Investigation of Parent Austenite Grains from Martensite Structure Using EBSD in a Wear Resistant Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Method
2.2. Material
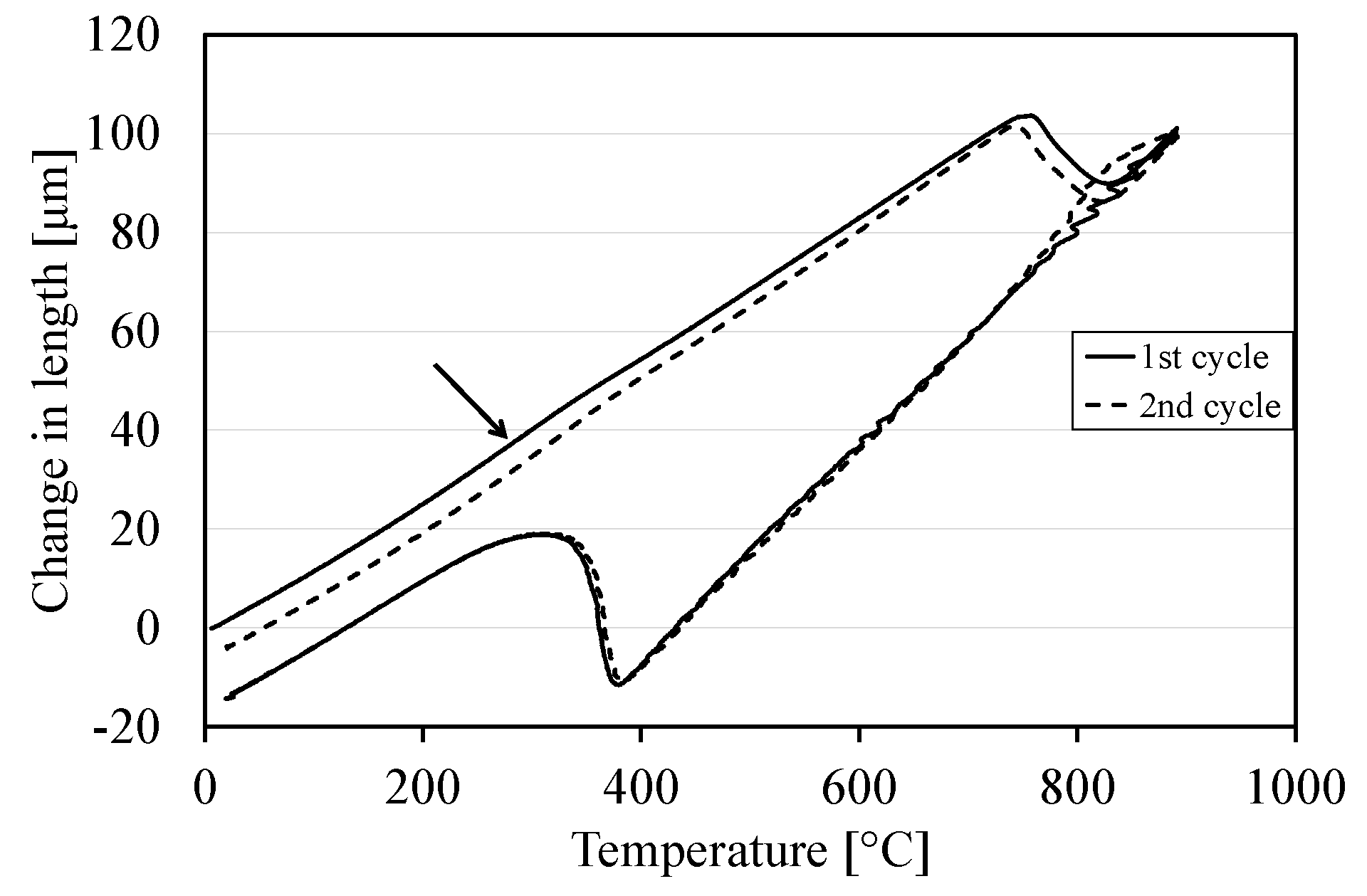
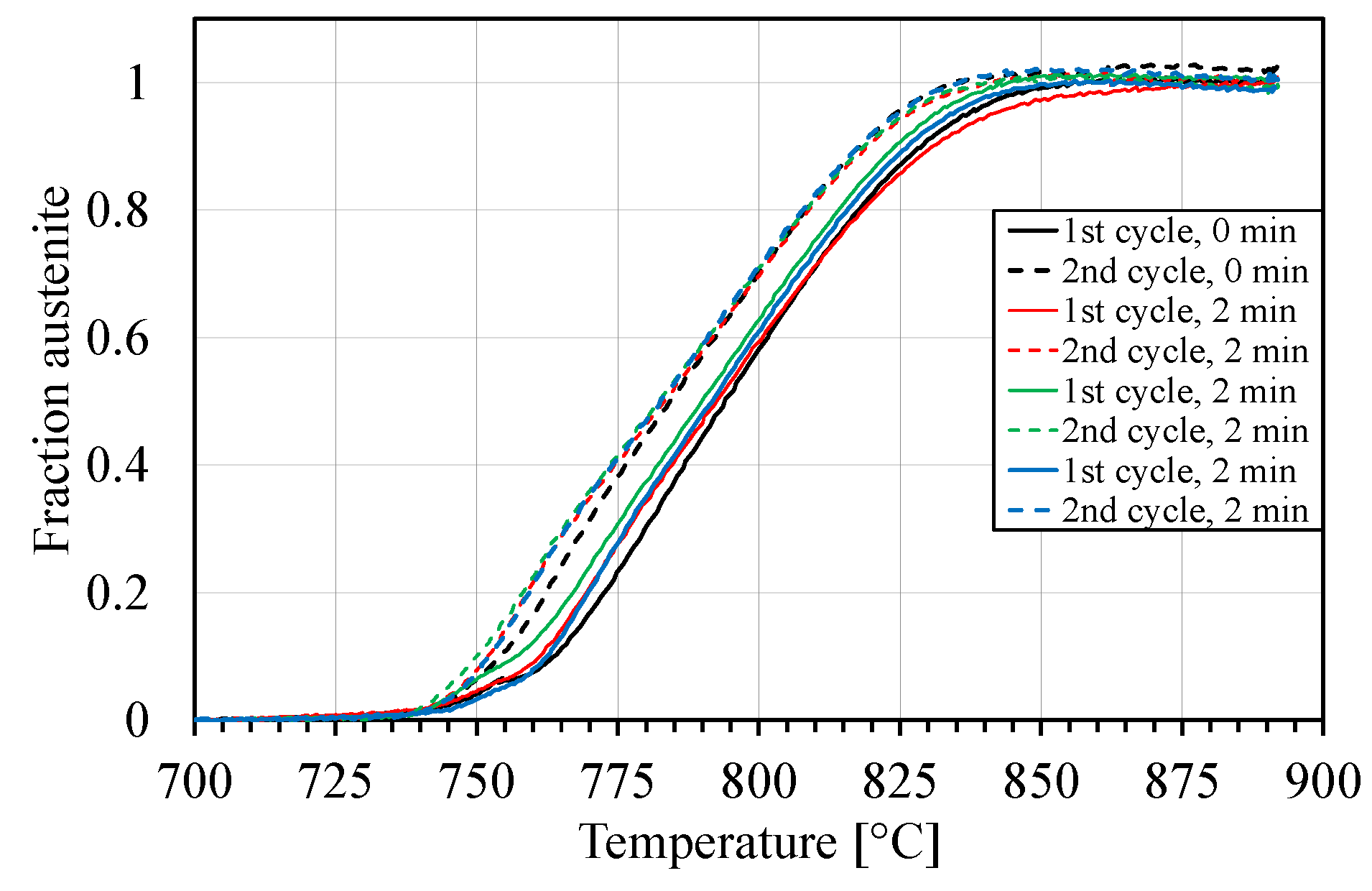
2.3. Dilatometry and Micro Hardness
2.4. EBSD-Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
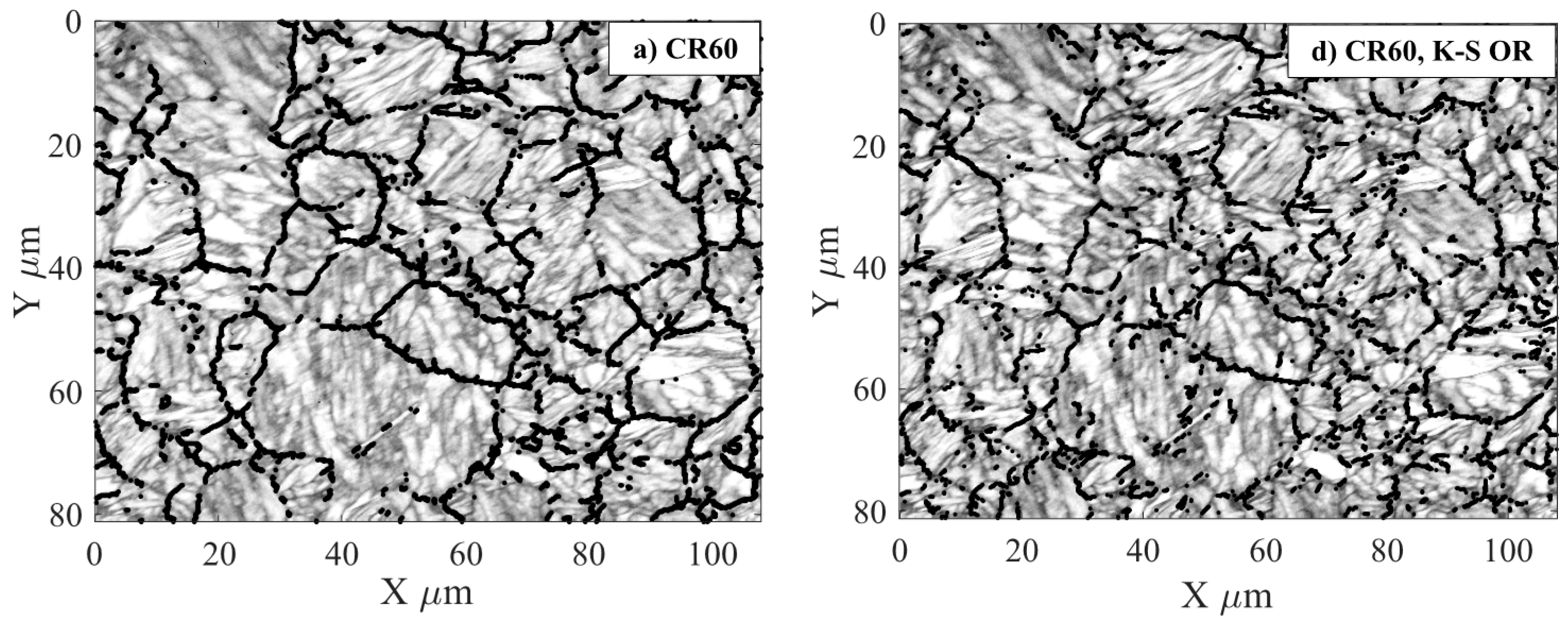
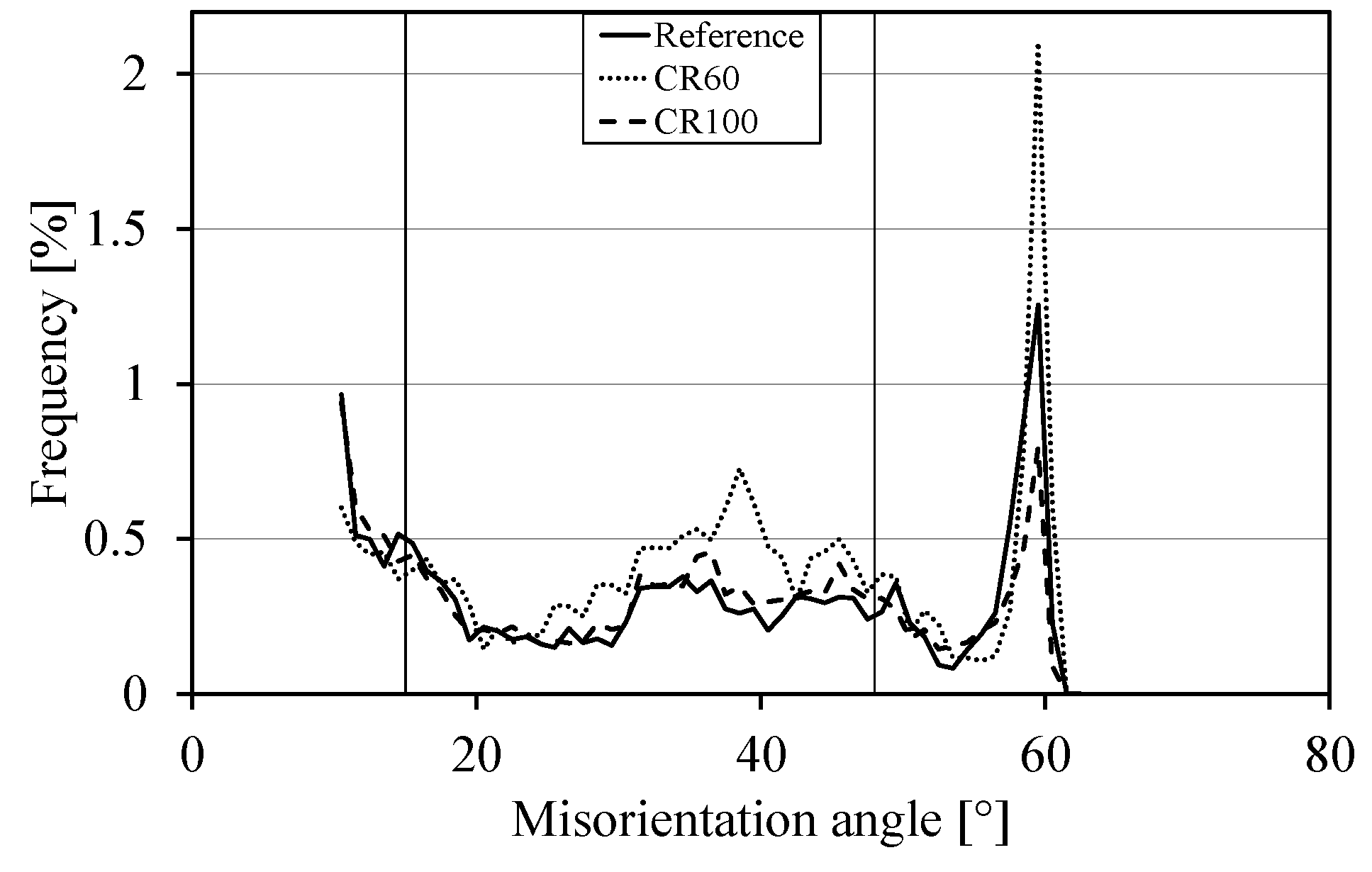
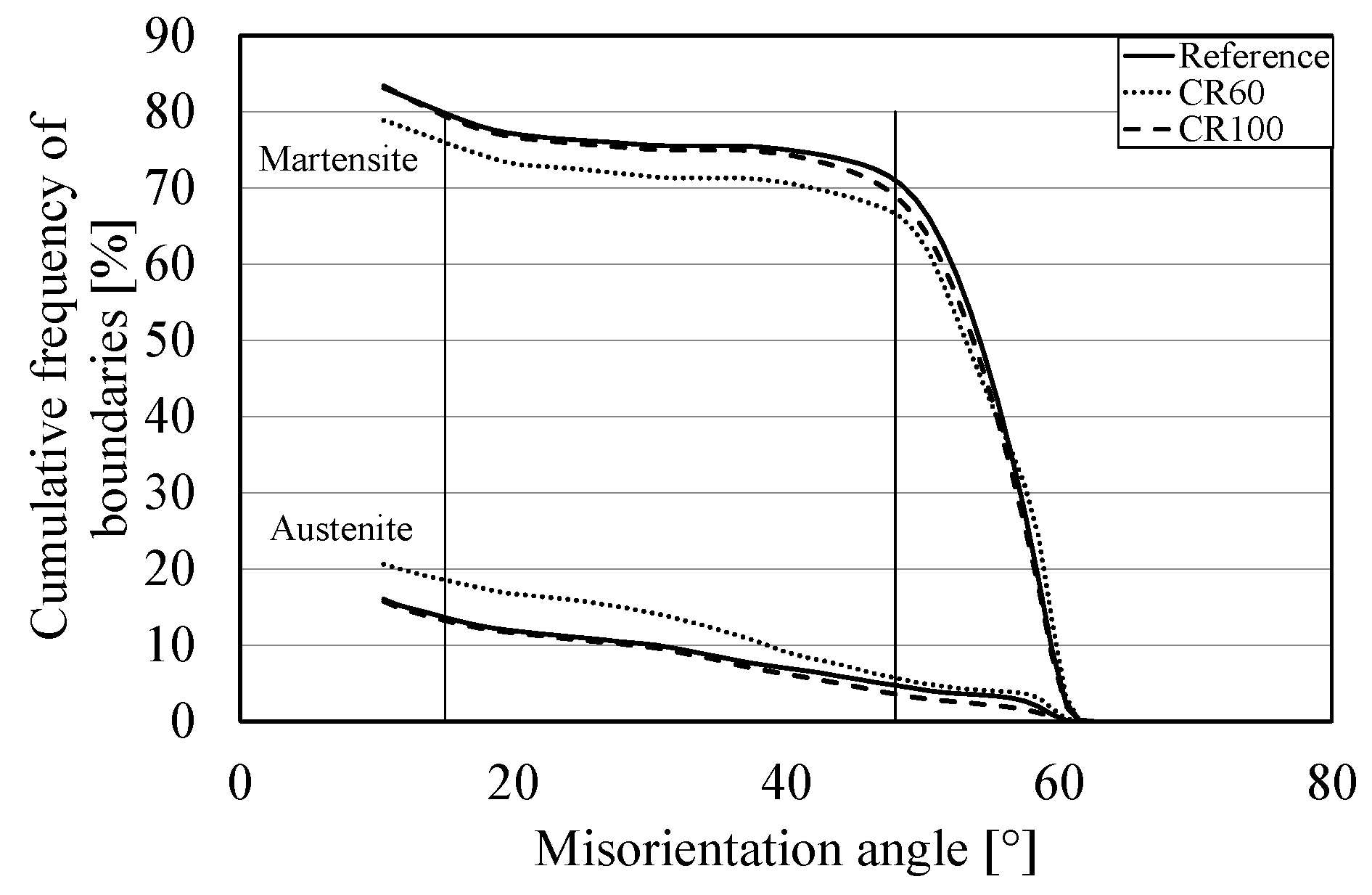
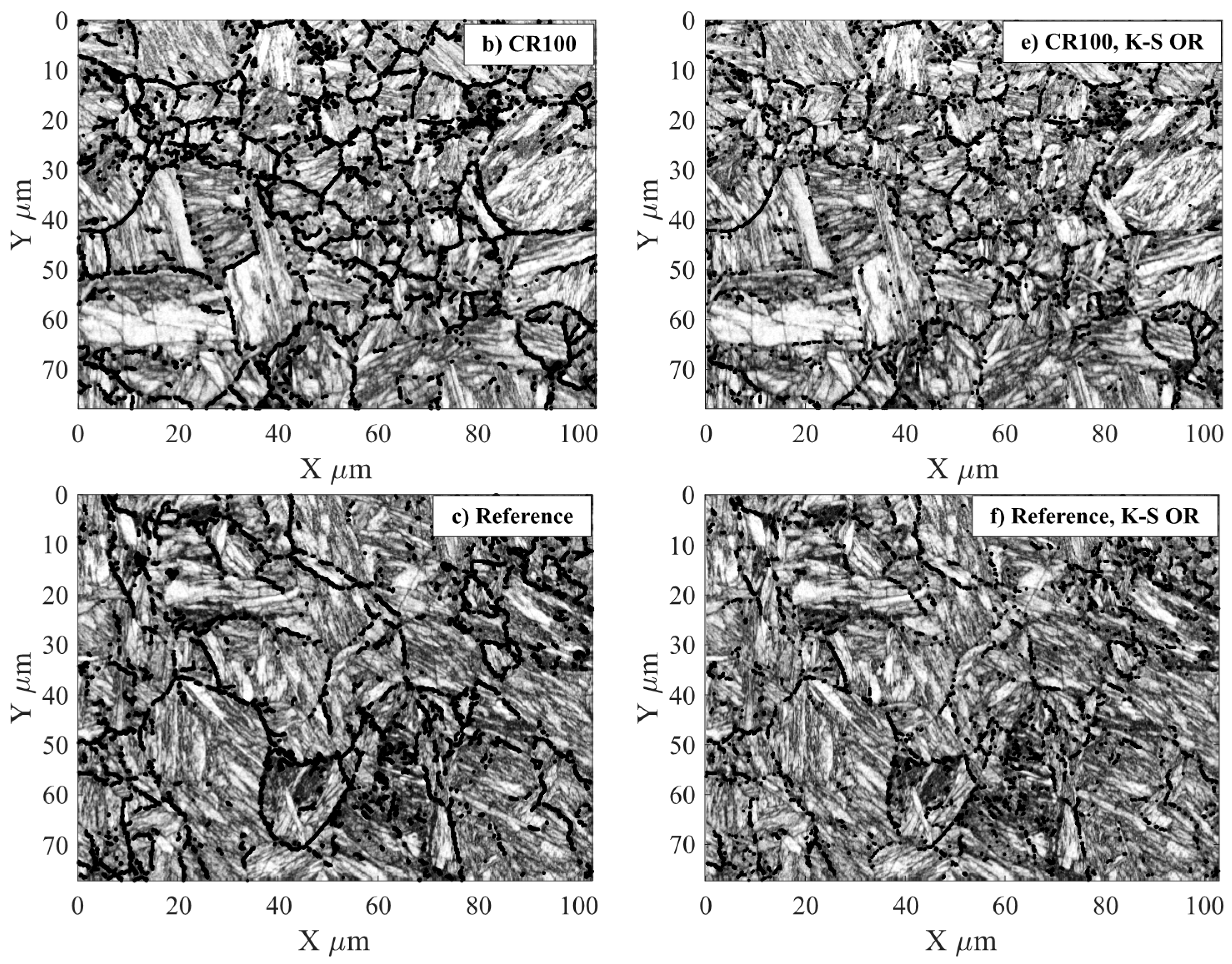
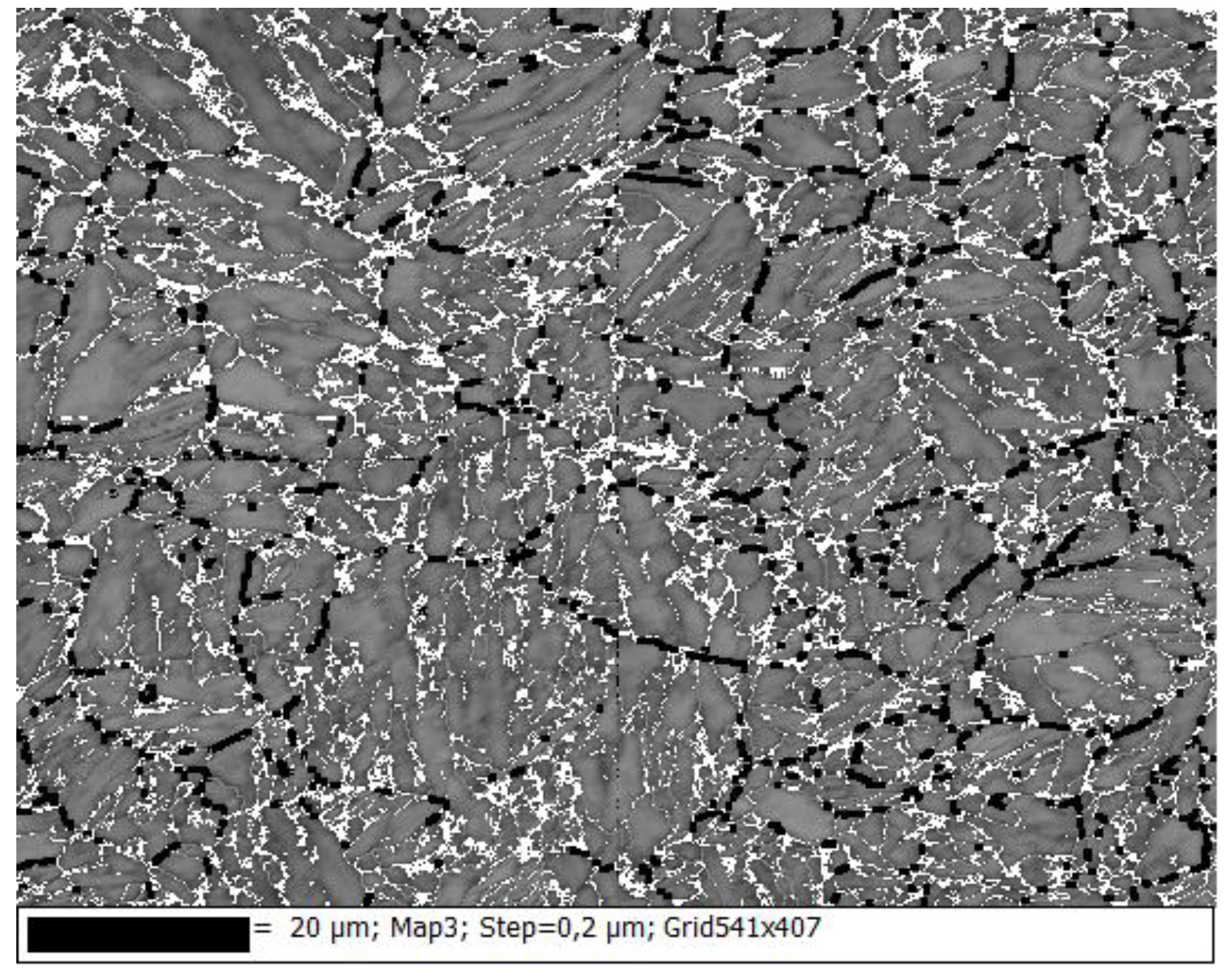
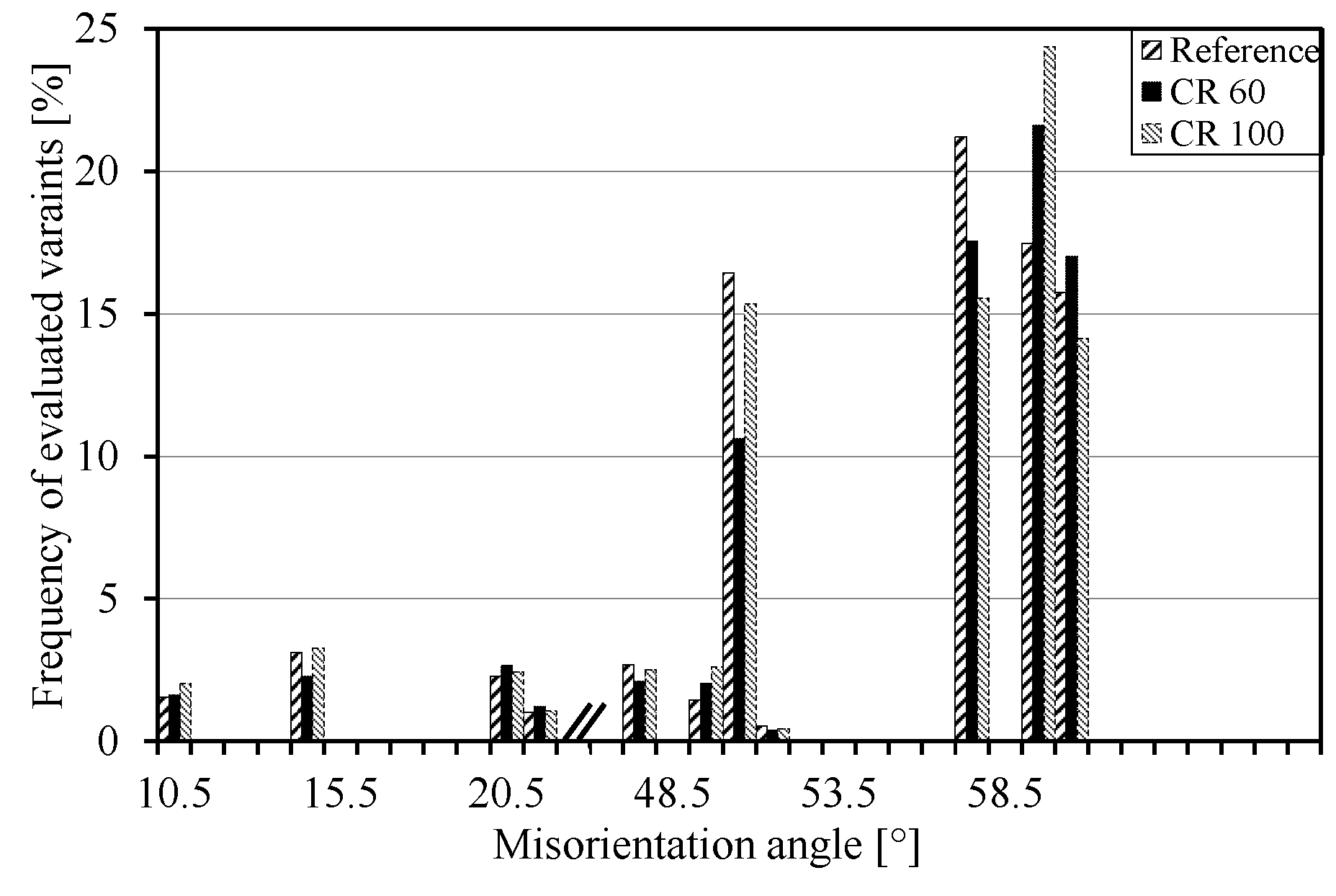
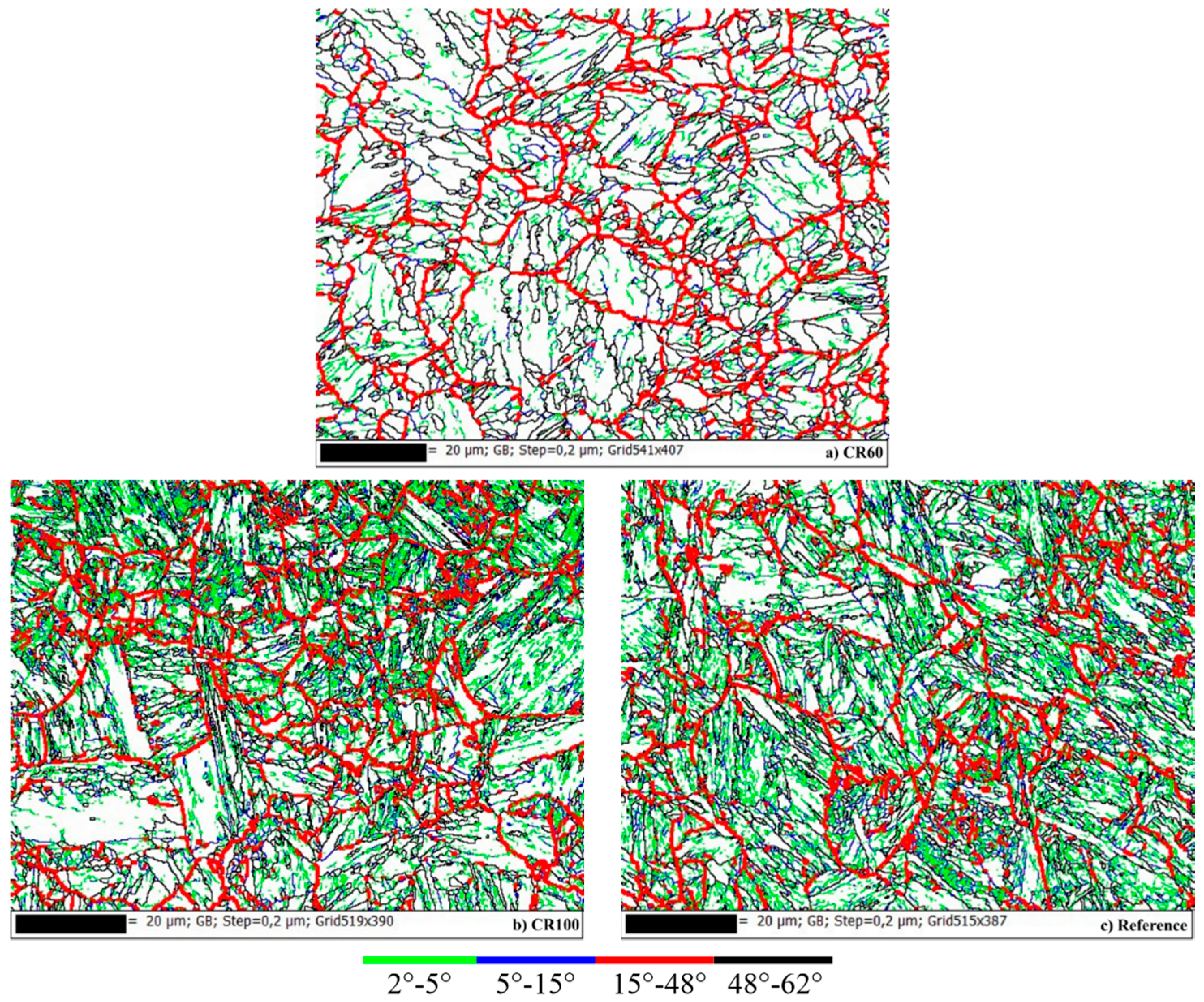
3.1. EBSD Measurements
3.2. Evaluation of EBSD Data
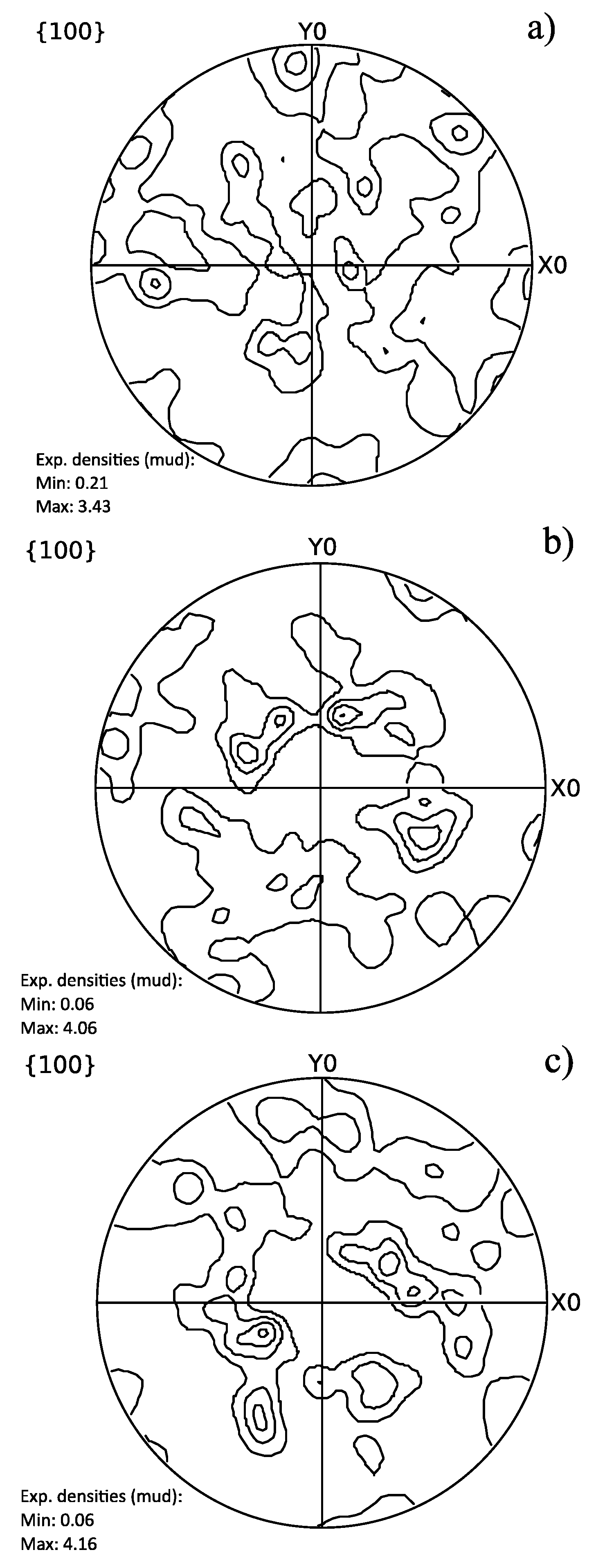
3.3. Texture Analysis
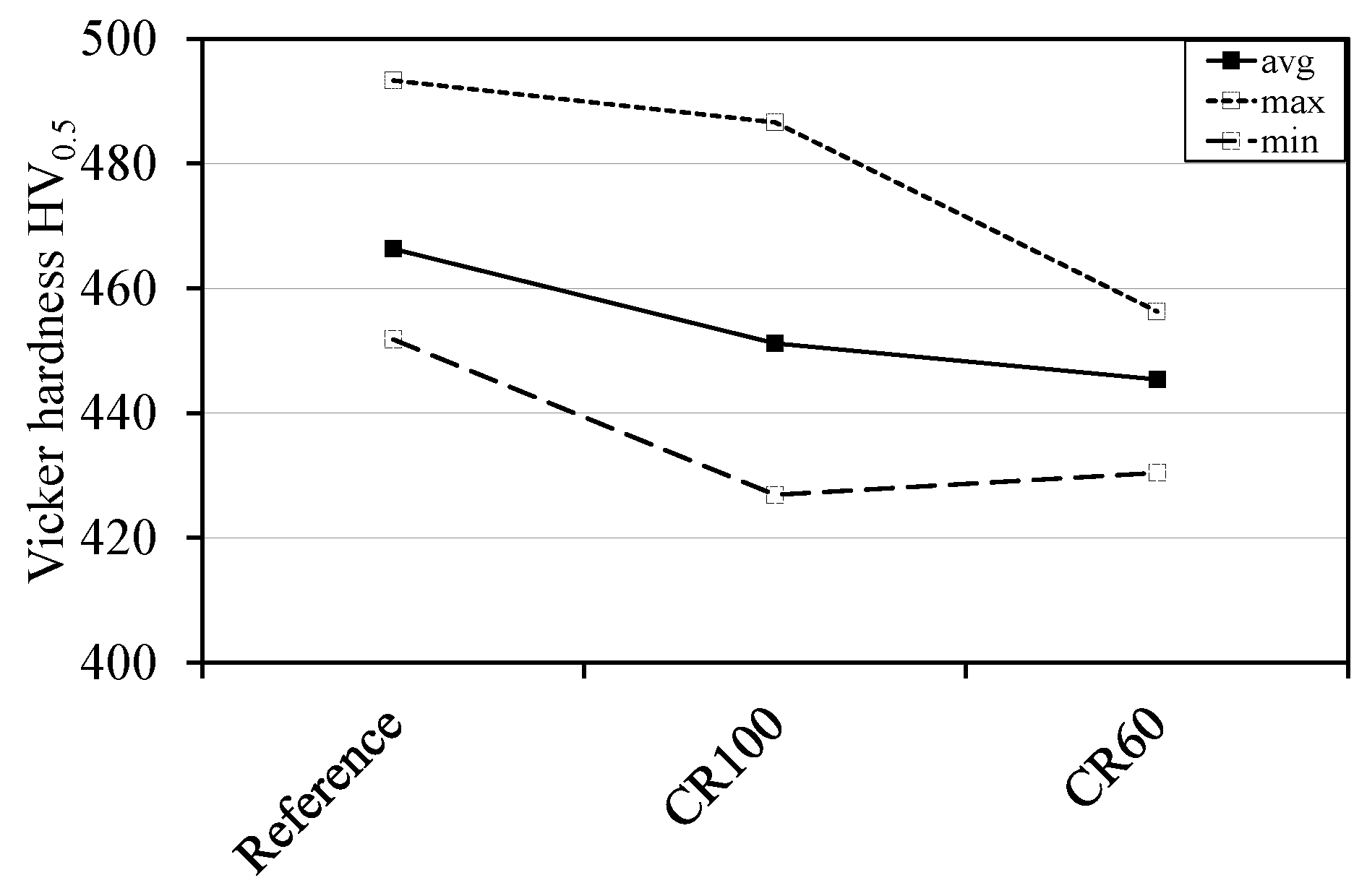
3.4. Dilatometry and Hardness Measurements
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EBSD | Electron Backscatter Diffraction |
| OR | Orientation Relationship |
| K-S | Kurdjumov-Sachs |
| CR | Cooling rate |
References
- Button, S.T. Volume 3-Advanced Forming Technologies. In Comprehensive Materials Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bramfitt, B.L. Metals Handbook Desk Edition, 2nd ed.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Worked Examples in the Geometry of Crystals, 2nd ed.; The Institute of Metals: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Doane, D.V.; Kirkaldy, J.S. (Eds.) Hardenability Concepts with Applications to Steel; AIME: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Naghizadeh, M.; Mirzadeh, H. Microstructural evolution during annealing of plastically deformed AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel: Martensite reversion, grain refinement, recrystallization, and grain growth. Miner. Metals Mater. Soc. ASM Int. 2016, 47, 4210–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, J.W. Physical Properties of Martensite and Bainite: Military Transformations—An Introductory Survey; Humphries & Co Ltd.: London, UK; Bradford, UK, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Krauss, G. Steels: Processing, Structure and Performance; ASM International: Russell Township, OH, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Maki, T. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ferrous martensites. Mater. Sci. Forum 1990, 56–58, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, A.; Morito, S.; Furuhara, T.; Maki, T. Substructures of lenticular martensites with different start temperatures in ferrous alloys. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillert, M.; Ågren, J.; Borgenstam, A. Mikro Och Nanostrukturer i Materialdesign; Kungliga Tekniska Högskolan: Stockholm, Sweden, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Suikkanen, P.P.; Cayron, C.; DeArdo, A.J.; Karjalainen, L.P. Crystallographic analysis of martensite in 0.2C-2.0Mn-1.5Si-0.6Cr steel using EBSD. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2011, 27, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungunes, H.; Yasar, E.; Durlu, T.N. The effect of austenitizing time on martensite morphologies and magnetic properties of martensite in Fe-24.5%Ni-4.5%Si alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 6102–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitahara, H.; Ueji, R.; Tsuji, N.; Minamino, Y. Crystallographic features of lath martensite in low-carbon steel. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.R.; Cohen, M. Criterion for the action of applied stress in the martensitic transformation. Acta Metall. 1953, 1, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Verma, A.K.; Sharma, V. Quantitative analysis of variant selection for displacive transformations under stress. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 2552–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morito, S.; Adachi, Y.; Ohba, T. Morphology and crystallography of sub-blocks in ultra-low carbon lath martensite steel. Mater. Trans. 2009, 50, 1919–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morito, S.; Tanaka, H.; Konishi, R.; Furuhara, T.; Maki, T. The morphology and crystallography of lath martensite in Fe-C alloys. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 1789–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, G. Martensite in steel: Strength and structure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 273–275, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarr, T.; Krauss, G. The effect of structure on the deformation of as-quenched and tempered martensite in an Fe-0.2%C alloy. Metall. Trans. A 1976, 7, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, B. Characterisation of Polycrystal Deformation by Numerical Modelling and Neutron Diffraction Measurements; Technical Report; Risø National Laboratory: Roskilde, Denmark, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, R.; Boratto, F.; Yue, S.; Jonas, J.J. The influence of chemical composition on the recrystallization behaviour of microalloyed steels. Process. Microstruct. Prop. HSLA Steels 1987, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, S.; Jonas, J.J. The three critical temperatures of steel rolling and their experimental determination. Mater. Forum 1990, 14, 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- RoseLuo, J.M.; Piehler, H.R. Calculation of the Taylor factor and lattice rotations for bcc metals deforming by pencil glide. Metall. Trans. 1971, 2, 257–259. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, J.W. Strengthening Methods in Crystals; Elsevier Pub. Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Winchell, P.G.; Cohen, M. The strength of martensite. Trans. ASM 1962, 55, 347–360. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, S.W. Structural characteristics of transition-iron-carbide precipitates formed during the first stage of tempering in 4340 steel. Mater. Charact. 2015, 106, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, G. Steels: Heat Treatment and Processing Principles; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]



| OR | Plane | Direction |
|---|---|---|
| Kurdjumov-Sachs (K-S) | ||
| Nishiyama-Wasserman (N-W) | or | |
| Greninger-Troiano (G-T) | ||
| Bain |
| Variant | Austenite OR K-S | Martensite OR K-S | Misorientation Angle from V1 | Misorientation Axis to V1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (111)[−101] | (011)[−1−11] | – | – | – | – |
| 2 | (111)[−101] | (011)[−111] | 60.00 | 0.577 | −0.577 | 0.577 |
| 3 | (111)[01−1] | (011)[−1−11] | 60.00 | 0 | −0.707 | −0.707 |
| 4 | (111)[01−1] | (011)[−11−1] | 10.53 | 0 | −0.707 | 0.707 |
| 5 | (111)[1−10] | (011)[−1−11] | 60.00 | 0 | 0.707 | 0.707 |
| 6 | (111)[1−10] | (011)[−11−1] | 49.47 | 0 | 0.707 | 0.707 |
| 7 | (1−11)[10−1] | (011)[−1−11] | 49.47 | −0.577 | −0.577 | 0.577 |
| 8 | (1−11)[10−1] | (011)[−11−1] | 10.53 | 0.577 | −0.577 | 0.577 |
| 9 | (1−11)[−1−10] | (011)[−1−11] | 50.51 | −0.186 | 0.767 | 0.615 |
| 10 | (1−11)[−1−10] | (011)[−11−1] | 50.51 | −0.490 | −0.463 | 0.739 |
| 11 | (1−11)[011] | (011)[−1−11] | 14.88 | 0.354 | −0.933 | −0.065 |
| 12 | (1−11)[011] | (011)[−11−1] | 57.21 | 0.357 | −0.714 | 0.603 |
| 13 | (−111)[0−11] | (011)[−1−11] | 14.88 | 0.933 | 0.354 | 0.065 |
| 14 | (−111)[0−11] | (011)[−11−1] | 50.51 | −0.739 | 0.463 | 0.490 |
| 15 | (−111)[−10−1] | (011)[−1−11] | 57.21 | −0.246 | −0.628 | −0.738 |
| 16 | (−111)[−10−1] | (011)[−11−1] | 20.61 | 0.659 | 0.659 | 0.363 |
| 17 | (−111)[110] | (011)[−1−11] | 51.73 | −0.659 | 0.363 | −0.659 |
| 18 | (−111)[110] | (011)[−11−1] | 47.11 | −0.302 | −0.626 | −0.719 |
| 19 | (11−1)[−110] | (011)[−1−11] | 50.51 | −0.615 | 0.186 | −0.767 |
| 20 | (11−1)[−110] | (011)[−11−1] | 57.21 | −0.357 | −0.603 | −0.714 |
| 21 | (11−1)[0−1−1] | (011)[−1−11] | 20.61 | 0.955 | 0 | −0.296 |
| 22 | (11−1)[0−1−1] | (011)[−11−1] | 47.11 | −0.719 | 0.302 | −0.626 |
| 23 | (11−1)[101] | (011)[−1−11] | 57.21 | −0.738 | −0.246 | 0.628 |
| 24 | (11−1)[101] | (011)[−11−1] | 21.06 | 0.912 | 0.410 | 0 |
| Element | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt % | 0.19 | 0.70 | 1.60 | 0.025 | 0.010 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.004 |
| Sample | Taylor Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | |
| CR60 | 2.42 | 2.46 | 2.40 |
| CR100 | 2.51 | 2.46 | 2.50 |
| Reference | 2.49 | 2.48 | 2.43 |
| Specimen | CR60 | CR100 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average (μm) | 2.0262 | 1.4285 | 1.4457 |
| Standard deviation (μm) | 1.6693 | 1.0989 | 1.0921 |
| Minimum value (μm) | 0.71365 | 0.71365 | 0.71365 |
| Maximum value (μm) | 15.056 | 13.001 | 10.369 |
| Size of the data set (μm) | 1393 | 2219 | 2300 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gyhlesten Back, J.; Engberg, G. Investigation of Parent Austenite Grains from Martensite Structure Using EBSD in a Wear Resistant Steel. Materials 2017, 10, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10050453
Gyhlesten Back J, Engberg G. Investigation of Parent Austenite Grains from Martensite Structure Using EBSD in a Wear Resistant Steel. Materials. 2017; 10(5):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10050453
Chicago/Turabian StyleGyhlesten Back, Jessica, and Göran Engberg. 2017. "Investigation of Parent Austenite Grains from Martensite Structure Using EBSD in a Wear Resistant Steel" Materials 10, no. 5: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10050453
APA StyleGyhlesten Back, J., & Engberg, G. (2017). Investigation of Parent Austenite Grains from Martensite Structure Using EBSD in a Wear Resistant Steel. Materials, 10(5), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10050453





