Effect of Coiling Temperature on Microstructure, Properties and Resistance to Fish-Scaling of Hot Rolled Enamel Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
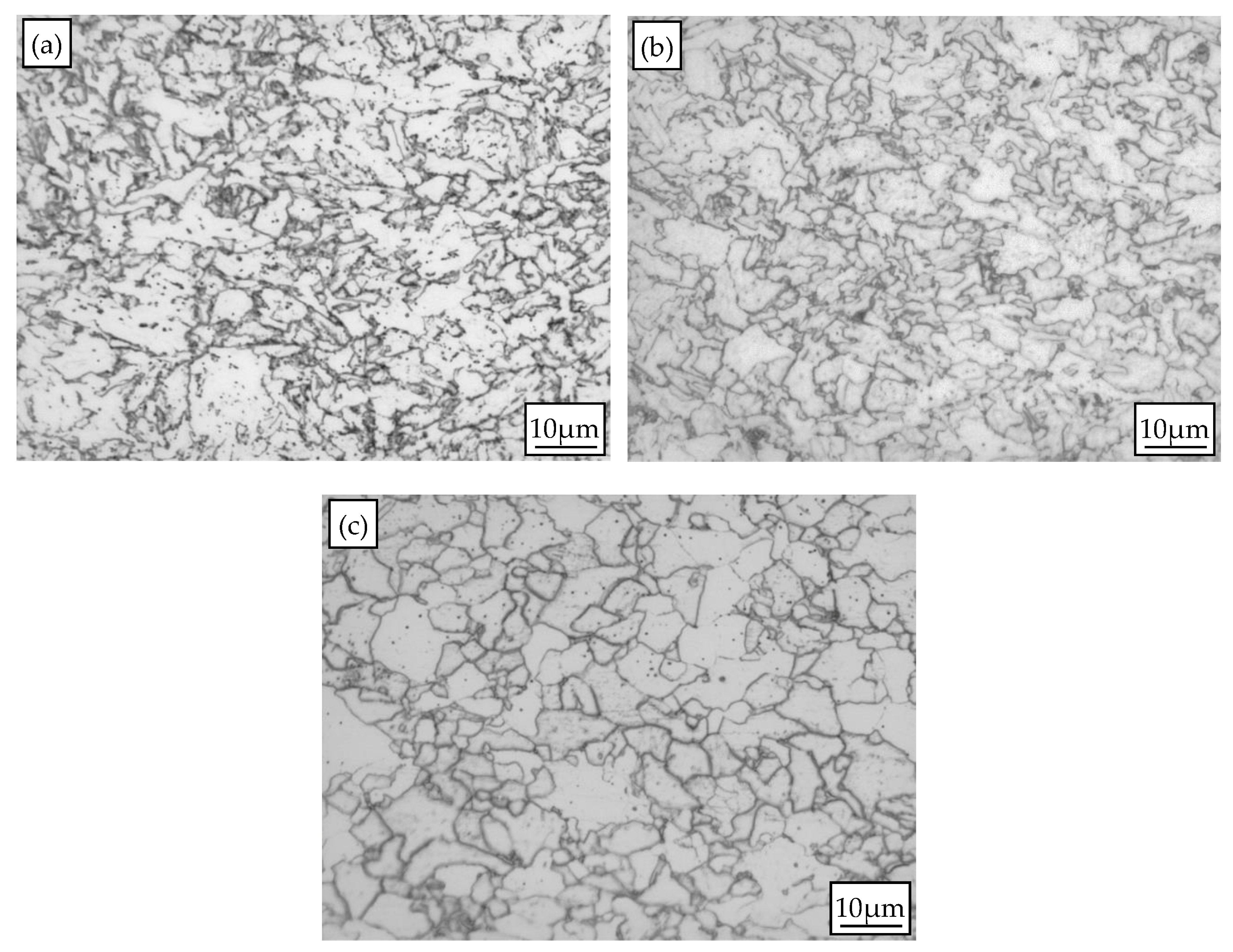
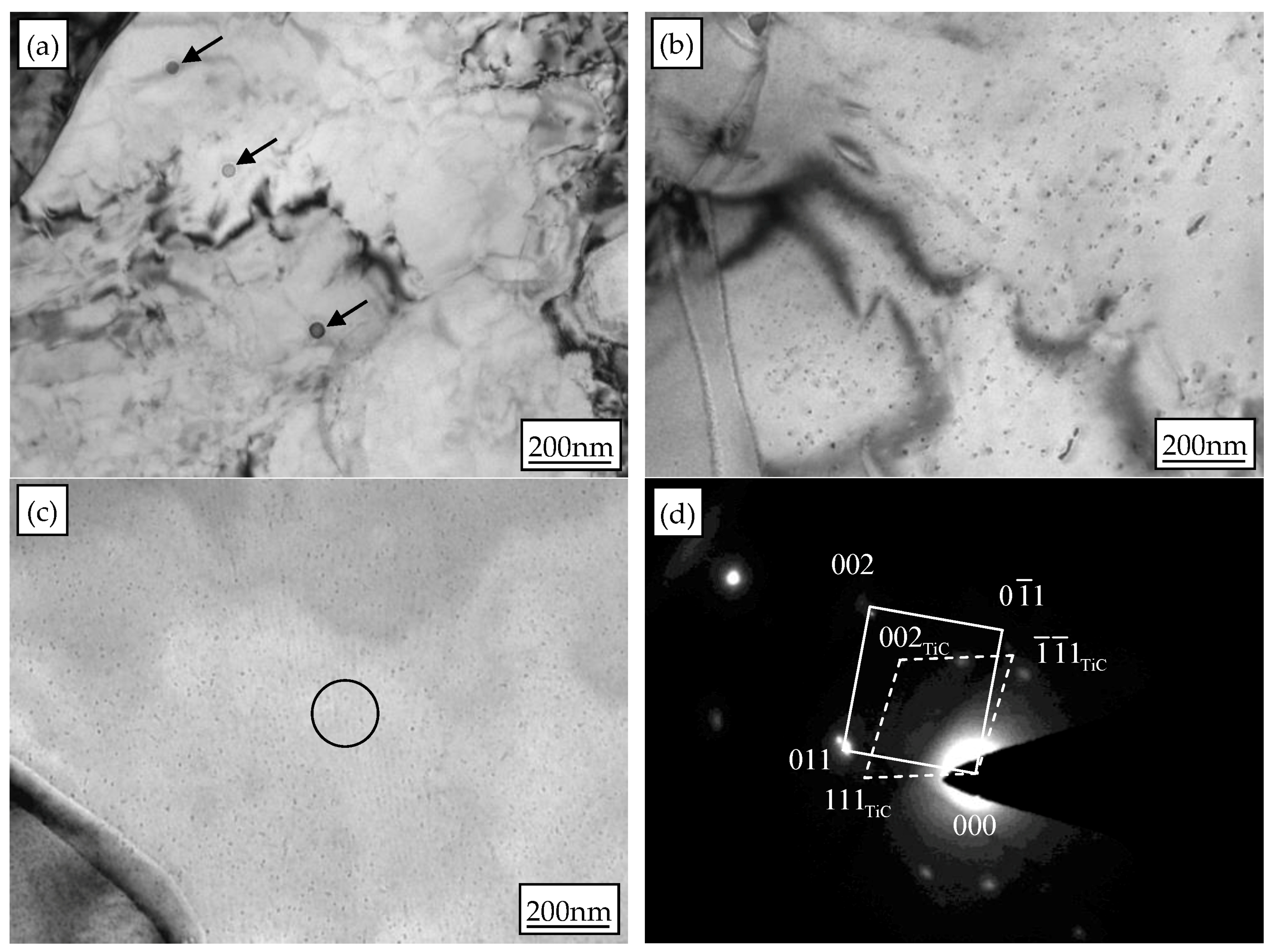
3.1. Microstructure
3.2. Mechanical Properties
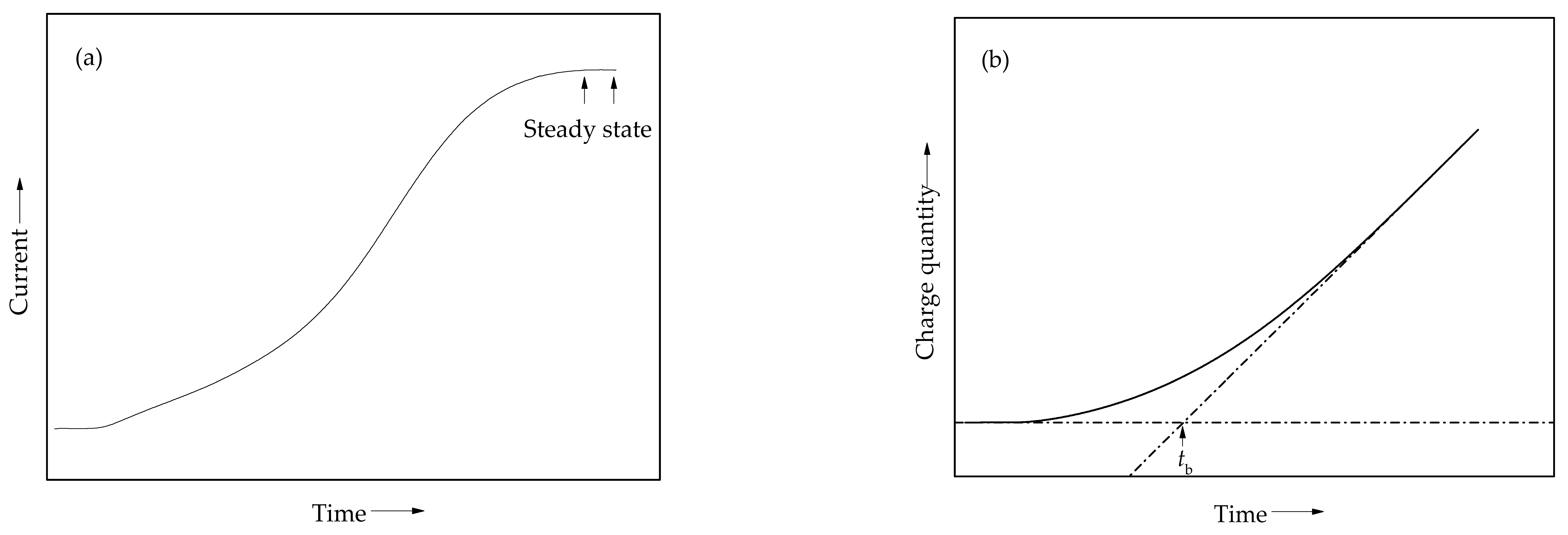
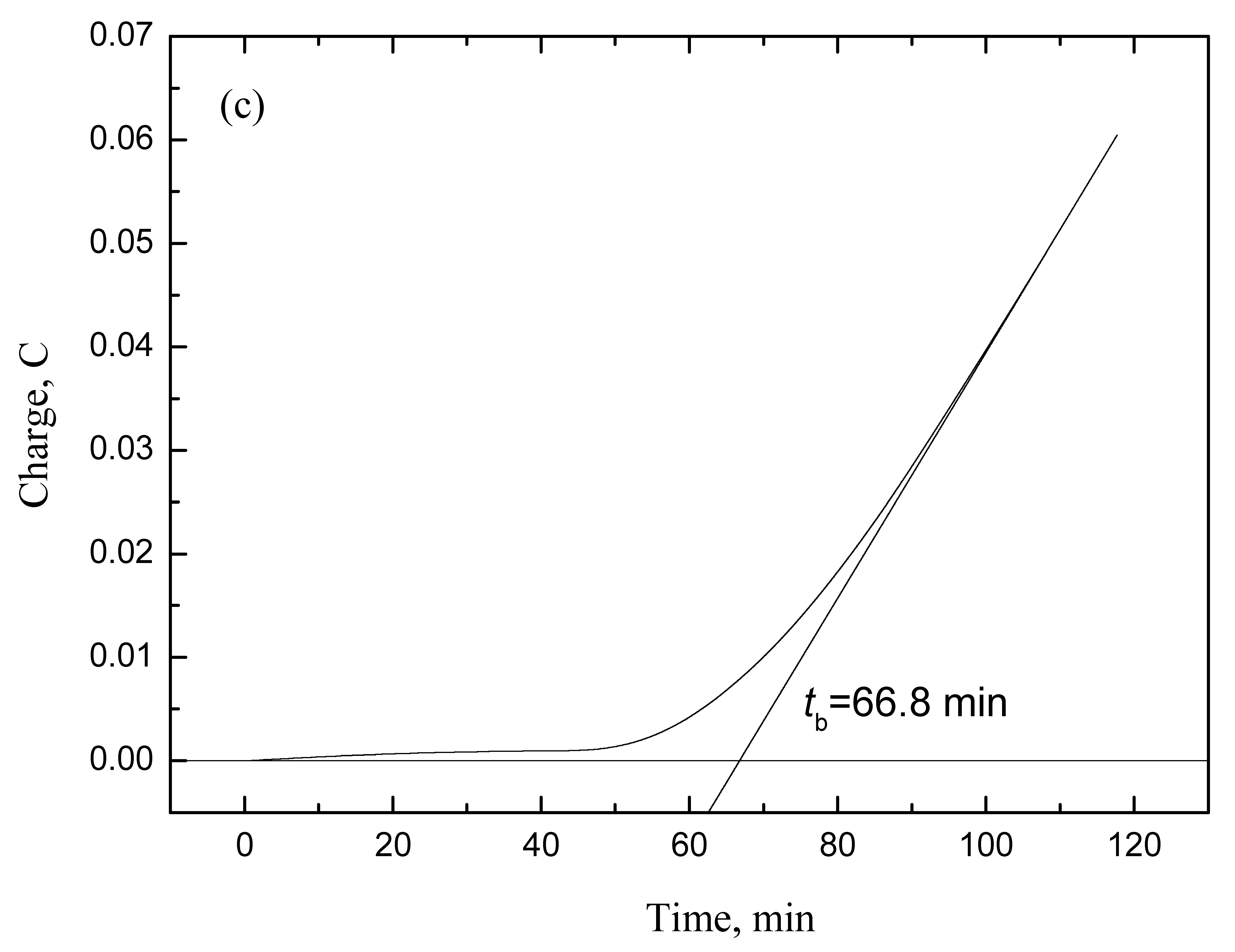
3.3. Resistance to Fish-Scaling
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- At coiling temperatures of 650 and 700 °C, there are large quantities of interphase precipitates of TiC in hot rolled enamel steel. While at coiling temperature of 600 °C, there are a few randomly dispersed precipitates containing Ti.
- (2)
- Coiling at low temperature, the microstructure was characterized by elongated ferrite grain. On the other hand, coiling at high temperature can lead to polygonal ferrite and low yield strength and ultimate tensile strength.
- (3)
- At a temperature range of 600–700 °C, the resistance to fish-scaling is best when the coiling temperature is 700 °C, because of the large quantities of nano-sized interphase precipitates of TiC in hot rolled enamel steel. The main irreversible hydrogen trapping sites are matrix-TiC interfaces, and nano-sized interphase precipitates are beneficial to the improvement of the resistance to fish-scaling.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malnieks, K.; Mezinskis, G.; Pavlovska, I.; Bidermanis, L.; Pludons, A. Black enamel for concentrated solar-power receivers. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 13321–13327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Montes-de-Oca, N.F.; de-la-Garza, M.; Alvarez-Elcoro, I.; Pérez-González, F.A.; Colás, R. Evidence of gas permeation in electrostatically painted steel cylinders. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2014, 42, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Jiang, Z.; Wei, D.; Jiao, S.; Xu, C. Analysis of fishscaling resistance of low carbon heavy plate steels. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2014, 21, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challa, V.S.A.; Zhou, W.H.; Misra, R.D.K.; O’Malley, R.; Jansto, S.G. The effect of coiling temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a niobium-titanium microalloyed steel processed via thin slab casting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 595, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanathan, M.A.V.; Stachurski, Z. The adsorption and diffusion of electrolytic hydrogen in palladium. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1962, 270, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.S.; Cao, W.B.; Wang, C.D.; Li, S.J.; Zhao, J.Y.; Sun, Y.F. Effect of microstructures and inclusions on hydrogen-induced cracking and blistering of A537 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 642, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winzer, N.; Rott, O.; Thiessen, R.; Thomas, I.; Mraczek, K.; Höche, T.; Wright, L.; Mrovec, M. Hydrogen diffusion and trapping in Ti-modified advanced high strength steels. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Li, J.; Chu, W.; Zhang, W.; Yang, D. Study of hydrogen diffusion of enameled steel sheet. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot. 2010, 30, 269–272. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yen, H.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Yang, J.R. Characterization of interphase-precipitated nanometer-sized carbides in a Ti–Mo-bearing steel. Scr. Mater. 2009, 61, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Song, S.W.; Seo, S.J.; Hong, S.; Lee, C.S. Development of Ti and Mo micro-alloyed hot-rolled high strength sheet steel by controlling thermomechanical controlled processing schedule. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 565, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.N.; Sun, M.X.; Yi, H.L.; Liu, Z.Y. The blocking effects of interphase precipitation on dislocations’ movement in Ti-bearing micro-alloyed steels. Mater. Lett. 2015, 139, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Miyamoto, G.; Shinbo, K.; Furuhara, T.; Ohmura, T.; Suzuki, T.; Tsuzaki, K. Effects of transformation temperature on VC interphase precipitation and resultant hardness in low-carbon steels. Acta Mater. 2015, 84, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyamas, T.; Nishimoto, A.; Kurokawa, T. New type cold rolled steel sheet for enamelling produced by the continuous casting method. Vitreous Enamel. 1990, 41, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Atrens, A. Reversible hydrogen trapping in a 3.5 NiCrMoV medium strength steel. Corros. Sci. 2015, 96, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, A.J.; Muzaka, K.; Dunne, D.P.; Calka, A.; Pereloma, E.V. Effect of microstructure and composition on hydrogen permeation in X70 pipeline steels. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 2544–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.G.; Tsuzaki, K. Quantitative analysis on hydrogen trapping of TiC particles in steel. Metall. Trans. A 2006, 37, 331–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Lee, J.Y. The effect of the interface character of TiC particles on hydrogen trapping in steel. Acta Metall. 1987, 35, 2695–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, J.; Kawakami, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Tarui, T. The first direct observation of hydrogen trapping sites in TiC precipitation-hardening steel through atom probe tomography. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
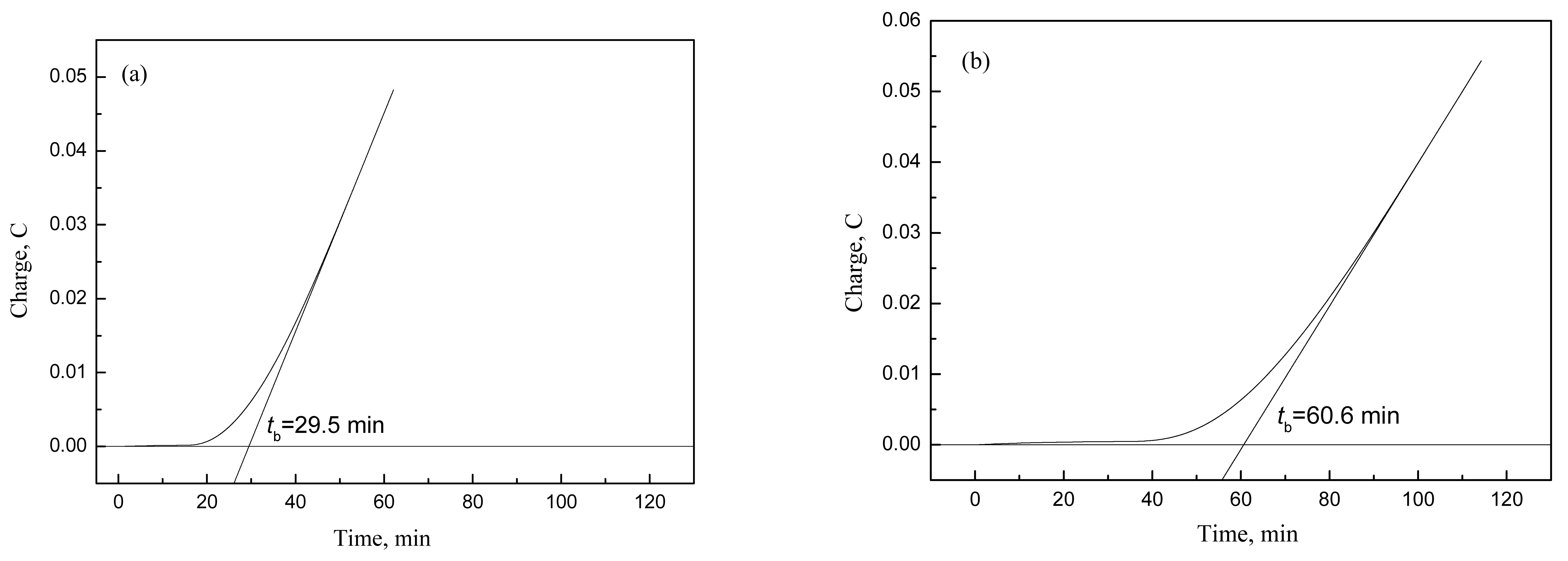
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Al | Ti | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.07 | 0.028 | 1.2 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.012 | 0.13 | Bal. |
| Coiling Temperature (°C) | YS (MPa) | UTS (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 700 | 493 | 598 | 32.8 |
| 650 | 535 | 605 | 20.2 |
| 600 | 560 | 611 | 19.4 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Huang, X.; Yu, B.; Yuan, X.; Liu, X. Effect of Coiling Temperature on Microstructure, Properties and Resistance to Fish-Scaling of Hot Rolled Enamel Steel. Materials 2017, 10, 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091012
Zhao Y, Huang X, Yu B, Yuan X, Liu X. Effect of Coiling Temperature on Microstructure, Properties and Resistance to Fish-Scaling of Hot Rolled Enamel Steel. Materials. 2017; 10(9):1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091012
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yang, Xueqi Huang, Bo Yu, Xiaoyun Yuan, and Xianghua Liu. 2017. "Effect of Coiling Temperature on Microstructure, Properties and Resistance to Fish-Scaling of Hot Rolled Enamel Steel" Materials 10, no. 9: 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091012
APA StyleZhao, Y., Huang, X., Yu, B., Yuan, X., & Liu, X. (2017). Effect of Coiling Temperature on Microstructure, Properties and Resistance to Fish-Scaling of Hot Rolled Enamel Steel. Materials, 10(9), 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091012





