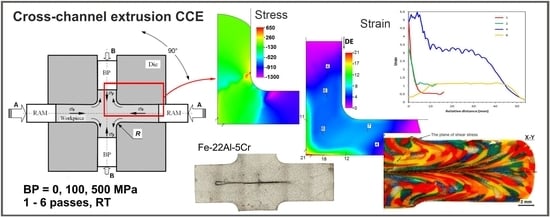
Severe Plastic Deformation of Fe-22Al-5Cr Alloy by Cross-Channel Extrusion with Back Pressure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
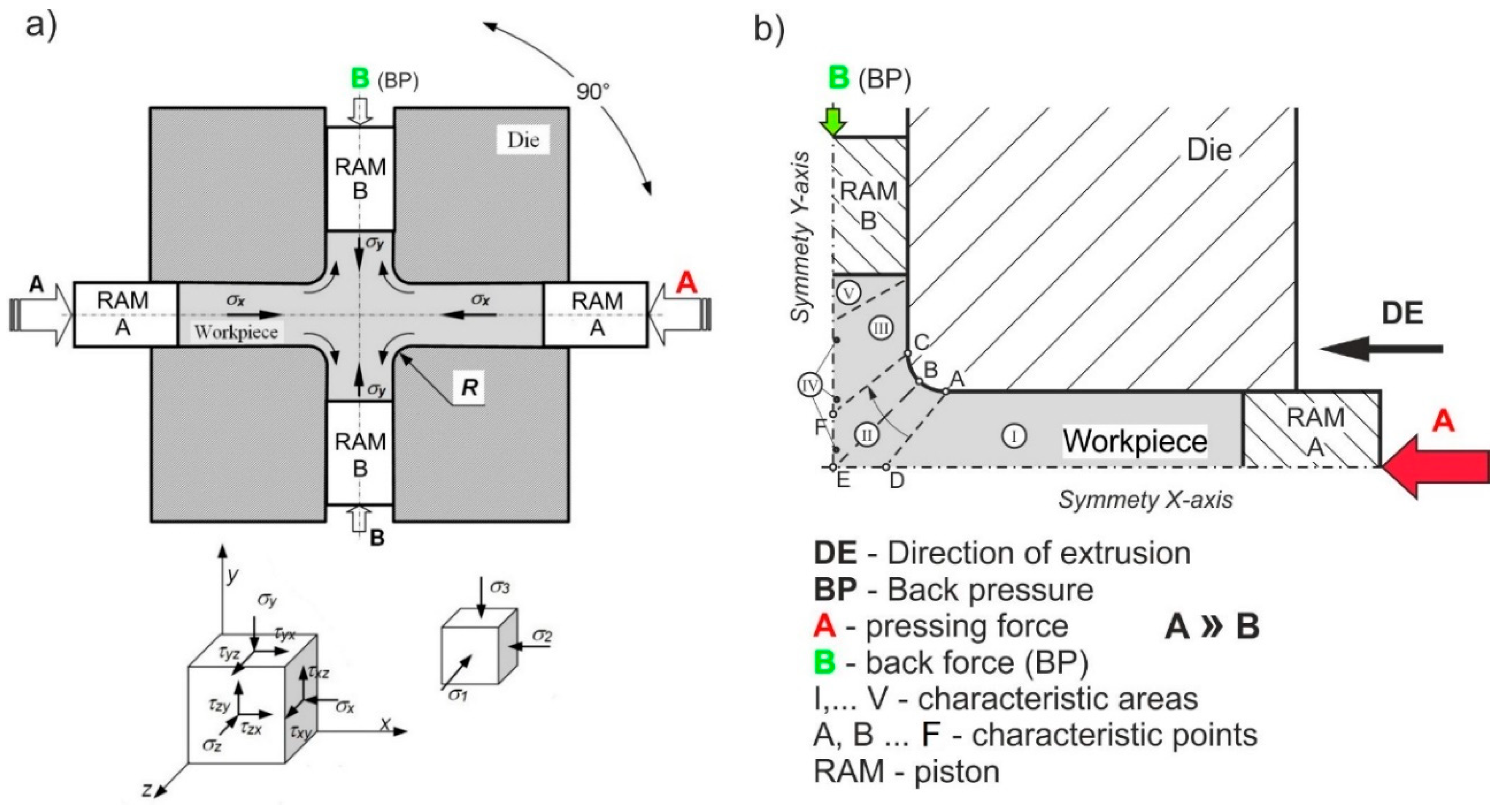
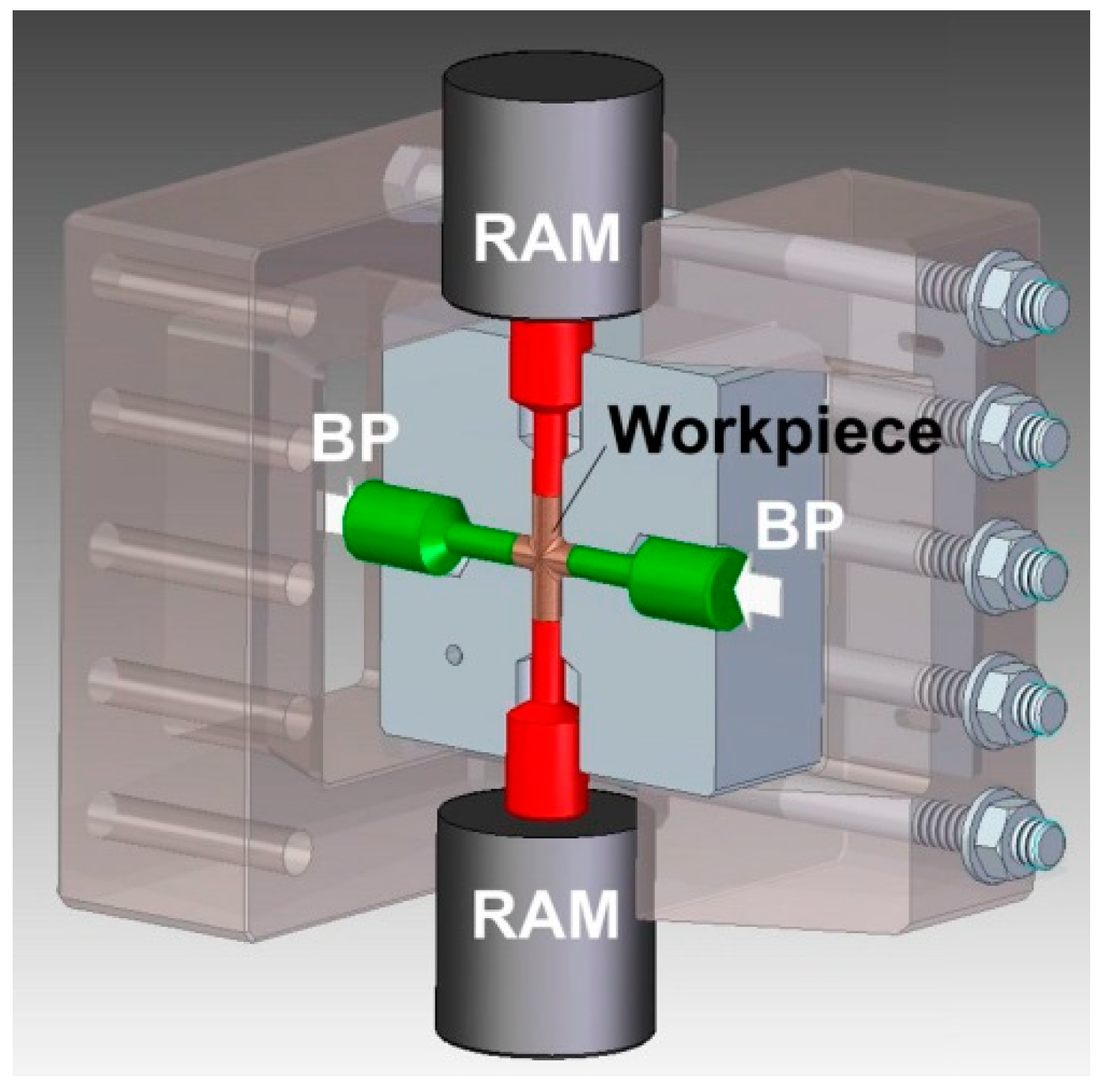
2. Experiment Details
| —stress intensity | V—volume |
| —average hydrostatic stress | S—surface area |
| ν—strain rate of material’s volume | Fi—heat flow |
| —strain rate intensity | —material constant. |
3. Simulation of Cross-Channel Extrusion—Results and Discussion
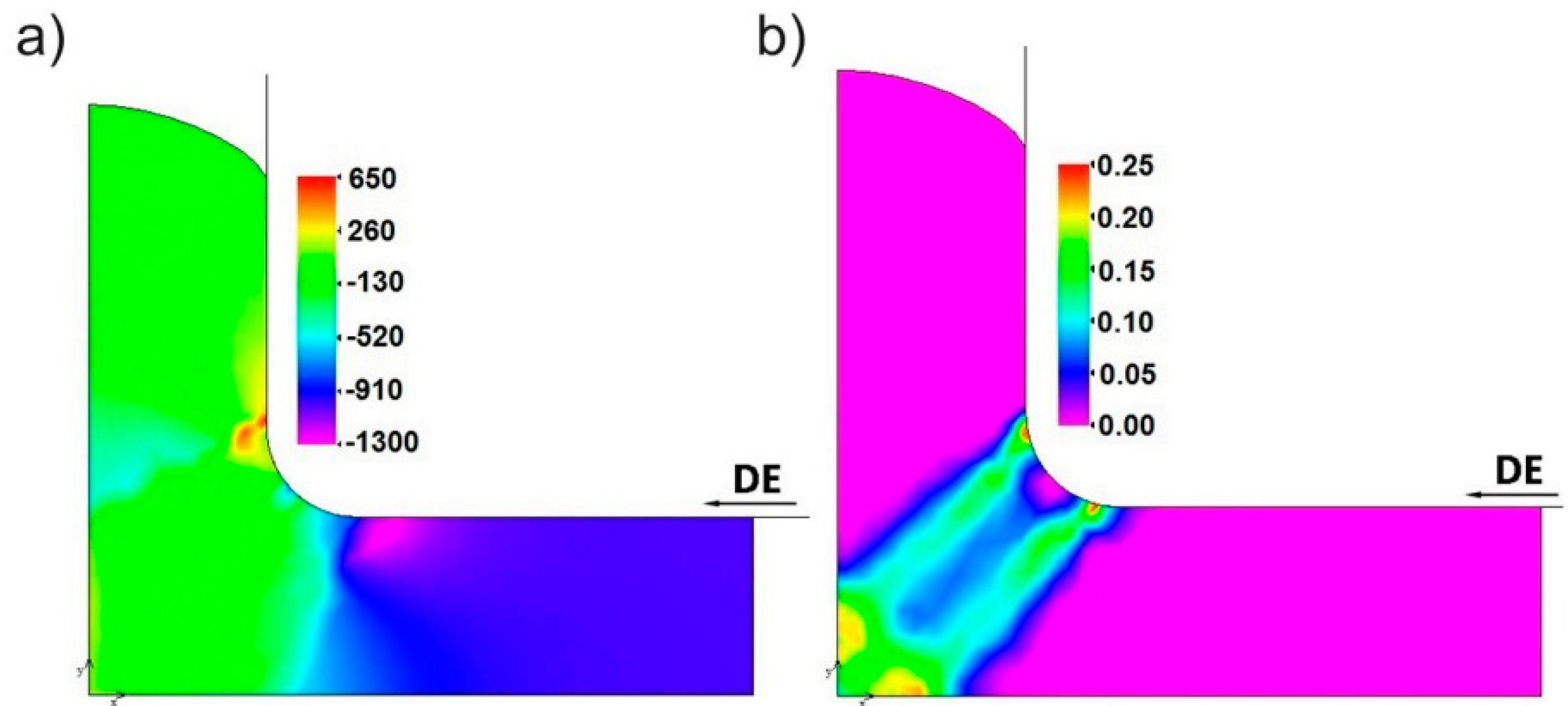
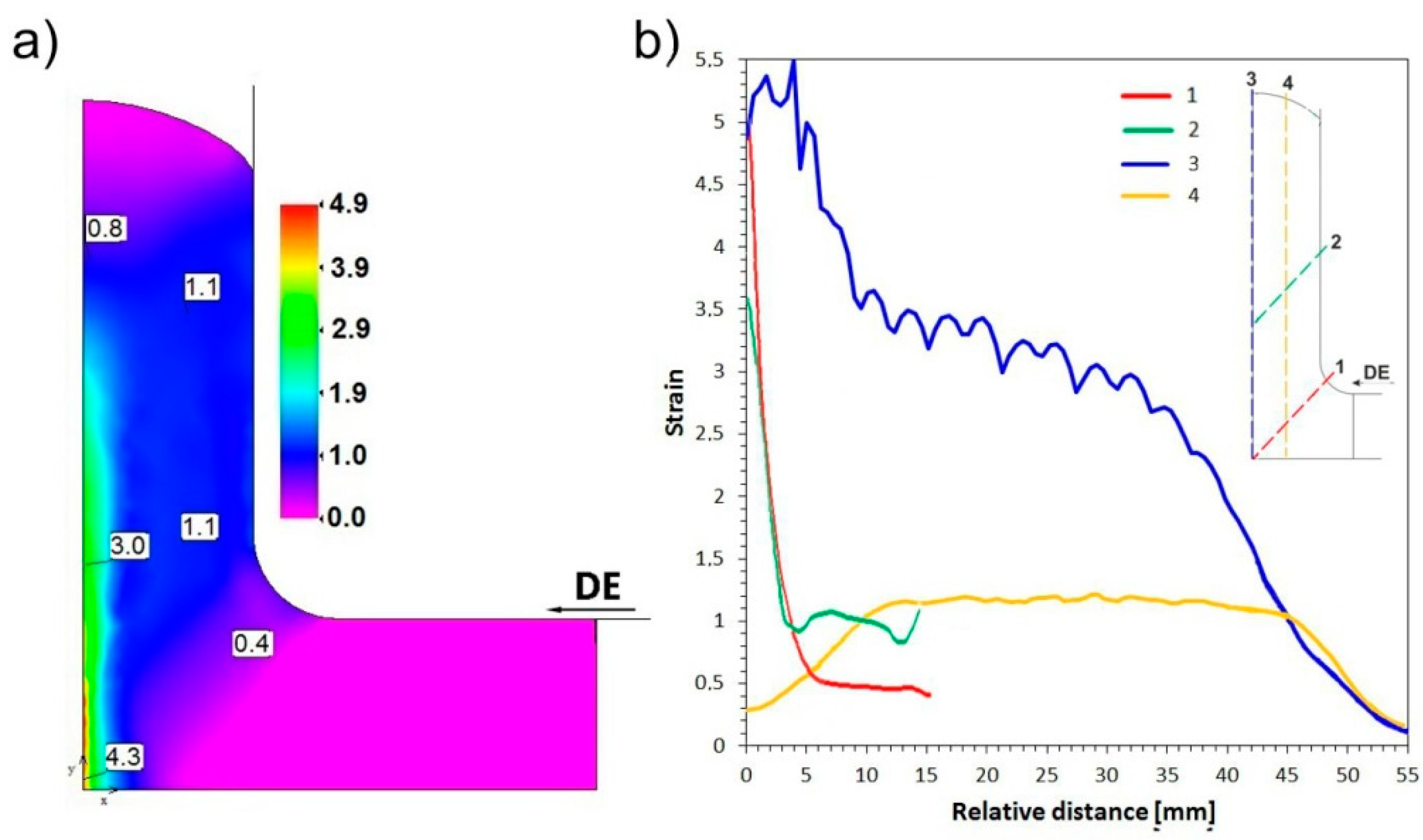
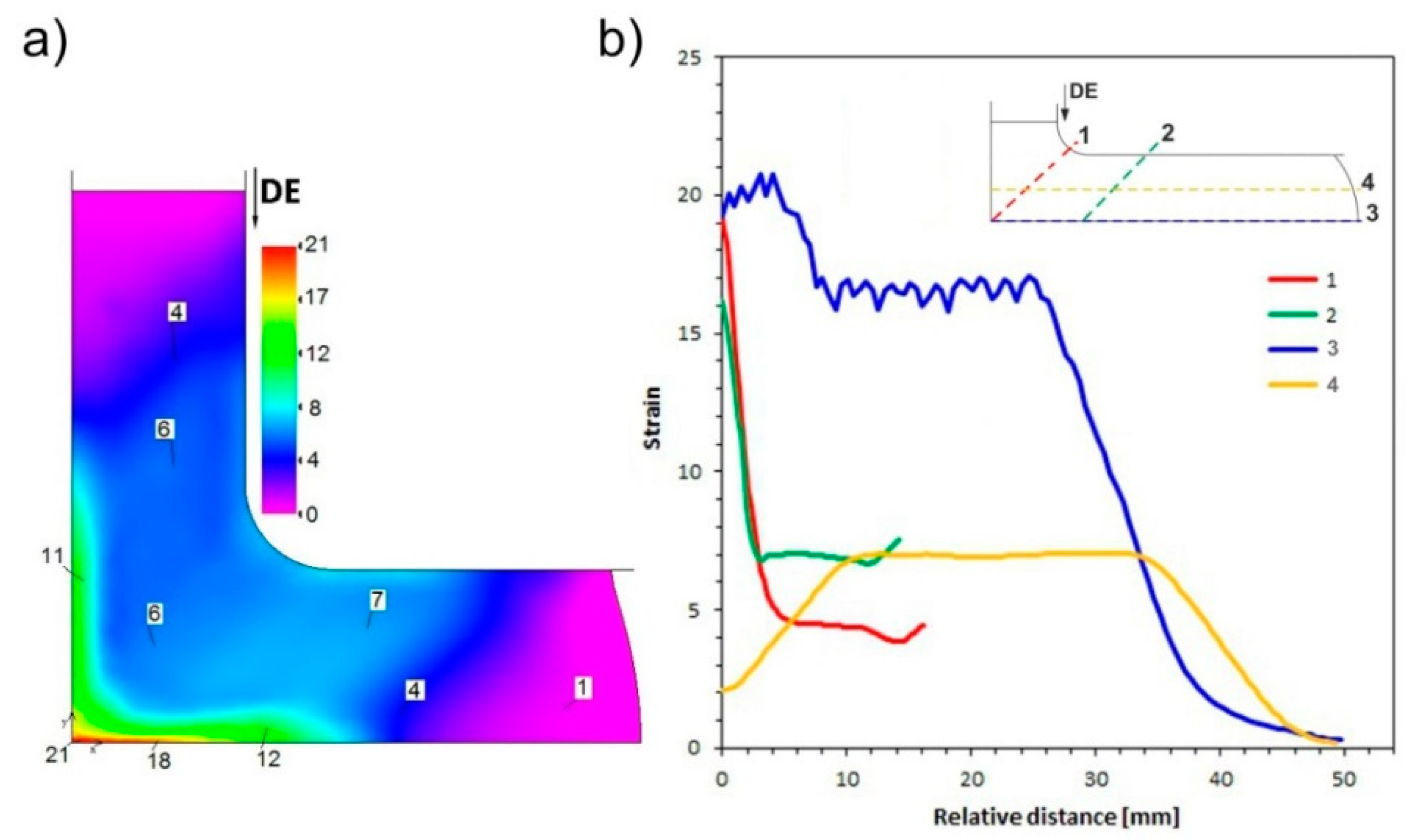
3.1. FEM Simulation
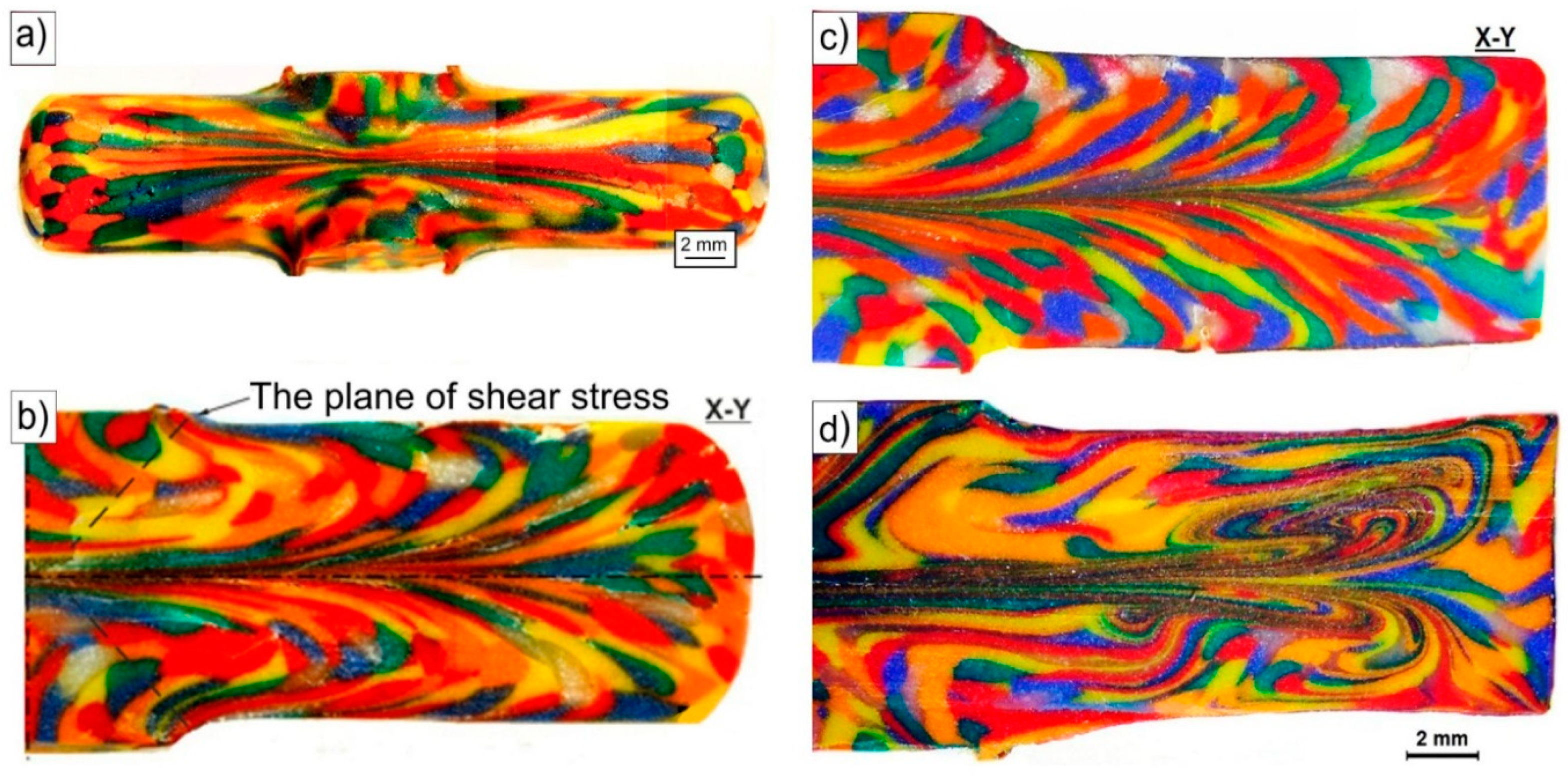
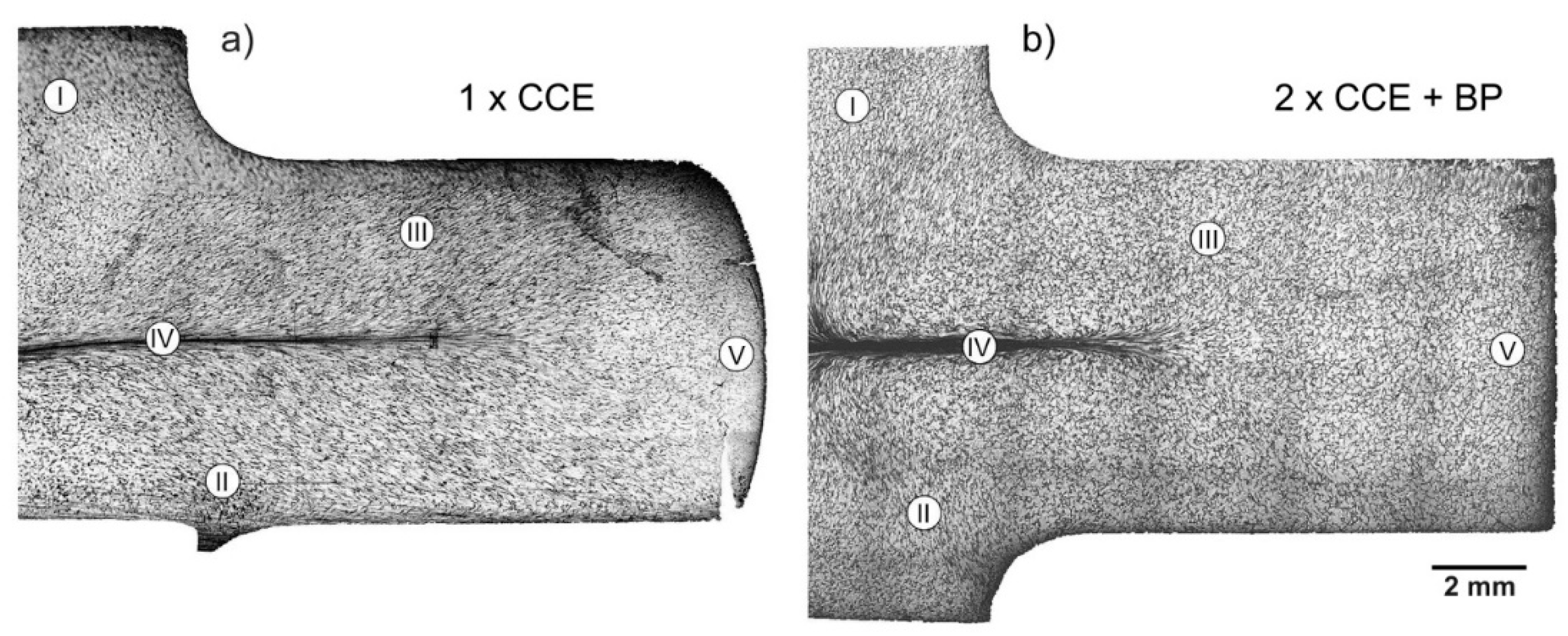
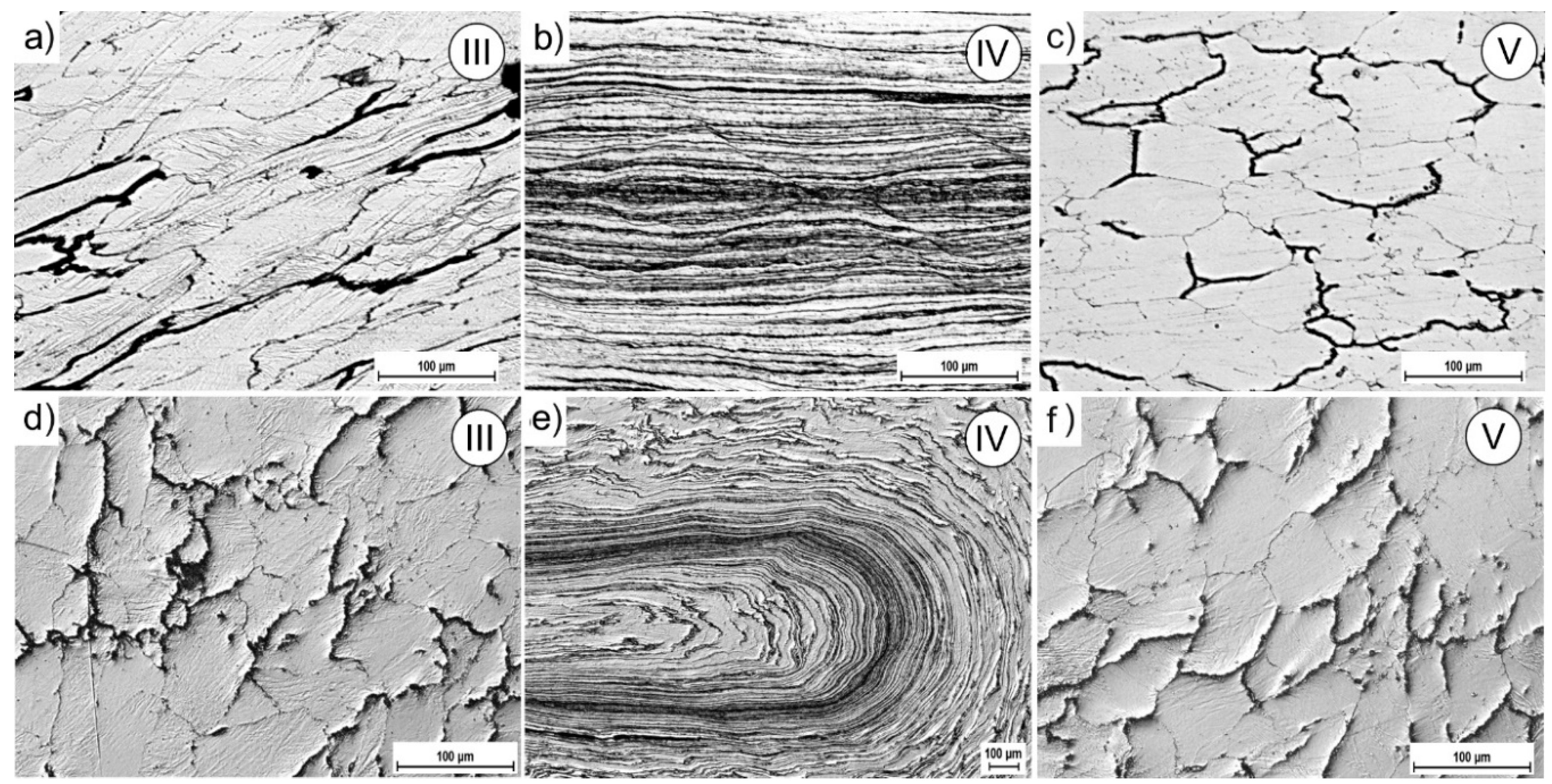
3.2. Physical Simulation
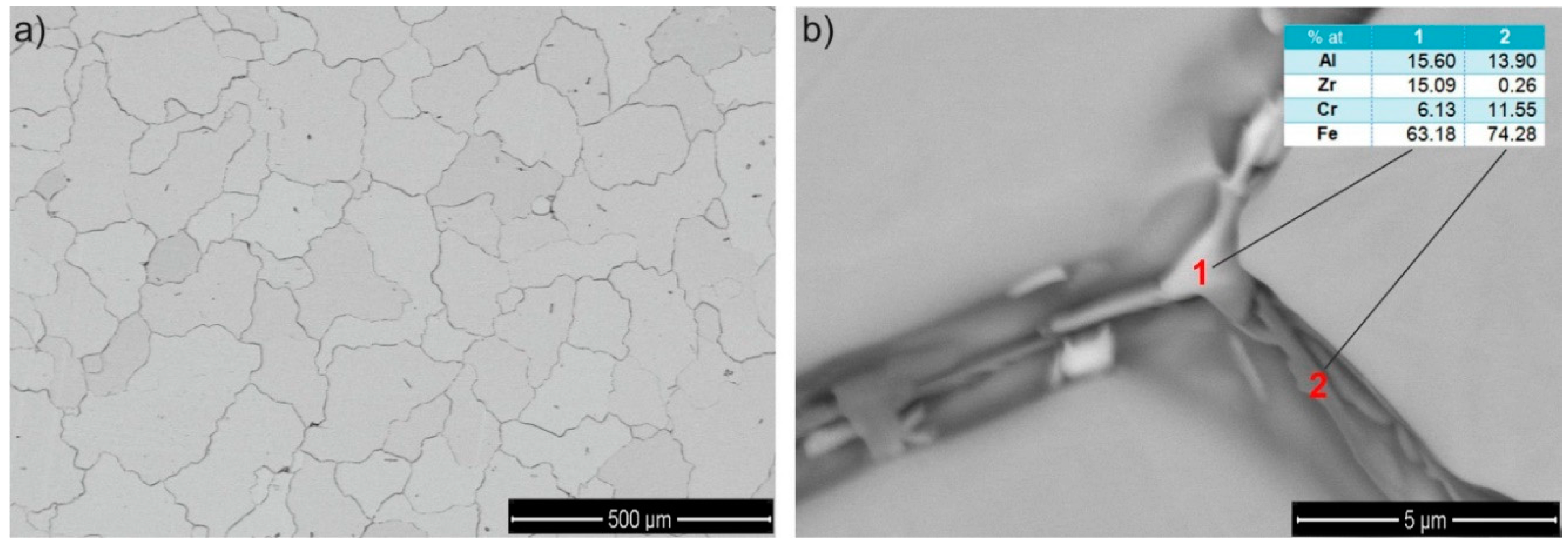
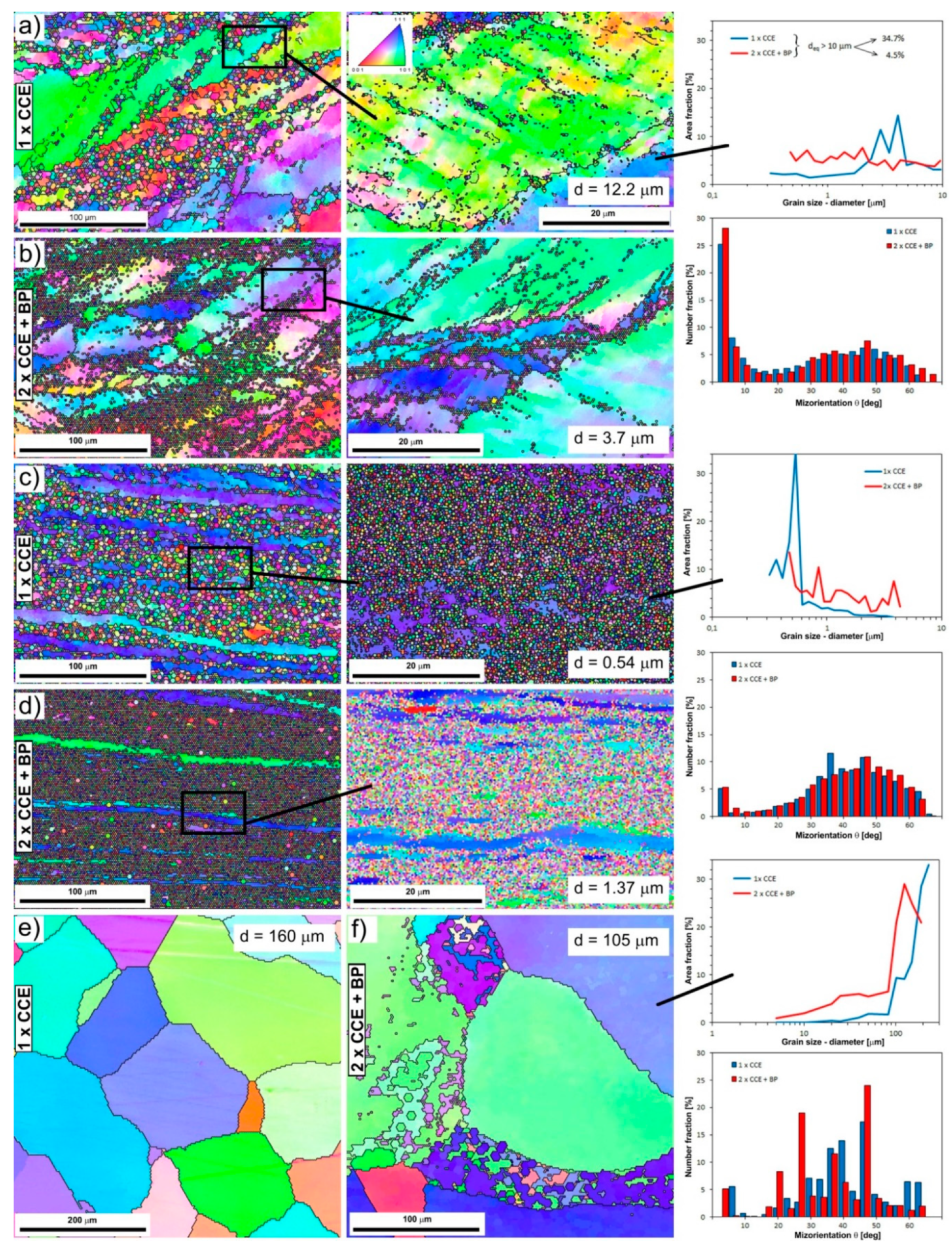
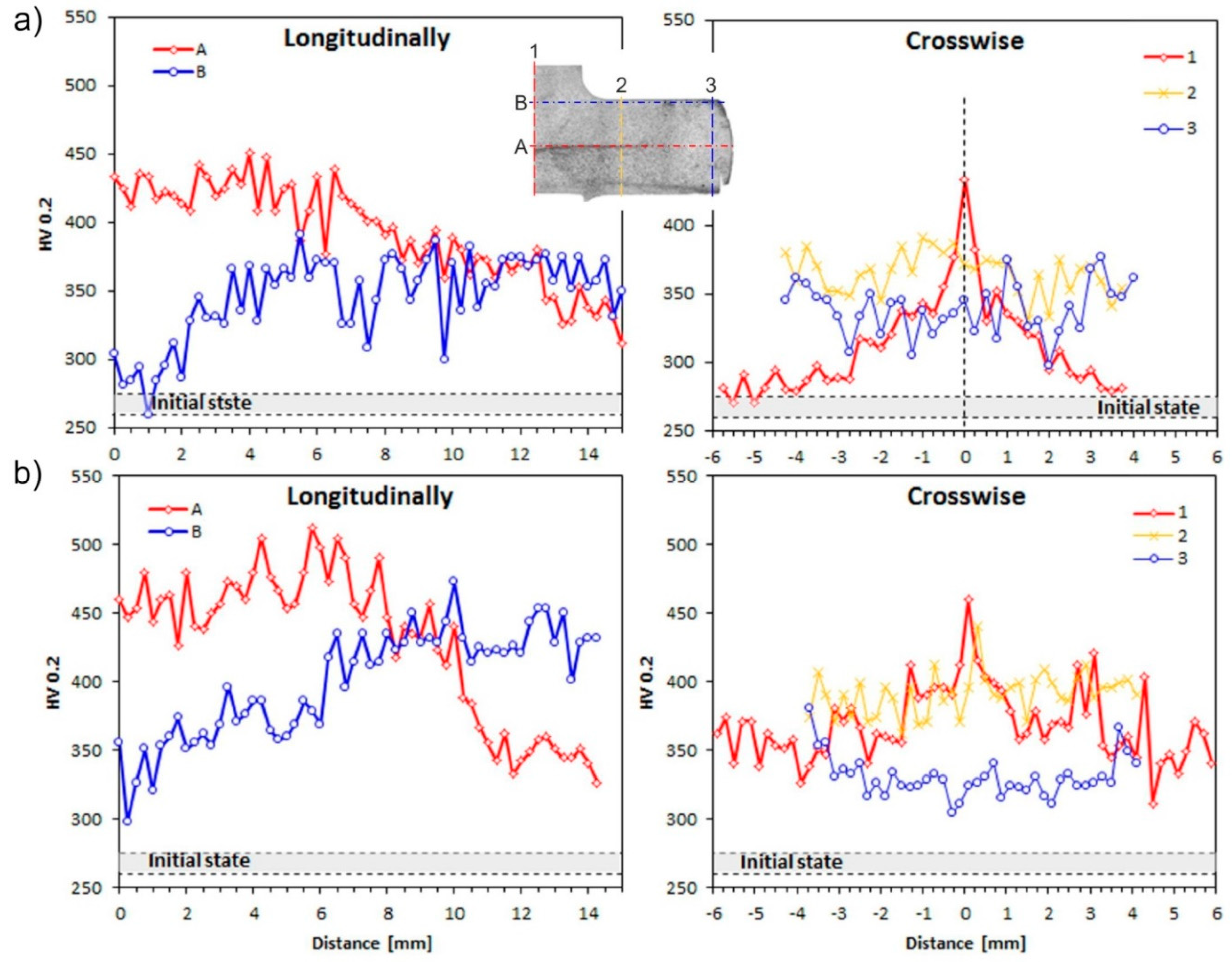
3.3. The Cross-Channel Extrusion of Fe-22Al-5Cr Alloy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valiev, R.Z.; Islamgaliev, R.K.; Alexandrov, I.V. Bulk nanostructured materials from severe plastic deformation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2000, 45, 103–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korznikov, A.V.; Tram, G.; Dimitrov, O.; Korznikova, G.F.; Idrisova, S.R.; Pakieła, Z. The mechanism of nanocrystalline structure formation in Ni3Al during SPD. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.S.; Meredith, C.S. Thermo-mechanical response of Al 6061 with and without equal channel angular pressing (ECAP). Int. J. Plast. 2010, 26, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodachenkova, M.; Barlat, F.; Wen, W.; Bastos, A.; Grácio, J.J. A microstructure-based model for describing the material properties of Al–Zn alloys during high pressure torsion. Int. J. Plast. 2015, 68, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdon, T.G. Twenty-five years of ultrafine-grained materials: Achieving exceptional properties through grain refinement. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 7035–7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azushima, A.; Kopp, R.; Korhonen, A.; Yang, D.Y.; Micari, F.; Lahoti, G.D.; Groche, P.; Yanagimoto, J.; Tsuji, N.; Rosochowski, A.; et al. Severe plastic deformation (SPD) processes for metals. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2008, 57, 716–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polkowski, W.; Jóźwik, P.; Łyszkowski, R. Effect of hot differential speed rolling on microstructure and mechanical properties of Fe3Al-based intermetallic alloy. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2016, 107, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumal, B.B.; Korneva, A.; Zięba, P. Phase transitions in metallic alloys driven by the high pressure torsion. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2014, 14, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.Y.; Lee, S.L.; Lin, J.C. Effects of cross-channel extrusion on microstructure and mechanical properties of AA6061 aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 485, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.Y.; Lee, S.L.; Lin, J.C. Effects and deformation characteristics of cross-channel extrusion process on pure Sn and Al–7Si–0.3Mg alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 107, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, Y.; Arima, H.; Kim, J.C.; Ando, T. Rotary-die ECAP of an Al–7Si–0.35Mg alloy. Scr. Mater. 2001, 45, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.; Nishida, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Shigematsu, I.; Saito, N. Characteristics of plastic deformation by rotary-die ECAP. Scr. Mater. 2005, 52, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosochowski, A.; Olejnik, L.; Richert, J.; Rosochowska, M.; Richert, M. Equal channel angular pressing with converging billets—Experiment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 560, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystrzycki, J.; Fraczkiewicz, A.; Łyszkowski, R.; Mondon, M.; Pakieła, Z. Microstructure and tensile behavior of Fe-16Al-based alloy after severe plastic deformation. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łyszkowski, R.; Czujko, T.; Varin, R.A. Multi-axial forging of the Fe3Al-base intermetallic alloy and its mechanical properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 2902–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łyszkowski, R.; Bystrzycki, J. Influence of temperature and strain rate on the microstructure and flow stress of iron aluminides. Arch. Met. Mater. 2007, 52/2, 347–350. [Google Scholar]
- Karczewski, K.; Jóźwiak, S.; Bojar, Z. Mechanisms of strength properties anomaly of Fe-Al sinters by compression tests at elevated temperature. Arch. Met. Mater. 2007, 52, 361–366. [Google Scholar]
- Łazińska, M.; Durejko, T.; Zasada, D.; Bojar, Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a Fe-28%Al-5%Cr-1%Nb-2%B alloy fabricated by laser engineered net shaping. Mater. Lett. 2017, 196, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemiaszko, D.; Kowalska, B.; Jóźwik, P.; Kwiatkowska, M. The effect of oxygen partial pressure on microstructure and properties of Fe40Al alloy sintered under vacuum. Materials 2015, 8, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabłońska, M.; Kuc, D.; Bednarczyk, I. Influence of deformation parameters on the structure in selected intermetallic from Al-Fe diagram. Solid State Phenom. 2014, 212, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapovok, R. The role of back-pressure in ECAP. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, A.; Lapovok, R.; Toth, L.S.; Molinari, A. Deformation field variations in equal channel angular extrusion due to back pressure. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, M.; Wu, X.; Xu, W.; Xia, K. Mechanical properties of bulk aluminum consolidated from mechanically milled particles by back pressure equal channel angular pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 6533–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.C.; Jeong, H.G.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.S. Analysis of plastic deformation behavior during back pressure ECAP by the FEM. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2013, 77, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djavanroodi, F.; Ebrahimi, M. Effect of die channel angle, friction and back pressure in ECAP using 3D FEM simulation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangiabadi, A.; Kazeminezhad, M. Computation on new deformation routes of tube channel pressing considering back pressure and friction effects. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2012, 59, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribbe, J.; Schmitz, G.; Rösner, H.; Lapovok, R.; Estrin, Y.; Wildea, G.; Divinski, S.V. Effect of back pressure during equal-channel angular pressing on deformation-induced porosity in copper. Scr. Mater. 2013, 68, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasekhar, A.V.; Kim, H.S. Plastic deformation characteristics of cross-equal channel angular pressing. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazani, M.S.; Eghbali, B. Finite element simulation of cross equal channel angular pressing. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2013, 74, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, V.M. Engineering and commercialization of equal channel angular extrusion (ECAE). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 386, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, L. Physical Modeling of Metal Forming Processes; WiZP ITE: Radom, Poland, 1995; ISBN 83-86148-38-1. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Manna, R.; Agrawal, P.; Joshi, S.; Mudda, B.K.; Mukhopadhyay, N.K.; Sastry, G.V.S. Physical modeling of equal channel angular pressing using plasticine. Scr. Mater. 2005, 53, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H. Physical modeling of the forging of a blade with a damper platform using plasticine. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 117, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komoria, K.; Mizuno, K. Study on plastic deformation in cone-type rotary piercing process using model piercing mill for modeling clay. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 4994–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdon, T. The processing of ultrafine-grained materials through the application of SPD. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 3388–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, L.; Chelariu, R.; Comaneci, R. Multiple direct extrusion—A new technique in grain refinement. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 550, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenwarter, A. Incremental HPT as a novel SPD process: Processing features and application to copper. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 626, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łyszkowski, R.; Šimeček, P. Numerical analysis of cross-channel pressing with extrusion at braked outflow of material. Hut. Wiadomości Hut. 2014, 1, 21–25. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Sofuoglu, H.; Gedikli, H. Physical and numerical analysis of three dimensional extrusion process. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2004, 31, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasundar, I.; Rao, M.S.; Raghu, T. Equal channel angular pressing die to extrude a variety of materials. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.Z.; Zhang, Z.F.; Wu, S.D.; Li, S.X. Investigation on the geometrical aspect of deformation during equal-channel angular pressing by in-situ physical modeling experiments. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 476, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.F.; Hodgson, P.D.; Chong, C.J.; Thomson, P.F. Physical modelling with application to metal working, especially to hot rolling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1996, 62, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Baker, I. An experimental study of ECAP. Scr. Mater. 1997, 37, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.J.; Luri, R. Study of ECAE process by the upper bound method considering the correct die design. Mech. Mater. 2008, 40, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.J.; Ding, H.; Ren, Y.P.; Hao, S.M.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.T. Finite element simulation of deformation behavior of pure aluminum during equal channel angular pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 410–411, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, F.; Li, P.; Ma, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, L. Micro-structural evolution in metals subjected to simple shear by a particular severe plastic deformation method. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 2944–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvíl, P.; Dobes, F.; Pesicka, J.; Málek, P.; Bursík, J.; Vodicková, V.; Hanus, P. Microstructure and high temperature mechanical properties of Zr-alloyed Fe3Al-type aluminides: The effect of carbon. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 548, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepahi-Boroujeni, S.; Fereshteh-Saniee, F. Expansion equal channel angular extrusion, as a novel severe plastic deformation technique. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 3908–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogucheva, A.; Babich, E.; Ovsyannikov, B.; Kaibyshev, R. Microstructural evolution in a 5024 aluminum alloy processed by ECAP with and without back pressure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 560, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.Y.; Hao, T.; Wang, X.P.; Luo, G.N.; Liu, C.S.; Fang, Q.F. Structure and mechanical behavior of Fe–Cr alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 640, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitdikova, O.; Sakaia, T.; Miura, H.; Hama, C. Temperature effect on fine-grained structure formation in high-strength Al alloy 7475 during hot severe deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 516, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonova, M.; Kaibyshev, R.; Fang, X.; Wang, W.; Belyakov, A. Grain boundary assembles developed in an austenitic stainless steel during large strain warm working. Mater. Charact. 2012, 70, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Topping, T.; Zhu, Y.; Valiev, R.Z.; Lavernia, E.J. Influence of microstructure on thermal stability of ultrafine-grained Cu processed by ECAP. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 13173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, J.A.; Higuera, O.F.; Cabrera, J.M. Microstructural and mechanical study in the plastic zone of ARMCO iron processed by ECAP. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 697, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Li, W.; Hao, T.; Jiang, W.; Fang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.O.; Zhang, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, L. Mechanical property and damping capacity of ultrafine-grained Fe-13Cr-2Al-1Si alloy produced by equal channel angular pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 695, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polkowski, W.; Jóźwik, P.; Bojar, Z. Electron Backscatter Diffraction Study on Microstructure, Texture, and Strain Evolution in Armco Iron Severely Deformed by the Differential Speed Rolling Method. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 2216–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabłońska, M.; Śmiglewicz, A. A study of mechanical properties of high manganese steels after different rolling conditions. Metalurgija 2015, 54, 619–622. [Google Scholar]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Łyszkowski, R.; Polkowski, W.; Czujko, T. Severe Plastic Deformation of Fe-22Al-5Cr Alloy by Cross-Channel Extrusion with Back Pressure. Materials 2018, 11, 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112214
Łyszkowski R, Polkowski W, Czujko T. Severe Plastic Deformation of Fe-22Al-5Cr Alloy by Cross-Channel Extrusion with Back Pressure. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112214
Chicago/Turabian StyleŁyszkowski, Radosław, Wojciech Polkowski, and Tomasz Czujko. 2018. "Severe Plastic Deformation of Fe-22Al-5Cr Alloy by Cross-Channel Extrusion with Back Pressure" Materials 11, no. 11: 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112214
APA StyleŁyszkowski, R., Polkowski, W., & Czujko, T. (2018). Severe Plastic Deformation of Fe-22Al-5Cr Alloy by Cross-Channel Extrusion with Back Pressure. Materials, 11(11), 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112214