Experimental Investigation and Thermodynamic Calculation of Ni–Al–La Ternary System in Nickel-Rich Region: A New Intermetallic Compound Ni2AlLa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
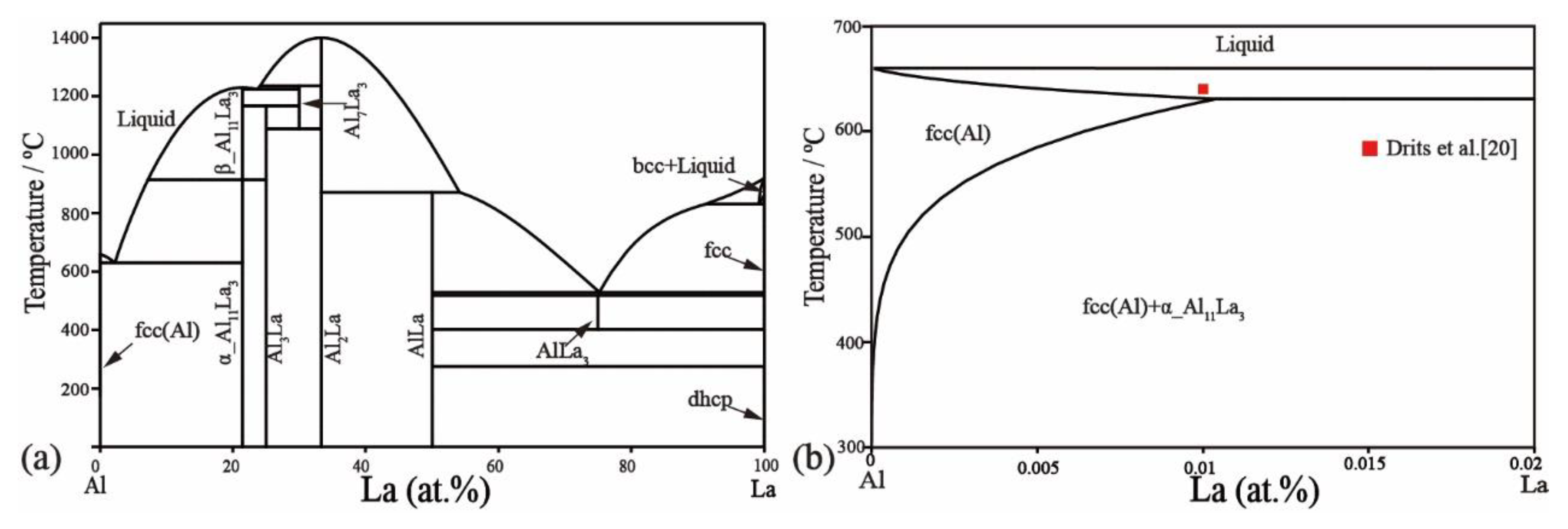
2.1. Al–La Binary System
2.2. Ni–La Binary System
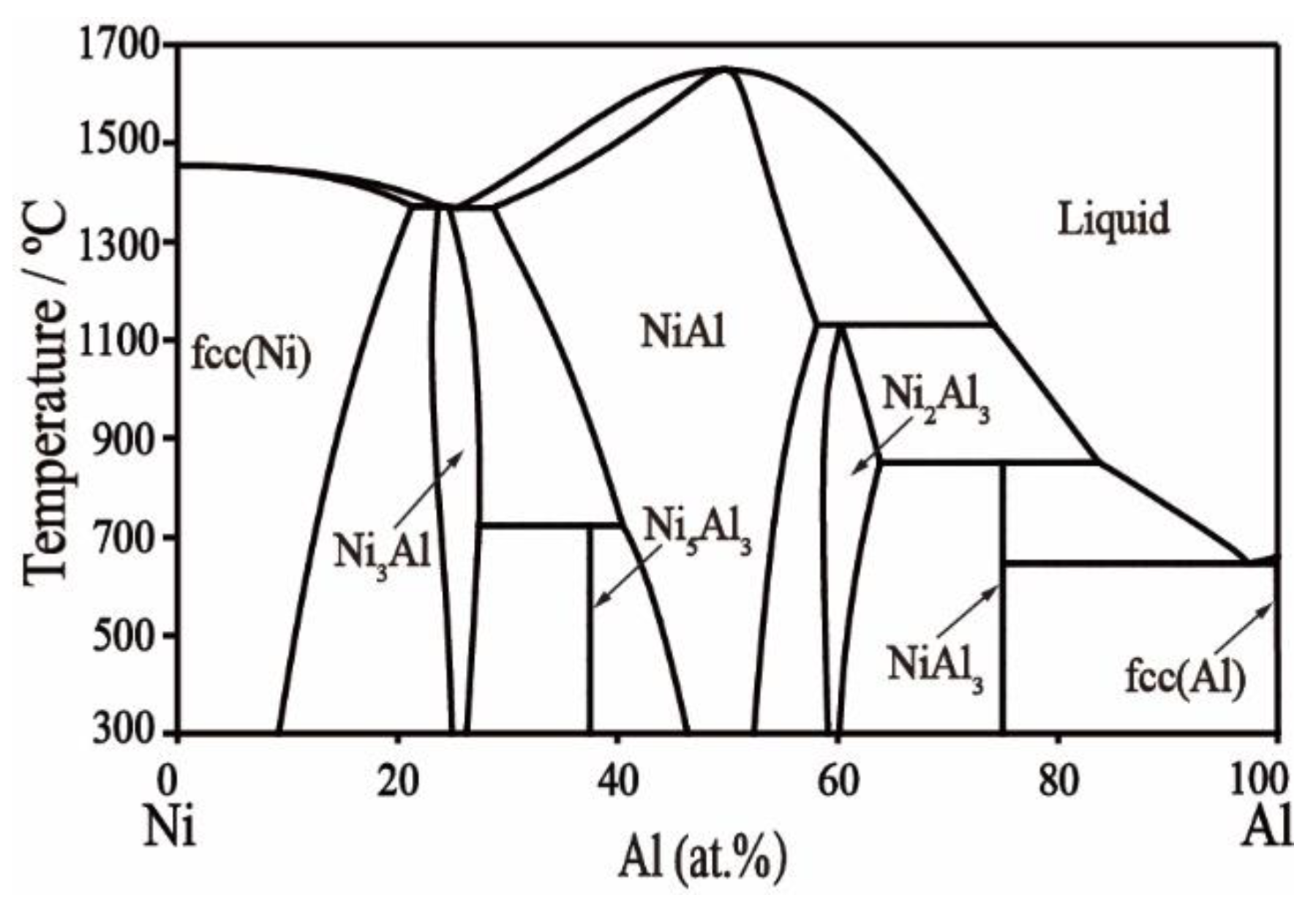
2.3. Ni–Al Binary System
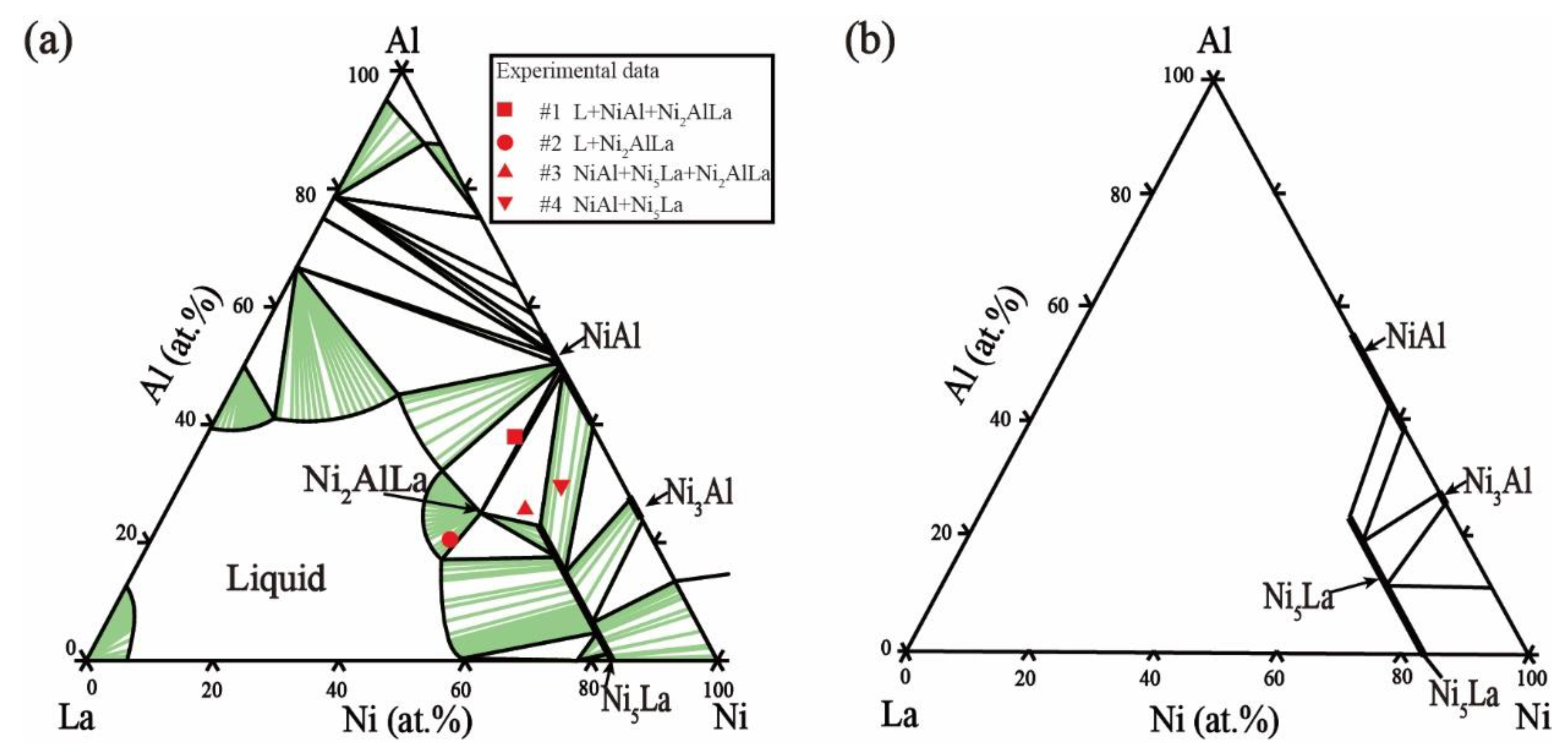
2.4. Ni–Al–La Ternary System
3. Materials and Methods
4. Calculations
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Microstructure and Phase Equilibria
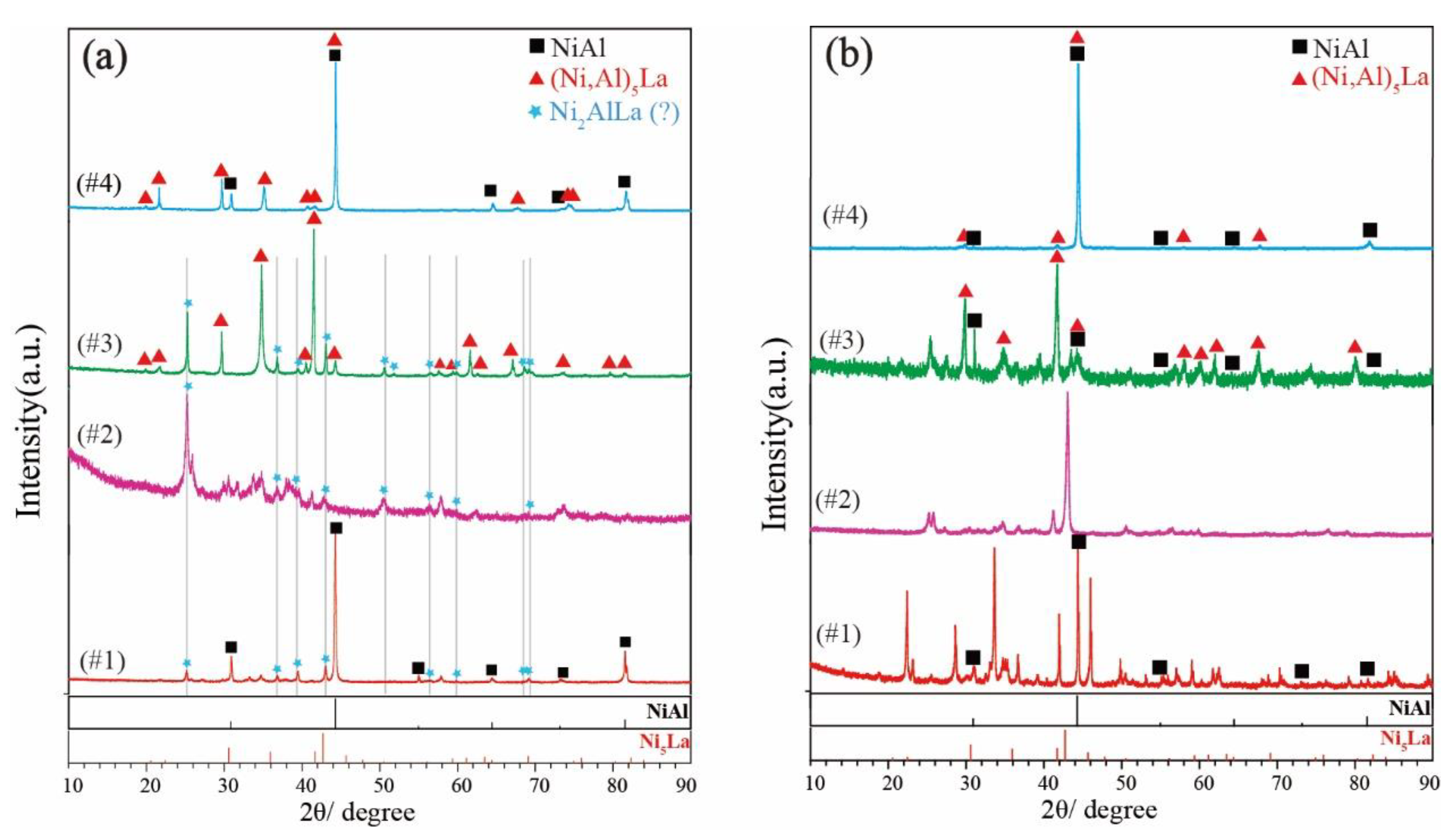
5.2. Phase Determination
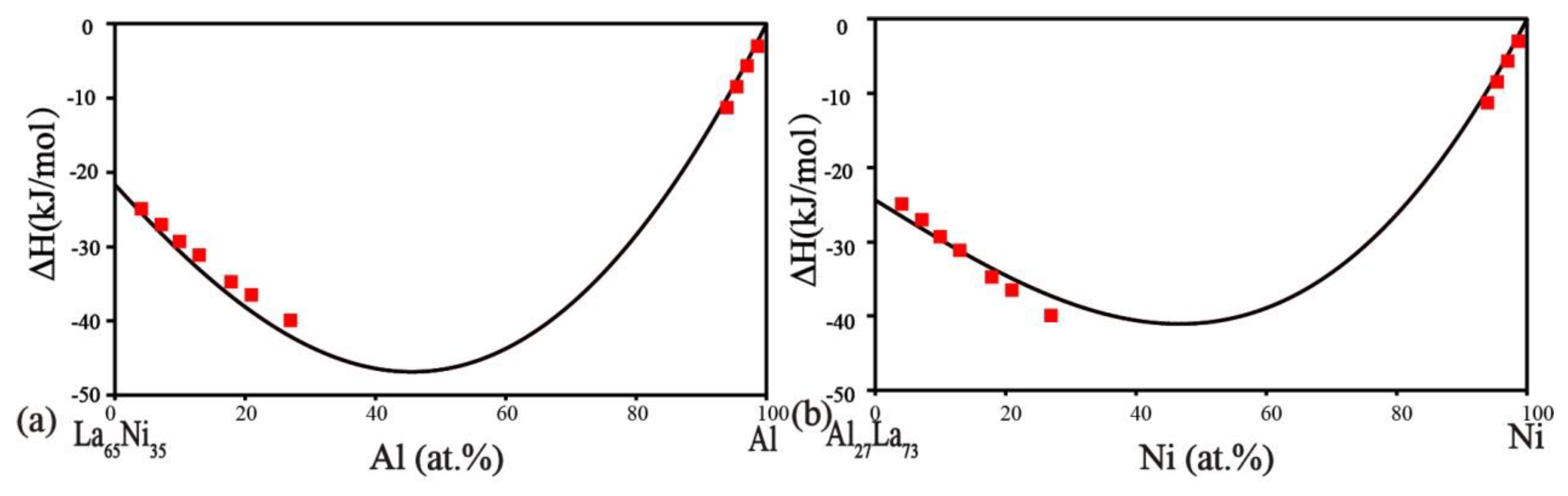
5.3. Thermodynamic Calculation
6. Conclusions
- The nickel-rich-region isothermal sections of the Ni–Al–La ternary system were updated at 800 °C and 1000 °C. The maximum solubility of Al in Ni5La was in the order of 23.53 at.% at 800 °C. When the temperature increased to 1000 °C, the maximum solubility of Al in Ni5La was 19.84 at.%.
- A new phase, termed Ni2AlLa, has been discovered experimentally and confirmed for the first time. The structural information of the new ternary intermetallic compound Ni2AlLa was determined. The investigated compound crystallizes in the trigonal system, space group R3 (no. 146) with a = 4.1985 Å, c = 13.6626 Å.
- Based on the current experimental data and experimental information reported in the literature, a thermodynamic optimization of the Ni–Al–La ternary system was carried out using the CALPHAD method. The solubility of La in the fcc (Ni) and fcc (Al) and an allotropic transformation of the Al11La3 phase were considered, and the Al–La and Ni–La binary systems were re-optimized. All optimized results and experimental information reflect good consistency. This work can be used as part of a thermodynamic database of multicomponent nickel-based alloys.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reed, R.C. The Superalloys: Fundamentals and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Caron, P.; Lavigne, O. Recent studies at onera on superalloys for single crystal turbine blades. Onera Aerosp. Lab. J. 2011, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, F.W.; Zhang, G.Q.; Sun, J.F.; Li, Z. Hot deformation behavior of a spray formed superalloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 204, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, T.M.; Tin, S. Nickel-based superalloys for advanced turbine engines: Chemistry, microstructure and properties. J. Propuls. Power 2006, 22, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, D.A.; Fullagar, K.P.L.; Bhangu, H.K.; Thomas, M.C.; Burkholder, P.S.; Korinko, P.S.; Harris, K.; Wahl, J.B. Improved performance rhenium containing single crystal alloy turbine blades utilizing PPM levels of the highly reactive elements lanthanum and yttrium. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 1999, 121, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. Effects of temperature and rare earth content on oxidation resistance of Ni-based superalloy. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2011, 21, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.; Wahl, J.B. Improved single crystal superalloys, CMSX-4(SLS)[La + Y] and CMSX-486. Superalloys 2004, 2004, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, H.T.; Edmonds, I.M.; Jones, C.N.; Stone, H.J.; Rae, C.M.F. Effects of Y and La additions on the processing and properties of a second generation single crystal Nickel-base superalloy CMSX-4. Superalloys 2012, 2012, 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Hoglund, Z.L.; Larsson, H.; Reed, R.C. Isolation of Optimal Compositions of Single Crystal Superalloys by Mapping of a Material’s Genome. Acta Mater. 2015, 90, 330–343. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, R.C.; Tao, T.; Warnken, N. Alloys-by-Design: Application to Nickel-Based Single Crystal Superalloys. Acta Mater 2009, 57, 5898–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, H.; Fries, S.G.; Sundman, B. Computation Thermodynamics—The Calphad Method; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rettig, R.; Singer, R.F. Numerical modelling of precipitation of topologically close-packed phases in nickel-base superalloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthod, P.; Michon, S.; Martino, J.D. Thermodynamic calculations for studying high temperature oxidation of superalloys. Calphad 2003, 27, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compu-Therm LLC, PanNickel Database. Available online: www.computherm.com (accessed on 27 November 2018).
- Abramyan, A.K. Study of Interactions in the Nickel-rich Phases of the Aluminum-Lanthanum-Nickel system. VINITI 1979, 3782, 212–214. [Google Scholar]
- Buschow, K.H.J. The lanthanum-aluminium system. Philips. Res. Rep. 1965, 20, 337–348. [Google Scholar]
- Mesquita, A.H.G.D.; Buschow, K.H.J. The crystal structure of so-called α-LaAl4 (La3Al11). Acta Cryst. 1967, 22, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononenko, V.I.; Golubev, S.V. On phase diagrams for binary systems of aluminium with La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Eu, Yb, Sc and Y. Izvestiya Akademii Nauk SSSR Metally 1990, 19, 197–199. [Google Scholar]
- Ferro, R.; Saccone, A.; Delfino, S.; Cardinale, A.M.; Macciò, D. Inverse melting in binary systems: Morphology and microscopy of catatectic alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1996, 27, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drits, M.E.; Kadaner, Z.S.; Nguyen, T.S. Solubility of Rare Earth Metals in Solid Stte Aluminium. Izvestiya Akademii Nauk SSSR Metally 1969, 1, 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Thermodynamic Optimization for Al-La System. Calphad 1994, 18, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Su, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, M.; Shi, Y. A thermodynamic assessment of the La-Al system. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 1, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciamani, G.; Ferro, R. Thermodynamic modeling of Some aluminium-rare earth binary systems: Al-La, Al-Ce and Al-Nd. Calphad 2001, 25, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.H.; Napolitano, R.E. Phase equilibria and thermodynamic limits for partitionless crystallization in the Al–La binary system. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Kang, Y.B.; Chartrand, P.; Fuerst, C.D. Thermodynamic evaluation and optimization of Al-La, Al-Ce, Al-Pr, Al-Nd and Al-Sm systems using the modified quasichemical model for liquids. Calphad 2011, 35, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Tang, J.; Gschneidner, K.A. A redetermination of the LaNi phase diagram from LaNi to LaNi5 (50–83.3 at.% Ni). J. Less-Common Met. 1991, 169, 467–480. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, G.J.; Li, Z.Q.; Yazawa, A.; Itagaki, K. High-temperature phase-relations in Ni-La, Ni-Ce, Ni-Pr, Ni-Nd binary and ternary alloy systems. Mater. Trans. JIM 1989, 30, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.; Mal, H.H.V. Phase relations and hydrogen absorption in the lanthanum-nickel system. J. Less-Common Met. 1972, 29, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H. La-Ni (Lanthanum-Nickel). J. Phase Equilib. 1991, 12, 615–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.Y.; Nash, P. La-Ni (lanthanum-nickel). J. Phase Equilib. 2002, 23, 287–288. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, T.; Inui, H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Sato, K.; Fujitani, S.; Yonezu, I. Microstructures and hydrogen absorption/desorption properties of La-Ni alloys in the composition range of La 77.8∼83.2 at.% Ni. Acta Mater. 1997, 45, 5213–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Férey, A.; Cuevas, F.; Latroche, M.; Knosp, B.; Bernard, P. Elaboration and characterization of magnesium-substituted La5Ni19 hydride forming alloys as active materials for negative electrode in Ni-MH battery. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 1710–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inui, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Zhang, D.; Yamaguchi, M. Microstructures and defect structures in intermetallicbcompounds in the La-Ni alloy system. J. Alloys Compd. 1999, 293, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inui, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Zhang, D.; Yamaguchi, M. Characterization of stacking Faults on basal planes in intermetallic compounds La5Ni19 and La2Ni7. Intermetallics 2000, 8, 391–397. [Google Scholar]
- Dischinger, J.; Schaller, H.J. Constitution and thermodynamics of Ni-La alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 312, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.B.; Jin, Z.P. Thermodynamic reassessment of the La-Ni system. Zeitschrift Metallkunde 2000, 91, 739–743. [Google Scholar]
- An, X.H.; Gu, Q.F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Chen, S.L.; Yu, X.B.; Li, Q. Experimental investigation and thermodynamic reassessment of La-Ni and LaNi5-H systems. Calphad 2013, 40, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yang, B.; Chen, H. Thermodynamic optimisation of the Ni-Al-Y ternary System. J. Phase Equilib. Diff. 2015, 36, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Chang, Y.A. A Thermodynamic Analysis of the Ni-Al System. Intermetallics 1998, 6, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, R.; Zanicchi, G.; Marazza, R.; Petzow, G. Aluminium-Lanthanum-Nickel in Ternary Alloys: A Comprehensive Compendium of Evaluated Constitutional Data and Phase Diagrams; Petzow, G., Effenberg, G., Eds.; Wiley-VHC: Weinheim, Germany, 1993; Volume 6, pp. 318–327. [Google Scholar]
- Raghavan, V. Al-La-Ni (Aluminum-Lanthanum-Nickel). J. Phase Equilb. Diff. 2006, 27, 392. [Google Scholar]
- Gödecke, T.; Sun, W.; Lück, R.; Lu, K. Metastable Al-Nd-Ni and Stable Al-La-Ni Phase Equilibria. Zeitschrift Metallkunde 2001, 92, 717–722. [Google Scholar]
- Cordier, G.; Dörsam, G.; Kniep, R. New intermediate phases in the ternary systems rare earth-transition element-aluminium. J. Magn. Magn. Mat. 1988, 76, 653–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, T.; Malik, S.K.; Wallace, W.E. Hydrogen absorption in RNi4Al (R = Rare Earth) ternary compounds. J. Solid State, Chem. 1978, 23, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirklin, S.; Saal, J.E.; Meredig, B.; Thompson, A.; Doak, J.W.; Aykol, M.; Rühl, S.; Wolverton, C. The Open Quantum Materials Database (OQMD): Assessing the accuracy of DFT formation energies. NPJ Comput. Mater. 2015, 1, 15010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Ong, S.P.; Hautier, G.; Chen, W.; Richards, W.D.; Dacek, S.; Cholia, S.; Gunter, D.; Skinner, D.; Ceder, G.; et al. The Materials Project: A materials genome approach to accelerating materials innovation. APL Mater. 2013, 1, 011002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossett, E.; Toher, C.; Oses, C.; Isayev, O.; Legrain, F.; Rose, F.; Zurek, E.; Carrete, J.; Mingo, N.; Tropsha, A.; et al. AFLOW-ML: A RESTful API for machine-learning predictions of materials properties. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2017, 152, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feufel, H.; Schuller, F.; Schmid, J.; Sommer, F. Calorimetric study of ternary liquid Al-La-Ni alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 1997, 257, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, F.; Schmid, J.; Schuller, F. Temperature and concentration dependence of the enthalpy of formation of liquid Al-La-Ni Alloys. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1996, 205, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, J.; Sommer, F. Heat Capacity of Liquid Al-La-Ni Alloys. Thermochim. Acta 1998, 314, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasturel, A.; Chatillon-Colinet, C.; Guegan, A.P. Thermodynamic properties of LaNi4M compounds and their related hydrides. J. Less-Common Met. 1982, 84, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzone, G.; Raggio, R.; Delsante, S. Chemical and thermodynamic properties of several Al-Ni-R systems. Intermetallics 2003, 11, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheary, R.W.; Coelho, A.A. Fundamental parameters approach to X-ray line-profile fitting. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2010, 25, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, A.A. Indexing of powder diffraction patterns by iterative use of singular value decomposition. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Chen, S.L.; Zhang, F.; Wu, K.; Yang, Y.; Chang, Y.A. Pandat Software with PanEngine, PanOptimizer and PanPrecipitation for Multi-component Phase Diagram Calculation and Materials Property Simulation. Calphad 2009, 33, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinsdale, A.T. SGTE date for pure elements. Calphad 1991, 15, 317–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Crystal System | Space Group | Structure Type | Lattice Constants (Å) | Source | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | ||||
| Ni9Al2La | Cmmm | - | 8.599 | 5.040 | 8.062 | OQMD |
| F1 | - | 5.048 | 8.599 | 8.035 | Materials project | |
| Ni4AlLa | P6/mmm | CaCu5 | 5.069 | 5.069 | 4.074 | [51] |
| NiAlLa | Pnma | - | 7.199 | 4.203 | 16.085 | [52] |
| Ni2AlLa | Fm-3m | Cu2MnAl | 6.724 | 6.724 | 6.724 | OQMD |
| P4/mmm | - | 4.640 | 4.640 | 3.1615 | Aflow | |
| P4/mmm | - | 3.117 | 3.117 | 6.793 | Aflow | |
| P4/mmm | - | 3.074 | 3.074 | 6.900 | Aflow | |
| P4/mmm | - | 3.126 | 3.126 | 6.919 | Aflow | |
| Cm | - | 4.001 | 7.189 | 5.641 | Aflow | |
| Fm-3m | - | 6.536 | 6.536 | 6.536 | Aflow | |
| Pmm2 | - | 3.129 | 3.159 | 6.875 | Aflow | |
| F-43m | - | 6.591 | 6.591 | 6.591 | Aflow | |
| Cmmm | - | 6.574 | 6.596 | 3.141 | Aflow | |
| I-4m2 | - | 4.012 | 4.012 | 8.892 | Aflow | |
| Temperature | Alloys (at.%) | Annealed Time | Phase by XRD | Phase | Composition (at.%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| by SEM and EDS | Ni | Al | La | ||||
| 800 °C | Ni50Al35La15 (#1) | 30 days | NiAl + Ni2AlLa | NiAl | 49.68 | 50.28 | 0.05 |
| Ni2AlLa | 53.63 | 23.02 | 23.36 | ||||
| Liquid | 22.87 | 43.30 | 33.83 | ||||
| Ni50Al18La32 (#2) | 30 days | Ni2AlLa | Ni2AlLa | 53.47 | 23.74 | 22.79 | |
| Liquid | 50.04 | 6.61 | 43.38 | ||||
| Ni57Al23La20 (#3) | 30 days | Ni2AlLa + Ni5La | NiAl | 50.48 | 49.05 | 0.47 | |
| Ni2AlLa | 51.83 | 24.30 | 23.86 | ||||
| Ni5La | 60.77 | 23.53 | 15.37 | ||||
| Ni60Al30La10 (#4) | 30 days | NiAl + Ni5La | NiAl | 52.33 | 47.50 | 0.17 | |
| Ni5La | 63.35 | 21.71 | 14.94 | ||||
| 1000 °C | Ni50Al35La15 (#1) | 15 days | NiAl | NiAl | 51.35 | 48.65 | 0.00 |
| Liquid | 51.05 | 20.38 | 28.57 | ||||
| Ni50Al18La32 (#2) | 15 days | Liquid | 57.03 | 10.72 | 27.85 | ||
| Ni57Al23La20 (#3) | 15 days | NiAl + Ni5La | NiAl | 47.18 | 52.66 | 0.15 | |
| Ni5La | 65.09 | 19.78 | 15.13 | ||||
| Liquid | 55.29 | 17.89 | 26.82 | ||||
| Ni57Al23La20 (#4) | 15 days | NiAl + Ni5La | NiAl | 46.74 | 53.26 | 0.00 | |
| Ni5La | 66.95 | 17.95 | 15.09 | ||||
| Liquid | 55.29 | 17.75 | 26.96 | ||||
| Crystal System | Space Group | Lattice Constants (Å) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | ||
| Hexagonal/Trigonal | P3c1 | 10.740 | 10.740 | 3.367 |
| R3 | 4.189 | 4.189 | 14.663 | |
| P31c | 8.138 | 8.138 | 3.396 | |
| Orthorhombic | F222 | 9.739 | 10.130 | 2.195 |
| C222 | 3.263 | 2.733 | 7.021 | |
| Phase | Models | Parameters | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid | (Al,Ni,La) | This work | |
| This work | |||
| This work | |||
| fcc | (Al,Ni,La) | This work | |
| This work | |||
| This work | |||
| This work | |||
| bcc | (Al,Ni,La) | This work | |
| α_Al11La3 | (Al)11(La)3 | This work | |
| β_Al11La3 | (Al)11(La)3 | This work | |
| Ni5La | (La) (Al,Ni)5 | Ref [38] | |
| This work | |||
| This work | |||
| Ni2AlLa | (Ni)2(Al)(La) | = | This work |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, T.-Y. Experimental Investigation and Thermodynamic Calculation of Ni–Al–La Ternary System in Nickel-Rich Region: A New Intermetallic Compound Ni2AlLa. Materials 2018, 11, 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122396
Liao J, Wang H, Chen T-Y. Experimental Investigation and Thermodynamic Calculation of Ni–Al–La Ternary System in Nickel-Rich Region: A New Intermetallic Compound Ni2AlLa. Materials. 2018; 11(12):2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122396
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Jinfa, Hang Wang, and Tzu-Yu Chen. 2018. "Experimental Investigation and Thermodynamic Calculation of Ni–Al–La Ternary System in Nickel-Rich Region: A New Intermetallic Compound Ni2AlLa" Materials 11, no. 12: 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122396
APA StyleLiao, J., Wang, H., & Chen, T.-Y. (2018). Experimental Investigation and Thermodynamic Calculation of Ni–Al–La Ternary System in Nickel-Rich Region: A New Intermetallic Compound Ni2AlLa. Materials, 11(12), 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122396






