A Facile Way to Prolong Service Life of Double Base Propellant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Propellant Preparation
2.3. Characterization and Analysis
2.3.1. Mechanical Properties Test
2.3.2. SEM Measurement
2.3.3. Thermal Property
2.3.4. Crosslinking Density
3. Simulations
4. Results and Discussion
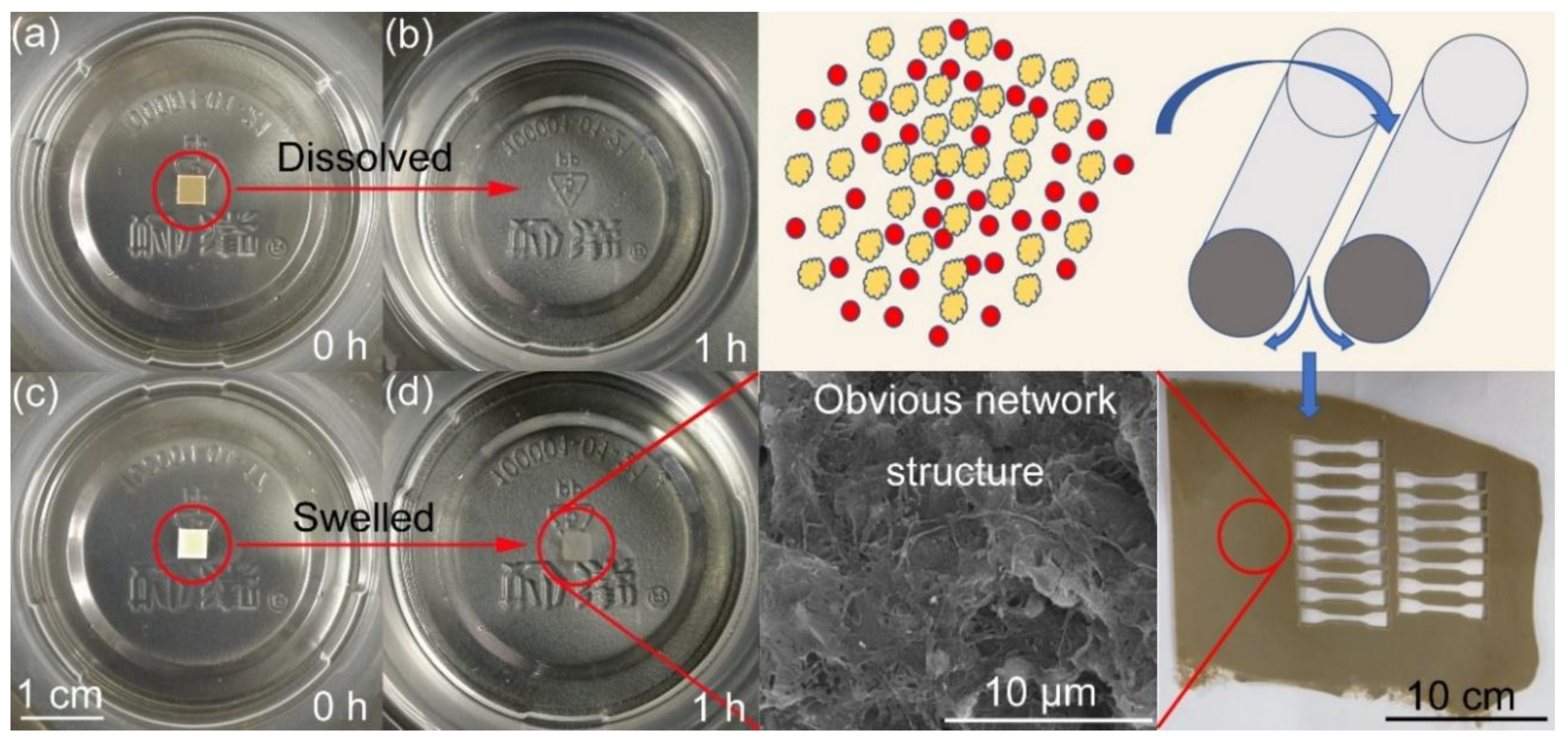
4.1. Morphology of PTFE in Propellant
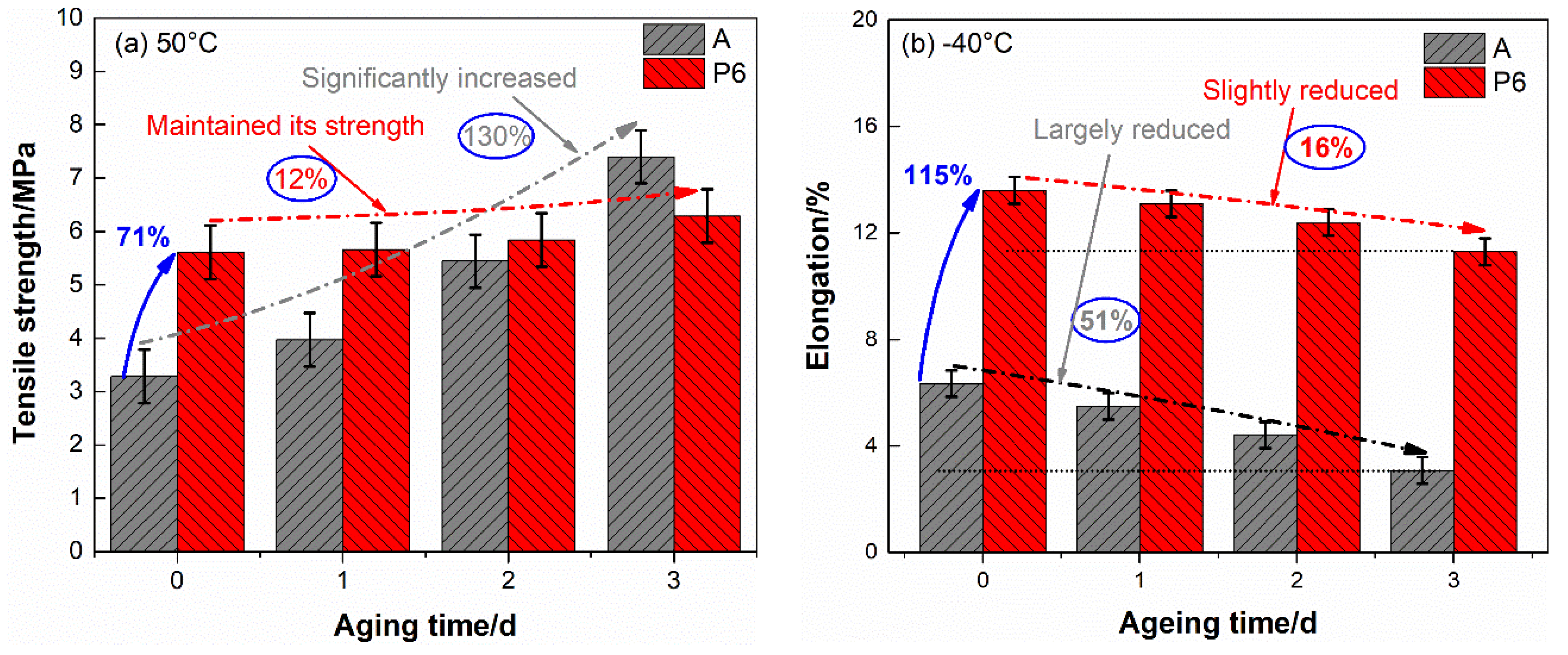
4.2. Tensile Properties of DB Propellants
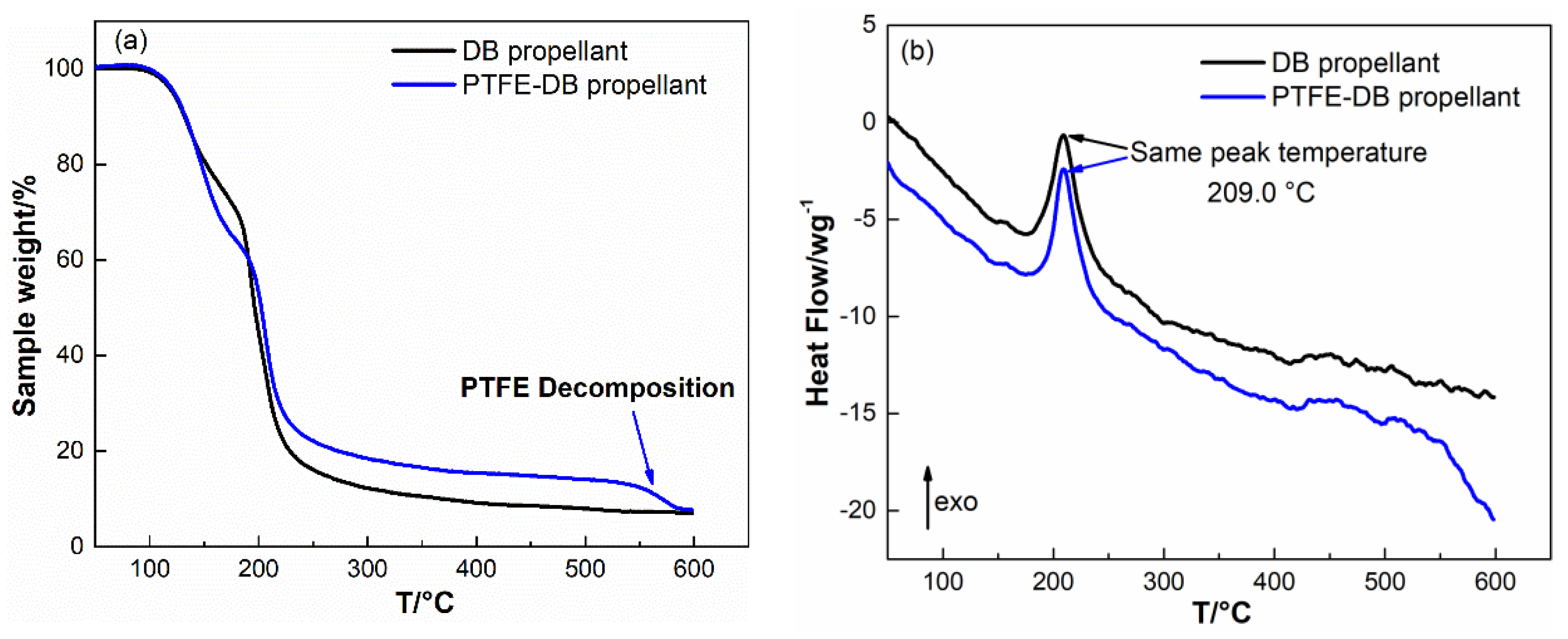
4.3. Thermal Properties of DB Propellants
4.4. Kinetics of NG Evaporation
4.5. Kinetics of NG Diffusion
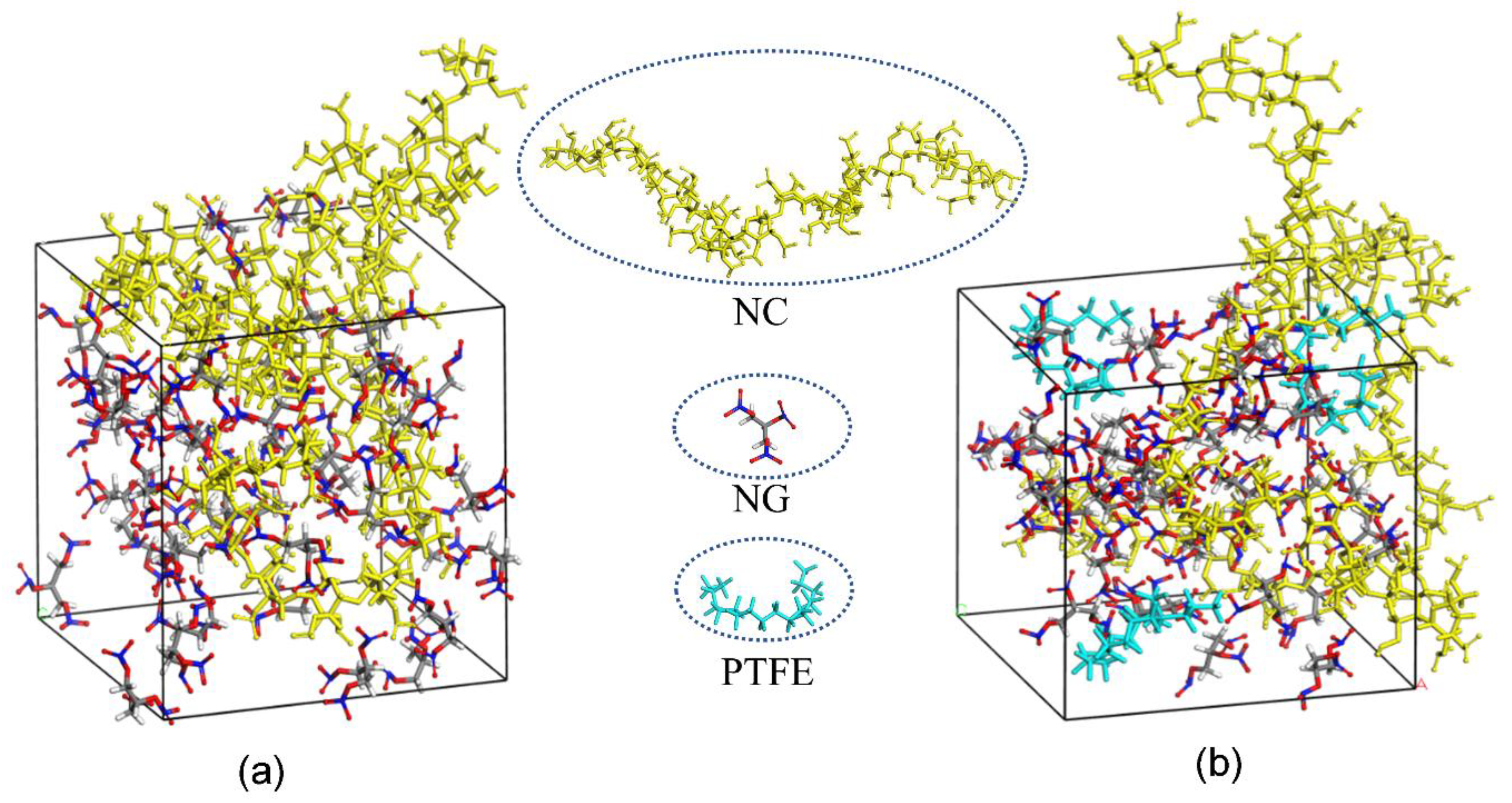
4.6. MD Simulation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, H.M. The Chemistry and Technology of Solid Rocket Propellant; Beijing Institute of Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 202–226. [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, N. Energetics of Propellants and Explosives; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2015; pp. 90–106. [Google Scholar]
- Zayed, M.A.; El-Begawy, S.E.M.; Hassan, H.E.S. Mechanism study of stabilization of double-base propellants by using zeolite stabilizers (nano- and micro-clinoptilolite). Arabian J. Chem. 2017, 10, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, M.A.; Hassan, M.A. Stability of non-isothermally treated double-base propellants containing different stabilizers in comparison with molecular orbital calculations. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2010, 35, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, M.A.; Mohamed, A.A.; Hassan, M.A.M. Stability studies of double-base propellants with centralite and malonanilide stabilizers using mo calculations in comparison to thermal studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trache, D.; Khimeche, K. Study on the influence of ageing on thermal decomposition of double-base propellants and prediction of their in-use time. Fire Mater. 2013, 37, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trache, D.; Khimeche, K. Study on the influence of ageing on chemical and mechanical properties of n,n′-dimethyl-n,n′-diphenylcarbamide stabilized propellants. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 111, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trache, D.; Tarchoun, A.F. Stabilizers for nitrate ester-based energetic materials and their mechanism of action: A state-of-the-art review. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 100–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, M.A. Prediction of life times of propellants-improved kinetic description of the stabilizer consumption. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 1994, 19, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, M.A. Kinetic modelling of the concentrations of the stabilizer dpa and some of its consecutive products as function of time and temperature. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2001, 65, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, M.A. Prediction of in-service time period of three differently stabilized single base propellants. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2009, 34, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, M.A.; Eisenreich, N. Kinetic modelling of the stabilizer consumption and of the consecutive products of the stabilizer in a gun propellant. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 1997, 22, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, M.A.; Volk, F. Aging behavior of propellants investigated by heat generation, stabilizer consumption, and molar mass degradation. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 1992, 17, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Heng, S.; Hu, R.; Gao, H.; Han, F. A study of kinetic behaviours of the effective centralite/stabilizer consumption reaction of propellants using a multi-temperature artificial accelerated ageing test. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 145, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asthana, S.N.; Divekar, C.N.; Khare, R.R.; Singh, H. Evaluation of various dihydric and trihydric phenols as stabilizers for composite modified double base (CMDB) propellants. J. Hazard. Mater. 1991, 27, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellerby, J.M.; Sammour, M.H. Stabilizer reactions in cast double base rocket propellants. Part I: Hplc determination of stabilizers and their derivatives in a propellant containing the stabilizer mixture para-nitro-n-methylaniline and 2-nitrodiphenylamine aged at 80°C and 90°C. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 1991, 16, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammour, M.H. Stabilizer reactions in cast double base rocket propellants. Part V: Prediction of propellant safe life. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 1994, 19, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellerby, J.M.; Sammour, M.H. Stabilizer reactions in cast double base rocket propellants. Part II: Formation and subsequent reactions of n-nitroso derivatives of para-nitro-n-methylaniline and 2-nitrodiphenylamine in mixed-stabilizer propellants aged at 80 °C and 90 °C. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 1991, 16, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, A.J.; Sammour, M.H.; Bellerby, J.M. Stabilizer reactions in cast double base rocket propellants. Part IV: A comparison of some potential secondary stabilizers for use with the primary stabilizer 2-nitrodiphenylamine. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 1993, 18, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzyzga, O. Diphenylamine and derivatives in the environment: A review. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, S.Y.; Han, F.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, J.P.; Yue, P. Estimation method and results of safe storage life for nitrate ester propellants. Chin. J. Explos. Propellants 2006, 29, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Sućeska, M.; Mušanić, S.M.; Houra, I.F. Kinetics and enthalpy of nitroglycerin evaporation from double base propellants by isothermal thermogravimetry. Thermochim. Acta 2010, 510, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, J.P.; Singh, H. Qualitative assessment of nitroglycerin migration from double-base and composite modified double-base rocket propellants: Concepts and methods of prevention. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 1993, 18, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, J.P.; Agawane, N.T.; Diwakar, R.P.; Chandra, R. Nitroglycerine (NG) migration to various unsaturated polyesters and chloropolyesters used for inhibition of rocket propellants. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 1999, 24, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-P.; Nie, H.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Tan, L.-M.; Yin, H.-L.; Ma, X.-G. Migration kinetics and mechanisms of plasticizers, stabilizers at interfaces of NEPE propellant/HTPB liner/edpm insulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 229, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y. Study on inhibition of double-based propellant by silicone rubber. Explos. Mater. 2016, 45, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.Q.; Wang, X.H.; Bao, G.L.; Zhang, Y. Effect of silica aerogel on properties of silicone rubber used for inhibiting solid rocket propellants. Energy Mater. 1997, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan, D.; Srinivasan, M.; Reddy, K.A.; Pendse, V.V. The migration of plasticizer in solid propellant grains. Polym. Int. 1993, 32, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Sun, S.; Ge, Z.; Luo, Y. Kinetics of Bu-NENA evaporation from Bu-NENA/NC propellant determined by isothermal thermogravimetry. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2017, 42, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.S.; Park, Y.C. A study on the aliphatic energetic plasticizers containing nitrate ester and nitramine. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2009, 15, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, R.V. Volatility of NENA and other energetic plasticizers determined by thermogravimetric analysis. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 1995, 20, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damse, R.S.; Singh, A. Evaluation of energetic plasticisers for solid gun propellant. Def. Sci. J. 2008, 58, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.A.; Stewart, C.W.; Thomas, E.W.; Stahl, W.M. Reinforcement with fluoroplastic additives. Rubber World 1991, 204, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Kowsari, M.H.; Alavi, S.; Ashrafizaadeh, M.; Najafi, B. Molecular dynamics simulation of imidazolium-based ionic liquids. I. Dynamics and diffusion coefficient. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 129, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, R.; Van Baten, J.M. Diffusion of alkane mixtures in zeolites: Validating the maxwell-stefan formulation using MD simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 6386–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurczuk, K.; Galeski, A. Thermoplastic elastomers reinforced with poly(tetrafluoroethylene) nanofibers. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 80, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompa, A.S. Thermal analysis of liquid and solid propellants. J. Hazard. Mater. 1980, 4, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuorwel, K.K.; Cran, M.J.; Sonneveld, K.; Miltz, J.; Bigger, S.W. Migration of antimicrobial agents from starch-based films into a food simulant. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, S.; Du, W.; Luo, Y. Simulation of GAP/HTPB phase behaviors in plasticizers and its application in composite solid propellant. e-Polymers 2018, 18, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | 50 °C | 20 °C | −40 °C | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| σ (a)/MPa | ε (b)/% | σ (a)/MPa | ε (b)/% | σ (a)/MPa | ε (b)/% | ||
| Unaged | A | 3.28 | 33.9 | 11.5 | 19.6 | 51.2 | 6.34 |
| P6 | 5.61 | 69.5 | 15.3 | 51.5 | 64.5 | 13.6 | |
| 1d | A | 3.97 | 29.2 | 11.9 | 16.5 | 55.2 | 5.49 |
| P6 | 5.66 | 66.4 | 15.6 | 49.4 | 63.5 | 13.1 | |
| 2d | A | 5.44 | 22.5 | 12.9 | 12.3 | 61.6 | 4.41 |
| P6 | 5.84 | 64.2 | 16.2 | 47.7 | 66.1 | 12.4 | |
| 3d | A | 7.40 | 19.3 | 15.4 | 9.79 | 55.9 | 3.08 |
| P6 | 6.29 | 65.5 | 16.7 | 45.1 | 61.3 | 11.4 | |
| Sample | kvap/s−1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 °C | 60 °C | 70 °C | 80 °C | 90 °C | 100 °C | |
| DB | 0.00011 | 0.00024 | 0.00059 | 0.00123 | 0.00304 | 0.00535 |
| PTFE-DB | 0.00007 | 0.00022 | 0.00054 | 0.00131 | 0.00221 | 0.00533 |
| Sample | Evap/(kJ·mol−1) | Avap |
|---|---|---|
| DB | 80.13 | 2.50 × 109 s−1 |
| PTFE-DB | 83.04 | 2.19 × 109 s−1 |
| Ref. [22] | 81.9 | 5.6 × 107 s−1 |
| Sample | D1/(×10−12 m2·s−1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120 °C | 110 °C | 100 °C | 90 °C | 80 °C | 70 °C | 60 °C | 50 °C | |
| DB | 3.38 | 1.84 | 1.35 | 0.783 | 0.285 | 0.151 | 0.0577 | 0.0247 |
| PTFE-DB | 3.04 | 1.68 | 1.08 | 0.568 | 0.245 | 0.127 | 0.0508 | 0.0217 |
| Reduction | 10.0% | 8.73% | 20.0% | 27.4% | 14.0% | 15.9% | 12.0% | 12.2% |
| Sample | D2/(×10−13 m2·s−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120 °C | 110 °C | 100 °C | 90 °C | 80 °C | |
| DB | 5.22 | 4.08 | 3.32 | 2.46 | 1.64 |
| PTFE-DB | 3.27 | 2.76 | 2.19 | 1.40 | 1.10 |
| Reduction | 37.4% | 32.2% | 34.1% | 43.1% | 32.9% |
| Sample | D3/(×10−12 m2·s−1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120 °C | 110 °C | 100 °C | 90 °C | 80 °C | 70 °C | 60 °C | 50 °C | |
| DB | 16.4 | 7.58 | 4.07 | 2.36 | 1.21 | 0.61 | 0.31 | 0.26 |
| PTFE-DB | 14.9 | 6.72 | 3.45 | 1.94 | 0.96 | 0.49 | 0.26 | 0.21 |
| Reduction | 9.15 | 11.3 | 15.2 | 17.8 | 20.7 | 19.6 | 16.2 | 19.2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, S.; Ma, S.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, G.; Luo, Y. A Facile Way to Prolong Service Life of Double Base Propellant. Materials 2018, 11, 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112236
Sun S, Ma S, Zhao B, Zhang G, Luo Y. A Facile Way to Prolong Service Life of Double Base Propellant. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112236
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Shixiong, Song Ma, Benbo Zhao, Guangpu Zhang, and Yunjun Luo. 2018. "A Facile Way to Prolong Service Life of Double Base Propellant" Materials 11, no. 11: 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112236
APA StyleSun, S., Ma, S., Zhao, B., Zhang, G., & Luo, Y. (2018). A Facile Way to Prolong Service Life of Double Base Propellant. Materials, 11(11), 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112236





