Ultrasonic Processing of Aluminum–Magnesium Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
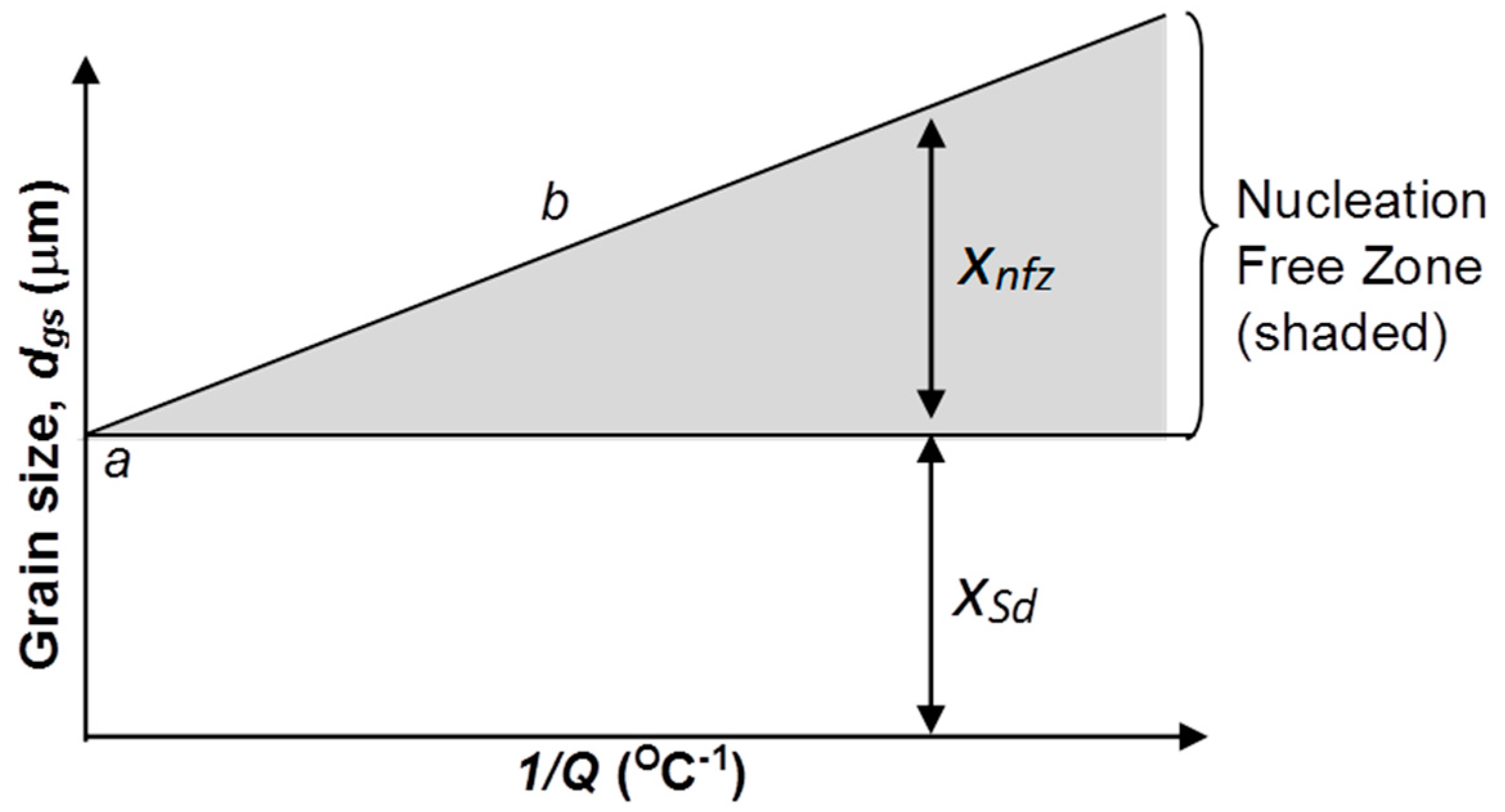
Theory
2. Materials and Methods
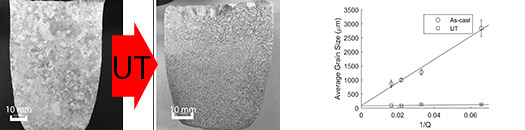
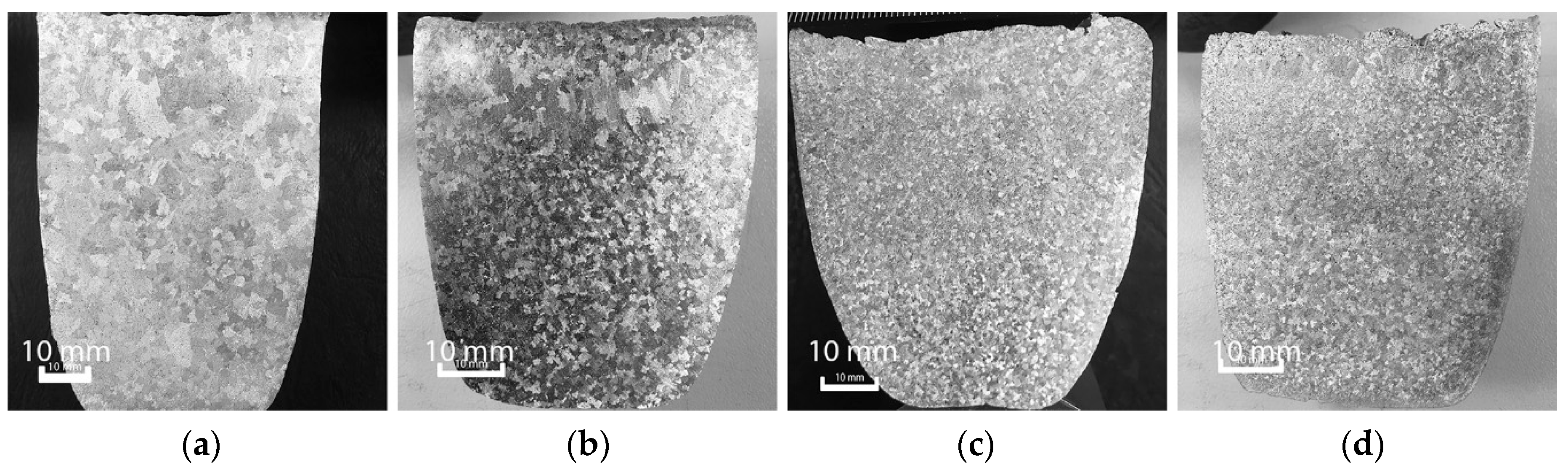
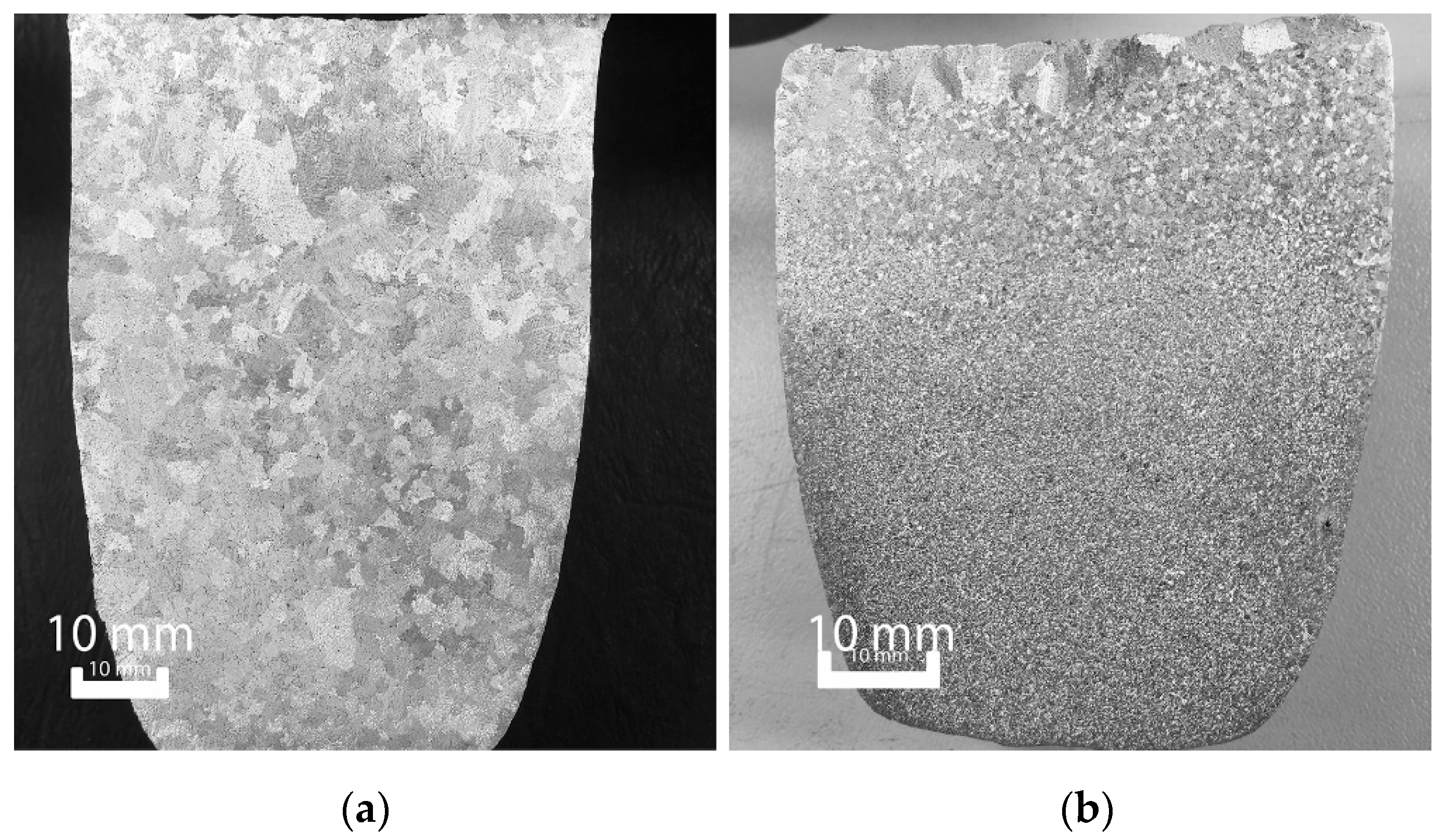
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polmear, I.J.; StJohn, D.; Nie, J.-F.; Qian, M. (Eds.) Light Alloys: Metallurgy of the Light Metals/Ian Polmear, 5th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Birru, A.K.; Karunakar, D.B.; Mahapatra, M.M. A Study on hot tearing susceptibility of Al–Cu, Al–Mg, and Al–Zn alloys. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2012, 65, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaumi, H.; Tsuchiya, K. Effects of Mg contents on porosity formation in Al-Mg alloy DC slabs. J. Jpn. Inst. Light Met. 2002, 52, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zolotorevsky, V.S.; Belov, N.A.; Glazoff, M.V. Casting Aluminum Alloys; Elsevier Science: Burlington, VT, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, E.O. The deformation and ageing of mild steel: III Discussion of results. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. B 1951, 64, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petch, N.J.J. The Cleavage Strength of Polycristals. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1953, 174, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, G.; Park, J.; Nam, S.; Shin, S.E.; Shin, J.; Bae, D.; Choi, H. The effect of grain size on the mechanical properties of aluminum. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2015, 60, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Dahle, A.K.; StJohn, D.H. Grain Refinement of Magnesium. In Proceedings of the Magnesium Technology 2000, Nashville, TN, USA, 12–16 March 2000; The Minerals, Metals & Metals Society: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2000; pp. 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Easton, M.; Wang, H.; Grandfield, J.; StJohn, D.; Sweet, E. An analysis of the effect of grain refinement on the hot tearing of aluminium alloys. In Materials Forum; Institute of Materials Engineering Australasia Ltd.: Brisbane, Australia, 2004; pp. 224–229. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, R.S.; Purohit, R.; Das, S. Reviews on the influences of alloying elements on the microstructure and mechanical properties of aluminum alloys and aluminum alloy composites. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2012, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ravi, K.R.; Manivannan, S.; Phanikumar, G.; Murty, B.S.; Sundarraj, S. Influence of Mg on grain refinement of near eutectic Al-Si alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 2028–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohatgi, S.; Tiwari, M.; Rathi, A.; Sharma, A. Role of undercooling and effect of solute particles on grain refinement of aluminium alloys. Indian Foundry J. 2015, 62, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Buraś, J.; Szucki, M.; Piwowarski, G.; Krajewski, W.K.; Krajewski, P.K. Strength properties examination of high zinc aluminium alloys inoculated with Ti addition. China Foundry 2017, 14, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, G.; Backerud, L.; Arnberg, L. Relation between grain size and coherency parameters in aluminium alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1995, 11, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; He, Z.; Jie, W. Model for evaluation of grain sizes of aluminum alloys with grain refinement additions. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2007, 23, 619–622. [Google Scholar]
- StJohn, D.H.; Easton, M.A.; Cao, P.; Qian, M. New approach to analysis of grain refinement. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2007, 20, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, A.; Schmid-Fetzer, R. Growth restriction factor in Al-Si-Mg-Cu alloys. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2012, 27, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StJohn, D.H.; Qian, M.; Easton, M.A.; Cao, P. The interdependence theory: The relationship between grain formation and nucleant selection. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 4907–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, D.G. Grain refining of aluminium and its alloys using inoculants. Int. Mater. Rev. 1989, 34, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, V.M.; Eskin, D.G. A new Al-Zr-Ti master alloy for ultrasonic grain refinement of wrought and foundry aluminum alloys. JOM 2016, 68, 3088–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, B.S.; Kori, S.A.; Chakraborty, M. Grain refinement of aluminium and its alloys by heterogeneous nucleation and alloying. Int. Mater. Rev. 2002, 47, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ėskin, G.I. Ultrasonic Treatment of Light Alloy Melts; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Han, Q.; Zhai, Q. Review of grain refinement methods for as-cast microstructure of magnesium alloy. Chin. Foundry 2009, 6, 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Eskin, D.G.; Katgerman, L. Influence of ultrasonic melt treatment on the formation of primary intermetallics and related grain refinement in aluminum alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 5252–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, N.Q.; Puga, H.; Barbosa, J.; Pinto, A.M.P. Grain refinement of Al-Mg-Sc alloy by ultrasonic treatment. Met. Mater. Int. 2015, 21, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.P.; Li, X.Q.; Zhang, M. Investigation on the mechanism of grain refinement in aluminum alloy solidified under ultrasonic vibration. Met. Mater. Int. 2015, 21, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, E.Q.; Prasad, A.; Dargusch, M.; StJohn, D.H. Grain Refinement of Al-Si Hypoeutectic Alloys by Al3Ti1B Master Alloy and Ultrasonic Treatment. In Shape Casting: 6th International Symposium; Murat, T., Mark, J., Glenn, B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Dargusch, M.S.; Qian, M.; Eskin, D.G.; StJohn, D.H. The role of ultrasonic treatment in refining the as-cast grain structure during the solidification of an Al–2Cu alloy. J. Cryst. Growth 2014, 408, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Momono, T.; Fu, Y.; Jia, Z.; Tayu, Y. Effect of ultrasonic stirring on temperature distribution and grain refinement in Al-1.65%Si alloy melt. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2007, 17, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskin, D.G. Ultrasonic processing of molten and solidifying aluminium alloys: Overview and outlook. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Croaker, P.; Dargusch, M.; McGuckin, D.; StJohn, D. Simulation of convective flow and thermal conditions during ultrasonic treatment of an Al-2Cu alloy. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2017, 134, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Dargusch, M.S.; Eskin, D.G.; StJohn, D.H. Identifying the stages during ultrasonic processing that reduce the grain size of aluminum with added Al3Ti1B master alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, W.; Tsunekawa, Y.; Okumiya, M. Effect of ultrasonic melt treatment on microstructure of A356 aluminium cast alloys. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2008, 21, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhingole, P.P.; Chaudhari, G.P. Synergy of nano carbon black inoculation and high intensity ultrasonic processing in cast magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 556, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, A.; Qian, M.; Davis, B.; Wilks, T.; StJohn, D.H. Potency of high-intensity ultrasonic treatment for grain refinement of magnesium alloys. Scr. Mater. 2008, 59, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E112-10, Standard Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size, ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA. 2010. Available online: http://www.astm.org/cgi-bin/resolver.cgi?E112 (accessed on 13 October 2018).
- StJohn, D.H.; Easton, M.A.; Qian, M.; Taylor, J.A. Grain refinement of magnesium alloys: A review of recent research, theoretical developments, and their application. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 2935–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Hari-Babu, N.; Scamans, G.M.; Fan, Z. Influence of intensive melt shearing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of an Al-Mg alloy with high added impurity content. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiwata, Y.; Komarov, S.; Takeda, Y. Investigation of Acoustic Streaming in Aluminum Melts Exposed to High-Intensity Ultrasonic Irradiation. In ICAA13 Pittsburgh; Hasso, W., Anthony, D.R., William, A.C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 183–188. [Google Scholar]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mills, K.; Wang, G.; StJohn, D.; Dargusch, M. Ultrasonic Processing of Aluminum–Magnesium Alloys. Materials 2018, 11, 1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101994
Mills K, Wang G, StJohn D, Dargusch M. Ultrasonic Processing of Aluminum–Magnesium Alloys. Materials. 2018; 11(10):1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101994
Chicago/Turabian StyleMills, Kurt, Gui Wang, David StJohn, and Matthew Dargusch. 2018. "Ultrasonic Processing of Aluminum–Magnesium Alloys" Materials 11, no. 10: 1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101994
APA StyleMills, K., Wang, G., StJohn, D., & Dargusch, M. (2018). Ultrasonic Processing of Aluminum–Magnesium Alloys. Materials, 11(10), 1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101994