Investigation on the Effect of a Pre-Center Drill Hole and Tool Material on Thrust Force, Surface Roughness, and Cylindricity in the Drilling of Al7075
Abstract
:1. Introduction
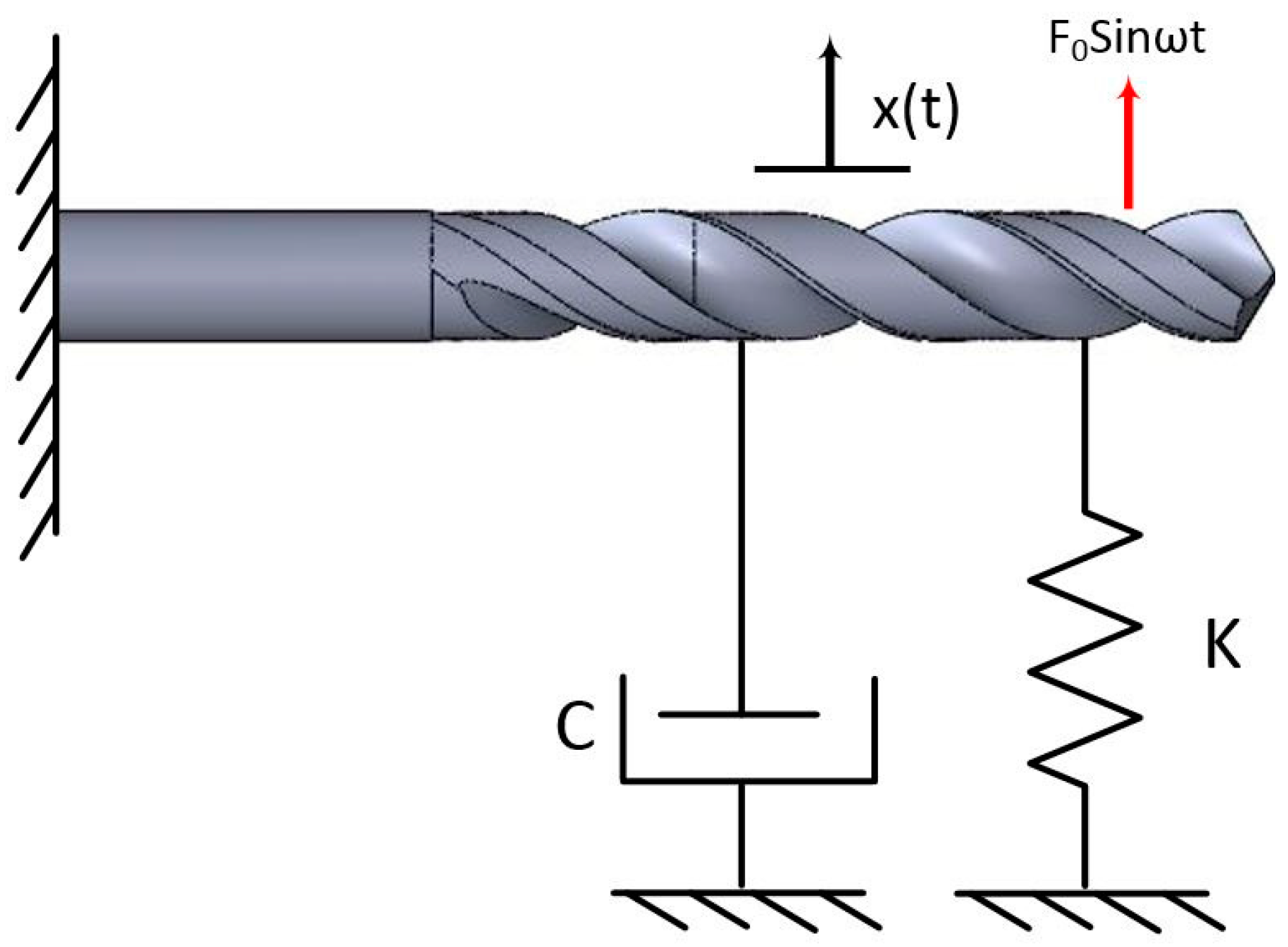
2. Material and Methods
3. Result and Discussion
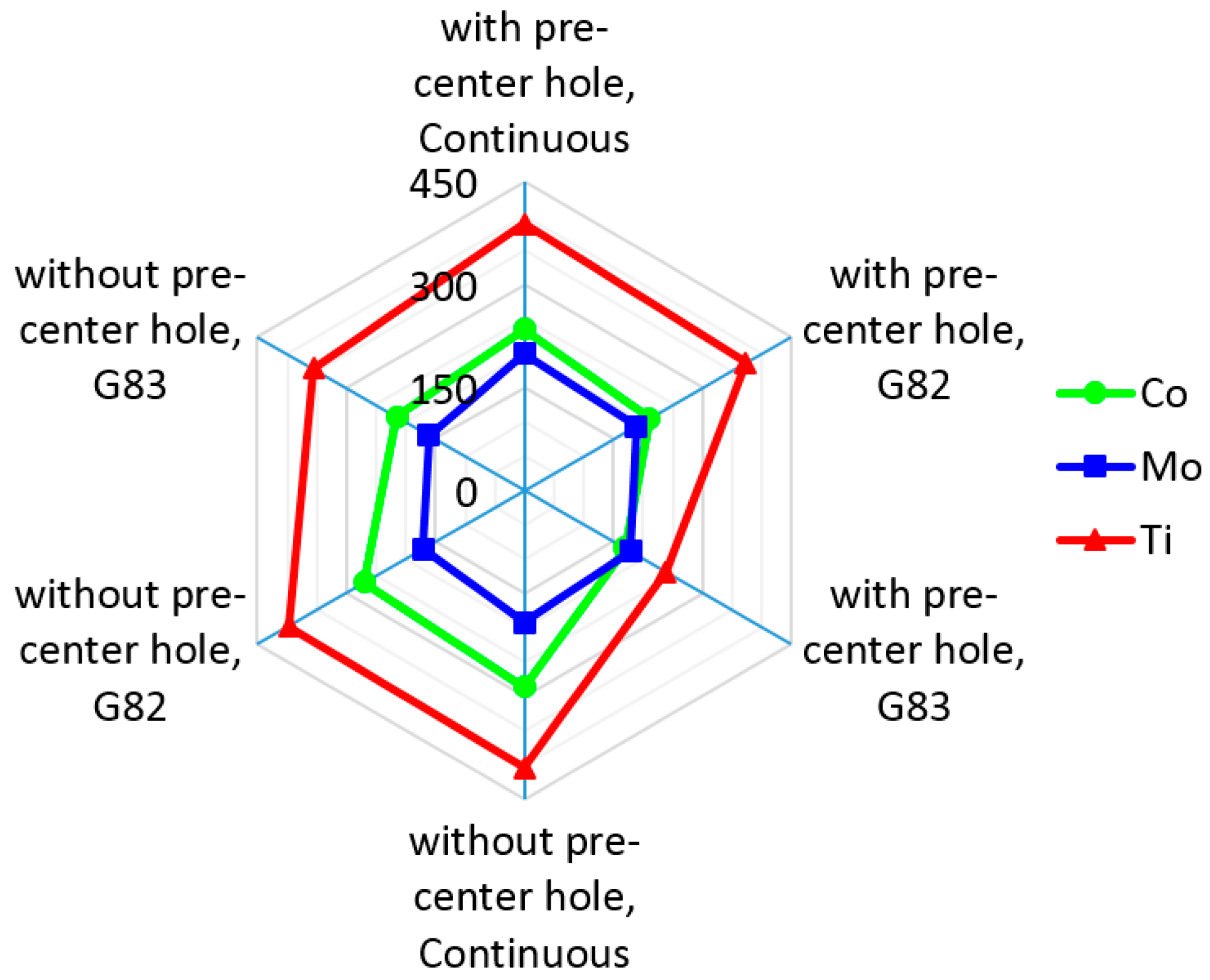
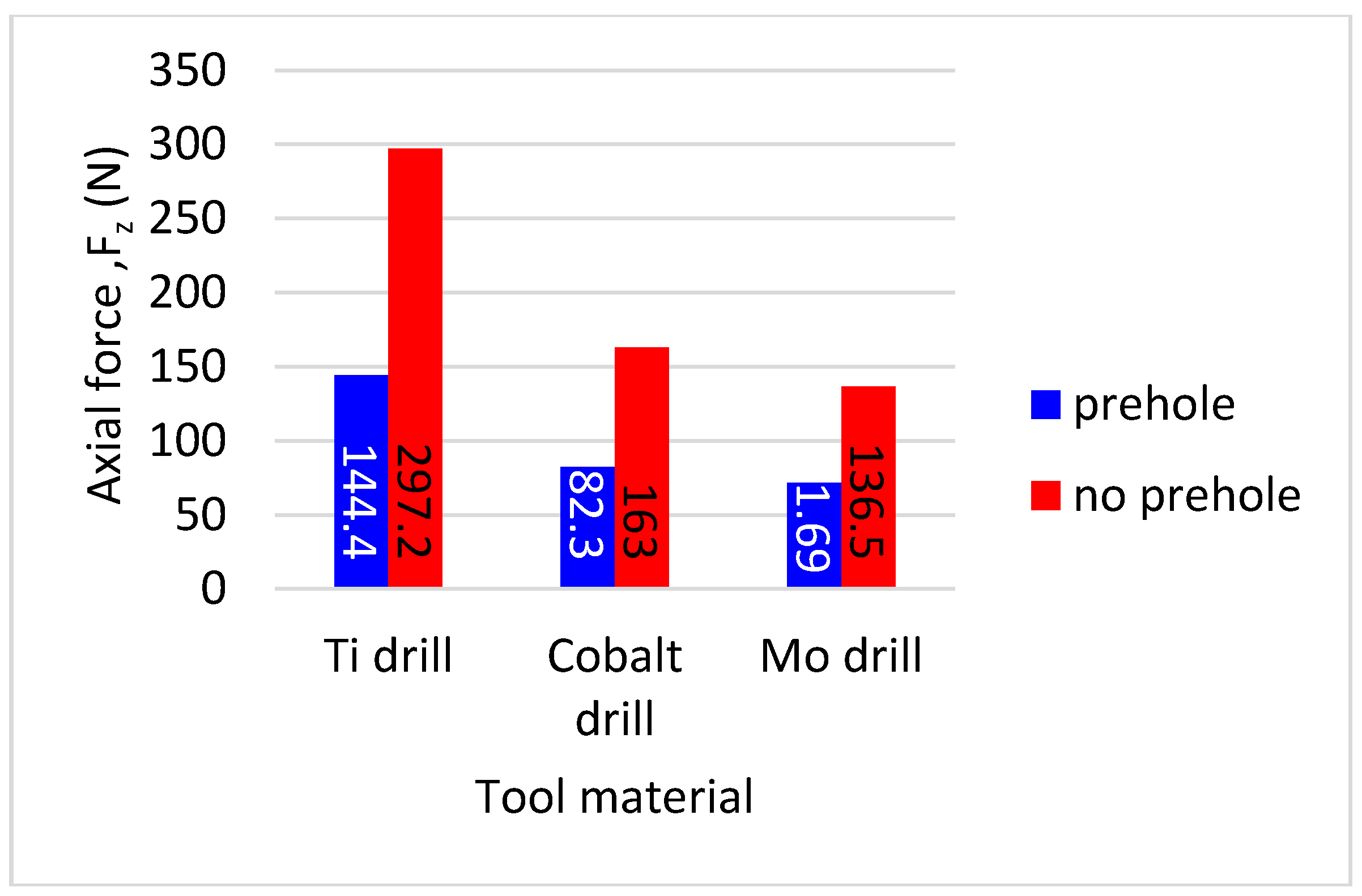
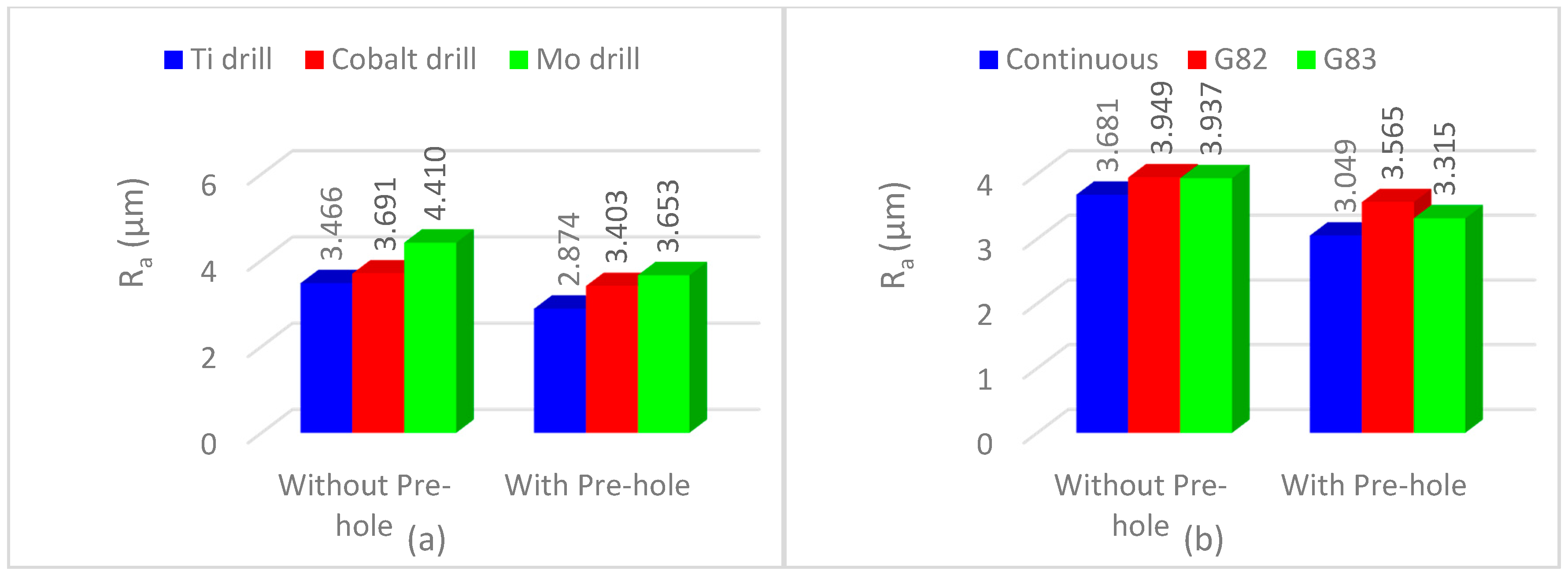
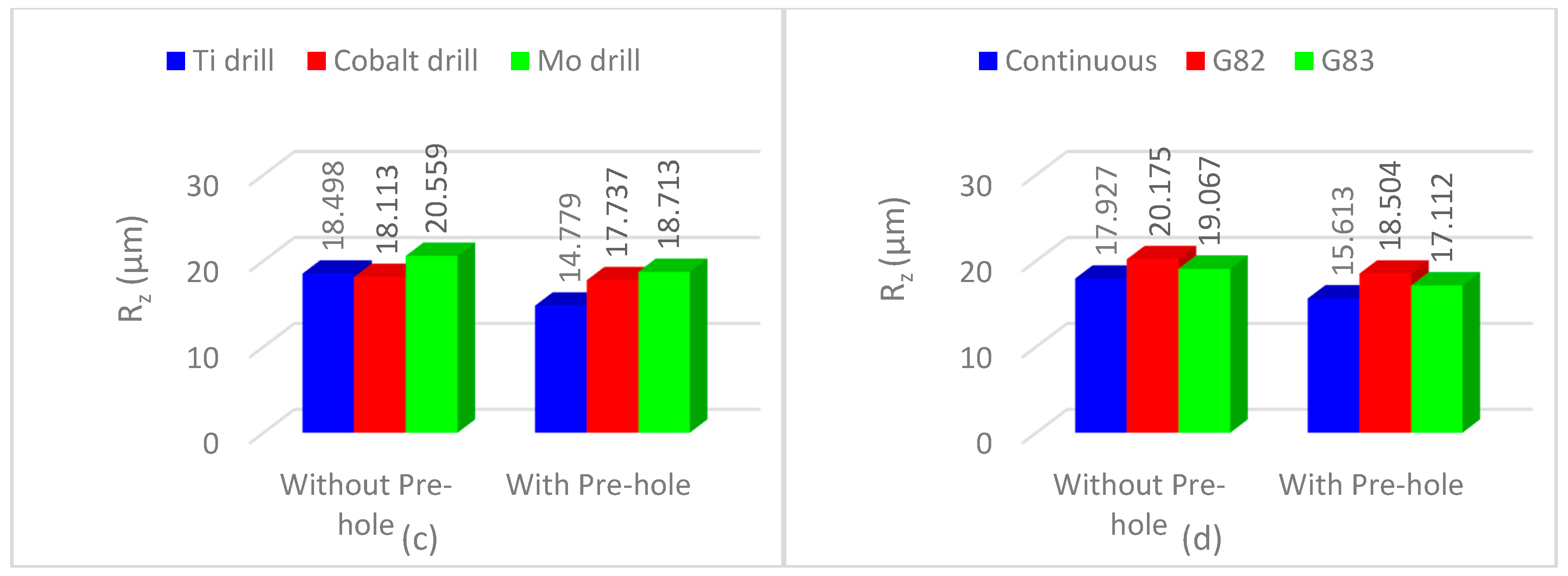
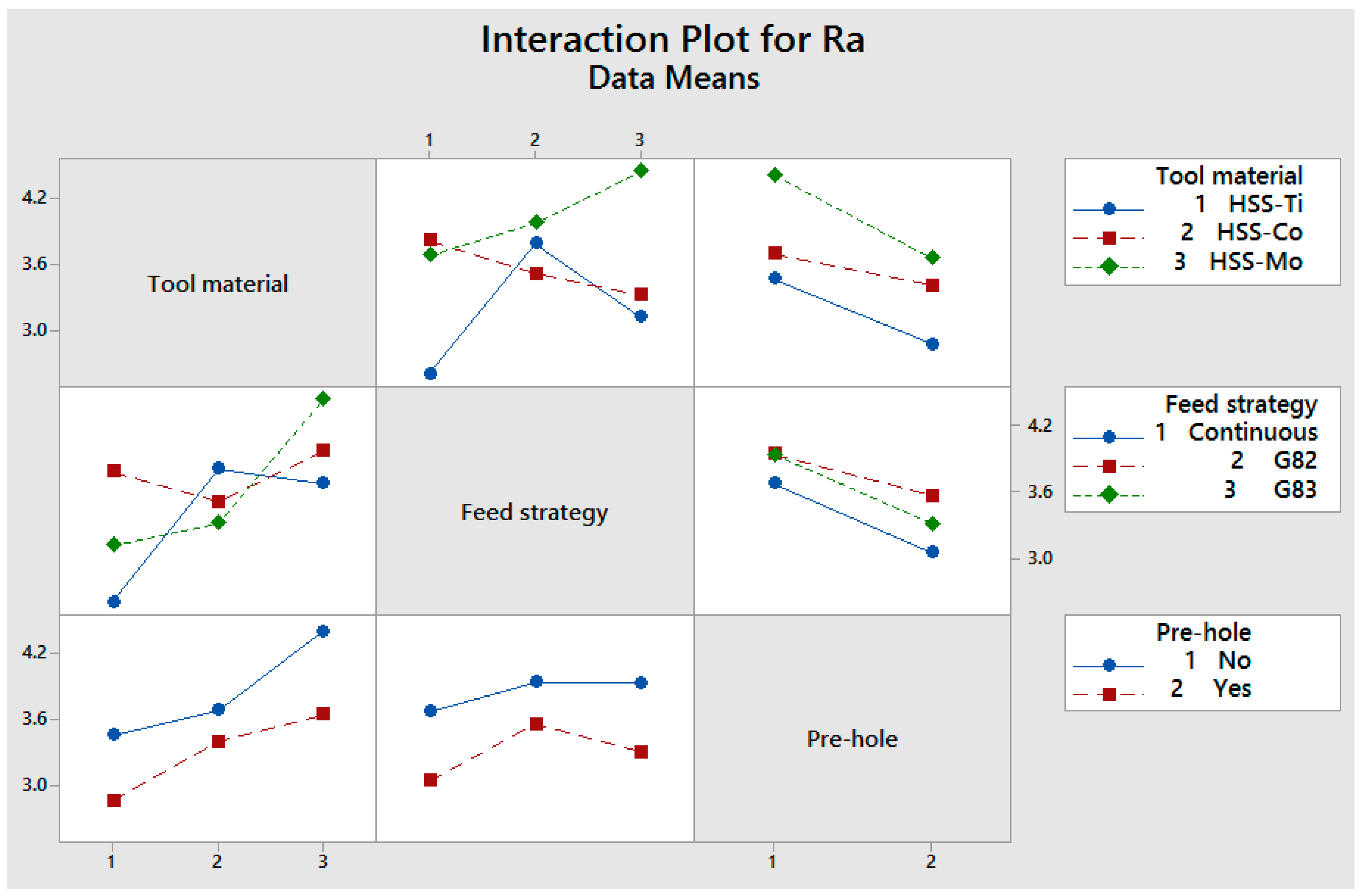
3.1. Thrust Force and Surface Roughness
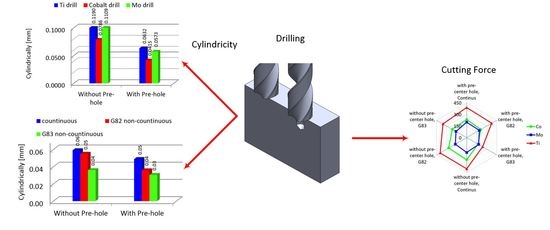
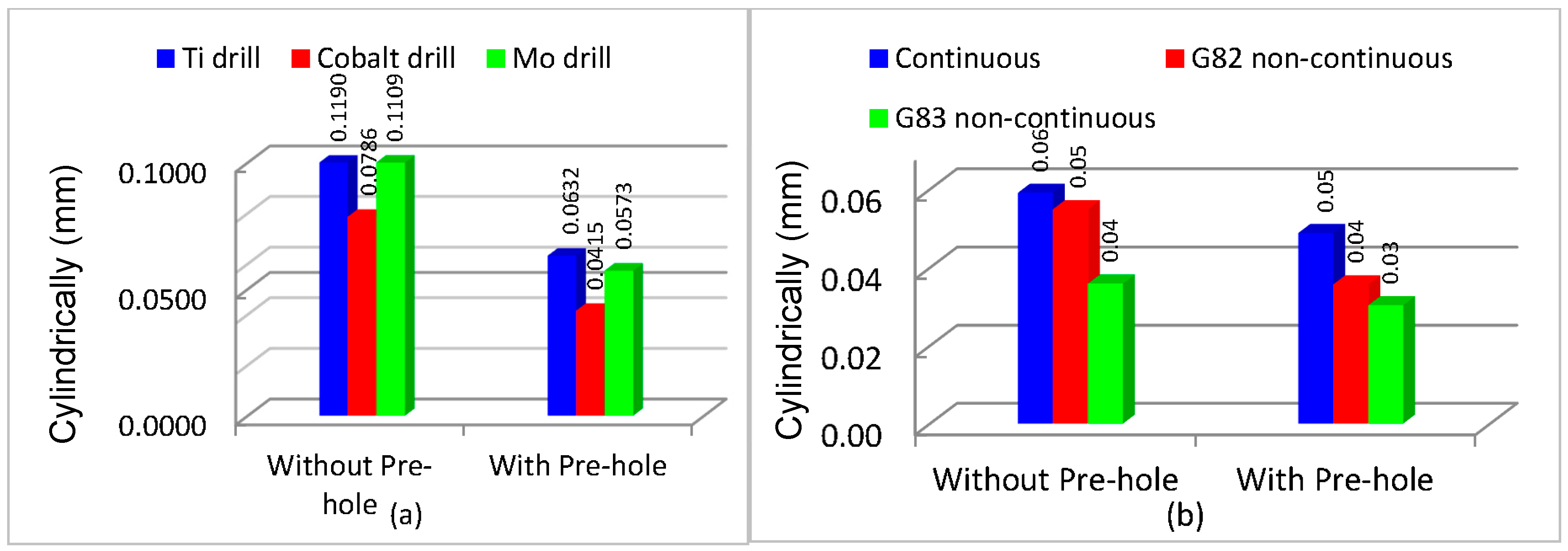
3.2. Geometrical Dimension and Tolerance
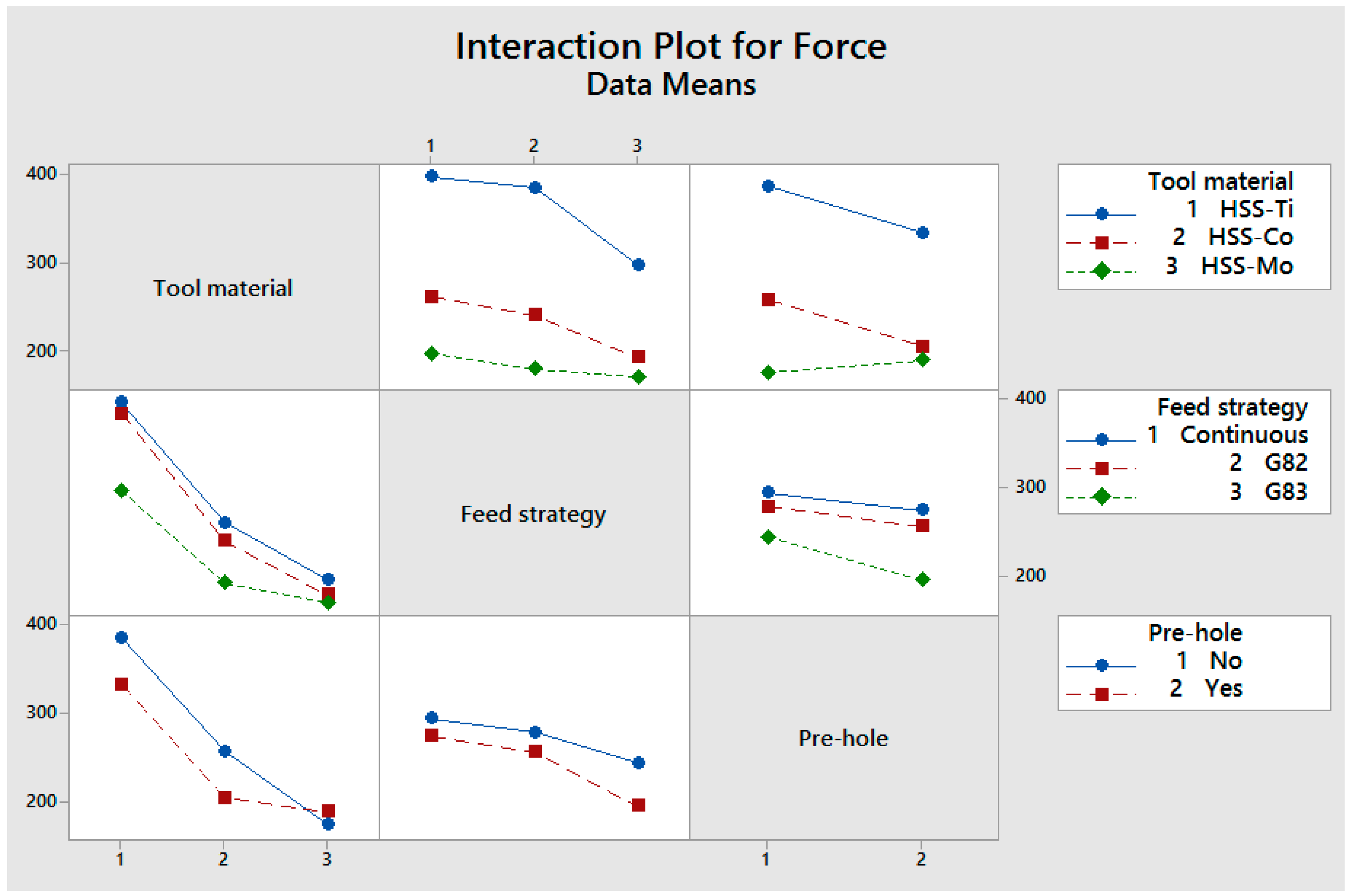
4. The Interaction of Cutting Parameters on Cutting Forces
5. Conclusions
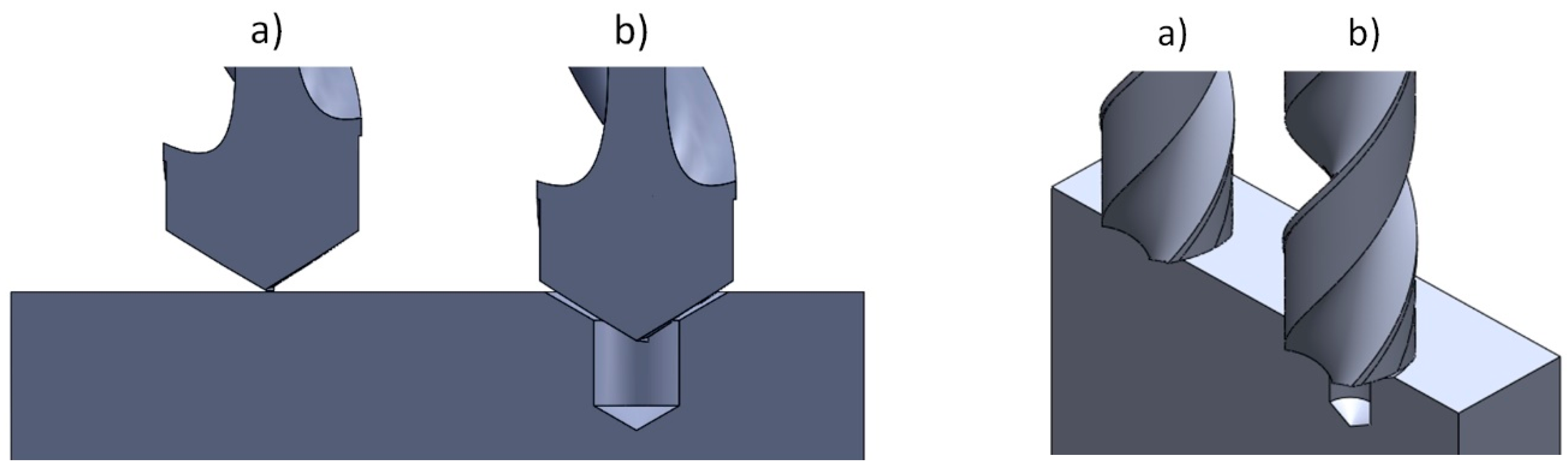
- A pre-center drill hole reduces the engagement force, whilst no effect was observed for the average thrust force. This is associated with the difference in material removal rate in each process.
- The best cutting strategy was non-continuous (G83) with full reciprocating movement that reduced the mean value of the thrust force, tool wear, and cylindricity. The effect of cutting edges in subsequent machining passes using this strategy, however, increases surface roughness.
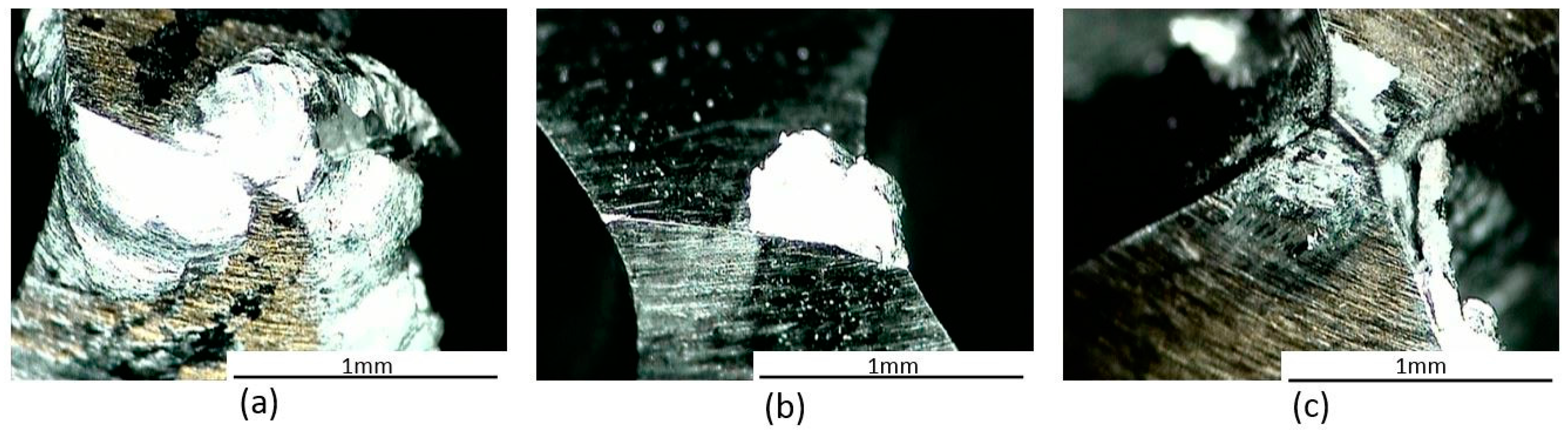
- Using HSS-Mo reduces the maximum value of cutting forces, which is reliant on lower friction coefficients, better surface preparation, and a lower tendency to form built-up edges.
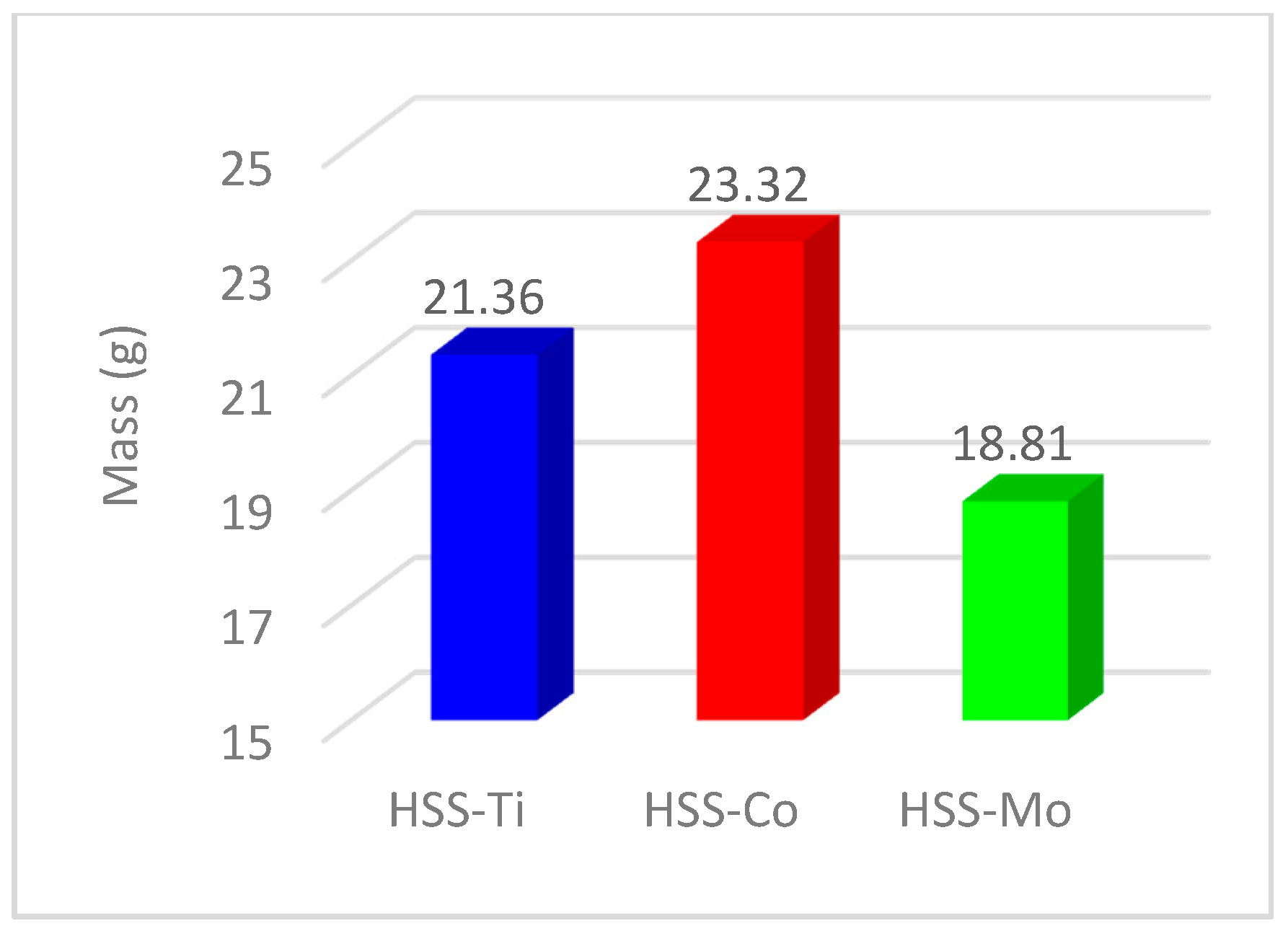
- Cylindricity was found to be a direct function of temperature and using a non-continuous drilling strategy results in better cylindricity and lower dimensional deviations. Indeed, the higher mass for HSS-Co cutters leads to a lower damping frequency and a subsequent reduction in the value of cylindricity.
- Performing these experiments leads to an improvement in dimensional tolerances without interfering with the cost of production.
- By using a pre-center drill hole, manufacturing lead-time and subsequently production cost can be saved.
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giasin, K.; Ayvar-Soberanis, S. Evaluation of Workpiece Temperature during Drilling of GLARE Fiber Metal Laminates Using Infrared Techniques: Effect of Cutting Parameters, Fiber Orientation and Spray Mist Application. Materials 2016, 9, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramulu, M.; Spaulding, M. Drilling of Hybrid Titanium Composite Laminate (HTCL) with Electrical Discharge Machining. Materials 2016, 9, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezende, B.; Silveira, M.L.; Vieira, L.M.G.; Abrão, A.M.; Faria, P.E.; Rubio, J.C.C. Investigation on the Effect of Drill Geometry and Pilot Holes on Thrust Force and Burr Height When Drilling an Aluminium/PE Sandwich Material. Materials 2016, 9, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.; Kim, H.Y.; Jeon, J.W.; Chang, W.S.; Cho, S.-H. Vibration-Assisted Femtosecond Laser Drilling with Controllable Taper Angles for AMOLED Fine Metal Mask Fabrication. Materials 2017, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, M.; Ullah, A.S.; Anwar, S. Drilling High Precision Holes in Ti6Al4V Using Rotary Ultrasonic Machining and Uncertainties Underlying Cutting Force, Tool Wear, and Production Inaccuracies. Materials 2017, 10, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klocke, F.; Krieg, T. Coated tools for metal cutting–features and applications. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 1999, 48, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.; Cotterell, M. Minimal lubrication machining of aluminium alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 120, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.; Hocheng, H. The effect of chisel length and associated pilot hole on delamination when drilling composite materials. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2003, 43, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paro, J.; Gustafsson, T.; Koskinen, J. Drilling of X2CrNi 19 11 stainless steel with hiped NiTi coating. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 150, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkal, M.; Shih, A.J.; McSpadden, S.B.; Scattergood, R.O. Thrust force, torque, and tool wear in drilling the bulk metallic glass. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astakhov, V.P.; Galitsky, V.V. Tool life testing in gundrilling: An application of the group method of data handling (GMDH). Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagci, E.; Ozcelik, B. Analysis of temperature changes on the twist drill under different drilling conditions based on Taguchi method during dry drilling of Al 7075-T651. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 29, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, F.; Ni, J.; Stephenson, D. Chip thickening in deep-hole drilling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 1500–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocheng, H.; Tsao, C. Effects of special drill bits on drilling-induced delamination of composite materials. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 1403–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, M.-B.; Xirouchakis, P. Mechanical load distribution along the main cutting edges in drilling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşkesen, A.; Kütükde, K. Experimental investigation and multi-objective analysis on drilling of boron carbide reinforced metal matrix composites using grey relational analysis. Measurement 2014, 47, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olovsjö, S.; Wretland, A.; Sjöberg, G. The effect of grain size and hardness of wrought Alloy 718 on the wear of cemented carbide tools. Wear 2010, 268, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Lemoine, P.; Keys, D.; Doyle, P.; Malinov, S.; Zhao, Q.; Qin, X.; Jin, Y. Hole-making processes and their impacts on the microstructure and fatigue response of aircraft alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, X.; Geng, D. Study on rotary ultrasonic-assisted drilling of titanium alloys (Ti6Al4V) using 8-facet drill under no cooling condition. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 90, 3249–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, R.; Henerichs, M.; Harsch, D.; Kuster, F.; Wegener, K. Optimised approach for characterisation of cutting edge micro-geometry in drilling carbon fibre reinforced plastics(CFRP). Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 90, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouam, J.; Djebara, A.; Songmene, V. Experimental investigation on the effect of pre-holes on drilling process performance of aluminum alloys: Forces, surface finish and dust emission. Adv. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2014, 3, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieslony, P.; Cichosz, P.; Krolczyk, G.M.; Legutko, S.; Smyczek, D.; Kolodziej, M. Experimental studies of the cutting force and surface morphology of explosively clad Ti–steel plates. Measurement 2016, 78, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieslony, P.; Krolczyk, G.M.; Zak, K.; Maruda, R.W.; Legutko, S. Comparative assessment of the mechanical and electromagnetic surfaces of explosively clad Ti–steel plates after drilling process. Precis. Eng. 2017, 47, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percin, M.; Aslantas, K.; Ucun, I.; Kaynak, Y.; Çicek, A. Micro-drilling of Ti–6Al–4V alloy: The effects of cooling/lubricating. Precis. Eng. 2016, 45, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzosa, F.; de Agustina, B.; Rubio, E. Tool Selection in Drilling of Magnesium UNSM11917 Pieces under Dry and MQL Conditions Based on Surface Roughness. Procedia Eng. 2017, 184, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azghandi, B.V.; Kadivar, M.; Razfar, M. An Experimental Study on Cutting Forces in Ultrasonic Assisted Drilling. Procedia CIRP 2016, 46, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Mahapatra, S.S.; Abhishek, K. Simulation and optimization of machining parameters in drilling of titanium alloys. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2016, 62, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaaz, T.S.; Sulong, A.B.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Nassir, M.H.; Al-Amiery, A.A. Optimizing Injection Molding Parameters of Different Halloysites Type-Reinforced Thermoplastic Polyurethane Nanocomposites via Taguchi Complemented with ANOVA. Materials 2016, 9, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-J.; Chang, S.-N.; Tang, C.-W. Application of the Taguchi Method for Optimizing the Process Parameters of Producing Lightweight Aggregates by Incorporating Tile Grinding Sludge with Reservoir Sediments. Materials 2017, 10, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrão, A.M.; Rubio, J.C.C.; Faria, P.E.; Davim, J.P. The effect of cutting tool geometry on thrust force and delamination when drilling glass fibre reinforced plastic composite. Mater. Des. 2008, 29, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucca, D.A.; Seo, Y.W.; Komanduri, R. Effect of Tool Edge Geometry on Energy Dissipation in Ultraprecision Machining. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 1993, 42, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglam, H.; Yaldiz, S.; Unsacar, F. The effect of tool geometry and cutting speed on main cutting force and tool tip temperature. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, V. Cutting edge preparation. In Proceedings of the 9th IFR International Conference, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 24–28 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Özel, T. Modeling of hard part machining: Effect of insert edge preparation in CBN cutting tools. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 141, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özel, T.; Hsu, T.-K.; Zeren, E. Effects of cutting edge geometry, workpiece hardness, feed rate and cutting speed on surface roughness and forces in finish turning of hardened AISI H13 steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2005, 25, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davim, J.P. Machining of Titanium Alloys; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ezugwu, E.; Wang, Z. Titanium alloys and their machinability—A review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1997, 68, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasani, A.M.; Goldberg, M.; Doeven, E.H.; Littlefair, G. Titanium in Biomedical Applications—Properties and Fabrication: A Review. J. Biomater. Tissue Eng. 2015, 5, 593–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasani, A.M.; Gibson, L.; Goldberg, M.; Nornani, J.; Littlefair, G. Machinability of Metallic and Ceramic Biomaterials: A review. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2016, 8, 1491–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, T.L.; Donalson, R. Predicting high-speed machining dynamics by substructure analysis. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2000, 49, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.A.; Kennedy, M.D. Tool point frequency response prediction for high-speed machining by RCSA. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2001, 123, 700–707. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, T.; Davies, M.A.; Snyder, J. Improving high-speed machining material removal rates by rapid dynamic analysis. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2001, 50, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, T.; Burns, T. Receptance Coupling for High-speed machining dynamics prediction. In Proceedings of the 21st International Modal Analysis Conference, Kissimmee, FL, USA, 3–6 February 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kivanc, E.; Budak, E. Structural modeling of end mills for form error and stability analysis. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2004, 44, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, G.S.; Schmitz, T. An improved RCSA model for tool point frequency response prediction. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Modal Analysis Conference, Lille, France, 4–6 November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, M.; Beauchamp, Y.; Youssef, Y.A. Effect of Lathe Boring Cutting Parameters on Surface Roughness Ani Tool Dynamic Forces. In Proceedings of the 13th Symposium on Engineering Applications of Mechanics: Manufacturing Science and Engineering, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 7–9 May 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Patwari, M.A.U.; Bashar, K.; Habib, M.A.; Alam, M. Development of a Passive Damping Tool Holder for the Improvement of Surace Roughness in Turning Operation of Stainless Steel. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D. Deep hole drill with positive taper and principle for elimination of drill deviation using cutting fluid. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 89, 3195–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
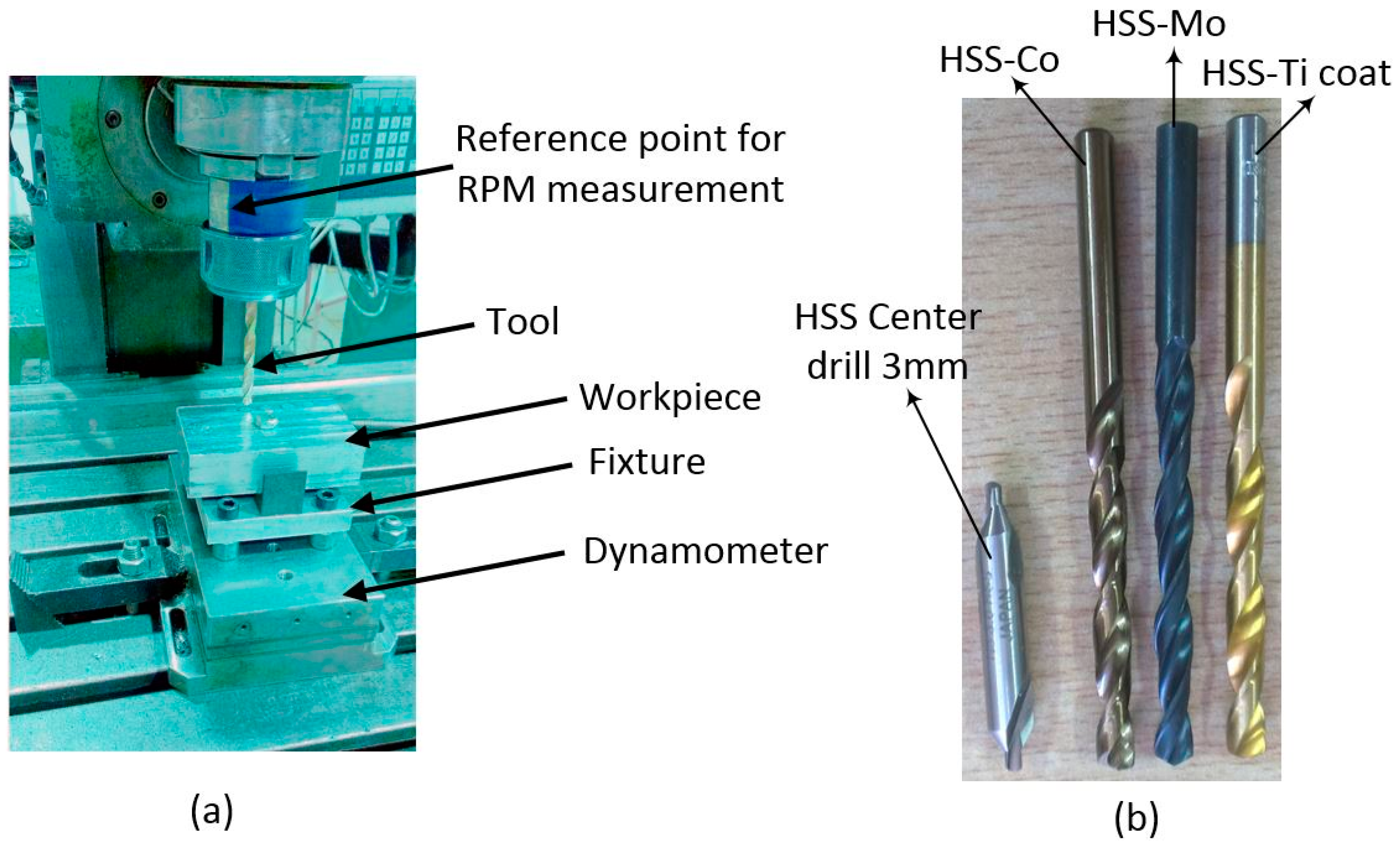
| Alloy | Al% | Zn% | Mg% | Cu% | Fe% | Mn% | Si% | Cr% | Ti% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % Weight | Base | 5.5 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 0.35 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Parameter | HSS-Ti | HSS-Co | HSS-Mo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tool diameter (mm) | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| Tool length (mm) | 109.45 | 109.45 | 109.45 |
| Helix angle (°) | 65 | 65 | 65 |
| Helix length (mm) | 72.61 | 72.61 | 72.61 |
| Chisel length (mm) | 1.19 | 0.31 | 1.23 |
| Rake angle (°) | 8.5 | 5.6 | 9.5 |
| Cheap angle (°) | 58.85 | 56 | 63 |
| Head angle (°) | 123 | 137 | 114 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Cutting speed | 25 m/min (1137 RPM) |
| Feed rate | 50 mm/min (0.44 mm/rev) |
| Tool overhang length | 73.52 mm |
| Test Number | Feed Rate Mode | Tool Material | Pre-Center Drill Hole |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Continuous | HSS-Ti coat | No |
| 2 | G82 | HSS-Ti coat | No |
| 3 | G83 | HSS-Ti coat | No |
| 4 | Continuous | HSS-Co | No |
| 5 | G82 | HSS-Co | No |
| 6 | G83 | HSS-Co | No |
| 7 | Continuous | HSS-Mo | No |
| 8 | G82 | HSS-Mo | No |
| 9 | G83 | HSS-Mo | No |
| 10 | Continuous | HSS-Ti coat | Yes |
| 11 | G82 | HSS-Ti coat | Yes |
| 12 | G83 | HSS-Ti coat | Yes |
| 13 | Continuous | HSS-Co | Yes |
| 14 | G82 | HSS-Co | Yes |
| 15 | G83 | HSS-Co | Yes |
| 16 | Continuous | HSS-Mo | Yes |
| 17 | G82 | HSS-Mo | Yes |
| 18 | G83 | HSS-Mo | Yes |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghasemi, A.H.; Khorasani, A.M.; Gibson, I. Investigation on the Effect of a Pre-Center Drill Hole and Tool Material on Thrust Force, Surface Roughness, and Cylindricity in the Drilling of Al7075. Materials 2018, 11, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010140
Ghasemi AH, Khorasani AM, Gibson I. Investigation on the Effect of a Pre-Center Drill Hole and Tool Material on Thrust Force, Surface Roughness, and Cylindricity in the Drilling of Al7075. Materials. 2018; 11(1):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010140
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhasemi, Amir Hossein, Amir Mahyar Khorasani, and Ian Gibson. 2018. "Investigation on the Effect of a Pre-Center Drill Hole and Tool Material on Thrust Force, Surface Roughness, and Cylindricity in the Drilling of Al7075" Materials 11, no. 1: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010140
APA StyleGhasemi, A. H., Khorasani, A. M., & Gibson, I. (2018). Investigation on the Effect of a Pre-Center Drill Hole and Tool Material on Thrust Force, Surface Roughness, and Cylindricity in the Drilling of Al7075. Materials, 11(1), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010140