Use of Gold Nanoparticles as Substrate for Diffusive Monitoring of Gaseous Mercury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Adsorbent Materials
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Diffusive Samplers
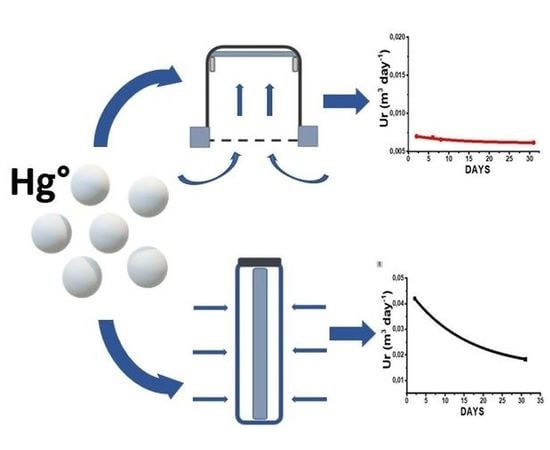
- A glass cylinder (inner diameter 20 mm, 25 mm in depth) with a cap and a diffusion teflon net (mesh 100 µm) (Figure 1), aimed to avoid undesired adsorption by using metallic nets.
- Three Radial diffusive bodies made of polyethylene (PE) with a microporous structure, 1.5 mm in thickness, an average porosity of 20 ± 5 μm, has been used for the radial diffusion sampling (Figure 2).
- A polystyrene (PS) holding grid, 85 mm × 40 mm, has been used to hold three samplers exposed directly to the ambient vapor mercury concentration, without any diffusion barrier (Figure 3).
2.4. Samplers Preparation
2.5. Samplers Exposures
3. Results and Discussions
Sampling Rate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bjørklund, G.; Dadar, M.; Mutter, J.; Aaseth, J. The toxicology of mercury: Current research and emerging trends. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, C.T.; Mason, R.P.; Chan, H.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Pirrone, N. Mercury as a Global Pollutant: Sources, Pathways, and Effects. Environ. Sci.Technol. 2013, 47, 4967–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundseth, K.; Pacyna, J.M.; Pacyna, E.G.; Pirrone, N.; Thorne, R.J. Global sources and pathways of mercury in the context of human health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, W.H.; Munthe, J. Atmospheric mercury—An overview. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wright, L.P.; Blanchard, P. A review of current knowledge concerning dry deposition of atmospheric mercury. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5853–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, S.E.; Brooks, S.; Lin, C.J.; Scott, K.J.; Landis, M.S.; Stevens, R.K.; Goodsite, M.; Richter, A. Dynamic oxidation of gaseous mercury in the arctic troposphere at polar sunrise. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gworek, B.; Dmuchowski, W.; Baczewska, A.H.; Brągoszewska, P.; Bemowska-Kałabun, O.; Wrzosek-Jakubowska, J. Air Contamination by Mercury, Emissions and Transformations—A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Xie, Z. Total gaseous mercury along a transect from coastal to central Antarctic: Spatial and diurnal variations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, M.T.; McLennan, D.; Lapalme, M.; Mooney, C.; Watt, C.; Mintz, R. Total gaseous mercury concentration measurements at fort mcmurray, Alberta, Canada. Atmosphere 2013, 4, 472–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprovieri, F.; Pirrone, N.; Bencardino, M.; Amore, F.D.; Carbone, F.; Cinnirella, S.; Mannarino, V.; Landis, M.; Ebinghaus, R.; Weigelt, A.; et al. Atmospheric mercury concentrations observed at ground-based monitoring sites globally distributed in the framework of the GMOS network. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 11915–11935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xu, X.; Xu, Z.; Shang, L.; Qiu, G. Total mercury and methylmercury accumulation in wild plants grown at wastelands composed of mine tailings : Insights into potential candidates for phytoremediation. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risch, M.R.; Kenski, D.M. Spatial patterns and temporal changes in atmospheric-mercury deposition for the Midwestern USA, 2001–2016. Atmosphere 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencarelli, C.N.; Bieser, J.; Carbone, F.; De Simone, F.; Hedgecock, I.M.; Matthias, V.; Travnikov, O.; Yang, X.; Pirrone, N. Sensitivity model study of regional mercury dispersion in the atmosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngan, F.; Cohen, M.; Luke, W.; Ren, X.; Draxler, R. Meteorological modeling using the WRF-ARW Model for Grand Bay intensive studies of atmospheric mercury. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 209–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustin, M.S.; Amos, H.M.; Huang, J.; Miller, M.B.; Heidecorn, K. Measuring and modeling mercury in the atmosphere: A critical review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5697–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustin, M.; Jaffe, D. Reducing the uncertainty in measurement and understanding of mercury in the atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2222–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klánová, J.; Harner, T. The challenge of producing reliable results under highly variable conditions and the role of passive air samplers in the Global Monitoring Plan. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 46, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wania, F.; Shen, L.; Lei, Y.D.; Teixeira, C.; Muir, D.C.G. Development and Calibration of a Resin-Based Passive Sampling System for Monitoring Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ie, E.V.; Namies, A.K.J.; Partyka, M.; Wasik, A. Passive sampling and/or extraction techniques in environmental analysis : A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 381, 279–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lyman, S.N.; Hartman, J.S.; Gustin, M.S. A review of passive sampling systems for ambient air mercury measurements. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 374–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mclagan, D.S.; Mazur, M.E.E.; Mitchell, C.P.J.; Wania, F. Passive air sampling of gaseous elemental mercury : A critical review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 3061–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urba, A.; Kvietkus, K.; Sakalys, J.; Xiao, Z.; Lindqvist, O. A new sensitive and portable mercury vapor analyzer Gardis-1A. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1995, 80, 1305–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J.Z.; Lucas, D.; Koshland, C.P. Gold nanoparticle films as sensitive and reusable elemental mercury sensors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 9557–9562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabri, Y.M.; Kandjani, A.E.; Ippolito, S.J.; Bhargava, S.K. Nanosphere Monolayer on a Transducer for Enhanced Detection of Gaseous Heavy Metal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, K.M.M.; Ippolito, S.J.; Esmaielzadeh, A.; Sabri, Y.M.; Bhargava, S.K. Nano-engineered surfaces for mercury vapor sensing : Current state and future possibilities. Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 88, 77–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.; Woodward, C.; Peri, L.; Weisberg, P.J.; Gustin, M.S. Application of tree rings [dendrochemistry] for detecting historical trends in air Hg concentrations across multiple scales. Biogeochemistry 2014, 120, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tong, Y.; Hu, D.; Ou, L.; Wang, X. Characterization of atmospheric mercury concentrations along an urban e rural gradient using a newly developed passive sampler. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 47, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantopoulou, I.; Skodras, G.; Sakellaropoulos, G.P. Sorption of mercury by activated carbon in the presence of flue gas components. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.B.; Ferlin, S.; Fostier, A.H.; Mazali, I.O. Using Gold Nanoparticles as Passive Sampler for Indoor Monitoring of Gaseous Elemental Mercury. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2017, 28, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.J.C.; Burdon, M.K.; Brown, A.S.; Kim, K. Assessment of pumped mercury vapour adsorption tubes as passive samplers using a micro-exposure chamber. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 2456–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Choi, H.D.; Landis, M.S.; Holsen, T.M. An application of passive samplers to understand atmospheric mercury concentration and dry deposition spatial distributions. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 2976–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustin, M.S.; Lyman, S.N.; Kilner, P.; Prestbo, E. Development of a passive sampler for gaseous mercury. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5805–5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, F.; Vitaliano, R.; Battocchio, C.; Fratoddi, I. Synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles stabilized by palladium (II) phosphine thiol. J. Organomet. Chem. 2008, 693, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintiliani, M.; Bassetti, M.; Pasquini, C.; Battocchio, C.; Rossi, M.; Mura, F.; Matassa, R.; Fontana, L.; Russoa, M.V.; Fratoddi, I. Network assembly of gold nanoparticles linked through fluorenyl dithiol bridges. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 2517–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, L.; Bassetti, M.; Battocchio, C.; Venditti, I.; Fratoddi, I. Synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles functionalized with organic dithiols. Colloid. Surf. A 2017, 532, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearzotti, A.; Papa, P.; Macagnano, A.; Zampetti, E.; Venditti, I.; Fioravanti, R.; Fontana, L.; Matassa, R.; Familiari, G.; Fratoddi, I. Environmental Hg vapours adsorption and detection by using functionalized gold nanoparticles network. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4706–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumarey, R.; Brown, R.J.C.; Corns, W.T.; Brown, A.S.; Stockwell, P.B. Elemental mercury vapour in air : The origins and validation of the “Dumarey equation” describing the mass concentration at saturation. Accredit. Qual. Assur. 2010, 15, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Chen, M.; Greene, G.W.; Horn, R.G. Mercury Vapor Sorption and Amalgamation with a Thin Gold Film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 23172–23181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusilao-Makiese, J.; Tessier, E.; Amouroux, D.; Cukrowska, E. Analytical performances of nanostructured gold supported on metal oxide sorbents for the determination of gaseous mercury. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levlin, M.; Ikävalko, E.; Laitinen, T. Adsorption of mercury on gold and silver surfaces. Fresenius. J. Anal. Chem. 1999, 365, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolnai, B.; Gelencsér, A.; Hlavay, J. Theoretical approach to non-constant uptake rates for tube-type diffusive samplers. Talanta 2001, 54, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sampler | Indoor SR (m3 day−1) | Adj. R-Square | Outdoor SR (m3 day−1) | Adj. R-Square |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axial | 0.006 | 0.99 | 0.005 | 0.97 |
| Radial | 0.030 | 0.99 | 0.010 | 0.92 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papa, P.; Fratoddi, I.; Venditti, I.; Vichi, F.; Macagnano, A.; Zampetti, E.; Bearzotti, A. Use of Gold Nanoparticles as Substrate for Diffusive Monitoring of Gaseous Mercury. Materials 2018, 11, 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112119
Papa P, Fratoddi I, Venditti I, Vichi F, Macagnano A, Zampetti E, Bearzotti A. Use of Gold Nanoparticles as Substrate for Diffusive Monitoring of Gaseous Mercury. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112119
Chicago/Turabian StylePapa, Paolo, Ilaria Fratoddi, Iole Venditti, Francesca Vichi, Antonella Macagnano, Emiliano Zampetti, and Andrea Bearzotti. 2018. "Use of Gold Nanoparticles as Substrate for Diffusive Monitoring of Gaseous Mercury" Materials 11, no. 11: 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112119
APA StylePapa, P., Fratoddi, I., Venditti, I., Vichi, F., Macagnano, A., Zampetti, E., & Bearzotti, A. (2018). Use of Gold Nanoparticles as Substrate for Diffusive Monitoring of Gaseous Mercury. Materials, 11(11), 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112119