Study on the Shielding Effectiveness of an Arc Thermal Metal Spraying Method against an Electromagnetic Pulse
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Experimental Variables
2.2. Test Specimens for Experiments
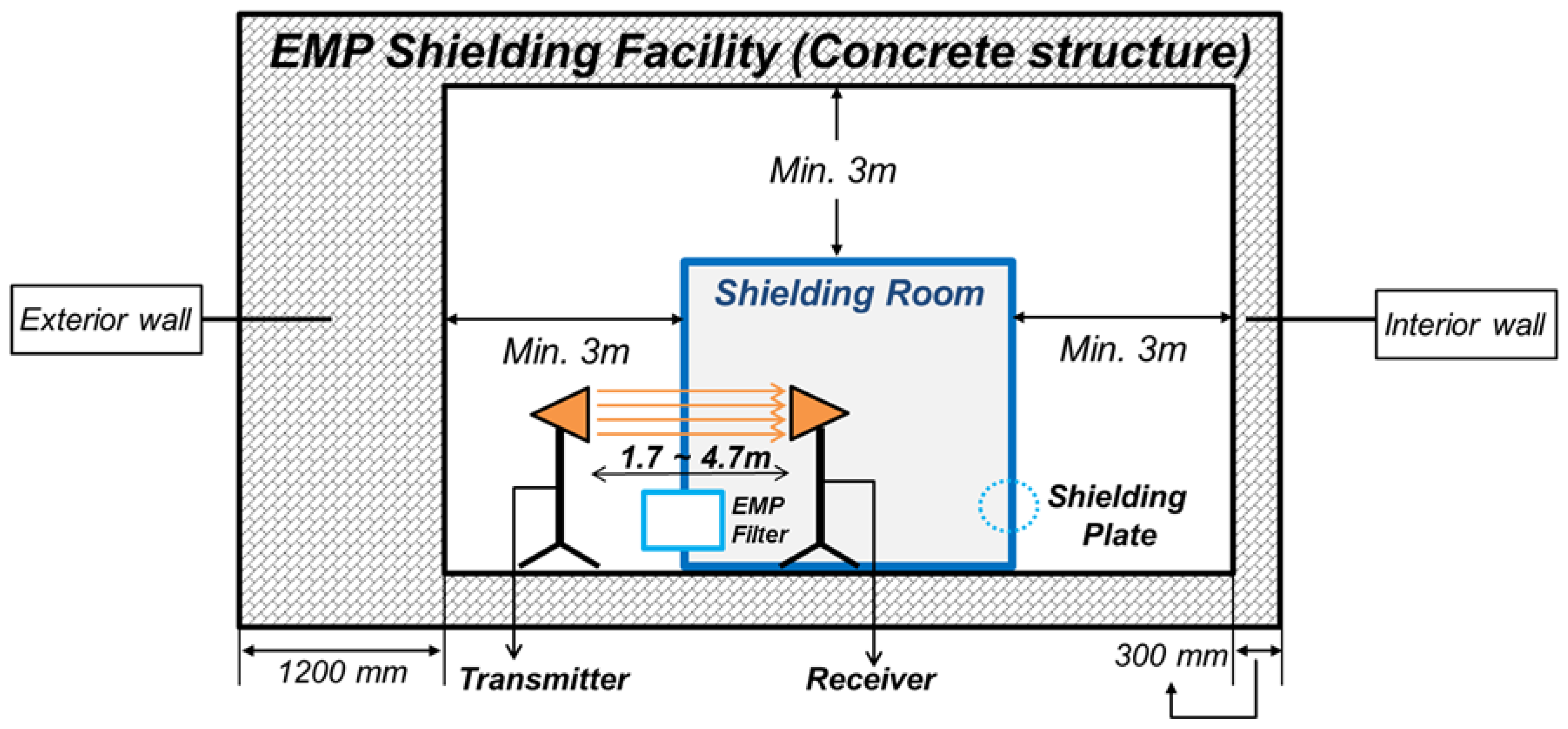
2.3. Experimental Procedures
2.4. Standards on Shielding Effectiveness against EMP and SE Tests
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Shielding Effectiveness of Tempered Glass
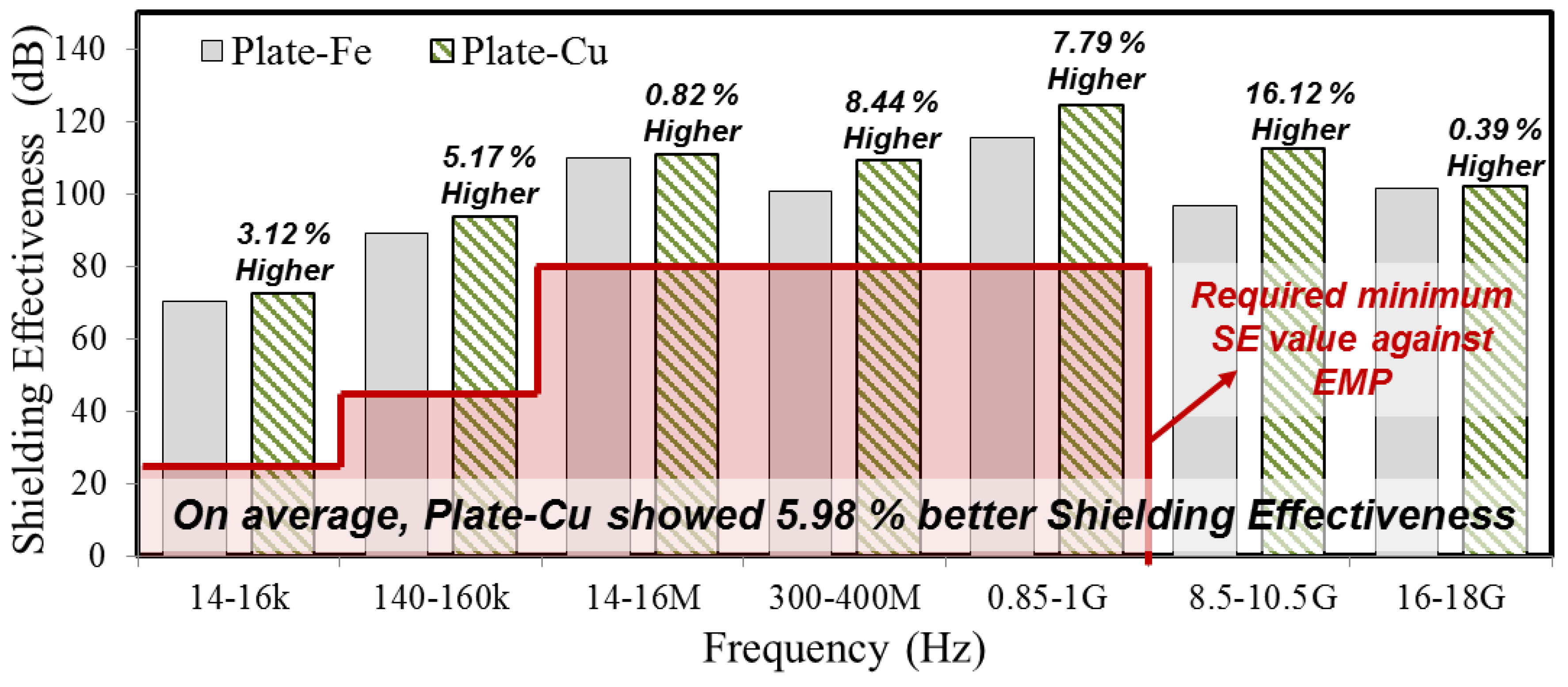
3.2. Shielding Effectiveness of Metal Plate
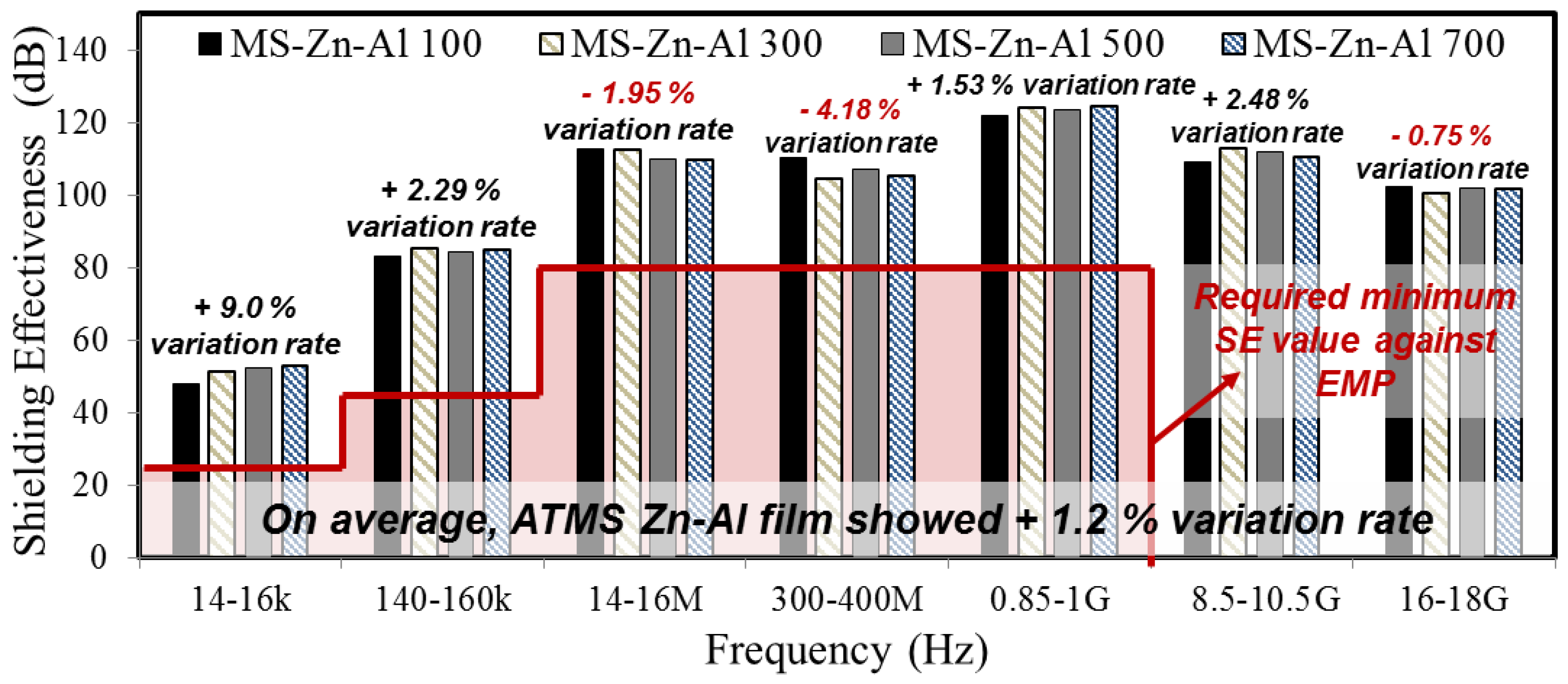
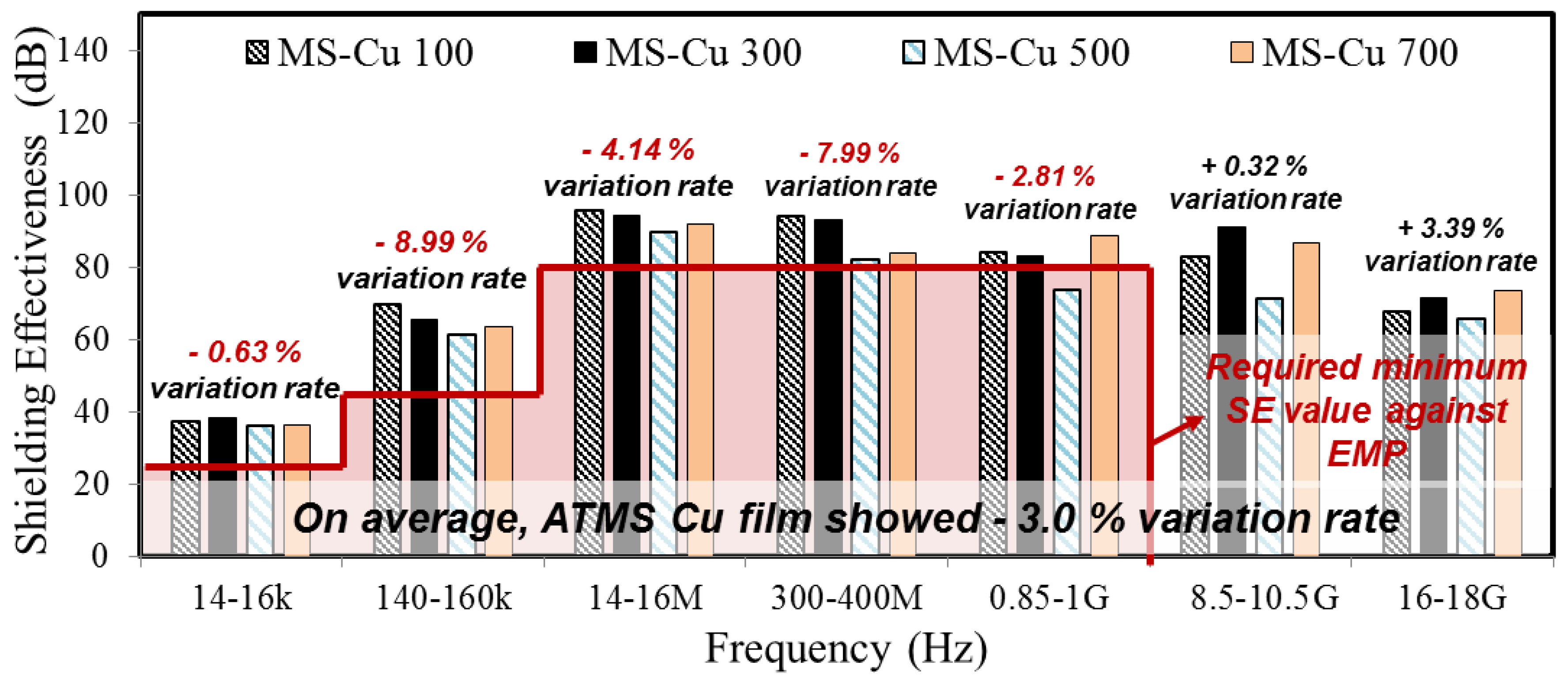
3.3. Shielding Effectiveness of ATMS Coating
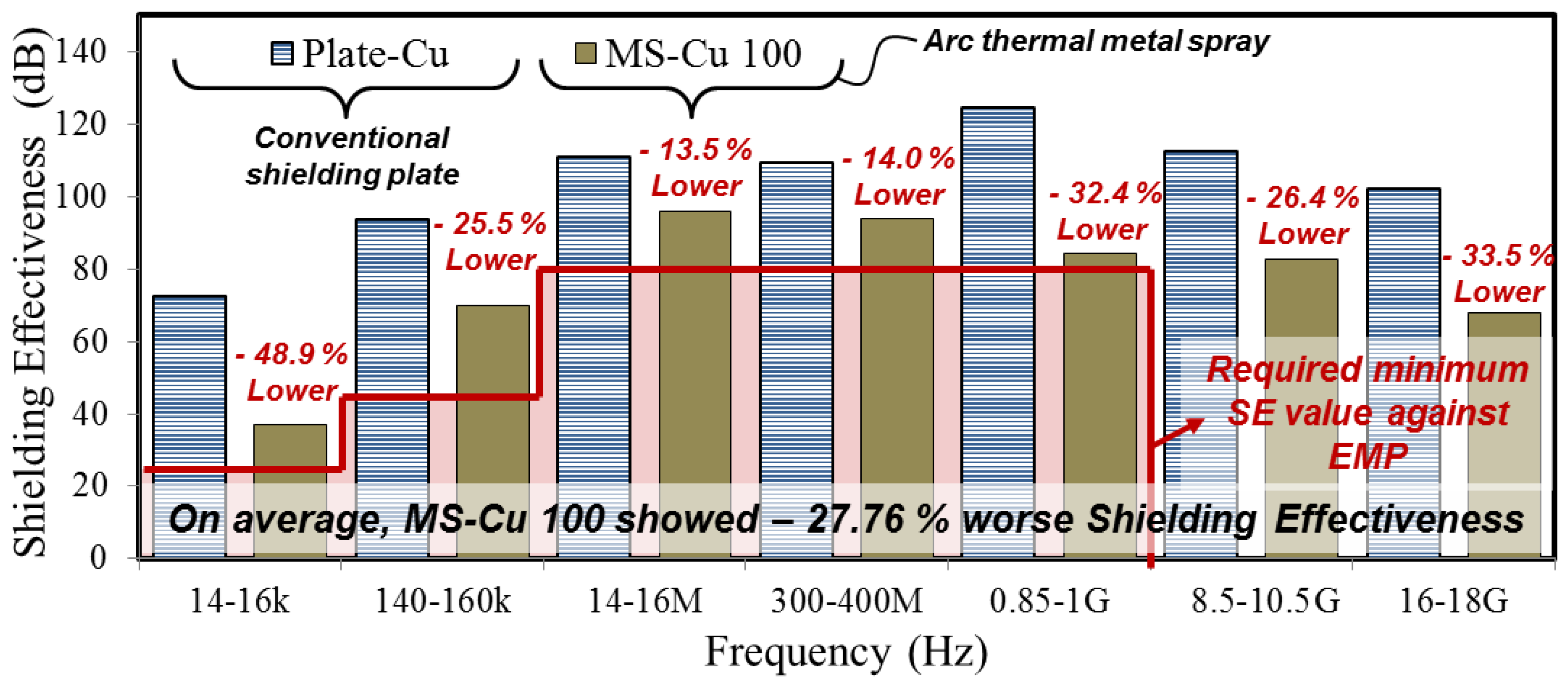
3.4. Shielding Effectiveness between Metal Plate and ATMS Coating
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H. Truth of EMP threat and development plan. DefenseTech 2013, 414, 98–103. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Choi, T.; Cho, W. Countermeasure of Electromagnetic Pulse (EMP). DefenseTech 1992, 157, 54–59. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Cho, G.; Cheon, J. Study on defense measure of EMP of nuclear and electromagnetic pulse weapon. DefenseTech 2007, 345, 52–59. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, G. The Swiss EMP Concept of General Defense. IEEE Antennas Propag. Soc. Newsl. 1987, 29, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Fugetsu, B.; Sano, E.; Sunada, M.; Sambongi, Y.; Shibuya, T.; Wang, X.; Hiraki, T. Electrical conductivity and electromagnetic interference shielding efficiency of carbon nanotube/cellulose composite paper. Carbon 2008, 46, 1256–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Kim, K.; Lee, C.Y.; Joo, J.; Cho, S.J.; Yoon, H.S.; Pejakovic, D.A.; Yoo, J.W.; Epstein, A. Electrical conductivity and electromagnetic interference shielding of multiwalled carbon nanotube composites containing Fe catalyst. J. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 589–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Huang, Y.; Du, F.; He, X.B.; Lin, X.; Gao, H.J.; Ma, Y.F.; Li, F.F.; Chen, Y.S.; Eklund, P.C. Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Shielding of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Epoxy Composites. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saleh, M.H.; Sundararaj, U. Electromagnetic interference shielding mechanisms of CNT/polymer composites. Carbon 2009, 47, 1738–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.F.; Guo, T.Y.; Chen, Y.S. Molecular-Level Dispersion of Graphene into Poly(vinyl alcohol) and Effective Reinforcement of their Nanocomposites. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 2297–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomassin, J.M.; Pagnoulle, C.; Bednarz, L.; Huynen, I.; Jerome, R.; Detrembleur, C.J. Foams of polycaprolactone/MWNT nanocomposites for efficient EMI reduction. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Theilmann, P.; Yang, K.Q.; Rao, A.M.; Bandaru, P.R. The influence of coiled nanostructure on the enhancement of dielectric constants and electromagnetic shielding efficiency in polymer composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 043115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.B.; Zheng, W.G.; Yan, Q.; Yang, Y.; Lu, Z.H.; Wang, J.W.; Ji, G.Y.; Yu, Z.Z. Electrically conductive polyethylene terephthalate/graphene nanocomposites prepared by melt compounding. Polymer 2010, 51, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.H.; Liu, Y.Y.; Li, J.Y. Comparison of the effective conductivity between composites reinforced by graphene nanosheets and carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 243121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.B.; Li, Z.M.; Shi, L.; Bian, X.C.; Xiang, Z.D. Ultralight Conductive Carbon-Nanotube–Polymer Composite. Small 2007, 3, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.L.; Gupta, M.C. Novel Carbon Nanotube−Polystyrene Foam Composites for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 2131–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.L.; Gupta, M.C.; Dudley, K.L.; Lawrence, R.W. Conductive carbon nano fiber polymer foam structures. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1999–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-B.; Yan, Q.; Zheng, W.-G.; He, Z.; Yu, Z.-Z. Tough Graphene-Polymer Microcellular Foams for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esawi, A.M.K.; Farag, M.M. Carbon nanotube reinforced composites: Potential and current challenges. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 2394–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W. Defense measure of EMP and required technique. Proc. Korea Electromagnet. Eng. Sci. 2013, 24, 79–96. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Fei, G.; Bihua, Z.; Cheng, G.; Hailin, C. Analysis of shielding effectiveness of conductive cement-based materials in HEMP environment. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology (ICMMT 2008), Nanjing, China, 21–24 April 2008; Available online: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=4540721 (accessed on 10 March 2015).
- Fei, G.; Bihua, Z. Analysis of shielding effectiveness of monolayer and double layer cement shield rooms to HEMP. In Proceedings of the 2008 China-Japan Joint Microwave Conference, Shanghai, China, 10–12 September 2008; pp. 505–508. [Google Scholar]
- Hyun, S.Y.; Du, J.K.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, C.S.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, W.D.; Yook, J.G. Analysis of shielding effectiveness of reinforced concrete against high-altitude electromagnetic pulse. IEEE. Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2014, 56, 1488–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, C.; Yun, Yi.; Cheng, G.; Bihua, Z.; Wei, W. Analysis of shielding effectiveness of reinforced concrete in high power electromagnetic environment. In Proceedings of the 2003 Asia-Pacific Conference on Environmental Electromagnetics (CEEM 2003), Hangzhou, China, 4–7 November 2003; pp. 547–553. Available online: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=1282391 (accessed on 11 Sepetember 2016).
- Nenghong, X.; Xueqin, Y.; Wenwu, S. Shielding effectiveness and coupling characteristic of metallic enclosures with apertures under EMP. In Proceedings of the 2009 Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC 2009), Wuhan, China, 27–31 March 2009; pp. 1–4. Available online: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=4918742 (accessed on 25 June 2017).
- Cheng, G.; Bihua, Z.; Bin, C.; Yun, Y.; Yanxin, L. The penetrating of EMP fields into a metal shielding enclosure by a slot. In Proceedings of the 2002 3rd International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Beijing, China, 21–24 May 2002; pp. 127–130. Available online: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=1177382 (accessed on 1 July 2017).
- Seo, M.J.; Chi, S.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, W.C.; Kang, H.J.; Huh, C.S. Electromagnetic wave shielding effectiveness measurement method of EMP protection facility. J. Korea Inst. Electromagnet. Eng. Sci. 2014, 25, 548–558. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, L. The Science and Engineering of Thermal Spray Coatings, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.-S.; Singh, J.K.; Ismail, M.A.; Bhattacharya, C. Corrosion resistance properties of aluminum coating applied by arc thermal metal spray in SAE J2334 solution with exposure periods. Metals 2016, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Singh, J.K.; Park, J.H. Pore blocking characteristics of corrosion products formed on Aluminum coating produced by arc thermal metal spray process in 3.5wt. % NaCl solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 113, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Park, J.-H.; Singh, J.K.; Ismail, M.A. Protection of reinforced concrete structure of waste water treatment reservoirs with stainless steel coating using arc thermal spraying technique in acidified water. Materials 2016, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaliampalias, D.; Vourlias, G.; Pavlidou, E.; Stergioudis, G.; Skolianos, S.; Chrissafis, K. High temperature oxidation and corrosion in marine environments of thermal spray deposited coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 3104–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Singh, J.K.; Ismail, M.A. An effective and novel pore sealing agent to enhance the corrosion resistance performance of Al coating in artificial ocean water. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.H.; Lee, M.S. Experimental study on the corrosion protection properties and anticorrosive life of the Zn/Al metal spray method according to the contents ratio of Zn and Al. J. Arch. Inst. Korea 2003, 19, 59–65. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Choe, H.B.; Lee, H.S.; Shin, J. Experimental study on the electrochemical anti-corrosion properties of steel structures applying the arc thermal metal spraying method. Materials 2014, 7, 7722–7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Ismail, M.A.; Choe, H.B. Arc thermal metal spray for the protection of steel structures: An overview. Corros. Rev. 2015, 33, 31–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Lee, H.S. An experimental study on the electromagnetic shielding efficiency of concrete applying metal spraying finishing method. Proc. Arch. Inst. Korea 2005, 25, 225–228. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- High-Altitude Electromagnetic Pulse (HEMP) Protection for Ground-Based C4I Facilities Performing Critical, Time-Urgent Missions Part 1 Fixed Facilities, MIL-STD-188-125-1, United States Military Standard. Available online: http://www.futurescience.com/emp/MIL-STD-188-125-1.pdf. (accessed on 1 October 2017).
- The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). IEEE Standard Method for Measuring the Effectiveness of Electromagnetic Shielding Enclosures, IEEE Std 299-1997; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA.
- Yang, J.H.; Nam, S.W. Electromagnetic pulse coupling into naval warship and protective measures. J. Korea Inst. Electromagnet. Eng. Sci. 2014, 25, 426–433. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, D.; Masi, J. Composite Material for EMI/EMP Hardening Protection in Marine Environments. US5066424 A, 20 June 1990. [Google Scholar]
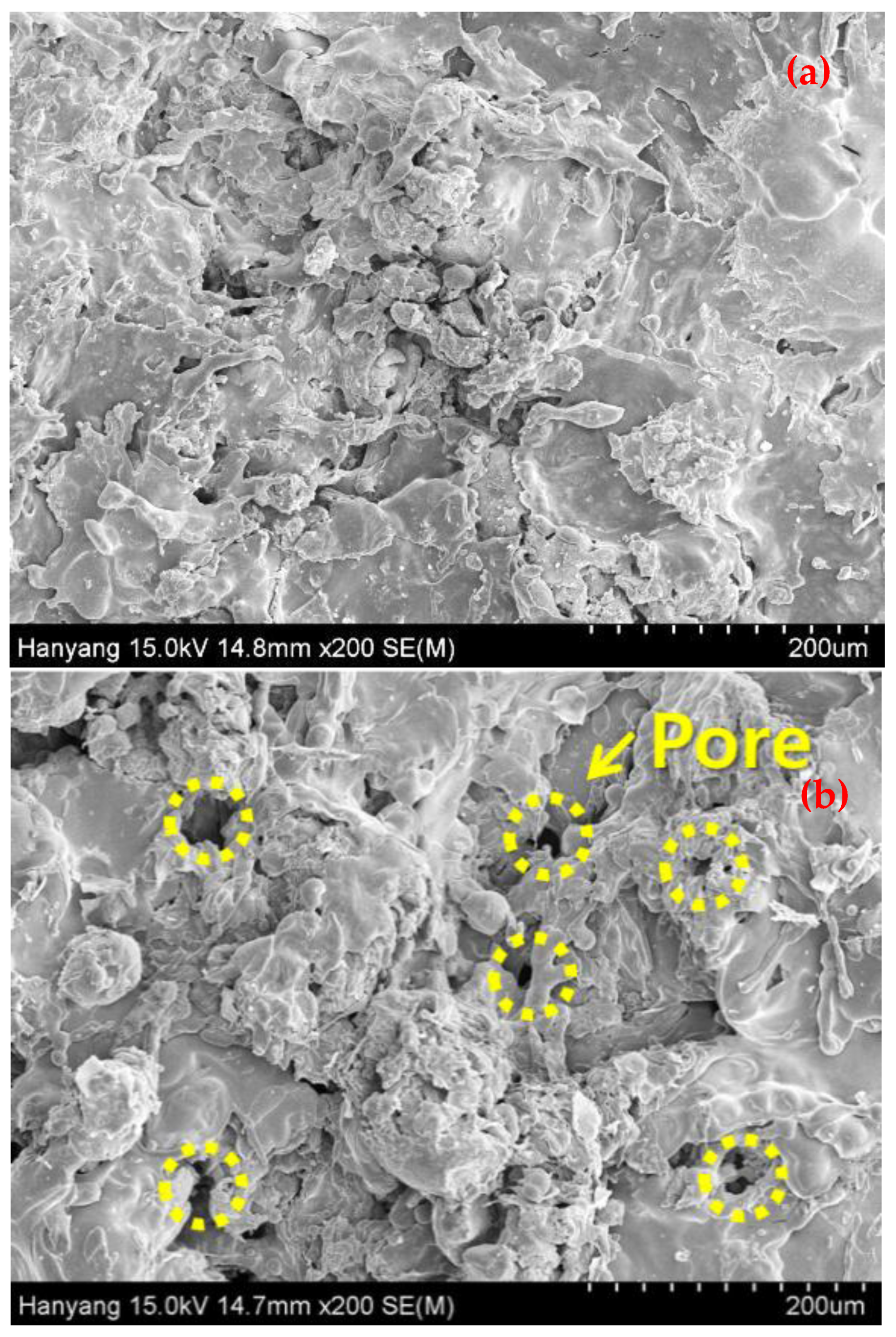




| Experimental Variables | Experimental Parameters |
|---|---|
| EMP Shielding method | Conventional shielding plate |
| Arc thermal metal spray | |
| EMP Shielding material | Fe |
| Cu | |
| Zn-Al | |
| Thickness of ATMS coating | 100 μm |
| 300 μm | |
| 500 μm | |
| 700 μm |
| No. | Specimens | Shielding Material | Shielding Method | Coating Thickness (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tempered glass1 | - | - | - |
| 2 | Plate2-Fe | Fe (steel) | Metal plate | 3000 |
| 3 | Plate-Cu | Cu (copper) | 3000 | |
| 4 | MS3-Zn-Al 100 | Zn-Al4 (zinc and aluminum) | Arc thermal metal spraying method | 100 |
| 5 | MS-Zn-Al 300 | 300 | ||
| 6 | MS-Zn-Al 500 | 500 | ||
| 7 | MS-Zn-Al 700 | 700 | ||
| 8 | MS-Cu 100 | Cu | 100 | |
| 9 | MS-Cu 300 | 300 | ||
| 10 | MS-Cu 500 | 500 | ||
| 11 | MS-Cu 700 | 700 |
| Frequency (Hz) | Required Minimum SE (dB) | Shielding Effectiveness (dB) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tempered Glass | Plate-Fe | Plate-Cu | ||
| 14–16 k | 23.5 | 0.4 | 70.4 | 72.6 |
| 140–160 k | 43.5 | 0.1 | 89.0 | 93.6 |
| 14–16 M | 80 | 1.5 | 109.9 | 110.8 |
| 300–400 M | 80 | 0.5 | 100.7 | 109.2 |
| 0.85–1 G | 80 | 1.5 | 115.6 | 124.6 |
| 8.5–10.5 G | - | 1.3 | 96.8 | 112.4 |
| 16–18 G | - | 1.1 | 101.5 | 101.9 |
| Average SE (dB) | 0.91 | 97.70 | 103.59 | |
| Frequency (Hz) | Required Minimum SE (dB) | Shielding Effectiveness (dB) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS-Zn-Al 100 | MS-Zn-Al 300 | MS-Zn-Al 500 | MS-Zn-Al 700 | ||
| 14–16 k | 23.5 | 47.8 | 51.2 | 52.3 | 52.8 |
| 140–160 k | 43.5 | 82.9 | 85.4 | 84.2 | 84.8 |
| 14–16 M | 80 | 112.7 | 112.3 | 109.7 | 109.5 |
| 300–400 M | 80 | 110.1 | 104.4 | 107.0 | 105.1 |
| 0.85–1 G | 80 | 122.0 | 123.9 | 123.4 | 124.3 |
| 8.5–10.5 G | - | 108.9 | 112.8 | 111.7 | 110.3 |
| 16–18 G | - | 102.1 | 100.5 | 102.0 | 101.5 |
| Average SE (dB) | 98.07 | 98.64 | 98.61 | 98.33 | |
| Frequency (Hz) | Required Minimum SE (dB) | Shielding Effectiveness (dB) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS-Cu 100 | MS-Cu 300 | MS-Cu 500 | MS-Cu 700 | ||
| 14–16 k | 23.5 | 37.1 | 38.2 | 36.0 | 36.4 |
| 140–160 k | 43.5 | 69.7 | 65.4 | 61.4 | 63.5 |
| 14–16 M | 80 | 95.8 | 94.1 | 89.6 | 91.8 |
| 300–400 M | 80 | 93.9 | 93.2 | 82.1 | 83.9 |
| 0.85–1 G | 80 | 84.2 | 83.0 | 73.7 | 88.8 |
| 8.5–10.5 G | - | 82.7 | 91.2 | 71.2 | 86.5 |
| 16–18 G | - | 67.8 | 71.3 | 65.5 | 73.5 |
| Average SE (dB) | 75.89 | 76.63 | 68.50 | 74.91 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.-S.; Choe, H.-B.; Baek, I.-Y.; Singh, J.K.; Ismail, M.A. Study on the Shielding Effectiveness of an Arc Thermal Metal Spraying Method against an Electromagnetic Pulse. Materials 2017, 10, 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101155
Lee H-S, Choe H-B, Baek I-Y, Singh JK, Ismail MA. Study on the Shielding Effectiveness of an Arc Thermal Metal Spraying Method against an Electromagnetic Pulse. Materials. 2017; 10(10):1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101155
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Han-Seung, Hong-Bok Choe, In-Young Baek, Jitendra Kumar Singh, and Mohamed A. Ismail. 2017. "Study on the Shielding Effectiveness of an Arc Thermal Metal Spraying Method against an Electromagnetic Pulse" Materials 10, no. 10: 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101155
APA StyleLee, H.-S., Choe, H.-B., Baek, I.-Y., Singh, J. K., & Ismail, M. A. (2017). Study on the Shielding Effectiveness of an Arc Thermal Metal Spraying Method against an Electromagnetic Pulse. Materials, 10(10), 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101155







