Aspects of Solvent Chemistry for Calcium Hydroxide Medicaments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Solvents and Their Effects on Solubility
3. Measurements of pH of Calcium Hydroxide Preparations and Their Interpretation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pierce, A. Pulpal injury: Pathology, diagnosis and periodontal reactions. Aust. Endod. J. 1998, 24, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, R.M. Intraradicular space: What happens within roots of infected teeth? Ann. R. Australas. Coll. Dent. Surg. 2000, 15, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Love, R.M.; Jenkinson, H.F. Invasion of dentinal tubules by oral bacteria. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2002, 13, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, B.H.; Piskin, B.; Demirci, T. Observation of bacteria and fungi in infected root canals and dentinal tubules by SEM. Endod. Dent. Traumatol. 1995, 11, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, J.F.; Rôças, I.N.; Lopes, H.P. Patterns of microbial colonization in primary root canal infections. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2002, 93, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, C.T.; Rossi, M.A.; Leonardo, M.R.; Rocha, L.B.; Nelson-Filho, P.; Silva, L.A. Biofilm on the apical region of roots in primary teeth with vital and necrotic pulps with or without radiographically evident apical pathosis. Int. Endod. J. 2008, 41, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foschi, F.; Nucci, C.; Montebugnoli, L.; Marchionni, S.; Breschi, L.; Malagnino, V.A.; Prati, C. SEM evaluation of canal wall dentine following use of Mtwo and ProTaper NiTi rotary instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2004, 37, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raisingani, D.; Meshram, G.K. Cleanliness in the Root Canal System: An Scanning Electron Microscopic Evaluation of Manual and Automated Instrumentation using 4% Sodium Hypochlorite and EDTA (Glyde File Prep)—An in vitro Study. Int. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2010, 3, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, S.; Prakash, S.; Siddharth, P.R.; Saha, S.; Geojan, N.E.; Ramachandran, M. Comparative Evaluation of Smear Layer and Debris on the Canal Walls prepared with a Combination of Hand and Rotary ProTaper Technique using Scanning Electron Microscope. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2016, 17, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frank, A.L. Calcium hydroxide: The ultimate medicament? Dent. Clin. N. Am. 1979, 23, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gencoglu, N.; Külekçi, G. Antibacterial efficacy of root canal medicaments. J. Nihon Univ. Sch. Dent. 1992, 34, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, J.F.; de Uzeda, M. Disinfection by calcium hydroxide pastes of dentinal tubules infected with two obligate and one facultative anaerobic bacteria. J. Endod. 1996, 22, 674–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, R.M. Enterococcus faecalis—A mechanism for its role in endodontic failure. Int. Endod. J. 2001, 34, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chivatxaranukul, P.; Dashper, S.G.; Messer, H.H. Dentinal tubule invasion and adherence by Enterococcus faecalis. Int. Endod. J. 2008, 41, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good, M.; El, K.I.; Hussey, D.L. Endodontic ‘solutions’ part 1: A literature review on the use of endodontic lubricants, irrigants and medicaments. Dent. Update 2012, 39, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good, M.; El Karim, I.A.; Hussey, D.L. Endodontic ‘Solutions’. Part 2: An audit comparing current practice in Belfast with UK and Republic of Ireland Dental Schools. Dent. Update 2012, 39, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, W.N.; Duckmanton, P.; Kahler, B.; Walsh, L.J. A survey of various endodontic procedures related to mineral trioxide aggregate usage by members of the Australian Society of Endodontology. Aust. Endod. J. 2016, 42, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madarati, A.A.; Zafar, M.S.; Sammani, A.M.N.; Mandorah, A.O.; Bani-Younes, H.A. Preference and usage of intracanal medications during endodontic treatment. Saudi Med. J. 2017, 38, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, P.V. Medicaments: Aids to success in endodontics. Part 2. Clinical recommendations. Aust. Dent. J. 1990, 35, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, K.; Saunders, W.P.; Foye, R.H.; Sharkey, S.W. Calcium ion diffusion from calcium hydroxide-containing materials in endodontically-treated teeth: An in vitro study. Int. Endod. J. 1996, 29, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanassiadis, B.; Abbott, P.V.; Walsh, L.J. The use of calcium hydroxide, antibiotics and biocides as antimicrobial medicaments in endodontics. Aust. Dent. J. 2007, 52 (Suppl. S1), S64–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orstavik, D. Root canal disinfection: A review of concepts and recent developments. Aust. Endod. J. 2003, 29, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundqvist, G.; Figdor, D.; Persson, S.; Sjögren, U. Microbiologic analysis of teeth with failed endodontic treatment and the outcome of conservative re-treatment. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 1998, 85, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, J.F.; Sen, B.H. Fungi in endodontic infections. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2004, 97, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, G.H.; Liewehr, F.R.; Buxton, T.B.; Mc Pherson, J.C. Apical diffusion of calcium hydroxide in an in vitro model. J. Endod. 2005, 31, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, J.F.; Rôças, I.N.; Lopes, H.P.; Magalhães, F.A.; de Uzeda, M. Elimination of Candida albicans infection of the radicular dentin by intracanal medications. J. Endod. 2003, 29, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanassiadis, B.; Abbott, P.V.; George, N.; Walsh, L.J. An in vitro study of the antimicrobial activity of some endodontic medicaments and their bases using an agar well diffusion assay. Aust. Dent. J. 2009, 54, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirife, J.; Herszage, L.; Joseph, A.; Bozzini, J.P.; Leardini, N.; Kohn, E.S. In vitro anti-microbial activity of concentrated polyethylene glycol 400 solutions. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1983, 24, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanassiadis, B.; Abbott, P.V.; George, N.; Walsh, L.J. An in vitro study of the antimicrobial activity of some endodontic medicaments against Enterococcus faecalis biofilms. Aust. Dent. J. 2010, 55, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanassiadis, B.; Abbott, P.V.; George, N.; Walsh, L.J. In vitro study of the inactivation by dentine of some endodontic medicaments and their bases. Aust. Dent. J. 2010, 55, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teoh, Y.Y.; Athanassiadis, B.; Walsh, L.J. The influence of aqueous and PEG 400 solvent vehicles on hydroxyl ion release from calcium hydroxide medicaments. Int. Dent. 2016, 11, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Fava, L.R.; Saunders, W.P. Calcium hydroxide pastes: Classification and clinical indications. Int. Endod. J. 1999, 32, 257–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lana, P.E.; Scelza, M.F.; Silva, L.E.; Mattos-Guaraldi, A.L.; Hirata Júnior, R. Antimicrobial activity of calcium hydroxide pastes on Enterococcus faecalis cultivated in root canal systems. Braz. Dent. J. 2009, 20, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, R.K.; Guerreiro-Tanomaru, J.M.; Faria-Júnior, N.B.; Tanomaru-Filho, M. Effectiveness of calcium hydroxide-based intracanal medicaments against Enterococcus faecalis. Int. Endod. J. 2012, 45, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreiro-Tanomaru, J.M.; Chula, D.G.; de Pontes Lima, R.K.; Berbert, F.L.; Tanomaru-Filho, M. Release and diffusion of hydroxyl ion from calcium hydroxide-based medicaments. Dent. Traumatol. 2012, 28, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrela, C.; Pécora, J.D.; Souza-Neto, M.D.; Estrela, C.R.; Bammann, L.L. Effect of vehicle on antimicrobial properties of calcium hydroxide pastes. Braz. Dent. J. 1999, 10, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Camões, I.C.; Salles, M.R.; Chevitarese, O.; Gomes, G.C. Influence on pH of vehicle containing glycerin used with calcium hydroxide. Dent. Traumatol. 2003, 19, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yücel, A.C.; Aksoy, A.; Ertaş, E.; Güvenç, D. The pH changes of calcium hydroxide mixed with six different vehicles. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2007, 103, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camões, I.C.; Salles, M.R.; Chevitarese, O. Ca2+ diffusion through dentin of Ca(OH)2 associated with seven different vehicles. J. Endod. 2003, 29, 822–825. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Camões, I.C.G.; Salles, M.R.; Chevitarese, O.; Gomes, L.N. Diffusion of Ca(OH)2 associated with different vehicles: Chromatographic study (high-performance liquid chromatography). J. Endod. 2004, 30, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, Z.; Dummer, P.M. Properties and applications of calcium hydroxide in endodontics and dental traumatology. Int. Endod. J. 2011, 44, 697–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flahaut, S.; Hartke, A.; Giard, J.C.; Auffray, Y. Alkaline stress response in Enterococcus faecalis: Adaptation, crossprotection, and changes in protein synthesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 812–814. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.; Davies, J.K.; Sundqvist, G.; Figdor, D. Mechanisms involved in the resistance of Enterococcus faecalis to calcium hydroxide. Int. Endod. J. 2002, 35, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, P.-D. Therapie Ocalexique, Etudes Endodontiques; Maloine: Paris, France, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Tremillon, B. Chemistry in Non-Aqueous Solvents; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Roses, M. Ionic equilibria in non-aqueous solvents. Part 1. General equations for calculation of pH, dissociation constants and reference potentials from potentiometric data. Anal. Chim. Acta 1993, 276, 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Quitmeyer, J. pH Measurement in aqueous and nonaqueous solutions: When used in combination with titration, pH measurement is a simple method to monitor bath concentration. Met. Finish. 2008, 106, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izutsu, K. Electrochemistry in Nonaqueous Solutions, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 180–183. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, B.G. Acids and Bases: Solvent Effects on Acid–Base Strength; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 2013; pp. 41–53. [Google Scholar]
- Chipperfield, J.R. Non-Aqueous Solvents; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 18–30. [Google Scholar]
- Audrieth, L.F.; Kleinberg, J. Non-Aqueous Solvents—Applications as Media for Chemical Reactions; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1953; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, R.G. Determination of pH. Theory and Practice; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1964; pp. 201–288. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, R. pH measurement. In Instrument Engineers’ Handbook, Volume 1: Process Measurement and Analysis, 4th ed.; Liptak, B.G., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 1580–1581. [Google Scholar]
- Hills, G.J. Reference electrodes in nonaqueous solutions. In Reference Electrodes, Theory and Practice; Ives, D.J.G., Janz, G.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1961; p. 433. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, C.K. Nonaqueous solvents for electroanalytical use. In Electroanalytical Chemistry, Volume 3; Bard, A.J., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1969; p. 57. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, J.N. Reference electrodes in aprotic organic solvents. In Advances in Electrochemistry and Electrochemical Engineering, Volume 7; Delahay, P., Tobias, C.W., Eds.; Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1970; p. 77. [Google Scholar]
- Lund, H. Practical problems in electrolysis. In Organic Electrochemistry, 4th ed.; Lund, H., Hammerich, O., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2001; p. 246. [Google Scholar]
- Izutsu, K. Reference electrodes for use in nonaqueous solutions. In Handbook of Reference Electrodes; Inzelt, G., Lewenstam, A., Scholz, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 145–187. [Google Scholar]
- Izutsu, K.; Nakamura, T.; Hiraoka, S. Use of pH-Sensitive ISFETs as Sensors for pH in Nonaqueous Solutions and for Proton Solvation. Chem. Lett. 1993, 22, 1843–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
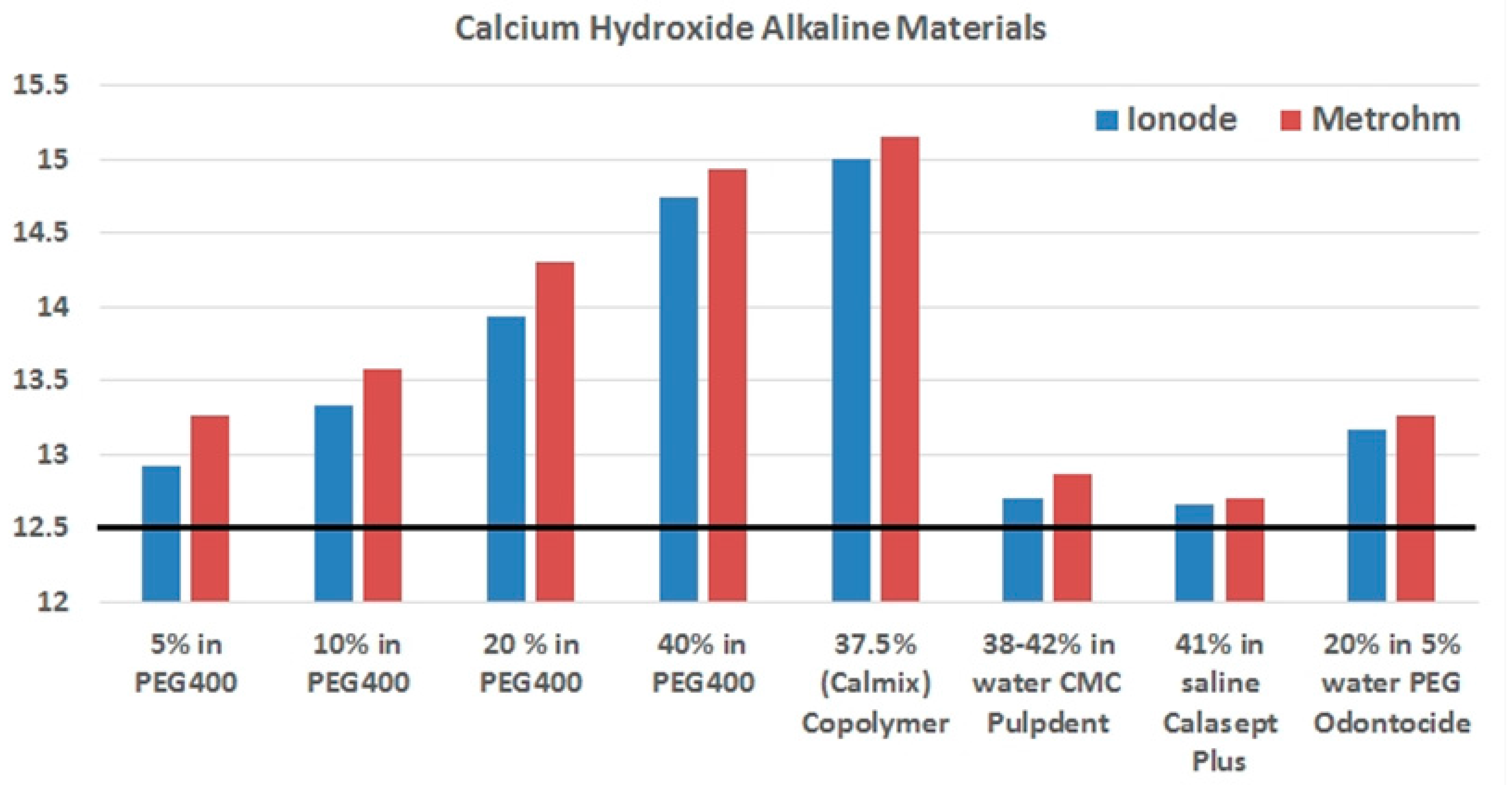
| Name | Ca(OH)2 Content and Vehicle | Measured pH |
|---|---|---|
| ApexCalTM | 29% in water + PEG + glycerin | 12.4 |
| CalenTM | 49.8% in PEG 400 | N/A |
| Calasept PlusTM | 41.1% in saline (water) | 12.6 |
| CalcipulpeTM | 20% in water | 11.8 |
| CalmixTM | 37.5% in PEG 400 + PEG 3350 | 15.0 |
| DT TempTM | 50% in water | 12.6 |
| OdontocideTM | 20% in PEG 400 + water | 13.2 |
| PulpdentTM | 42% in water | 12.7 |
| Ultracal XSTM | 35% in water | 12.5 |
| Solvent | Lower Limit | Upper Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 0 | 14 |
| Sulfolane | −10 | 31 |
| Methanol | 1.8 | 17.2 |
| Ammonia | 18 | 32.5 |
| Ethanol | −4 | 16 |
| Acetone | −5 | 20 |
| Product | KCl Electrode | TEABr Electrode |
|---|---|---|
| Pulpdent | 12.706 (0.006) | 12.862 (0.008) |
| Calasept Plus | 12.662 (0.017) | 12.710 (0.012) |
| Odontocide | 13.170 (0.025) | 13.062 (0.450) |
| Calmix | 14.996 (0.010) | 15.162 (0.108) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Athanassiadis, B.; Walsh, L.J. Aspects of Solvent Chemistry for Calcium Hydroxide Medicaments. Materials 2017, 10, 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101219
Athanassiadis B, Walsh LJ. Aspects of Solvent Chemistry for Calcium Hydroxide Medicaments. Materials. 2017; 10(10):1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101219
Chicago/Turabian StyleAthanassiadis, Basil, and Laurence J. Walsh. 2017. "Aspects of Solvent Chemistry for Calcium Hydroxide Medicaments" Materials 10, no. 10: 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101219
APA StyleAthanassiadis, B., & Walsh, L. J. (2017). Aspects of Solvent Chemistry for Calcium Hydroxide Medicaments. Materials, 10(10), 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101219






