Mesoscale Characterization of Fracture Properties of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete Using a Lattice–Particle Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Lattice–Particle Model for Fiber-Reinforced Concrete
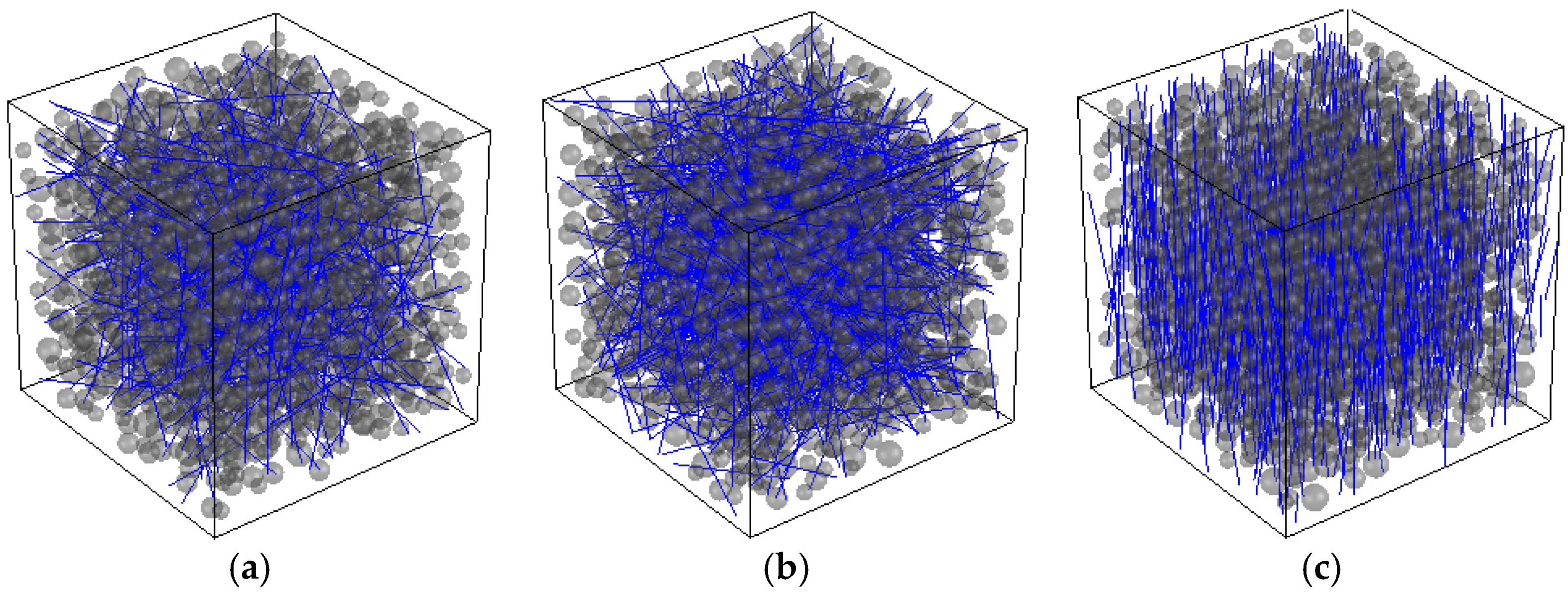
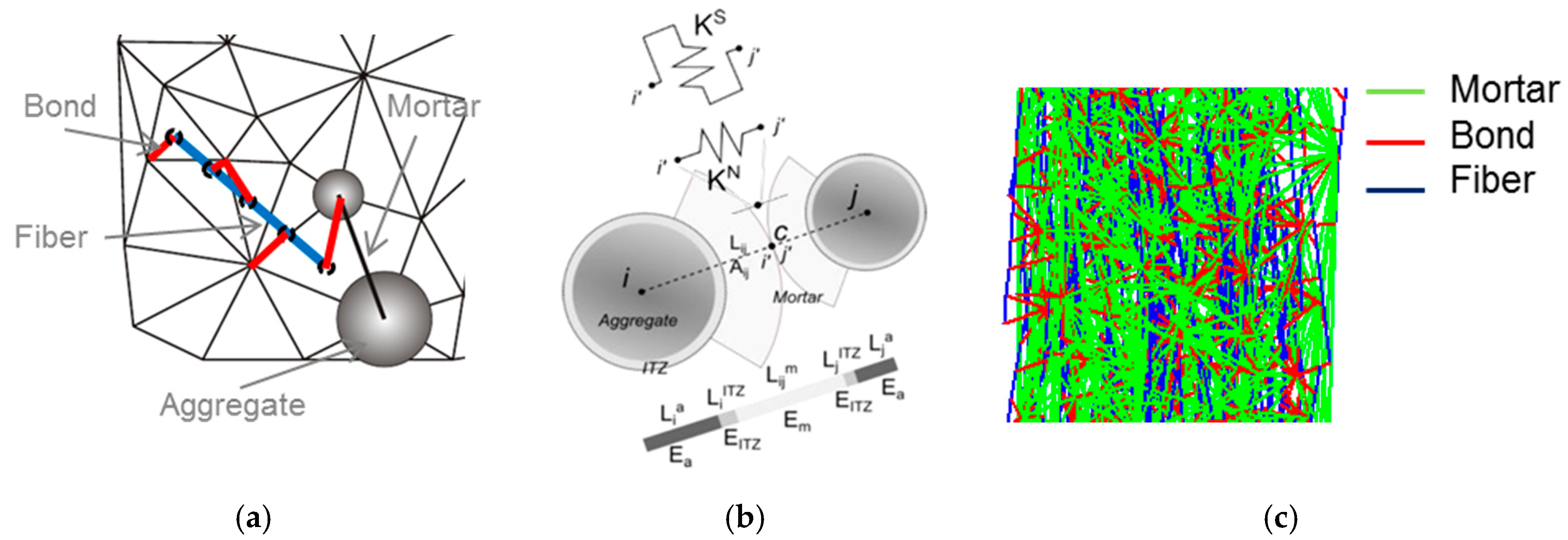
2.1. Mesostructure Generation
2.2. Mesomechanical Elastic Behavior
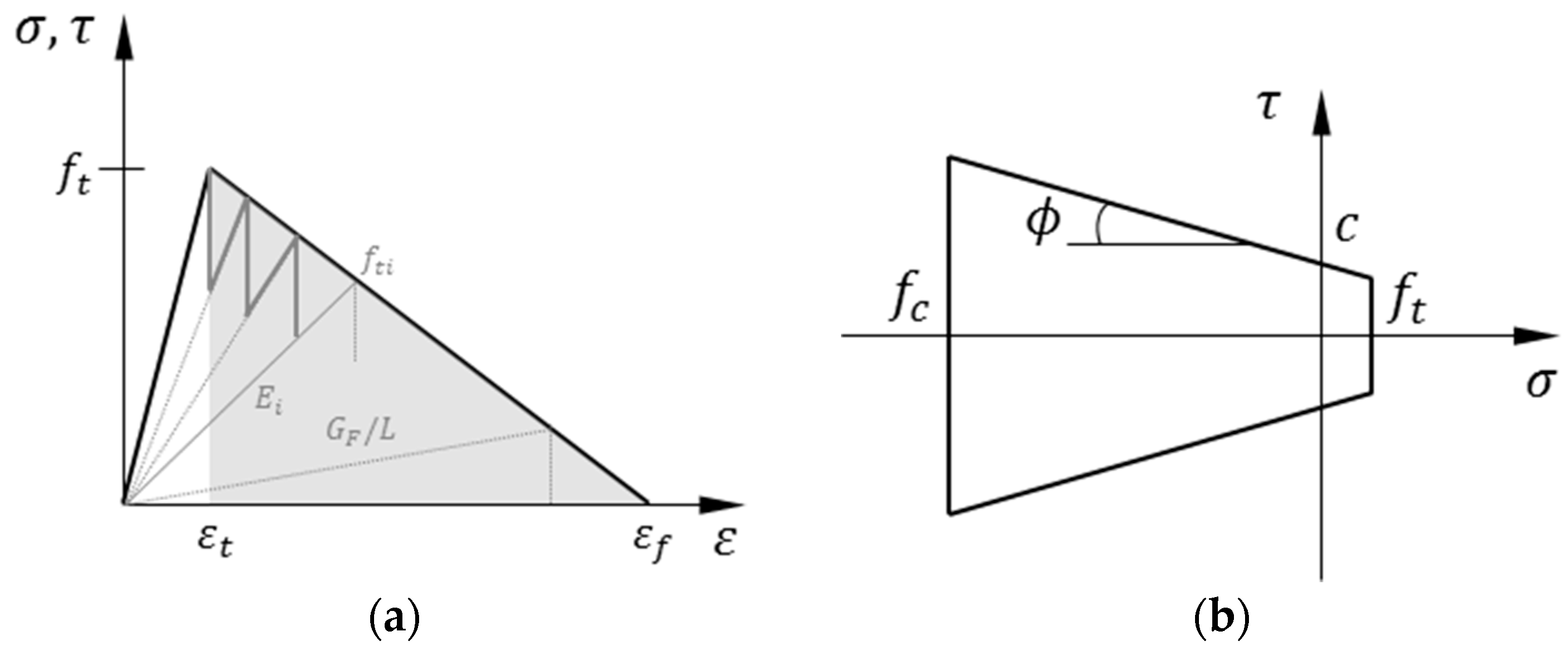
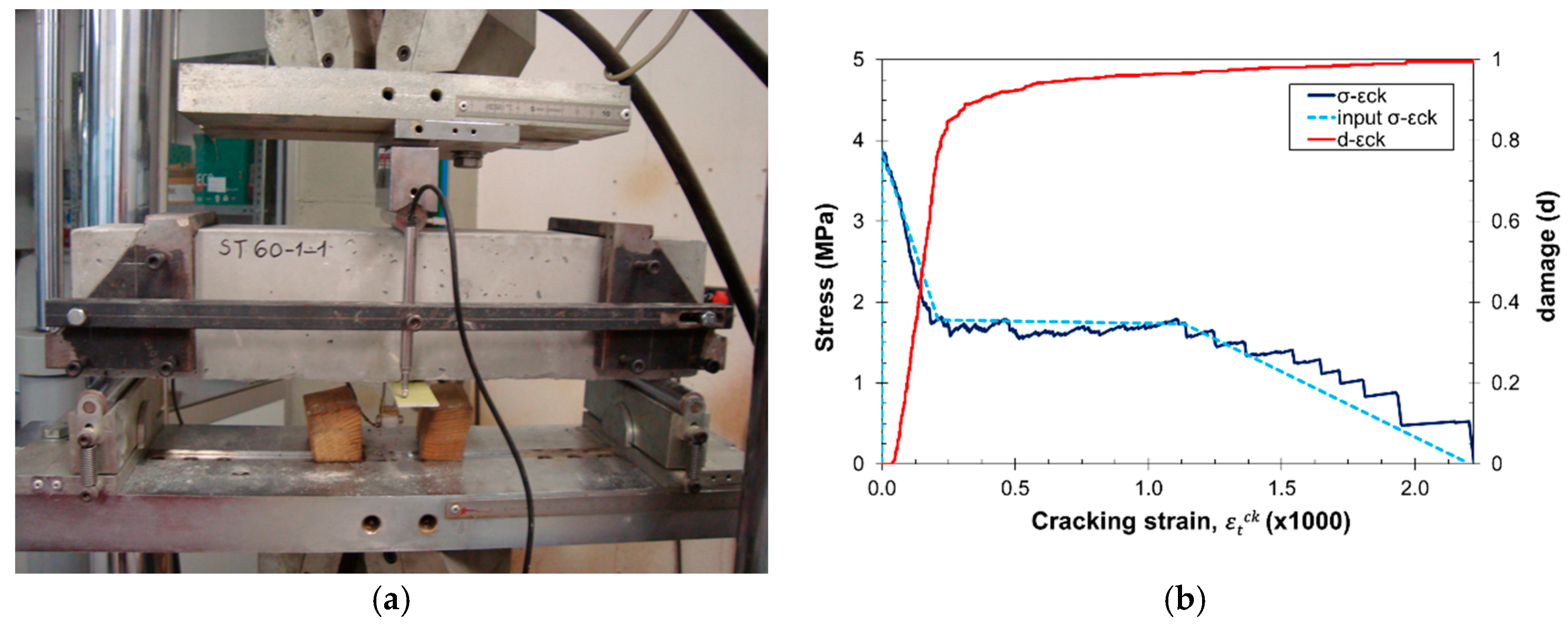
2.3. Mesoscale Fracture Behavior
2.4. Meso-Macro Upscaling Strategy
3. Results and Discussion
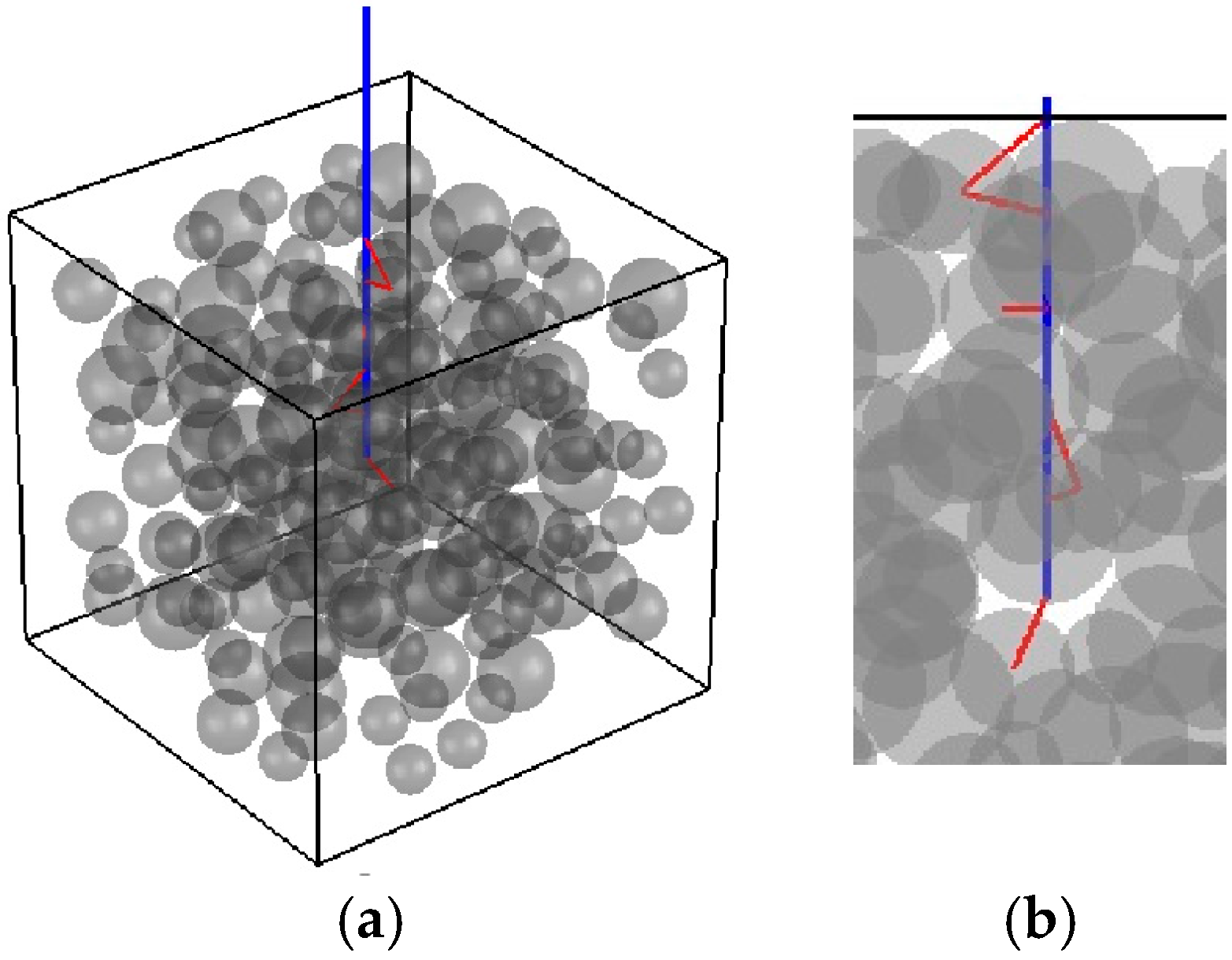
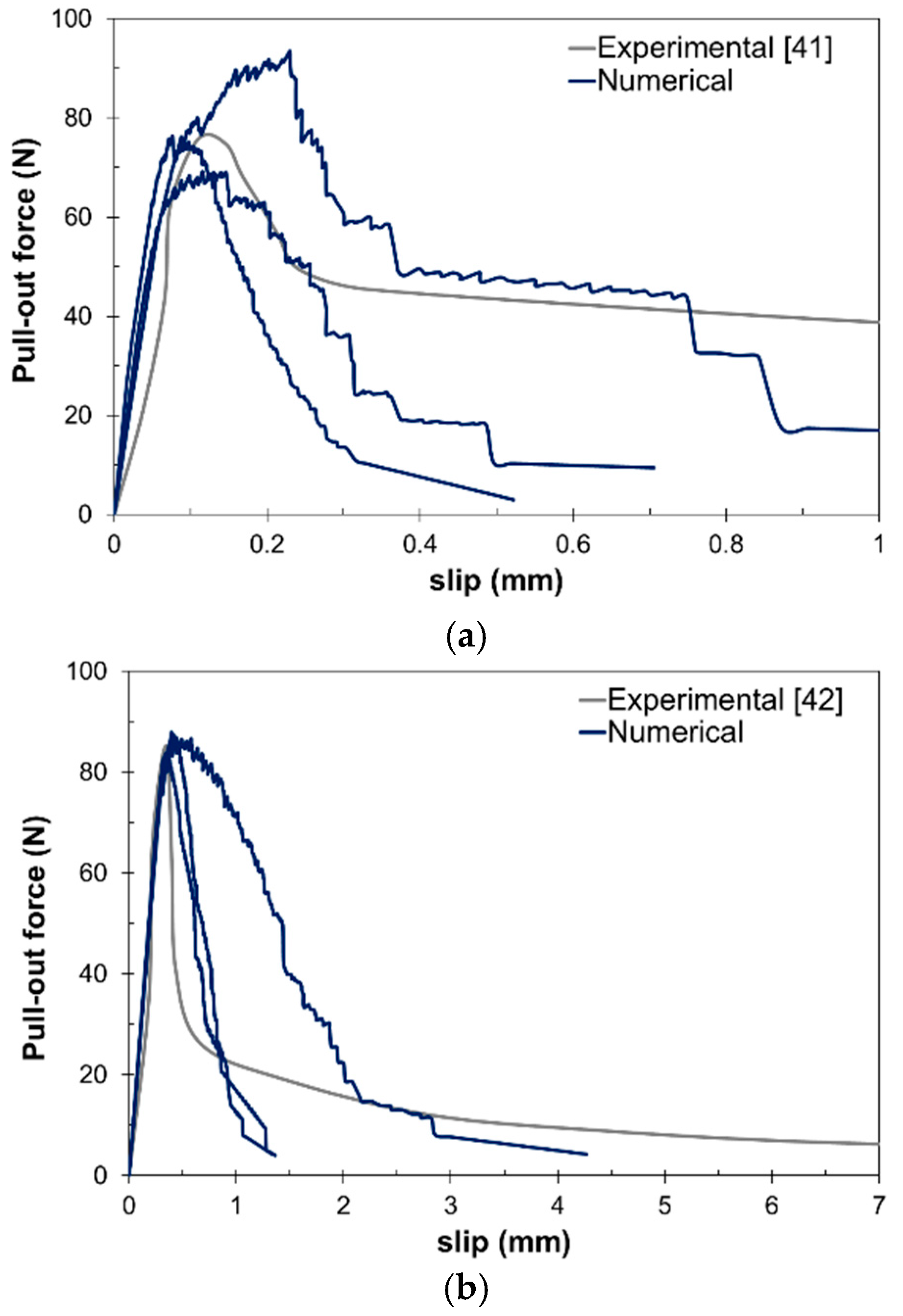
3.1. Pullout Test
3.2. Tensile Tests
3.2.1. Elastic Modulus
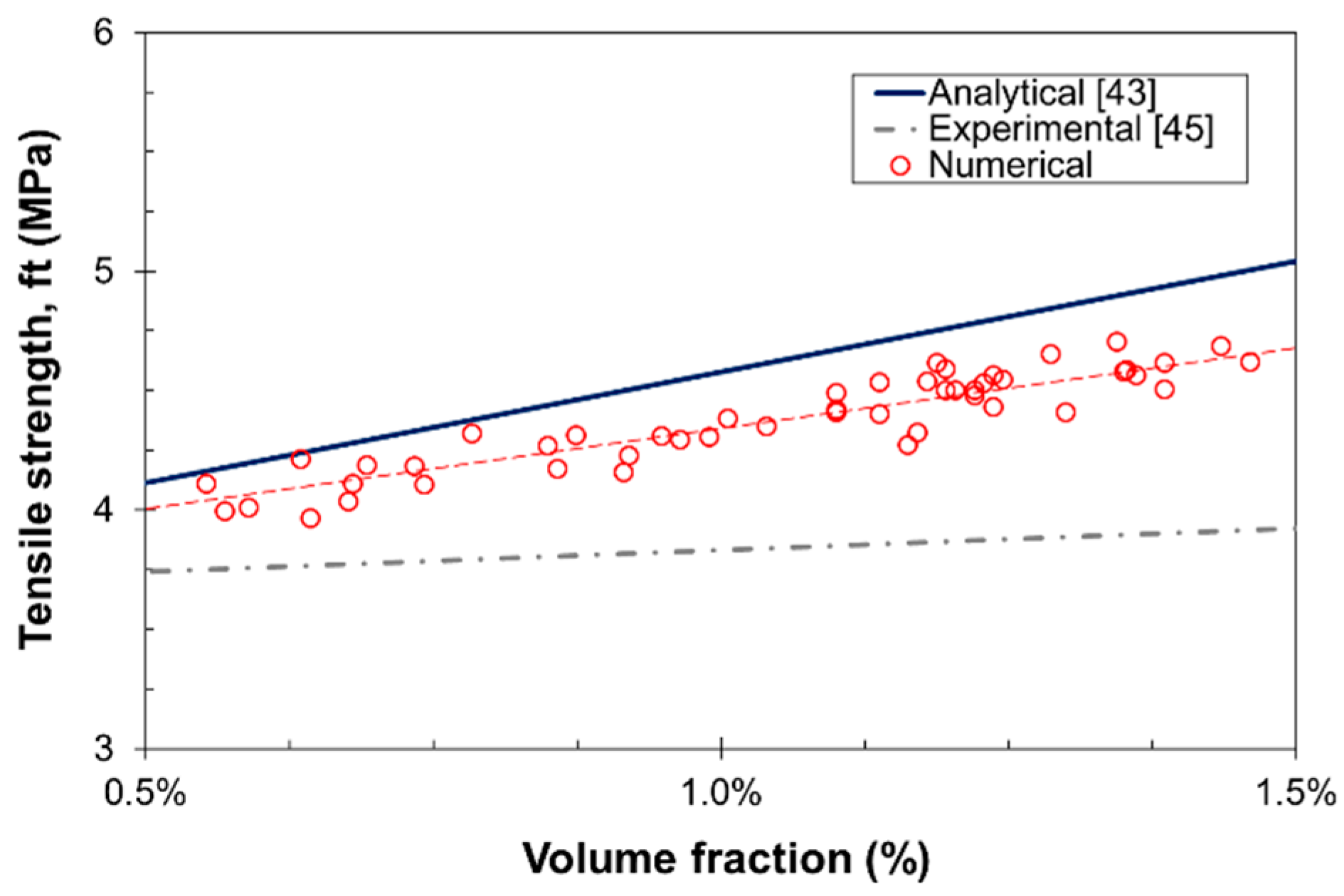
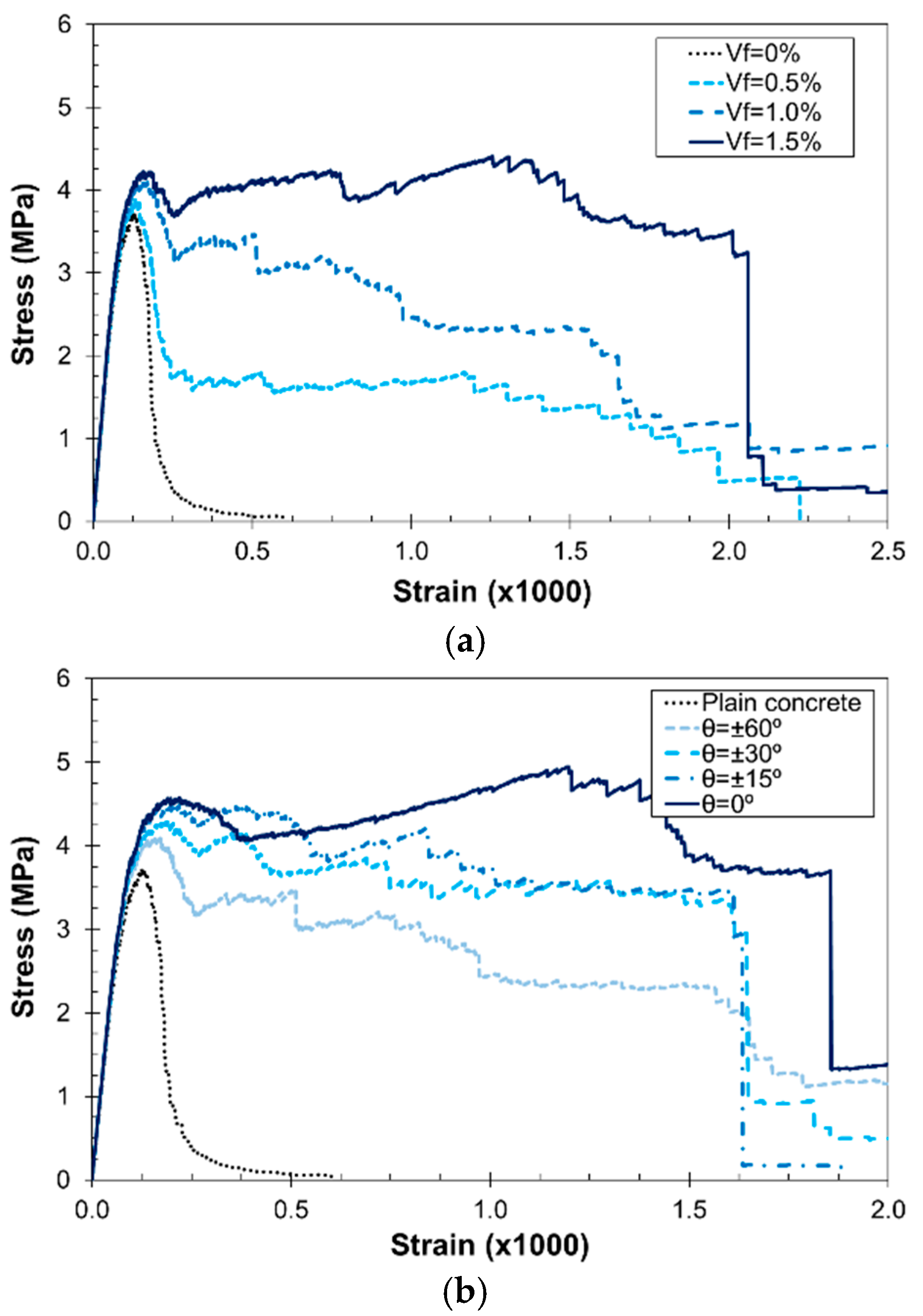
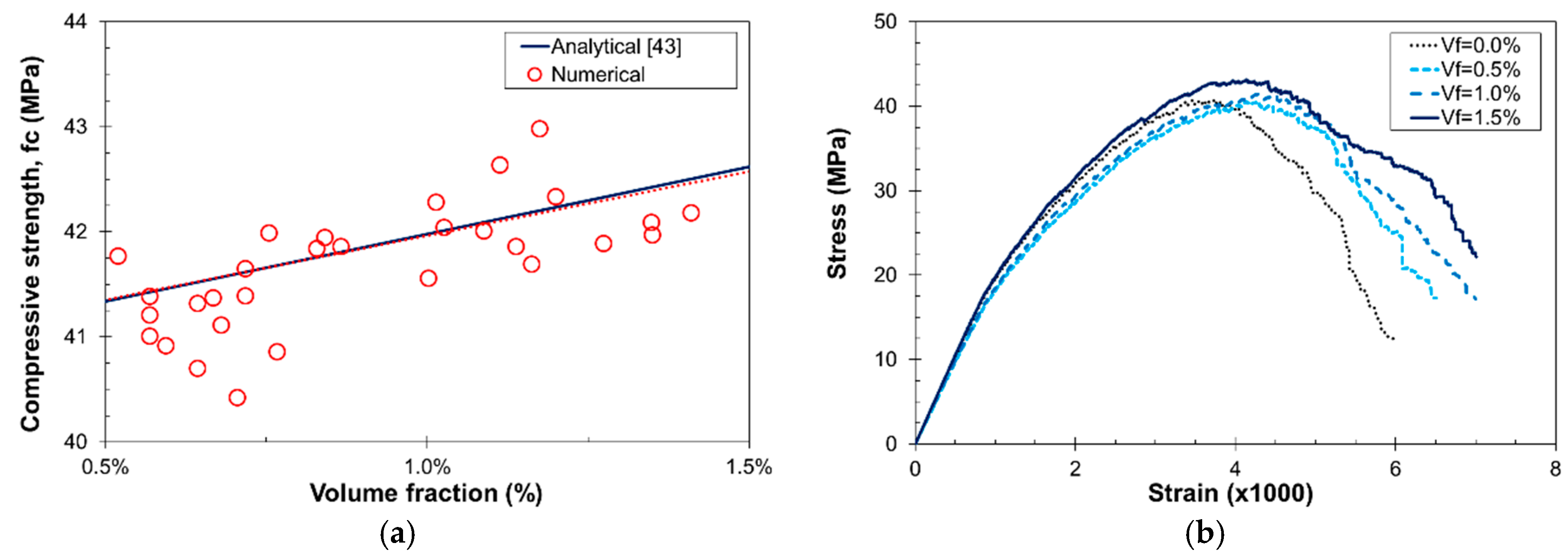
3.2.2. Tensile Strength
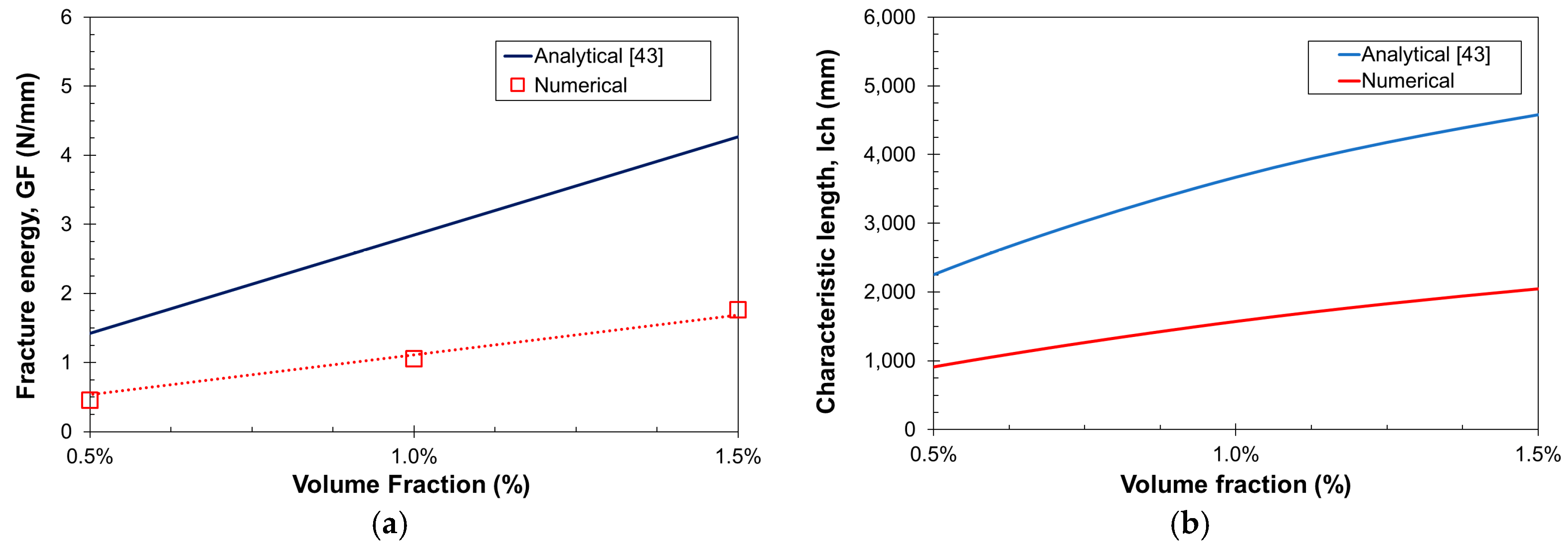
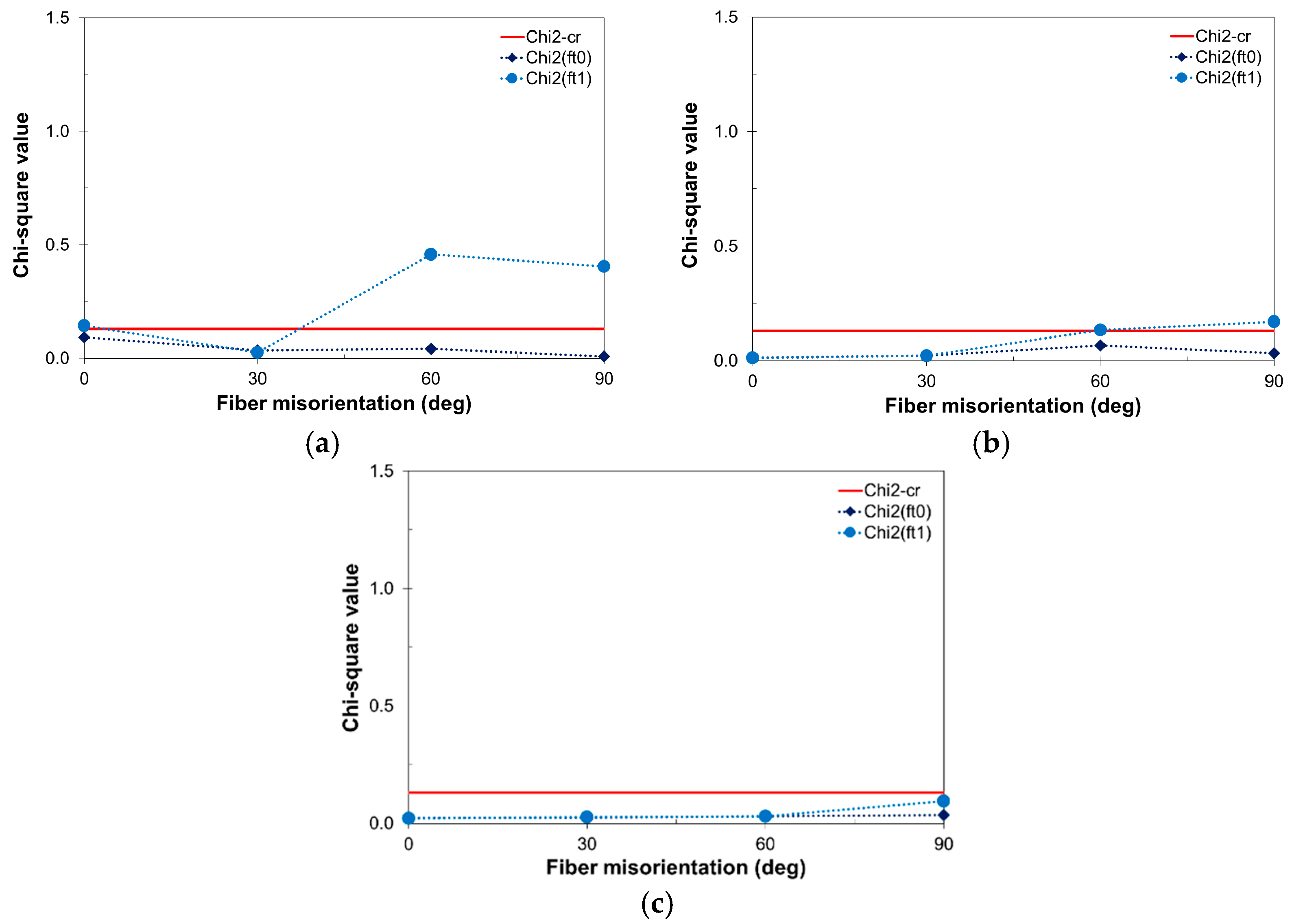
3.2.3. Fracture Energy and Characteristic Length
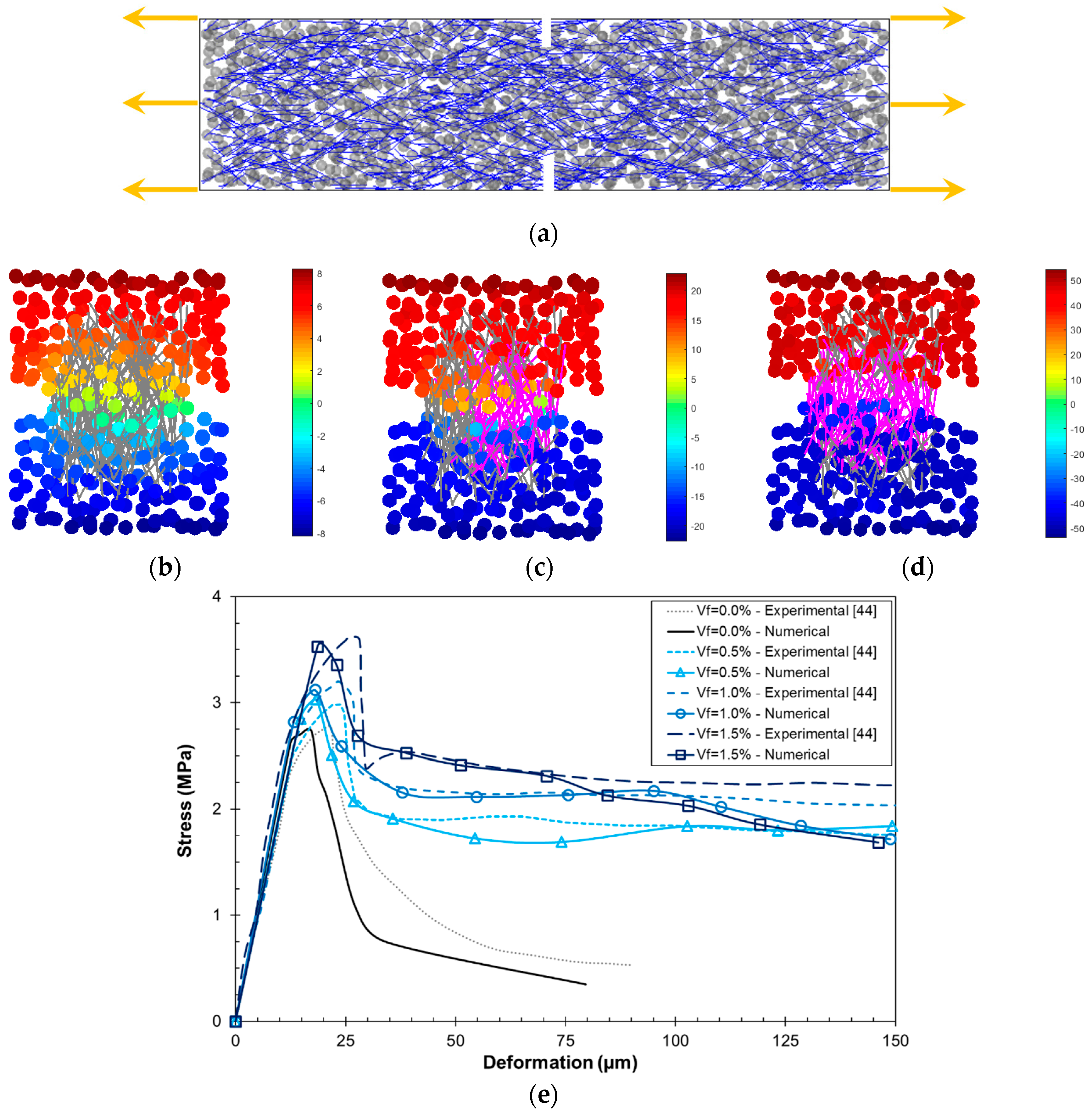
3.3. Compression Tests
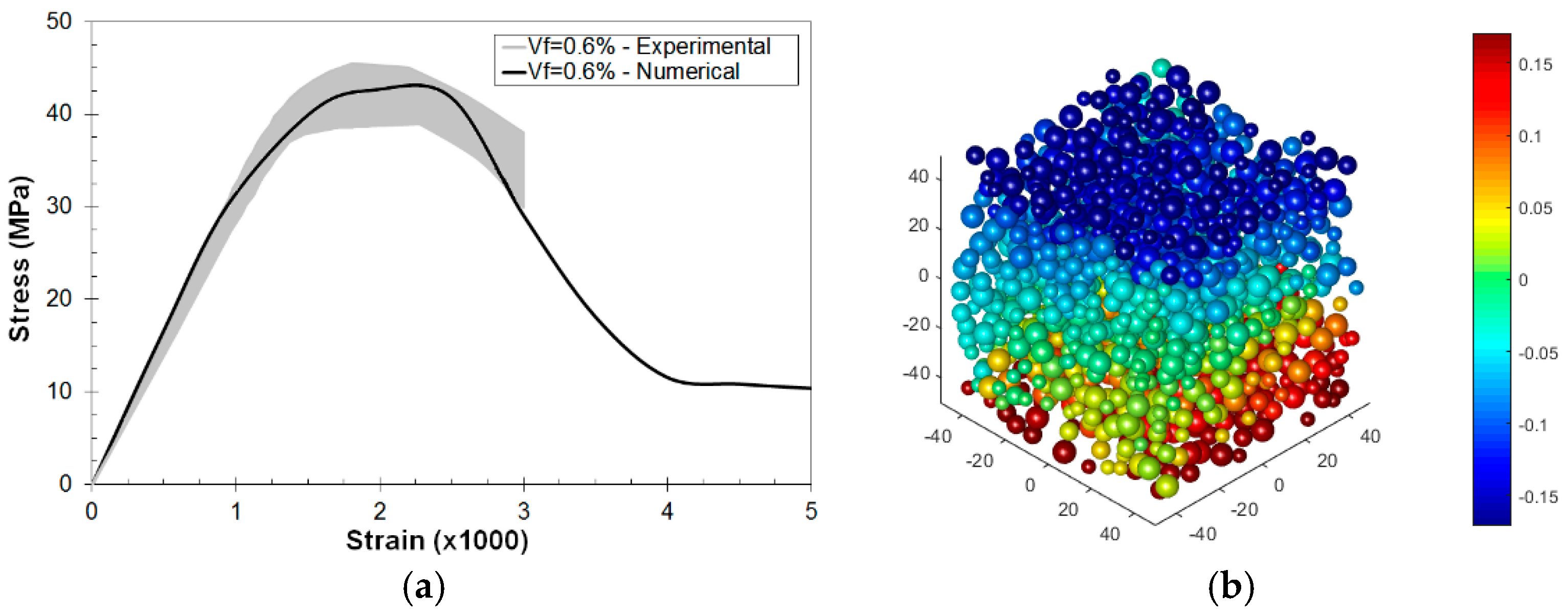
3.4. Macroscale Three-Point Bending Tests
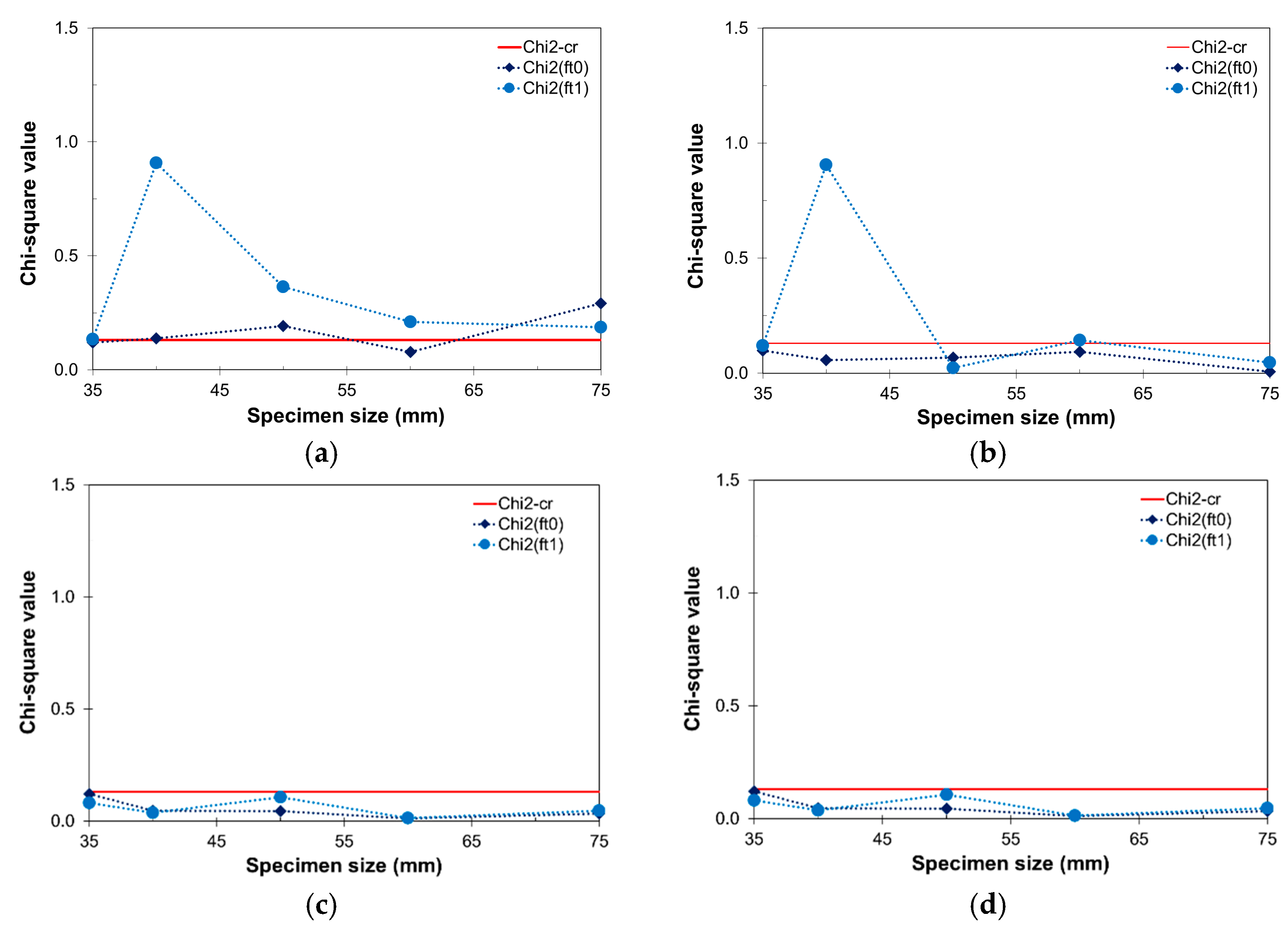
3.4.1. RVE Size Analysis
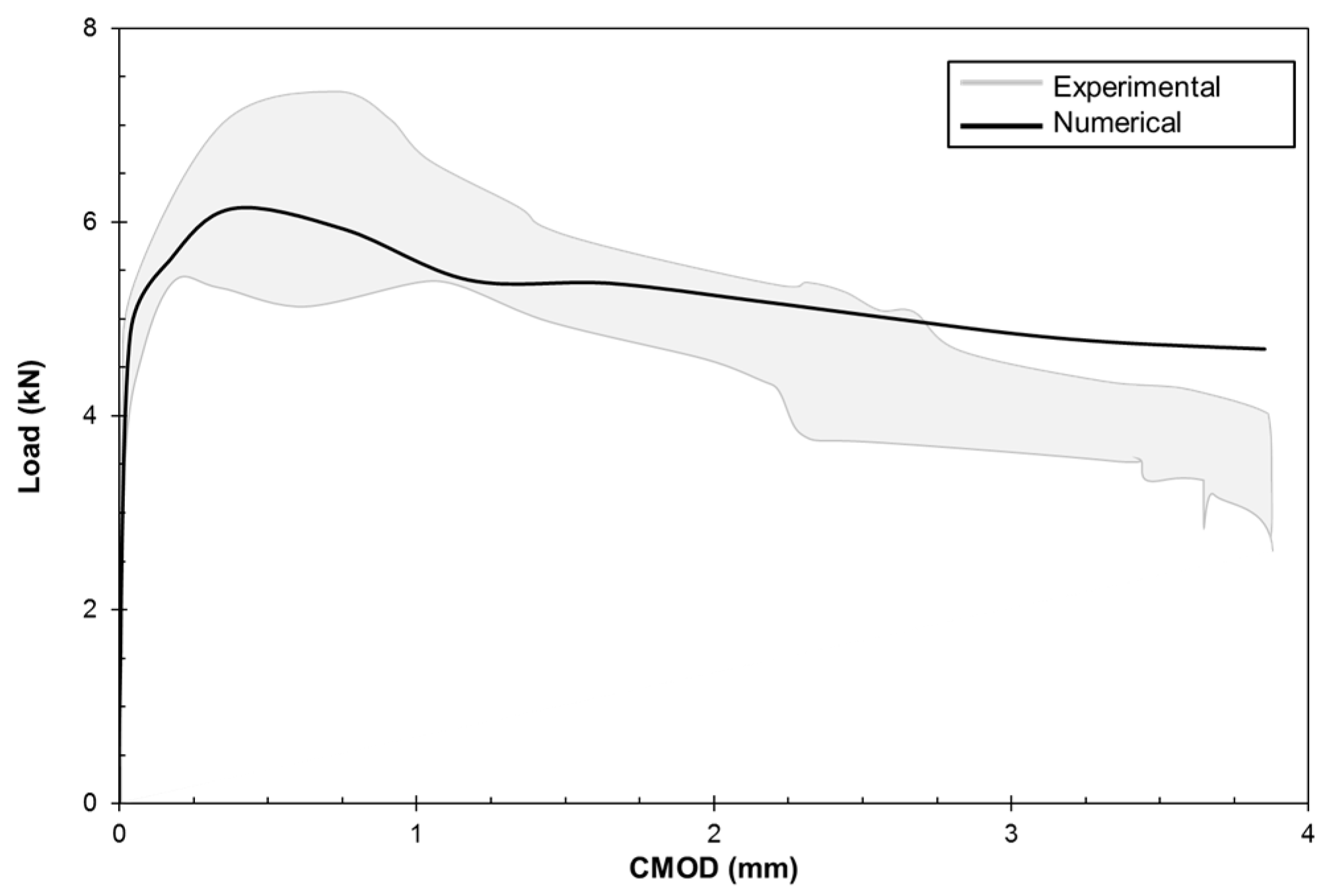
3.4.2. Experimental Validation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kosmatka, S.; Panarese, W.; Kerkhoff, B. Design and Control of Concrete Mixtures; Portland Cement Association: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor, J.; Wight, J.; Teng, S.; Irawan, P. Reinforced Concrete: Mechanics and Design; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bentur, A.; Mindess, S. Fibre Reinforced Cementitious Composites; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Konsta-Gdoutos, M.; Metaxa, Z.; Shah, S. Highly dispersed carbon nanotube reinforced cement based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, C.; Liu, F.; Wan, C.; Pu, X. Preparation of ultra-high performance concrete with common technology and materials. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2012, 34, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstemeyer, M. Integrated Computational Materials Engineering (ICME) for Metals: Using Multiscale Modeling to Invigorate Engineering Design with Science; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, J.A.; Figueiras, J.A. Model for the analysis of steel fibre reinforced concrete slabs on grade. Comput. Struct. 2001, 79, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, D.M.; Bayraktar, A.; Sahin, A.; Haktanir, T.; Türker, T. Experimental and finite element analysis on the steel fiber-reinforced concrete (SFRC) beams ultimate behavior. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1064–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, V.M.C.F.; Barros, J.A.O.; Sena-Cruz, J.M. A finite element model with discrete embedded elements for fibre reinforced composites. Comput. Struct. 2012, 94–95, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Paulino, G.H.; Roesler, J. Cohesive fracture model for functionally graded fiber reinforced concrete. Cem. Conc. Res. 2010, 40, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.C.; Cifuentes, H.; Rivero, I.; Ruiz, G.; Zhang, X. Dynamic behaviour in fibre-reinforced cementitious composites. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2016, 93, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke, F.K.F.; Simone, A.; Sluys, L.J. A partition of unity finite element method for simulating non-linear debonding and matrix failure in thin fibre composites. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2011, 86, 453–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.; Mora, D.F.; Huespe, A.E.; Weyler, R. A micromorphic model for steel fiber reinforced concrete. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2012, 49, 2990–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero-Chacón, F.; Schlangen, E.; Cifuentes, H.; Medina, F. A numerical approach for the design of multiscale fibre-reinforced cementitious composites. Phil. Mag. 2015, 95, 3305–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundall, P.A. A computer model for simulating progressive large scale movements in blocky rock systems. Proc. Int. Symp. Rock Fract. 1971, 1, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kawai, T. New discrete models and their application to seismic response analysis of structures. Nucl. Eng. Des. 1978, 48, 207–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolander, J.E.; Saito, S. Fracture analysis using spring network with random geometry. Eng. Fract. Mech. 1998, 113, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar]
- Zubelewicz, A.; Bažant, Z.P. Interface element modeling of fracture in aggregate composites. J. Eng. Mech.-ASCE 1987, 113, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bažant, Z.P.; Tabbara, M.R.; Kazemi, M.T.; Pijaudier-Cabot, G. Random particle model for fracture of aggregate or fiber composites. J. Eng. Mech.-ASCE 1990, 116, 1686–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusatis, G.; Bažant, Z.P.; Cedolin, L. Confinement-shear lattice model for concrete damage in tension and compression: I. Theory. J. Eng. Mech.-ASCE 2003, 129, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlangen, E.; Garboczi, E.J. Fracture simulations of concrete using lattice models: Computational aspects. Eng. Fract. Mech. 1997, 57, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolander, J.E.; Saito, S. Discrete modeling of short-fibers reinforcement in cementitious composites. Adv. Cem. Mater. 1997, 6, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunieda, M.; Ogura, H.; Ueda, N.; Nakamura, H. Tensile fracture process of Strain Hardening Cementitious Composites by means of three-dimensional meso-scale analysis. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2011, 33, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Kim, K.; Lim, Y.M.; Bolander, J.E. Modeling of fiber-reinforced cement composites: Discrete representation of fiber pullout. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2014, 10, 1970–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozicki, J.; Tejchman, J. Effect of steel fibres on concrete behavior in 2D and 3D simulations using lattice model. Arch. Mech. 2010, 62, 465–492. [Google Scholar]
- Montero, F.; Schlangen, E. Modelling of fracture in fibre-cement based materials. Brittle Matrix Compos. 2012, 10, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Schauffert, E.; Cusatis, G. Lattice discrete particle model for fiber-reinforced concrete. I: Theory. J. Eng. Mech.-ASCE 2011, 138, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Chacón, F.; Schlangen, E.; Medina, F. A lattice-particle approach for the simulation of fracture processes in fiber-reinforced high-performance concrete. In Proceedings of the VIII International Conference on Fracture Mechanics of Concrete and Concrete Structures, Toledo, Spain, 10–14 March 2013.
- Montero-Chacón, F.; Medina, F. A lattice-particle approach to determine the RVE size for quasi-brittle materials. Eng. Comp. 2013, 30, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitman, I.M.; Askes, H.; Sluys, L.J. Representative volume: Existence and size determination. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2007, 74, 2518–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.P.; Lloberas-Valls, O.; Stroeven, M.; Sluys, L.J. On the existence of representative volumes for softening quasi-brittle materials—A failure zone averaging scheme. Comp. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2010, 199, 3028–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Mier, J.G.M. Fracture Processes of Concrete, 1st ed.; CRC Press, Inc.: Boca Ratón, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wriggers, P.; Moftah, S.O. Mesoscale models for concrete: Homogenisation and damage behavior. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2006, 42, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeb, R.; Kulasegaram, S.; Karihaloo, B.L. 3D modelling of the flow of self-compacting concrete with or without steel fibres. Part I: Slump flow test. Comp. Part. Mech. 2014, 1, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebrab, T.T.; Soroushian, P. Mechanical properties of cement mortar: Development of structure-property relationships. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2011, 5, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.T.C.; Slate, F.O.; Sturman, G.M.; Winter, G. Microcracking of plain concrete and the shape of the stress-strain curve. J. ACI 1963, 60, 209–224. [Google Scholar]
- Rots, J.G.; Invernizzi, S. Regularized sequentially linear saw-tooth softening model. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2004, 28, 821–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-M.; Abu Al-Rub, R.K. Meso-scale computational modeling of the plastic-damage response of cementitious composites. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellart, W.P. Shear test results for cohesion and friction coefficients for different granular materials: Scaling implications for their usage in analogue modeling. Tectonophysics 2000, 324, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.P.; Stroeven, M.; Sluys, L.J. Multiscale continuous and discontinuous modeling of heterogeneous materials: A review on recent developments. J. Multiscale Mod. 2011, 3, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, V.; Barros, J.; Sena-Cruz, J. Pullout behavior of steel fibers in self-compacting concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2010, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Kang, S.; Lee, J. Influence of sand to coarse aggregate ratio on the interfacial bond strength of steel fibers in concrete for nuclear power plant. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2012, 252, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karihaloo, B.L.; Lange-Kornbak, D. Optimization techniques for the design of high-performance fibre-reinforced concrete. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2001, 21, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalaratnam, V.; Shah, S.P. Tensile failure of steel-fiber reinforced mortar. J. Eng. Mech.-ASCE 1987, 113, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.D.; Coleman, R.A. Strength and deformation of steel fiber reinforced mortar in uniaxial tension. In Fiber Reinforced Concrete; ACI SP-44; American Concrete Institute: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 1974; pp. 177–193. [Google Scholar]
- Comité Euro-International du Béton. CEB-FIP Model Code 1990, Bulletin D’Information; No. 213/214; Thomas Telford Services Ltd.: Lausanne, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Laranjeira, F.; Grünewald, S.; Walraven, J.; Blom, C.; Molins, C.; Aguado, A. Characterization of the orientation profile of steel fiber reinforced concrete. Mater. Struct. 2011, 44, 1093–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SIMULIA Corp. Abaqus Theory Manual, version 6.8; Dassault Systémes: Providence, RI, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]

| Phase | Input Properties |
|---|---|
| Matrix | Elastic: Em, Ea |
| Fracture: ft, fc, c, ϕ, GF | |
| Mix information: w/c, a/c, dmax | |
| Fiber | Elastic: Ef |
| Fracture: σ1, σ2, εf/εi | |
| Bond | Elastic: Eb |
| Fracture: τ1, τ2, εf/εi |
| Property | Values |
|---|---|
| Eb (GPa) | 1–10 |
| τ1 (MPa) | 1–10 |
| τ2 (MPa) | <2 |
| εf/εi | 5–15 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montero-Chacón, F.; Cifuentes, H.; Medina, F. Mesoscale Characterization of Fracture Properties of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete Using a Lattice–Particle Model. Materials 2017, 10, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10020207
Montero-Chacón F, Cifuentes H, Medina F. Mesoscale Characterization of Fracture Properties of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete Using a Lattice–Particle Model. Materials. 2017; 10(2):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10020207
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontero-Chacón, Francisco, Héctor Cifuentes, and Fernando Medina. 2017. "Mesoscale Characterization of Fracture Properties of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete Using a Lattice–Particle Model" Materials 10, no. 2: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10020207
APA StyleMontero-Chacón, F., Cifuentes, H., & Medina, F. (2017). Mesoscale Characterization of Fracture Properties of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete Using a Lattice–Particle Model. Materials, 10(2), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10020207






