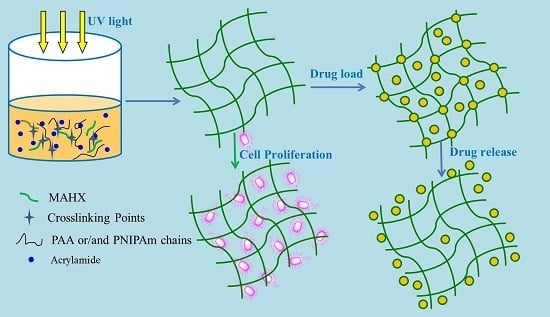
Xylan-Modified-Based Hydrogels with Temperature/pH Dual Sensitivity and Controllable Drug Delivery Behavior
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of MAHX or MAHX-Based Hydrogels
2.2.1. Preparation of MAHX
2.2.2. Preparation of MAHX-Based Hydrogels
2.3. The Swelling Behavior Studies of Hydrogels
2.4. Compression Test of Hydrogels
2.5. Characterization
2.6. Loading of Acetylsalicylic Acid and Theophylline into Hydrogels
2.7. In Vitro Drug Release
2.8. Cell Viability Study
3. Results and Discussion
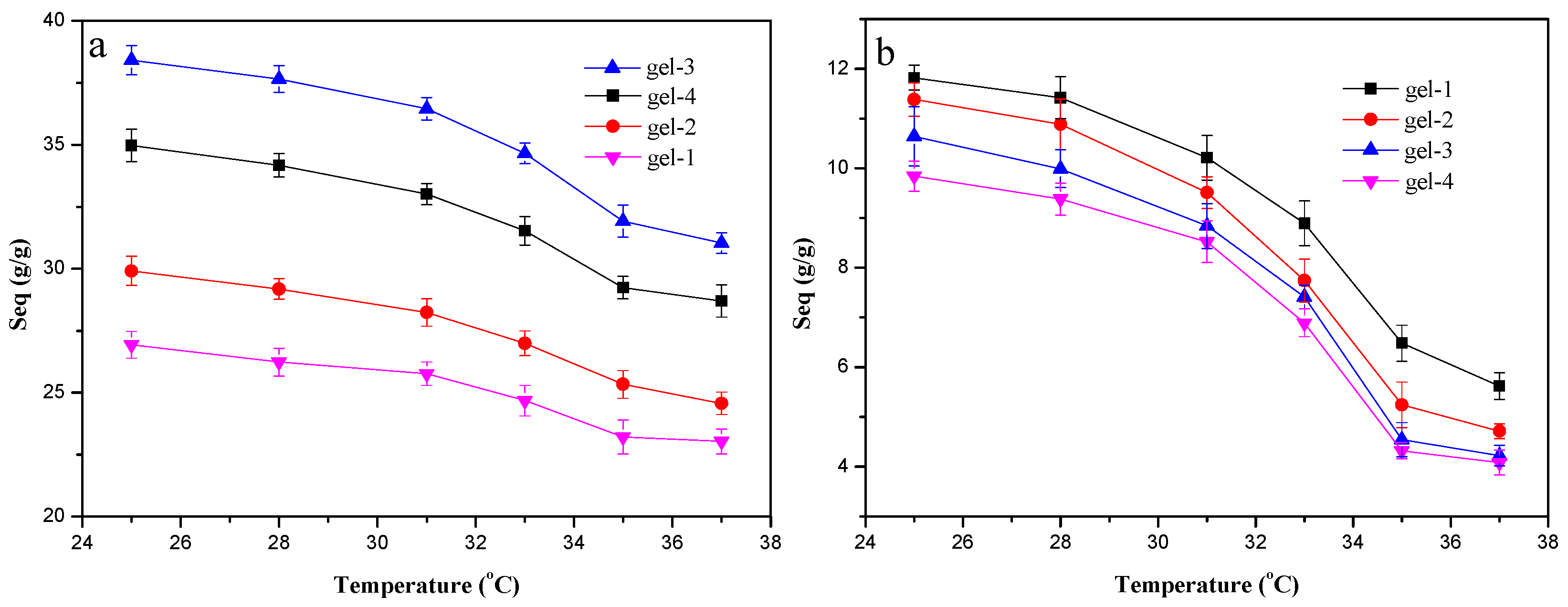
3.1. Temperature and pH-Dependent Swelling Behaviors of Hydrogels
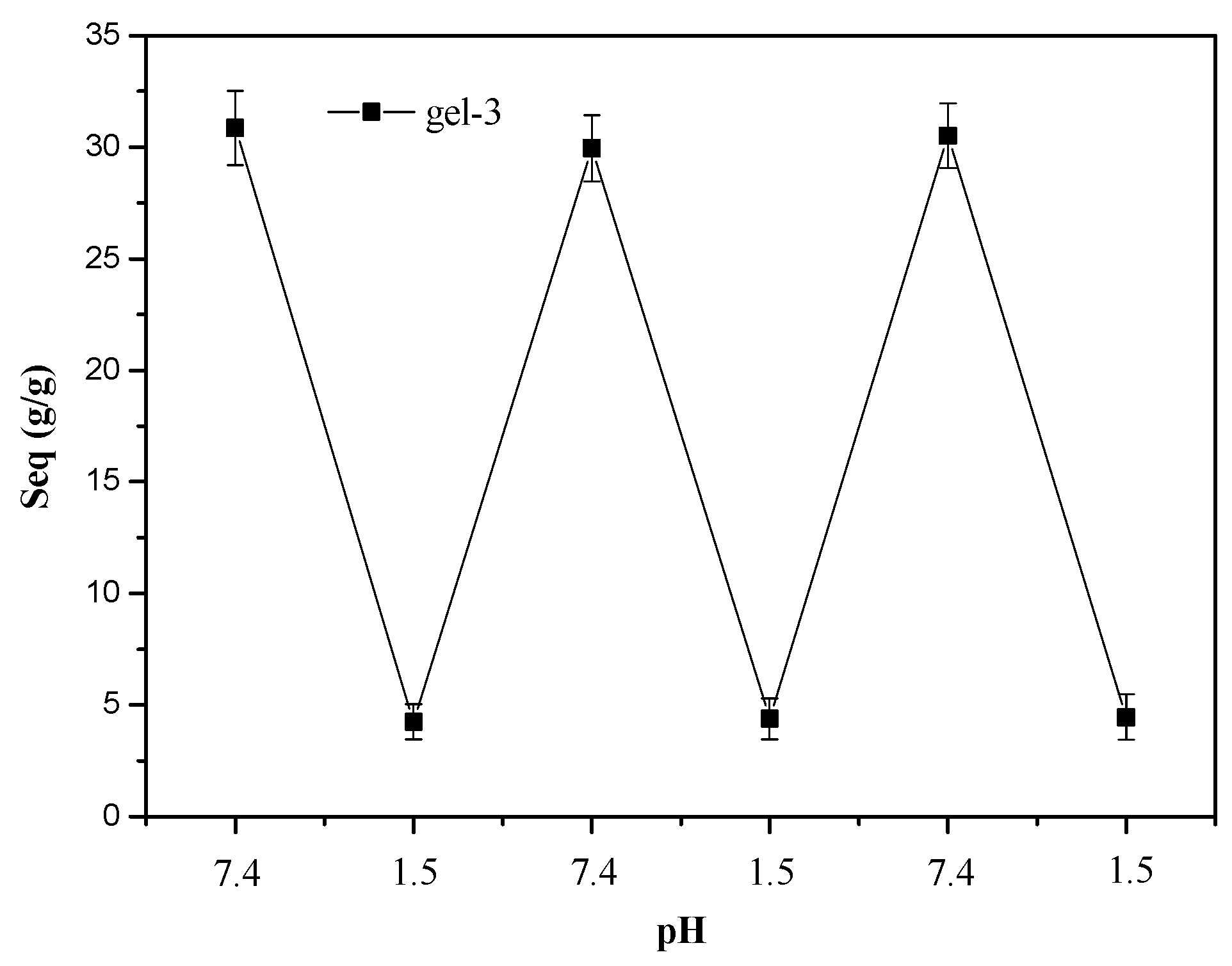
3.2. The Swelling and Deswelling Behaviors of Hydrogels in Buffers
3.3. Morphological Analysis
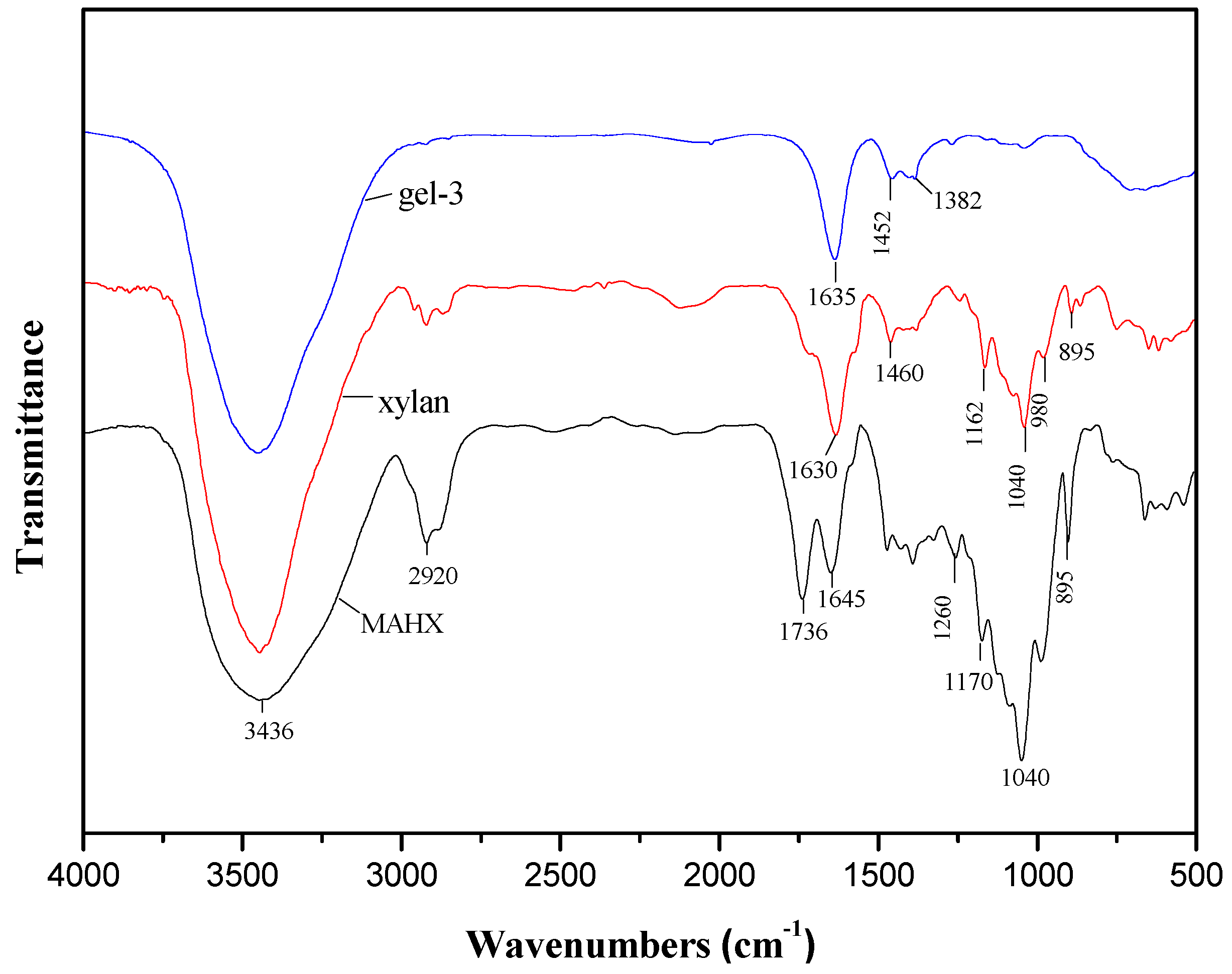
3.4. FTIR Spectra of Xylan, MAHX and Prepared Hydrogels
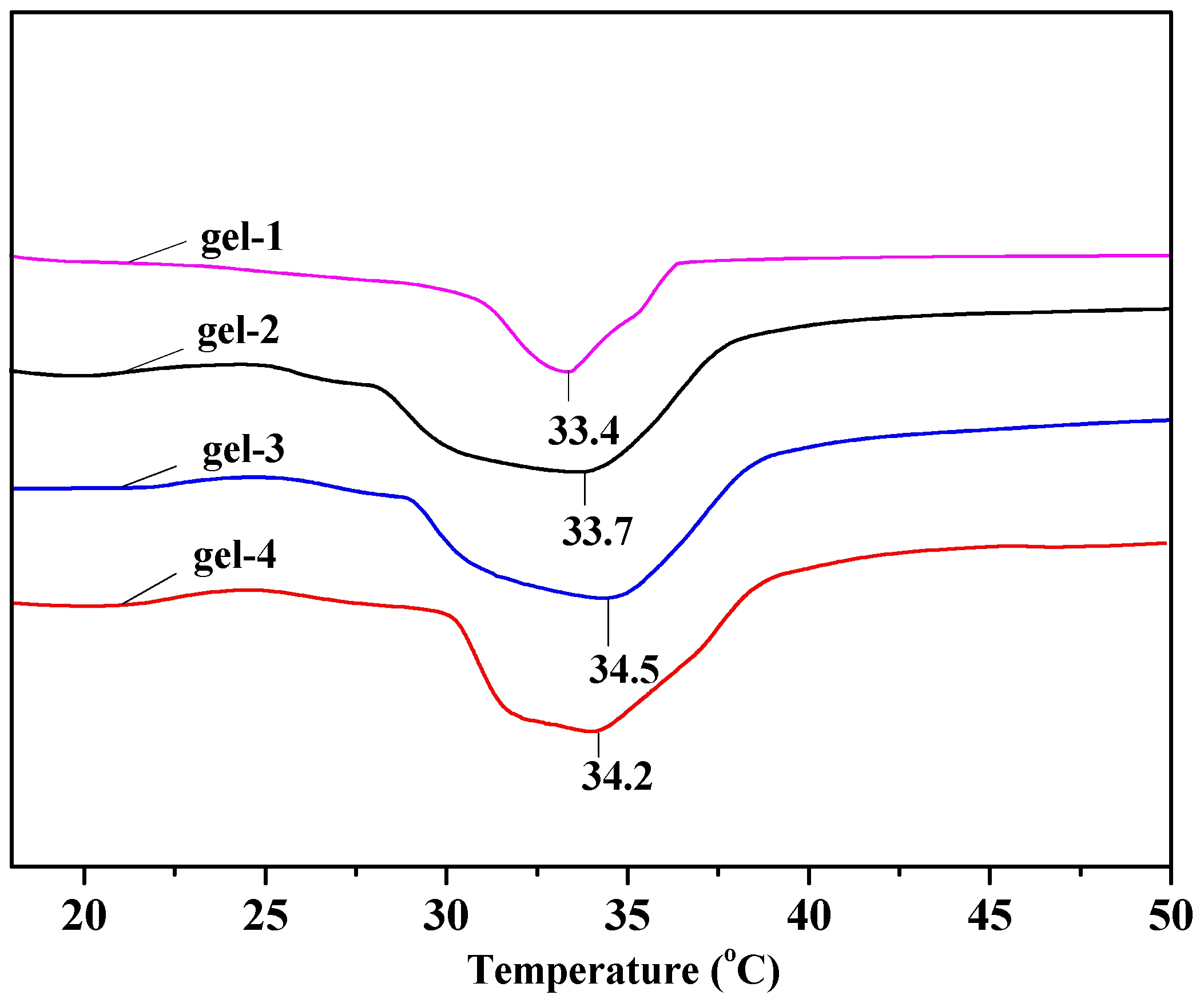
3.5. LCST of Hydrogels
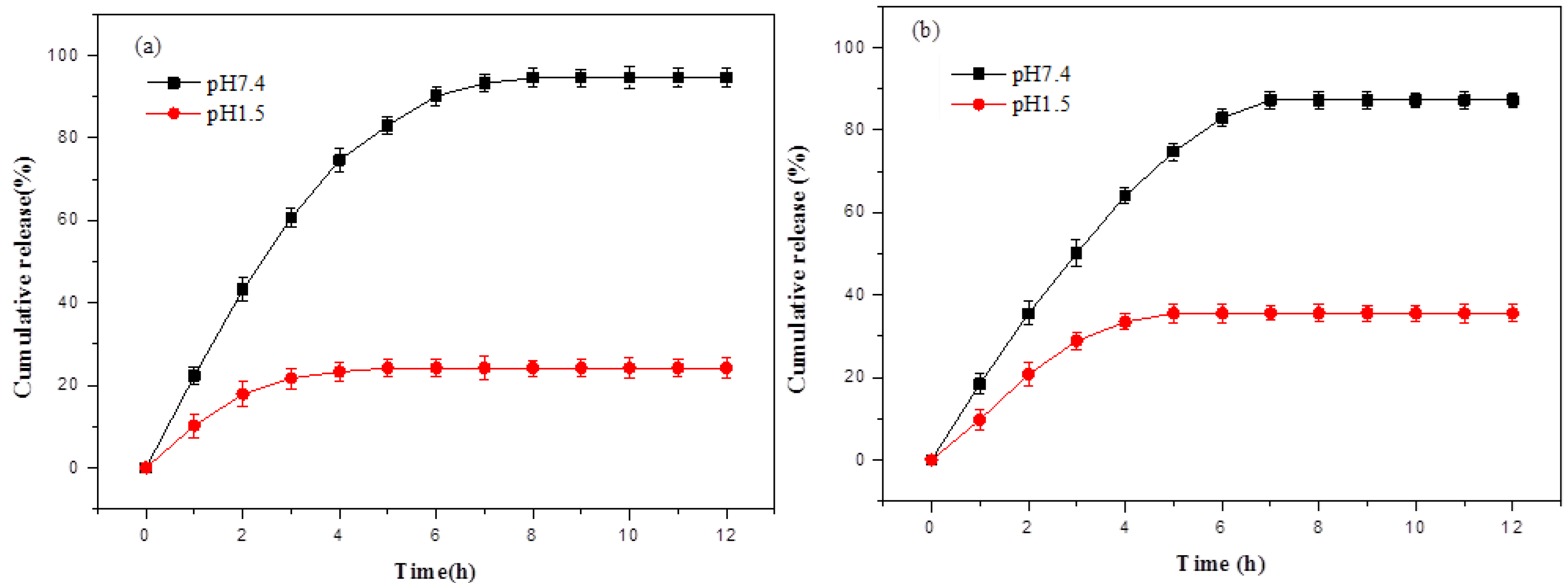
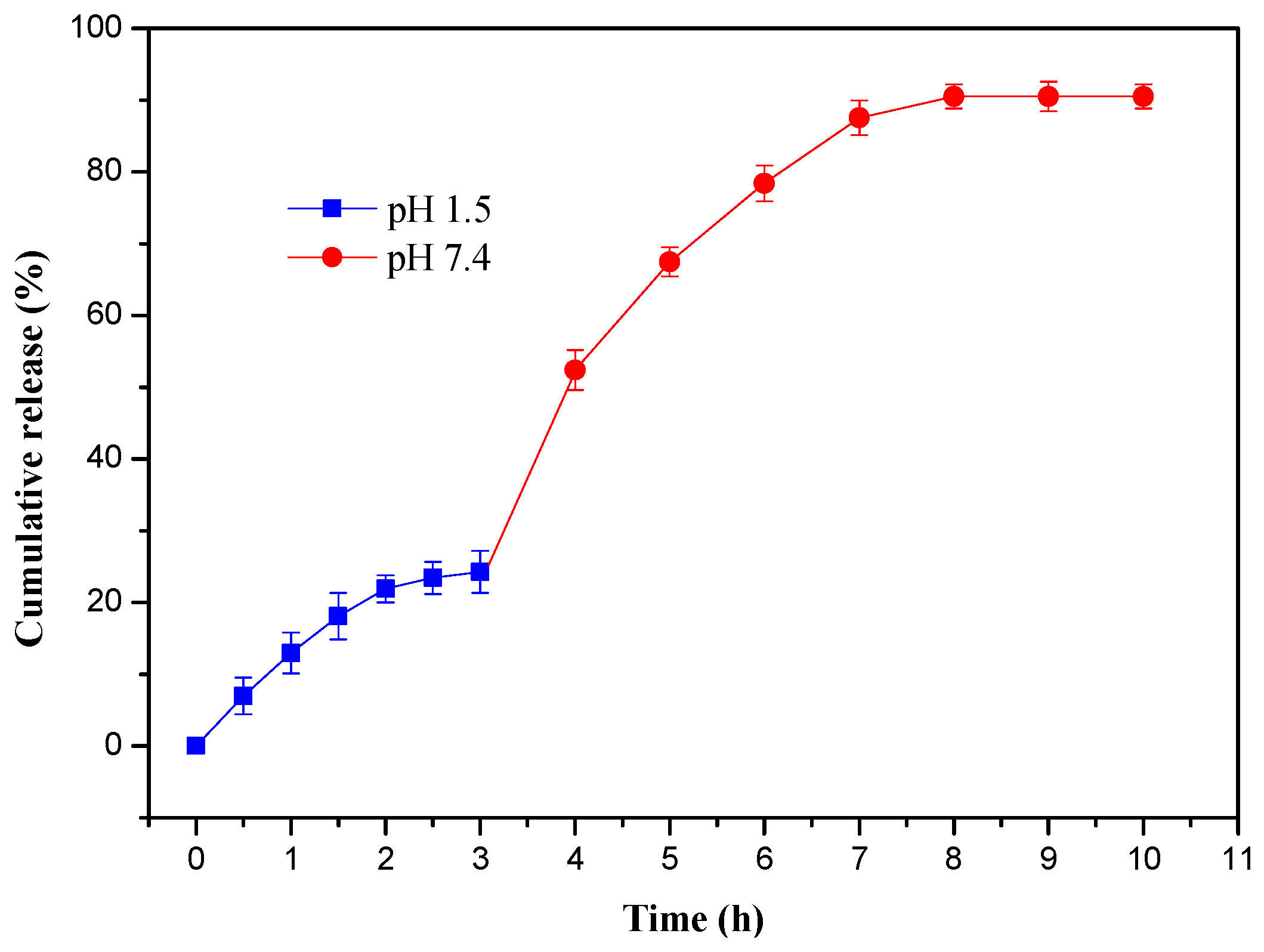
3.6. In Vitro Drug Release of Hydrogels
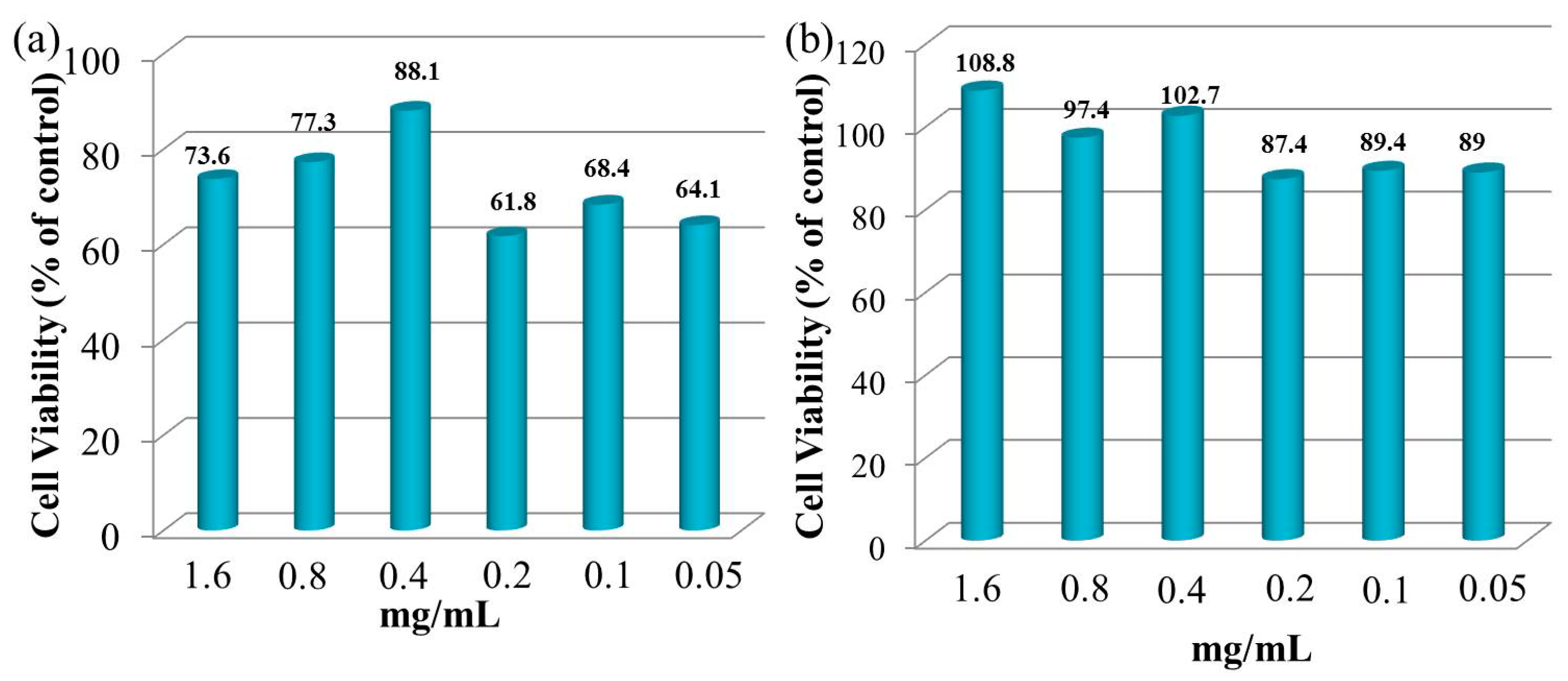
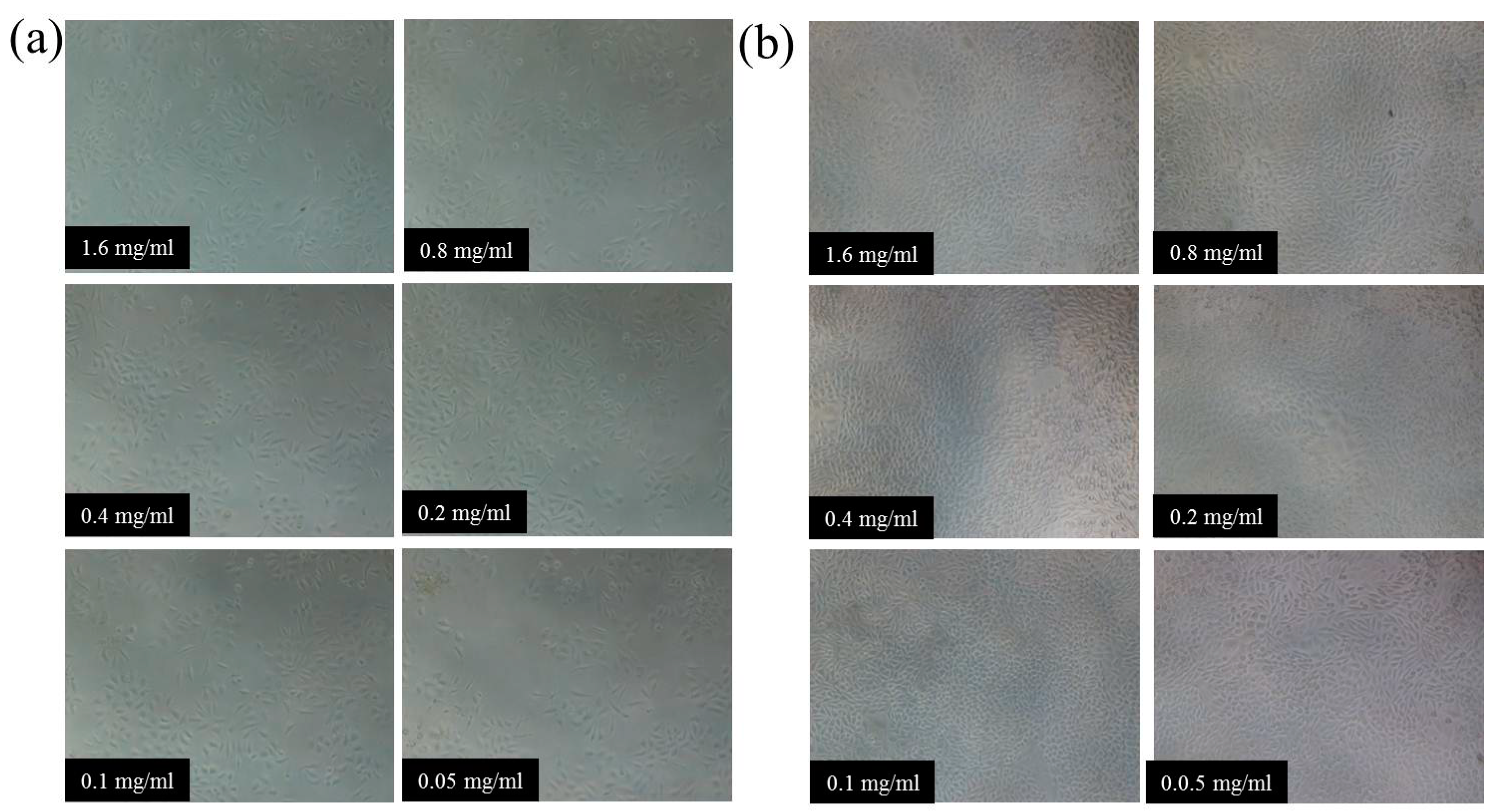
3.7. Cytocompatibility of Hydrogels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, P.; Vermani, K.; Garg, S. Hydrogels: From controlled release to pH-responsive drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2002, 7, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.P.; Neufeld, R.J.; Ribeiro, A.J.; Veiga, F.; Nanoencapsulation, I. Methods for preparation of drug-loaded polymeric nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2006, 2, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Park, K. Environment-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. Adv. Drug. Deliver. Rev. 2001, 53, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermonden, T.; Censi, R.; Hennink, W.E. Hydrogels for protein delivery. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2853–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromberg, L.E.; Ron, E.S. Temperature-responsive gels and thermogelling polymer matrices for protein and peptide delivery. Adv. Drug. Deliver. Rev. 1998, 31, 197–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, E.S.; Hudson, S.M. Stimuli-reponsive polymers and their bioconjugates. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2004, 29, 1173–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.; Kim, S.W.; Bae, Y.H. Thermosensitive sol–gel reversible hydrogels. Adv. Drug. Deliver. Rev. 2002, 54, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, T.; Uragami, T.; Nakamae, K. Biomolecule-sensitive hydrogels. Adv. Drug Deliver Rev. 2002, 54, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmaljohann, D. Thermo-and pH-responsive polymers in drug delivery. Adv. Drug. Deliver. Rev. 2006, 58, 1655–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, A.S. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug. Deliver. Rev. 2012, 64, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Peppas, N. Morphology of poly (methacrylic acid)/poly (N-isopropyl acrylamide) interpenetrating polymeric networks. J. Biomat. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2002, 13, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, N.; Gunn, J.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled, localized drug delivery. Adv. Drug. Deliver. Rev. 2010, 62, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.Q.; Huang, D.Y.; Xu, G.B.; Ren, J.L.; Liu, C.F.; Zhao, L.H.; Sun, R.C. Graphene Oxide/Polyacrylamide/Aluminum Ion Cross-Linked Carboxymethyl Hemicellulose Nanocomposite Hydrogels with Very Tough and Elastic Properties. Chem. Asian. J. 2016, 11, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C.; Metters, A.T. Hydrogels in controlled release formulations: Network design and mathematical modeling. Adv. Drug. Deliver. Rev. 2006, 58, 1379–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.D.; Ren, J.L.; Kong, W.Q.; Sun, R.C.; Chen, Q.F. Comparative study on temperature/pH sensitive xylan-based hydrogels: Their properties and drug controlled release. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 90671–90681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.F.; Gan, Z.; Jing, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, D.; Jin, Y. Adsorption of methylene blue on hemicellulose-based stimuli-responsive porous hydrogel. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, N.P.; Montanti, J.; Johnston, D.B.; Drapcho, C. Fractionation of corn fiber treated by soaking in aqueous ammonia (SAA) for isolation of hemicellulose B and production of C5 sugars by enzyme hydrolysis. App. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 164, 1390–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, E.E.; Silva, A.E.; Júnior, T.N.; Gomes, M.C.S.; Aguiar, L.M.; Marcelino, H.R.; Araújo, I.B.; Bayer, M.P.; Ricardo, N.M.; Oliveira, A.G.; et al. Xylan from corn cobs, a promising polymer for drug delivery: Production and characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5402–5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazayawoko, M.; Balatinecz, J.; Woodhams, R. Diffuse reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectra of wood fibers treated with maleated polypropylenes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 66, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokhade, A.P.; Agnihotri, S.A.; Patil, S.A.; Mallikarjuna, N.N.; Kulkarni, P.V.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Semi-interpenetrating polymer network microspheres of gelatin and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose for controlled release of ketorolac tromethamine. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 65, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlovich, G.L.; Bauer, B.A. Thermodynamics of solutions I: Benzoic acid and acetylsalicylic acid as models for drug substances and the prediction of solubility. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticehurst, M.D.; Storey, R.A.; Watt, C. Application of slurry bridging experiments at controlled water activities to predict the solid-state conversion between anhydrous and hydrated forms using theophylline as a model drug. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 247, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.W.; Ren, J.L.; Sun, R.C. Homogeneous esterification of xylan-rich hemicelluloses with maleic anhydride in ionic liquid. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 3519–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ding, Y. Creating micro-structured hydrogel-forming polymer films by photopolymerization in an evaporating solvent: Compositional and morphological evolutions. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 66, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y. Photocrosslinking-induced phase separation in evaporative solvents: Formation of skin layers and microspheres. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 4455–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.F.; Wang, H.H.; Jing, Z.X.; Mohanathas, R. Hemicellulose-based pH-sensitive and biodegradable hydrogel for controlled drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.H.; Krochta, J.M.; Kurth, M.J.; Hsieh, Y.L. Lactitol-based poly (ether polyol) hydrogels for controlled release chemical and drug delivery systems. J. Agirc. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 5278–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, P.; Sarkar, K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Mishra, R.; Kundu, P. pH sensitive N-succinyl chitosan grafted polyacrylamide hydrogel for oral insulin delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, Y.H.; Wu, T.M.; Wu, J.H.; Liao, J.W. Cytotoxicity and drug release behavior of PNIPAM grafted on silica-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Nanopar. Res. 2011, 13, 5065–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Gao, X.; He, P.; Xiao, C.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X. Facile synthesis of thermo-and pH-responsive biodegradable microgels. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2011, 289, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Fang, J. Synthesis and characterization of temperature sensitive hemicellulose-based hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohani, A.; Singh, G.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Hegde, R.R.; Verma, A. Tailored-interpenetrating polymer network beads of κ-carrageenan and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose for controlled drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 31, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Peng, X.; Zhong, L.; Sun, R. Multiresponsive hydrogels based on xylan-type hemicelluloses and photoisomerized azobenzene copolymer as drug delivery carrier. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10000–10007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.W.; Ren, J.L.; Zhong, L.X.; Peng, F.; Sun, R.C. Xylan-rich hemicelluloses-graft-acrylic acid ionic hydrogels with rapid responses to pH, salt, and organic solvents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8208–8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Sun, R.; Tomkinson, J.; Fowler, P. Acetylation of wheat straw hemicellulose B in a new non-aqueous swelling system. Carbohydr. Polym. 2000, 41, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Madan, R.; Bansal, M. Chemical composition of Pinus caribaea hemicellulose. Tappi J. 1987, 74, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Harzandi, A.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Modified carrageenan 3. Synthesis of a novel polysaccharide-based superabsorbent hydrogel via graft copolymerization of acrylic acid onto kappa-carrageenan in air. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beattie, D.A.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Beaussart, A.; George, V.F.; Kai, Y.Y. In situ particle film ATR FTIR spectroscopy of poly (N-isopropyl acrylamide)(PNIPAM) adsorption onto talc. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 25143–25151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, Y.; Higuchi, T.; Ikeda, I. Change in hydration state during the coil-globule transition of aqueous solutions of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) as evidenced by FTIR spectroscopy. Langmuir 2000, 16, 7503–7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Yu, X. Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: Their Characteristics and the Mechanisms behind Them. Gels 2017, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.X.; Peng, X.W.; Yang, D.; Cao, X.F.; Sun, R.C. Long-chain anhydride modification: A new strategy for preparing xylan films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Xia, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Q. Biocompatible poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)-g-carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogels as carriers for sustained release of cisplatin. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 4914–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Glavas, L.; Odelius, K.; Edlund, U.; Albertsson, A.C. A robust pathway to electrically conductive hemicellulose hydrogels with high and controllable swelling behavior. Polymer 2014, 55, 2967–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voepel, J.; Edlund, U.; Albertsson, A.C. Alkenyl-functionalized precursors for renewable hydrogels design. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2009, 47, 3595–3606. [Google Scholar]

| Samples | MAH/xylan | DS of MAHX | NIPAm/MAHX (g/g) | AA/MAHX (g/g) | MBA/MAHX (g/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gel-1 | 1:1 | 0.12 | 0.1 | 10:1 | 0.1 |
| gel-2 | 2:1 | 0.28 | 0.1 | 10:1 | 0.1 |
| gel-3 | 4:1 | 0.48 | 0.1 | 10:1 | 0.1 |
| gel-4 | 8:1 | 0.65 | 0.1 | 10:1 | 0.1 |
| Samples | Compression Stress (kPa) | Elasticity Modulus (kPa) | Drug a Loading (%) | Encapsulation Efficiency (%) | LCST (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gel-1 | 56.34 ± 3.68 | 78.54 ± 9.48 | 55.26 | 86.56 | 33.4 |
| gel-2 | 60.42 ± 4.23 | 128.25 ± 6.56 | 58.2 | 89.62 | 33.7 |
| gel-3 | 68.25 ± 3.34 | 168.67 ± 8.54 | 60.68 | 92.25 | 34.3 |
| gel-4 | 67.56 ± 2.68 | 164.34 ± 8.78 | 58.45 | 90.56 | 34.2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, W.-Q.; Gao, C.-D.; Hu, S.-F.; Ren, J.-L.; Zhao, L.-H.; Sun, R.-C. Xylan-Modified-Based Hydrogels with Temperature/pH Dual Sensitivity and Controllable Drug Delivery Behavior. Materials 2017, 10, 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10030304
Kong W-Q, Gao C-D, Hu S-F, Ren J-L, Zhao L-H, Sun R-C. Xylan-Modified-Based Hydrogels with Temperature/pH Dual Sensitivity and Controllable Drug Delivery Behavior. Materials. 2017; 10(3):304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10030304
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Wei-Qing, Cun-Dian Gao, Shu-Feng Hu, Jun-Li Ren, Li-Hong Zhao, and Run-Cang Sun. 2017. "Xylan-Modified-Based Hydrogels with Temperature/pH Dual Sensitivity and Controllable Drug Delivery Behavior" Materials 10, no. 3: 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10030304
APA StyleKong, W.-Q., Gao, C.-D., Hu, S.-F., Ren, J.-L., Zhao, L.-H., & Sun, R.-C. (2017). Xylan-Modified-Based Hydrogels with Temperature/pH Dual Sensitivity and Controllable Drug Delivery Behavior. Materials, 10(3), 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10030304