Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Bacteria Response to Antibiotics Using Nanoporous Membrane and Graphene Quantum Dot (GQDs)-Based Electrochemical Biosensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
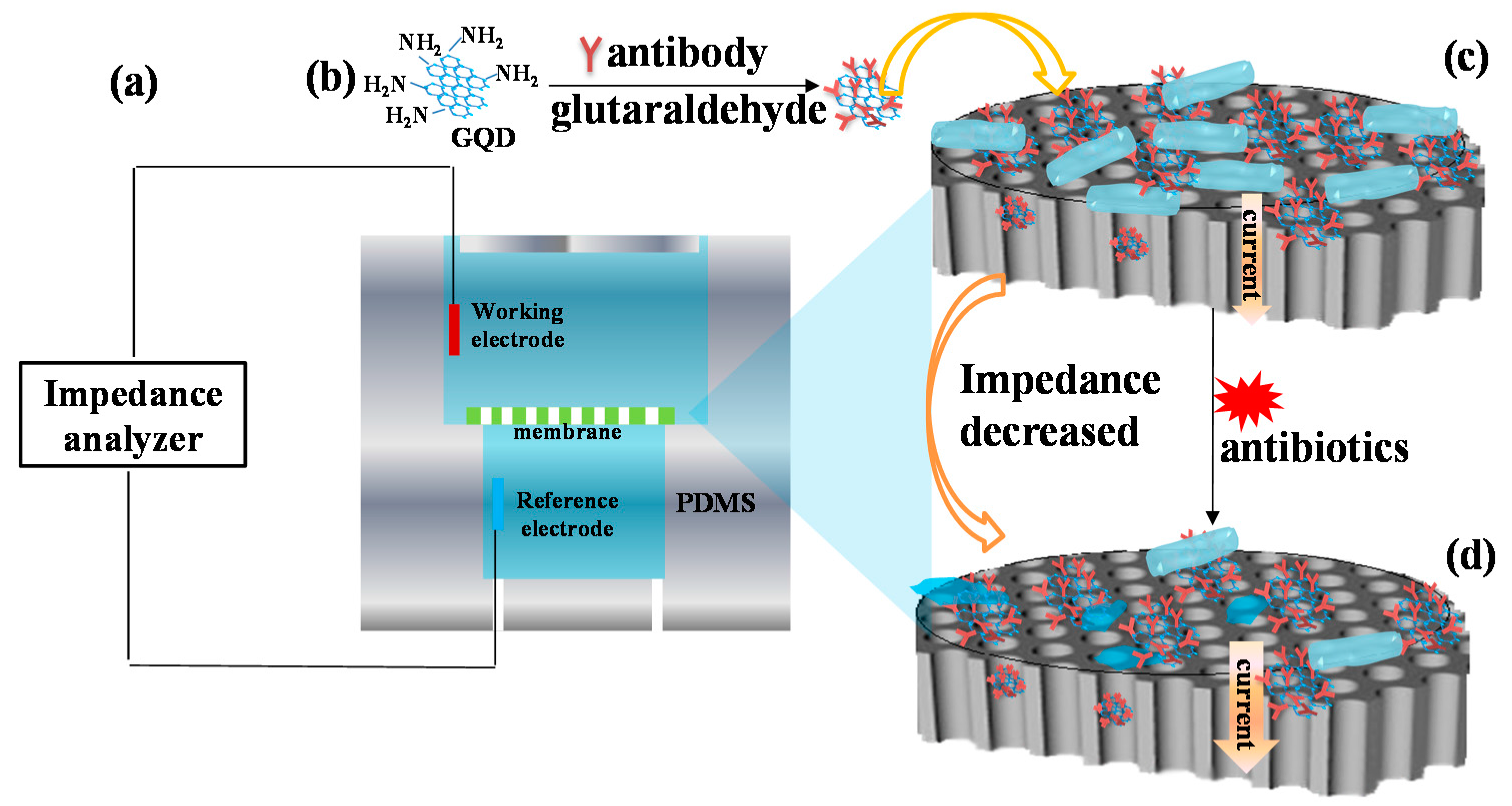
2.1. Mechanism of Bacterial Response to Antibiotics Detection
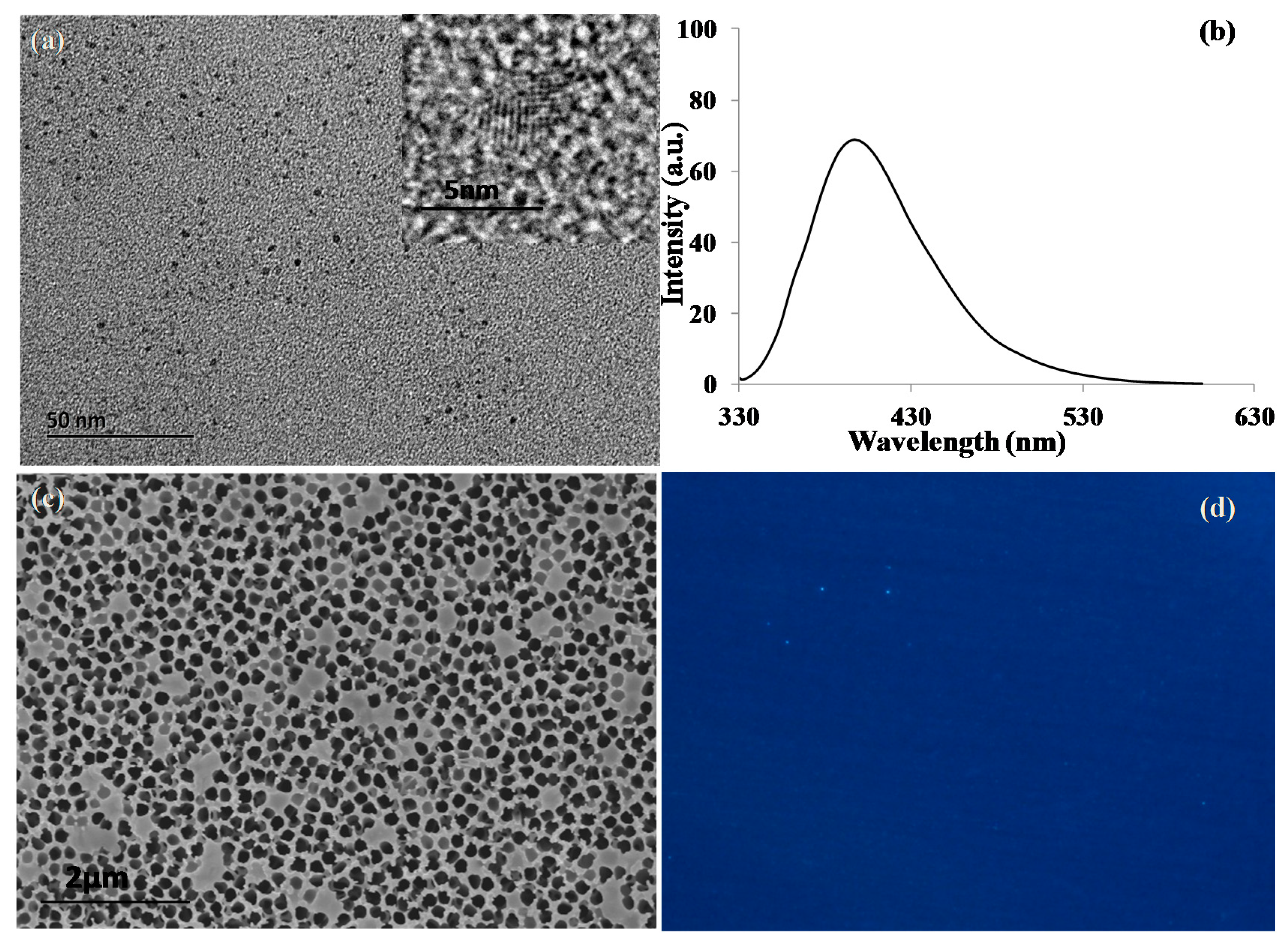
2.2. Characterization of GQDs and Nanoporous Alumina Membranes
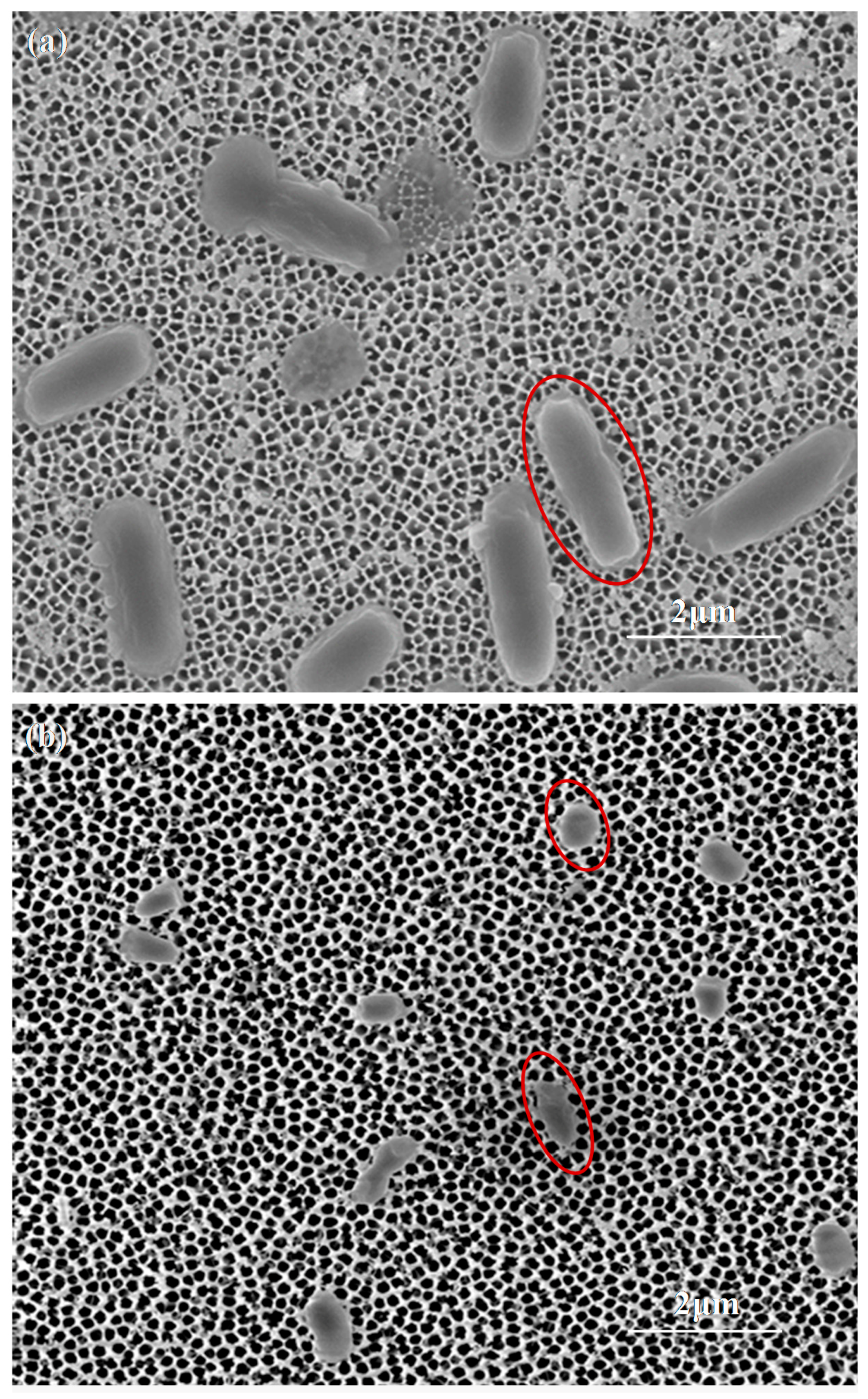
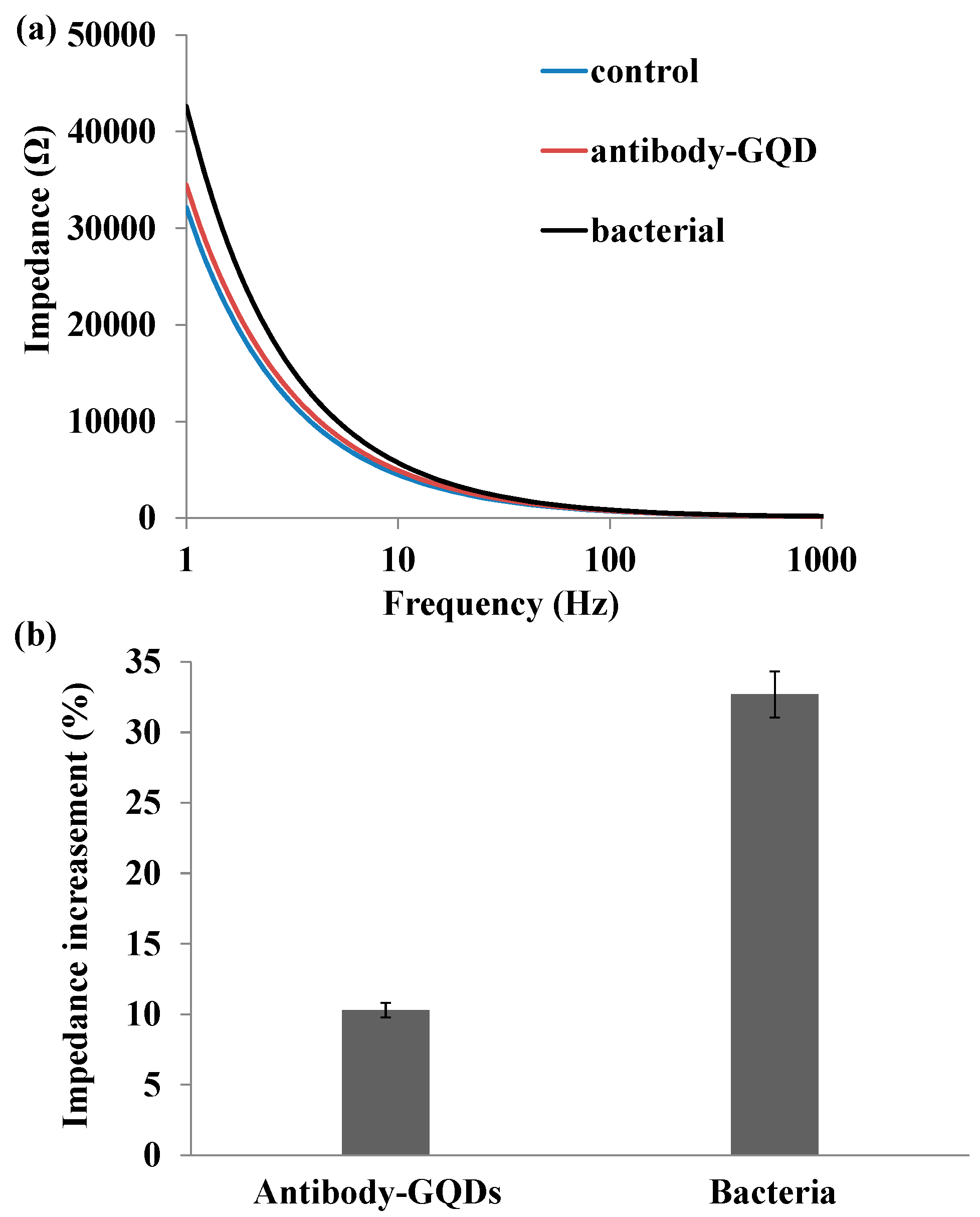
2.3. Impedance Sensing of Bacteria Capture on Nanoporous Alumina Membrane
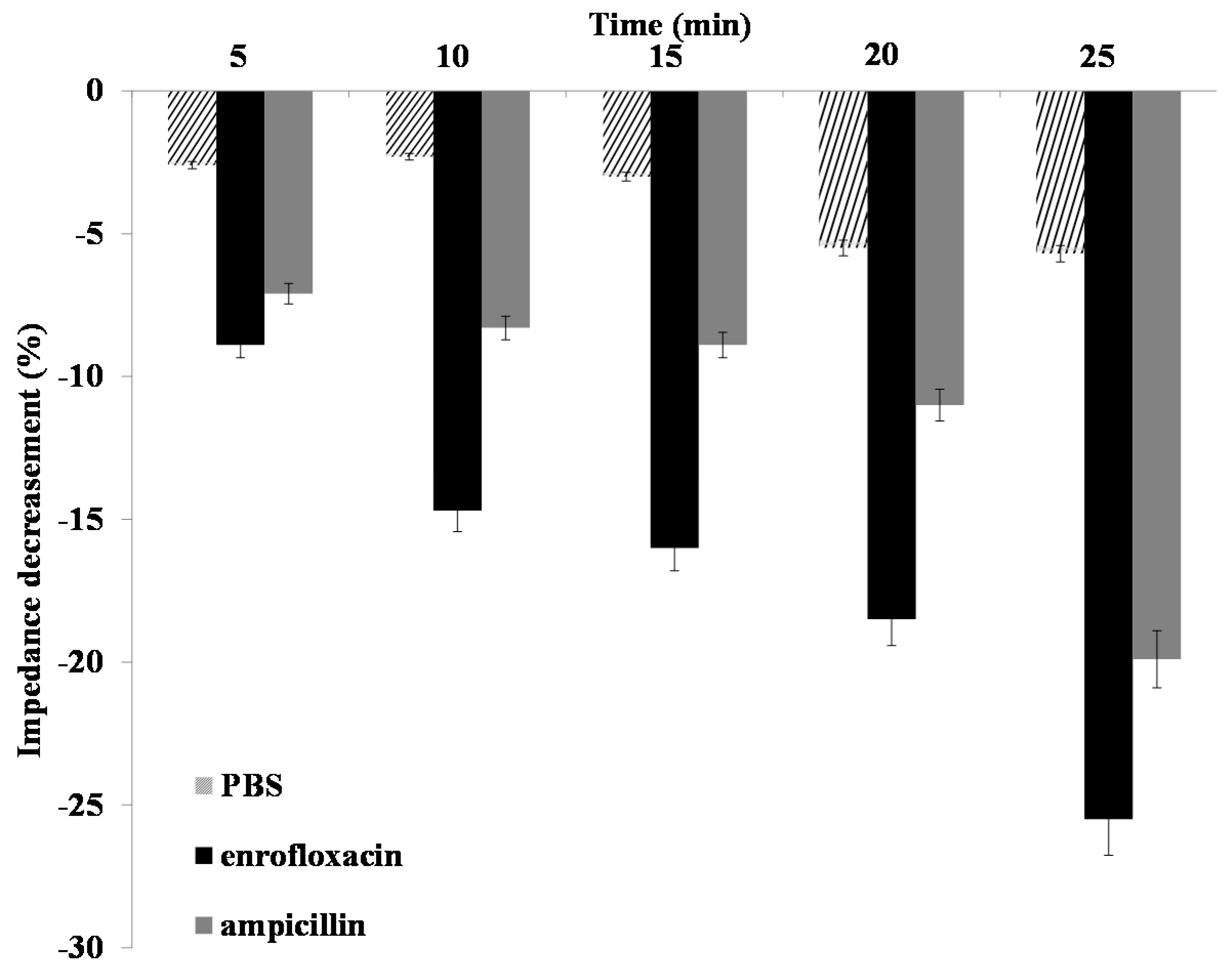
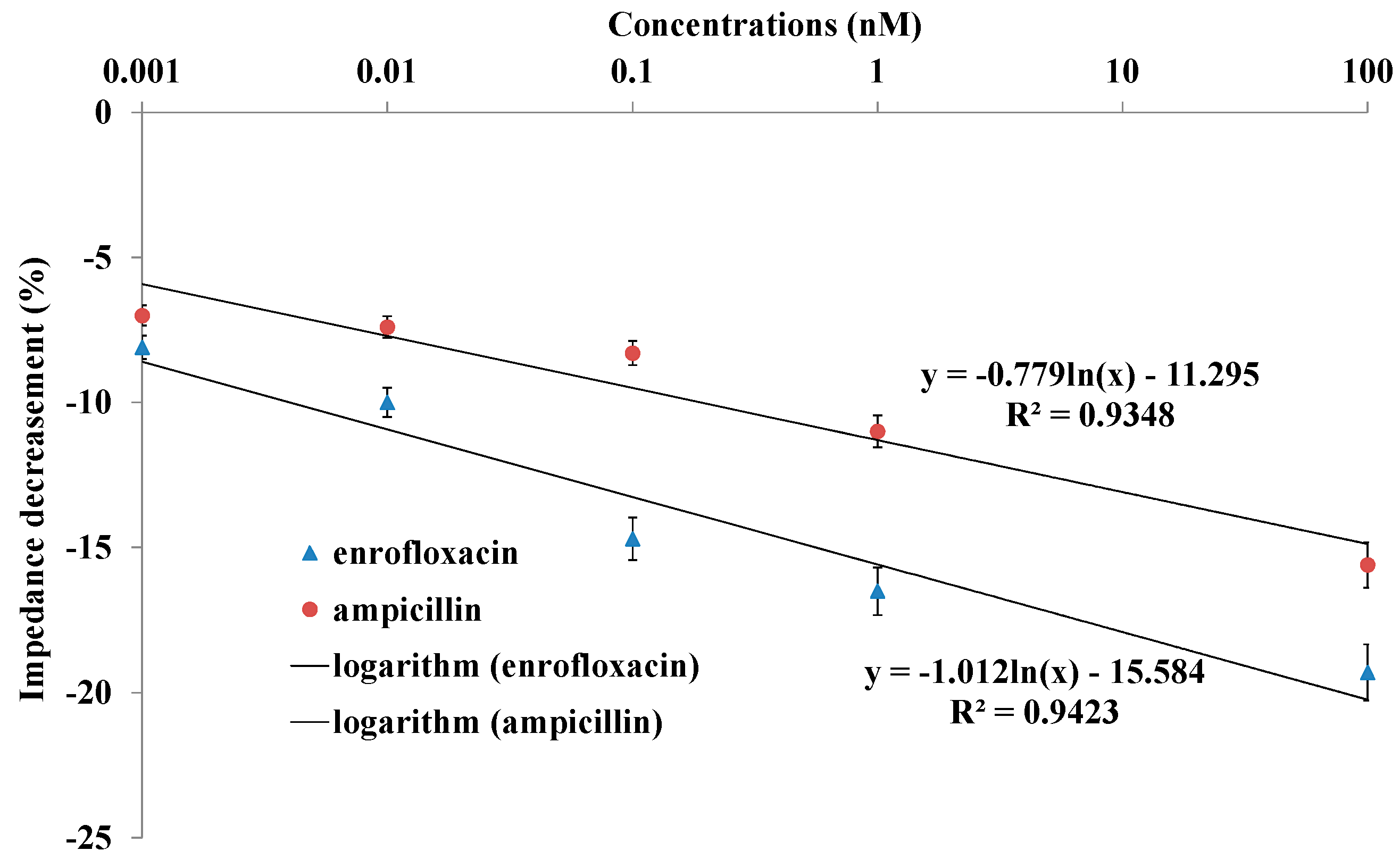
2.4. Impedance Sensing of Bacteria Cells Response to Antibiotics
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Nanoporous Alumina Membrane Surface Functionalization
3.2. PDMS Chamber and Functionalized Nanoporous Membrane Integration
3.3. Anti Salmonella Monoclonal Antibody Preparation and Analysis
3.4. Preparation of Biofunctional GQDs on Nanoporous Membrane
3.5. Bacterial Cell Culture and Plate Counting
3.6. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Measurement
3.7. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeissig, S.; Blumberg, R.S. Life at the beginning: Perturbation of the microbiota by antibiotics in early life and its role in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fey, P.D.; Safranek, T.J.; Rupp, M.E.; Dunne, E.F.; Ribot, E.; Iwen, P.C.; Bradford, P.A.; Angulo, F.J.; Hinrichs, S.H. Ceftriaxone-resistant salmonella infection acquired by a child from cattle. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, I.; Casewell, M.; Cox, T.; De Groot, B.; Friis, C.; Jones, R.; Nightingale, C.; Preston, R.; Waddell, J. Does the use of antibiotics in food animals pose a risk to human health? A critical review of published data. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 53, 28–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, B.M.; Levy, S.B. Food animals and antimicrobials: Impacts on human health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghdam, E.M.; Hejazi, M.S.; Barzegar, A. Riboswitches: From living biosensors to novel targets of antibiotics. Gene 2016, 592, 244–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamscher, G.; Sczesny, S.; Höper, H.; Nau, H. Determination of persistent tetracycline residues in soil fertilized with liquid manure by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambla-Alegre, M.; Peris-Vicente, J.; Esteve-Romero, J.; Carda-Broch, S. Analysis of selected veterinary antibiotics in fish by micellar liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection and validation in accordance with regulation 2002/657/EC. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverté, S.; Borrull, F.; Pocurull, E.; Marcé, R.M. Determination of antibiotic compounds in water by solid-phase extraction-high-performance liquid chromatography-(electrospray) mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1010, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Torres, R.; Consentino, M.O.; Lopez, M.A.B.; Mochon, M.C. Simultaneous determination of 11 antibiotics and their main metabolites from four different groups by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array-fluorescence (HPLC–DAD–FLD) in human urine samples. Talanta 2010, 81, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.H.; Wang, E.H.; Gurak, J.A.; Bhawal, S.; Deshmukh, R.; Wijeratne, A.B.; Edwards, B.L.; Foss, F.W., Jr.; Timmons, R.B.; Schug, K.A. Affinity mesh screen materials for selective extraction and analysis of antibiotics using transmission mode desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8046–8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, W.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of gentamycin residues in animal-derived foods. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino, J.C.; Martin, A.; Camacho, M.; Guerra, H.; Swings, J.; Portaels, F. Resazurin microtiter assay plate: Simple and inexpensive method for detection of drug resistance in mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2720–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diacon, A.H.; Maritz, J.S.; Venter, A.; van Helden, P.D.; Andries, K.; McNeeley, D.F.; Donald, P.R. Time to detection of the growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in MGIT 960 for determining the early bactericidal activity of antituberculosis agents. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehme, C.C.; Nabeta, P.; Hillemann, D.; Nicol, M.P.; Shenai, S.; Krapp, F.; Allen, J.; Tahirli, R.; Blakemore, R.; Rustomjee, R.; et al. Rapid molecular detection of tuberculosis and rifampin resistance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandara, A.B.; Zuo, Z.; Ramachandran, S.; Ritter, A.; Heflin, J.R.; Inzana, T.J. Detection of methicillin-resistant staphylococci by biosensor assay consisting of nanoscale films on optical fiber long-period gratings. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chen, Q.; Hassan, M.; Chen, X.; Ouyang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, J. A magnetite/PMAA nanospheres-targeting SERS aptasensor for tetracycline sensing using mercapto molecules embedded core/shell nanoparticles for signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoukroun-Barnes, L.R.; Wagan, S.; White, R.J. Enhancing the analytical performance of electrochemical RNA aptamer-based sensors for sensitive detection of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.J.; Bashir, R. Electrical/electrochemical impedance for rapid detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mungroo, N.A.; Neethirajan, S. Biosensors for the detection of antibiotics in poultry industry—A review. Biosensors 2014, 4, 472–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannoor, M.S.; Zhang, S.; Link, A.J.; McAlpine, M.C. Electrical detection of pathogenic bacteria via immobilized antimicrobial peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19207–19212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daprà, J.; Lauridsen, L.H.; Nielsen, A.T.; Rozlosnik, N. Comparative study on aptamers as recognition elements for antibiotics in a label-free all-polymer biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.Y.; Tian, F.; Lyu, J.; Yang, M. Nanoparticle based fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) for biosensing applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6989–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.W.; Guo, J.B.; Chen, S.; Yang, M. Nanoporous membrane based impedance sensors to detect the enzymatic activity of botulinum neurotoxin A. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 6544–6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.J.; Liu, Z.B.; Liu, Q.J.; Yuen, K.T.; Mak, A.F.T.; Yang, M.; Leung, P.H.M. A polyethylene glycol (PEG) microfluidic chip with nanostructures for bacteria rapid patterning and detection. Sens. Actuators A 2009, 154, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, M.K.; Ye, W.W.; Wang, G.J.; Li, J.M.; Yang, M.; Hao, J.H. Ultrasensitive detection of Ebola virus oligonucleotide based on upconversion nanoprobe/nanoporous membrane system. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.W.; Shi, J.Y.; Chan, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M. A nanoporous membrane based impedance sensing platform for DNA sensing with gold nanoparticle amplification. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 193, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.W.; Xu, Y.F.; Zheng, L.H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Sun, P.L. A nanoporous alumina membrane based electrochemical biosensor for histamine determination with biofunctionalized magnetic nanoparticles concentration and signal amplification. Sensors 2016, 16, E1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Dai, Z.H. Carbon nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors: An overview. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6420–6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Tang, L.H.; Li, J.H. Graphene-based materials in electrochemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3157–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razmi, H.; Mohammad-Rezaei, R. Graphene quantum dots as a new substrate for immobilization and direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase: Application to sensitive glucose determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Cao, X.D.; Liu, S.Q. Versatile immunosensor using a quantum dot coated silica nanosphere as a label for signal amplification. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6422–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalita, H.; Mohapatra, J.; Pradhan, L.; Mitra, A.; Bahadur, D.; Aslam, M. Efficient synthesis of rice based graphene quantum dots and their fluorescent properties. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 23518–23524. [Google Scholar]
- Kohanski, M.A.; Dwyer, D.J.; Hayete, B.; Lawrence, C.A.; Collins, J.J. A common mechanism of cellular death induced by bactericidal antibiotics. Cell 2007, 130, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasz, A. The mechanism of the irreversible antimicrobial effects of penicillins: How the beta-lactam antibiotics kill and lyse bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1979, 33, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Chopra, A.; Chaudhary, S.; Suri, C.R. Bio-nanomechanical detection of diabetic marker HbA1c. BioNanoScience 2012, 2, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, W.; Guo, J.; Bao, X.; Chen, T.; Weng, W.; Chen, S.; Yang, M. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Bacteria Response to Antibiotics Using Nanoporous Membrane and Graphene Quantum Dot (GQDs)-Based Electrochemical Biosensors. Materials 2017, 10, 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10060603
Ye W, Guo J, Bao X, Chen T, Weng W, Chen S, Yang M. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Bacteria Response to Antibiotics Using Nanoporous Membrane and Graphene Quantum Dot (GQDs)-Based Electrochemical Biosensors. Materials. 2017; 10(6):603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10060603
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Weiwei, Jiubiao Guo, Xianfeng Bao, Tian Chen, Wenchuan Weng, Sheng Chen, and Mo Yang. 2017. "Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Bacteria Response to Antibiotics Using Nanoporous Membrane and Graphene Quantum Dot (GQDs)-Based Electrochemical Biosensors" Materials 10, no. 6: 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10060603
APA StyleYe, W., Guo, J., Bao, X., Chen, T., Weng, W., Chen, S., & Yang, M. (2017). Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Bacteria Response to Antibiotics Using Nanoporous Membrane and Graphene Quantum Dot (GQDs)-Based Electrochemical Biosensors. Materials, 10(6), 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10060603





