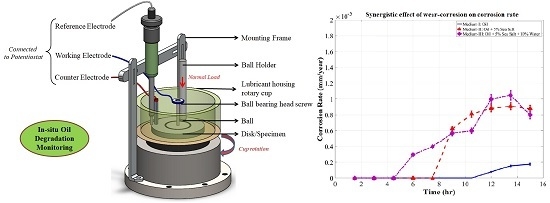
Performance Analysis of Retrofitted Tribo-Corrosion Test Rig for Monitoring In Situ Oil Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design and Experimentation
2.1. Retrofitting of Ball-On-Disk Test Rig
2.2. Materials
2.3. Experimentation
3. Results and Discussion
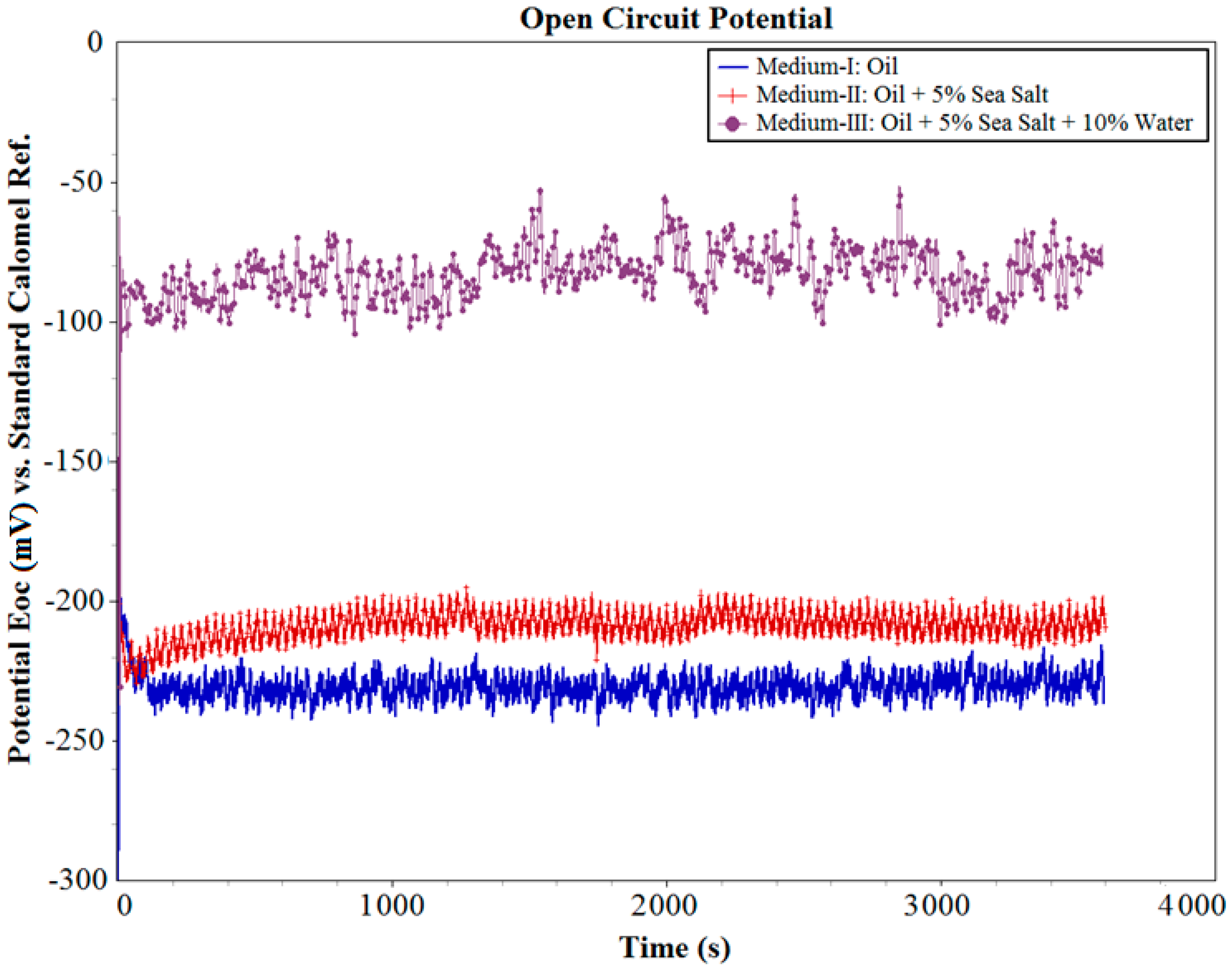
3.1. Open Circuit Potential (OCP)
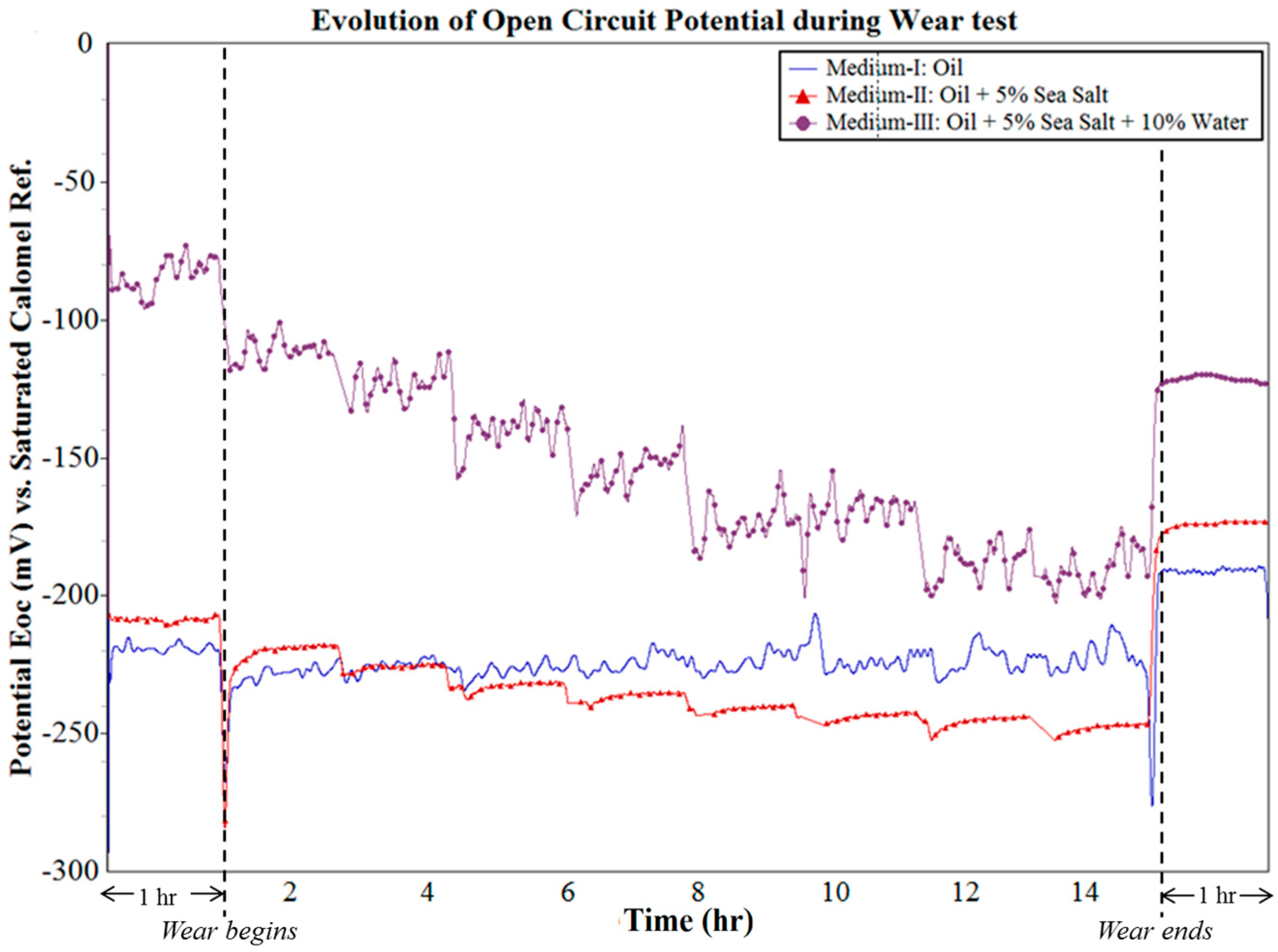
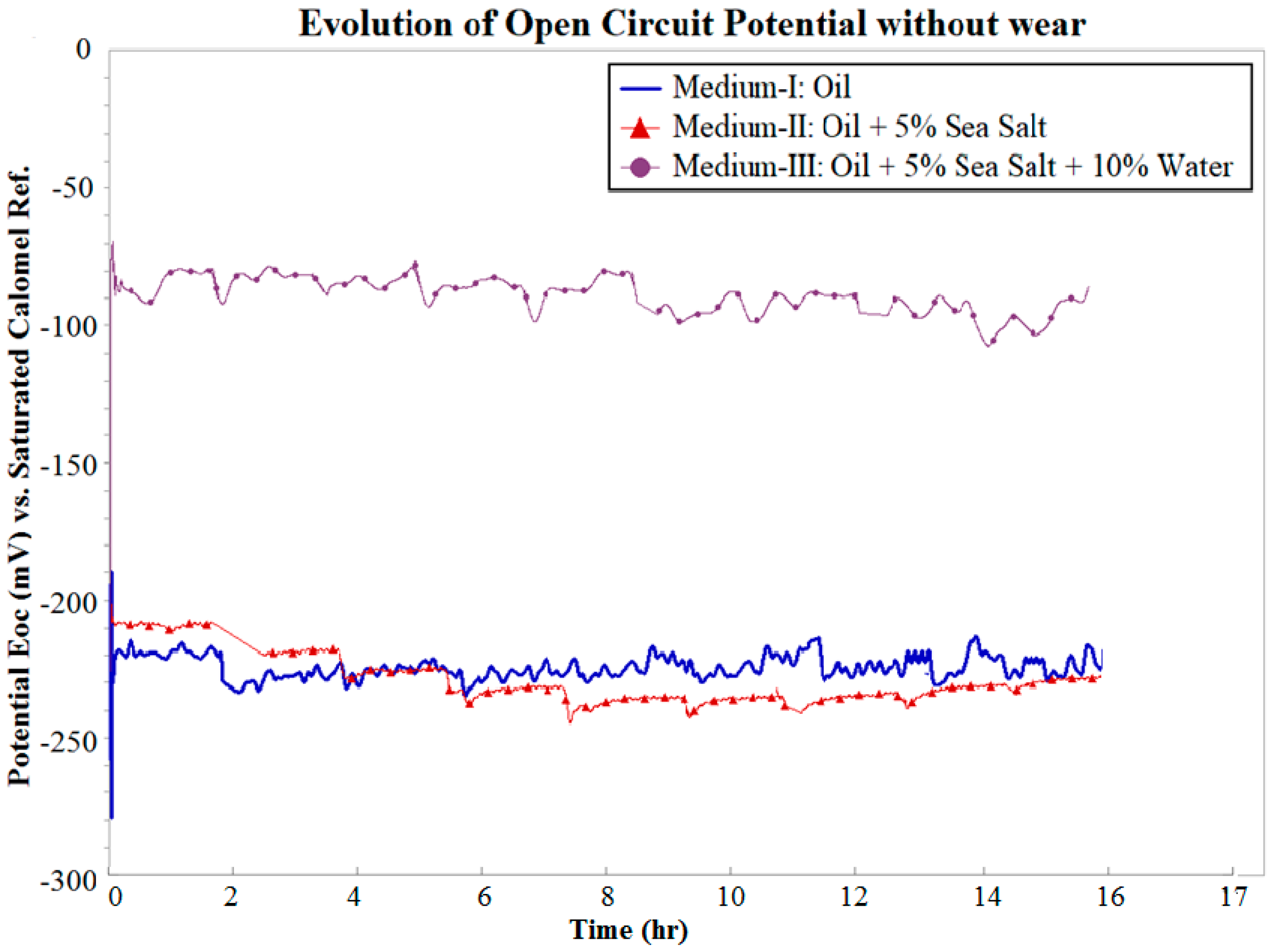
3.2. Influence of Wear on OCP
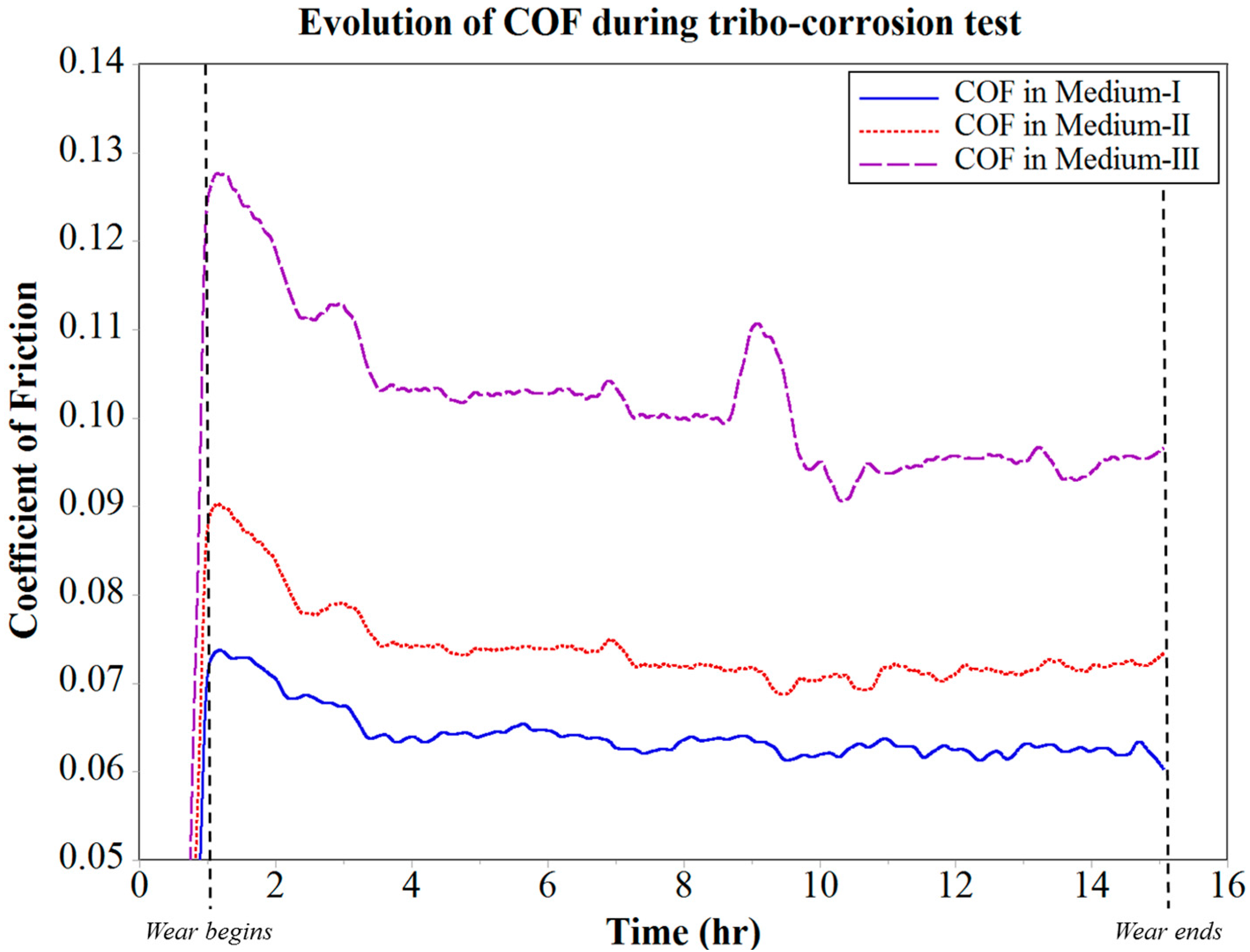
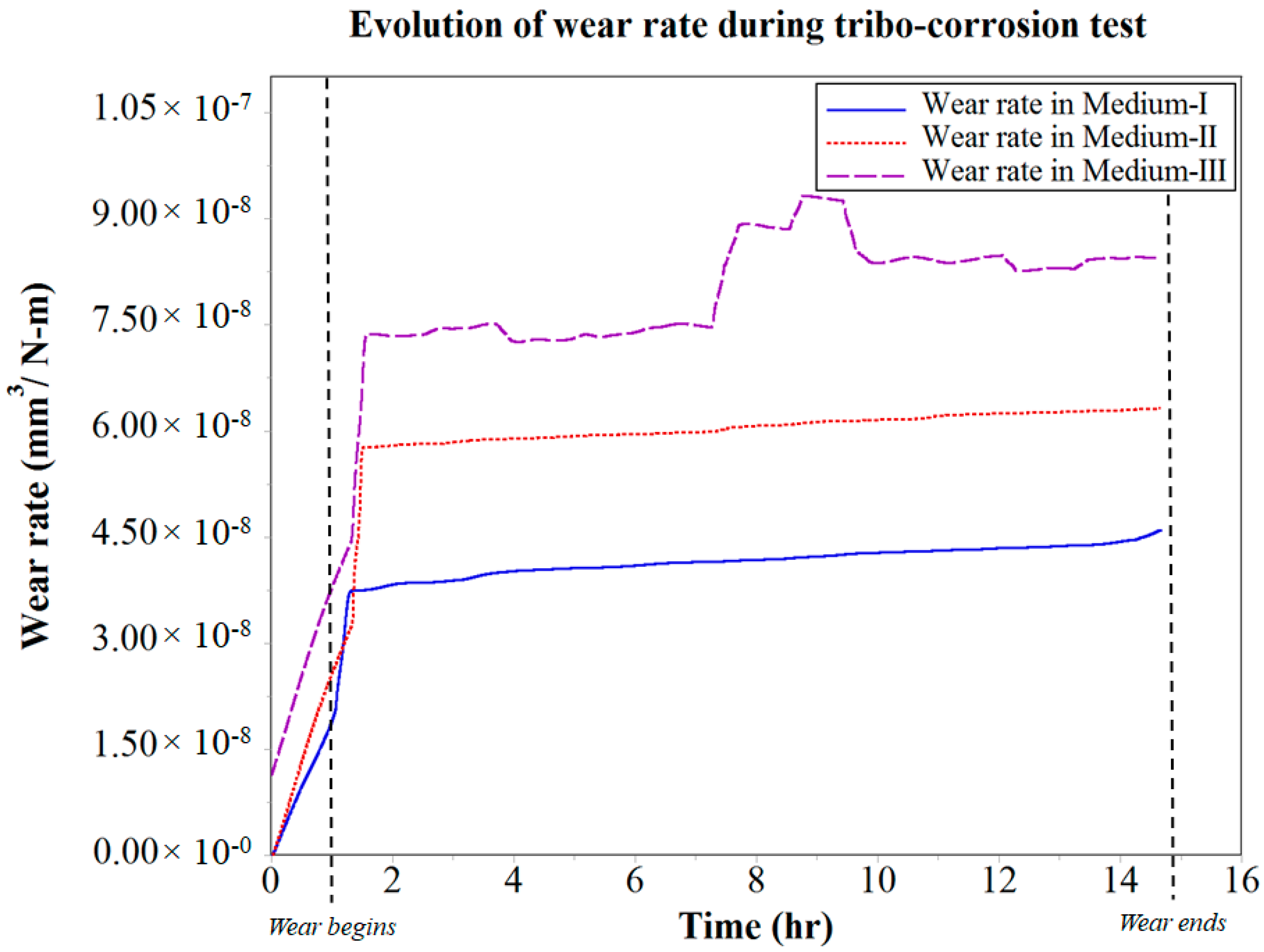
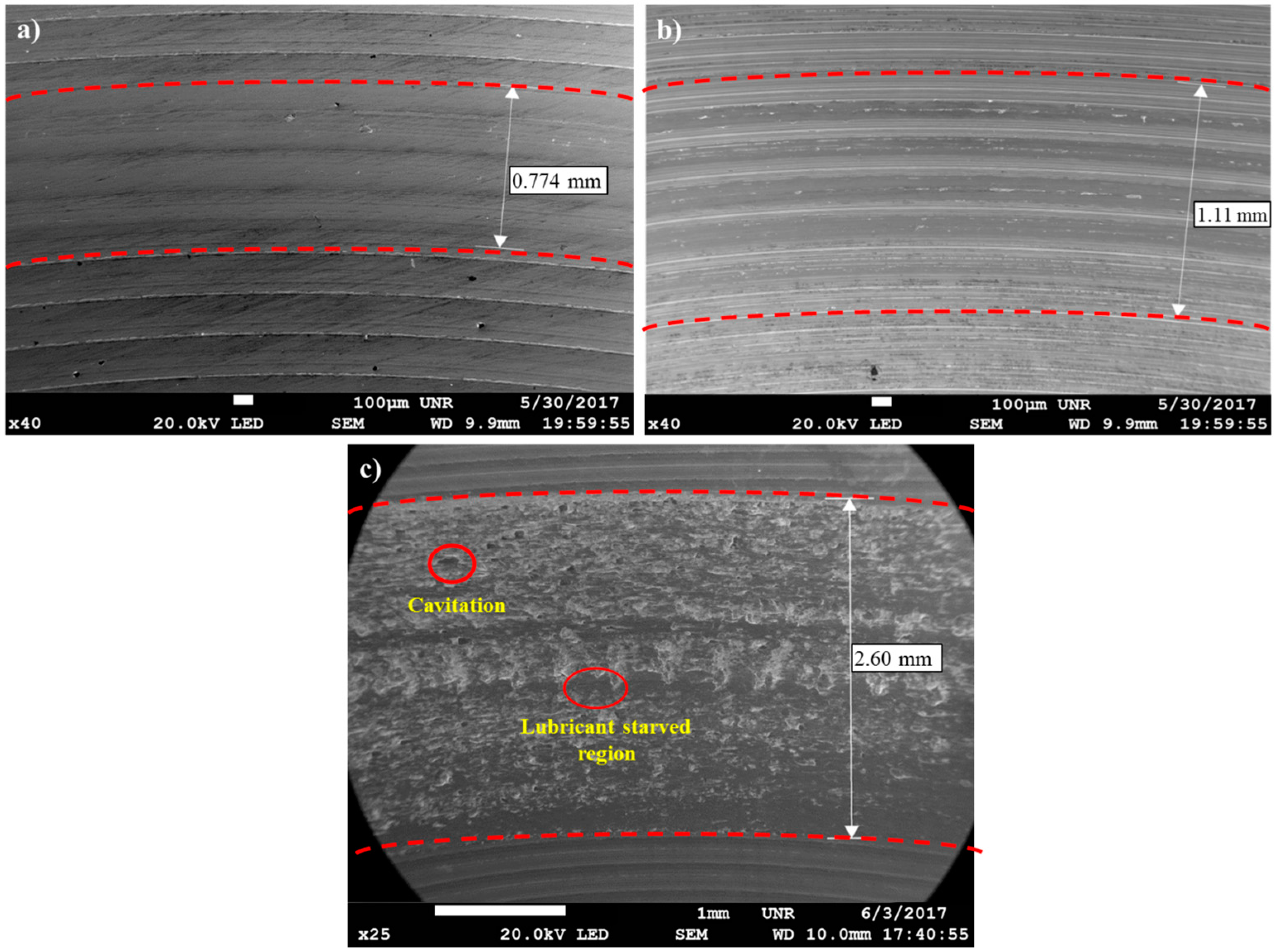
3.3. Analysis of Coefficient of Friction (COF) and Wear during Tribo-Corrosion Test
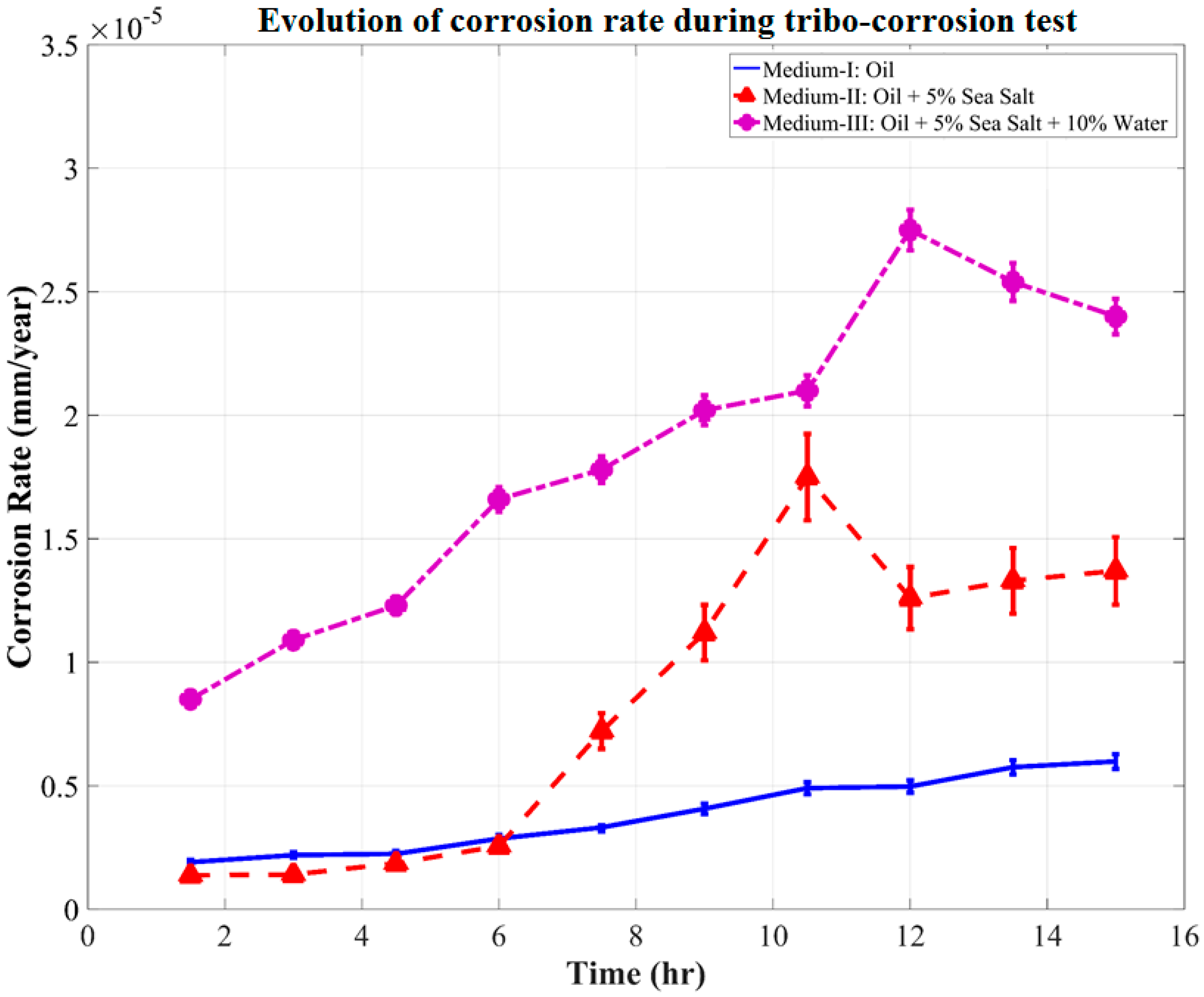
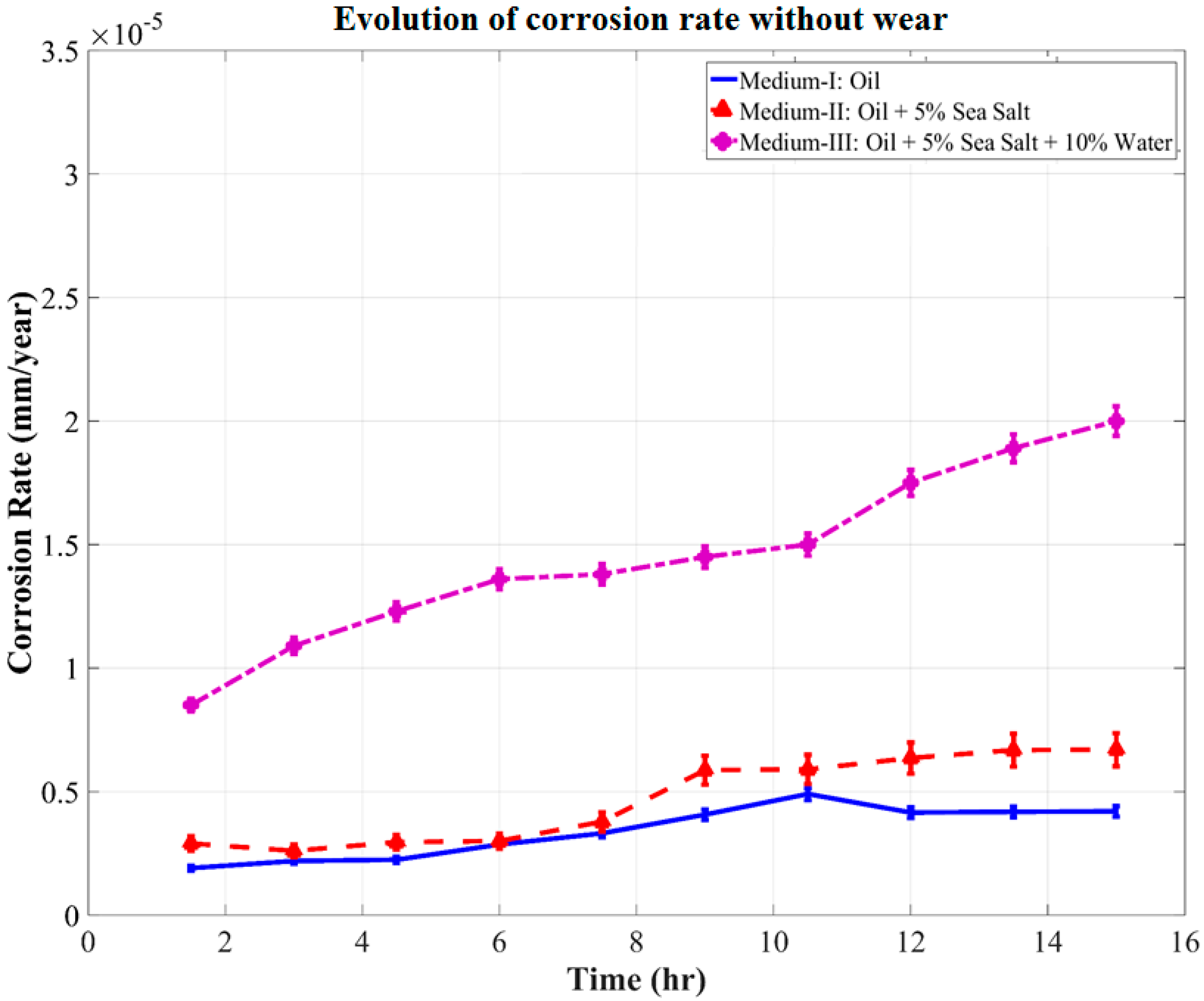
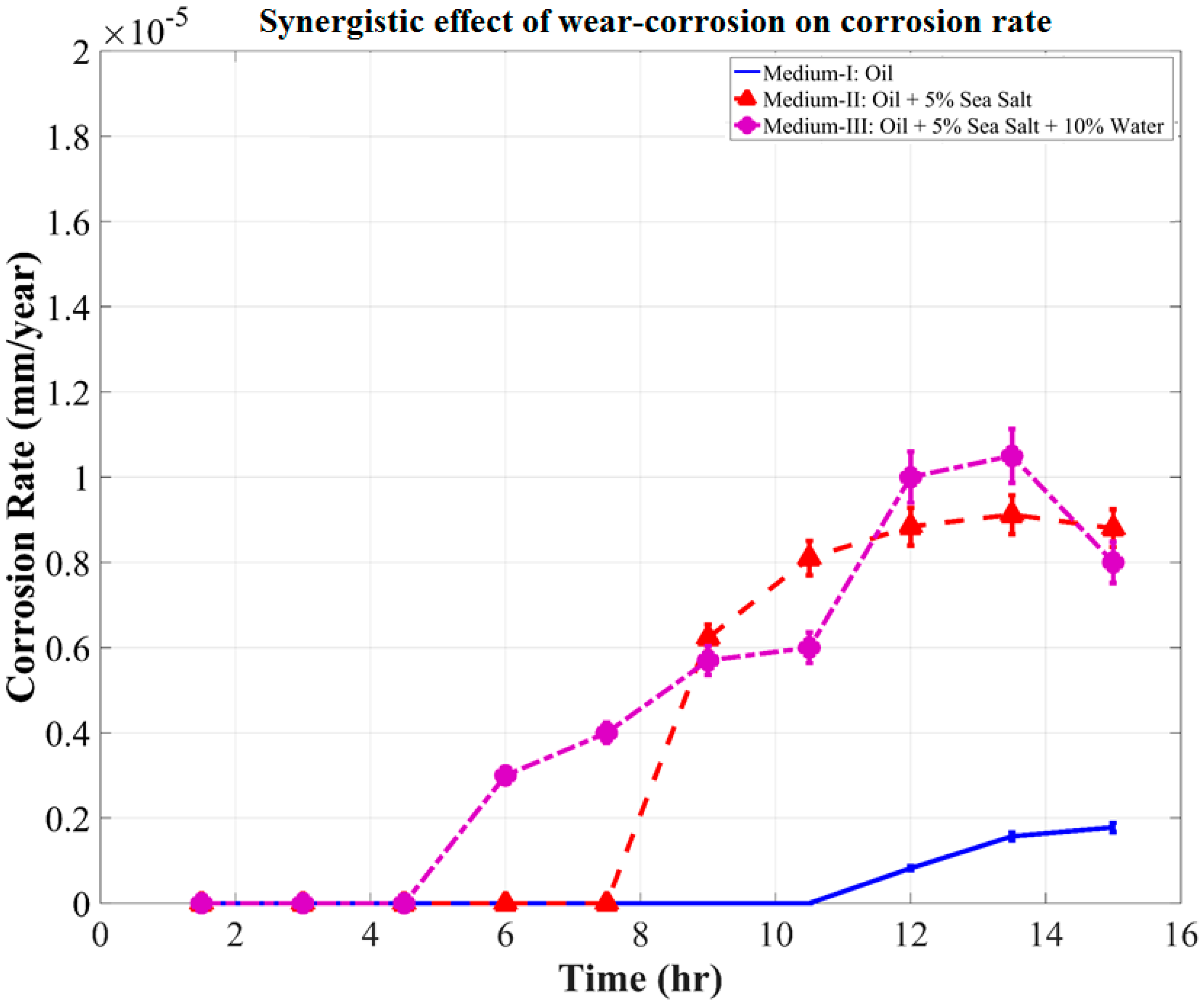
3.4. Evolution of Corrosion Rate during Tribo-Corrosion Test
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stachowiak, G.; Batchelor, A.W. Engineering Tribology; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 11–49. [Google Scholar]
- Speight, J.G. Handbook of Petroleum Product Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 26–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjeev, K.; Manoj, K. Assessing remaining useful life of lubricant using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2016, 22, 202–214. [Google Scholar]
- Zaharia, C.V.; Niculescu, R.; Iorga, V.; Ducu, C.; Clenci, A.; Aron, B. Diagnosing the Operation of a Locomotive Diesel Engine Based on the Analysis of Used Oil in the Period Between Two Technical Revisions. In CONAT 2016 International Congress of Automotive and Transport Engineering; Chiru, A., Ispas, N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2017; pp. 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- Lara, R.F.; Azcarate, S.M.; Cantarelli, M.Á.; Orozco, I.M.; Caroprese, M.E.; Savio, M.; Camiña, J.M. Lubricant quality control: A chemometric approach to assess wear engine in heavy machines. Tribol. Int. 2015, 86, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terhune, J.H.; Gordon, G.M. Corrosive Impurity Sensor. U.S. Patent 4628252 A, 9 December 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, K.; Hattori, T.; Atsumi, K.; Nishida, M. Machine Oil Deterioration Detection. U.S. Patent 4675662 A, 23 June 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Cipris, D.; Palanisamy, T.G.; Walsh, A.T. Lubricant Oil Monitoring System and Method of Monitoring Lubricant Oil Quality. U.S. Patent 4792791 A, 20 December 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Cipris, D.; Walsh, A.T. Lubricant Oil Monitoring System, Sensor for Monitoring Lubricant Oil Quality and Method of Manufacturing Sensor for Monitoring Lubricant Oil Quality. U.S. Patent 4782332 A, 1 November 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, A.T. Corrosion of Co-Cr alloys in aqueous environments. Biomaterials 1981, 2, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, F.; Suter, T.; Böhni, H. A new electrochemical technique to study tribocorrosion at the micrometric scale. Tribotest 1999, 6, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponthiaux, P.; Wenger, F.; Drees, D.; Celis, J.P. Electrochemical techniques for studying tribocorrosion processes. Wear 2004, 256, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, E.W.; Snider, M.J.; Olree, R.M.; Johnson, E.R. Automatic Engine Oil Life Determination with a Factor for Oil Quality. U.S. Patent 8710973 B2, 29 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bulsara, M.A.; Hinguz, A.D.; Patel, K. Prediction of residual life of lubricant oil in four stroke engine. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Materials and Product Design (AMPD 2015), Surat, India, 10–11 January 2015; pp. 409–413. [Google Scholar]
- Vong, C.M.; Wong, P.K.; Wong, K.I. Simultaneous-fault detection based on qualitative symptom descriptions for automotive engine diagnosis. Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 22, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, J.; Konecny, B.; Madac, K.; Fedorko, G.; Molnar, V. Degradation and chemical change of longlife oils following intensive use in automobile engines. Measurement 2014, 50, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; El Sayed, M.; Gadsden, S.A.; Tjong, J.; Habibi, S. Automotive Internal-Combustion-Engine Fault Detection and Classification Using Artificial Neural Network Techniques. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejkorová, M.; Glos, J. Analysis of Degradation of Motor Oils Used in Zetor Tractors. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2017, 65, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejkorová, M.; Hurtová, I.; Glos, J.; Pokorný, J. Definition of a Motor Oil Change Interval for High-Volume Diesel Engines Based on its Current Characteristics Assessment. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2017, 65, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, E.S.; Smolenski, D.J.; Keersmaekers, J.D.; Traylor, C.M.; Wallo, G.J. Automatic Engine Oil Change Indicator System. U.S. Patent 4742476 A, 3 May 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, R. Oil Degradation Warning System. U.S. Patent 4796204 A, 3 January 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Sawatari, T.; Nakamura, M.; Sugiura, T. Automotive Engine Oil Monitoring System. U.S. Patent 4677847 A, 7 July 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Kurre, S.K.; Garg, R.; Pandey, S. A review of biofuel generated contamination, engine oil degradation and engine wear. Biofuels 2017, 8, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, K.; Parboti Shankar, M.; Nirendra Mohan, M. Advancement and current status of wear debris analysis for machine condition monitoring: A review. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2013, 65, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sazzad, B.S.; Fazal, M.A.; Haseeb, A.S.M.A.; Masjuki, H.H. Retardation of oxidation and material degradation in biodiesel: A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 60244–60263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.; Brooks, R.; Shipway, P. Internal combustion engine cold-start efficiency: A review of the problem, causes and potential solutions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 82, 327–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, R.; Hassan, M.B.H.; Varman, M.; Mufti, R.A.; Kalam, M.A.; Zulkifli, N.W.B.M.; Gulzar, M. A Review on Effects of Lubricant Formulations on Tribological Performance and Boundary Lubrication Mechanisms of Non-Doped DLC/DLC Contacts. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2016, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Goel, V.; Chauhan, S.R. Impact of dual biofuel approach on engine oil dilution in CI engines. Fuel 2017, 207, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhong, C.; Zhe, J. Lubricating oil conditioning sensors for online machine health monitoring—A review. Tribol. Int. 2017, 109, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; He, D.; Bechhoefer, E. Survey of lubrication oil condition monitoring, diagnostics, and prognostics techniques and systems. J. Chem. Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, 100–115. [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan, I.M.; Jordan, J.R.; Whittington, H.W. Wear-debris detection and analysis techniques for lubricant-based condition monitoring. J. Phys. E Sci. Instrum. 1988, 21, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassel, V.A.; Peterson, C.A.; Abercrombie, F.N.; Kniseley, R.N. Simultaneous determination of wear metals in lubricating oils by inductively-coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1976, 48, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Du, L.; Zhe, J. A 3 × 3 wear debris sensor array for real time lubricant oil conditioning monitoring using synchronized sampling. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 83, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhe, J.; Carletta, J.; Veillette, R.; Choy, F. Real-time monitoring of wear debris in lubrication oil using a microfluidic inductive Coulter counting device. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2010, 9, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Yao, Z. Research on an on-line wear condition monitoring system for marine diesel engine. Tribol. Int. 2000, 33, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhu, X.; Han, Y.; Zhe, J. High Throughput Wear Debris Detection in Lubricants Using a Resonance Frequency Division Multiplexed Sensor. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 51, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruqiang, Y.; Gao, R.X. Complexity as a measure for machine health evaluation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2004, 53, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Nazir, M.H.; Khan, Z.A. A review of theoretical analysis techniques for cracking and corrosive degradation of film-substrate systems. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2017, 72, 80–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.H.; Saeed, A.; Khan, Z. A comprehensive predictive corrosion model incorporating varying environmental gas pollutants applied to wider steel applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 193, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.H.; Khan, Z.A.; Saeed, A.; Stokes, K. A model for cathodic blister growth in coating degradation using mesomechanics approach. Mater. Corros. 2016, 67, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattei, L.; Di Puccio, F.; Piccigallo, B.; Ciulli, E. Lubrication and wear modelling of artificial hip joints: A review. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 532–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez, M.-D.; Jiménez, A.-E.; Sanes, J.; Carrión, F.-J. Ionic Liquids as Advanced Lubricant Fluids. Molecules 2009, 14, 2888–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsaeian, P.; Ghanbarzadeh, A.; Wilson, M.; Van Eijk, M.C.P.; Nedelcu, I.; Dowson, D.; Neville, A.; Morina, A. An experimental and analytical study of the effect of water and its tribochemistry on the tribocorrosive wear of boundary lubricated systems with ZDDP-containing oil. Wear 2016, 358, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, M.T.; Runa, M.J.; Laurent, M.; Jacobs, J.J.; Rocha, L.A.; Wimmer, M.A. Tribocorrosion behavior of CoCrMo alloy for hip prosthesis as a function of loads: A comparison between two testing systems. Wear 2011, 271, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratu, F.; Benea, L.; Celis, J.-P. Tribocorrosion behaviour of Ni–SiC composite coatings under lubricated conditions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 6940–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.A.; Saeed, A.; Gregory, O.; Ghafoor, A. Biodiesel Performance within Internal Combustion Engine Fuel System: A Review. Tribol. Ind. 2016, 38, 197–213. [Google Scholar]
- Fatima, N.; Minami, I.; Holmgren, A.; Marklund, P.; Larsson, R. Surface chemistry of wet clutch influenced by water contamination in automatic transmission fluids. Tribol. Int. 2016, 96, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Morina, A.; Neville, A.; Vickerman, R. Tribochemistry on Clutch Friction Material Lubricated by Automatic Transmission Fluids and the Link to Frictional Performance. J. Tribol. 2013, 135, 041801–041811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Neville, A.; Morina, A.; Vickerman, R.; Durham, J. Improved anti-shudder performance of ATFs—Influence of a new friction modifier and surface chemistry. Tribol. Int. 2012, 46, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, W.G.; Zuzich, F. Automatic transmission gear materials and associated problems. SAE Int. Detroit Transm. Div. Gen. Motors Corp. 1956, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.S.; Singh, T.; Buffa, R.P.; Gayney, J.M.; Cousins, W.L.; Xie, Z.; Moorman, S.P.; Wilson, A.; Fannin, M.P.; Graham, M.L.; et al. General Motors Front Wheel Drive Seven Speed Dry Dual Clutch Automatic Transmission. SAE Int. J. Engines 2015, 8, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
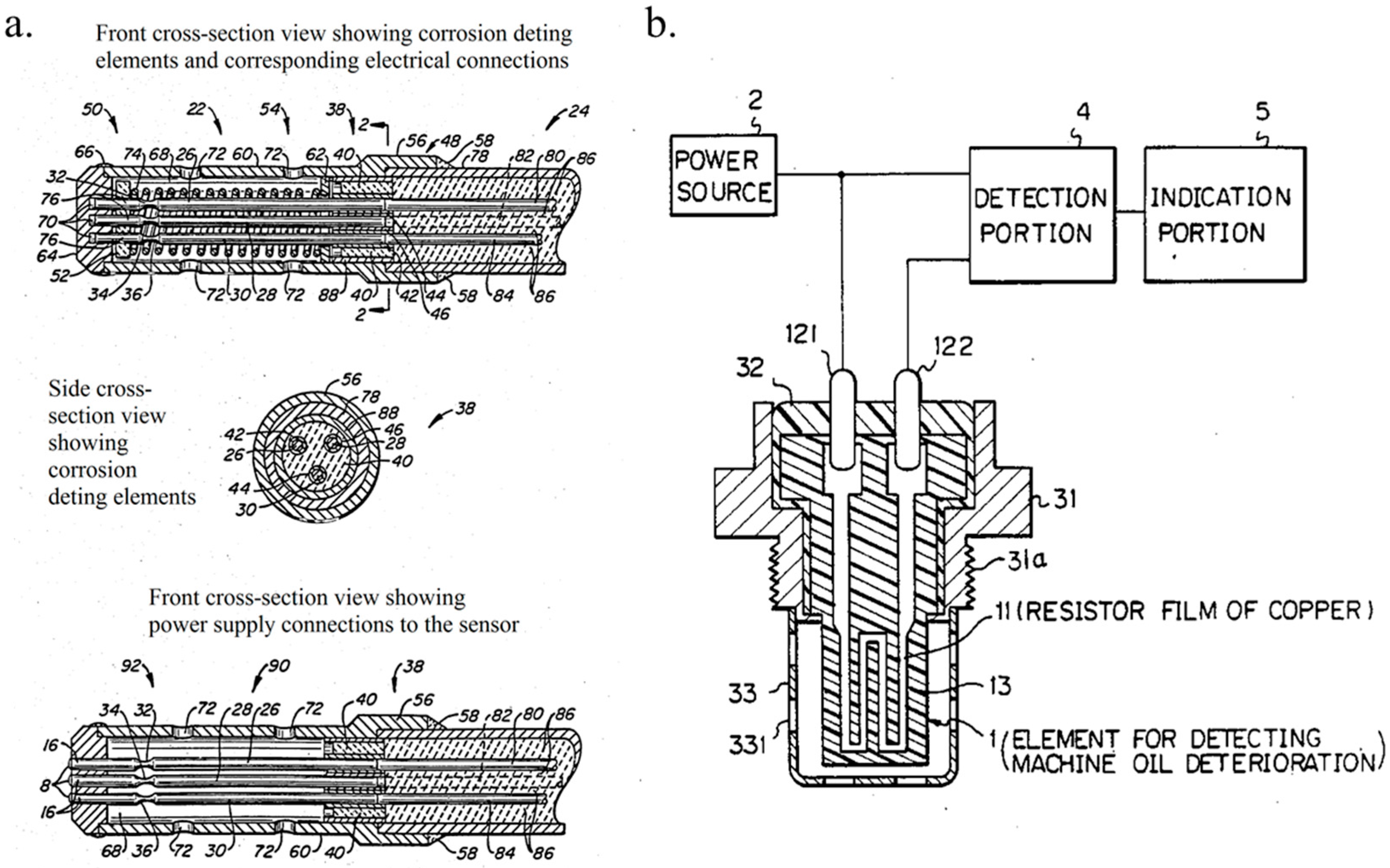
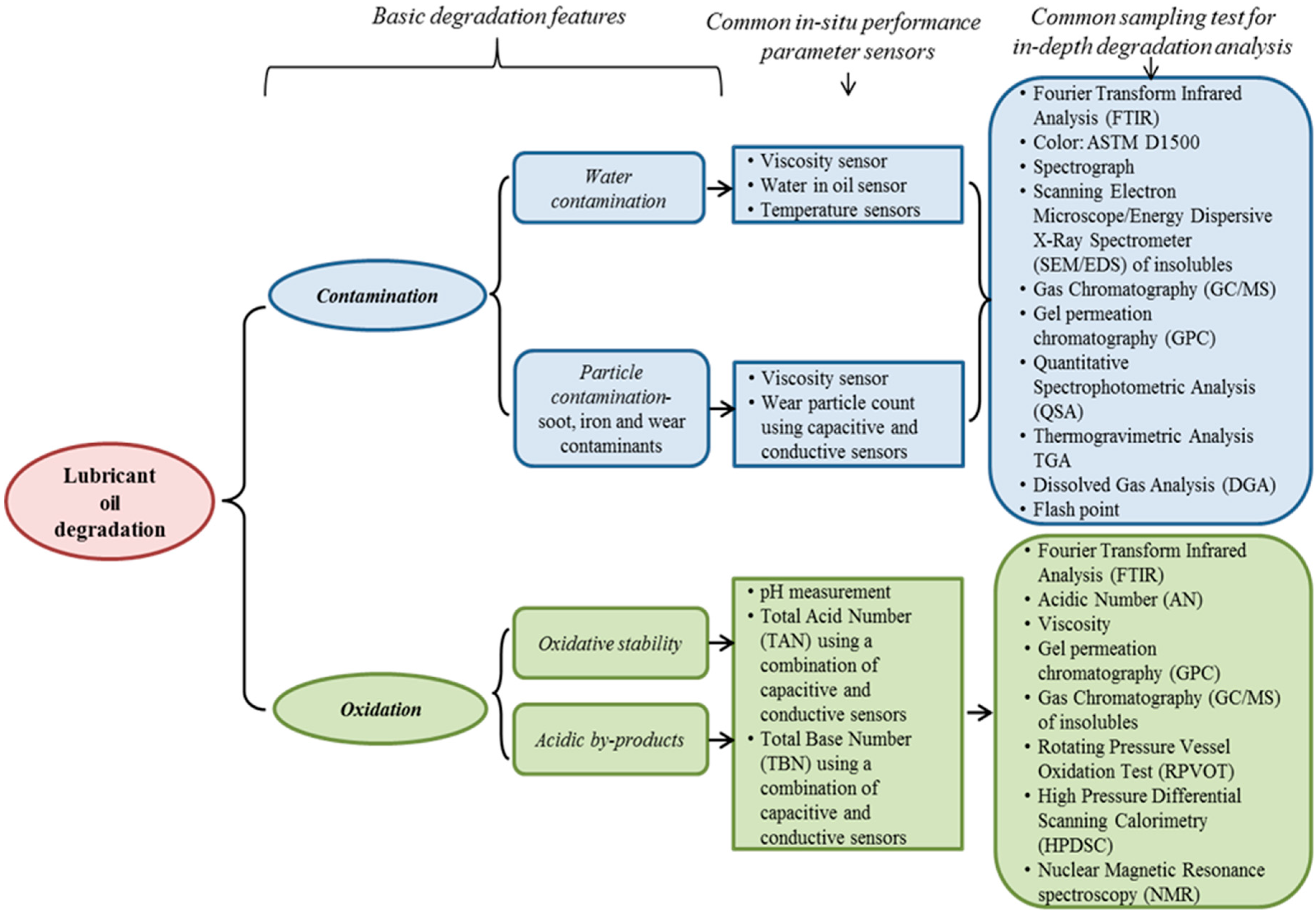
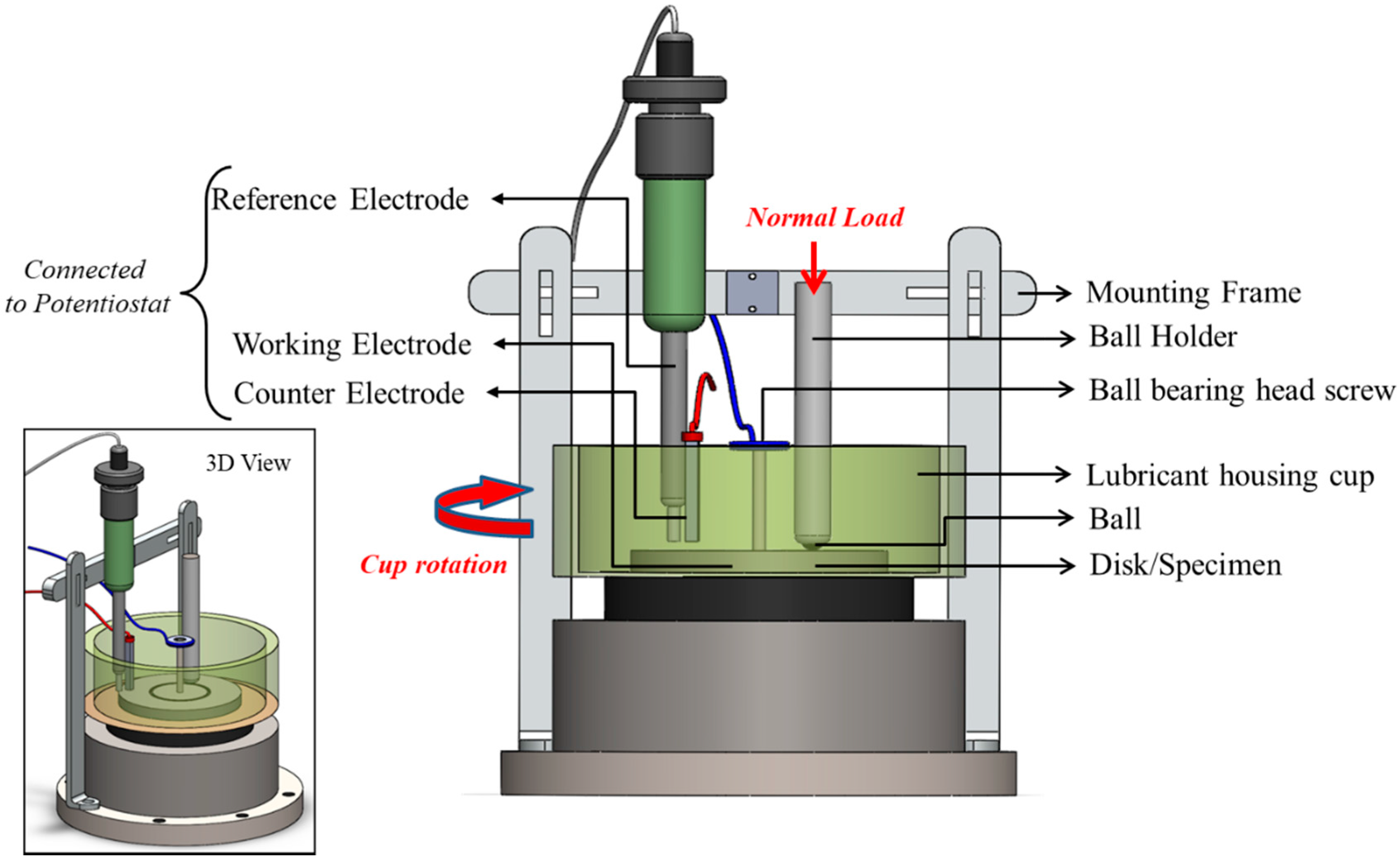
| Oil Specifications | Values |
|---|---|
| Mass density at 15 °C | 867 kg/m3 |
| Colour, ASTM | 6.5 |
| Viscosity at 40 °C | 32.26 mm2/s |
| Viscosity at 100 °C | 7.1 mm2/s |
| Viscosity index | 190 |
| Viscosity at 40 °C | 12,600 cP |
| Flash point | 183 °C |
| Pour Point | −48 °C |
| Test Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Normal Force | 10 N |
| Rotation speed | 50 rpm |
| Duration of wear | 15 h |
| Wear track radius | 15 mm |
| Ball diameter | 6.5 mm |
| Electrolyte/Lubricant medium | Commercial grade (refer Table 1) |
| Temperature | 24 °C (room) |
| Humidity ratio | 10% RH |
| Stage | Objective | Experiments | Data Recorded |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage-I | Establish control wear rate. | Ball-on-disk test in oil medium without corrosion cell. | Wear rate in oil medium. |
| Stage-II | Establish control for the synergistic effect of wear and corrosion without any external contaminants. | Ball-on-disk test in oil medium with corrosion cell. Static corrosion cell experiment in oil without wear, to isolate corrosion rate. | Synergistic effect of wear and corrosion in oil medium. |
| Stage-III | Effect of one external contaminant in the oil medium on the synergism of wear and corrosion. | Ball-on-disk test in oil +5% (wt.%) sea salt-medium with corrosion cell. Static corrosion cell experiment in oil +5% (wt.%) sea salt medium without wear, to isolate corrosion rate. | Synergistic effect of wear and corrosion in oil medium consisting of oil +5% (wt.%) sea salt. |
| Stage-IV | Effect of two external contaminants in the oil medium on the synergism of wear and corrosion. | Ball-on-disk test in oil +5% (wt.%) sea salt +10% (wt.%) water medium with corrosion cell. Static corrosion cell experiment in oil +5% (wt.%) sea salt +10% (wt.%) water medium without wear, to isolate corrosion rate. | Synergistic effect of wear and corrosion in oil medium +5% (wt.%) sea salt +10% (wt.%) water. |
| Oil Medium | Contaminate Introduce | Oil Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Medium-I | - | oil (uncontaminated) |
| Medium-II | 5% (wt.%) sea salt | oil contaminated with sea salt |
| Medium-III | 5% (wt.%) sea salt and 10% (wt.%) water | oil contaminated with sea salt and water |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siddaiah, A.; Khan, Z.A.; Ramachandran, R.; Menezes, P.L. Performance Analysis of Retrofitted Tribo-Corrosion Test Rig for Monitoring In Situ Oil Conditions. Materials 2017, 10, 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101145
Siddaiah A, Khan ZA, Ramachandran R, Menezes PL. Performance Analysis of Retrofitted Tribo-Corrosion Test Rig for Monitoring In Situ Oil Conditions. Materials. 2017; 10(10):1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101145
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiddaiah, Arpith, Zulfiqar Ahmad Khan, Rahul Ramachandran, and Pradeep L. Menezes. 2017. "Performance Analysis of Retrofitted Tribo-Corrosion Test Rig for Monitoring In Situ Oil Conditions" Materials 10, no. 10: 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101145
APA StyleSiddaiah, A., Khan, Z. A., Ramachandran, R., & Menezes, P. L. (2017). Performance Analysis of Retrofitted Tribo-Corrosion Test Rig for Monitoring In Situ Oil Conditions. Materials, 10(10), 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101145