Thermodynamic Study of the Corrosion of Refractories by Sodium Carbonate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Refractory Materials Preparation and Characterization
2.2. Thermochemical Experimental Apparatus and Procedure
2.3. Analytical Determinations
2.4. Thermochemical Equilibrium Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FactSage Thermodynamic Calculations
3.1.1. Decomposition and Synthesis Reactions of the Spinels
3.1.2. Reaction between the Six Refractory Materials and Na2CO3
3.1.3. Reaction of Intermediates
3.2. Thermodynamics Experiments
3.2.1. Effect of Temperature on the Reaction of Metallic Oxides with Sodium Carbonate
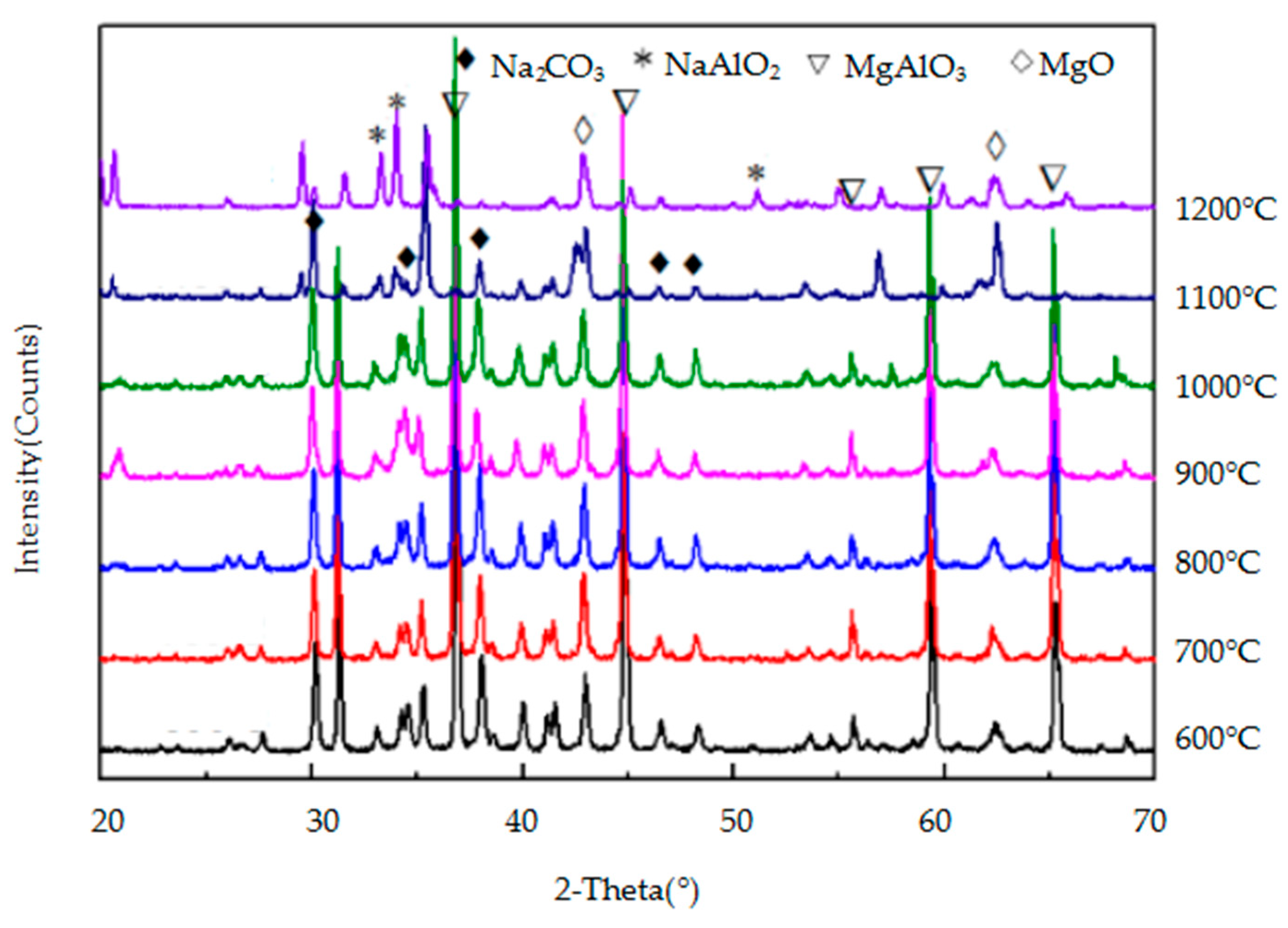
3.2.2. Effect of Temperature on the Reaction of the Three Spinels with Sodium Carbonate
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Spinel compounds in refractory materials are generally not susceptible to thermal decomposition reactions. The Mg-Cr and Mg-Al spinels are more difficultly pyrolysed and they have good thermal stability.
- (2)
- The chromium-containing spinel reacts easily with Na2CO3 to form Na2CrO4. However, Na2Cr2O4 is not stable and can be converted to Na2CrO4 and Cr2O3. In the presence of Na2CO3, the dibasic sodium salt is more easily converted to Na2CrO4, indicating that the presence of sodium salts causes chromium-containing refractories to be more susceptible to corrosion, which shortens their service life.
- (3)
- The difficulty of the reaction between the spinel and sodium carbonate is as follows: MgO·Al2O3, MgO·Fe2O3, and MgO·Cr2O3.
- (4)
- Chromium oxide can react with sodium carbonate at a lower temperature of 600 °C and it has the worst corrosion resistance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cruz, R.T.; Bielefeldt, W.V.; Bragança, S.R. Influence of ladle slag composition in the dissolution process of the dicalcium silicate (C2S) layer on doloma-C refractories. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 15360–15369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, K.; Petty, A.; Bennett, J.; Krabbe, R.; Thomas, H. Wear mechanisms of chromia refractories in slagging gasifiers. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2007, 4, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, H.W.; Guo, Q.H.; Yu, G.S. Refractory failure in entrained-flow gasifier: Vision-based macrostructure investigation in a bench-scale OMB gasifier. Appl. Energy 2017, 205, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qotaibi, Z.; Diouri, A.; Boukhari, A.; Taibi, M.; Aride, J. Analysis of magnesia chrome refractories weared in a rotary cement kiln. Ann. Chim. Sci. Mater. 1998, 23, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, M.; Song, S.Q.; Li, Y.W.; Xu, Y.B. Effect of Cr2O3 addition on corrosion mechanism of refractory castables for waste melting furnaces and concurrent formation of hexavalent chromium. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 2383–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, A.V.; Varona, C.; Chaucherie, X.; Goeuriot, D. Corrosion of Al2O3-SiO2 refractories by sodium and sulfur vapors: A case study on hazardous waste incinerators. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 5743–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, T.; Akiyama, K.; Yamamoto, H. Corrosion resistance of Cr2O3-Al2O3 ceramics by molten sodium sulphate-vanadium pentoxide. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 5927–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Huang, A.; Gu, H.Z.; Zhang, M.J.; Shao, Z.J. Corrosion of Al2O3-Cr2O3 refractory lining for high-temperature solid waste incinerator. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 14748–14753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, T.; Deguchi, A.; Ohta, S.; Morimoto, T.; Ike, M.; Uchida, N. Dependence of corrosion rate of alumina-chromia on properties of molten slags. Mater. Trans. 2001, 42, 2625–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, T.; Morimoto, T.; Ohta, S.; Uchida, N. Improvement of the corrosion resistance of alumina-chromia ceramic materials in molten slag. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 23, 2089–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, M.; Tripathi, H.S. Thermo-mechanical behavior of Al2O3-Cr2O3 refractories: Effect of TiO2. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 3109–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehre, P.; Aneziris, C.G.; Veres, D.; Parr, C.; Fryda, H.; Neuroth, M. Improved spinel-containing refractory castables for slagging gasifiers. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 33, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, A.; Biswas, S.; Prince, R.K.; Pal, A.R. Failure analysis of bullnose refractory in reheating furnace of Hot Strip Mill. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2016, 60, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moda, J.; Tanaka, K.; Kitamura, S. Chrome-free castables for waste melting furnances. J. Tech. Assoc. Refract. 2008, 28, 204–209. [Google Scholar]
- Igabo, K.; Sakida, S.; Benino, Y.; Nanba, T.M.; Yamaguchi, A. Development of Cr-free refractories for high temperature municipal waste incinerators. J. Tech. Assoc. Refract. 2008, 28, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Mishima, M.; Tsuda, H.; Hokii, T. Corrosion behavior of Cr-free MgO-TiO2-Al2O3 bricks for waste melting furnaces. J. Tech. Assoc. Refract. 2005, 25, 300–304. [Google Scholar]
- Brachhold, N.; Aneziris, C.G. Porous materials for alkali contaminated environments. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 33, 2013–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, H.; Yutaka, K.; Yukihiro, S.; Kakuichi, M. Development of Cr2O3-free castable for waste melting furnaces. J. Tech. Assoc. Refract. 2008, 28, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, S.; Miyagishi, Y. Development of a Cr2O3-free castable for waste melting furnaces (Part 2). J. Tech. Assoc. Refract. 2001, 21, 197. [Google Scholar]
- Miyaji, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Kudo, E. Role of Cr2O3 in Al2O3-Cr2O3 castable for waste melting furnaces. J. Tech. Assoc. Refract. 2002, 22, 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Reinmöller, M.; Klinger, M.; Thieme, E.; Meyer, B. Analysis and prediction of slag-induced corrosion of chromium oxide-free refractory materials during fusion of coal and biomass ash under simulated gasification conditions. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 149, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachhold, N.; Schafföner, S.; Aneziris, C.G. Investigation of alkali corrosion resistance of potassium aluminosilicates using statistical techniques. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigent, P.; Bouchetou, M.L.; Poirier, J. Andalusite: An amazing refractory raw material with excellent corrosion resistance to sodium vapours. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 2287–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehre, P.; Wenzel, C.; Aneziris, C.G. Investigation of shaped alumina based refractories used in slagging gasifiers. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 1701–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, P.; Criado, E.; Bakali, J.J.; Baudín, C. Dynamic corrosion of Al2O3-ZrO2-SiO2 and Cr2O3-containing refractories by molten frits. Part II: Microstructural study. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaafhausen, S.; Hugon, E.; Yazhenskikh, E.; Wilhelmi, B.; Müller, M. Corrosion of refractory materials in fluidised bed gasification of alkali rich fuels. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2015, 114, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stjernberg, J.; Lindblom, B.; Wikström, J.; Antti, M.L.; Odénc, M. Microstructural characterization of alkali metal mediated high temperature reactions in mullite based refractories. Ceram. Int. 2010, 36, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stjernberg, J.; Olivas-Ogaz, M.A.; Antti, M.L. Laboratory scale study of the degradation of mullite/corundum refractories by reaction with alkali-doped deposit materials. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Iida, E.; Shikama, H.; Inoue, K. Applicaton of chrome-free bricks for incinerated-ash melting furnaces. J. Tech. Assoc. Refract. 2005, 25, 232. [Google Scholar]
- Prigent, P.; Bouchetou, M.L.; Poirier, J.; Bilbao, E.D.E.; Blond, E. Corrosion of oxide bonded silicon carbide refractories by molten salts in solid waste-to-energy facilities. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 5643–5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Sample | Mineral Phase | Content of the Main Mineral Phase | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Al2O3 | analytical purity | Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| 2 | Fe2O3 | analytical purity, 99.0% | Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| 3 | Cr2O3 | analytical purity, 99.0% | Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| 4 | Spinel (MgO·Cr2O3) | 90 wt.% MgO·Cr2O3 | self-made |
| 5 | Spinel (MgO·Fe2O3) | 83 wt.% MgO·Fe2O3 | self-made |
| 6 | Spinel (MgO·Al2O3) | 85 wt.% MgO·Al2O3 | self-made |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Cheng, G.; Xiang, Y.; Long, F.; Dong, C. Thermodynamic Study of the Corrosion of Refractories by Sodium Carbonate. Materials 2018, 11, 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112197
Zhao Y, Cheng G, Xiang Y, Long F, Dong C. Thermodynamic Study of the Corrosion of Refractories by Sodium Carbonate. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112197
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Ying, Guishi Cheng, Yu Xiang, Fei Long, and Changqing Dong. 2018. "Thermodynamic Study of the Corrosion of Refractories by Sodium Carbonate" Materials 11, no. 11: 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112197
APA StyleZhao, Y., Cheng, G., Xiang, Y., Long, F., & Dong, C. (2018). Thermodynamic Study of the Corrosion of Refractories by Sodium Carbonate. Materials, 11(11), 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112197




