Al-Doped ZnO Monolayer as a Promising Transparent Electrode Material: A First-Principles Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Calculation Models and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Properties
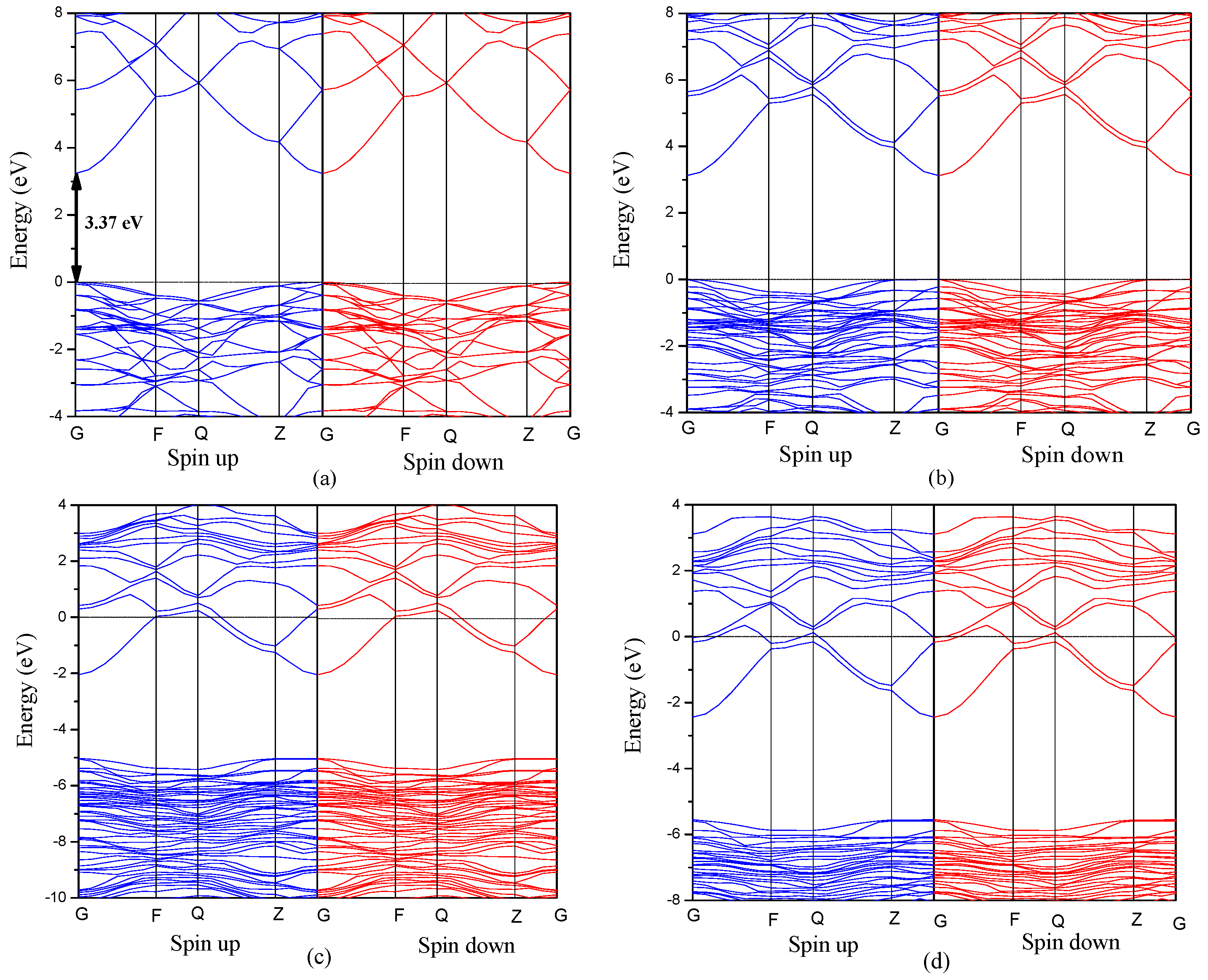
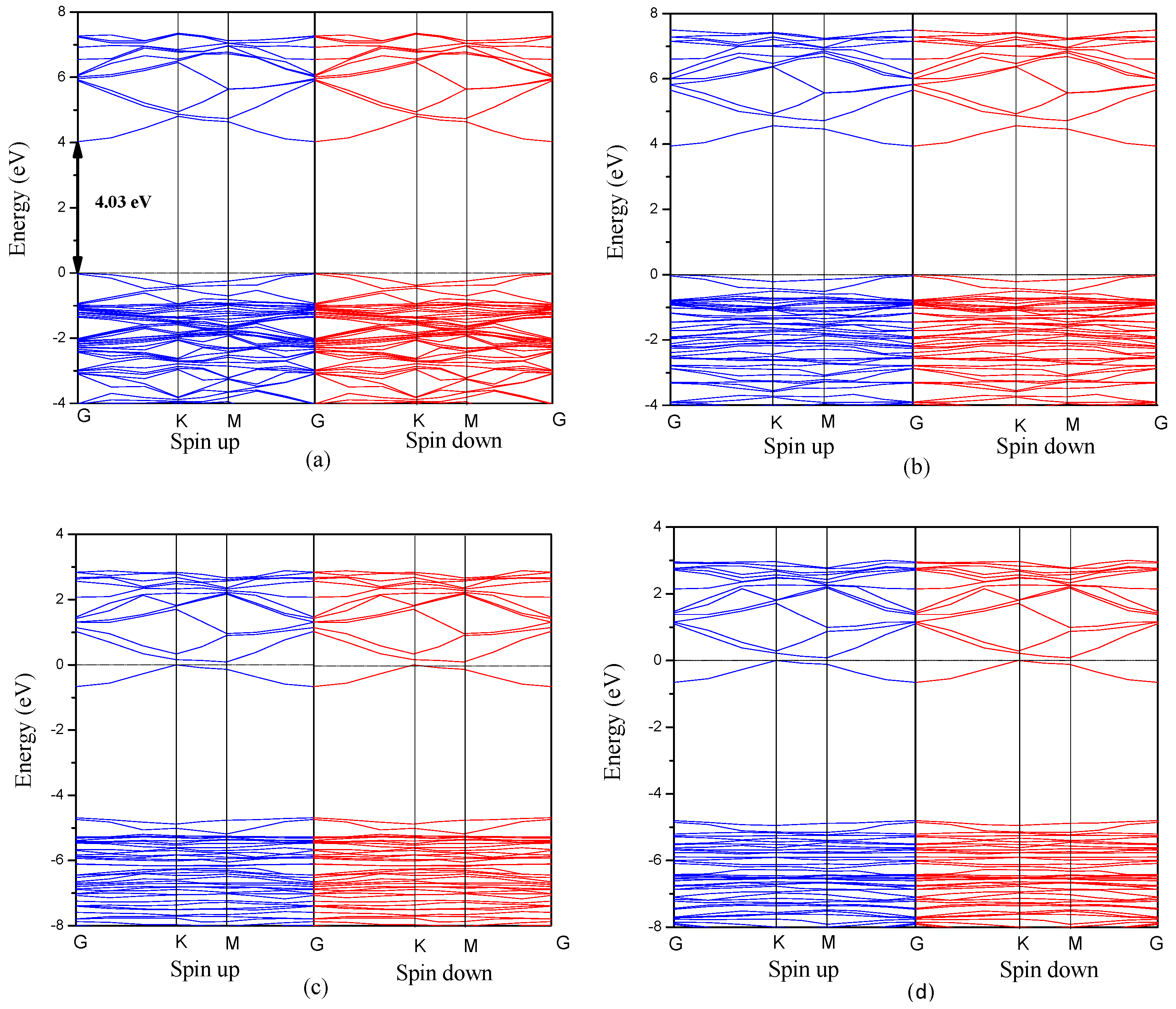
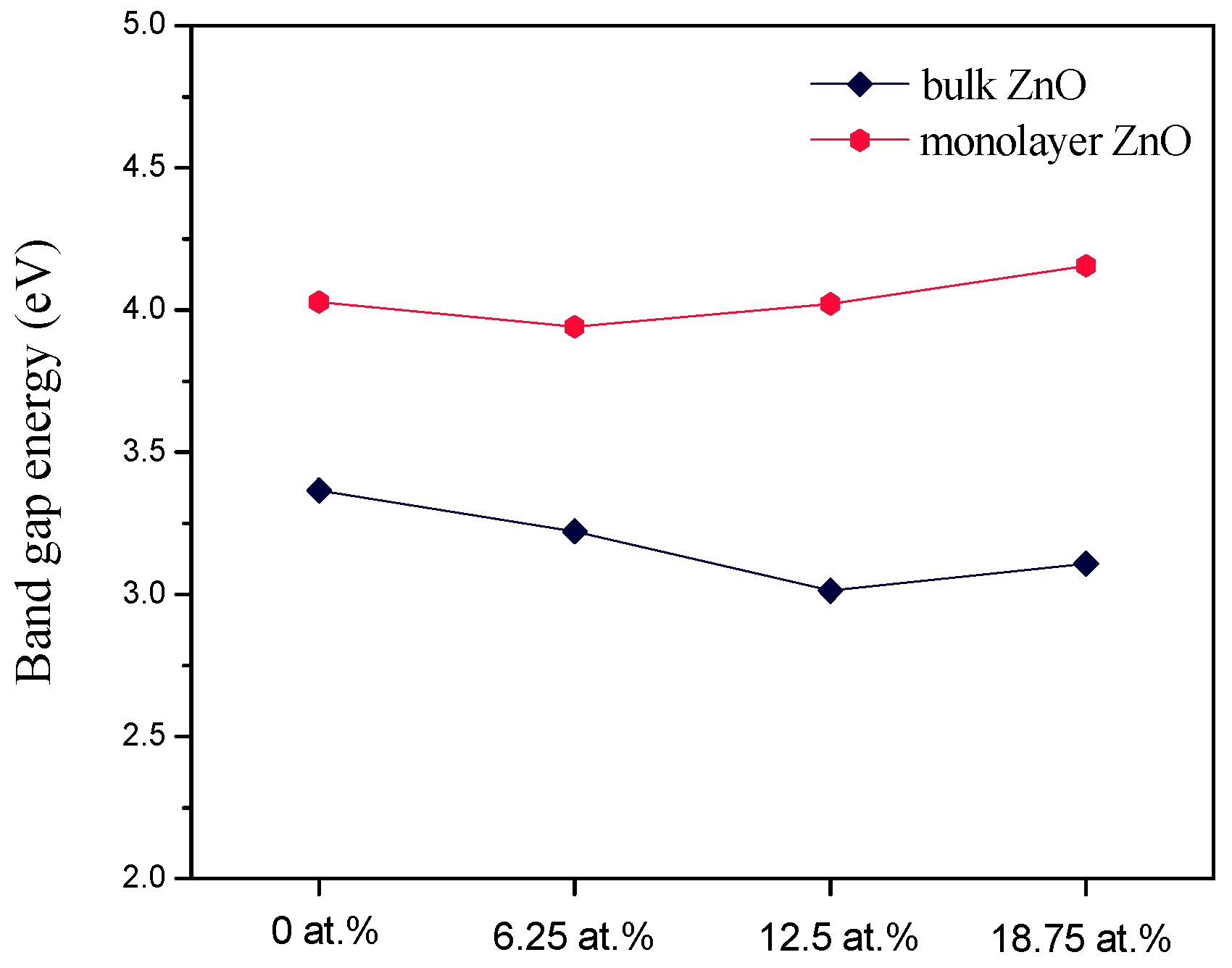
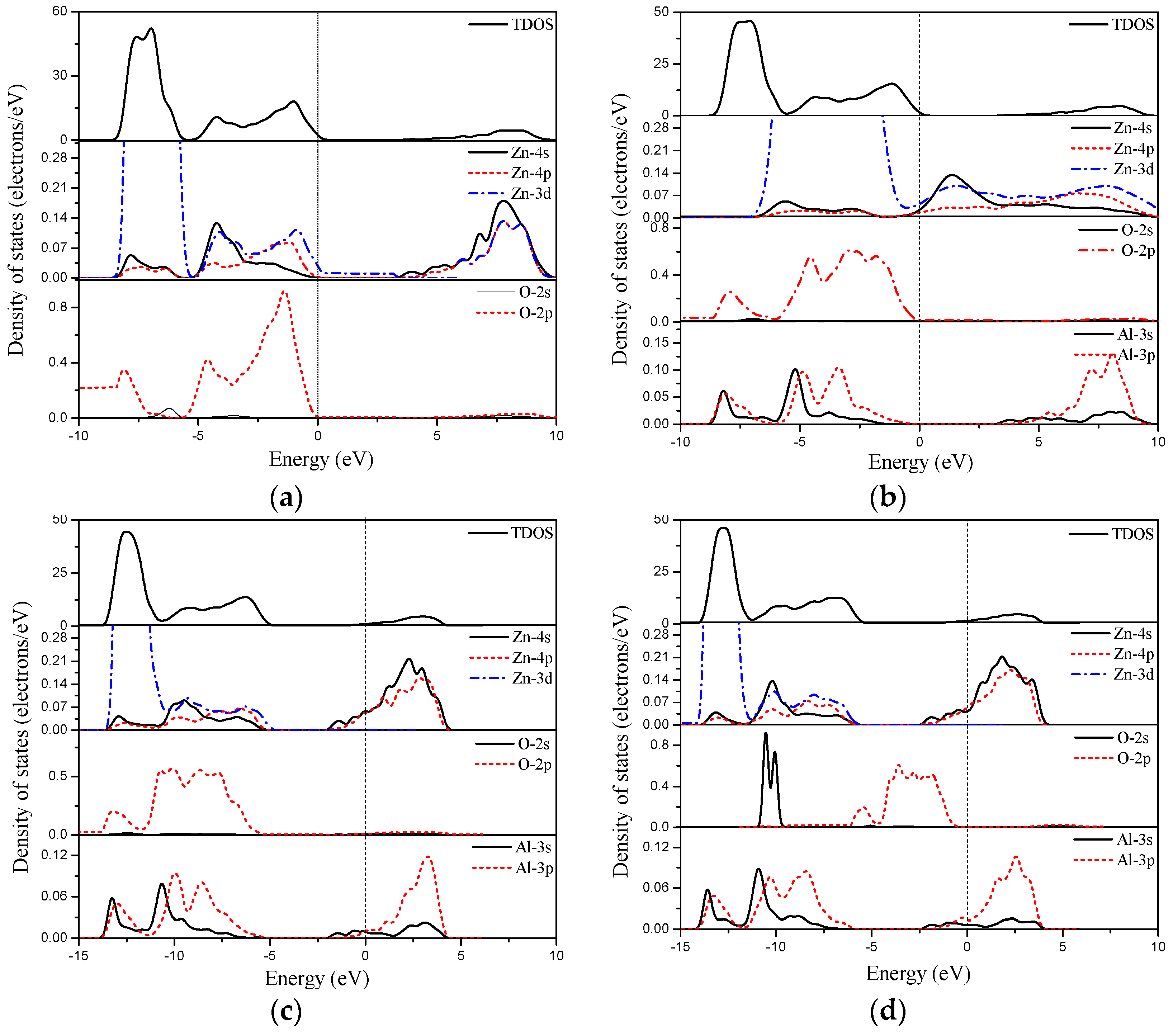
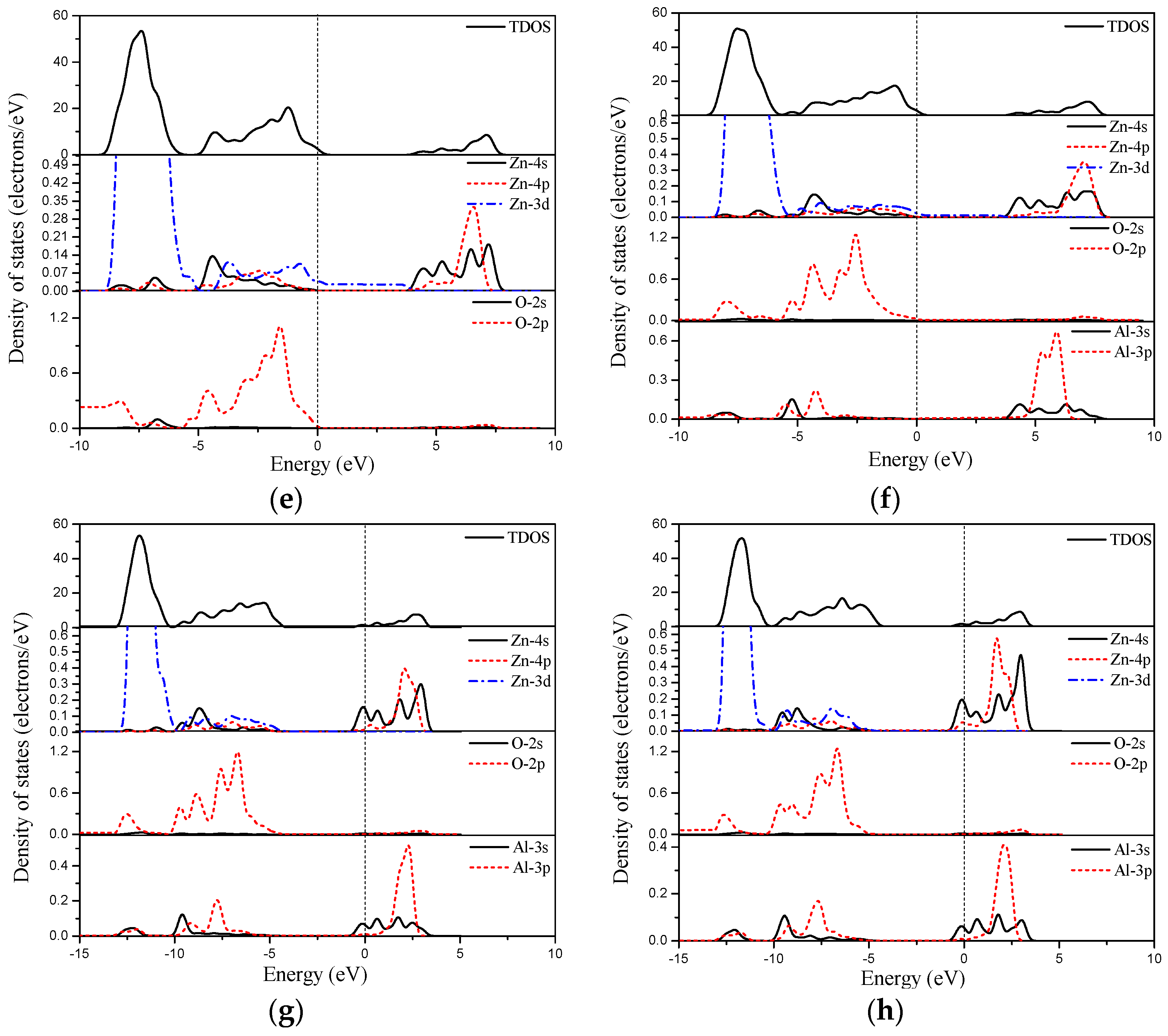
3.2. Electronic Properties
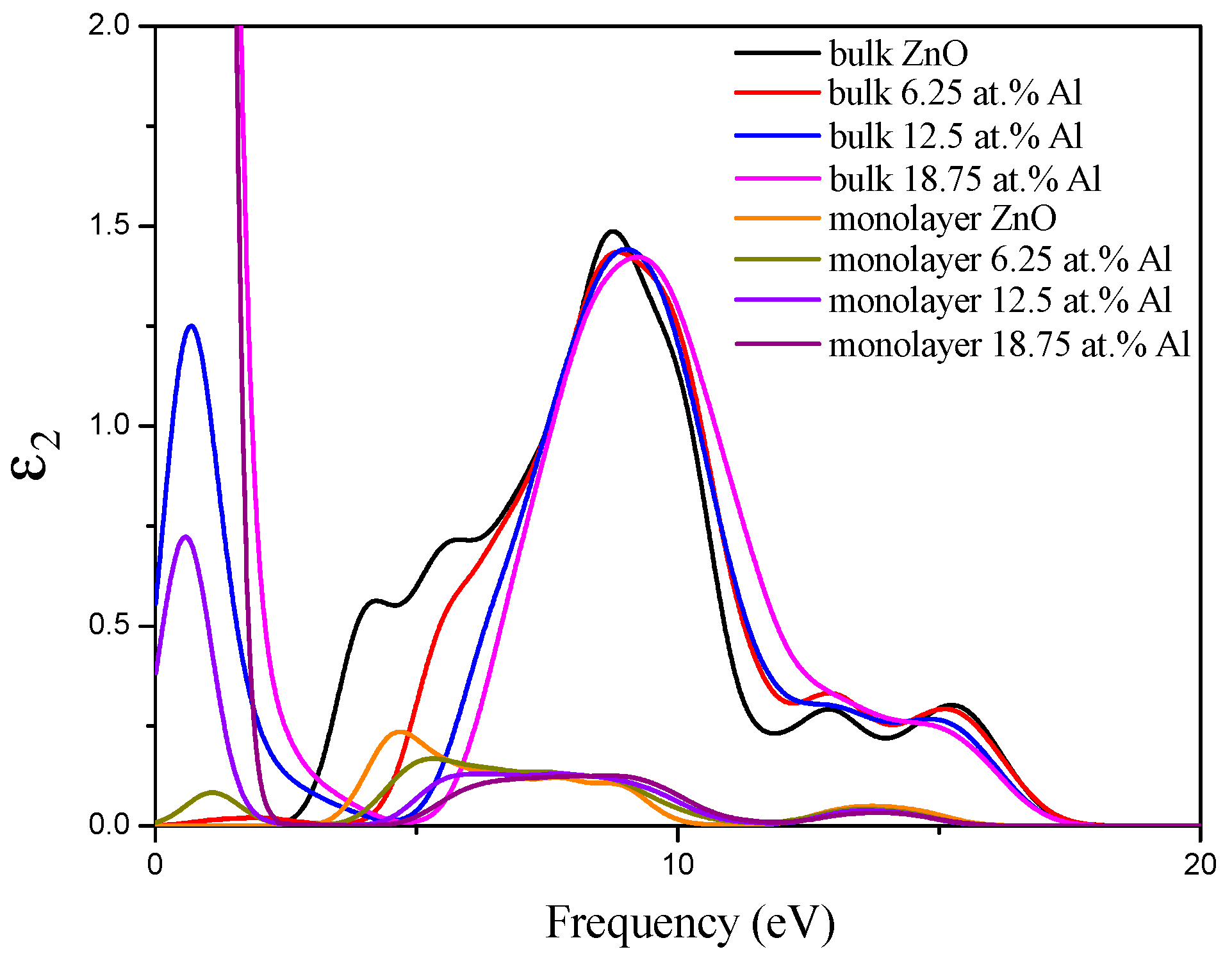
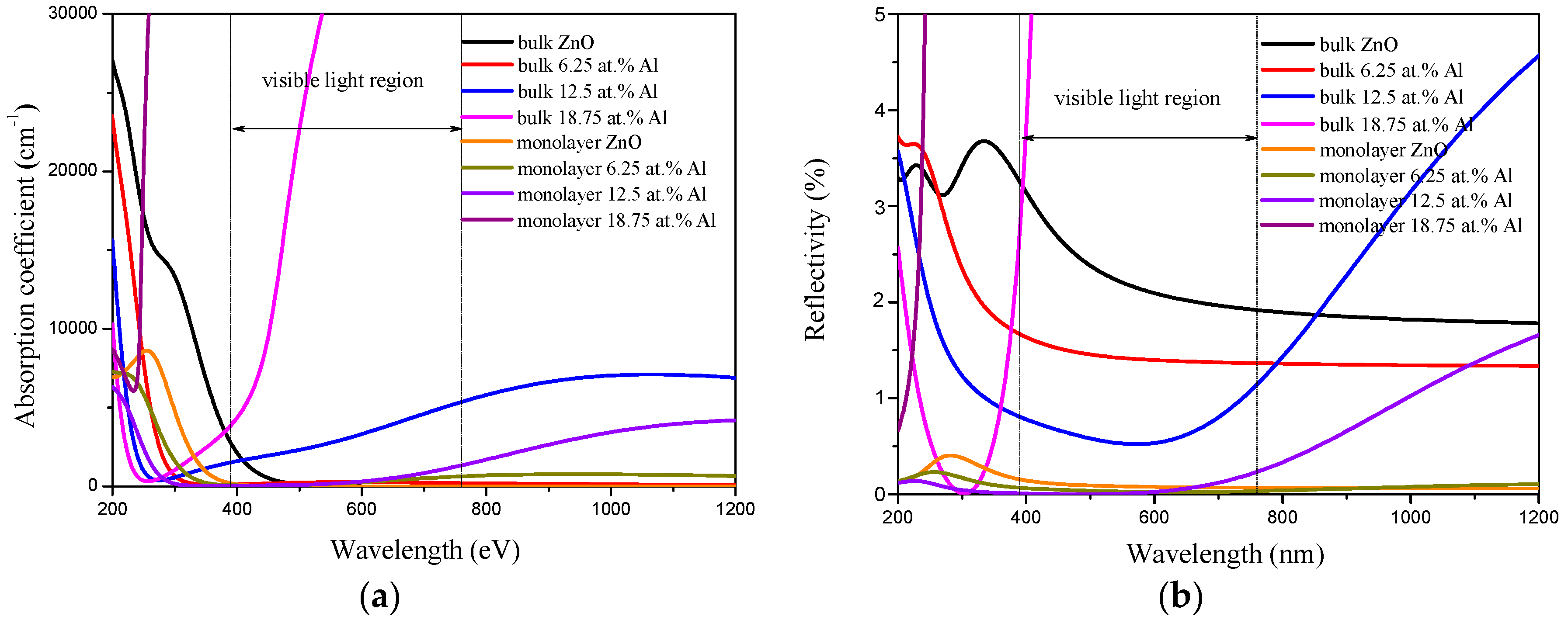
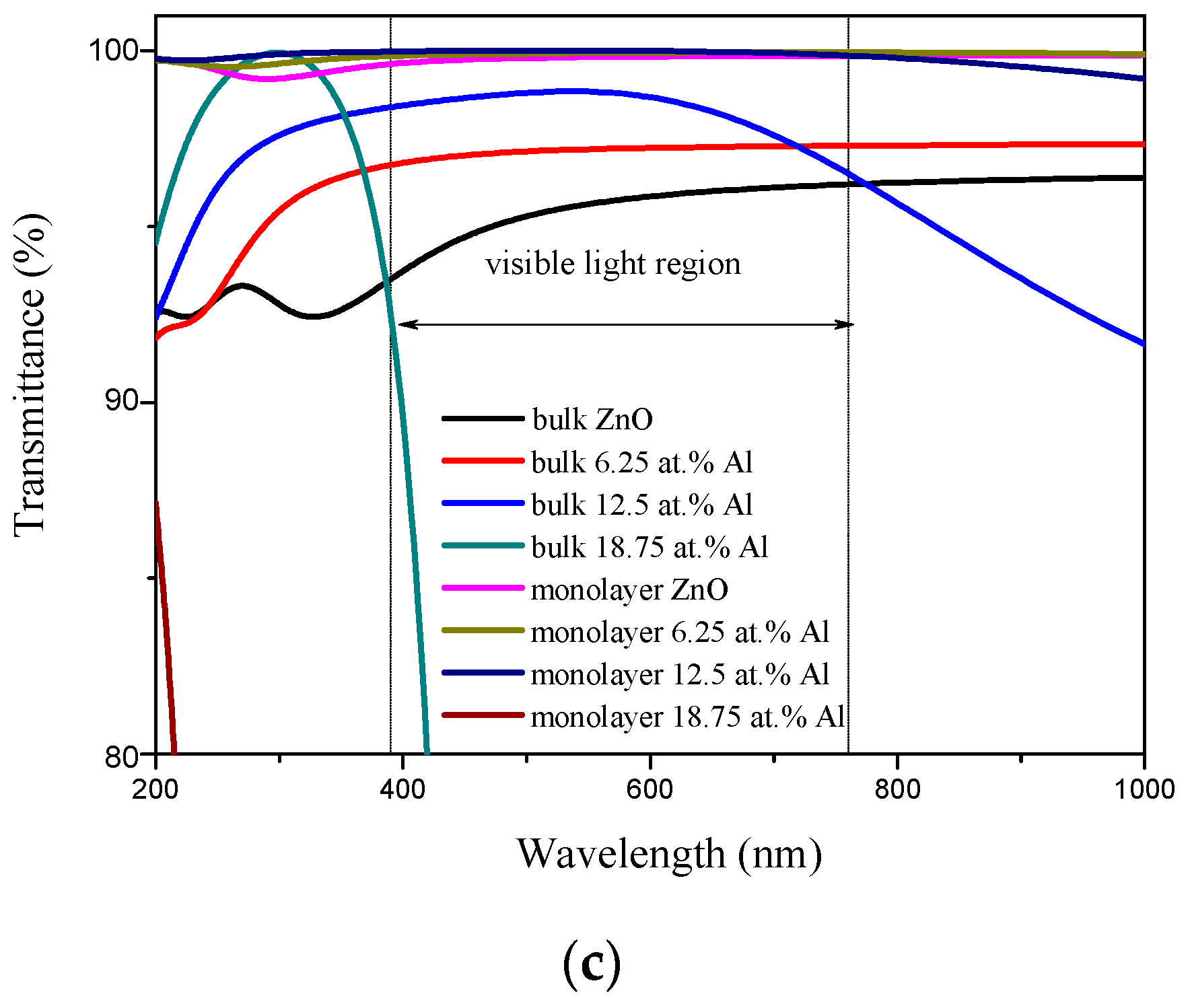
3.3. Optical Properties
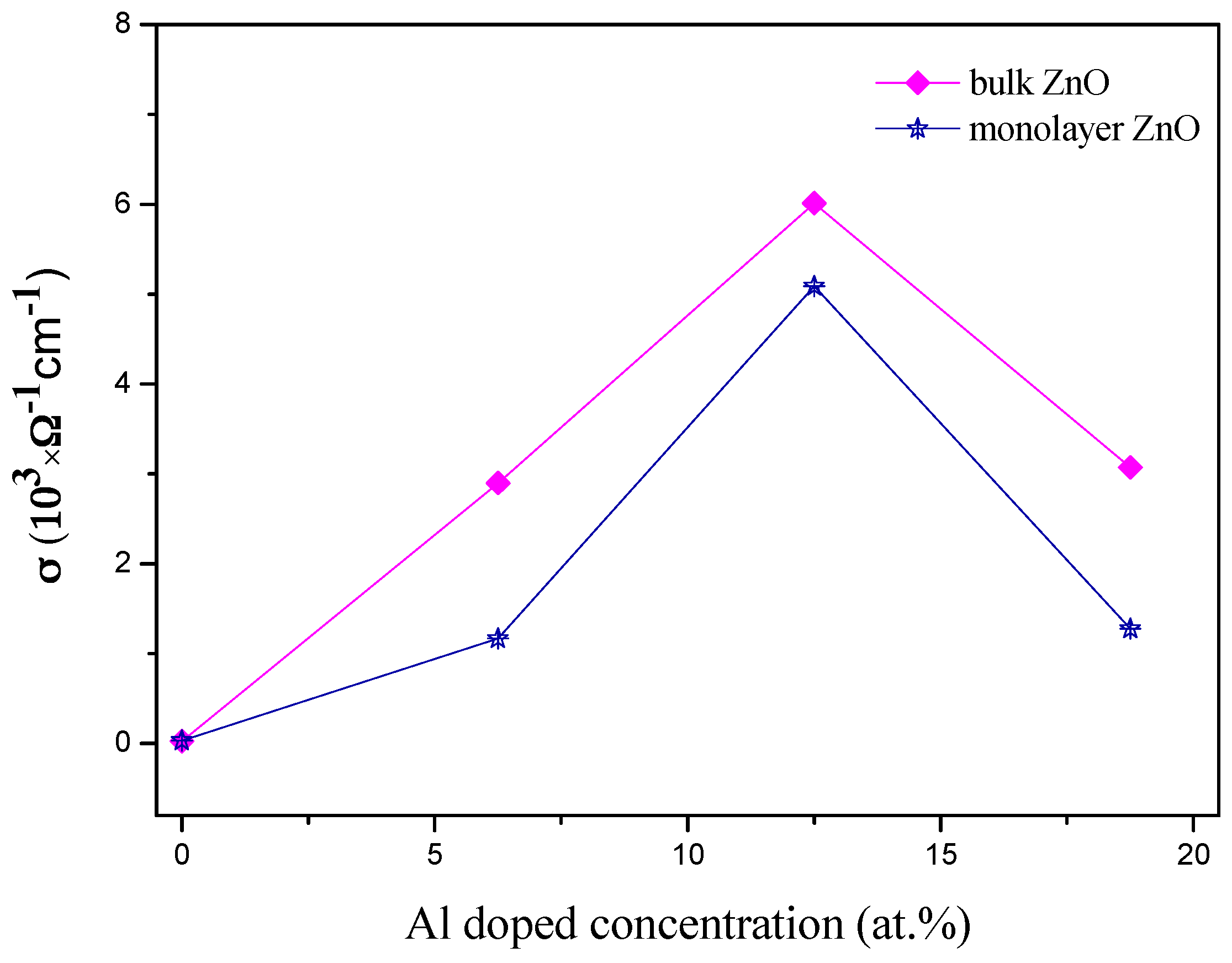
3.4. Transport Properties
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.S.; Hwang, W.J.; Eun, K.T.; Choa, S.H. Mechanical reliability of transparent conducting IZTO film electrodes for flexible panel displays. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 8134–8138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H.; Chen, Z.H.; Du, X.; Logan, J.M.; Sippel, J.; Nikolou, M.; Kamaras, K.; Reynolds, J.R.; Tanner, D.B.; Hebard, A.F.; et al. Transparent, conductive carbon nanotube films. Science 2004, 305, 1273–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhi, L.; Müllen, K. Transparent, conductive graphene electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Major, S.; Kumar, S.; Bhatnagar, M.; Chopra, K.L. Effect of hydrogen plasma treatment on transparent conducting oxides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1986, 49, 394–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, T. Transparent conducting oxide semiconductors for transparent electrodes. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2005, 20, S35–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilken, S.; Wilkens, V.; Scheunemann, D.; Nowak, R.E.; Maydell, K.V.; Parisi, J.; Borchert, H. Semitransparent Polymer-Based Solar Cells with Aluminum-Doped Zinc Oxide Electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayalakshmi, K.; Karthick, K. Influence of Mg doping on the microstructure and PL emission of wurtzite ZnO synthesized by microwave processing. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 6, 2067–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardo, G.C.; Gontijo, C.; Alfredo, A.P.N. Electrical, optical, and structural properties of thin films with tri-layers of AZO/ZnMgO/AZO grown by filtered vacuum arc deposition. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2012, 177, 1783–1787. [Google Scholar]
- Saniz, R.; Xu, Y.; Matsubara, M.; Amini, M.N.; Dixit, H.; Lamoen, D.; Partoens, B. A simplified approach to the band gap correction of defect formation energies: Al, Ga, and In-doped ZnO. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2013, 74, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagendorfer, H.; Lienau, K.; Nishiwaki, S.; Fella, C.M.; Kranz, L.; Uhl, A.R.; Jaeger, D.; Luo, L.; Gretener, C.; Buechler, S.; et al. Highly transparent and conductive ZnO: Al thin films from a low temperature aqueous solution approach. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crossay, A.; Buecheler, S.; Kranz, L.; Perrenoud, J.; Fella, C.M.; Romanyuk, Y.E.; Tiwari, A.N. Spray-deposited Al-doped ZnO transparent contacts for CdTe solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2012, 101, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.W.; Kuk, S.H.; Ji, K.S.; Lee, H.M.; Han, M.K. Effects of ITO precursor thickness on transparent conductive Al doped ZnO film for solar cell applications. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2012, 95, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Z.; Xu, J.; Xu, Q.B. Preparation and characterization of Al doped ZnO thin films by sol–gel process. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 542, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Zhou, Z. Graphene-analogous low-dimensional materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2013, 58, 1244–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liang, T.; Shi, M.; Chen, H. Graphene-like two-dimensional materials. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 3766–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koski, K.J.; Cui, Y. The new skinny in two-dimensional nanomaterials. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3739–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Hu, J.; Zeng, H. Two-dimensional semiconductors: Recent progress and future perspectives. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 2952–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miro, P.; Audiffred, M.; Heine, T. An atlas of two-dimensional materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6537–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Sakthivel, T.; Seal, S. Recent development in 2D materials beyond graphene. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 73, 44–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, S.Z.; Hollen, S.M.; Cao, L.Y. Progress, challenges, and opportunities in two-dimensional materials beyond graphene. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2898–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, C.L.; Claeyssens, F.; Allan, N.L.; Harding, J.H. Graphitic nanofilms as precursors to wurtzite films: Theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 066102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tusche, C.; Meyerheim, H.L.; Kirschner, J. Observation of depolarized ZnO(0001) monolayers: Formation of unreconstructed planar sheets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 026102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.L.; Sun, D.; Xu, D.S.; Tian, X.H.; Huang, Y.W. Tuning electronic structure and optical properties of ZnO monolayer by Cd doping. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 10997–11002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weirum, G.; Barcaro, G.; Fortunelli, A.; Weber, F.; Schennach, R.; Surnev, S.; Netzer, F.P. Growth and Surface Structure of Zinc Oxide Layers on a Pd(111) Surface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 15432–15439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, H.T.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Dianat, A.; Ortmann, F.; Zhao, J.; Warner, J.H.; Eckert, J.; Cunniberti, G.; Rummeli, M.H. In situ observations of free-standing graphene-like mono- and bilayer ZnO membranes. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11408–11413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, T.; Nayak, S.K.; Chelliah, P.; Raht, M.K.; Parida, B. Observations of two-dimensional monolayer zinc oxide. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 75, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.C. First-principles study on physical properties of a single ZnO monolayer with graphene-like structure. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2010, 7, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, N.; Kang, E.J.; Zeng, X.C.; Wu, X.J.; Yang, J.L. Tunable Magnetism in a Nonmetal-Substituted ZnO Monolayer: A First-Principles Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 11336–11342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, M.D.; Lindan, P.J.D.; Probert, M.J.; Pickard, C.J.; Hassnip, P.J.; Clark, S.J.; Payne, M.D. First-principles simulation: Ideas, illustrations and the CASTEP code. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 1990, 14, 7892–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderbilt, D. Ultrasoft pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 41, 7892–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Lu, B.; Li, D.; Shi, R.; Pan, C.; Zhu, Y. Origin of photocatalytic activation of silver orthophosphate from first-principles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 4680–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.C.; Peng, Y.C.; Chen, C.C. Effects of Ga concentration on electronic and optical properties of Ga-doped ZnO from first principles calculations. Opt. Mater. 2013, 35, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooten, F. Optical Properties of Solids; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Wang, H.; He, J.; Tian, Y. Ab initio investigations of optical properties of the high-pressure phases of ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 123132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, M. Optical Properties of Solids. Oxford Master Series in Condensed Matter Physics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, G.K.H.; Singh, D.J. A code for calculating band-structure dependent quantities. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2006, 175, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziman, J.M. Electrons and Phonons; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Uechara, K.; Klug, D.; Patchkovskii, S.; Tse, J.; Tritt, T. Theoretical studies on the thermopower of semiconductors and low-band-gap crystalline polymers. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 125202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaput, L.; Pécheur, P.; Tobola, J.; Scherrer, H. Transport in doped skutterudites: Ab initio electronic structure calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 085126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, G.K.H. Automated search for new thermoelectric materials: The case of LiZnSb. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vispute, R.D.; Talyansky, V.; Choopun, S.; Sharma, R.P.; Venkatesan, T.; He, M.; Salamanca-Riba, L.G. Heteroepitaxy of ZnO on GaN and its implications for fabrication of hybrid optoelectronic devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 348–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Lu, S.X.; Xu, W.G.; Yuan, F. First-principles study of Si atoms adsorbed on ZnO (0001) surface and the effect on electronic and optical properties. Surf. Sci. 2014, 625, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgur, U.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.A.; Dogan, S.; Avrutin, V.; Cho, S.J.; Morkoc, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.C.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, W.H.; Yan, J.F.; Yun, J.N. First-principles calculation of electronic structure and optical properties of AZO(ZnO:Al). Acta Opt. Sin. 2009, 29, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lee, K.E.; Hahn, S.H. Optical and photoluminescent properties of sol-gel Al-doped ZnO thin films. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 1118–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, S.; Ogawa, M.; Sawada, Y. Indium–Tin–Oxide thin films prepared by dip coating: Dependence of resistivity on film thickness and annealing atmosphere. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 40, L1244–L1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, K.P.; Singh, D.J.; Wu, P. Analysis of the thermoelectric properties of n-type ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 115110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compounds | Concentration | a (Å) | c (Å) | Formation Energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bulk | 0% | 3.313 | 5.329 | - |
| 6.25% | 3.312 | 5.315 | −0.096 | |
| 12.5% | 3.307 | 5.320 | −0.162 | |
| 18.75% | 3.306 | 5.324 | −0.231 | |
| monolayer | 0% | 4.437 | - | - |
| 6.25% | 4.426 | - | −0.059 | |
| 12.5% | 4.421 | - | −0.135 | |
| 18.75% | 4.408 | - | −0.199 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, M.; Sun, D.; Tan, C.; Tian, X.; Huang, Y. Al-Doped ZnO Monolayer as a Promising Transparent Electrode Material: A First-Principles Study. Materials 2017, 10, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10040359
Wu M, Sun D, Tan C, Tian X, Huang Y. Al-Doped ZnO Monolayer as a Promising Transparent Electrode Material: A First-Principles Study. Materials. 2017; 10(4):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10040359
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Mingyang, Dan Sun, Changlong Tan, Xiaohua Tian, and Yuewu Huang. 2017. "Al-Doped ZnO Monolayer as a Promising Transparent Electrode Material: A First-Principles Study" Materials 10, no. 4: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10040359
APA StyleWu, M., Sun, D., Tan, C., Tian, X., & Huang, Y. (2017). Al-Doped ZnO Monolayer as a Promising Transparent Electrode Material: A First-Principles Study. Materials, 10(4), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10040359







