Ti Reactive Sintering of Electrically Conductive Al2O3–TiN Composite: Influence of Ti Particle Size and Morphology on Electrical and Mechanical Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment and Characterization
2.1. Experimental Procedure
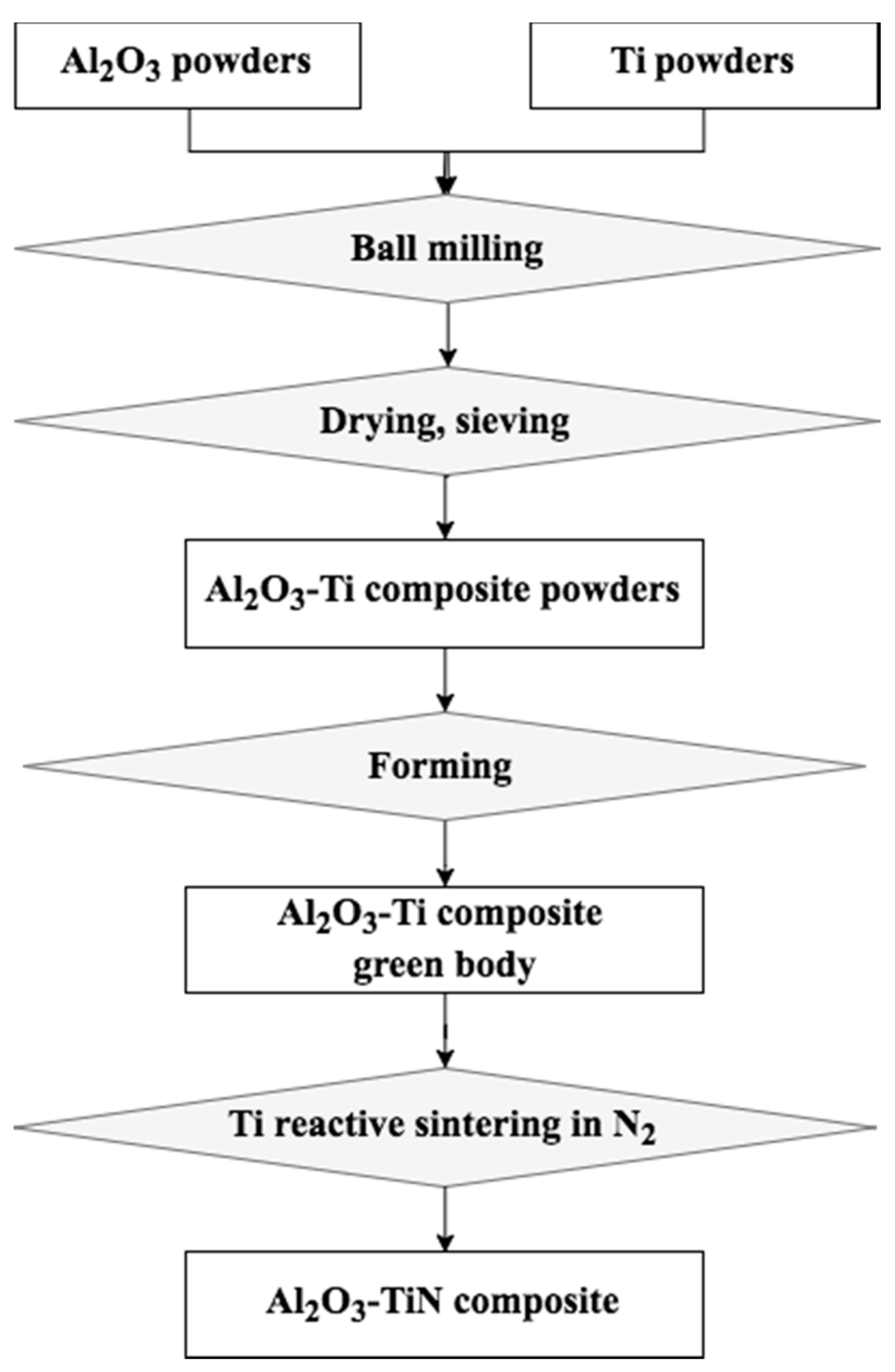
2.1.1. Ball Milling of Al2O3–Ti Composite Precursor Powders
2.1.2. Ti Reactive Sintering of Al2O3–TiN Ceramic Composites
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
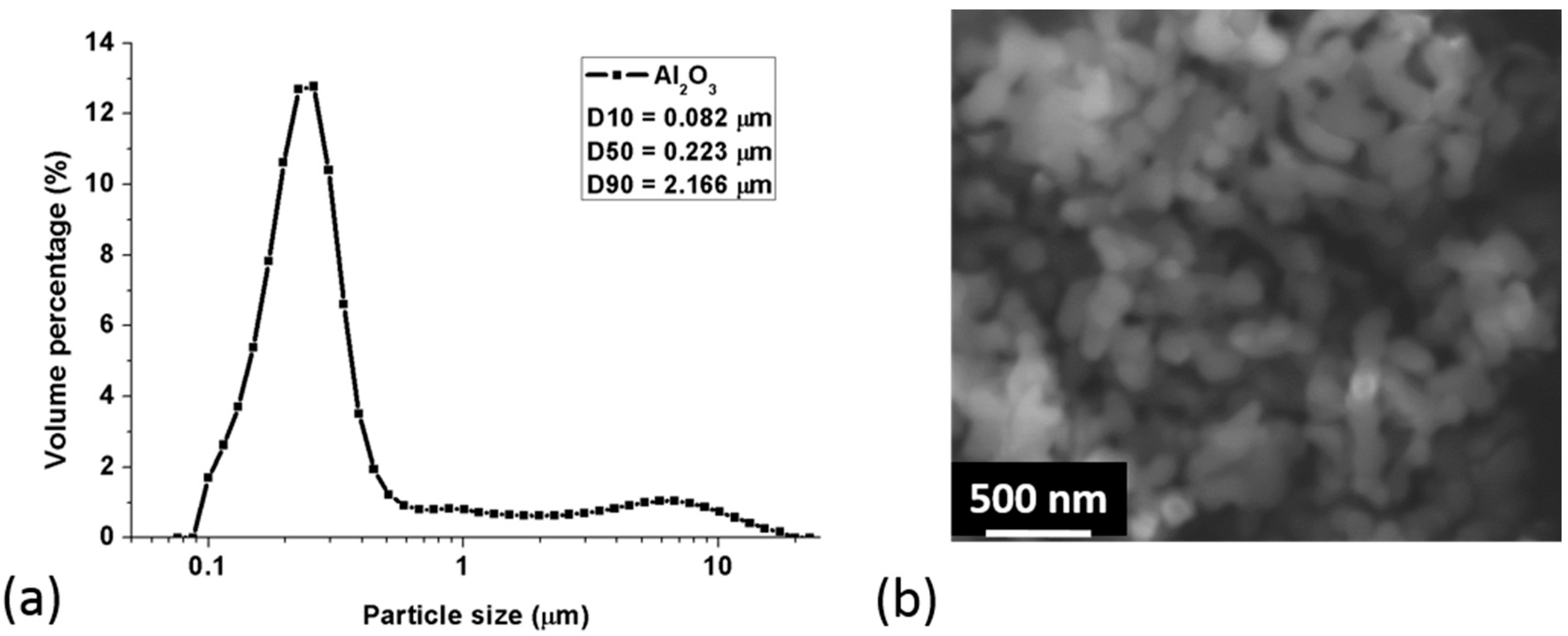
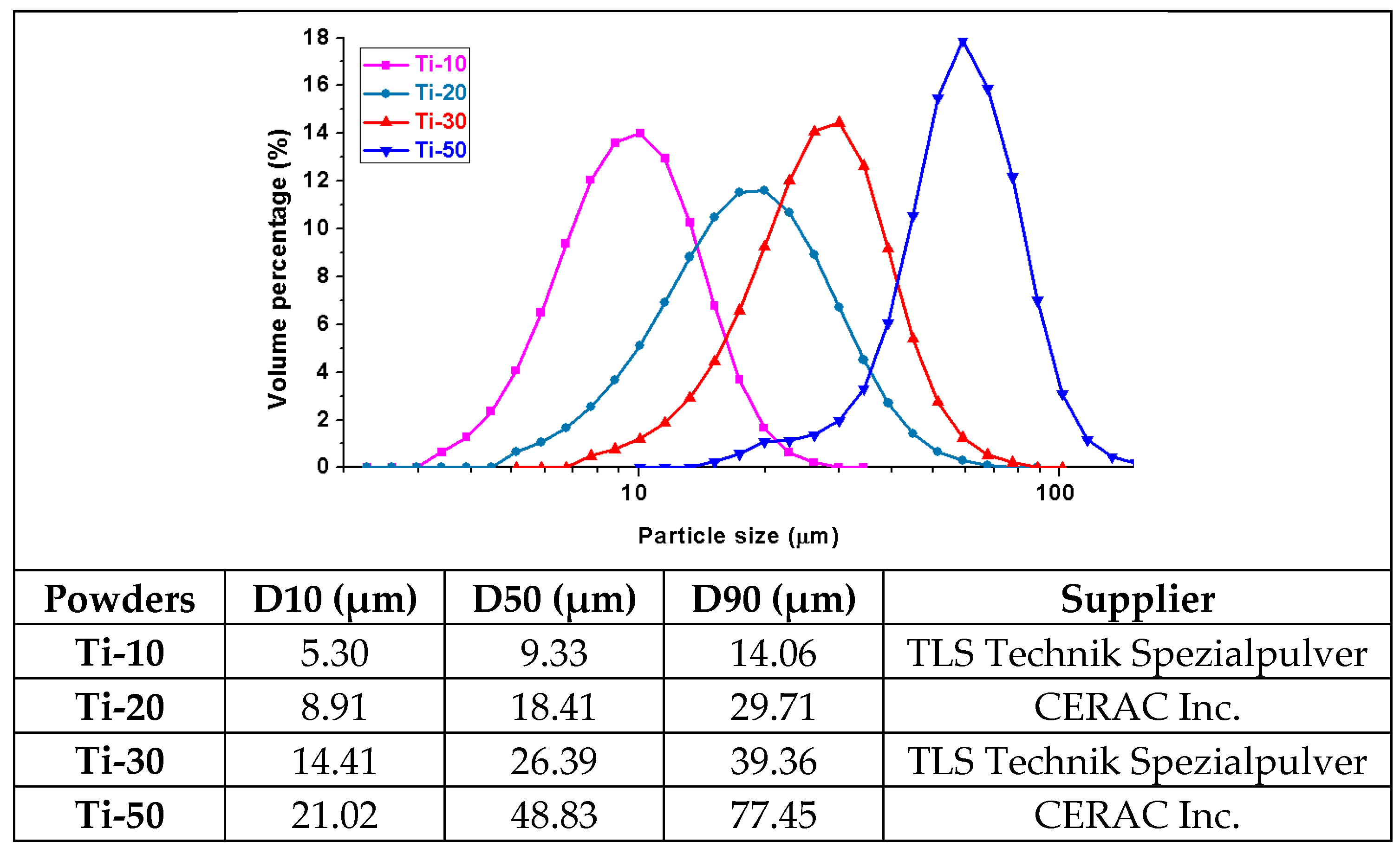
3.1. Particle Size
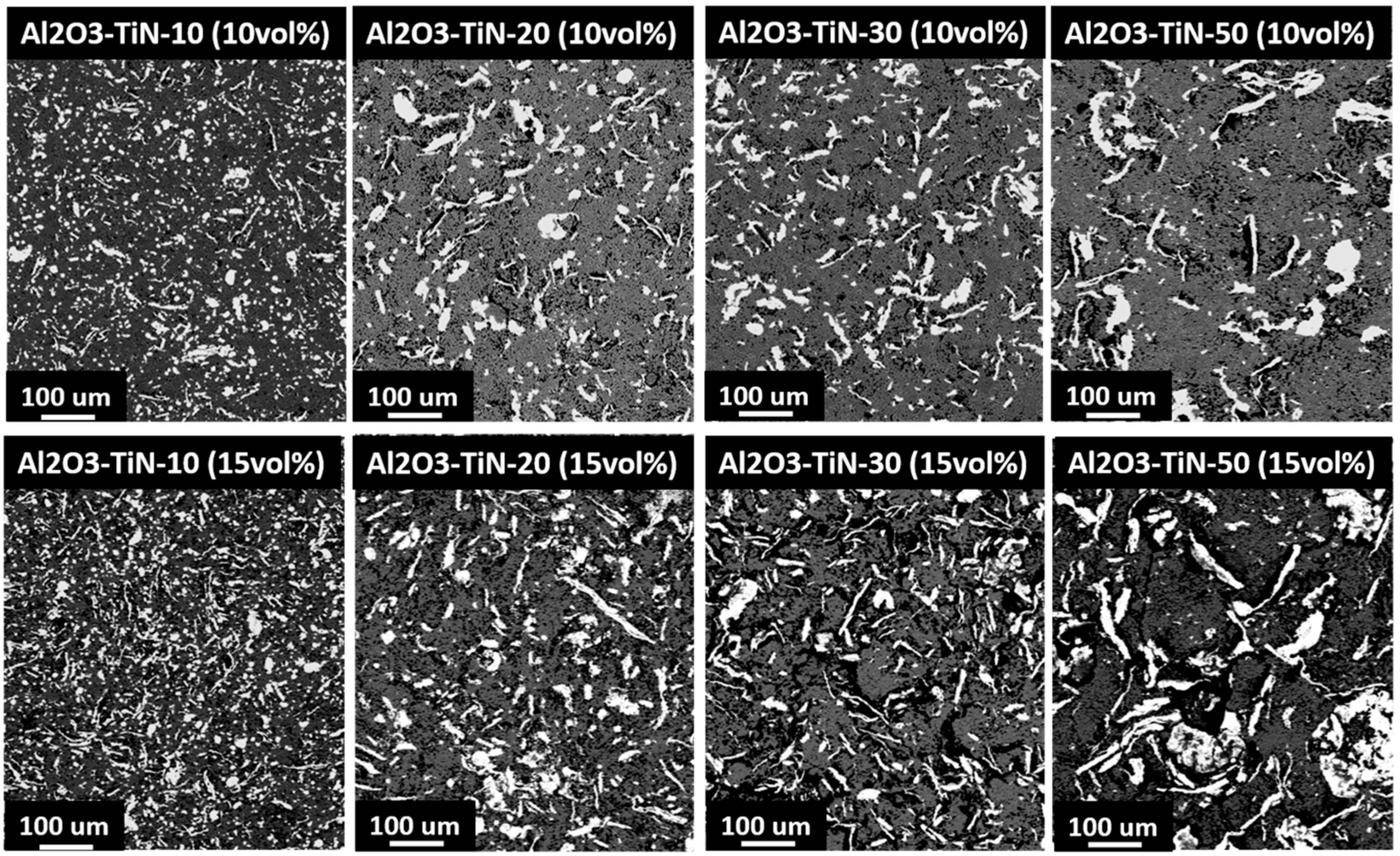
3.2. Powder Morphology
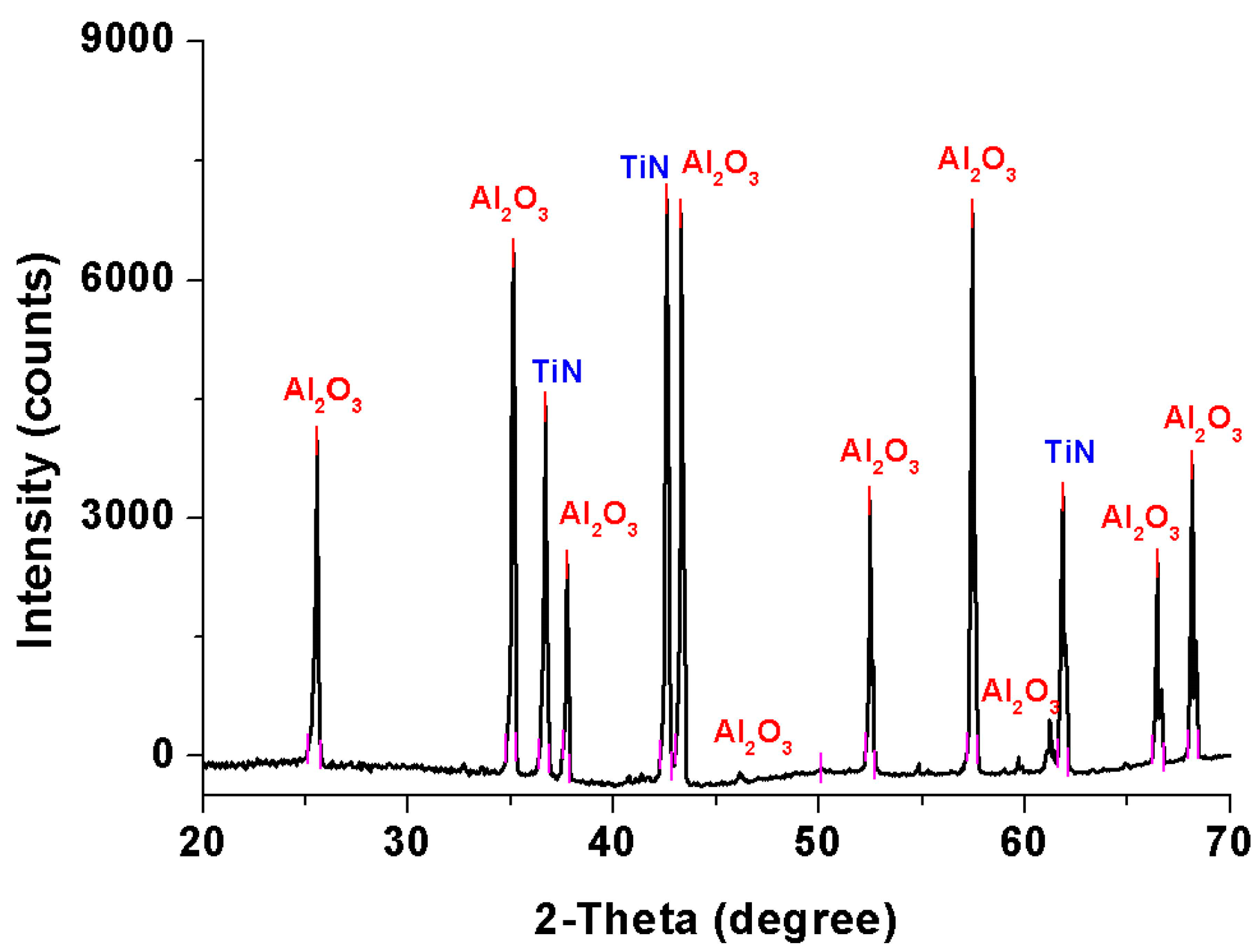
3.3. XRD
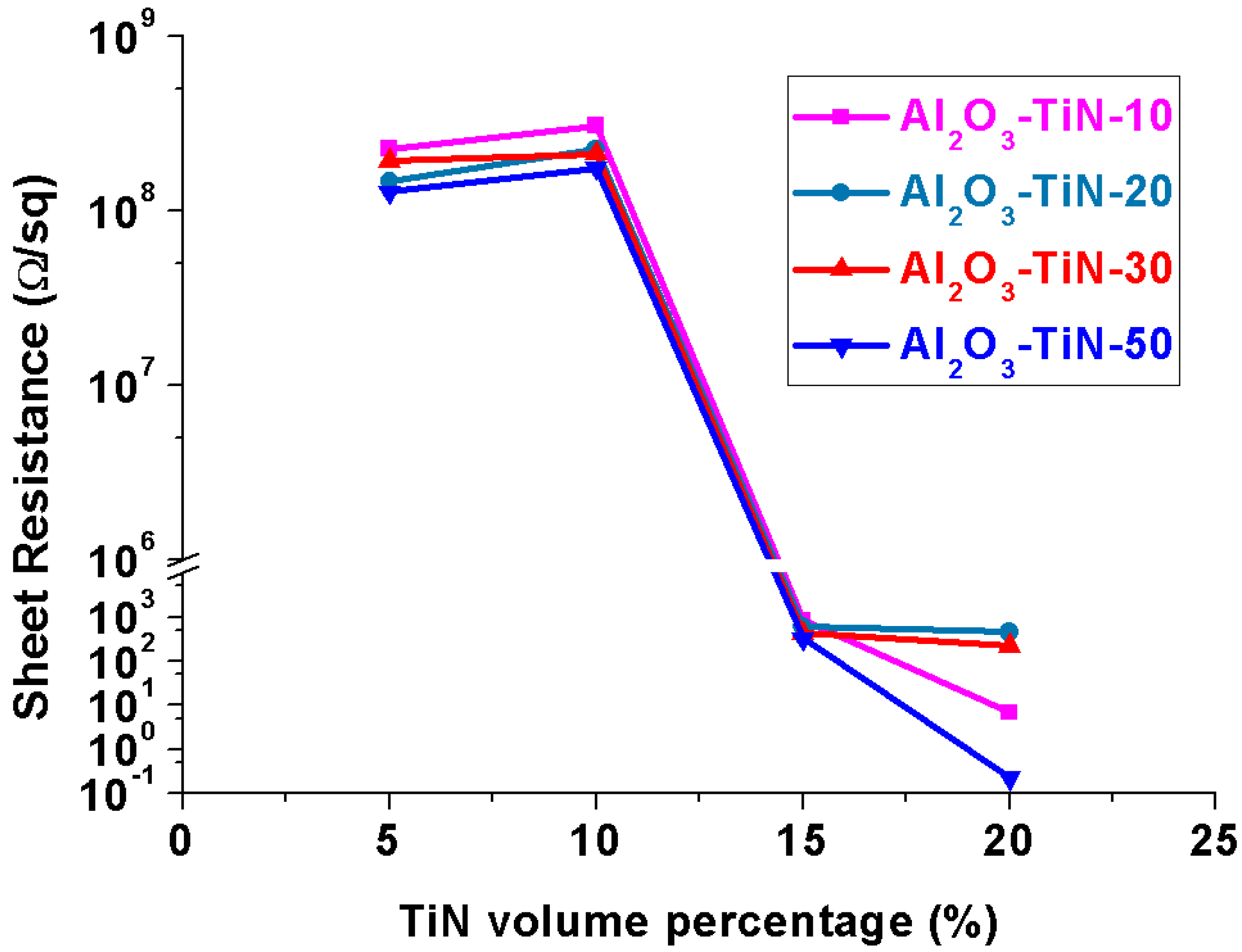
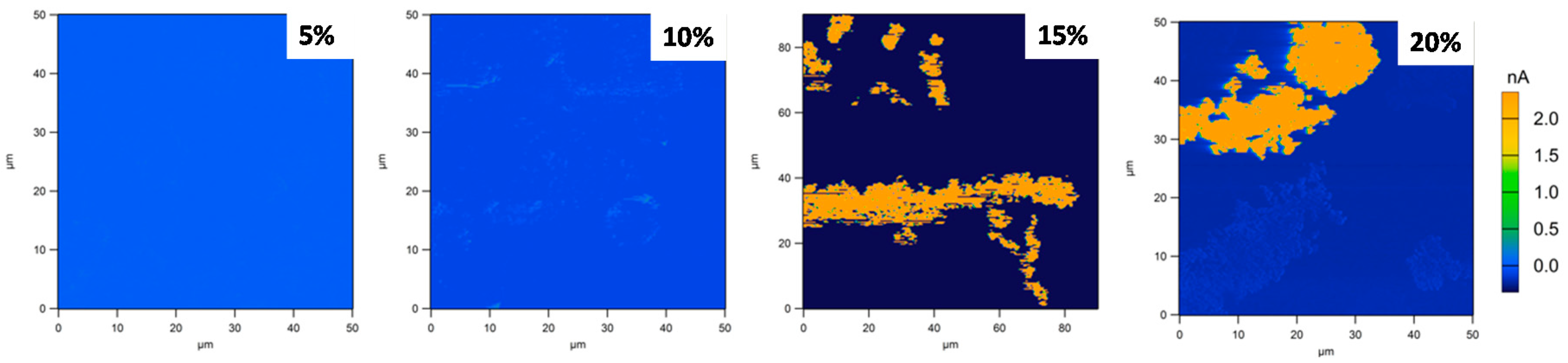
3.4. Electrical Properties
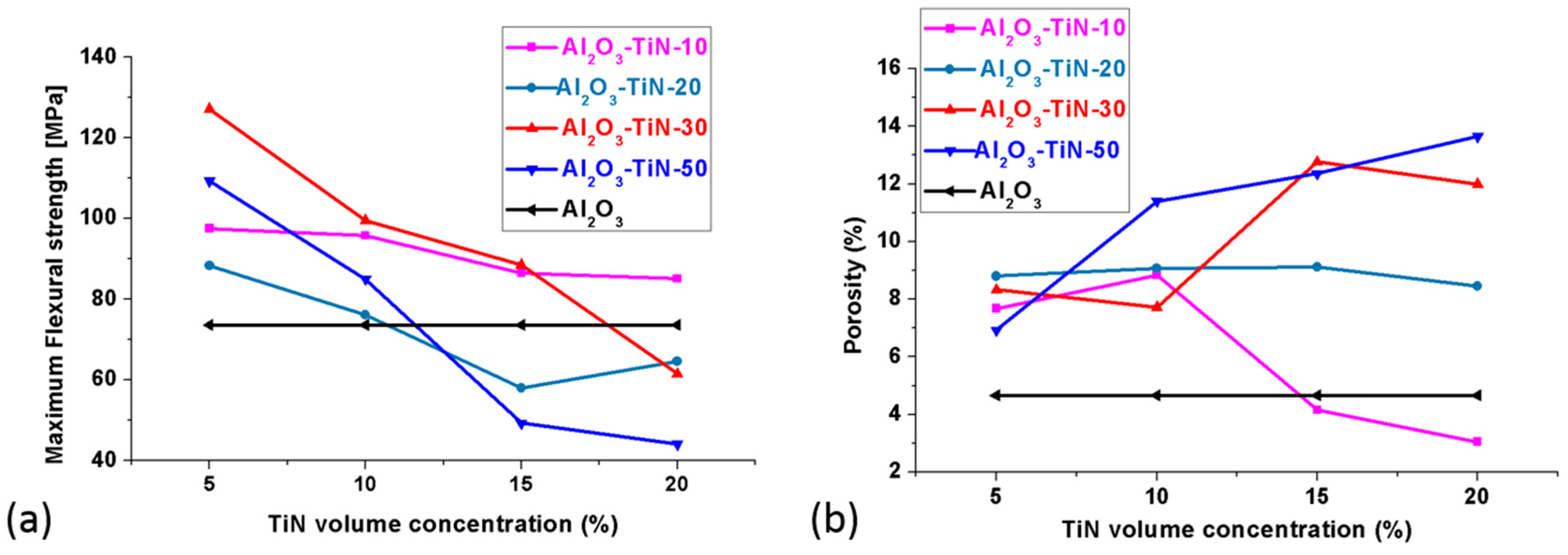
3.5. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padaki, M.; Murali, R.S.; Abdullah, M.S.; Misdan, N.; Moslehyani, A.; Kassim, M.A.; Hilal, N.; Ismail, A.F. Membrane technology enhancement in oil–water separation. A review. Desalination 2015, 357, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Peng, W.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Hong, H.; Zhang, Y. A review on anaerobic membrane bioreactors: Applications, membrane fouling and future perspectives. Desalination 2013, 314, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huotari, H.M.; Trägårdh, G.; Huisman, I.H. Crossflow membrane filtration enhanced by an external DC electric field: A review. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 1999, 77, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garboczi, E.J.; Snyder, K.A.; Douglas, J.F.; Thorpe, M.F. Geometrical percolation threshold of overlapping ellipsoids. Phys. Rev. E 1995, 52, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Sastry, A. Analytical approximation of the percolation threshold for overlapping ellipsoids of revolution. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2004, 460, 2353–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenhart, R.G.; Barra, G.M.O.; Fernandes, C.P. Simulation of percolation threshold and electrical conductivity in composites filled with conductive particles: Effect of polydisperse particle size distribution. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranzo, P.; Belmonte, M.; Osendi, M.I. From bulk to cellular structures: A review on ceramic/graphene filler composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 3649–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K. Rheological behavior of carbon nanotube-alumina nanoparticle dispersion systems. Powder Technol. 2007, 177, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landfried, R.; Kern, F.; Gadow, R. Electrically conductive ZTA-TiC ceramics: Influence of TiC particle size on material properties and electrical discharge machining. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2015, 49, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landfried, R.; Kern, F.; Burger, W.; Leonhardt, W.; Gadow, R. Development of electrical discharge machinable ZTA ceramics with 24 vol % of TiC, TiN, TiCN, TiB2 and WC as electrically conductive phase. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2013, 10, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, J. Effects of TiN content on mechanical properties and microstructure of ATN materials. Key Eng. Mater. 2013, 589–590, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Johnsson, M.; Nygren, M. TiN/Al2O3 composites and graded laminates thereof consolidated by spark plasma sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 23, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, L.; Guo, J.; Yan, D. Novel method to prepare electroconductive titanium nitride-aluminum oxide nanocomposites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 85, 724–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, L.; Guo, J. Mechanical properties and electrical conductivity of TiN–Al2O3 nanocomposites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 23, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, T.; Jiang, W.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Novel fabrication route to Al2O3-TiN nanocomposites via spark plasma sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 89, 1540–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, S.; Paseuth, A.; Kiyono, H. Coating and spark plasma sintering of nano-sized TiN on alumina particles of different size, shape and structure. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 117, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.; Shi, C.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zou, Q.; Yang, Q.; Deng, H.; Xing, Y. Enhancing the sinterability and fracture toughness of Al2O3-TiN0.3 composites. Ceram. Int. 2015, 42, 3965–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, Z.N. TiN modified SiC with enhanced strength and electrical properties. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM Subcommittee D20.10, Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials. Available online: https://www.astm.org/Standards/D790.htm (accessed on 23 November 2017).
- Menchavez, R.; Fuji, M.; Takahashi, M. Electrically conductive dense and porous alumina with in-situ synthesized nanoscale carbon networks. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 2345–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheb, N.; Hayat, U. Electrical conductivity and thermal properties of spark plasma sintered Al2O3-SiC-CNT hybrid nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 5715–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Xie, N.; Zhong, J. Carbon nanofibers and their composites: A review of synthesizing, properties and applications. Materials 2014, 7, 3919–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Feng, X.; Lauke, B.; Mai, Y. Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate-polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 933–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, I.; Suvaci, E.; Karademir, B.; Missiaen, J.; Carry, C.; Bouvard, D. Anisotropic sintering shrinkage in alumina ceramics containing oriented platelets. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 89, 1972–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, W.; Song, X.; Li, T.; Yu, B.; Lu, W.; Zeng, K. Ti Reactive Sintering of Electrically Conductive Al2O3–TiN Composite: Influence of Ti Particle Size and Morphology on Electrical and Mechanical Properties. Materials 2017, 10, 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121348
Zhai W, Song X, Li T, Yu B, Lu W, Zeng K. Ti Reactive Sintering of Electrically Conductive Al2O3–TiN Composite: Influence of Ti Particle Size and Morphology on Electrical and Mechanical Properties. Materials. 2017; 10(12):1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121348
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Wei, Xu Song, Tao Li, Bingxue Yu, Wanheng Lu, and Kaiyang Zeng. 2017. "Ti Reactive Sintering of Electrically Conductive Al2O3–TiN Composite: Influence of Ti Particle Size and Morphology on Electrical and Mechanical Properties" Materials 10, no. 12: 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121348
APA StyleZhai, W., Song, X., Li, T., Yu, B., Lu, W., & Zeng, K. (2017). Ti Reactive Sintering of Electrically Conductive Al2O3–TiN Composite: Influence of Ti Particle Size and Morphology on Electrical and Mechanical Properties. Materials, 10(12), 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121348





