Water Impact of Syntactic Foams
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Fabrication of Syntactic Foam Panels
2.2. Experimental Setup and Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
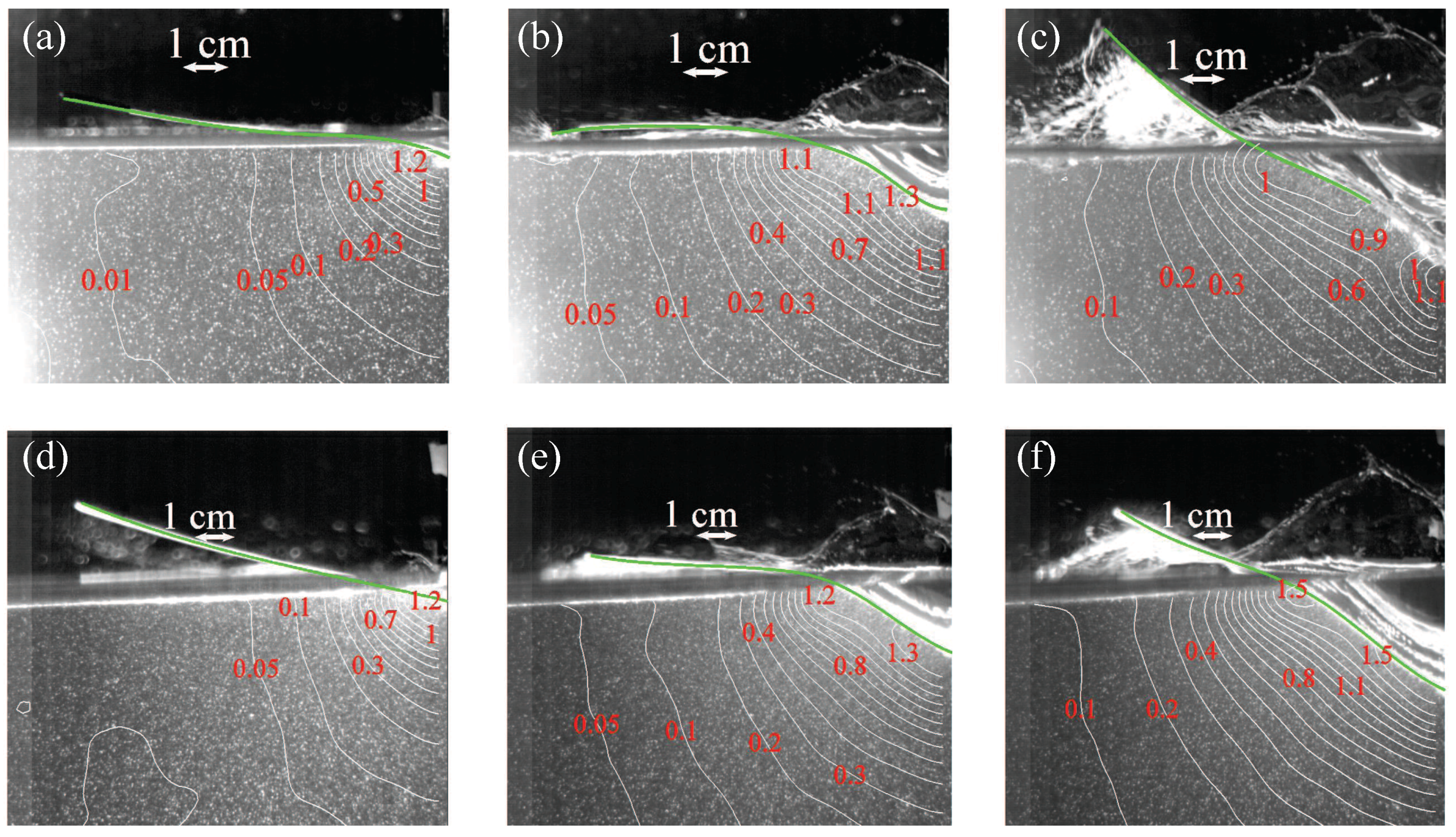
3.1. High-Speed Imaging of the Impact
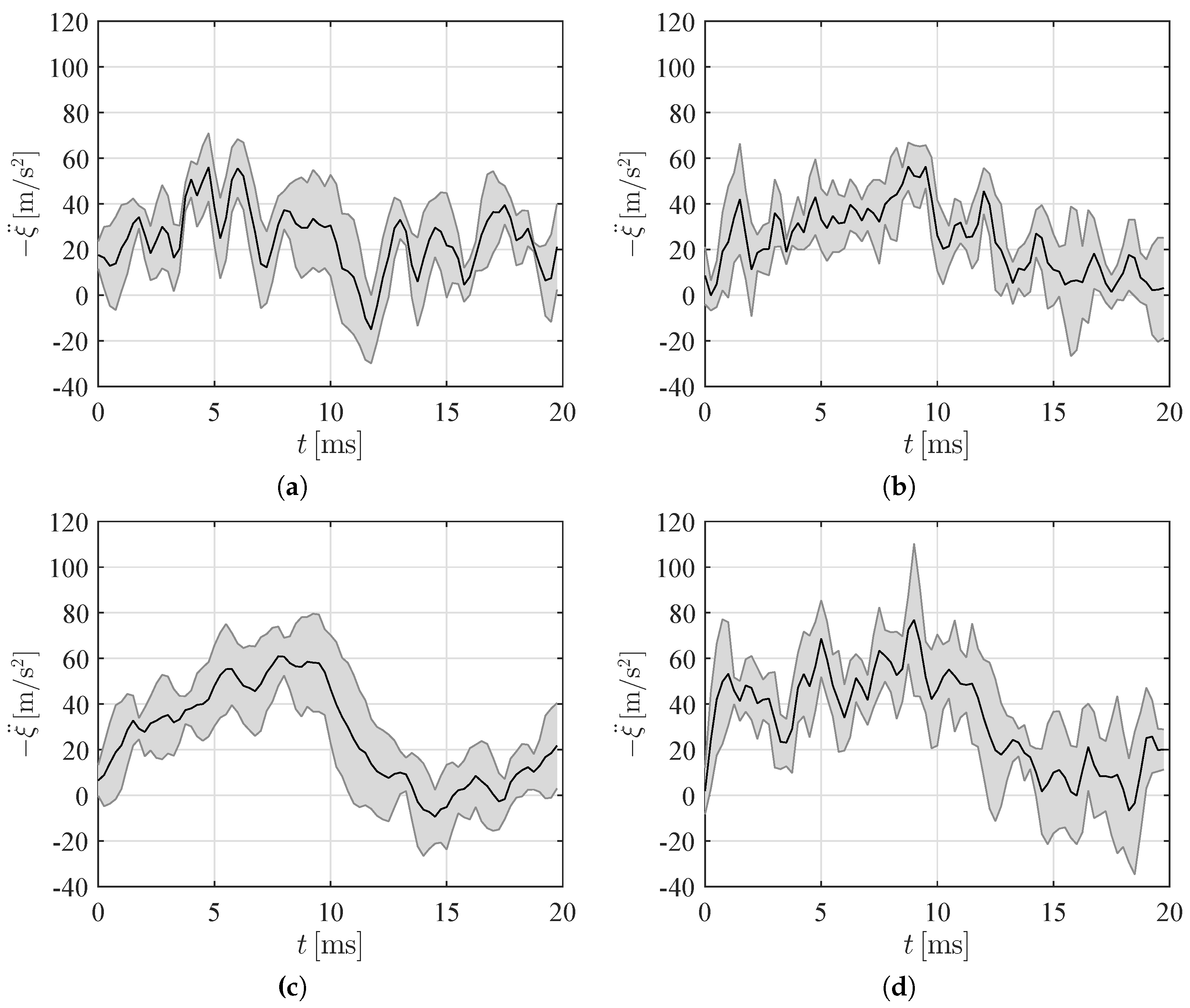
3.2. Analysis of the Wedge Motion
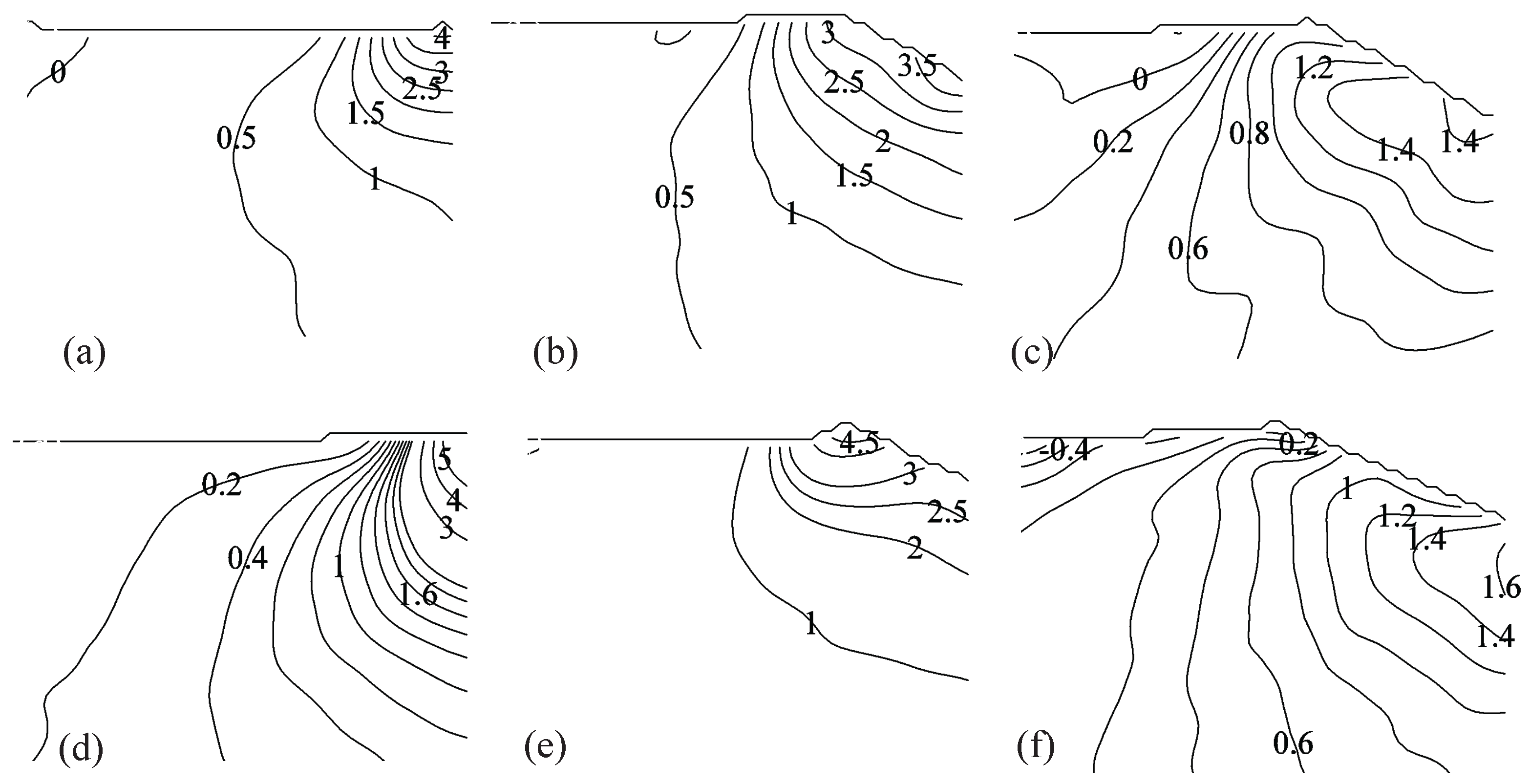
3.3. PIV-Based Reconstruction of the Pressure Field and Hydrodynamic Loading
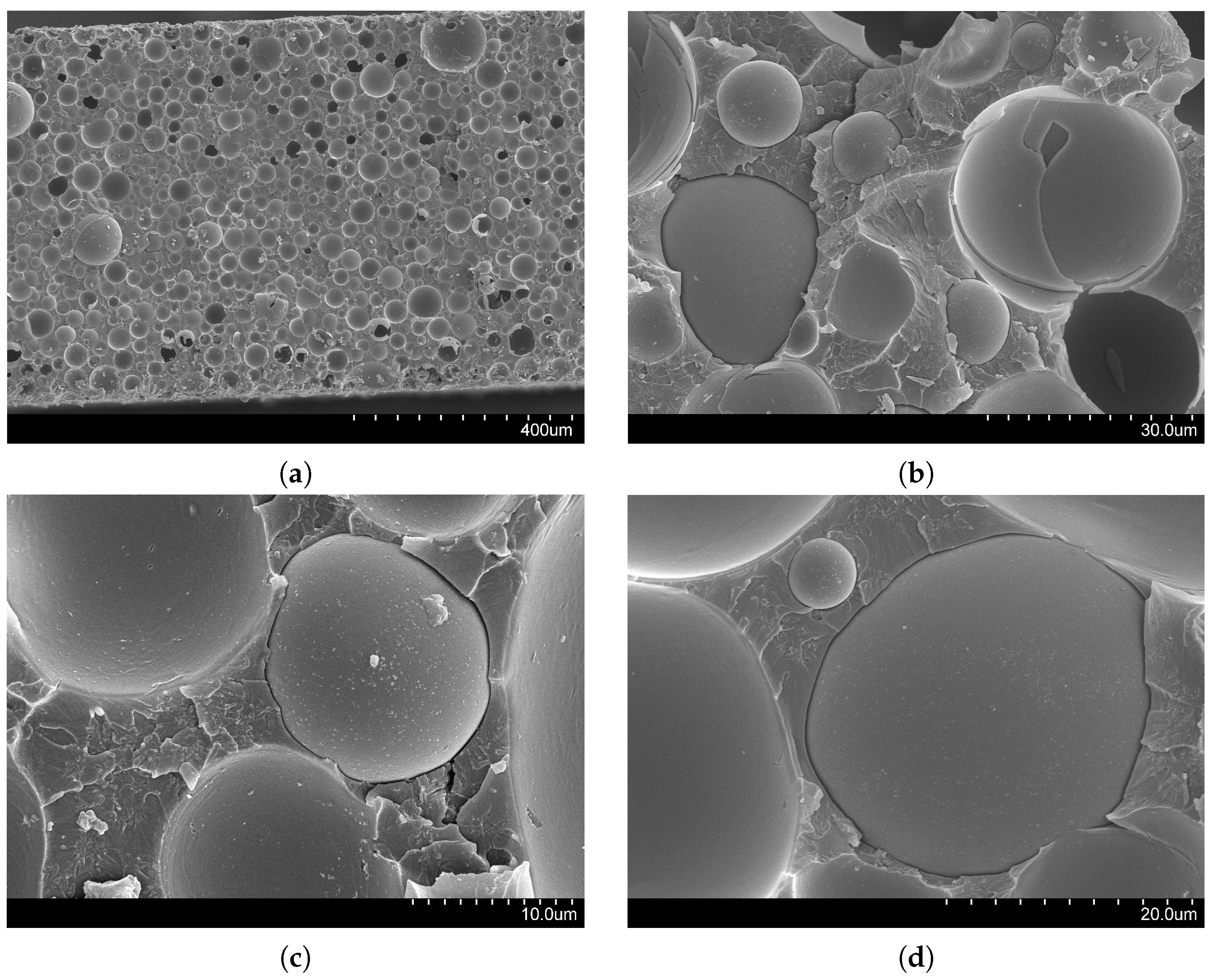
3.4. Fracture Features
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Narkis, M.; Kenig, S.; Puterman, M. Three-phase syntactic foams. Polym. Compos. 1984, 5, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladysz, G.M.; Perry, B.; Mceachen, G.; Lula, J. Three-phase syntactic foams: Structure-property relationships. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 4085–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouari, R.; Benhamida, A.; Dumontet, H. A micromechanical iterative approach for the behavior of polydispersed composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2008, 45, 3139–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardella, L.; Genna, F. On the elastic behavior of syntactic foams. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2001, 38, 7235–7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Ye, R.; Porfiri, M. Comparison of tensile and compressive characteristics of vinyl ester/glass microballoon syntactic foams. Compos. Part B Eng. 2010, 41, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvant-Moynot, V.; Gimenez, N.; Sautereau, H. Hydrolytic ageing of syntactic foams for thermal insulation in deep water: Degradation mechanisms and water uptake model. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 4047–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliavia, G.; Porfiri, M.; Gupta, N. Influence of moisture absorption on flexural properties of syntactic foams. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Pinisetty, D.; Shunmugasamy, V.C. Reinforced Polymer Matrix Syntactic Foams: Effect of Nano and Micro-Scale Reinforcement; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Zeltmann, S.E.; Shunmugasamy, V.C.; Pinisetty, D. Applications of polymer matrix syntactic foams. JOM 2014, 66, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shunmugasamy, V.C.; Anantharaman, H.; Pinisetty, D.; Gupta, N. Unnotched Izod impact characterization of glass hollow particle/vinyl ester syntactic foams. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 49, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zihlif, A.M.; Ragosta, G. Yielding and fracture toughness of glass microballoon-filled epoxy composites. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2001, 9, 345–350. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Oh, H.H. Manufacturing and impact behavior of syntactic foam. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 76, 1324–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Khamis, M.A. Fracture and impact behaviours of hollow micro-sphere/epoxy resin composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2001, 32, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Z. Tensile and impact properties of hollow glass bead-filled PVC composites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2002, 287, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouterso, E.M.; Boey, F.Y.C.; Hu, X.; Wong, S.C. Fracture and impact toughness of syntactic foam. J. Cell. Plast. 2004, 40, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Z. Impact fracture toughness of hollow glass bead-filled polypropylene composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Jones, N. Development of rubberized syntactic foam. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nji, J.; Li, G. A CaO enhanced rubberized syntactic foam. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; John, M. A crumb rubber modified syntactic foam. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 474, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldesenbet, E. Low velocity impact properties of nanoparticulate syntactic foams. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 496, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Z.; Wu, C.B. Gray relational analysis between size distribution and impact strength of polypropylene/hollow glass bead composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2009, 28, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.A.M.; Capela, C.; Costa, J.D. A study of the mechanical behaviour on fibre reinforced hollow microspheres hybrid composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusriah, L.; Mariatti, M. Effect of hybrid phenolic hollow microsphere and silica-filled vinyl ester composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2013, 47, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, L.F.; Abu, A.B. Fracture toughness and impact strength of hollow epoxy particles-toughened polyester composite. Sains Malays. 2013, 42, 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Abrate, S. Hull slamming. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2013, 64, 060803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.; Vignjevic, R.; Campbell, J.; De Vuyst, T.; Djordjevic, N.; Papagiannis, L. From aerospace to offshore: Bridging the numerical simulation gaps–Simulation advancements for fluid structure interaction problems. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2013, 61, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faltinsen, O.M. Sea Loads on Ships and Offshore Structures; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Faltinsen, O.M. The effect of hydroelasticity on ship slamming. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1997, 355, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charca, S.; Shafiq, B.; Just, F. Repeated slamming of sandwich composite panels on water. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 2009, 11, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charca, S.; Shafiq, B. Damage assessment due to single slamming of foam core sandwich composites. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 2010, 12, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battley, M.; Allen, T. Servo-hydraulic system for controlled velocity water impact of marine sandwich panels. Exp. Mech. 2012, 52, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panciroli, R.; Abrate, S.; Minak, G.; Zucchelli, A. Hydroelasticity in water-entry problems: Comparison between experimental and SPH results. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenius, I.; Rosén, A.; Battley, M.; Allen, T. Experimental hydroelastic characterization of slamming loaded marine panels. Ocean Eng. 2013, 74, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, R.J. Particle-imaging techniques for experimental fluid mechanics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1991, 23, 261–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panciroli, R.; Porfiri, M. Evaluation of the pressure field on a rigid body entering a quiescent fluid through particle image velocimetry. Exp. Fluids 2013, 54, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nila, A.; Vanlanduit, S.; Vepa, S.; Van Paepegem, W. A PIV-based method for estimating slamming loads during water entry of rigid bodies. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2013, 24, 045303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panciroli, R.; Porfiri, M. Analysis of hydroelastic slamming through particle image velocimetry. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 347, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panciroli, R.; Porfiri, M. Hydroelastic impact of piezoelectric structures. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2014, 66, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3M Home Page. Available online: http://multimedia.3m.com/mws/media/130063O/3mtm-glass-bubbles-selection-guide.pdf (accessed on 22 January 2017).
- Woldesenbet, E.; Gupta, N.; Jadhav, A. Effects of density and strain rate on properties of syntactic foams. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 4009–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalisendi, M.; Shams, A.; Panciroli, R.; Porfiri, M. Experimental reconstruction of three-dimensional hydrodynamic loading in water entry problems through particle image velocimetry. Exp. Fluids 2015, 56, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalisendi, M.; Osma, S.J.; Porfiri, M. Three-dimensional water entry of a solid body: A particle image velocimetry study. J. Fluids Struct. 2015, 59, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facci, A.L.; Porfiri, M.; Ubertini, S. Three-dimensional water entry of a solid body: A computational study. J. Fluids Struct. 2016, 66, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, A.; Porfiri, M. Treatment of hydroelastic impact of flexible wedges. J. Fluids Struct. 2015, 17, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliavia, G.; Porfiri, M.; Gupta, N. Analysis of flexural properties of hollow-particle filled composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2010, 41, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielicke, W.; Stamhuis, E. PIVlab—Towards user-friendly, affordable and accurate digital particle image velocimetry in MATLAB. J. Open Res. Softw. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panton, R.L. Incompressible Flow; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Facci, A.L.; Panciroli, R.; Ubertini, S.; Porfiri, M. Assessment of PIV-based analysis of water entry problems through synthetic numerical datasets. J. Fluids Struct. 2015, 55, 484–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, A.; Jalalisendi, M.; Porfiri, M. Experiments on the water entry of asymmetric wedges using particle image velocimetry. Phys. Fluids 2015, 27, 027103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, A. Failure Mechanics of Syntactic Foams with Applications to Marine Environments. Ph.D. Thesis, New York University Tandon School of Engineering, New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khabakhpasheva, T.I.; Korobkin, A.A. Elastic wedge impact onto a liquid surface: Wagner’s solution and approximate models. J. Fluids Struct. 2013, 36, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panciroli, R.; Biscarini, C.; Falcucci, G.; Jannelli, E.; Ubertini, S. Live monitoring of the distributed strain field in impulsive events through fiber Bragg gratings. J. Fluids Struct. 2016, 61, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Batra, R.C. Local slamming impact of sandwich composite hulls. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2009, 46, 2011–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Condition | Syntactic Foam | H (cm) | (m/s) | (mm) | (mm) | (ms) | (m/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light-Short | VE220-60 | 20 | 0.024 | |||||
| Heavy-Short | VE460-60 | 20 | 0.029 | |||||
| Light-High | VE220-60 | 40 | 0.016 | |||||
| Heavy-High | VE460-60 | 40 | 0.021 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shams, A.; Zhao, S.; Porfiri, M. Water Impact of Syntactic Foams. Materials 2017, 10, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10030224
Shams A, Zhao S, Porfiri M. Water Impact of Syntactic Foams. Materials. 2017; 10(3):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10030224
Chicago/Turabian StyleShams, Adel, Sam Zhao, and Maurizio Porfiri. 2017. "Water Impact of Syntactic Foams" Materials 10, no. 3: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10030224
APA StyleShams, A., Zhao, S., & Porfiri, M. (2017). Water Impact of Syntactic Foams. Materials, 10(3), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10030224






