Synthesis of Al2Ca Dispersoids by Powder Metallurgy Using a Mg–Al Alloy and CaO Particles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
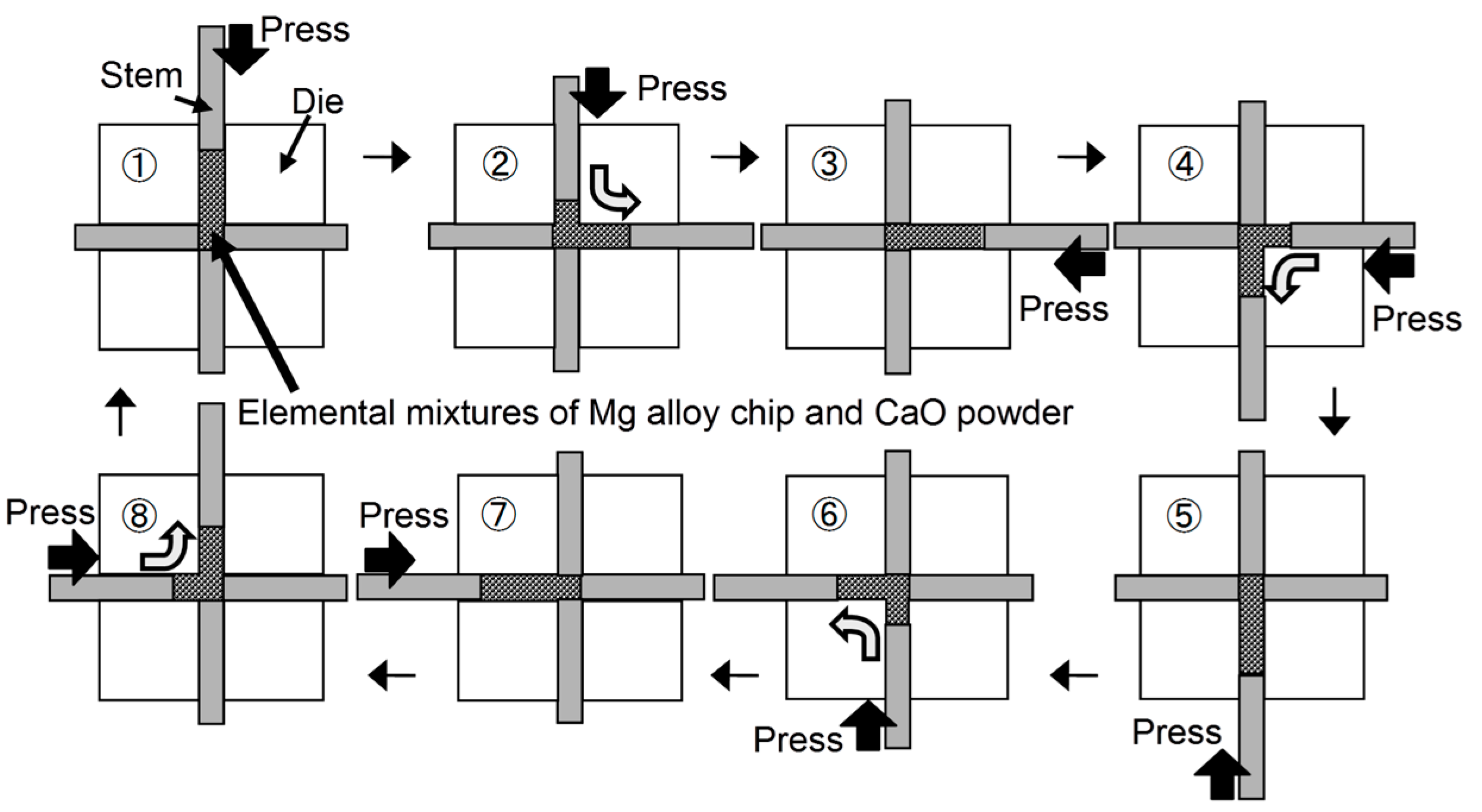
2.1. Preparation of AZ61B Precursors Containing CaO Particles
2.2. Heat Treatment of AZ61B Composite Precursor with CaO Particles
2.3. Microstructural Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
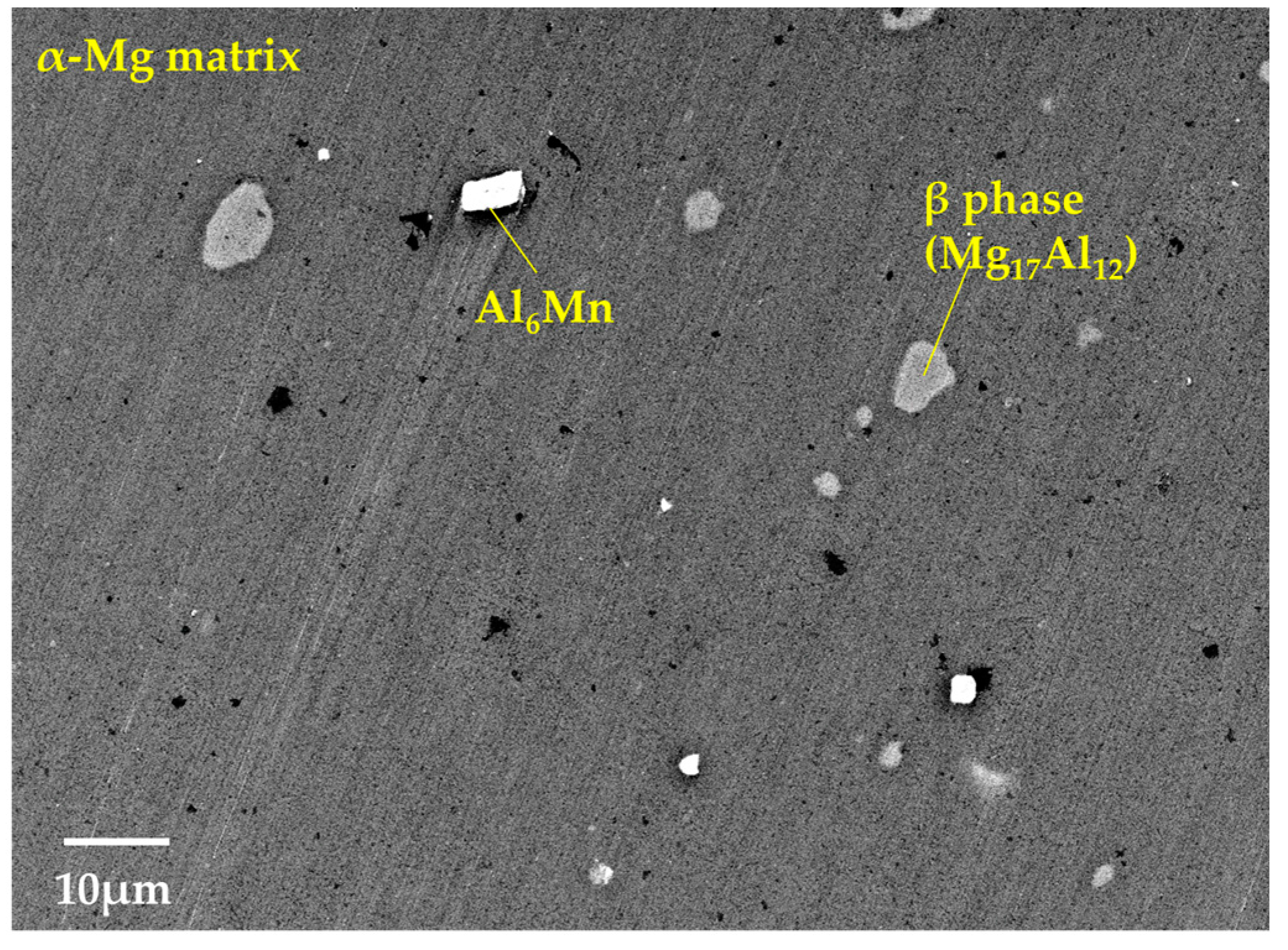
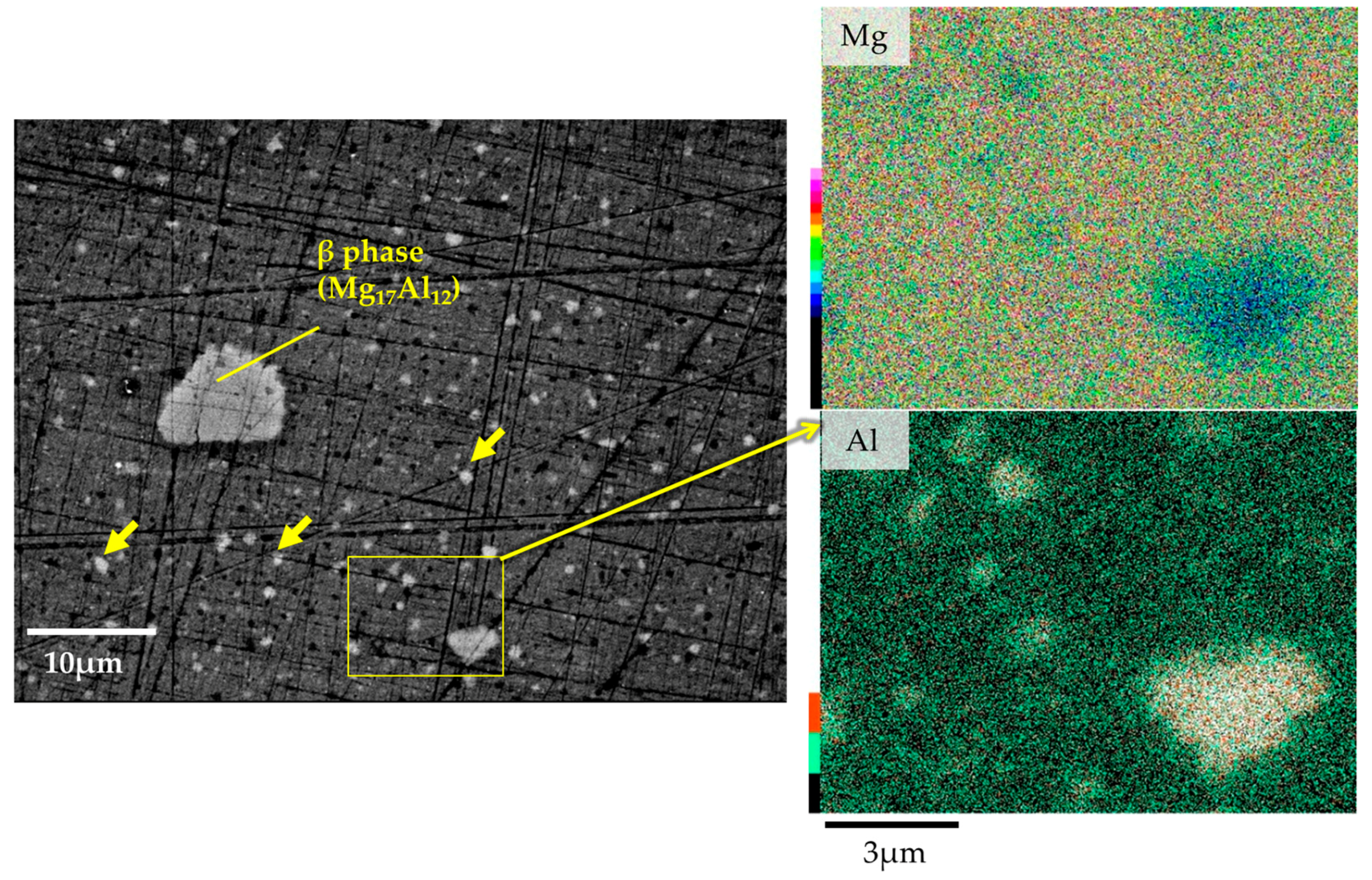
3.1. Microstructural and Compositional Analysis on the AZ61B Matrix with No CaO Particle
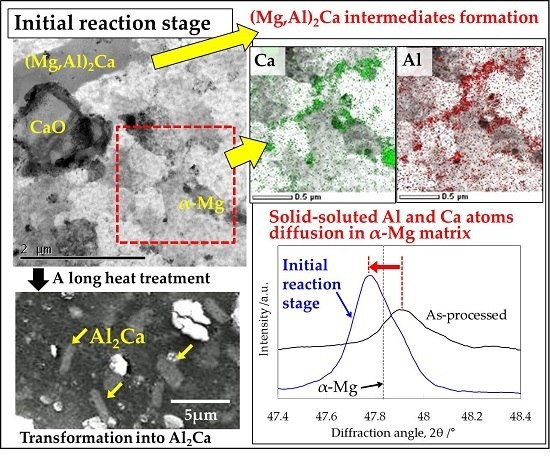
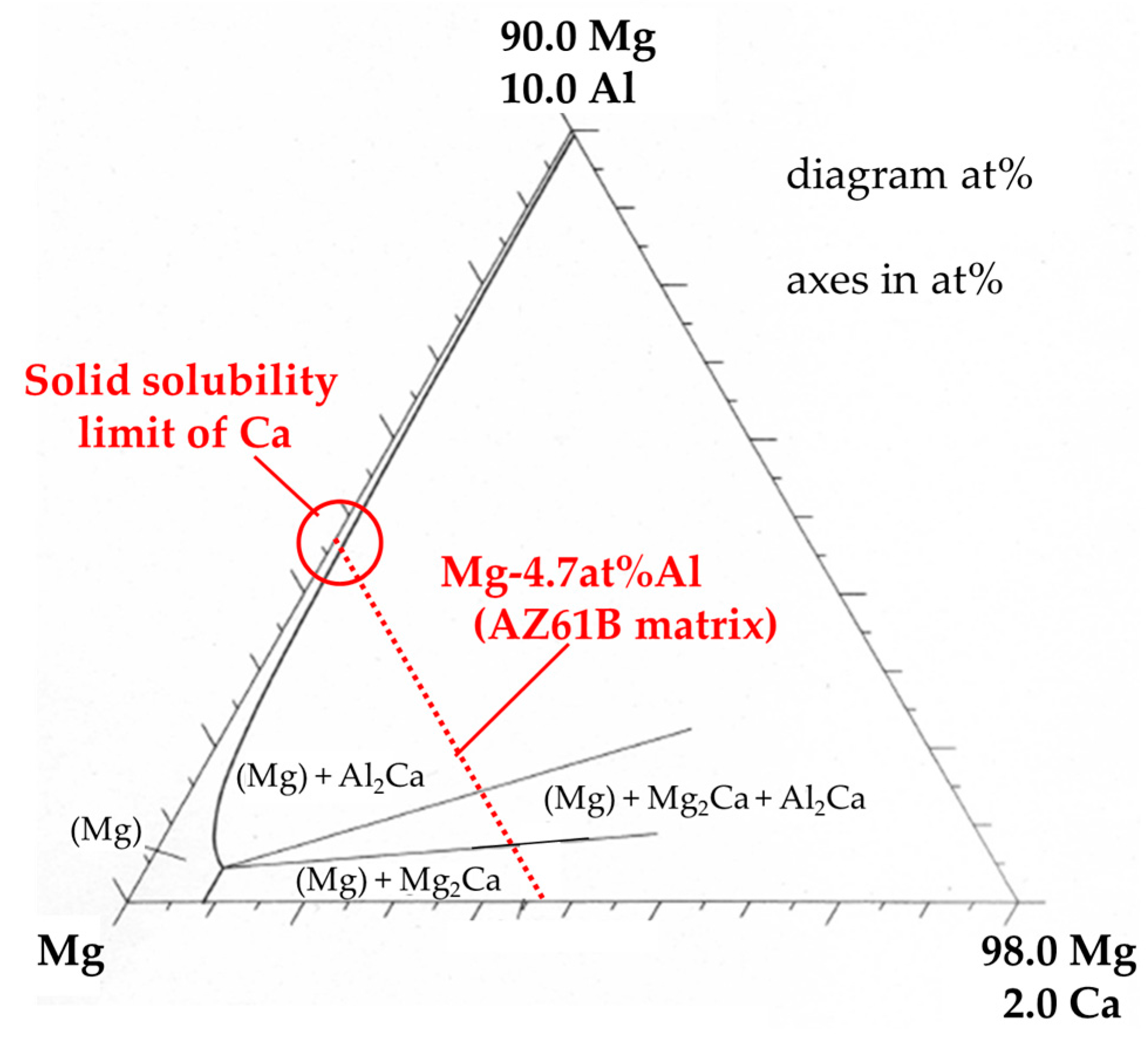
3.2. Microstructural Analysis on the α-Mg Phase of Mg–Al–CaO Precursors
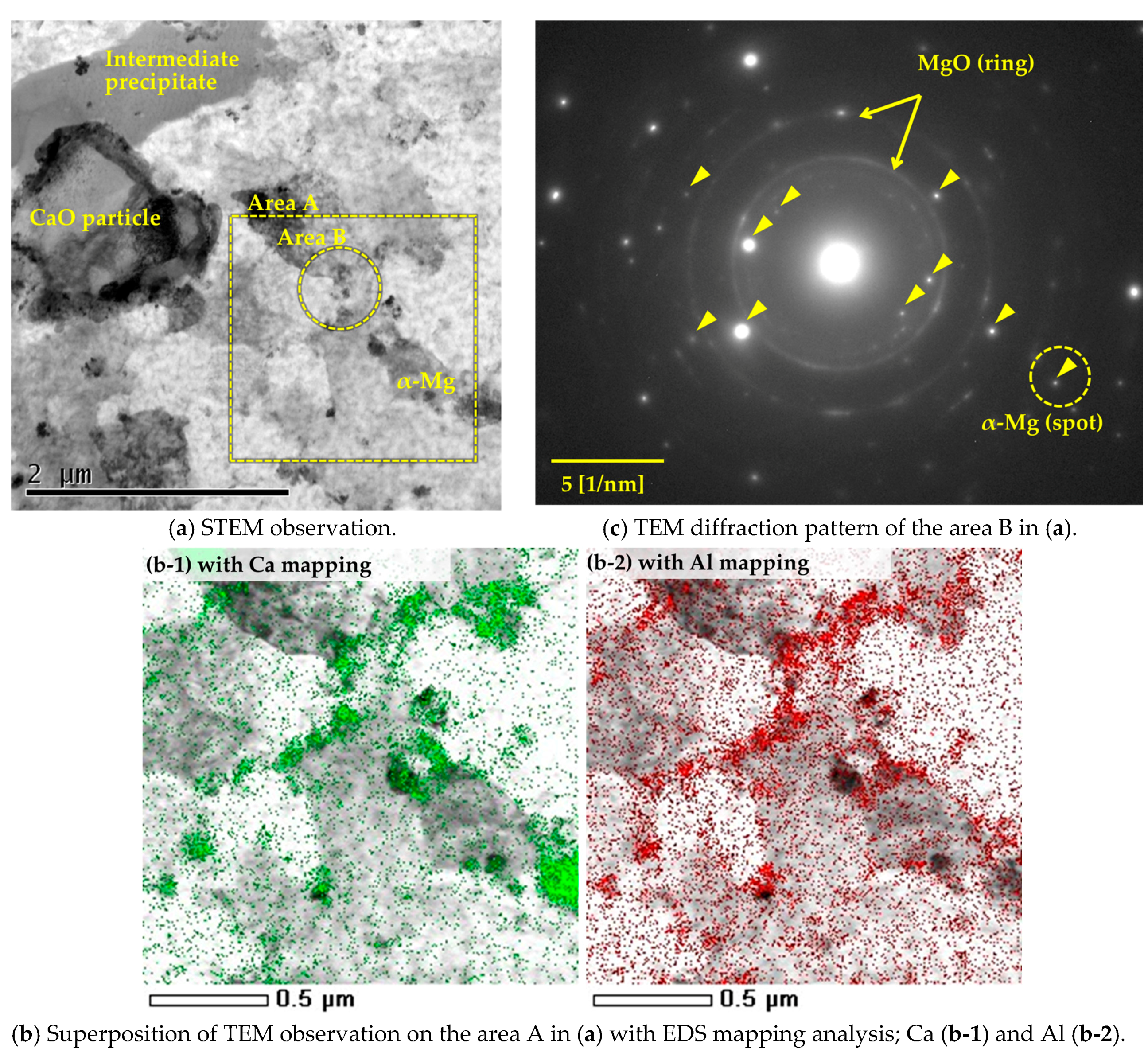
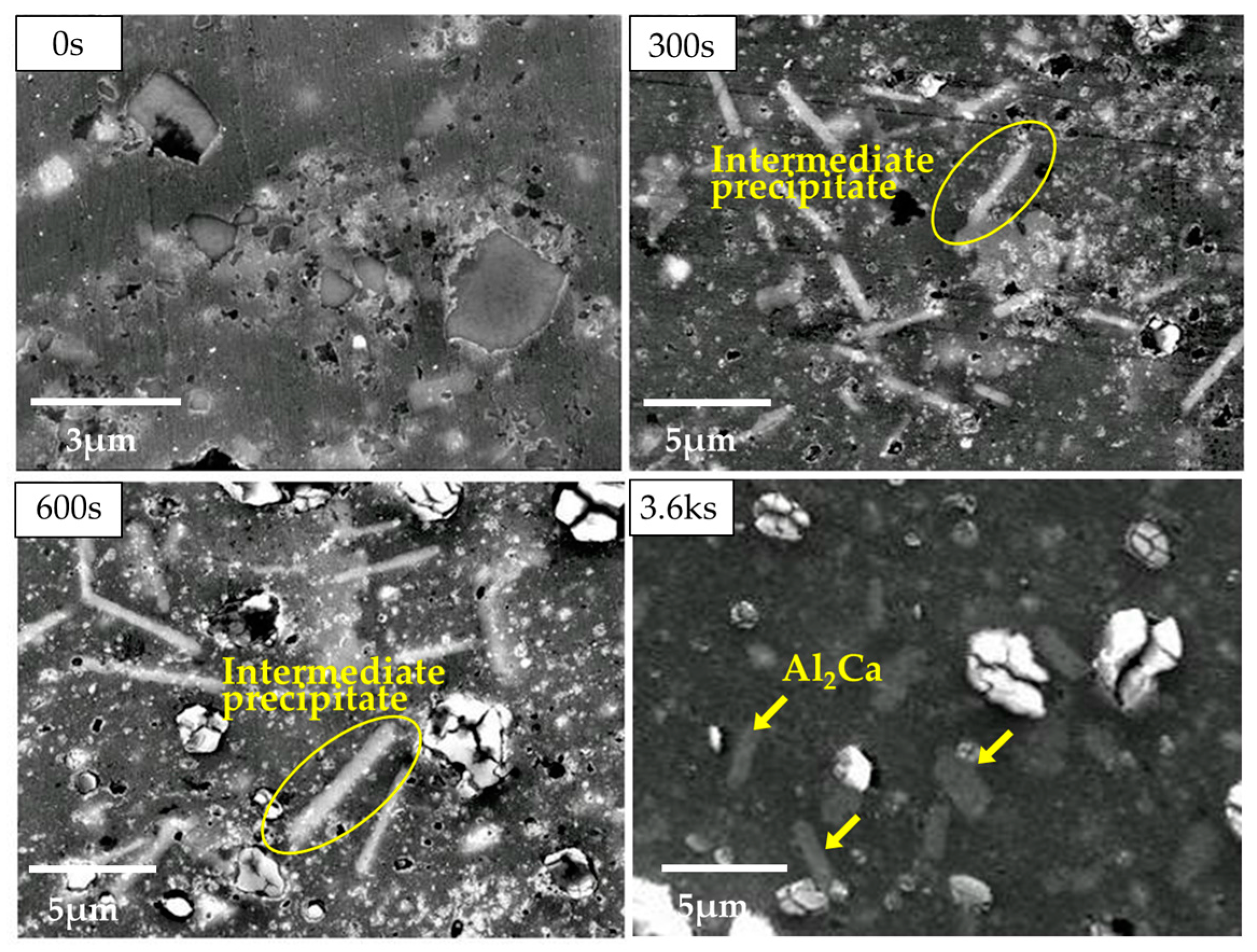
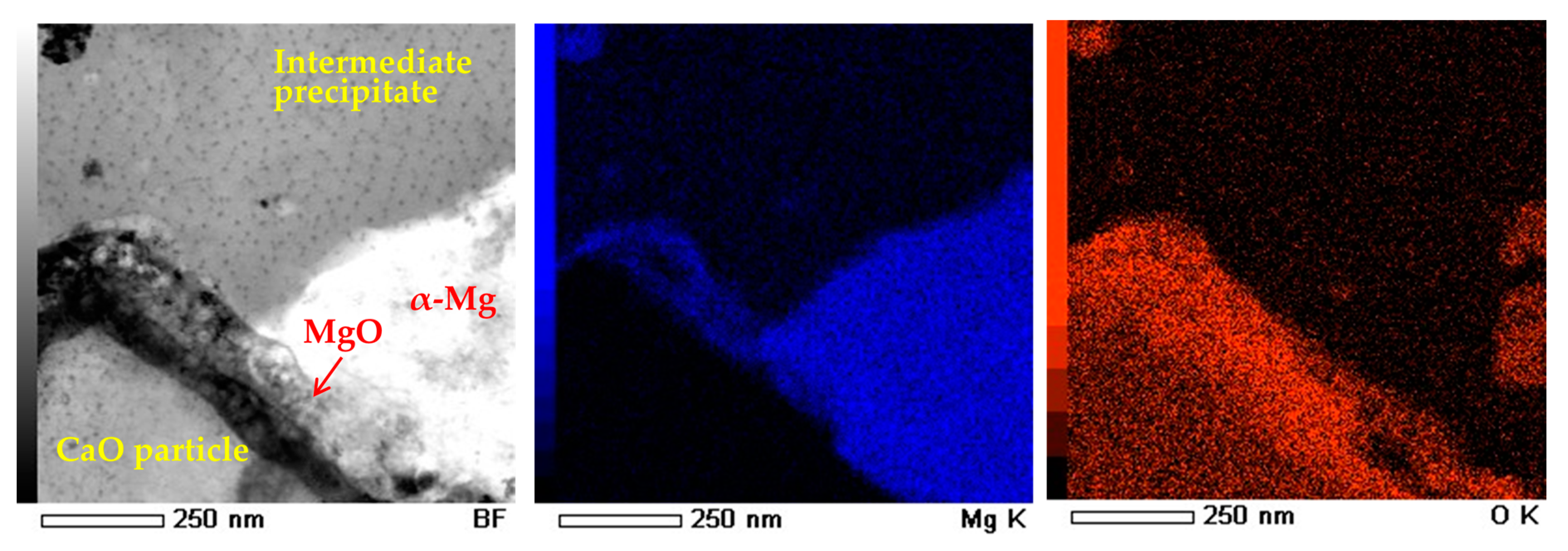
3.3. Mirostructural Analysis of the Intermediate Precipitates by TEM-EDS
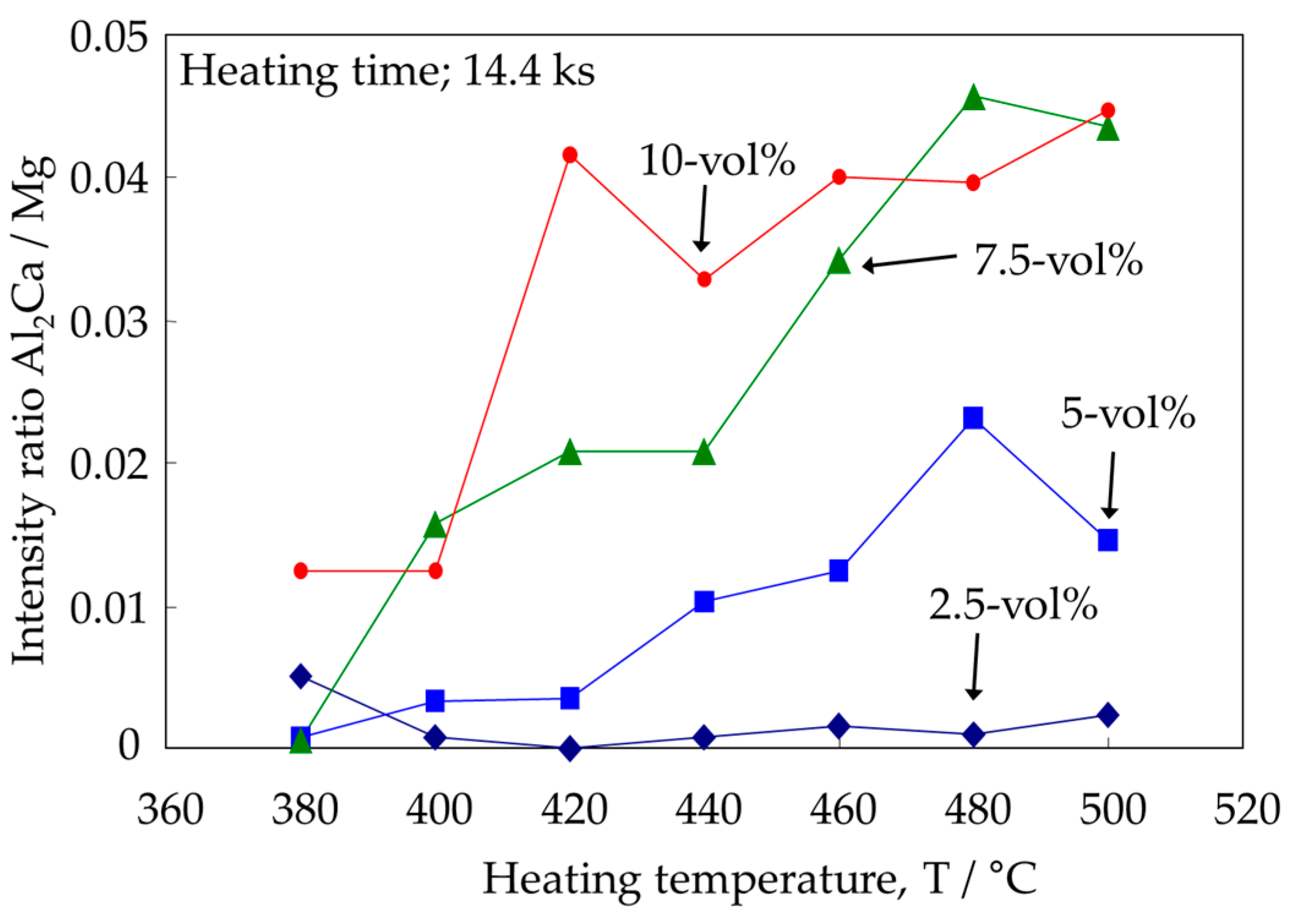
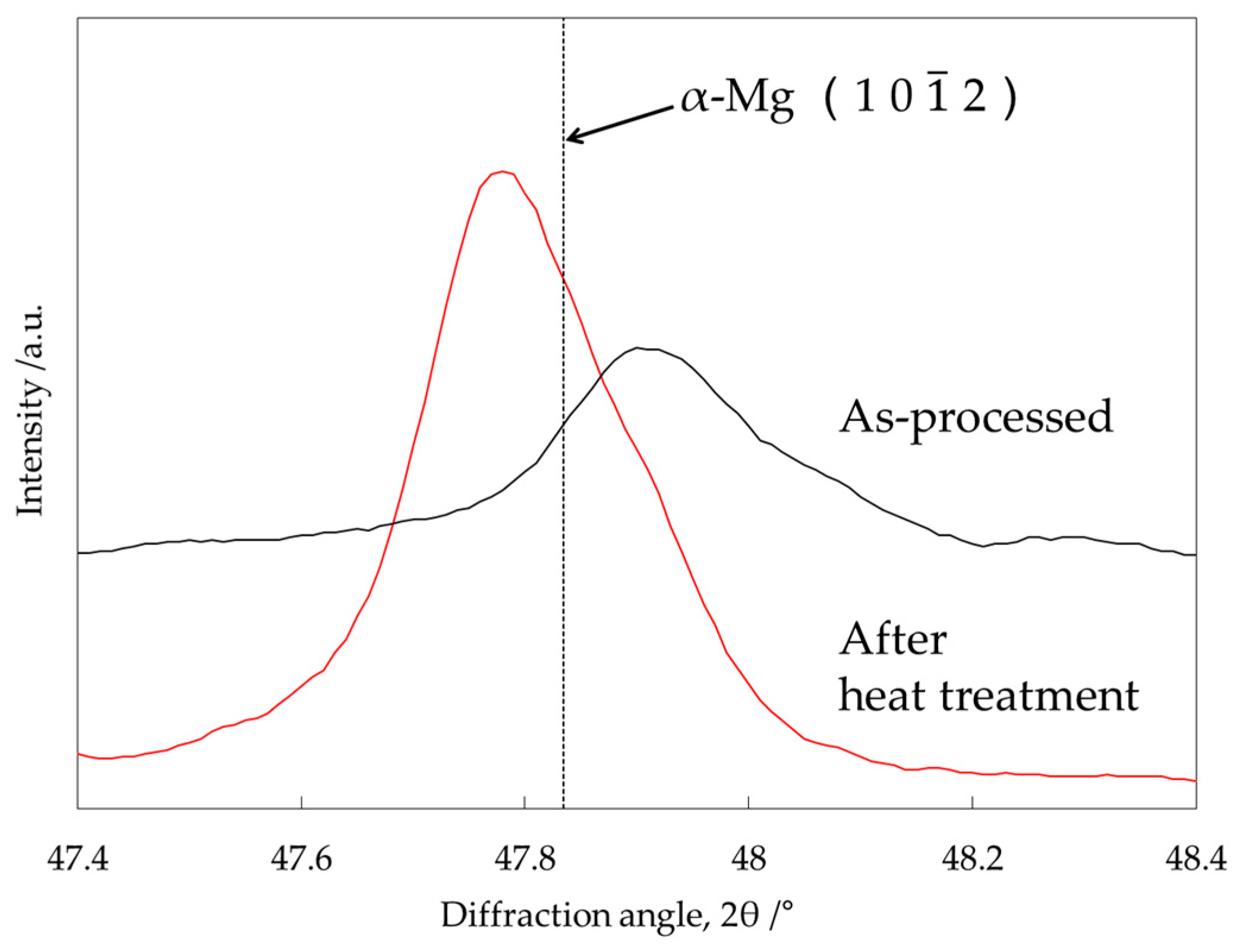
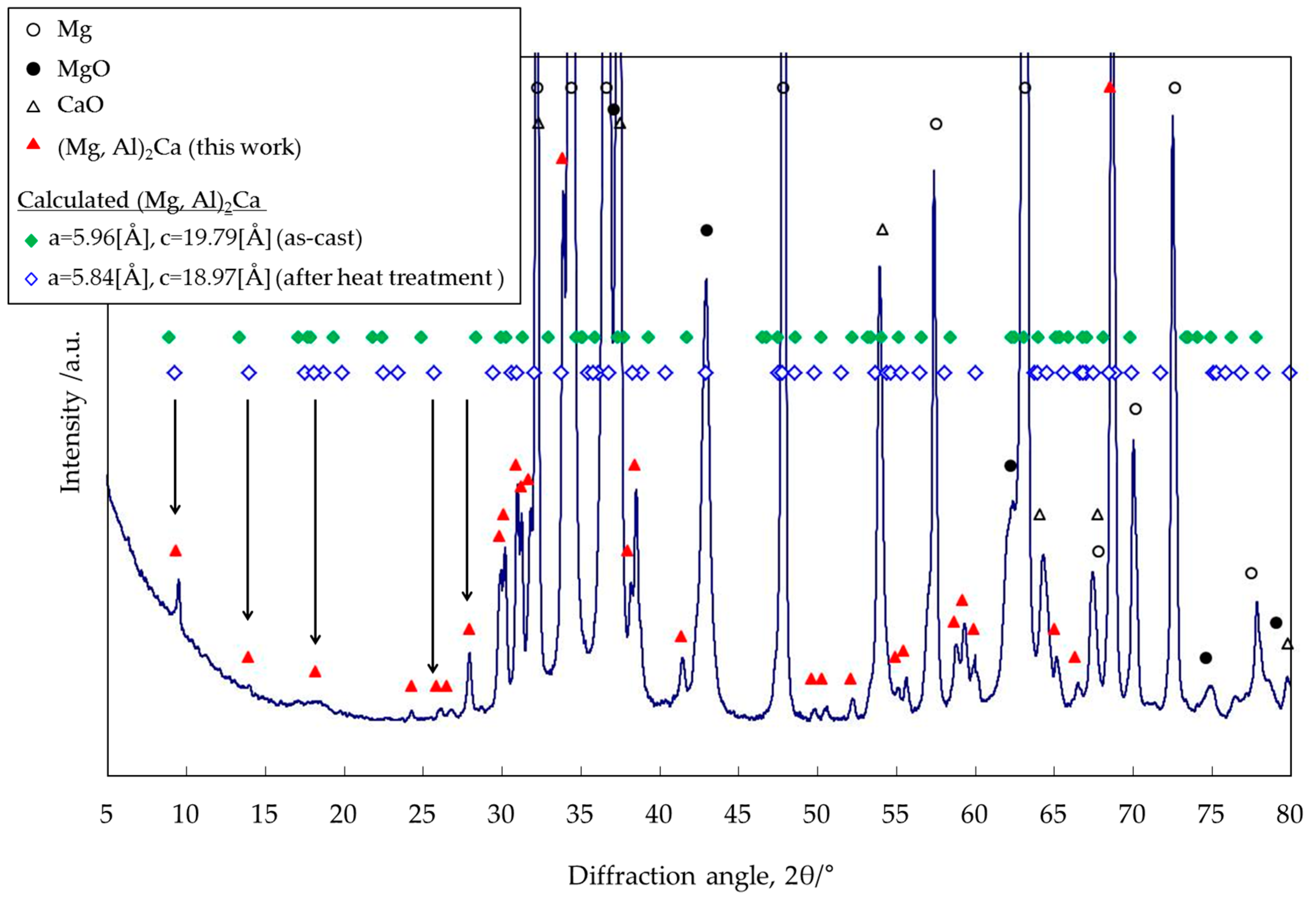
3.4. Identification of the Intermediate Precipitates by XRD
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, M.; Sharon, N.M.L. Magnesium, Magnesium Alloys, and Magnesium Composites; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2015.
- Tharumarajah, A.; Koltun, P. Is there an environmental advantage of using magnesium components for light-weighting cars? J. Clean. Prod. 2007, 15, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.A. Magnesium casting technology for structural applications. J. Magnes. Alloys 2013, 1, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettles, C.J.; Gibson, M.A.; Zhu, S.M. Microstructure and mechanical behaviour of an elevated temperature Mg-rare earth based alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 505, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekguleryuz, M.O.; Kaya, A.A. Creep resistant magnesium alloys for powertrain applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2003, 5, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyanwu, I.A.; Gokan, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Kamado, S.; Kojima, Y.; Takeda, S.; Ishida, T. Effect of substituting cerium-rich mischmetal with lanthanum on high temperature properties of die-cast Mg–Zn–Al–Ca–RE alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 380, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amberger, D.; Eisenlohr, P.; Göken, M. Microstructural evolution during creep of Ca-containing AZ91. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 510, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondori, B.; Mahmudi, R. Effect of Ca additions on the microstructure, thermal stability and mechanical properties of a cast AM60 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 2014–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.W.; Matsumoto, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Kamado, S.; Honma, T.; Kojima, Y. High temperature tensile properties of as-cast Mg–Al–Ca alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 509, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingham, H.J.T. The physical chemistry of process metallurgy. J. Soc. Chem. Ind. 1944, 63, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh, K.; Fujita, J.; Umeda, J.; Imai, H.; Enami, K.; Ohara, M.; Igarashi, T. Thermo-dynamic analysis on solid-state reduction of CaO particles dispersed in Mg–Al alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 129, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enami, K.; Ohara, M.; Igarashi, T.; Fujita, J.; Kondoh, K. Development of Heat-Resistant Magnesium Composites by Bulk Mechanical Alloying Method. J. Jpn. Soc. Powder Powder Metall. 2009, 56, 717–721. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enami, K.; Fujita, Y.; Motoe, Y.; Ohara, M.; Igarashi, T.; Kondoh, K. Development of magnesium alloy composites by bulk mechanical alloying process. J. Jpn. Soc. Powder Metall. 2008, 55, 244–249. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massalski, T.B. Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams; American Society for Metals: Metals Park, OH, USA, 1986; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, A.; Saddock, N.D.; Jones, J.W.; Pollock, T.M. Structure and transition of eutectic (Mg,Al)2Ca Laves phase in a die-cast Mg–Al–Ca base alloy. Scr. Mater. 2004, 51, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzow, G.; Effenberg, G. Ternary Alloys, A Comprehensive Compendium of Evaluated Constitutional Data and Phase Diagrams; Verlagsgesellschaft: Weinheim, Germany, 1990; Volume 3, p. 614. [Google Scholar]
- Nakaura, Y.; Watanabe, A.; Ohori, K. Effects of Ca, Sr Additions on Properties of Mg–Al Based Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzychoń, T.; Chmiela, B. The influence of tin on the microstructure and creep properties of a Mg-5Al-3Ca-0.7Sr-0.2Mn magnesium alloy. Solid State Phenom. 2012, 191, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Saddock, N.D.; Jones, J.W.; Pollock, T.M. Solidification paths and eutectic intermetallic phases in Mg–Al–Ca ternary alloys. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 2823–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Liu, J.; Witt, R.A.; Sohn, Y.; Liu, Z. Al2(Mg,Ca) phases in Mg-Al-Ca ternary system: First-principles prediction and experimental identification. Scr. Mater. 2006, 55, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Saddock, N.D.; Jones, J.W.; Pollock, T.M. Phase Equilibria in the Mg–Al–Ca Ternary System at 773 and 673 K. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 975–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janz, A.; Grobner, J.; Cao, H.; Zhu, J.; Chang, Y.A.; Schmid-Fetzer, R. Thermodynamic modeling of the Mg–Al–Ca system. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevorkov, D.; Medraj, M.; Li, J.; Essadiqi, E.; Chartrand, P. The 400 °C isothermal section of the Mg–Al–Ca system. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


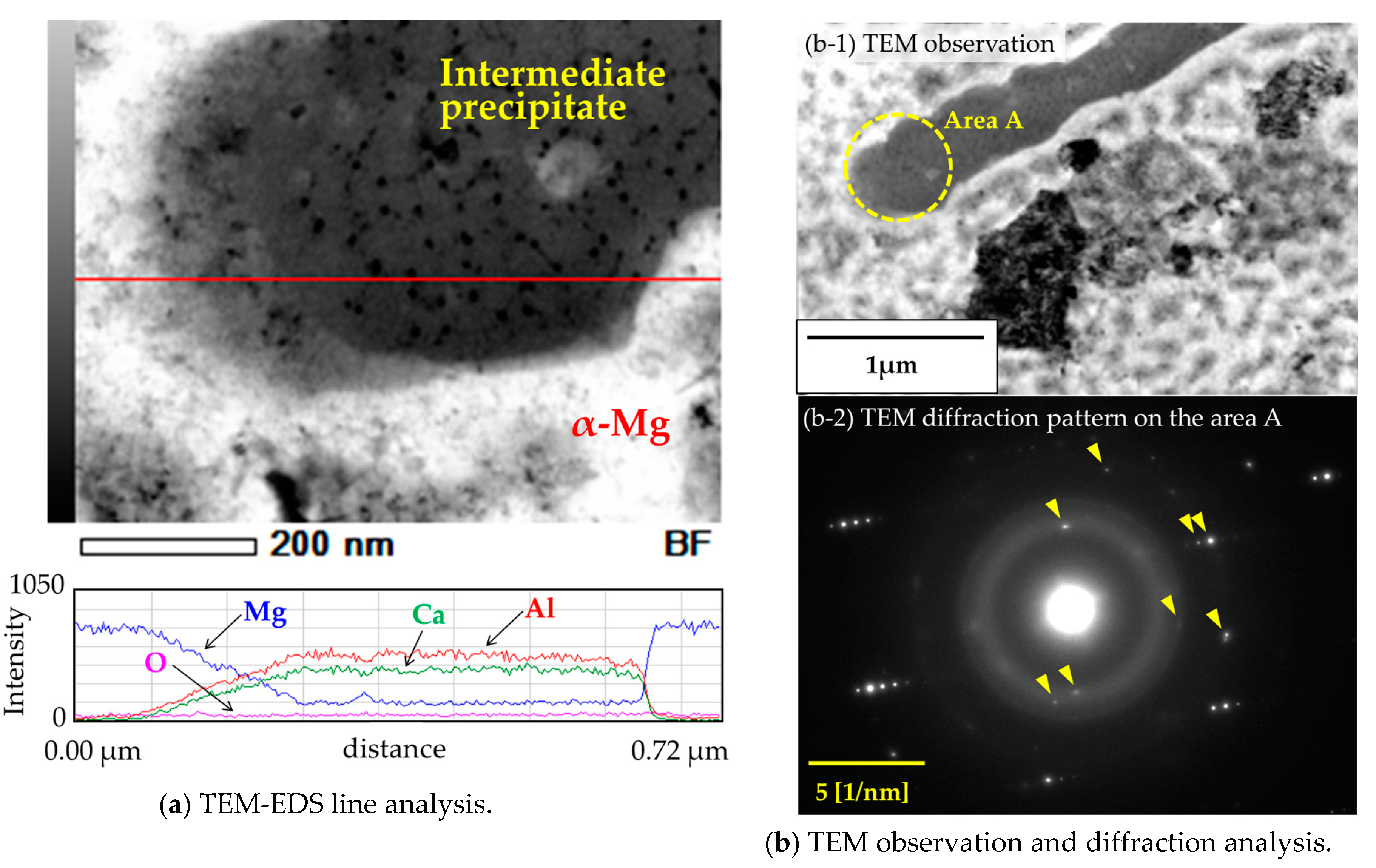
| Element (at %) | Al | O | Zn | Mn | Mg | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Mg matrix | 4.70 | 0.27 | 0.26 | 0.03 | 94.74 | 100.00 |
| Element (at %) | Mg | Al | Ca | O | Mn | Zn | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intermediate precipitate | 12.34 | 48.84 | 29.29 | 8.98 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 100.00 |
| XRD Peak Degree, 2θ (°) | Calculated Lattice Spacing, d (Å) |
|---|---|
| 29.44 | 3.033 |
| 30.65 | 2.916 |
| 33.53 | 2.673 |
| 38.20 | 2.356 |
| 43.01 | 2.103 |
| 49.54 | 1.840 |
| 56.80 | 1.621 |
| 61.57 | 1.506 |
| Compound | Type | Structure | Lattice Parameter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a (Å) | c (Å) | |||
| (Mg,Al)2Ca | C36 | di-hexagonal (as-cast) | 5.96 | 19.79 |
| di-hexagonal (after heat treatment) | 5.84 | 18.97 | ||
| Miller Indice | Diffraction Angle, 2θ (°) | Miller Indice | Diffraction Angle, 2θ (°) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| h | k | i | l | As-Cast (a = 5.96(Å)) (c = 19.79(Å)) | After Heat Treatment (a = 5.84(Å)) (c = 18.97(Å)) | h | k | i | l | As-Cast (a = 5.96(Å)) (c = 19.79(Å)) | After Heat Treatment (a = 5.84(Å)) (c = 18.97(Å)) |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4.46 | 4.66 | 2 | 1 | −3 | 4 | 50.27 | 51.55 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 8.94 | 9.32 | 2 | 1 | −3 | 5 | 52.28 | 53.69 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 13.42 | 14.01 | 3 | 0 | −3 | 0 | 53.24 | 54.42 |
| 1 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 17.18 | 17.53 | 3 | 0 | −3 | 1 | 53.46 | 54.65 |
| 1 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 17.76 | 18.15 | 3 | 0 | −3 | 2 | 54.10 | 55.35 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 17.93 | 18.71 | 3 | 0 | −3 | 3 | 55.17 | 56.49 |
| 1 | 0 | −1 | 2 | 19.40 | 19.89 | 3 | 0 | −3 | 4 | 56.64 | 58.07 |
| 1 | 0 | −1 | 3 | 21.86 | 22.51 | 3 | 0 | −3 | 5 | 58.49 | 60.05 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 22.46 | 23.45 | 2 | 2 | −4 | 0 | 62.31 | 63.74 |
| 1 | 0 | −1 | 4 | 24.93 | 25.75 | 2 | 2 | −4 | 1 | 62.51 | 63.95 |
| 1 | 0 | −1 | 5 | 28.42 | 29.43 | 2 | 2 | −4 | 2 | 63.10 | 64.58 |
| 1 | 1 | −2 | 0 | 29.98 | 30.62 | 2 | 2 | −4 | 3 | 64.07 | 65.63 |
| 1 | 1 | −2 | 1 | 30.33 | 30.99 | 3 | 1 | −4 | 0 | 65.16 | 66.68 |
| 1 | 1 | −2 | 2 | 31.35 | 32.07 | 3 | 1 | −4 | 1 | 65.36 | 66.88 |
| 1 | 1 | −2 | 3 | 32.98 | 33.81 | 2 | 2 | −4 | 4 | 65.41 | 67.07 |
| 2 | 0 | −2 | 0 | 34.76 | 35.50 | 3 | 1 | −4 | 2 | 65.93 | 67.50 |
| 2 | 0 | −2 | 1 | 35.06 | 35.82 | 3 | 1 | −4 | 3 | 66.88 | 68.52 |
| 1 | 1 | −2 | 4 | 35.15 | 36.12 | 2 | 2 | −4 | 5 | 67.12 | 68.91 |
| 2 | 0 | −2 | 2 | 35.96 | 36.78 | 3 | 1 | −4 | 4 | 68.19 | 69.93 |
| 2 | 0 | −2 | 3 | 37.42 | 38.33 | 3 | 1 | −4 | 5 | 69.87 | 71.74 |
| 1 | 1 | −2 | 5 | 37.79 | 38.92 | 4 | 0 | −4 | 0 | 73.37 | 75.14 |
| 2 | 0 | −2 | 4 | 39.38 | 40.42 | 4 | 0 | −4 | 1 | 73.55 | 75.33 |
| 2 | 0 | −2 | 5 | 41.78 | 42.98 | 4 | 0 | −4 | 2 | 74.10 | 75.92 |
| 2 | 1 | −3 | 0 | 46.55 | 47.57 | 4 | 0 | −4 | 3 | 75.00 | 76.89 |
| 2 | 1 | −3 | 1 | 46.79 | 47.82 | 4 | 0 | −4 | 4 | 76.25 | 78.25 |
| 2 | 1 | −3 | 2 | 47.50 | 48.58 | 4 | 0 | −4 | 5 | 77.86 | 79.98 |
| 2 | 1 | −3 | 3 | 48.67 | 49.83 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujita, J.; Umeda, J.; Kondoh, K. Synthesis of Al2Ca Dispersoids by Powder Metallurgy Using a Mg–Al Alloy and CaO Particles. Materials 2017, 10, 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070716
Fujita J, Umeda J, Kondoh K. Synthesis of Al2Ca Dispersoids by Powder Metallurgy Using a Mg–Al Alloy and CaO Particles. Materials. 2017; 10(7):716. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070716
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujita, Junji, Junko Umeda, and Katsuyoshi Kondoh. 2017. "Synthesis of Al2Ca Dispersoids by Powder Metallurgy Using a Mg–Al Alloy and CaO Particles" Materials 10, no. 7: 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070716
APA StyleFujita, J., Umeda, J., & Kondoh, K. (2017). Synthesis of Al2Ca Dispersoids by Powder Metallurgy Using a Mg–Al Alloy and CaO Particles. Materials, 10(7), 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070716