Gallic Acid as an Oxygen Scavenger in Bio-Based Multilayer Packaging Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Film Properties
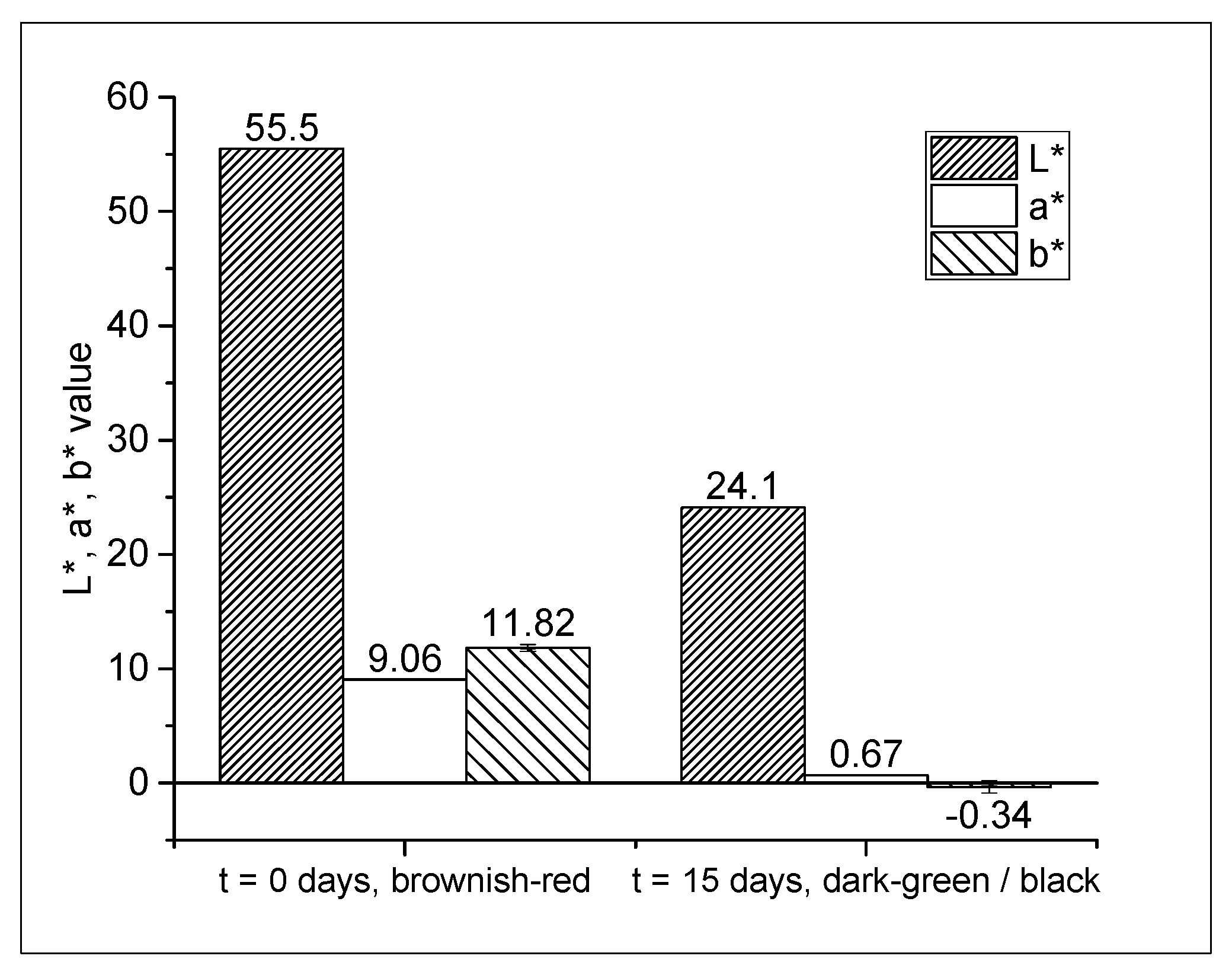
2.2. Film Color
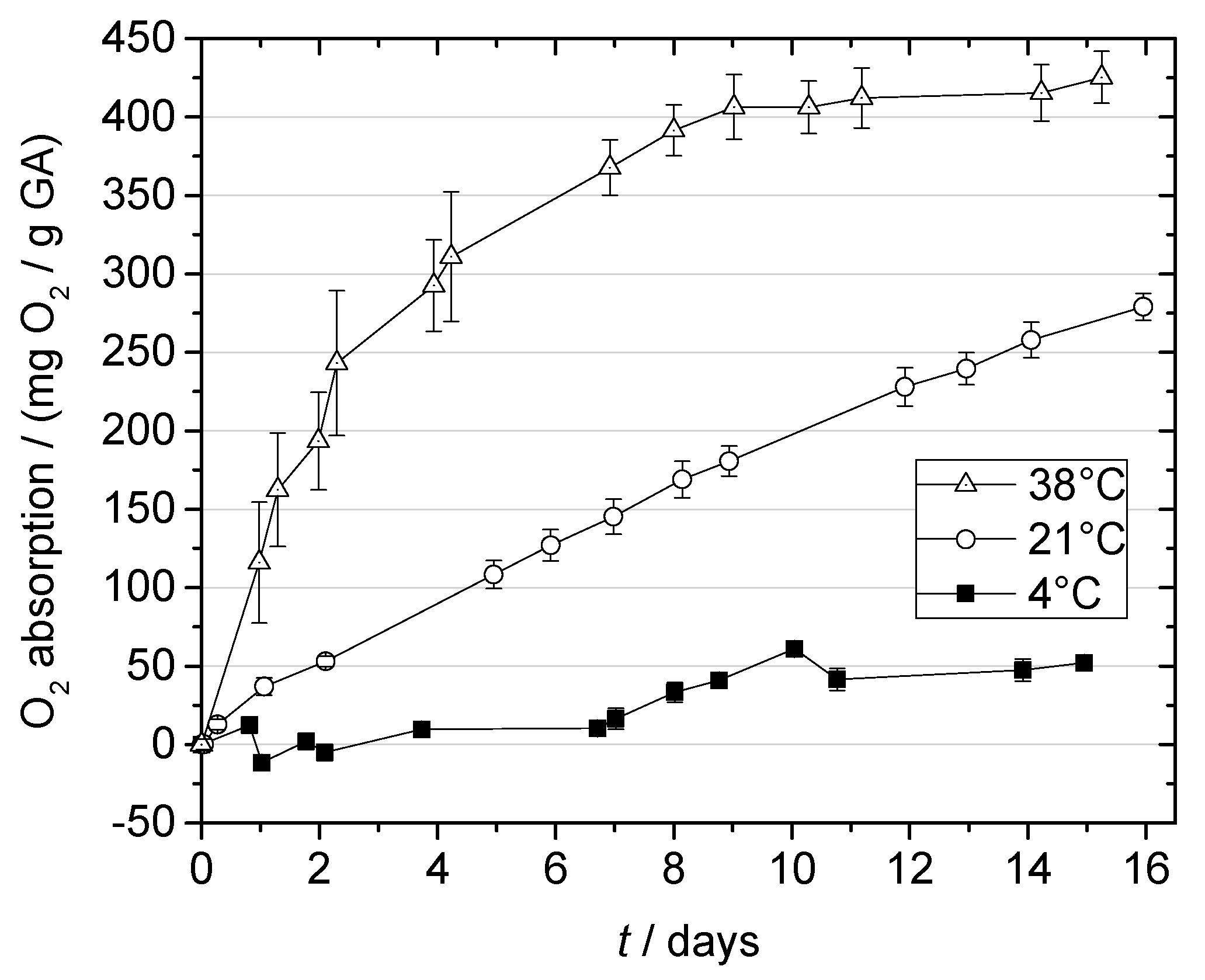
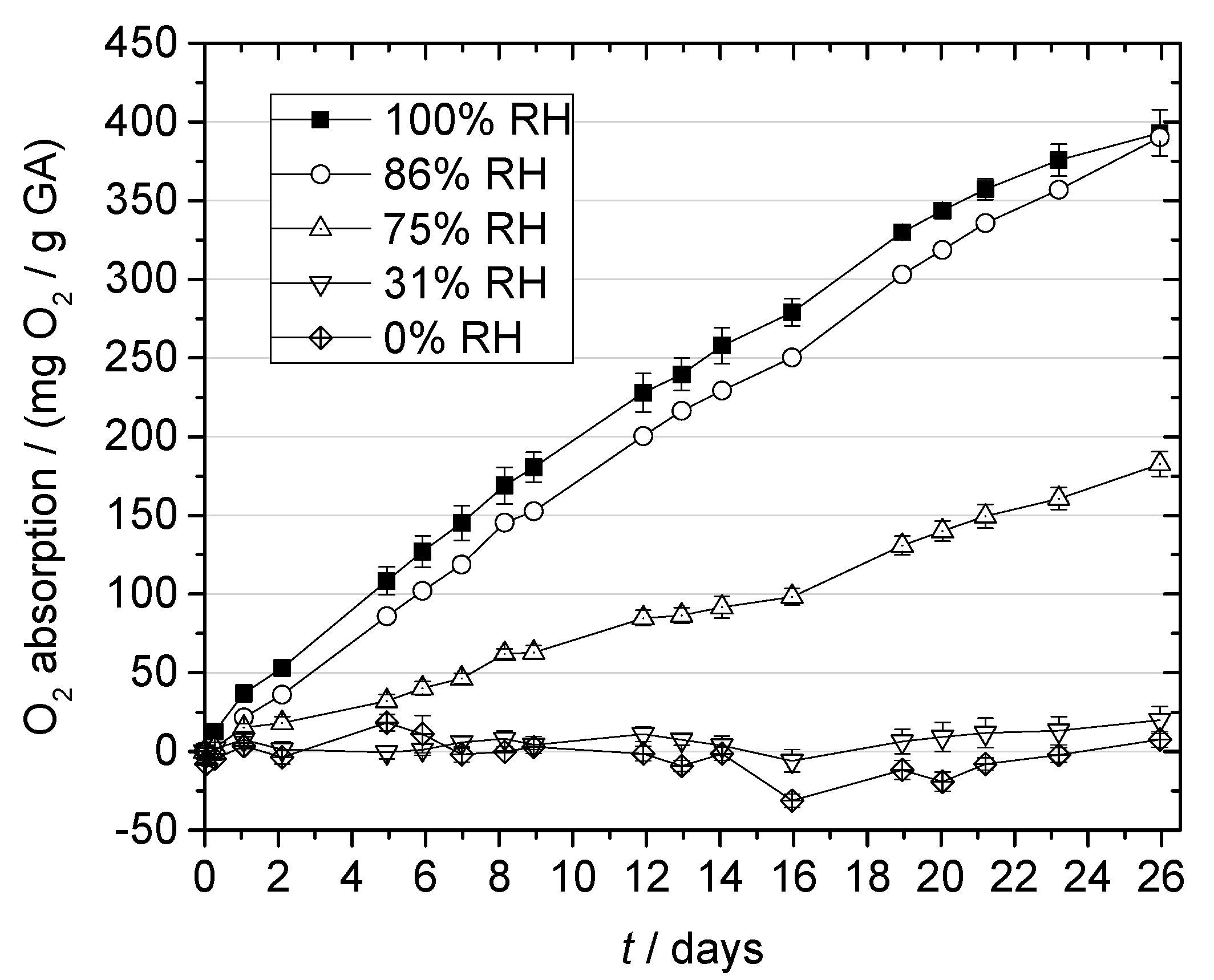
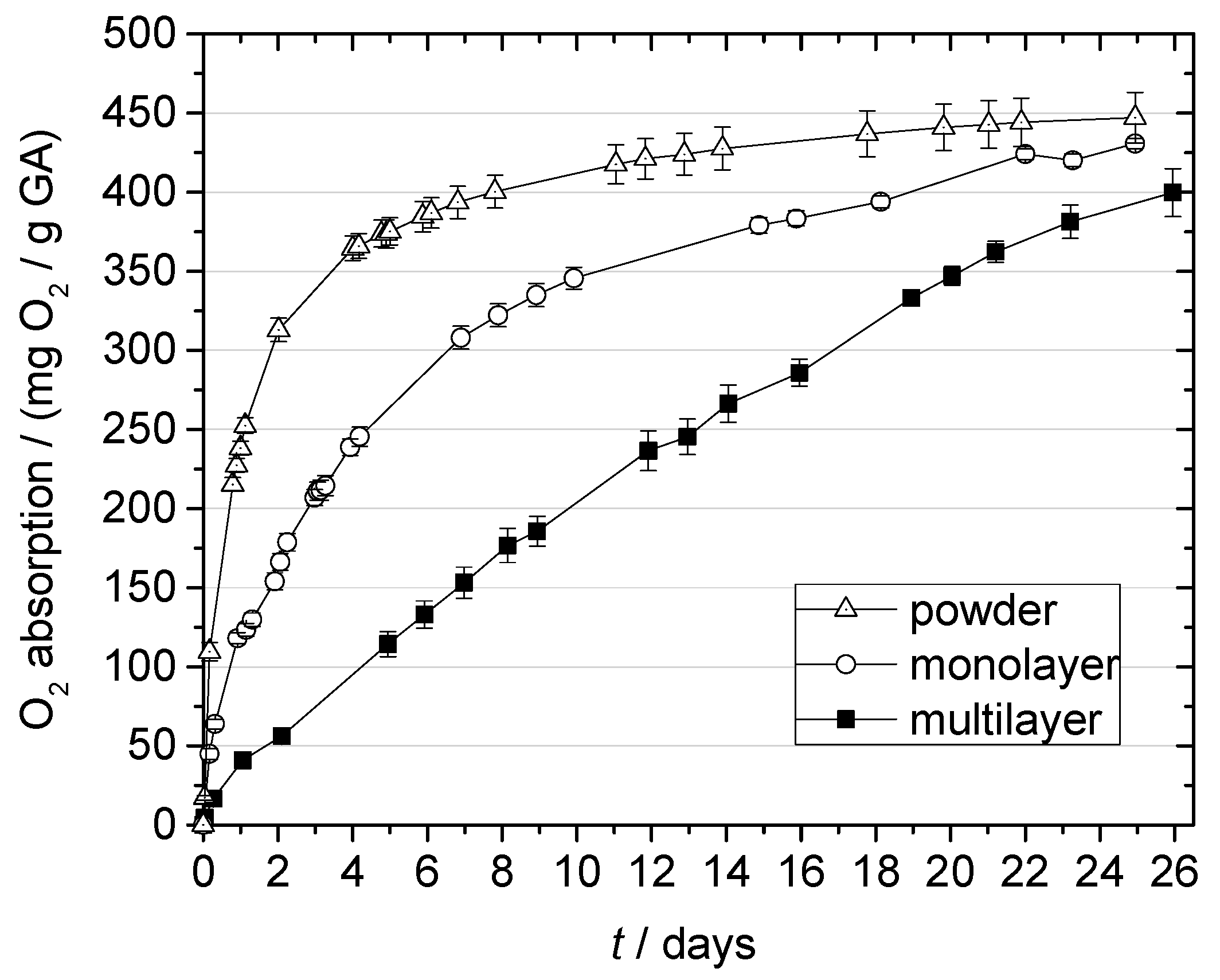
2.3. Oxygen Absorption of Gallic Acid
2.3.1. Effect of Temperature
2.3.2. Effect of Relative Humidity
2.3.3. The Effect of Film Structure
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Film Production
3.2.1. Compounding
3.2.2. Cast Film Extrusion
3.2.3. Lamination
3.2.4. Thermoforming
3.3. Film Characterization
3.3.1. Layer Thickness
3.3.2. Color Measurement
3.3.3. Oxygen Absorption
3.4. Data Treatment
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, P.; Abas Wani, A.; Saengerlaub, S. Active packaging of food products: Recent trends. Nutr. Food Sci. 2011, 41, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Realini, C.E.; Marcos, B. Active and intelligent packaging systems for a modern society. Meat Sci. 2014, 98, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooney, M.L. Oxygen-scavenging packaging. In Innovations in Food Packaging; Han, J.H., Ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2005; pp. 123–137. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeiren, L.; Devlieghere, F.; van Beest, M.; de Kruijf, N.; Debevere, J. Developments in the active packaging of foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, M.; Schlemmer, D.; Sängerlaub, S. Recycling of blends made of polypropylene and an iron-based oxygen scavenger—influence of multiple extrusions on the polymer stability and the oxygen absorption capacity. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 122, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amberg-Schwab, S.; Weber, U.; Burger, A.; Nique, S.; Xalter, R. Development of passive and active barrier coatings on the basis of inorganic–organic polymers. Monatsh. Chem. 2006, 137, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.; Sängerlaub, S.; Kramer, A.; Huber, C.; Fritsch, K. Temperature-dependent oxygen permeation through pet/mxd6-barrier blend bottles with and without oxygen absorber. BrewingScience 2011, 64, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Hong, P.; Liao, M.; Kong, S.; Huang, N.; Ou, C.; Li, S. Preparation and characterization of chitosan—Agarose composite films. Materials 2016, 9, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Hinz, L.-V.; Wild, F.; Noller, K. Effects of hydrolysed whey proteins on the techno-functional characteristics of whey protein-based films. Materials 2013, 6, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurul Fazita, M.R.; Jayaraman, K.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Mohamad Haafiz, M.K.; Saurabh, C.; Hussin, M.; H.P.S., A.K. Green composites made of bamboo fabric and poly (lactic) acid for packaging applications—A review. Materials 2016, 9, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarfato, P.; Avallone, E.; Galdi, M.R.; Di Maio, L.; Incarnato, L. Preparation, characterization, and oxygen scavenging capacity of biodegradable α-tocopherol/pla microparticles for active food packaging applications. Polym. Compos. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjarasskul, T.; Min, S.C.; Krochta, J.M. Triggering mechanisms for oxygen-scavenging function of ascorbic acid-incorporated whey protein isolate films. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 2939–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanner, G.T. O2-zehrende und -anzeigende Packstoffe für Lebensmittelverpackungen. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität München, München, Germany, 2010. Available online: https://mediatum.ub.tum.de/doc/972162/document.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2017).
- Shahidi, F.; Naczk, M. Phenolics in Food and Nutraceuticals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tulyathan, V.; Boulton, R.B.; Singleton, V.L. Oxygen uptake by gallic acid as a model for similar reactions in wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1989, 37, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langowski, H.-C.; Wanner, T. Organic Oxygen Scavenger/Indicator. WO Patent 2007059901, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Goldhan, G.; Wanner, T.; Saengerlaub, S.; Amberg-Schwab, S.; Weber, U.; Nique, S. Enhancement and indication of food quality by combinations of oxygen scavenger and indicator systems. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2007, 19, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, B.J.; Gaikwad, K.K.; Lee, Y.S. Characterization and properties of ldpe film with gallic-acid-based oxygen scavenging system useful as a functional packaging material. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.M.; Ferreira, A.C.S.; De Freitas, V.; Silva, A.M.S. Oxidation mechanisms occurring in wines. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumada, K. Studies on the colour of humic acids. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1965, 11, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galotto, M.J.; Anfossi, S.; Guarda, A.; Guarda, A. Oxygen Absorption Kinetics of Sheets and Films Containing a Commercial Iron-based Oxygen Scavenger. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2007, 15, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibis, D.; Rieblinger, K. Oxygen scavenging films for food application. Procedia Food Sci. 2011, 1, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis, J.A.; Rodgers, B.D. Factors affecting the performance of new oxygen scavenging polymer for packaging applications. J. Plast. Film Sheet. 2001, 17, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, V.A.; Miltz, J. Modeling of the temperature effect on oxygen absorption by iron-based oxygen scavengers. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, E76–E85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, F.; Sanchez, J.; Gontard, N. Absorption kinetics of oxygen and carbon dioxide scavengers as part of active modified atmosphere packaging. J. Food Eng. 2006, 72, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, G.; Jayas, D.S.; Jeremiah, L.E.; Holley, R.A. Absorption kinetics of oxygen scavengers. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langowski, H.-C. Permeation of gases and condensable substances through monolayer and multilayer structures. In Plastic Packaging; Piringer, O.G., Baner, A.L., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 297–347. [Google Scholar]
- Atkins, P.; Paula, J.d. Atkins’s Physical Chemistry, 9th ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Marino, T.; Galano, A.; Russo, N. Radical scavenging ability of gallic acid toward oh and ooh radicals. Reaction mechanism and rate constants from the density functional theory. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 10380–10389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sängerlaub, S.; Gibis, D.; Kirchhoff, E.; Tittjung, M.; Schmid, M.; Müller, K. Compensation of pinhole defects in food packages by application of iron-based oxygen scavenging multilayer films. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2013, 26, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, H.-G. Trockenprodukte - sorptionsisothermen - haltbarkeit. In Lebensmittel- Und Bioverfahrenstechnik: Molkereitechnologie; Mit 109 Tabellen, 4th ed.; Kessler, H.-G., Ed.; Kessler: München, Germany, 1996; pp. 255–264. [Google Scholar]
- Di Maio, L.; Scarfato, P.; Galdi, M.R.; Incarnato, L. Development and oxygen scavenging performance of three-layer active pet films for food packaging. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, T.Y.; Goodrich, J.; CAI, K.; Yang, H. Tasteless oxygen scavenging polymers a new platform technology for food packaging based on controlled oxidation. In Proceedings of the Oxygen Absorbers 2001 and Beyond, Chicago, IL, USA, 9–26 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Ashcraft, D.K.; Freeman, B.D.; Stewart, M.E.; Jank, M.K.; Clark, T.R. Non-invasive headspace measurement for characterizing oxygen-scavenging in polymers. Polymer 2008, 49, 4541–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, H.; Walter, W. Lehrbuch der Organischen Chemie, 22., Überarbeitete Und Aktualisierte Auflage; S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart: Stuttgart, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Grulke, E.A.; Immergut, E.; Brandrup, J. Polymer Handbook; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Garlotta, D. A literature review of poly(lactic acid). J. Polym. Environ. 2001, 9, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhner, N.; Rieblinger, K. Impact of different visible light spectra on oxygen absorption and surface discoloration of bologna sausage. Meat Sci. 2016, 121, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieblinger, K.; Ziegleder, G.; Berghammer, A.; Sandmeier, D. Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Bestimmung der Haltbarkeit von Lebensmitteln und Dessen Verwendung. DE Patent 19528400 c1, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan, L. Humidity fixed points of binary saturated aqueous solutions. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand Sect. A Phys. Chem. 1977, 81, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wexler, A. Practical laboratory data. In Crc Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 1998–1999, 79th ed.; Lide, D.R., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998; Section 15; pp. 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Budavari, S. Constant humidity solutions. In The Merck Index an Encyclopedia of Chemical, Drugs, and Biologicals, 11th ed.; Budavari, S., Ed.; Merck & Co.: Rahway, NJ, USA, 1989; p. MISC–109. [Google Scholar]


| Scavenger Type | Absorption Capacity mg O2/g Scavenger | References |
|---|---|---|
| OSc powder (gallic acid + sodium carbonate, 2:1) | 298 | this study |
| polymer additive with iron powder (SHELFPLUS® O2 2710) | 39–48 | [5] |
| polymer additive: copolyester-based polymer (Amosorb DFC 4020, Colormatrix Europe, Liverpool, UK) | 43–47 | [32] |
| polymer: ethylene methylacrylate cyclohexenylmethyl acrylate ‘OSP™’ | 60–100 | [23,33] |
| polymer: metal-catalysed poly(1,4-butadiene) | 140 | [34] |
| coating: cyclo-olefin bonded to a silicate backbone ‘ORMOCER®’ | 90 | [6] |
| Thermal Properties | Gas Permeability | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer | Glass Transition Temperature °C | Melting Temperature °C | Crystallinity Degree % | O2 cm3 (STP) 100 µm/(m2 d bar) | H2O g 100 µm/(m2 d) |
| BioPE | n.d. | 125.6 | 24.6 | 1898 | 1 |
| PLA | 60.1 | 152.3 | 39.1 | 153 | 58 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pant, A.F.; Sängerlaub, S.; Müller, K. Gallic Acid as an Oxygen Scavenger in Bio-Based Multilayer Packaging Films. Materials 2017, 10, 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10050489
Pant AF, Sängerlaub S, Müller K. Gallic Acid as an Oxygen Scavenger in Bio-Based Multilayer Packaging Films. Materials. 2017; 10(5):489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10050489
Chicago/Turabian StylePant, Astrid F., Sven Sängerlaub, and Kajetan Müller. 2017. "Gallic Acid as an Oxygen Scavenger in Bio-Based Multilayer Packaging Films" Materials 10, no. 5: 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10050489
APA StylePant, A. F., Sängerlaub, S., & Müller, K. (2017). Gallic Acid as an Oxygen Scavenger in Bio-Based Multilayer Packaging Films. Materials, 10(5), 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10050489







