Achieving High Strength and Good Ductility in As-Extruded Mg–Gd–Y–Zn Alloys by Ce Micro-Alloying
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
3. Results
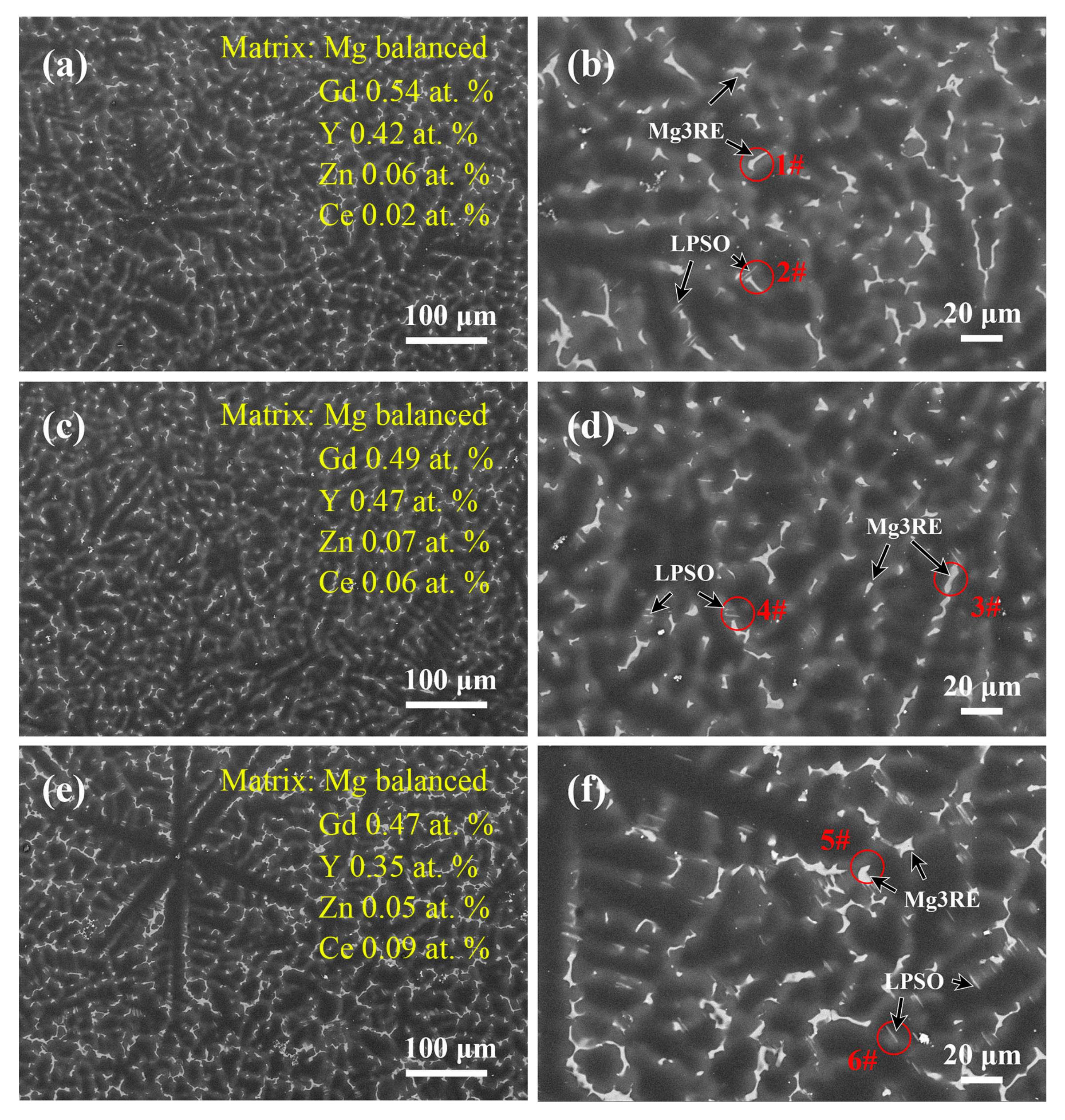
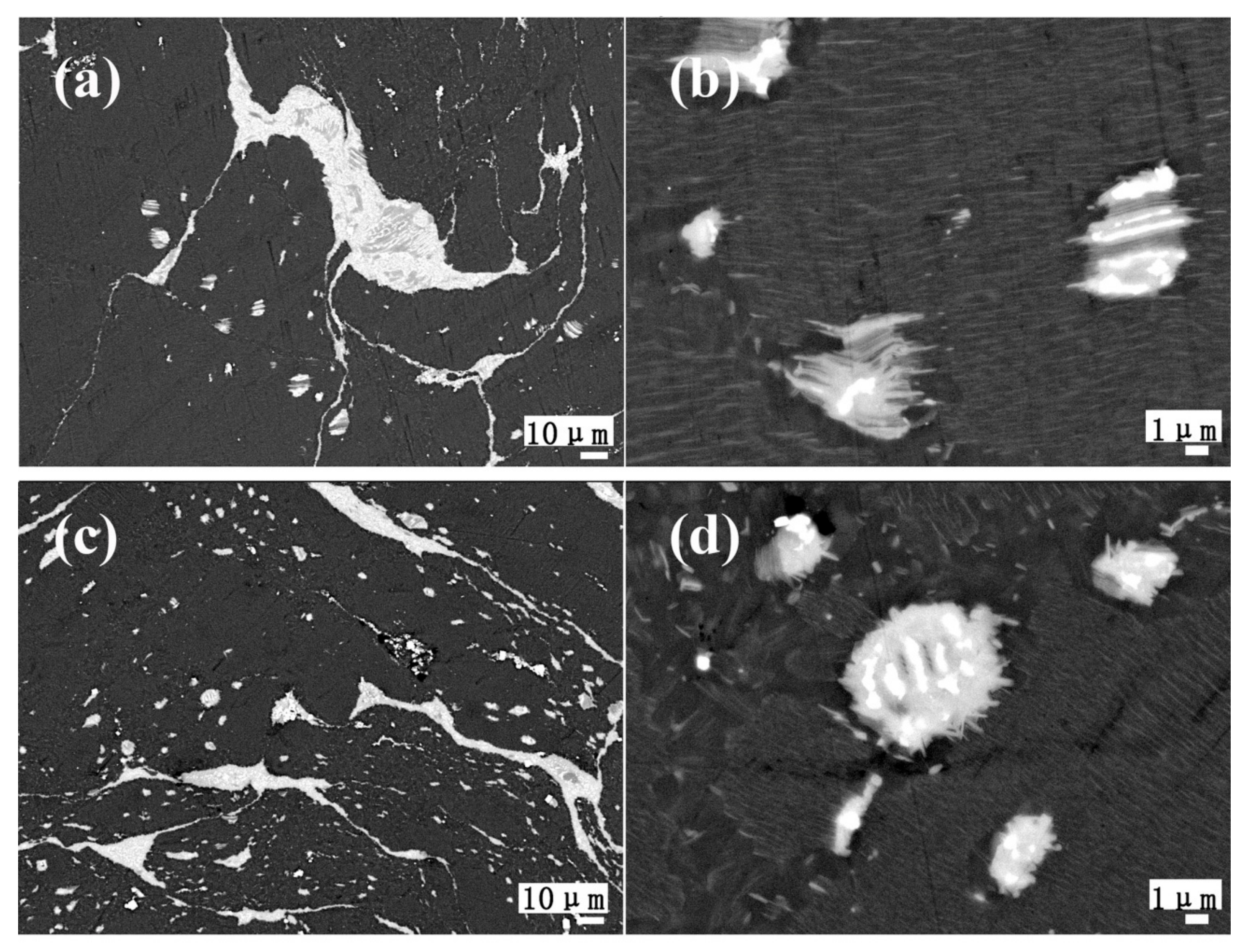
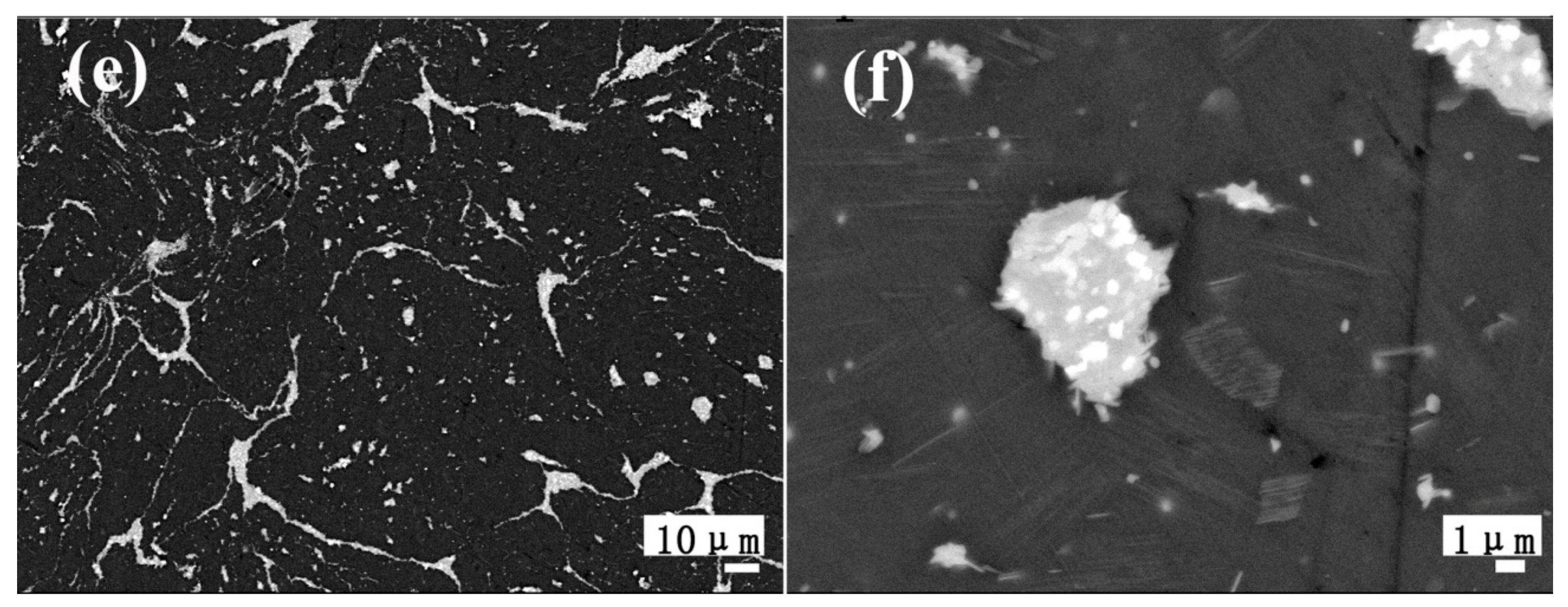
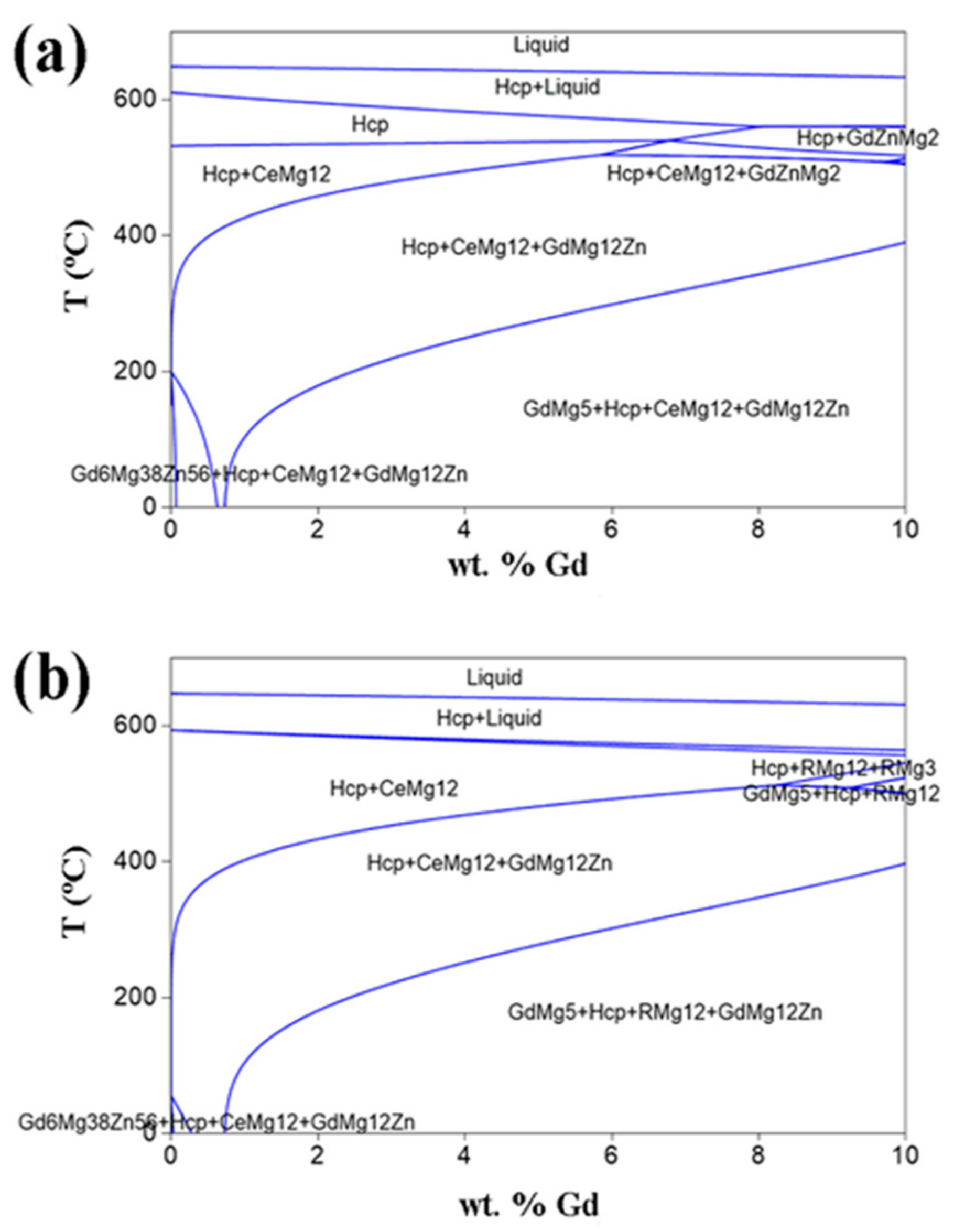
3.1. Microstructures of the As-Cast Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Ce Alloys
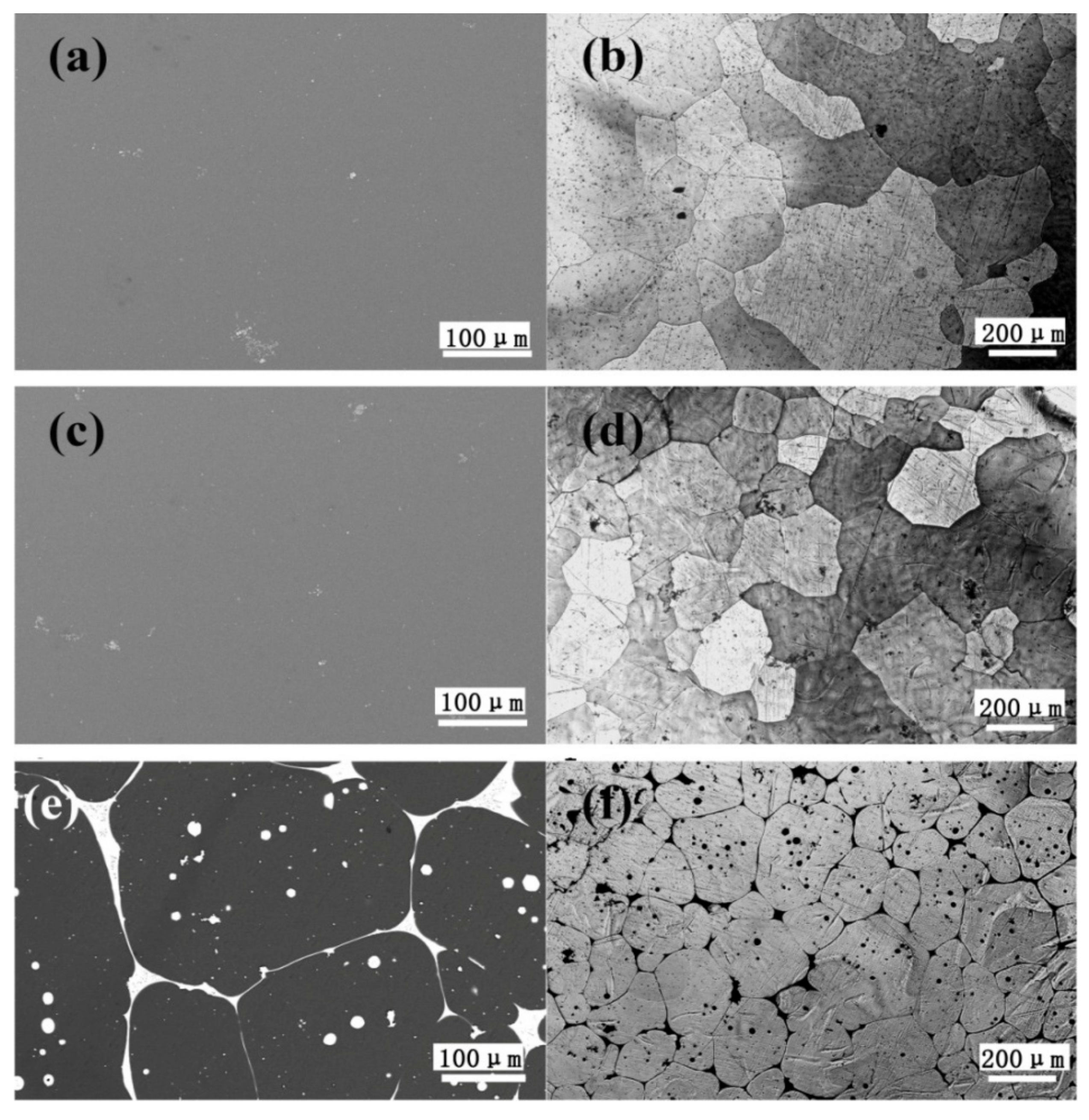
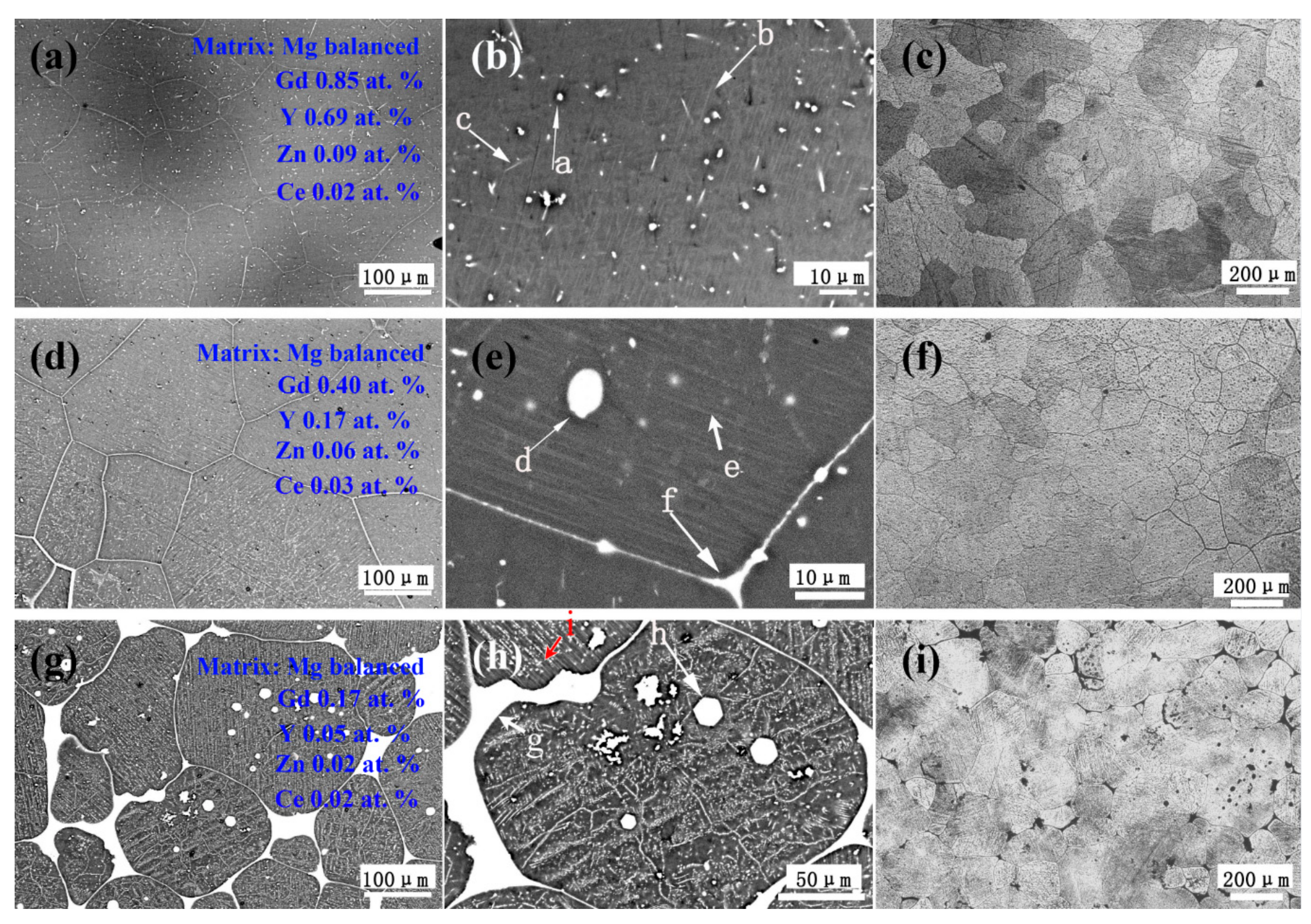
3.2. Microstructures of the As-Homogenized and As-Aged Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Ce Alloys
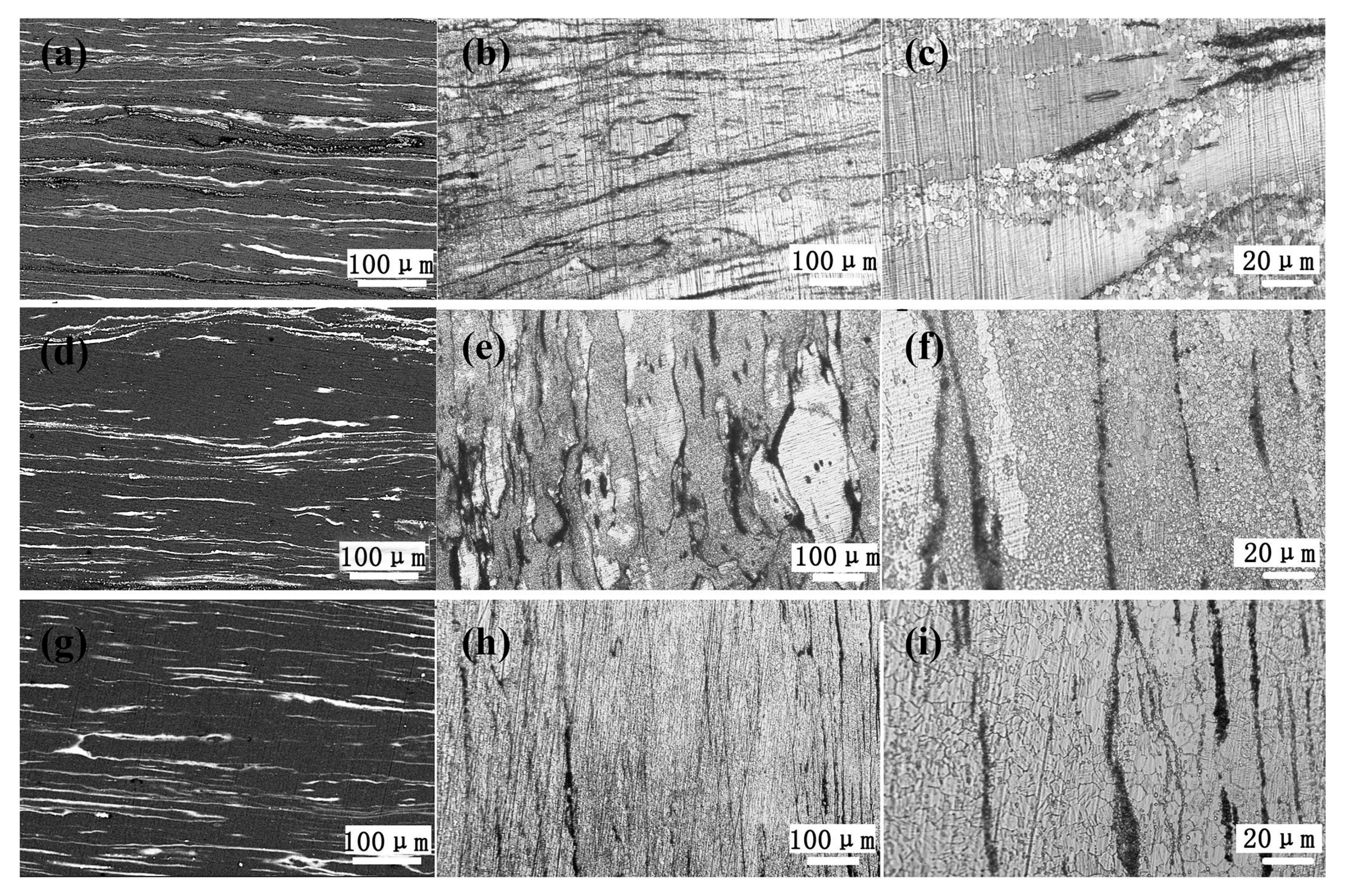
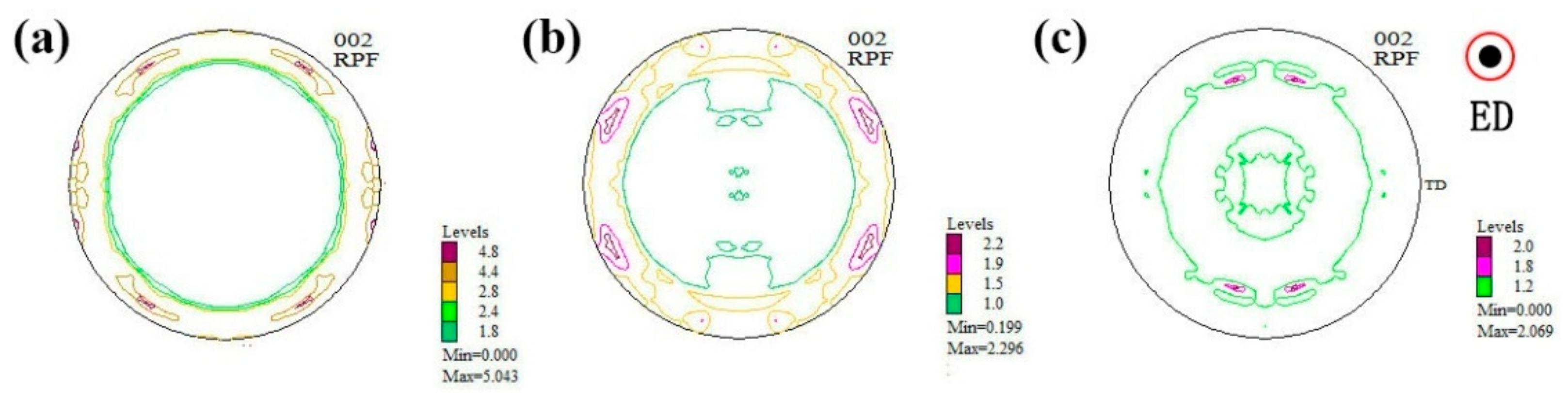
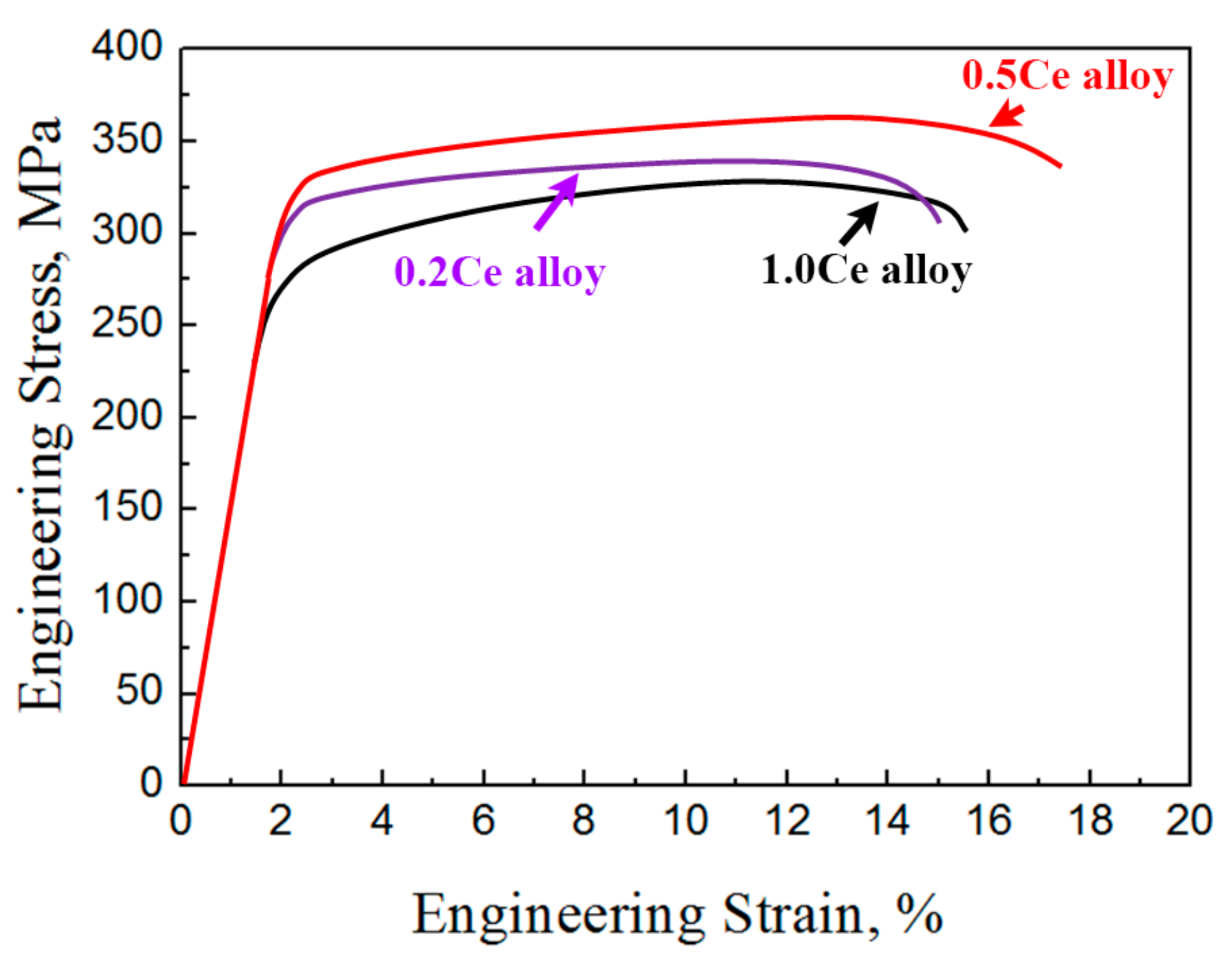
3.3. Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of the As-Extruded Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Ce Alloys
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Ce addition promotes the formation of LPSO phases in the as-cast Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Ce alloys. The high content of Ce addition reduces the maximum solubility of Gd and Y in the Mg matrix, and leads to a higher density of Mg12Ce phases in the as-homogenized alloys;
- (2)
- the main second phases in the as-extruded alloys are bulk micron-sized LPSO phases, nano-sized stripe LPSO phases and broken Mg12Ce and Mg5RE phases. The recrystallized grain size of the as-extruded 0.2Ce, 0.5Ce and 1.0Ce alloys can be refined to ~4.3 μm, ~1.0 μm and ~8.4 μm, respectively. This can be attributed to the synthesized effect of the driving force of the micron phases and the dragging effect of the nano phases on dynamic recrystallization;
- (3)
- with the increasing content of Ce, tension, strength and ductility of as-extruded samples would firstly increase and then decrease. The as-extruded 0.5Ce alloy exhibits optimal mechanical properties.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- You, S.; Huang, Y.; Kainer, K.U.; Hort, N. Recent research and developments on wrought magnesium alloys. J. Magnes. Alloys 2017, 5, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Jin, B.; Lu, Y.; Lu, J. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of a smated Mg alloy under in situ sem tensile testing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Fu, H.; Ren, Y.; Huang, Q.; Gao, Z.; She, J.; Qin, G.; Yang, Q.; Song, B.; Pan, F. Effect of Cu/Zn on microstructure and mechanical properties of extruded Mg–Sn alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Fu, H.; Song, B.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, C.; Qin, G. Formation of profuse dislocations in deformed calcium-containing magnesium alloys. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2016, 96, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Ren, Y.; Fu, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Meng, X.; Qin, G. Recent developments in rare-earth free wrought magnesium alloys having high strength: A review. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 663, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Qin, G.; Xu, M.; Fu, H.; Ren, Y.; Pan, F.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Q.; She, J.; et al. Enhancing mechanical properties of Mg–Sn alloys by combining addition of Ca and Zn. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Tang, A.; Ma, S.; Pan, H.; Song, B.; Gao, Z.; Rashad, M.; Pan, F. Enhancing thermal conductivity of Mg–Sn alloy sheet by cold rolling and aging. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 2356–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, M.R.; Nave, M.D.; Bettles, C.J. Deformation microstructures and textures of some cold rolled mg alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 386, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, M.; Gandikota, I.; Rais-Rohani, M.; Motoyama, K. Design of lightweight magnesium car body structure under crash and vibration constraints. J. Magnes. Alloys 2014, 2, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Du, Z.; Li, Y.; Ma, M.; Shi, G. Dynamic precipitation during multi-axial forging of an Mg–7Gd–5Y–1Nd–0.5Zr alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys 2013, 1, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Peng, J.; Peng, Y.; Tang, A. The effect of addition of Nd and Ce on the microstructure and mechanical properties of ZM21 Mg alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys 2013, 1, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Gan, W.; Mendis, C.L.; Zhong, Z.; Brokmeier, H.G.; Hort, N.; Meng, J. Microstructure evolution of Mg–11Gd–4.5Y–1Nd–1.5Zn–0.5Zr (wt %) alloy during deformation and its effect on strengthening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 657, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Mendis, C.L.; Hort, N.; Meng, J. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of Mg–11Gd–4.5Y–1Nd–1.5Zn–0.5Zr alloy prepared via pre-ageing and hot extrusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 624, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagihara, K.; Kinoshita, A.; Sugino, Y.; Yamasaki, M.; Kawamura, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Umakoshi, Y. Effect of long-period stacking ordered phase on mechanical properties of Mg97Zn1Y2 extruded alloy. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 6282–6293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Hagihara, K.; Kawamura, Y. Effect of multimodal microstructure evolution on mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Y extruded alloy. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 3646–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tane, M.; Nagai, Y.; Kimizuka, H.; Hagihara, K.; Kawamura, Y. Elastic properties of an Mg–Zn–Y alloy single crystal with a long-period stacking-ordered structure. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 6338–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagihara, K.; Yokotani, N.; Umakoshi, Y. Plastic deformation behavior of Mg12YZn with 18R long-period stacking ordered structure. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garces, G.; Morris, D.G.; Muñoz-Morris, M.; Pérez, P.; Tolnai, D.; Mendis, C.; Stark, A.; Lim, H.; Kim, S.; Shell, N. Plasticity analysis by synchrotron radiation in a Mg97Y2Zn1 alloy with bimodal grain structure and containing lpso phase. Acta Mater. 2015, 94, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Pan, H.; Tang, A.; Ren, Y.; Song, B.; Qin, G.; Zhang, M.; Pan, F. On the dynamic mechanical property and deformation mechanism of as-extruded Mg–Sn–Ca alloys under tension. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 664, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Qin, G.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Ren, Y.; Song, B.; Chai, L.; Zhao, Z. Activating profuse pyramidal slips in magnesium alloys via raising strain rate to dynamic level. J Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zong, X.; Xu, C.; You, Z.; Nie, K. Effects of ca on the formation of lpso phase and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Y–Mn alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 648, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Shang, S.L.; Wang, Y.; Mei, Z.G.; Darling, K.A.; Kecskes, L.J.; Mathaudhu, S.N.; Hui, X.D.; Liu, Z.K. Effects of alloying elements on stacking fault energies and electronic structures of binary Mg alloys: A first-principles study. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 2, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh-Ishi, K.; Mendis, C.; Homma, T.; Kamado, S.; Ohkubo, T.; Hono, K. Bimodally grained microstructure development during hot extrusion of Mg–2.4Zn–0.1Ag–0.1Ca–0.16Zr (at %) alloys. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 5593–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Mishra, R.S. Grain size and texture effects on deformation behavior of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 558, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, M.; Yuan, F.; Wu, G.; Wei, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Y. Heterogeneous lamella structure unites ultrafine-grain strength with coarse-grain ductility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14501–14505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Samples | Gd | Y | Zn | Ce |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2Ce alloy | 7.68 | 3.77 | 0.3 | 0.21 |
| 0.5Ce alloy | 6.77 | 3.42 | 0.3 | 0.47 |
| 1.0Ce alloy | 7.55 | 3.69 | 0.28 | 1.05 |
| Points | Mg | Gd | Y | Zn | Ce |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 89.38 | 5.36 | 3.50 | 1.12 | 0.63 |
| 2# | 94.47 | 1.11 | 1.86 | 2.54 | 0.01 |
| 3# | 88.29 | 5.94 | 4.65 | 0.55 | 0.58 |
| 4# | 93.0 | 1.46 | 1.72 | 3.61 | 0.22 |
| 5# | 87.14 | 5.46 | 4.19 | 1.74 | 1.47 |
| 6# | 92.01 | 1.89 | 1.82 | 3.90 | 0.38 |
| Points | Mg | Gd | Y | Zn | Ce |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 86.79 | 3.4 | 9.21 | 0.46 | 0.15 |
| b | 94.94 | 1.04 | 1.69 | 2.28 | 0.05 |
| c | 97.13 | 1.20 | 1.50 | 0.09 | 1.5 |
| d | 87.00 | 3.05 | 9.34 | 0.23 | 0.38 |
| e | 92.62 | 1.1 | 2.28 | 3.38 | 0.62 |
| f | 86.57 | 4.47 | 3.80 | 3.27 | 3.89 |
| g | 80.46 | 7.07 | 6.64 | 0.5 | 5.33 |
| h | 58.87 | 8.94 | 30.45 | 0.66 | 1.08 |
| i | 88.13 | 3.64 | 2.94 | 3.06 | 2.24 |
| As-Extruded Samples | Length of Nano-LPSO Phase | Length of Bulk LPSO Phase | Width of Bulk LPSO Phase | Fraction of Second Phases | DRXed Grain Sizes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2Ce alloy | ~3.0 μm | ~300 μm | ~35 μm | 4% (nano) 10% (micron) | ~4.3 μm |
| 0.5Ce alloy | ~1.5 μm | ~260 μm | ~25 μm | 5% (nano) 11% (micron) | ~1.7 μm |
| 1.0Ce alloy | ~1.0 μm | ~200 μm | ~15 μm | 2% (nano) 16% (micron) | ~8.4 μm |
| Samples | Yield Strength (MPa) | Ultimate Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2Ce alloy (tension) | 286.4 | 340.7 | 13 |
| 0.5Ce alloy (tension) | 302.2 | 365.3 | 15 |
| 1.0Ce alloy (tension) | 263.5 | 327.3 | 13.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Z.; Hu, L.; Li, J.; An, Z.; Li, J.; Huang, Q. Achieving High Strength and Good Ductility in As-Extruded Mg–Gd–Y–Zn Alloys by Ce Micro-Alloying. Materials 2018, 11, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010102
Gao Z, Hu L, Li J, An Z, Li J, Huang Q. Achieving High Strength and Good Ductility in As-Extruded Mg–Gd–Y–Zn Alloys by Ce Micro-Alloying. Materials. 2018; 11(1):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010102
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Zhengyuan, Linsheng Hu, Jinfeng Li, Zhiguo An, Jun Li, and Qiuyan Huang. 2018. "Achieving High Strength and Good Ductility in As-Extruded Mg–Gd–Y–Zn Alloys by Ce Micro-Alloying" Materials 11, no. 1: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010102
APA StyleGao, Z., Hu, L., Li, J., An, Z., Li, J., & Huang, Q. (2018). Achieving High Strength and Good Ductility in As-Extruded Mg–Gd–Y–Zn Alloys by Ce Micro-Alloying. Materials, 11(1), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010102




