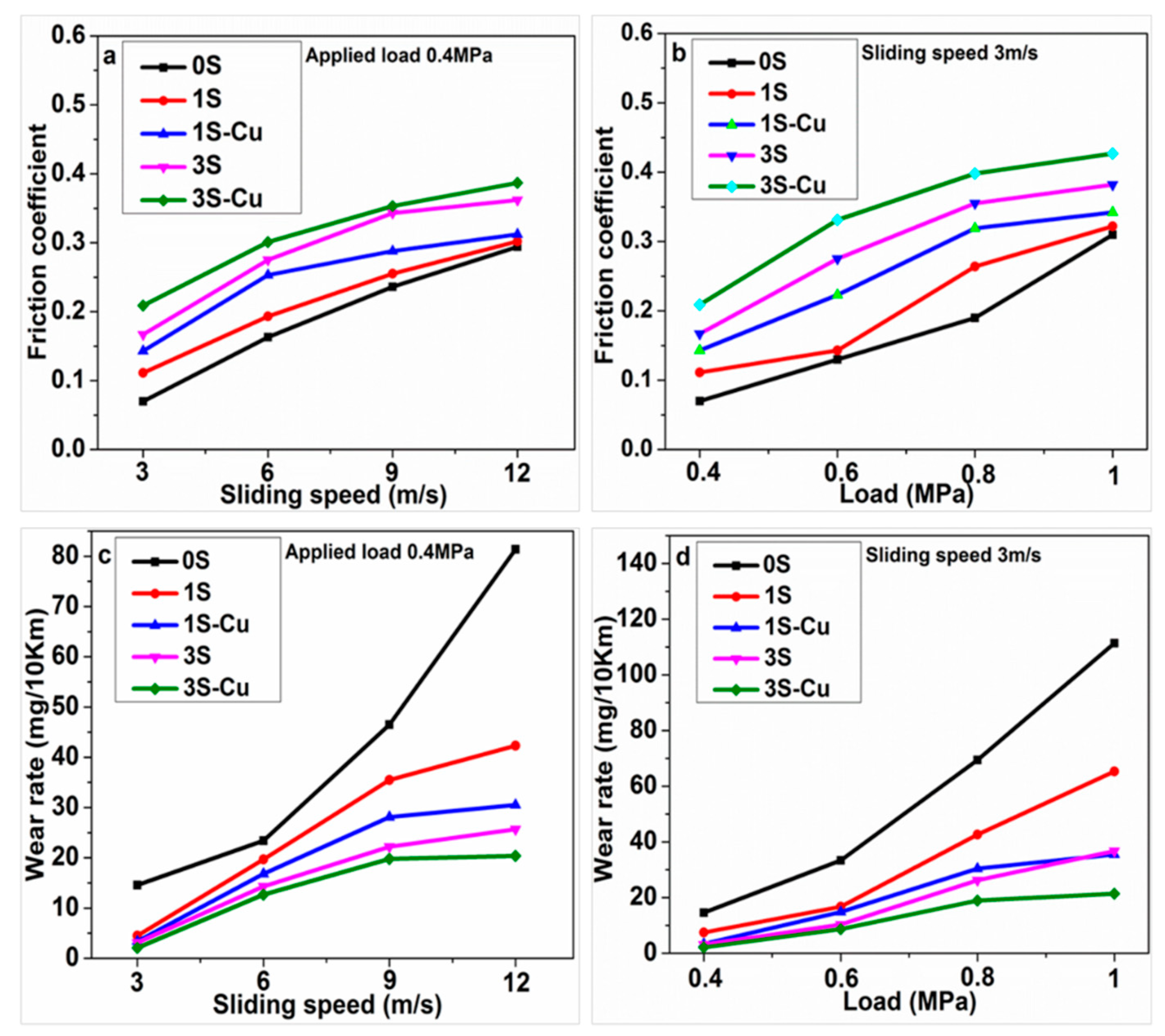
3.2. Friction and Wear Characteristics
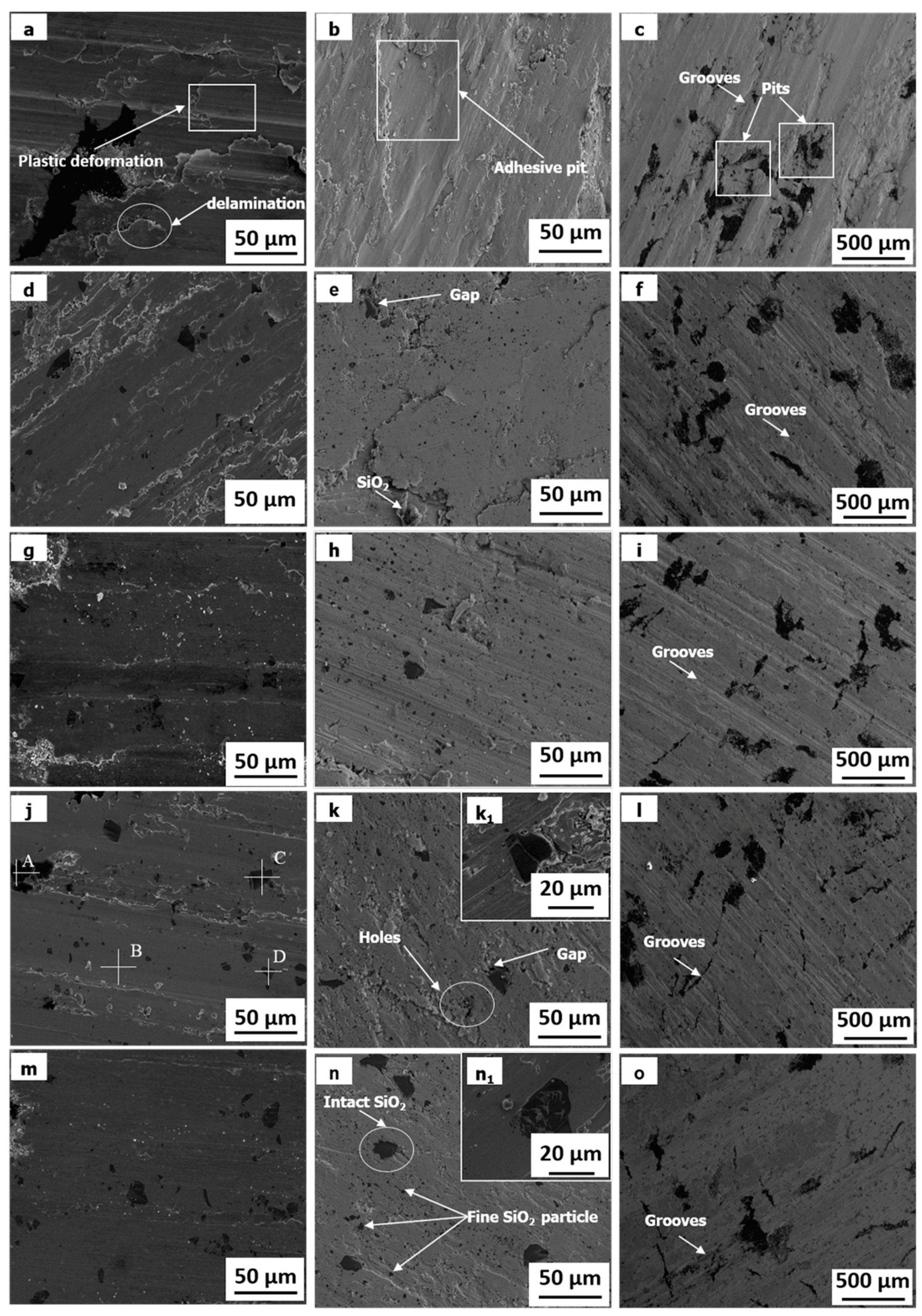
3.3. Worn Surface and Wear Debris
4. Discussions
4.1. Effect of SiO2
4.2. Effect of Cu Coating
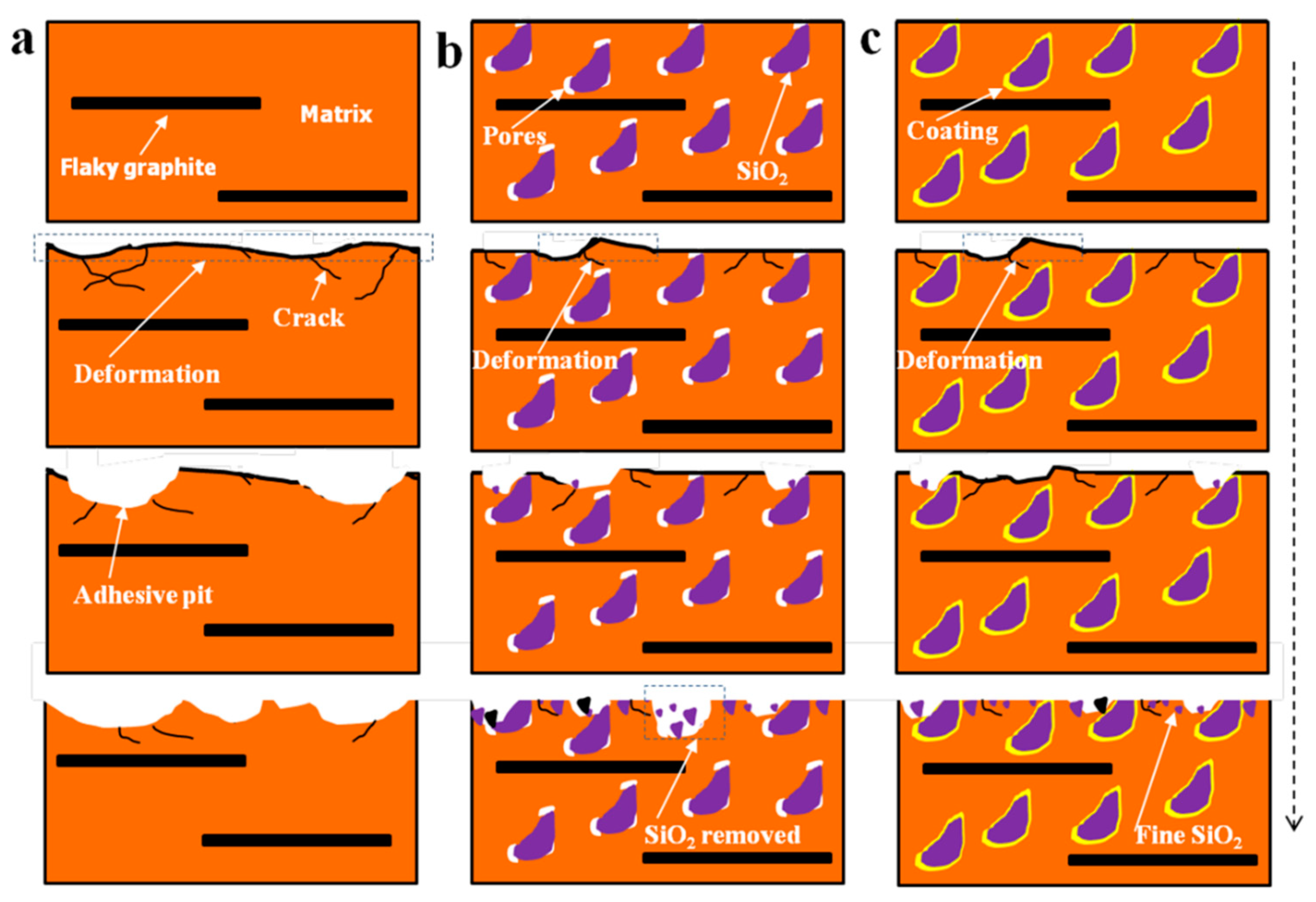
4.3. Wear Process
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The hardness of the composites increases with the increase of SiO2 content. However, the poor interfacial bonding between SiO2 particles and Cu matrix, result in the relative density decreased with the increase of SiO2 particles for uncoated SiO2 particles reinforced composites. Electroless copper coating is helpful to increase the relative density of composites by improve the interfacial bonding between SiO2 particles and copper matrix.
- (2)
- The addition of SiO2 lead to increasing of friction stability, friction coefficient, and decreasing of wear rate. This should be attributed to the hard SiO2 can restrict the severe plastic deformation and adhesion contact in the process of wear.
- (3)
- The electroless copper plating improve the interfacial bonding between SiO2 and copper matrix, which helps to prevent SiO2 pull out from copper matrix and further increase tribological properties of the composites.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, P.; Sheng, H.; Xiong, X.; Huang, X.B. Worn surface characteristics of Cu-based powder metallurgy bake materials for aircraft. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2007, 17, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilardi, R.; Alzati, L.; Thiam, M.; Brunel, J.F.; Desplanques, Y.; Dufrenoy, P.; Sharma, S.; Bijwe, J. Copper substitution and noise reduction in brake pads: Graphite type selection. Materials 2012, 5, 2258–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y. High-speed sliding characteristics of Cu–Sn-based composite materials containing lamellar solid lubricants by contact resistance studies. Wear 2008, 264, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, P.; Fan, K.; Zhou, H.; Gong, T.; Zhao, L.; Deng, M. Mechanical and tribological behaviors of copper metal matrix composites for brake pads used in high-speed trains. Tribol. Int. 2018, 119, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Luo, R.; Han, S.; Li, M. Effect of the ratio of graphite/pitch coke on the mechanical and tribological of copper–carbon composites. Wear 2010, 268, 1337–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Zhang, G. The role of graphite particles in the high-temperature wear of copper hybrid composites against steel. Mater. Des. 2006, 27, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Mondal, S. Microstructure and properties of graphite-reinforced copper matrix composites. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, T.R. Effects of solid lubricants, load, and sliding speed on the tribological behavior of silica reinforced composites using design of experiments. Mater. Des. 2015, 77, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ren, S.; He, X.; Qu, X. Properties and microstructure of nickel-coated graphite flakes/copper composites fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Carbon 2017, 121, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.J.; Liu, K.; Yang, Q.Z.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Fu, Q.; Han, Z.H.; Bai, Y. The influence of size and distribution of graphite on the friction and wear behavior of Ni–graphite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 252, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaghi, F.; Zare-Bidaki, A. Influence of graphite content on the dry sliding and oil impregnated sliding wear behavior of Al 2024-graphite composites produced by in situ powder metallurgy method. Wear 2009, 266, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestursatya, M.; Kim, J.K.; Rohatgi, P.K. Wear performance of copper–graphite composite and leaded copper alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 339, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavarajappa, S.; Chandramohan, G.; Mahadevan, A.; Thangavelu, M.; Subramanian, R.; Gopalakrishnan, P. Influence of sliding speed on the dry sliding wear behaviour and the subsurface deformation on hybrid metal matrix composite. Wear 2007, 262, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.B.; Lin, C.B.; Wang, T.C.; Chu, H.Y. The tribological characteristics of A356.2Al alloy/Gr(p) composites. Wear 2004, 257, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, S.F.; Abdel-Hamid, Z.; Abd-Elhay, A.M. Copper matrix SiC and Al2O3 particulate composites by powder metallurgy technique. Mater. Lett. 2002, 53, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.J.; Wexler, D.; Calka, A. Mechanochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline Al2O3 dispersed copper. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 4659–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkovic, V.; Bozic, D.; Jovanovic, M.T. Properties of copper matrix reinforced with various size and amount of Al2O3 particles. J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 2008, 200, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, K.; Aravindan, S. Tribological performance of microwave sintered copper–TiC–graphite hybrid composites. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemanth, J. Quartz (SiO2p) reinforced chilled metal matrix composite (CMMC) for automotive applications. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seah, K.H.W.; Hemanth, J.; Sharma, S.C. Mechanical properties of aluminum/quartz particulate composites cast using metallic and non-metallic chills. Mater. Des. 2003, 24, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.; Sayuti, M.; Samin, R. Mechanical properties of the as-cast quartz particulate reinforced LM6 alloy matrix composites. J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 2008, 21, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, T.R.; Varma, V.K.; Vedantam, S. Effect of reinforcement type, size, and volume fraction on the tribological behavior of Fe matrix composites at high sliding speed conditions. Wear 2014, 309, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohatgi, P.K.; Schultz, B.F.; Daoud, A.; Zhang, W.W. Tribological performance of A206 aluminum alloy containing silica sand particles. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, K.A.; Abdel-Karim, R.; Farag, S.; El-Raghy, S.M.; Ahmed, H.A. Influence of SiC, SiO2 and graphite on corrosive wear of bronze composites subjected to acid rain. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosroshahi, N.B.; Mousavian, R.T.; Khosroshahi, R.A.; Brabazon, D. Mechanical properties of rolled A356 based composites reinforced by Cu-coated bimodal ceramic particles. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhika, N.; Ramprasad, R.; Nivethan, S. Experimental investigation on adhesive wear behavior of Al–Si6Cu/Ni Coated SiC composite under unlubricated condition. Trans. Indian. Inst. Met. 2018, 71, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.L.; Lee, S.L.; Chuang, C.L.; Lin, J.C. Effects of SiCp reinforcement by electroless copper plating on properties of Cu/SiCp composites. Powder Metall. 1999, 42, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alidokht, S.A.; Abdollah-zadeh, A.; Assadi, H. Effect of applied load on the dry sliding wear behavior and the subsurface deformation on hybrid metal matrix composites. Wear 2013, 305, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, C.; Pascual, M.; Busquets, D.; Rayon, E. Tribological study of Fe-Cu-Cr-graphite alloy and cast iron railway brake shoes by pin-on-disc technique. Wear 2010, 268, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekaran, S.; Gnanamoorthy, R. Dry sliding friction and wear characteristics of Fe-C-Cu alloy containing molybdenum di sulphide. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalchenko, A.M.; Fushchich, O.I.; Danyluk, S. The tribological properties and mechanism of wear of Cu-based sintered powder materials containing molybdenum disulfide and molybdenum diselenite under unbricated sliding against copper. Wear 2012, 30, 106–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Lu, J. Effect of sliding speed on surface modification and tribological behavior of copper–graphite composite. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 41, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yin, B.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, S.; Qiao, Z. The tribological properties and wear mechanism of copper coated graphite doped sialon ceramic composites at wide range temperature from 25 to 800 °C. Tribol. Int. 2018, 123, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J.F. Contact and rubbing of flat surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1953, 24, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, J.Q.; Yang, J.; Bi, Q.; Fu, L.; Liu, W. Dry-sliding tribological properties of a nano-eutectic Fe1.87C0.13 alloy. Wear 2010, 268, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpas, A.T.; Embury, J.D. Sliding and abrasive wear behavior of an aluminum (2014)-SiC particle reinforced composite. Scripta. Metall. Mater. 1990, 24, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Wu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Lin, H. The effects of nano-SiO2 additive on the zinc phosphating of carbon steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 3455–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chang, L.; Schlarb, A.K. The roles of nano-SiO2 particles on the tribological behavior of short carbon fiber reinforced PEEK. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CuSO4·5H2O | EDTA·2Na | KNaC4H6O6 | HCHO (Solution) | NaOH | Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 g/L | 25 g/L | 20 g/L | 14 mL/L | 14 g/L | 40 °C |
| Sample | Copper (mass %) | Flaky Graphite (mass %) | Silica (mass %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0S | 97 | 3 | 0 |
| 1S | 96 | 3 | 1 |
| 3S | 94 | 3 | 3 |
| 1S-Cu | 95.4 | 3 | 1 + 0.6 (weight of coating) |
| 3S-Cu | 92.2 | 3 | 3 + 1.8 (weight of coating) |
| Sample | Relative Density | Brinell Hardness (HBW) |
|---|---|---|
| 0S | 93.50% | 39.8 ± 0.5 |
| 1S | 92.55% | 40.6 ± 0.9 |
| 3S | 91.76% | 41.4 ± 1.1 |
| 1S-Cu | 93.10% | 41.2 ± 0.6 |
| 3S-Cu | 93.03% | 43.7 ± 1.0 |
| Point | Si | O | Cu | C | Possible Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | - | 0.8 | 10.3 | 88.9 | Graphite |
| B | - | 8.1 | 90.7 | 1.2 | Cu matrix |
| C | 30.3 | 63.2 | 6.2 | 0.3 | SiO2 |
| D | 29.6 | 61.5 | 8.5 | 0.4 | SiO2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, H.; Ran, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, S.; Hao, Z. Tribological Behavior of Copper–Graphite Composites Reinforced with Cu-Coated or Uncoated SiO2 Particles. Materials 2018, 11, 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122414
Zou H, Ran X, Zhu W, Wang Y, Zhan S, Hao Z. Tribological Behavior of Copper–Graphite Composites Reinforced with Cu-Coated or Uncoated SiO2 Particles. Materials. 2018; 11(12):2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122414
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Haohao, Xu Ran, Weiwei Zhu, Yong Wang, Siqi Zhan, and Zhikang Hao. 2018. "Tribological Behavior of Copper–Graphite Composites Reinforced with Cu-Coated or Uncoated SiO2 Particles" Materials 11, no. 12: 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122414
APA StyleZou, H., Ran, X., Zhu, W., Wang, Y., Zhan, S., & Hao, Z. (2018). Tribological Behavior of Copper–Graphite Composites Reinforced with Cu-Coated or Uncoated SiO2 Particles. Materials, 11(12), 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122414





