Study on the Anti-Poison Performance of Al–Y–P Master Alloy for Impurity Ca in Aluminum Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
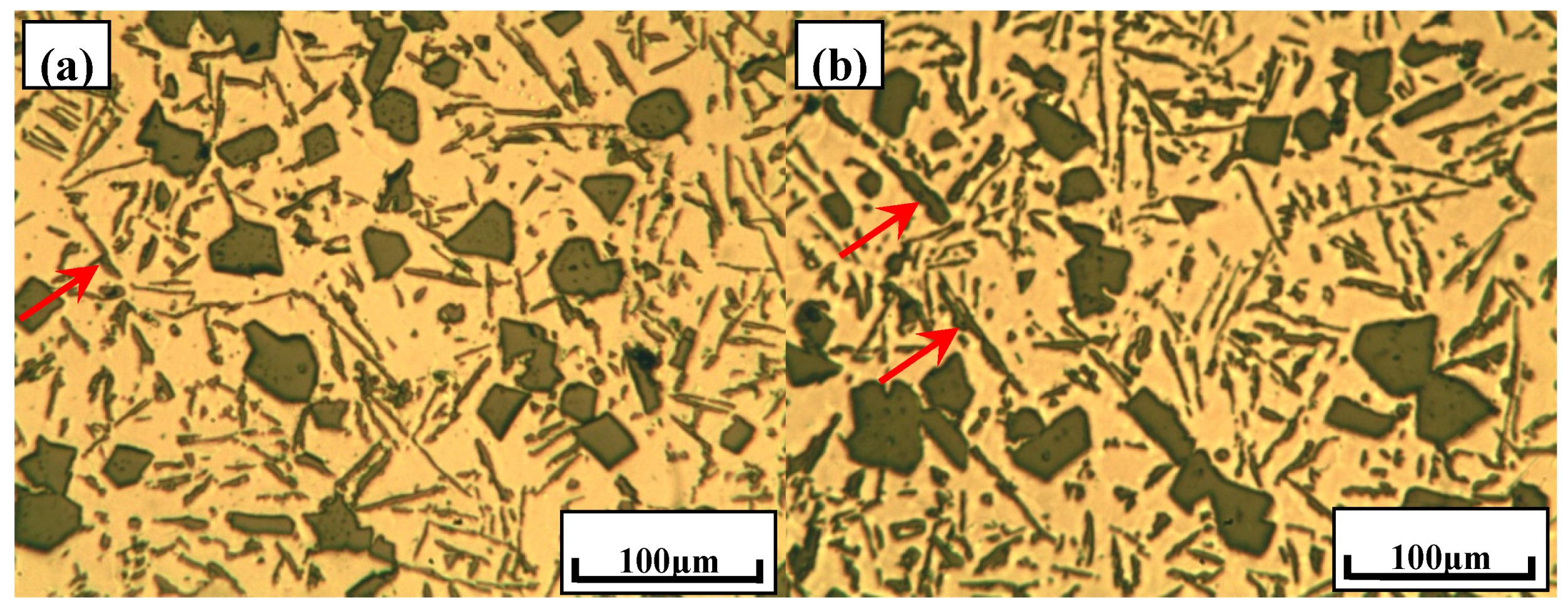
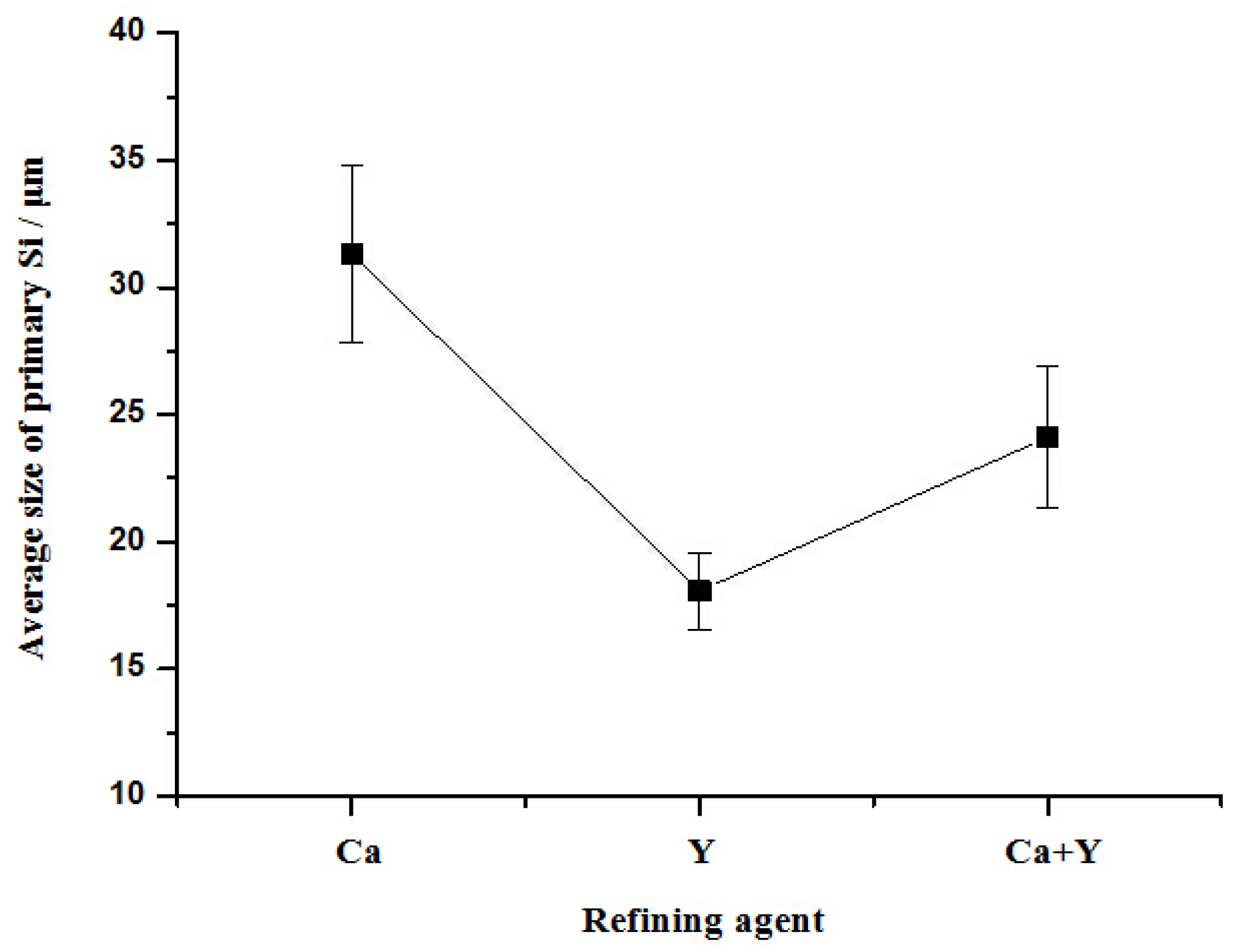
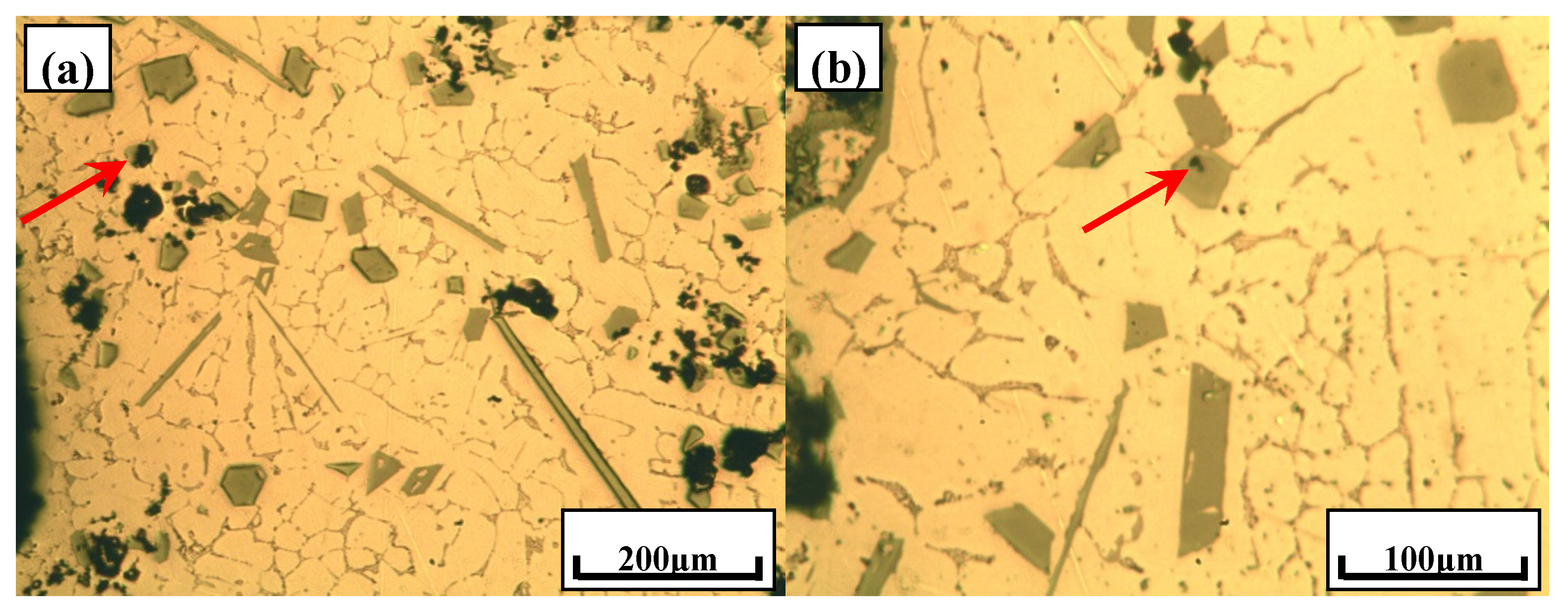
3.1. Typical Microstructures of Al–18Si Alloys with the Addition of Ca and/or P
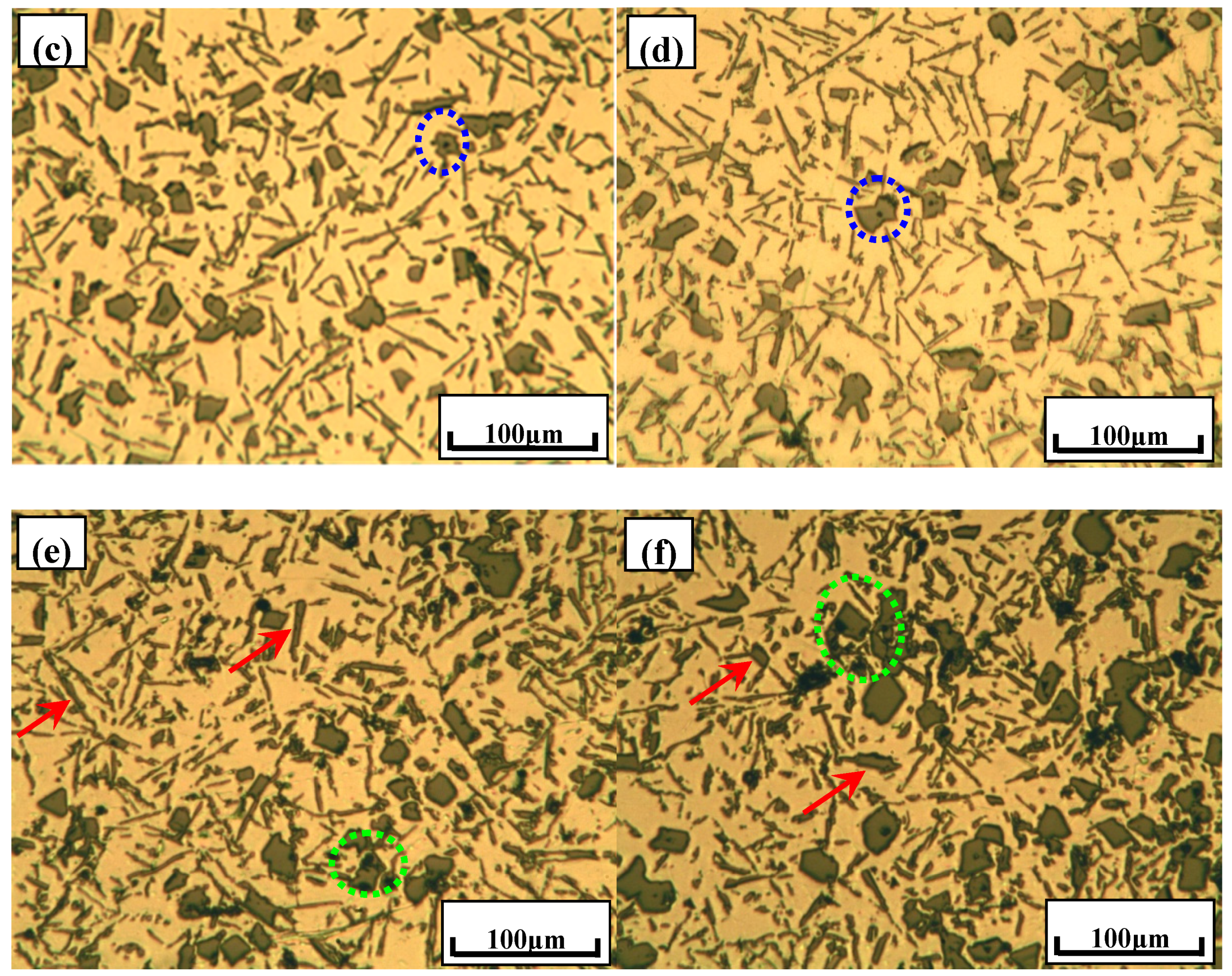
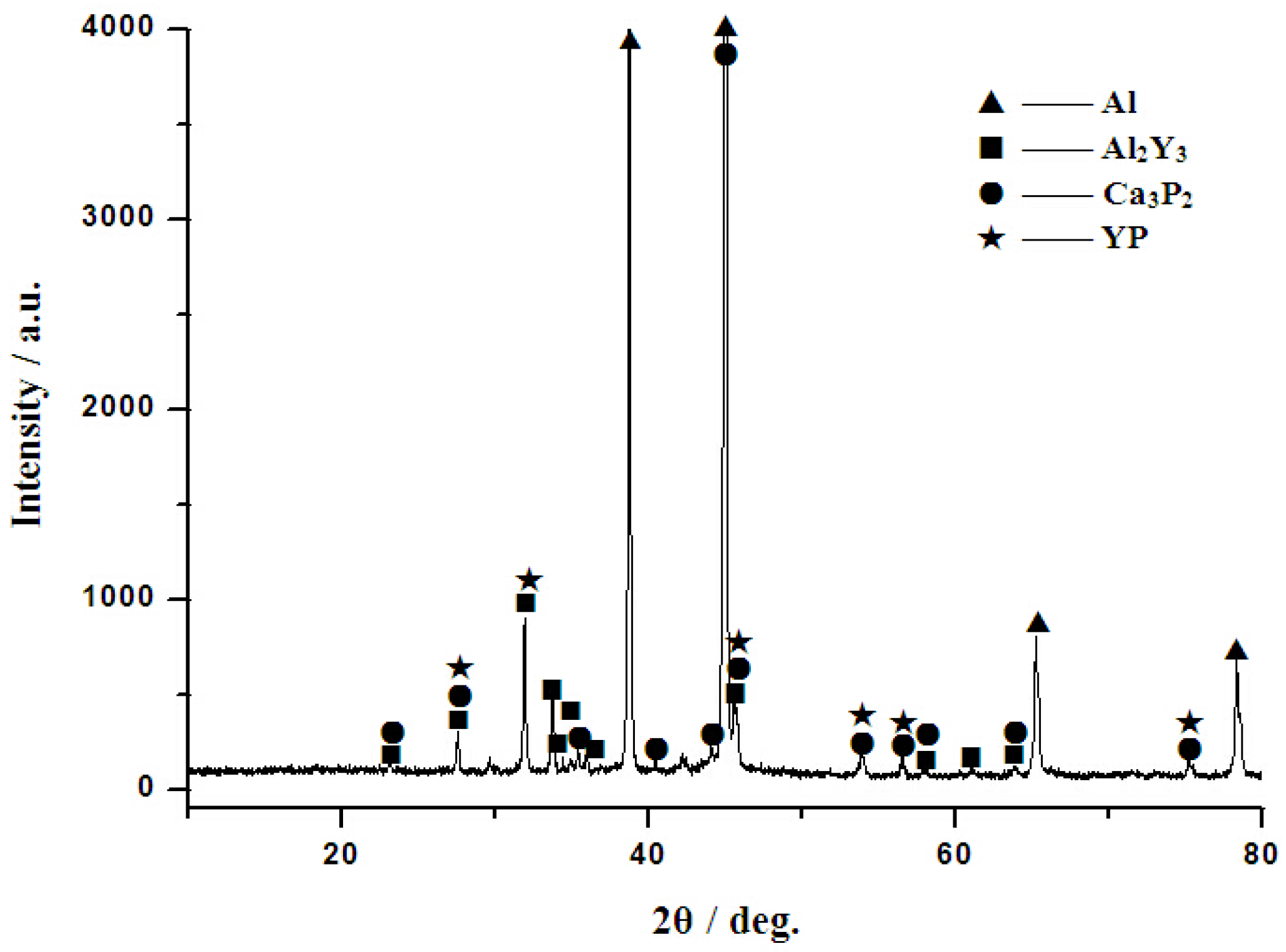
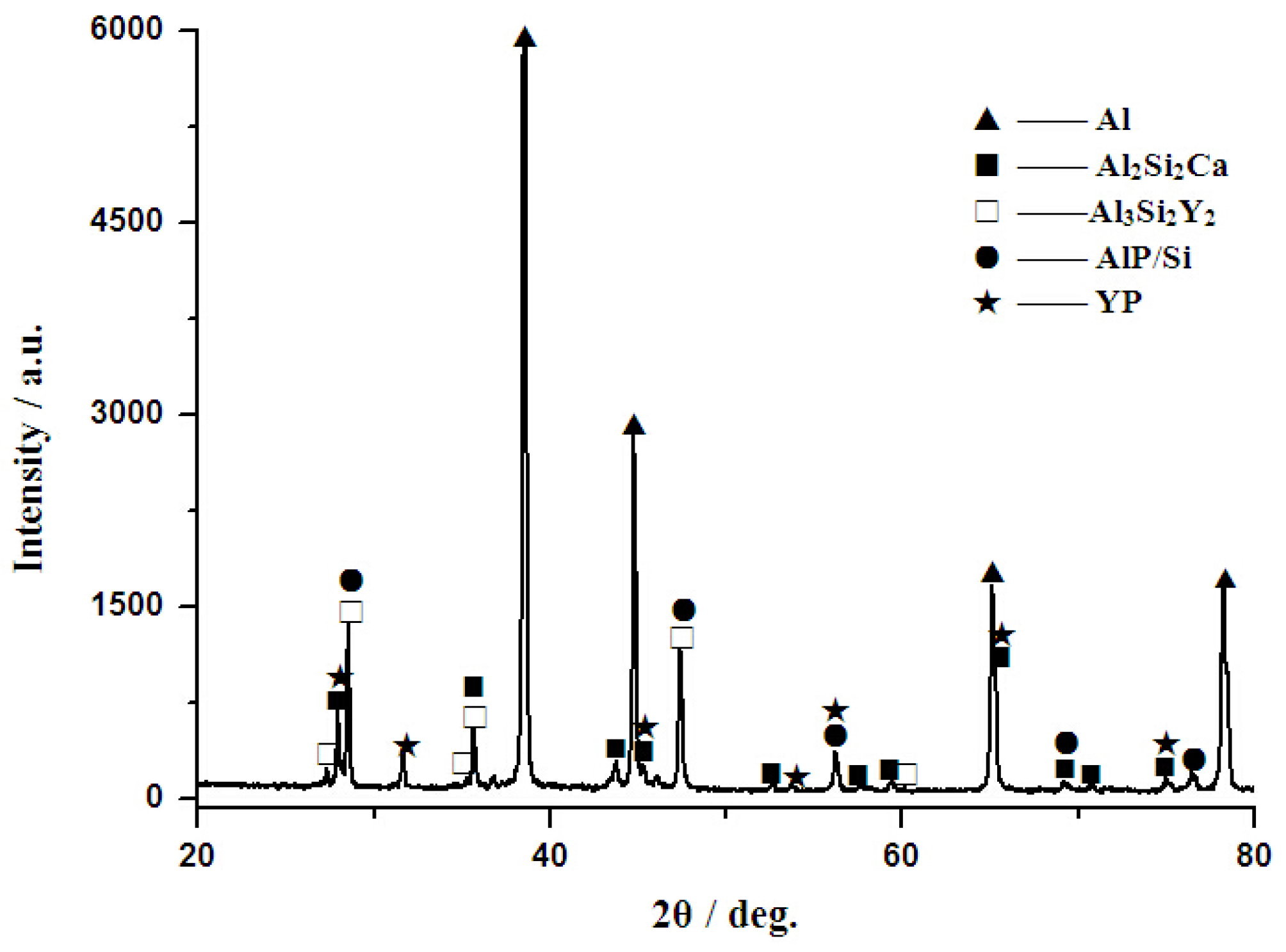
3.2. Phase Composition and Microstructure Analysis of Al–2Ca–3Y–1P Alloy
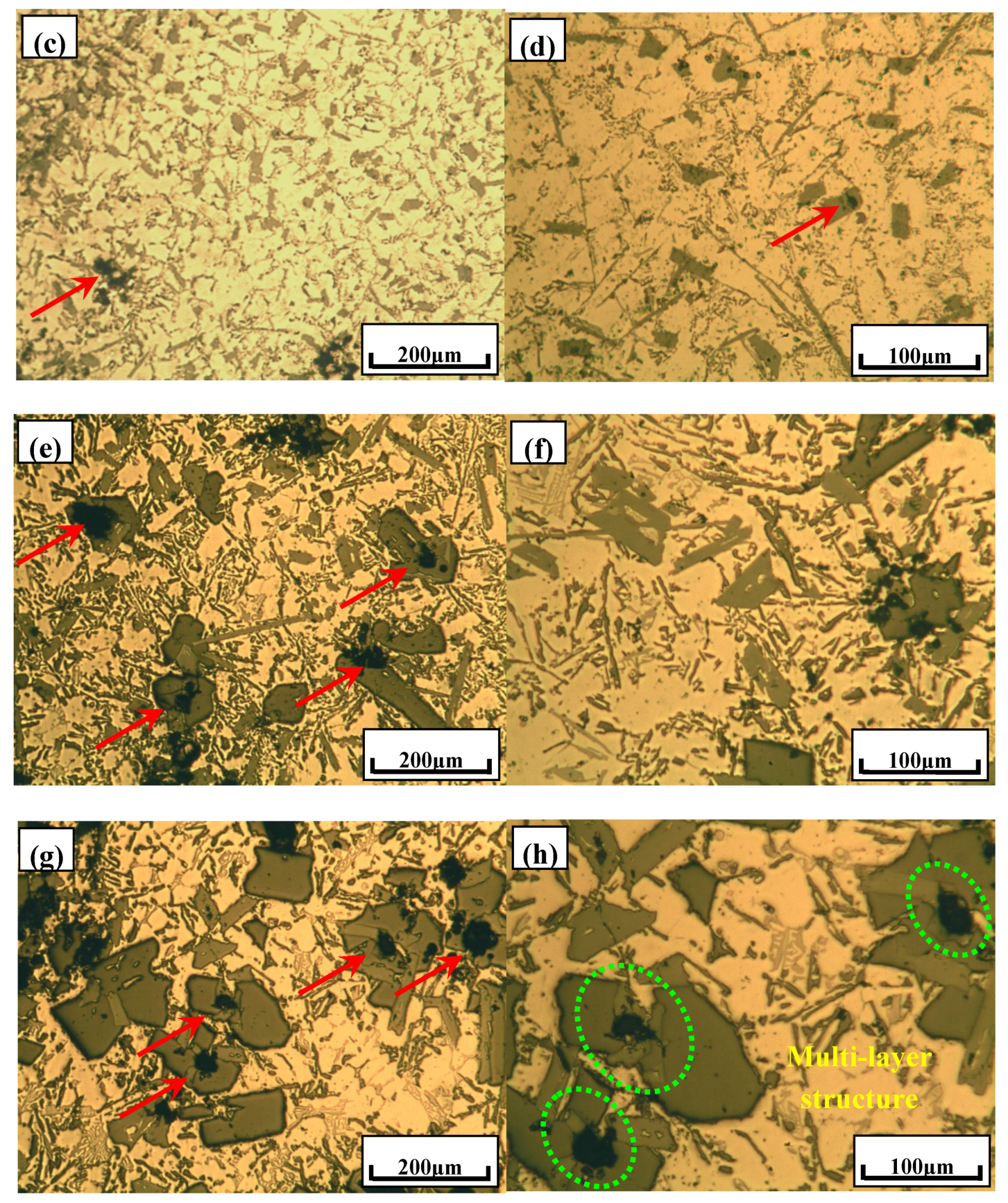
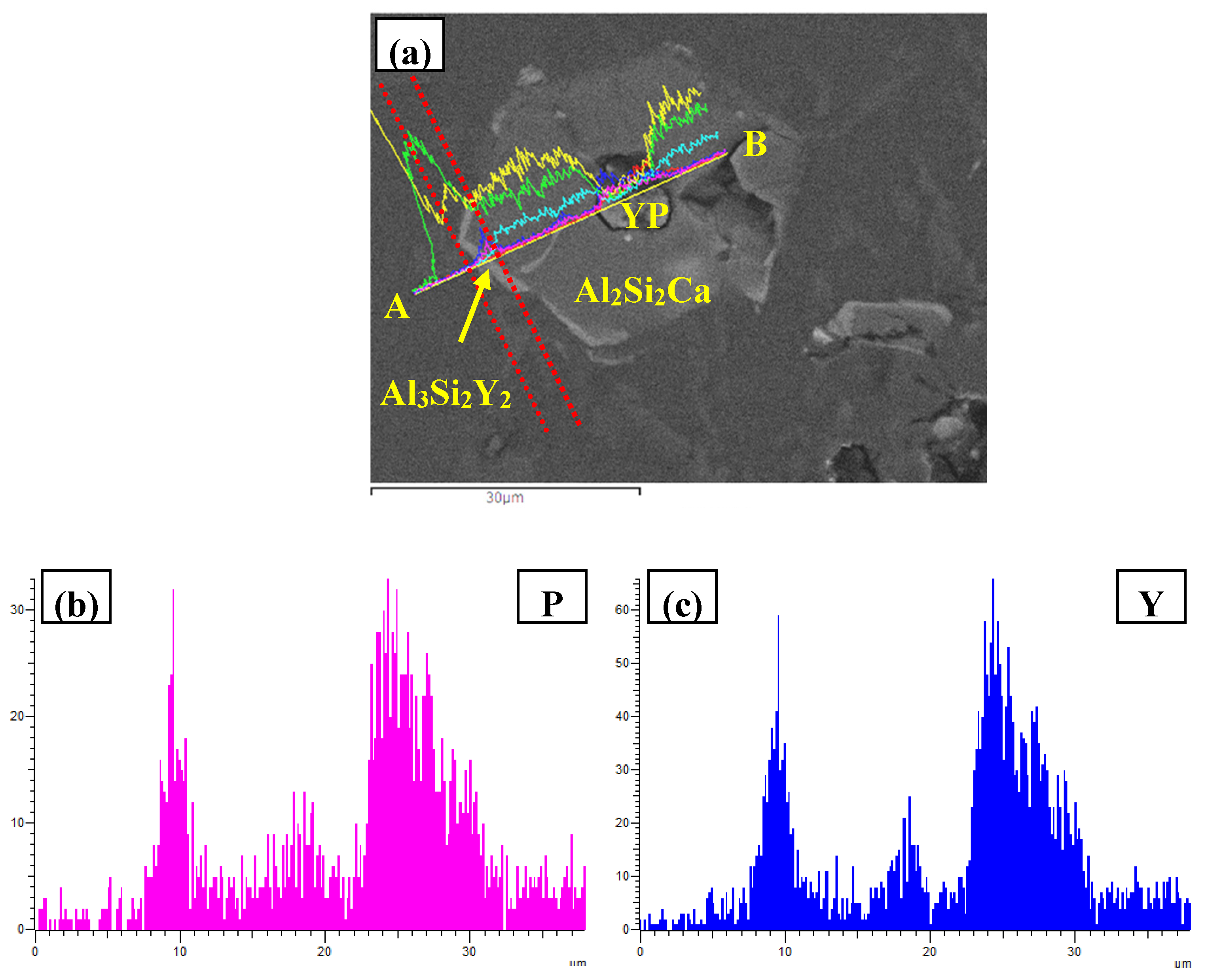
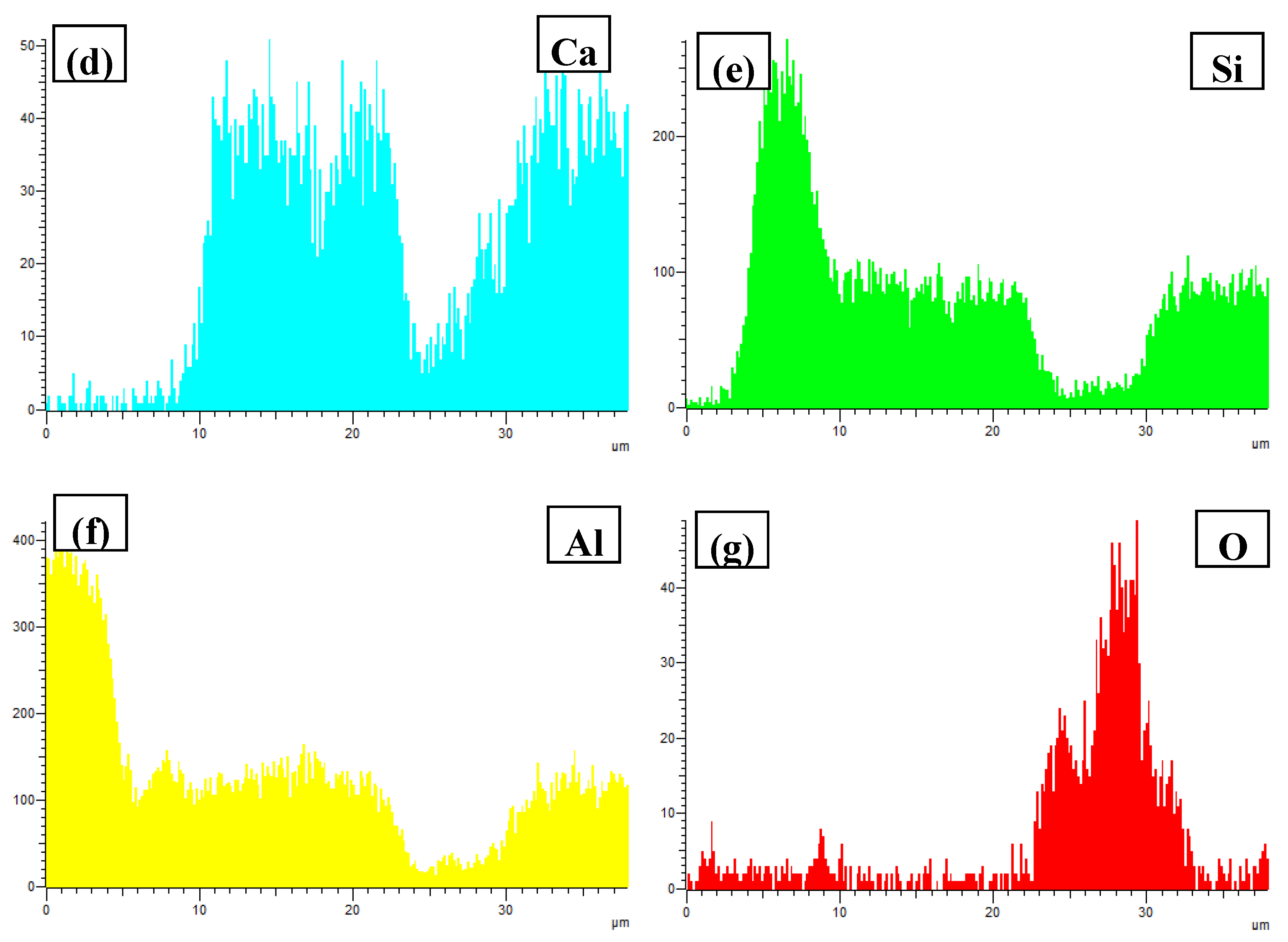
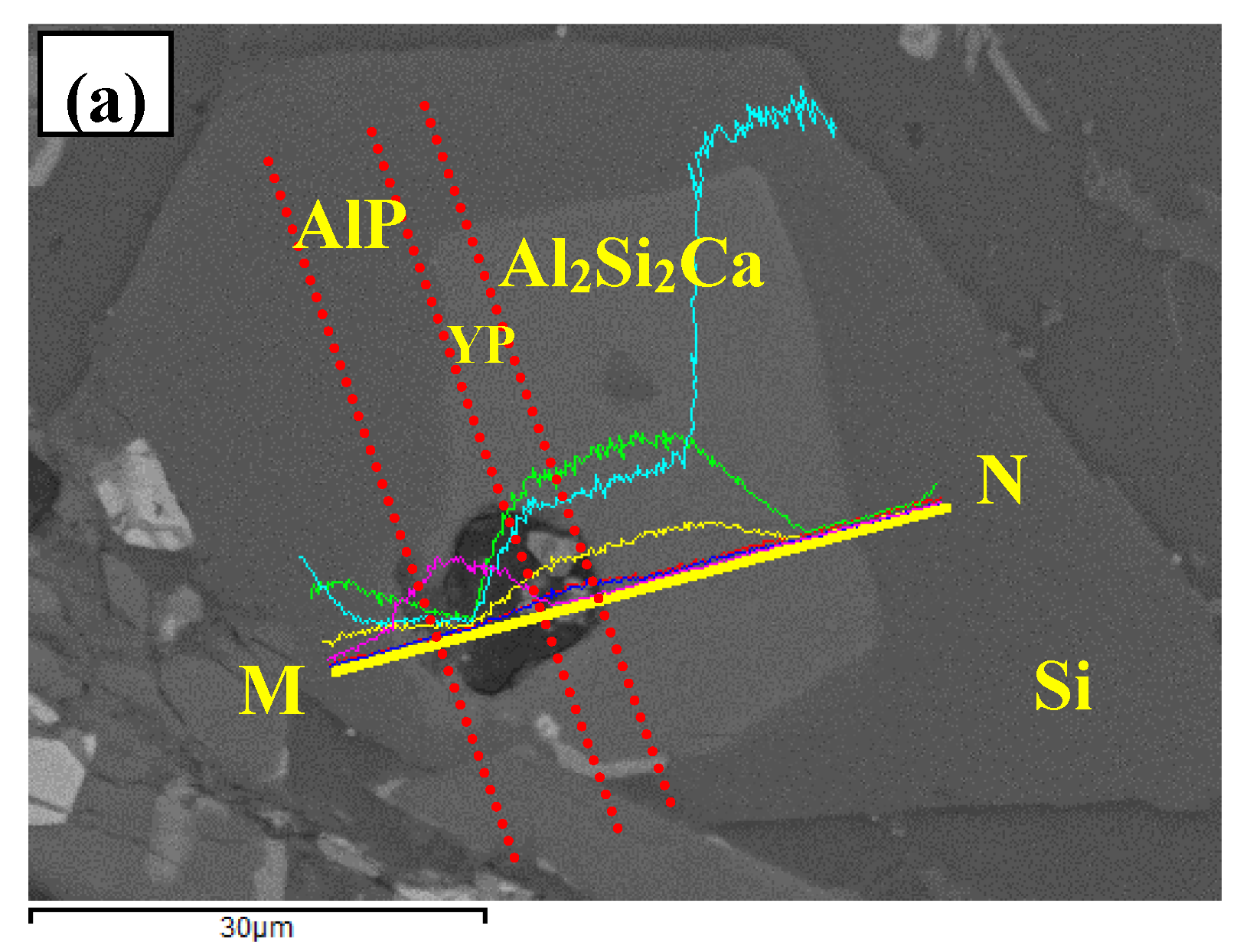
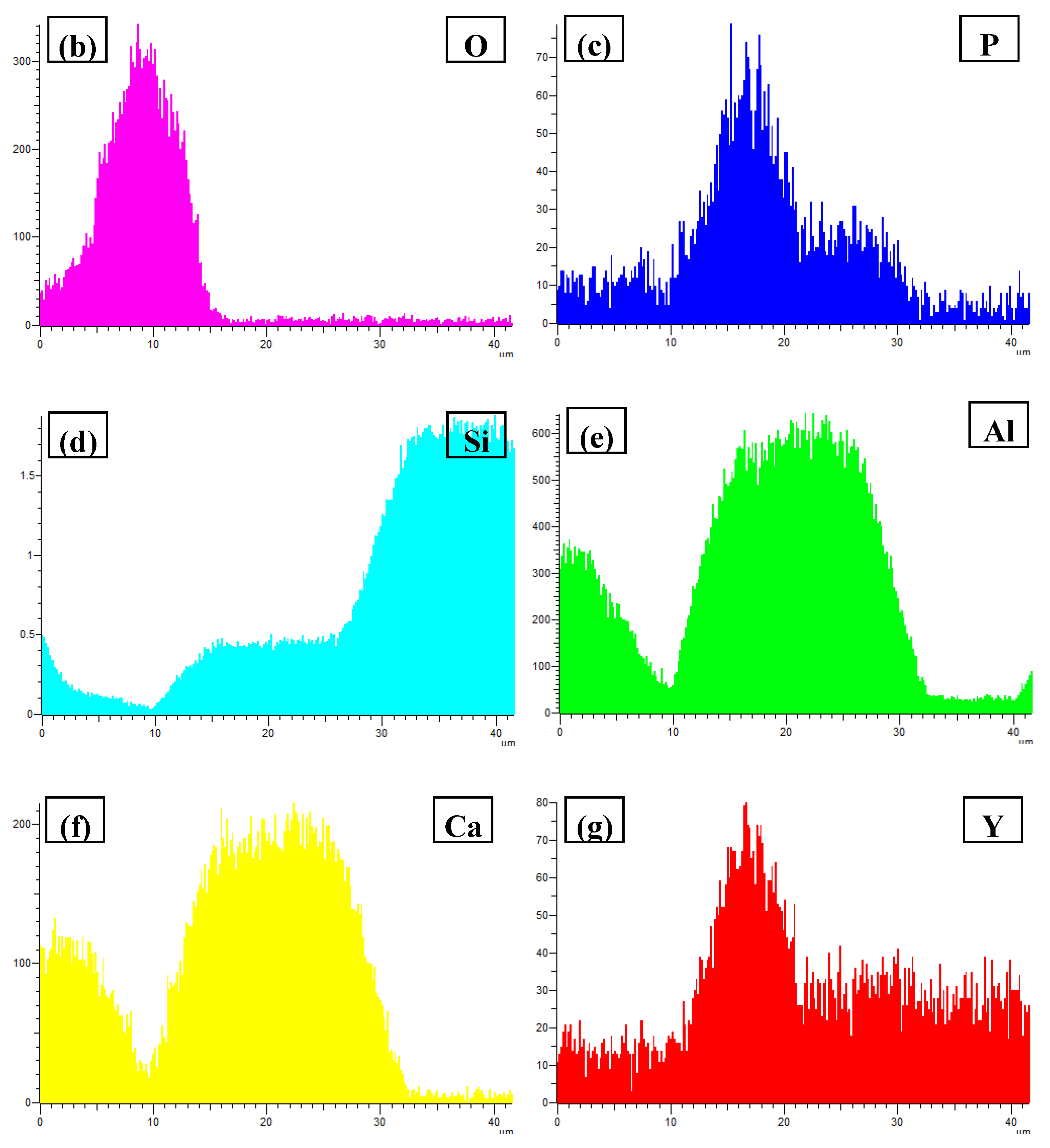
3.3. Phase Compositionsand Microstructure Analysisesof Al–xSi–2Ca–3Y–1P Alloys (x = 6, 12, 18, 30)
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- With the presence of Ca and Al–6Y–2P master alloy, the primary Si was relatively refined to about 24.1 μm and eutectic Si still remain the same or even coarse, which indicates that novel Al–6Y–2P master alloy has a limited anti-poison effect of Ca, with an application in Al–Si alloys.
- (2)
- In Al–2Ca–3Y–1P alloy, Al2Y3, Ca3P2, and YP compounds were detected besides of Al. Based on the microstructural analysis, it can be deduced that Ca could react with YP to form more stable Ca3P2 compounds, and residual Y would exist in the form of Al2Y3 and YP particles.
- (3)
- In Al–xSi–Ca–Y–P (x = 6, 12, 18, 30)alloys, the multi-encapsulation structures were observed, which were composed of three layers, i.e., the phosphides (AlP and YP), hexagonal Al2Si2Ca, the Al3Si2Y2 or primary Si from inside to outside in order. The formation of encapsulation structure as YP–Al2Si2Ca and AlP–Al2Si2Camaynjust be the reason for the limited refinement effect of Al–6Y–2P master alloy for aluminium alloys.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, H.; Konishi, H.; Li, X.C. Al2O3 nanoparticles induced simultaneous refinement and modification of primary and eutectic Si particles in hypereutectic Al–20Si alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 541, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M.; Khalilpour, H. Effect of phosphorus inoculation on creep behavior of a hypereutectic Al–Si alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 3467–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.Y.; Jia, Y.D.; Prashanth, K.G.; Ma, P.; Liu, J.S.; Scudino, S.; Huang, F.; Eckert, J.; Sun, J.F. Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast Al–50Si alloy due to heat treatment and P modifier content. Mater. Des. 2015, 74, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazahery, A.; Shabani, M.O. Modification mechanism and microstructural characteristics of eutectic Si in casting Al–Si alloys: A review on experimental and numerical studies. JOM 2014, 66, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, M.O.; Rahimipour, M.R.; Tofigh, A.A.; Davami, P. Refined microstructure of compo cast nanocomposites: The performance of combined neuro-computing, fuzzy logic and particle swarm techniques. Neural Comput. Appl. 2015, 26, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofigh, A.A.; Rahimipour, M.R.; Shabani, M.O.; Davami, P. Application of the combined neuro-computing, fuzzy logic and swarm intelligence for optimization of compo cast nanocomposites. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 49, 1653–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazahery, A.; Shabani, M.O. Mechanical properties of A356 matrix composites reinforced with nano-SiC particles. Strength Mater. 2012, 44, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, K.; Ojha, S.N. Effect of spray forming on the microstructure and wear properties of Al–Si alloys. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 5, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhu, S.Q.; Chen, Y.L. Effect of SiC particles on fatigue crack growth behavior of SiC particulate-reinforced Al–Si alloy composites produced by spray forming. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 3, 1694–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Cao, F.Y.; Hou, L.G.; Jia, Y.D. The study of preparation of spray formed 7075/Al–Si bimetallic gradient composite plate. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 32, 3109–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, M.; Zhao, D.G.; Teng, X.Y.; Geng, H.R.; Zhang, Z.S. Effect of P and Sr complex modification on Si phase in hypereutectic Al–30Si alloys. Mater. Des. 2013, 47, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Zhu, X.Z.; Qiao, H.; Liu, X.F. A new Al–Fe–P master alloy designed for application in low pressure casting and its refinement performance on primary Si in A390 alloy at low temperature. J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 607, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhong, Y.B.; Zheng, T.X.; Shen, Z.; Wang, J.; Fan, L.J.; Zhai, Y.; Peng, M.H.; Zhou, B.F.; Ren, W.L.; et al. Refinement of primary Si in the bulk solidified Al-20 wt.%Si alloy assisting by high static magnetic field and phosphorus addition. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 714, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.L.; Geng, H.R.; Zuo, M.; Long, F.; Peng, X. Effects of melt thermal rate treatment and modification of P and RE on hypereutectic Al–Si–Cu–Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.C.; Hong, S.J.; Hong, S.; Kim, H.S. Mechanical properties of equal channel angular pressed powder extrudates of a rapidly solidified hypereutectic Al-20 wt.% Si alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 449–451, 966–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiolek, W.Z.; Haase, M.; Khalifa, N.B.; Tekkaya, A.E.; Kleiner, M. High quality extrudates from aluminum chips by new billet compaction and deformation routes. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 61, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.L.; Ding, D.Y.; Gao, P. High volume fraction Si particle-reinforced aluminium matrix composites by a filtration squeeze casting route. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.R.; Cantor, B. Heterogeneous nucleation of solidification of Si in Al–Si and Al–Si–P alloys. Acta Metall. Mater. 1995, 43, 3231–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, B.; Jian, Z.Y.; Xu, J.F.; Chang, F.E.; Zhu, M. Effect of phosphorus and heat treatment on microstructure of Al-25%Si alloy. China Foundry 2017, 14, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Zhu, X.Z.; Gao, T.; Wu, Y.Y.; Liu, X.F. Influence of deformation on the microstructure and low-temperature refining behavior of Al–3.5P master alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Gao, T.; Zhu, X.Z.; Wu, Y.Y.; Qian, Z.; Liu, X.F. Generation and evolution of nanoscale AlP and Al13Fe4 particles in Al–Fe–P system. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 622, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, M.; Liu, X.F.; Sun, Q.Q.; Jiang, K. Effect of rapid solidification on the microstructure and refining performance of an Al–Si–P master alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 5504–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, G.J.; Zuo, M.; Li, D.K.; Li, Y.G.; Liu, X.F. The improvement of microstructures and mechanical properties of near eutectic Al–Si multicomponent alloy by an Al–8Zr–2P master alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 531, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, M.; Zhao, D.G.; Wang, Z.Q.; Geng, H.R. Complex modification of hypereutectic Al–Si alloy by a new Al–Y–P master alloy. Met. Mater. Int. 2015, 21, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, A.M.; Doty, H.W.; Gallardo, S.V.; Samuel, F.H. The effect of Bi–Sr and Ca–Sr interactions on the microstructure and tensile properties of Al–Si-based alloys. Materials 2016, 9, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Qian, G.Y. Removal of phosphorus in silicon by the formation of CaAl2Si2 phase at the solidification interface. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2017, 48, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, T.H.; Schaffer, P.L.; Arnberg, L. Influence of some trace elements on solidification path and microstructure of Al–Si foundry alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 3783–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaldívar-Cadena, A.A.; Flore-Valdés, A. Prediction and identification of calcium-rich phases in Al–Si alloys by electron backscatter diffraction EBSD/SEM. Mater. Charact. 2007, 58, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Qiao, J.G.; Wu, Y.Y.; Liu, X.J.; Bian, X.F. EPMA analysis of calcium-rich compounds in near eutectic Al–Si alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2005, 388, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, T.H.; Schonhovd Dæhlen, E.; Schaffer, P.L.; Arnberg, L. The effect of Ca and P interaction on the Al–Si eutectic in a hypoeutectic Al–Si alloy. J. Alloy.Compds. 2014, 586, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
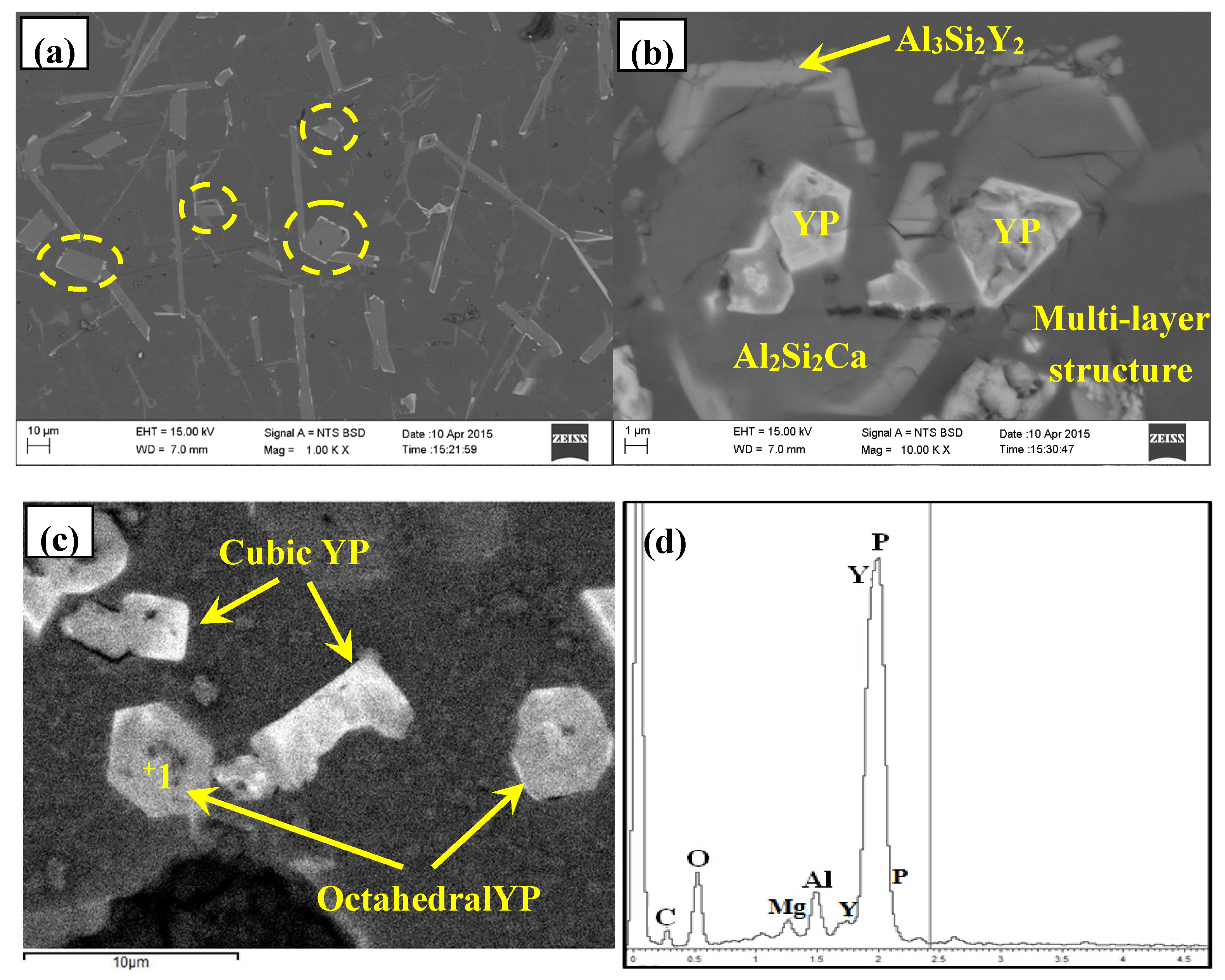

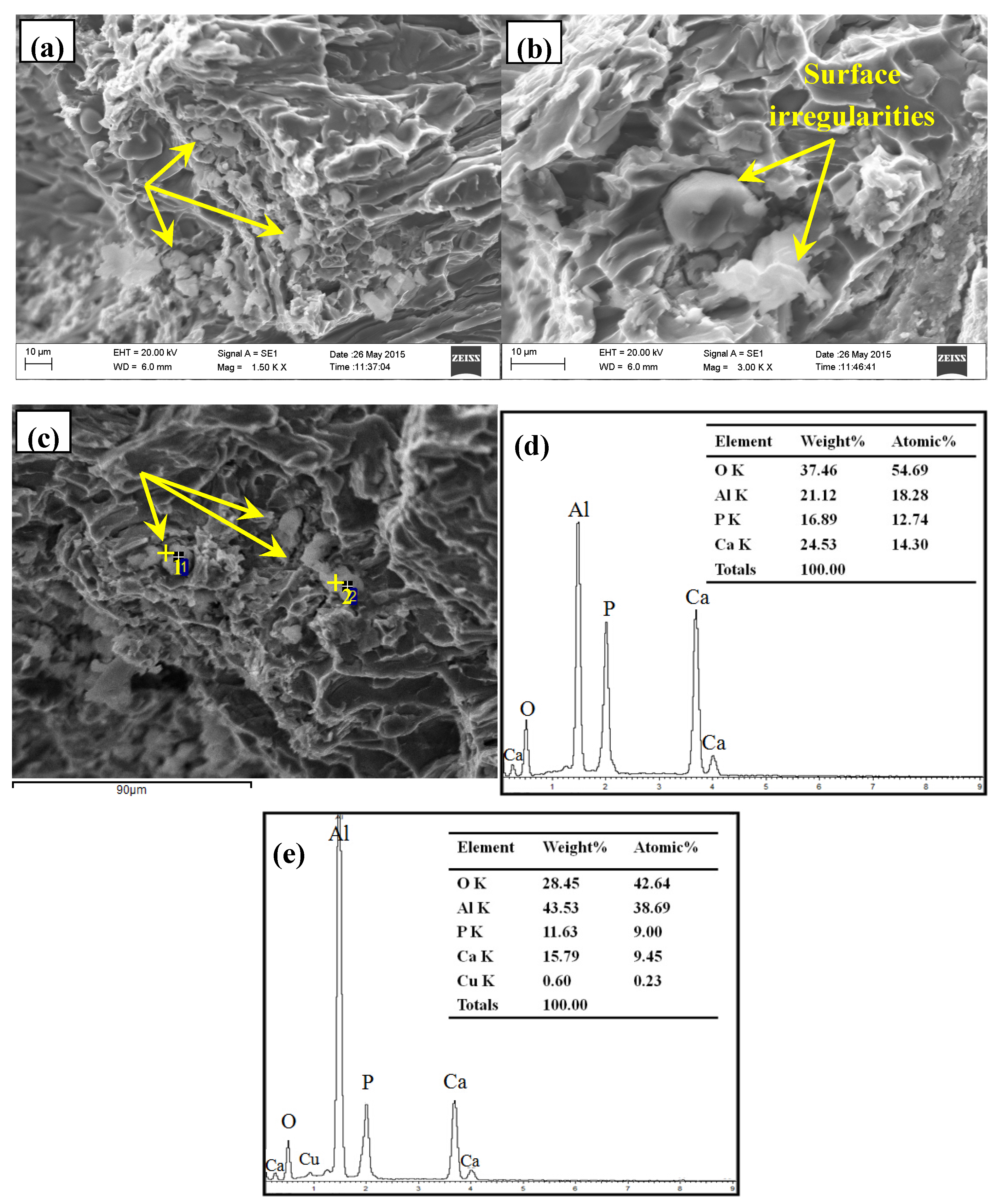
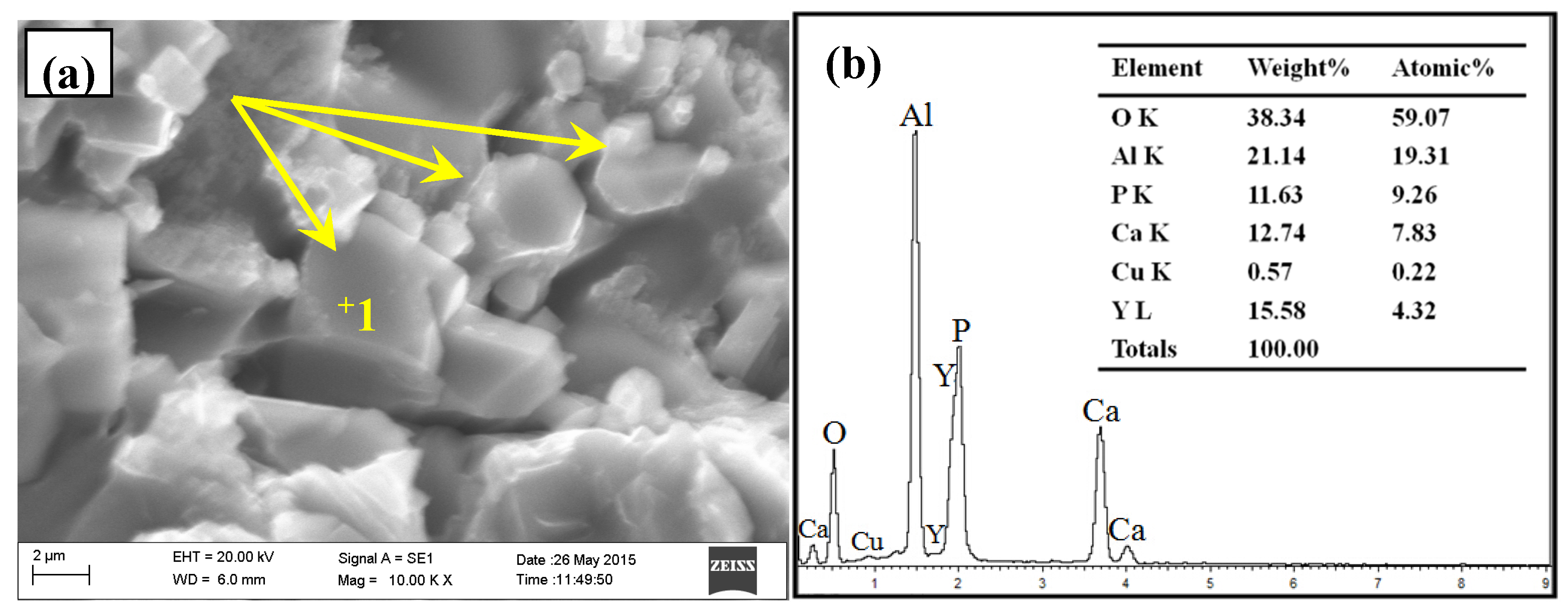

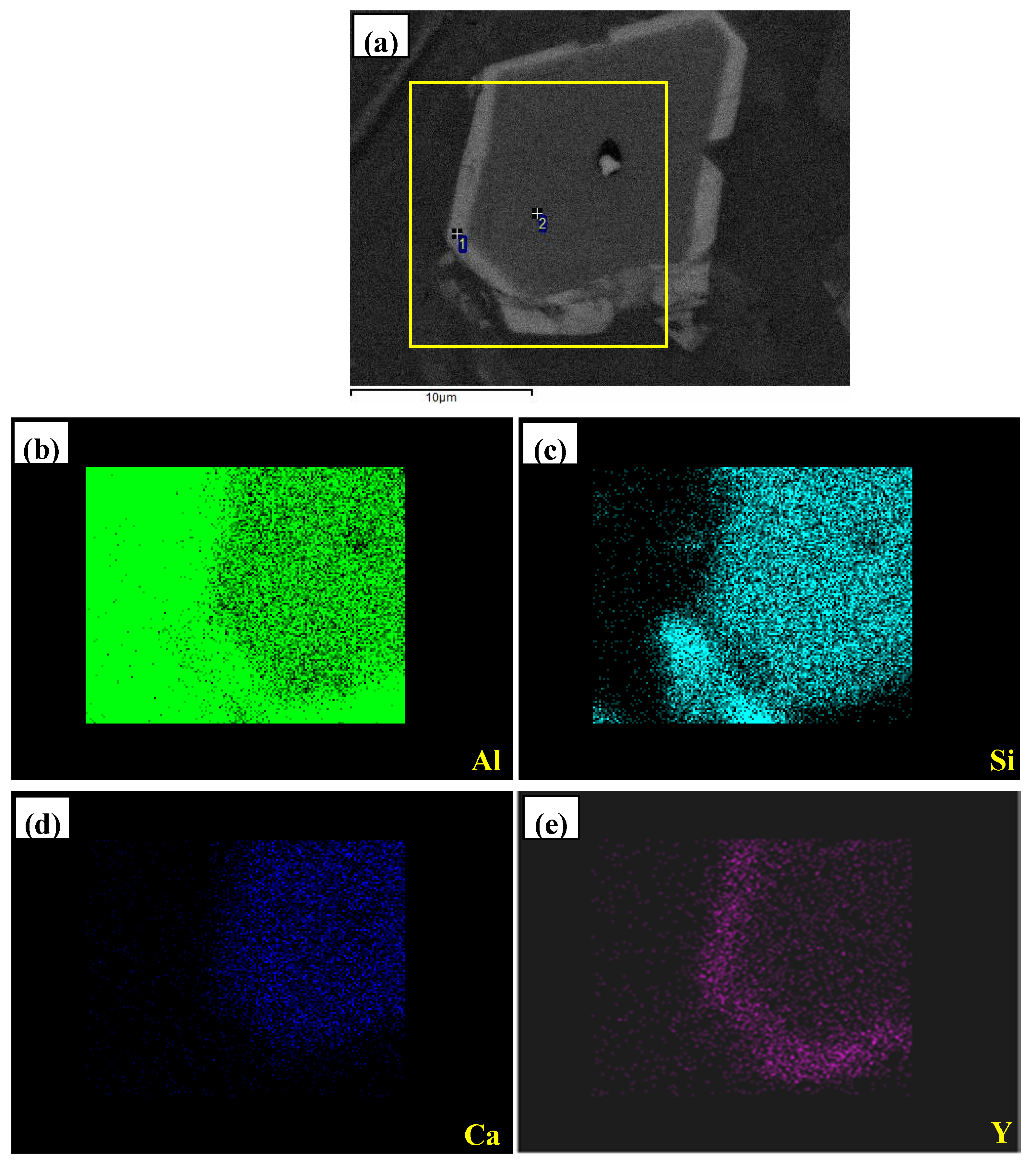
| Spot | Element | Weight% | Atomic% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Al | 26.89 | 42.97 |
| Si | 19.66 | 30.17 | |
| Ca | 1.59 | 1.71 | |
| Y | 51.86 | 25.15 | |
| 2 | C K | 13.38 | 27.81 |
| Al K | 31.71 | 29.33 | |
| Si K | 32.56 | 28.94 | |
| Ca K | 22.35 | 13.92 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuo, M.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Y.; Teng, X. Study on the Anti-Poison Performance of Al–Y–P Master Alloy for Impurity Ca in Aluminum Alloys. Materials 2017, 10, 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121356
Zuo M, Dong Y, Zhao D, Wang Y, Teng X. Study on the Anti-Poison Performance of Al–Y–P Master Alloy for Impurity Ca in Aluminum Alloys. Materials. 2017; 10(12):1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121356
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuo, Min, Yu Dong, Degang Zhao, Yan Wang, and Xinying Teng. 2017. "Study on the Anti-Poison Performance of Al–Y–P Master Alloy for Impurity Ca in Aluminum Alloys" Materials 10, no. 12: 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121356
APA StyleZuo, M., Dong, Y., Zhao, D., Wang, Y., & Teng, X. (2017). Study on the Anti-Poison Performance of Al–Y–P Master Alloy for Impurity Ca in Aluminum Alloys. Materials, 10(12), 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121356




