In Vitro Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Response to Ionic Dissolution Products from Lithium-Containing 45S5 Bioactive Glass
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Development and Characterization of Bioactive Glass Microparticles
2.2. Preparation of Culture Media Enriched with Ionic Dissolution Products from Bioactive Glasses
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.5. Determination of the Levels of β-Catenin by Western Blot
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Ethical Principles
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Production and Characterization of Bioactive Glasses
3.2. Study of the Angiogenic Effects In Vitro
3.2.1. Culture Media Enriched with Ionic Dissolution Products from Bioactive Glasses
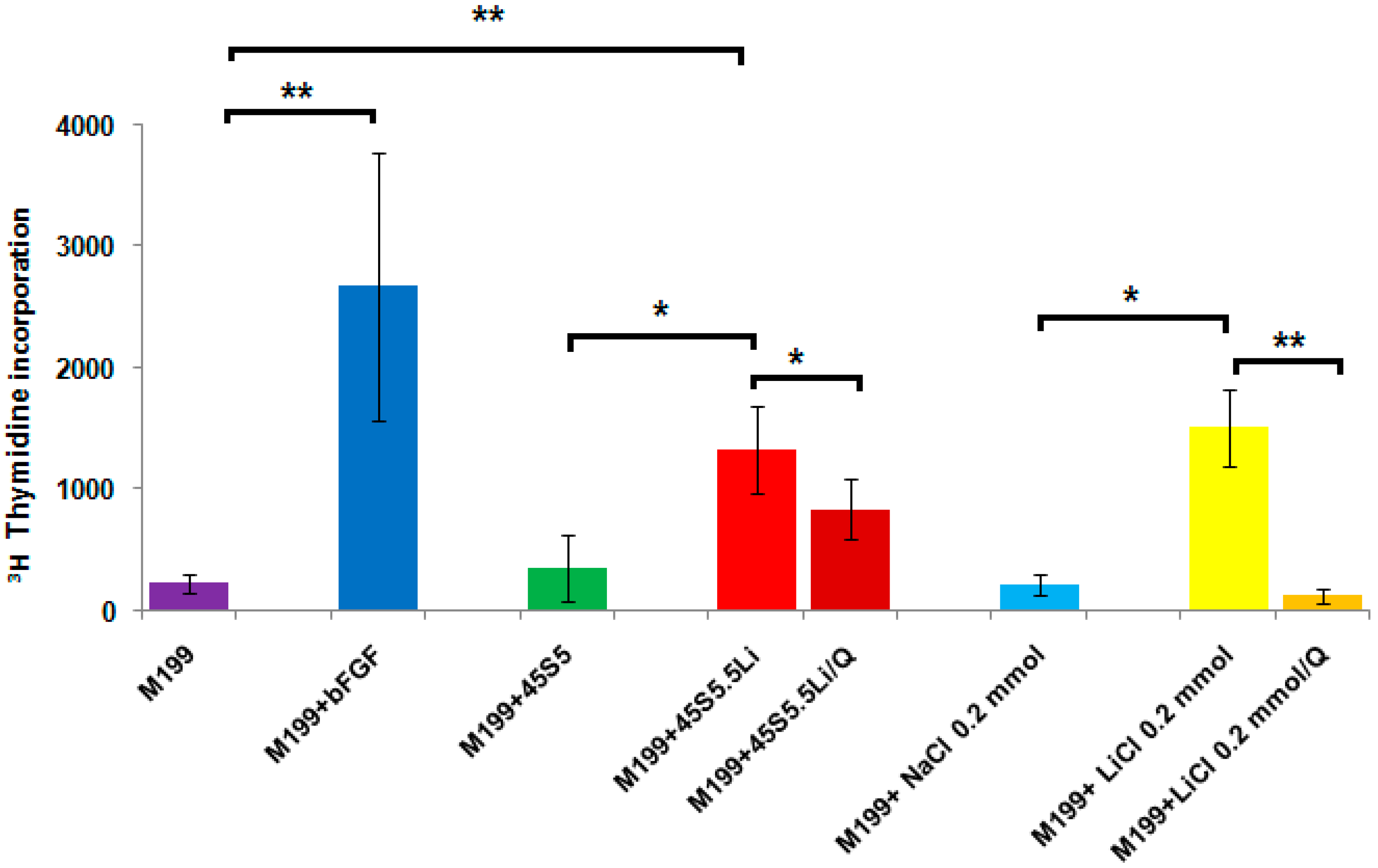
3.2.2. Proliferation Assay
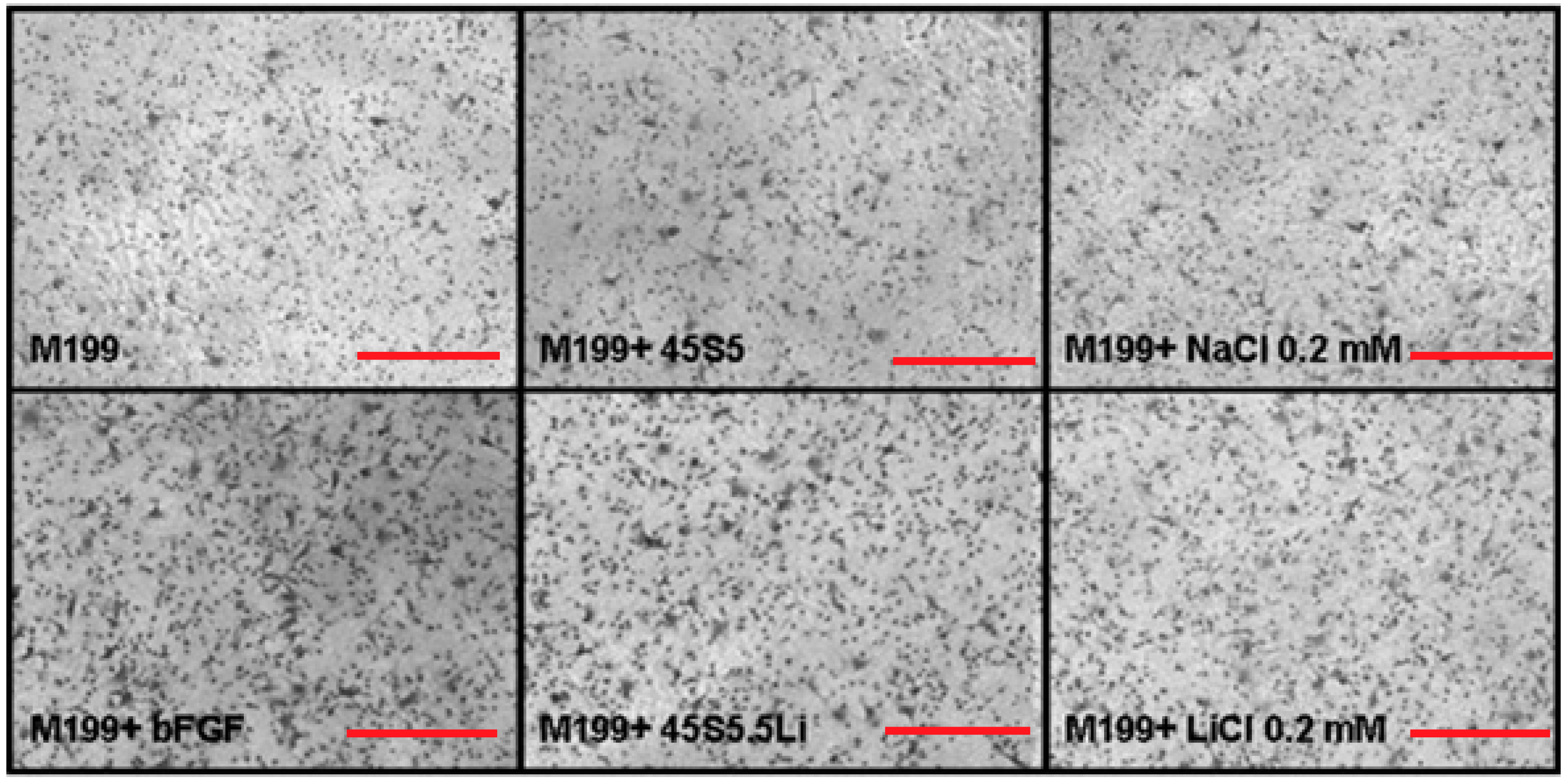
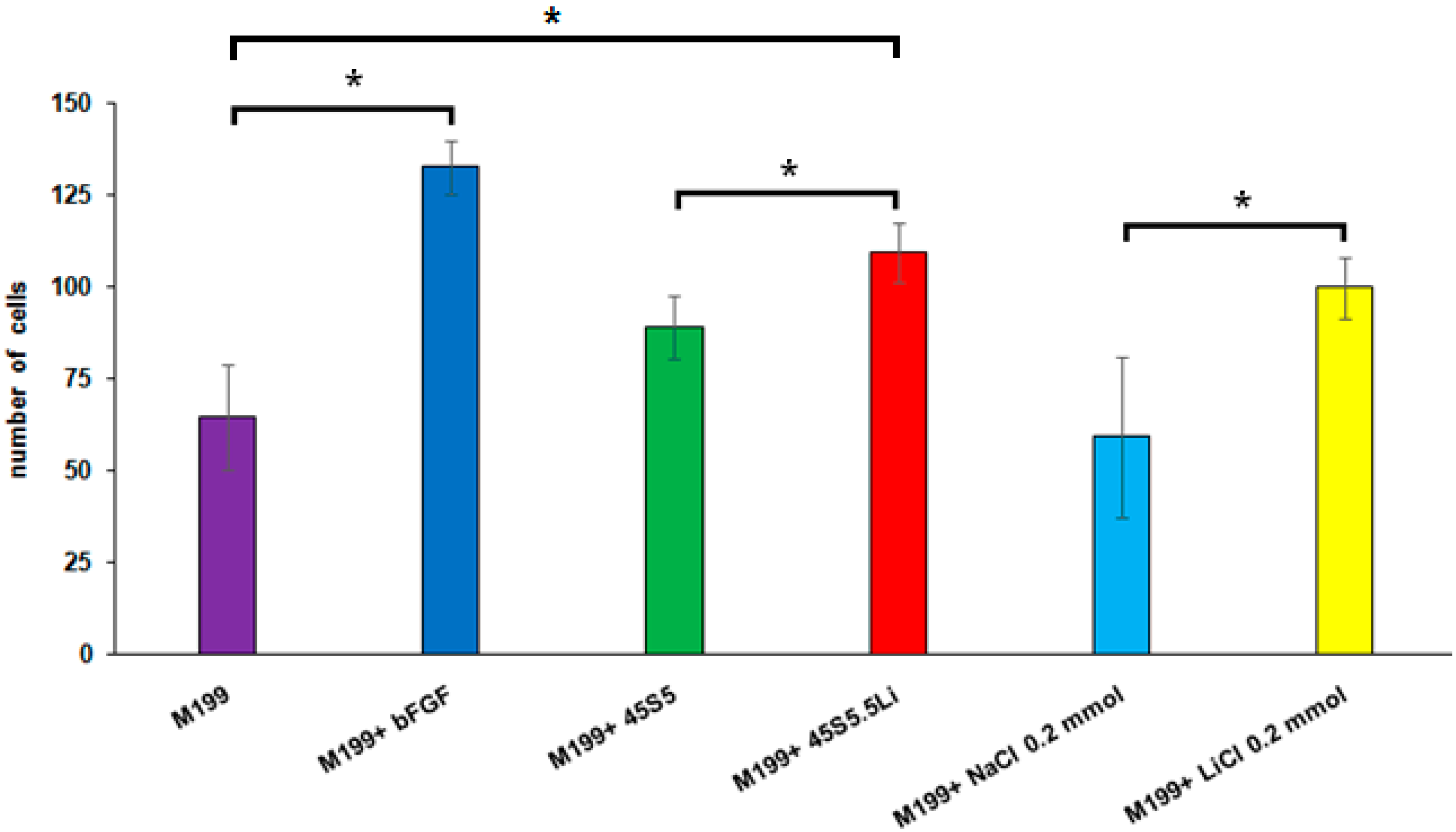
3.2.3. Migration Assay
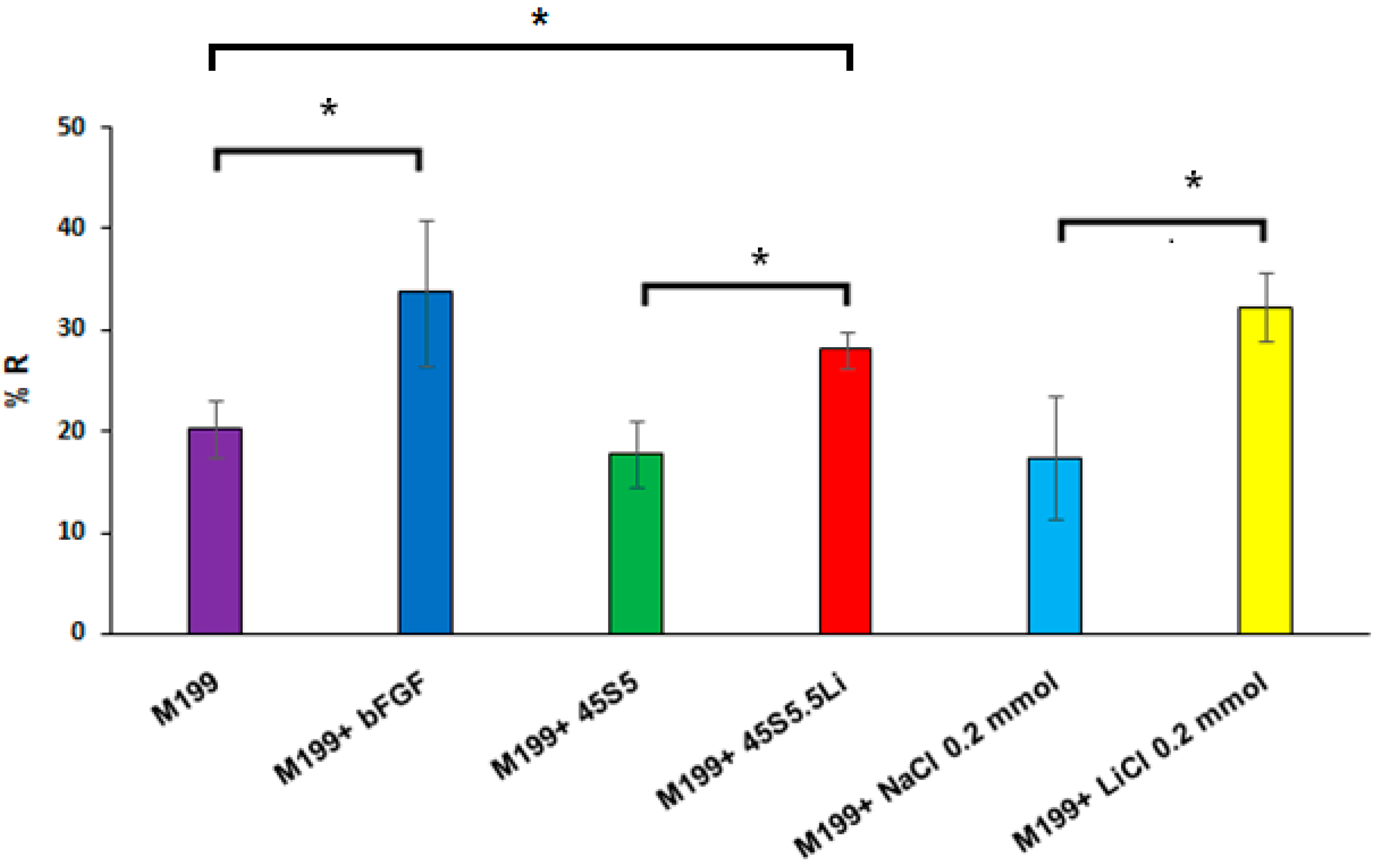
3.2.4. Transmigration Assay
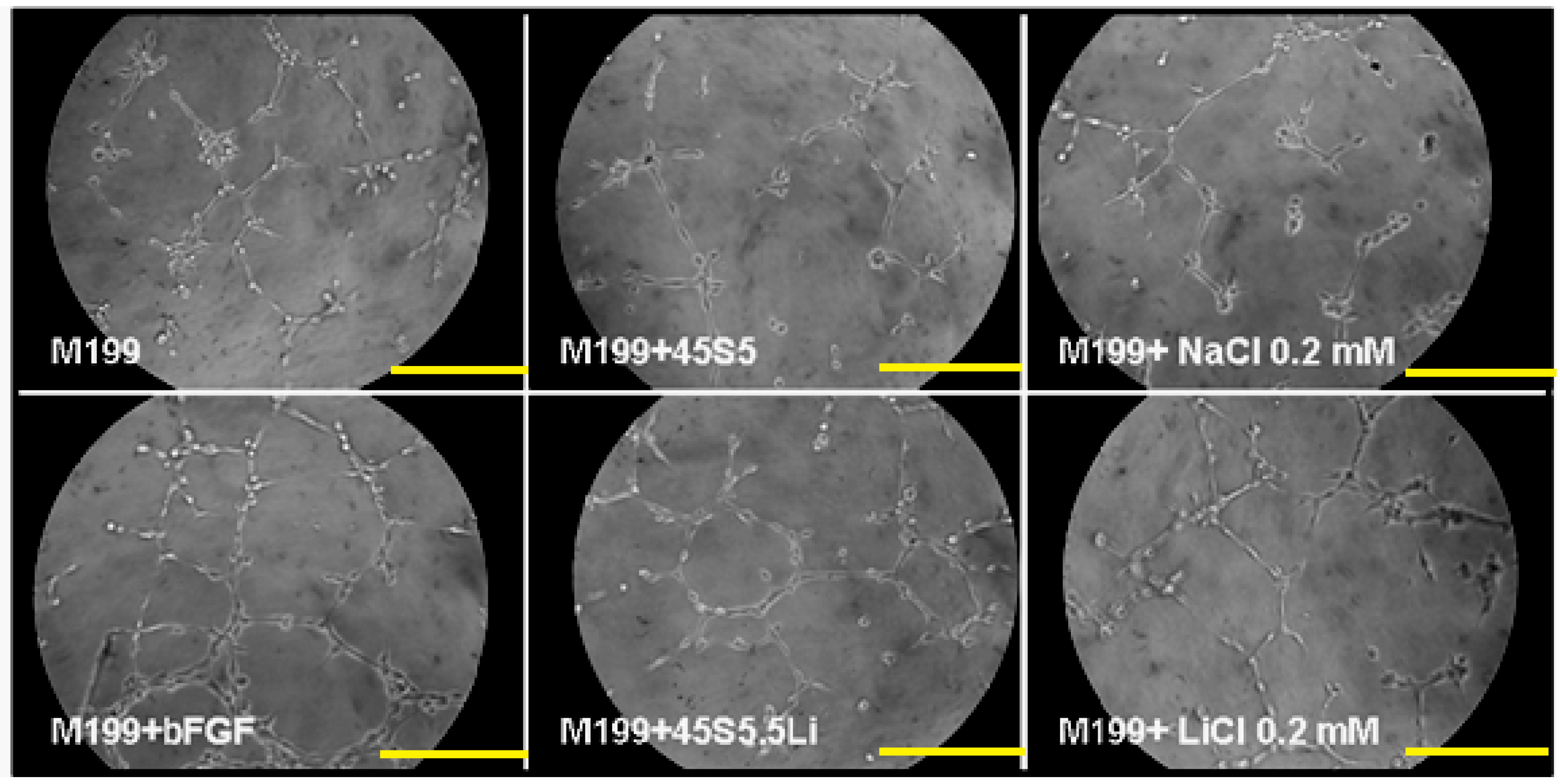
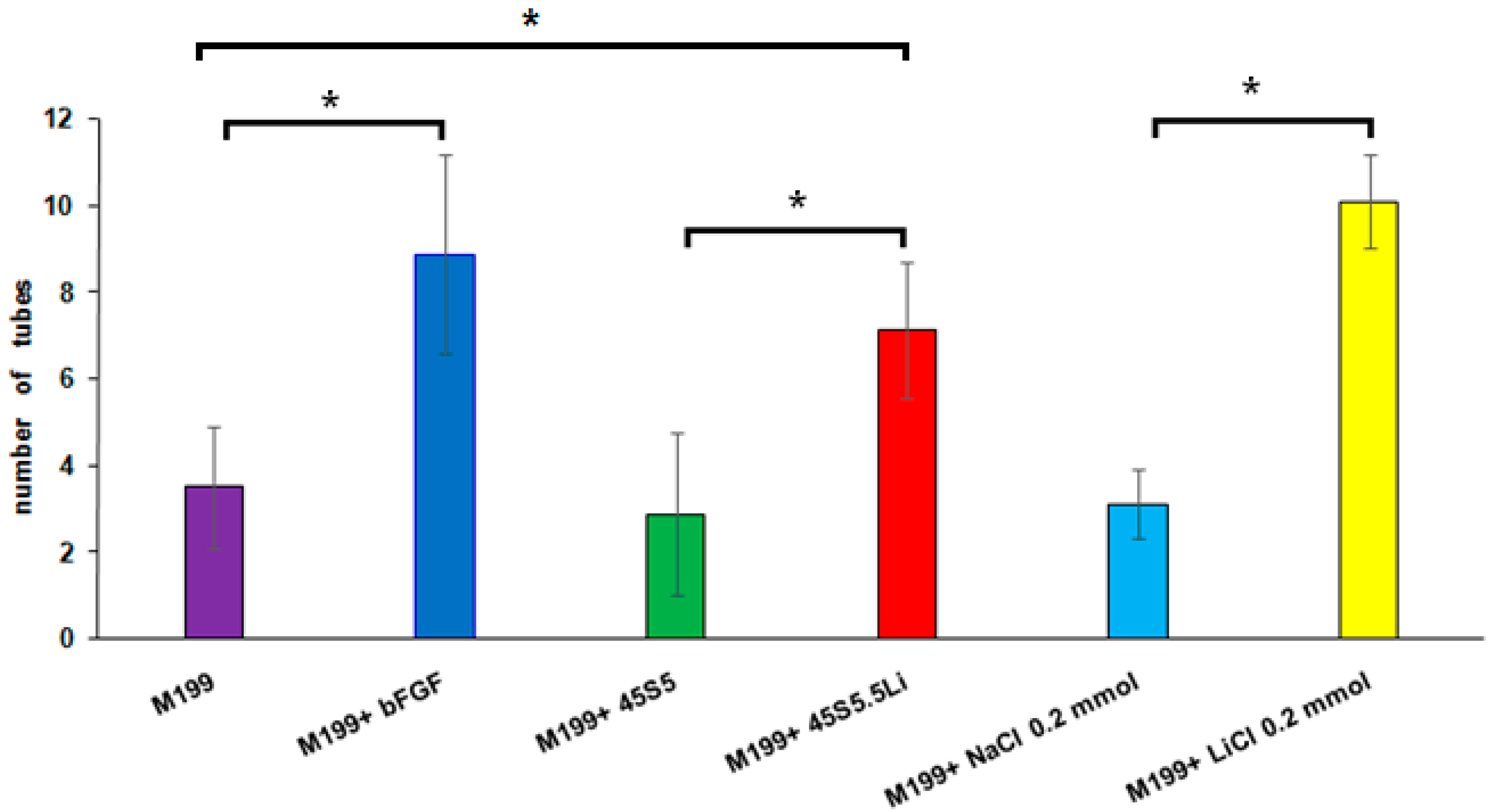
3.2.5. Tubulogenesis Assay in Matrigel™
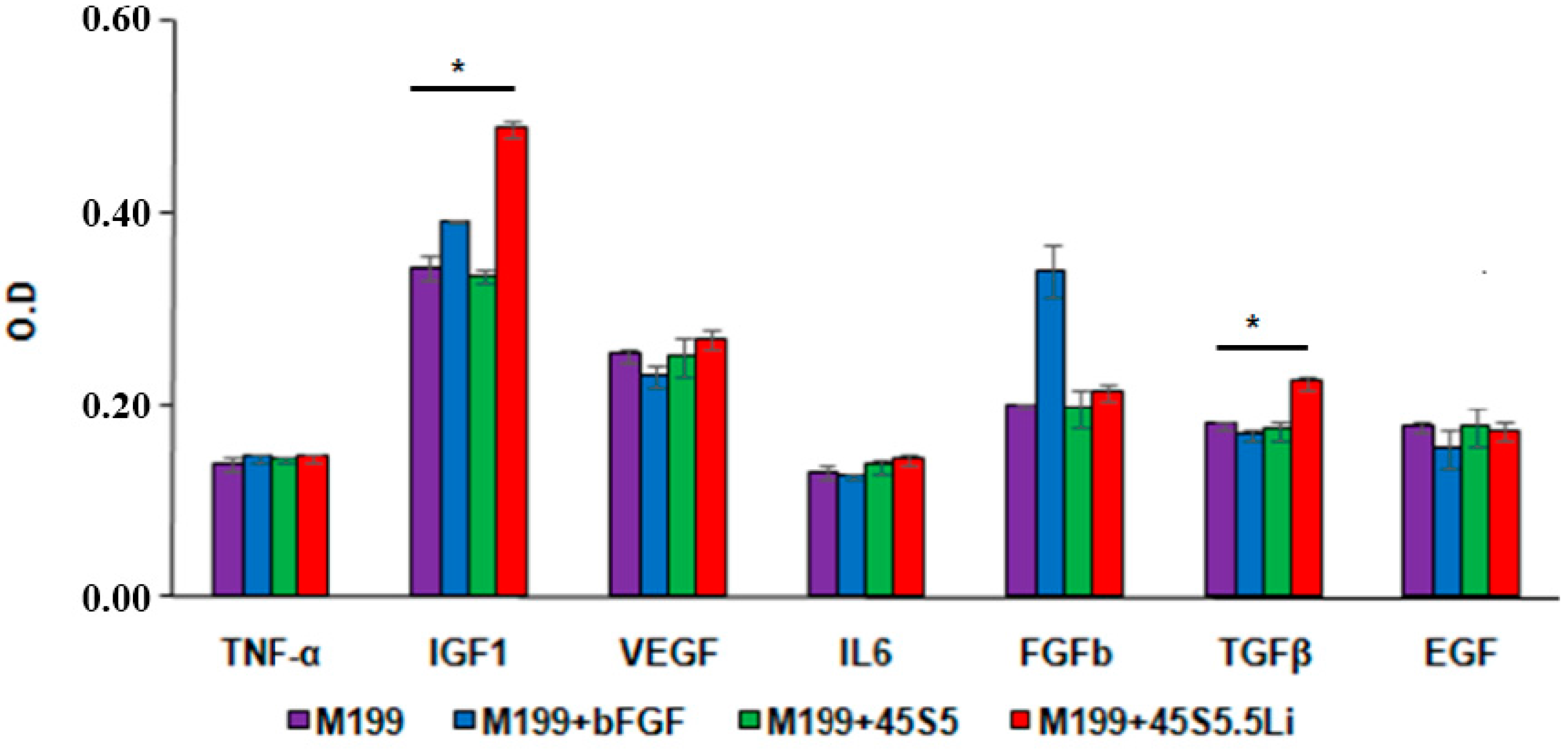
3.2.6. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
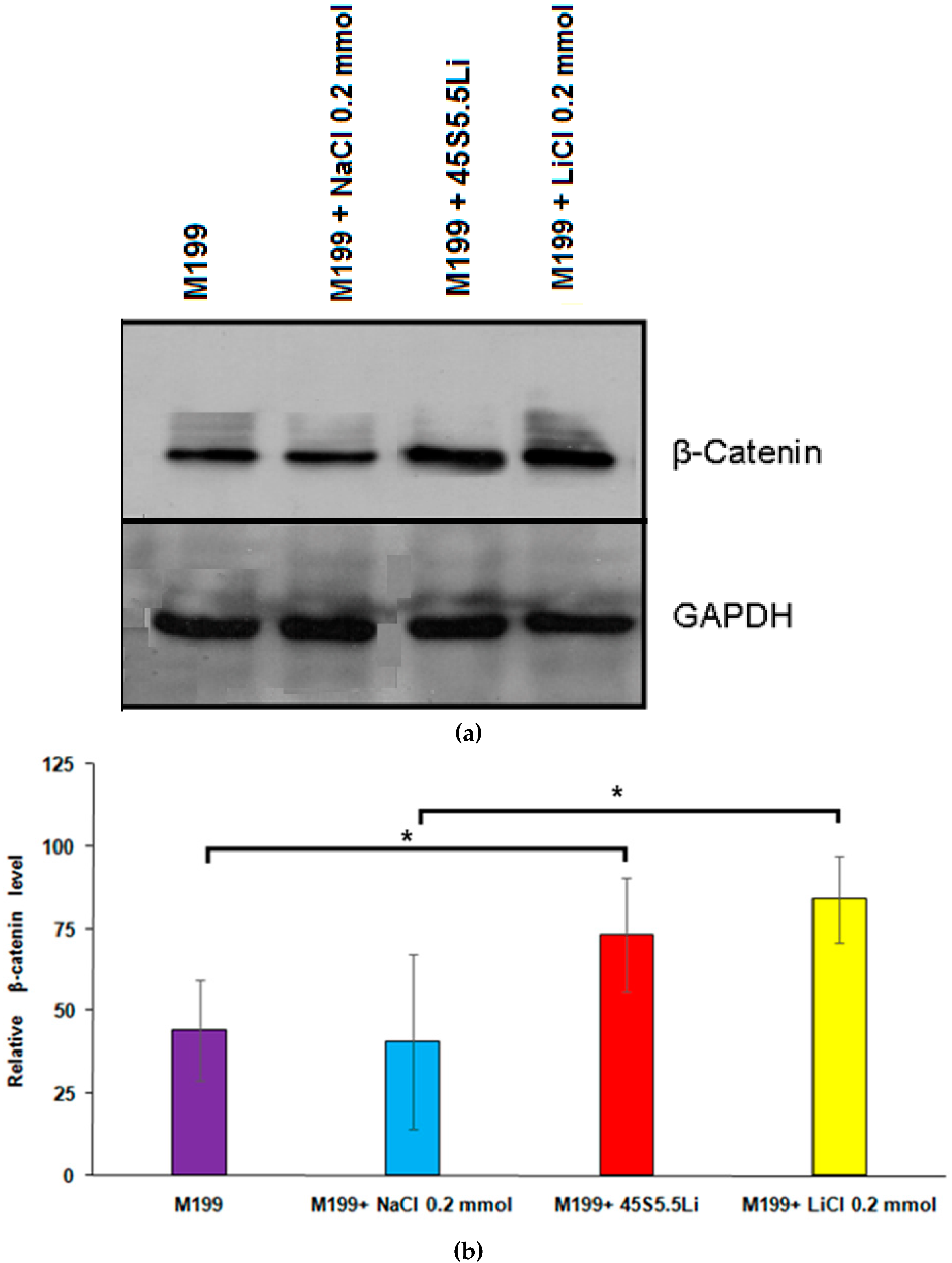
3.2.7. Determination of the Levels of β-Catenin by Western Blot
3.3. Summary
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Risau, W. Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature 1997, 386, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eilken, H.M.; Adams, R.H. Dynamics of endothelial cell behavior in sprouting angiogenesis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 2011, 473, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potente, M.; Gerhardt, H.; Carmeliet, P. Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell 2011, 146, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorustovich, A.; Roether, J.A.; Boccaccini, A.R. Effect of bioactive glasses on angiogenesis: A review of in vitro and in vivo evidences. Tissue Eng. B Rev. 2010, 16, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chang, J. Multifunctional mesoporous bioactive glasses for effective delivery of therapeutic ions and drug/growth factors. J. Control. Release 2014, 193, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stähli, C.; James-Bhasin, M.; Hoppe, A.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Nazhat, S.N. Effect of ion release from Cu-doped 45S5 Bioglass® on 3D endothelial cell morphogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2015, 19, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, N.; Rahaman, M.N.; Liu, Z.; Huang, W.; Zhang, C. Wound dressings composed of copper-doped borate bioactive glass microfibers stimulate angiogenesis and heal full-thickness skin defects in a rodent model. Biomaterials 2015, 53, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinlan, E.; Partap, S.; Azevedo, M.M.; Jell, G.; Stevens, M.M.; O’Brien, F.J. Hypoxia-mimicking bioactive glass/collagen glycosaminoglycan composite scaffolds to enhance angiogenesis and bone repair. Biomaterials 2015, 52, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haro Durand, L.A.; Góngora, A.; Porto López, J.M.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Zago, M.P.; Baldi, A.; Gorustovich, A. In Vitro endothelial cell response to ionic dissolution products from boron-doped bioactive glass in the SiO2–CaO–P2O5–Na2O system. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 7620–7630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detsch, R.; Stoor, P.; Grünewald, A.; Roether, J.; Lindfors, A.N.C.; Boccaccini, A.R. Increase in VEGF secretion from human fibroblast cells by bioactive glass S53P4 to stimulate angiogenesis in bone. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 4055–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Pickrell, G.; Sriranganathan, N.; Kumar, V.; Homa, D. Review and the state of the art: Sol-gel and melt quenched bioactive glasses for tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2016, 104, 1248–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota de Freitas, D.; Leverson, B.D.; Goossens, J.L. Lithium in Medicine: Mechanisms of Action. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2016, 16, 557–584. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oruch, R.; Elderbi, M.A.; Khattab, H.A.; Pryme, I.F.; Lund, A. Lithium: A review of pharmacology, clinical uses, and toxicity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forlenza, O.V.; De-Paula, V.J.; Diniz, B.S. Neuroprotective effects of lithium: Implications for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and related neurodegenerative disorders. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.T.; Wang, Z.; Hunsberger, J.G.; Chuang, D.M. Therapeutic potential of mood stabilizers lithium and valproic acid: Beyond bipolar disorder. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 105–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, J.; Wang, Q.W.; Kim, Y.; Yu, D.X.; Pham, S.; Yang, B.; Zheng, Y.; Diffenderfer, K.E.; Zhang, J.; Soltani, S.; et al. Differential responses to lithium in hyperexcitable neurons from patients with bipolar disorder. Nature 2015, 527, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wu, C.; Lu, P.; Hu, C.; Xiong, S.; Chang, J.; Heng, B.C.; Xiao, Y.; Ouyang, H.W. A bi-lineage conducive scaffold for osteochondral defect regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4473–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Xu, M.; Chang, J.; Chakravorty, N.; Wu, C.; Xio, Y. Lithium release from β-tricalcium phosphate inducing cementogenic and osteogenic differentiation of both hPDLCs and hBMSCs. Biomater. Sci. 2014, 2, 1230–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, S.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Song, D.; Hu, J. Systemic administration of lithium improves distracted bone regeneration in rats. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 96, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, D.; Wu, J.; Shao, H.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ping, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhu, X.; Xu, Y.; et al. Pharmaceutical inhibition of glycogen synthetase kinase 3 beta suppresses wear debris-induced osteolysis. Biomaterials 2015, 69, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorfve, A.; Lindahl, C.; Xia, W.; Igawa, K.; Lindahl, A.; Thomsen, P.; Palmquist, A.; Tengvall, P. Hydroxyapatite coating affects the Wnt signaling pathway during peri-implant healing in vivo. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorfve, A.; Bergstrand, A.; Ekström, K.; Lindahl, A.; Thomsen, P.; Larsson, A.; Tengvall, P. Gene expression profiling of peri-implant healing of PLGA-Li+ implants suggests an activated Wnt signaling pathway in vivo. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeilbeck, L.F.; Müller, B.; Knobloch, V.; Tamm, E.R.; Ohlmann, A. Differential angiogenic properties of lithium chloride in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Arai, K.; Stins, M.F.; Chuang, D.M.; Lo, E.H. Lithium upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor in brain endothelial cells and astrocytes. Stroke 2009, 40, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedgepeth, C.M.; Conrad, L.J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H.C.; Lee, V.M.; Klein, P.S. Activation of the Wnt signaling pathway: A molecular mechanism for lithium action. Dev. Biol. 1997, 185, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.H.; Ding, W.V.; McCormick, F. Wnt signaling to beta-catenin involves two interactive components. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibition and activation of protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17894–17899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanovich, M.A.; Castro, M.S.; Porto López, J.M. Improvement of the microstructure and microhardness of hydroxyapatite ceramics by addition of lithium. Mater. Lett. 1998, 33, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; de Groot, K.; van Blitterswijk, C.; de Boer, J. Electrolytic deposition of lithium into calcium phosphate coatings. Dent. Mater. 2009, 25, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorami, M.; Hesaraki, S.; Behnamghader, A.; Nazarian, H.; Shahrabi, S. In Vitro bioactivity and biocompatibility of lithium substituted 45S5 bioglass. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylkowski, M.; Brauer, D.S. Mixed alkali effects in Bioglass® 45S5. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2013, 376, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilarinho, P.M.; Barroca, N.; Zlotnik, S.; Félix, P.; Fernandes, M.H. Are lithium niobate (LiNbO3) and lithium tantalate (LiTaO3) ferroelectrics bioactive? Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2014, 39, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brückner, R.; Tylkowski, M.; Hupa, L.; Brauer, D.S. Controlling the ion release from mixed alkali bioactive glasses by varying modifier ionic radii and molar volume. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 3121–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguez-Pacheco, V.; Buttner, T.; Macon, A.L.B.; Jones, J.R.; Fey, T.; de Ligny, D.; Greil, P.; Chevalier, J.; Malchere, A.; Boccaccini, A.R. Development and characterization of lithium-releasing silicate bioactive glasses and their scaffolds for bone repair. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2016, 432, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomillion, C.T.; Lakhman, R.K.; Kasi, R.M.; Weiss, R.A.; Kuhn, L.T.; Goldberg, A.J. Lithium-end-capped polylactide thin films influence osteoblast progenitor cell differentiation and mineralization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015, 103, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Kady, A.M.; Farag, M.M.; El-Rashedi, A.M. Bioactive glass nanoparticles designed for multiple deliveries of lithium ions and drugs: Curative and restorative bone treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 91, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, R.; Li, B.; Liang, W.; Pan, H.; Cui, X.; Tang, J.; Li, B. Lithium doped calcium phosphate cement maintains physical mechanical properties and promotes osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahabzadeh, S.; Hack, V.K.; Bose, S. Lithium-doped β-tricalcium phosphate: Effects on physical, mechanical and in vitro osteoblast cell-material interactions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauer, D.S.; Brückner, R.; Tylkowski, M.; Hupa, L. Sodium-free mixed alkali bioactive glasses. Biomed. Glasses 2016, 2, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, P.K.; Mahato, A.; Kundu, B.; Nandi, S.K.; Mukherjee, P.; Datta, S.; Sarkar, S.; Mukherjee, J.; Nath, S.; Balla, V.K.; et al. Influence of single and binary doping of strontium and lithium on in vivo biological properties of bioactive glass scaffolds. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, J.G.; Babb, R.; Salzlechner, C.; Sharpe, P.T.; Brauer, D.S.; Gentleman, E. Optimisation of lithium-substituted bioactive glasses to tailor cell response for hard tissue repair. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 8832–8844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.; Alitalo, K.; Annex, B.H.; Augustin, H.G.; Beam, C.; Berk, B.C.; Byzova, T.; Carmeliet, P.; Chilian, W.; Cooke, J.P.; et al. State-of-the-art methods for evaluation of angiogenesis and tissue vascularization: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, e99–e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhao, G.; Panhwar, F.; He, X. Vitreous cryopreservation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells with low concentration of cryoprotective agents for vascular tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. C Methods 2016, 22, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauer, D.S. Bioactive glasses—Structure and properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 4160–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maçon, A.L.B.; Jacquemin, M.; Page, S.J.; Li, S.; Bertazzo, S.; Stevens, M.M.; Hanna, J.V.; Jones, J.R. Lithium-silicate sol–gel bioactive glass and the effect of lithium precursor on structure–property relationships. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.D.; Hoang, P.; DiCorleto, P.E. Lithium inhibits cell cycle progression and induces stabilization of p53 in bovine aortic endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 26180–26188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.W.; Smith, S.K.; Charnock-Jones, D.S. Wnt-1 signaling inhibits human umbilical vein endothelial cell proliferation and alters cell morphology. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 291, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struewing, I.T.; Durham, S.N.; Barnett, C.D.; Mao, C.D. Enhanced endothelial cell senescence by lithium-induced matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 17595–17606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chang, J. Stimulation of proangiogenesis by calcium silicate bioactive ceramic. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 5379–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xue, K.; Kong, N.; Liu, K.; Chang, J. Silicate bioceramics enhanced vascularization and osteogenesis through stimulating interactions between endothelia cells and bone marrow stromal cells. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3803–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, C.; Chen, X.; Miao, G.; Lin, C. Angiogenesis stimulated by novel nanoscale bioactive glasses. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrientos, S.; Brem, H.; Stojadinovic, O.; Tomic-Canic, M. Clinical application of growth factors and cytokines in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2014, 22, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, A.C.; Briquez, P.S.; Hubbell, J.A.; Cochran, J.R. Engineering growth factors for regenerative medicine applications. Acta Biomater. 2016, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Playford, M.P.; Bicknell, D.; Bodmer, W.F.; Macaulay, V.M. Insulin-like growth factor 1 regulates the location, stability, and transcriptional activity of beta-catenin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12103–12108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbois-Mouthon, C.; Cadoret, A.; Blivet-Van Eggelpoël, M.J.; Bertrand, F.; Cherqui, G.; Perret, C.; Capeau, J. Insulin and IGF-1 stimulate the beta-catenin pathway through two signalling cascades involving GSK-3beta inhibition and Ras activation. Oncogene 2001, 20, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganthi, M.; Sangeetha, G.; Benson, C.S.; Babu, S.D.; Sathyavathy, A.; Ramadoss, S.; Ravi Sankar, B. In vitro mechanisms involved in the regulation of cell survival by lithium chloride and IGF-1 in human hormone-dependent breast cancer cells (MCF-7). Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 214, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squassina, A.; Costa, M.; Congiu, D.; Manchia, M.; Angius, A.; Deiana, V.; Ardau, R.; Chillotti, C.; Severino, G.; Calza, S.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) expression is up-regulated in lymphoblastoid cell lines of lithium responsive bipolar disorder patients. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 73, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wei, L.; Sun, J.; Guan, G. Effect of ionic products of dicalcium silicate coating on osteoblast differentiation and collagen production via TGF-β1 pathway. J. Biomater. Appl. 2013, 27, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, P.; Wu, C.; Xiao, Y. The effect of silicate ions on proliferation, osteogenic differentiation and cell signalling pathways (WNT and SHH) of bone marrow stromal cells. Biomater. Sci. 2013, 1, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrin, F.; Deckers, M.; Bertolino, P.; Ten Dijke, P. TGF-beta receptor function in the endothelium. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 65, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goumans, M.J.; Liu, Z.; ten Dijke, P. TGF-beta signaling in vascular biology and dysfunction. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, L.A. Endothelial cells and the IGF system. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 54, R1–R13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsigkou, O.; Jones, J.R.; Polak, J.M.; Stevens, M.M. Differentiation of fetal osteoblasts and formation of mineralized bone nodules by 45S5 Bioglass conditioned medium in the absence of osteogenic supplements. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3542–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gendy, R.; Yang, X.B.; Newby, P.J.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Kirkham, J. Osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stromal cells on 45S5 Bioglass® based scaffolds in vitro and in vivo. Tissue Eng. A 2013, 19, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojansivu, M.; Vanhatupa, S.; Björkvik, L.; Häkkänen, H.; Kellomäki, M.; Autio, R.; J. Ihalainen, A.; Hupa, L.; Miettinen, S. Bioactive glass ions as strong enhancers of osteogenic differentiation in human adipose stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2015, 21, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detsch, R.; Alles, S.; Hum, J.; Westenberger, P.; Sieker, F.; Heusinger, D.; Kasper, C.; Boccaccini, A.R. Osteogenic differentiation of umbilical cord and adipose derived stem cells onto highly porous 45S5 Bioglass®-based scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015, 103, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varanasi, V.G.; Odatsu, T.; Bishop, T.; Chang, J.; Owyoung, J.; Loomer, P.M. Enhanced osteoprogenitor elongated collagen fiber matrix formation by bioactive glass ionic silicon dependent on Sp7 (osterix) transcription. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2016, 104, 2604–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satija, N.K.; Sharma, D.; Afrin, F.; Tripathi, R.P.; Gangenahalli, G. High throughput transcriptome profiling of lithium stimulated human mesenchymal stem cells reveals priming towards osteoblastic lineage. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Chen, Y.; Fuxing, P.; Zhang, H. Lithium chloride modulates adipogenesis and osteogenesis of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group | Li (mmol) | Si (mmol) | P (mmol) | Ca (mmol) | Na (mmol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M199 | Bld b) | 0.85 ± 0.03 | 6.81 ± 0.13 | 0.21 ± 0.05 | 191 ± 3 |
| M199 + 45S5 | Bld | 1.53 ± 0.07 | 16.30 ± 0.35 | 0.65 ± 0.02 | 291 ± 4 |
| M199 + 45S5.5Li | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 1.46 ± 0.07 | 18.10 ± 0.39 | 0.72 ± 0.02 | 276 ± 4 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haro Durand, L.A.; Vargas, G.E.; Vera-Mesones, R.; Baldi, A.; Zago, M.P.; Fanovich, M.A.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Gorustovich, A. In Vitro Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Response to Ionic Dissolution Products from Lithium-Containing 45S5 Bioactive Glass. Materials 2017, 10, 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070740
Haro Durand LA, Vargas GE, Vera-Mesones R, Baldi A, Zago MP, Fanovich MA, Boccaccini AR, Gorustovich A. In Vitro Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Response to Ionic Dissolution Products from Lithium-Containing 45S5 Bioactive Glass. Materials. 2017; 10(7):740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070740
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaro Durand, Luis A., Gabriela E. Vargas, Rosa Vera-Mesones, Alberto Baldi, María P. Zago, María A. Fanovich, Aldo R. Boccaccini, and Alejandro Gorustovich. 2017. "In Vitro Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Response to Ionic Dissolution Products from Lithium-Containing 45S5 Bioactive Glass" Materials 10, no. 7: 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070740
APA StyleHaro Durand, L. A., Vargas, G. E., Vera-Mesones, R., Baldi, A., Zago, M. P., Fanovich, M. A., Boccaccini, A. R., & Gorustovich, A. (2017). In Vitro Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Response to Ionic Dissolution Products from Lithium-Containing 45S5 Bioactive Glass. Materials, 10(7), 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070740






