Signal Construction-Based Dispersion Compensation of Lamb Waves Considering Signal Waveform and Amplitude Spectrum Preservation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
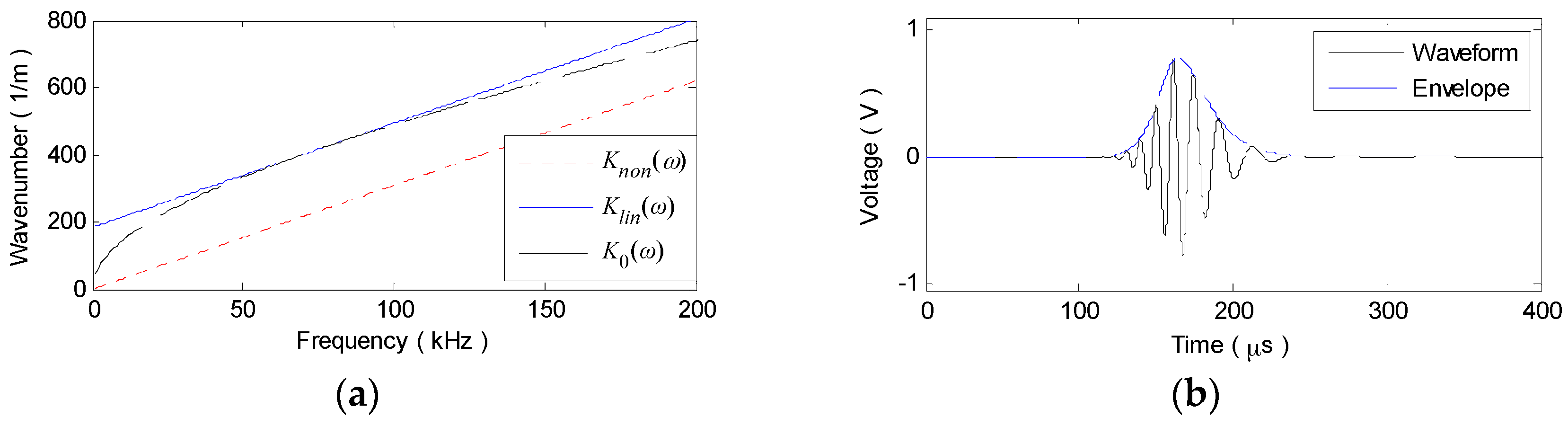
2. Effects of Different Dispersion Relations on Lamb Waves
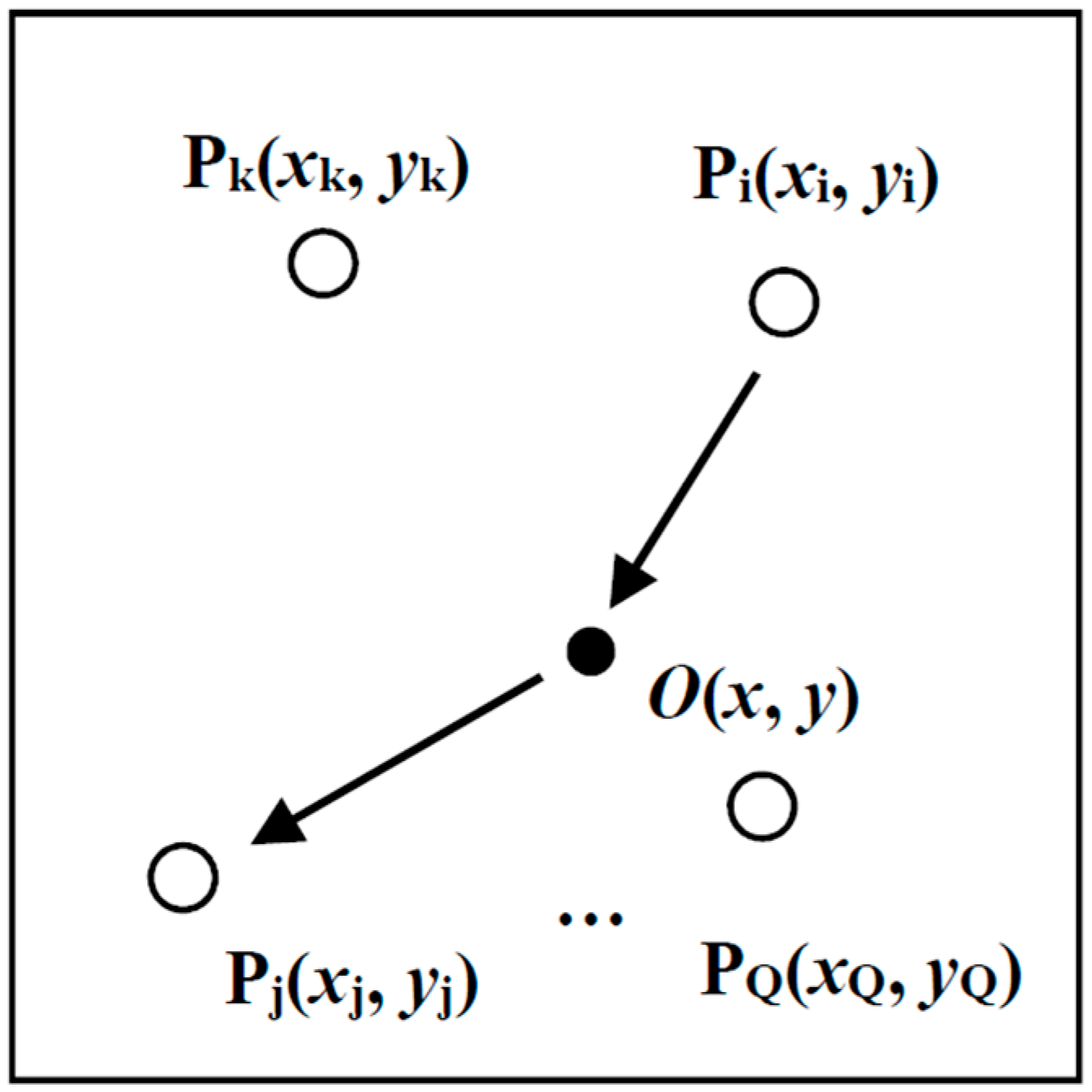
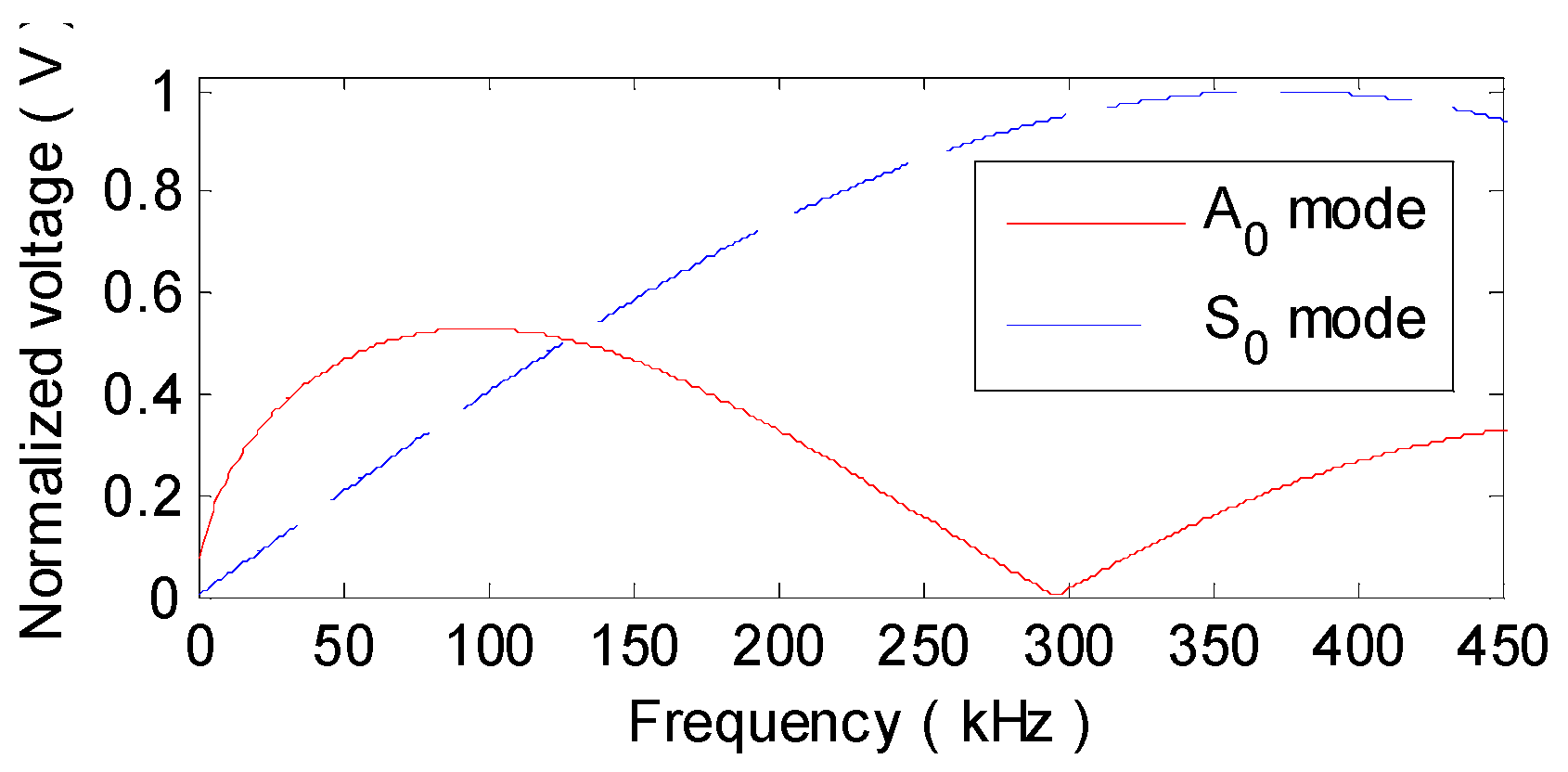
2.1. Sensing Model in Frequency Domain
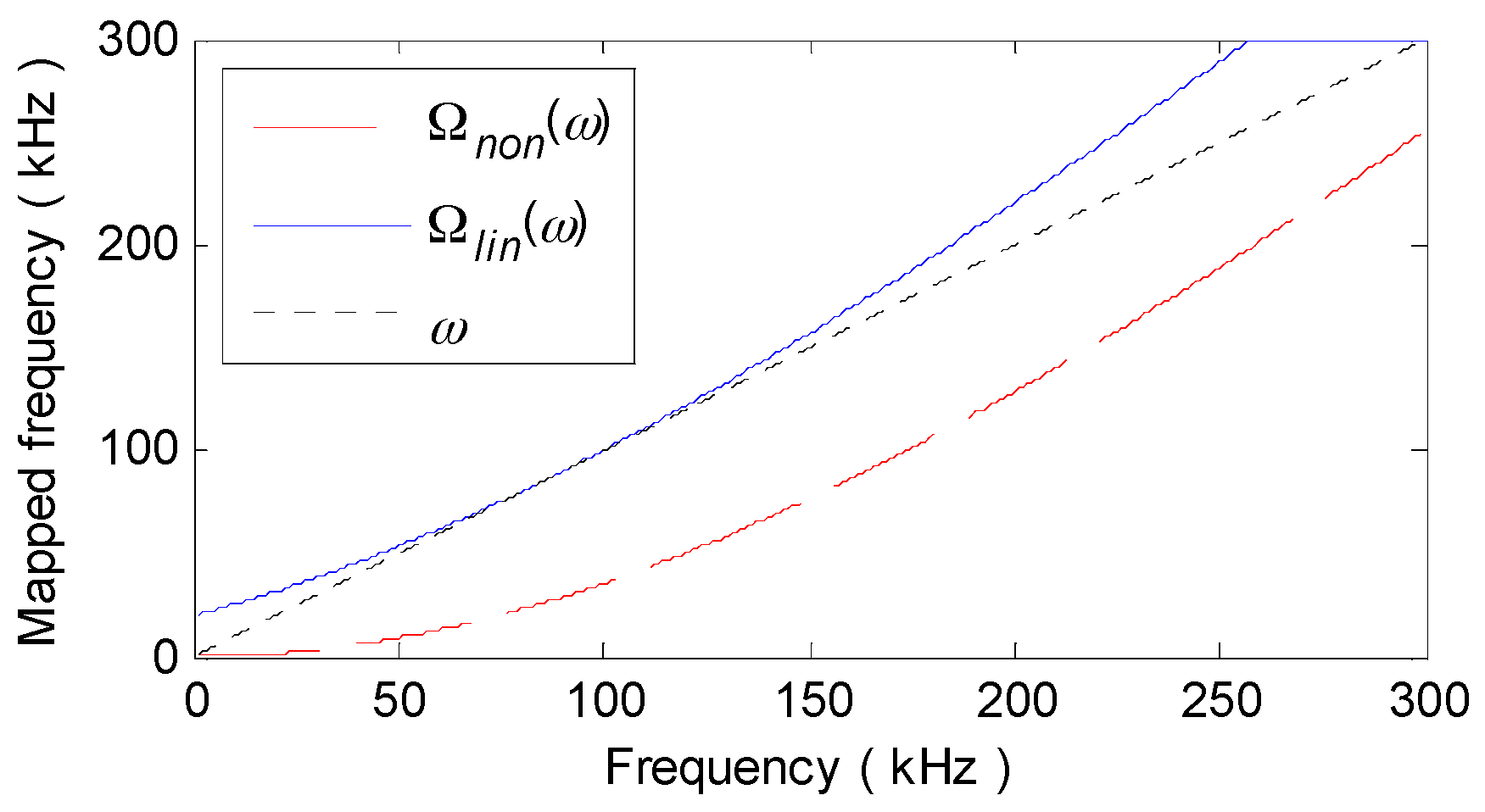
2.2. Linear-Dispersion and Non-Dispersion Effects
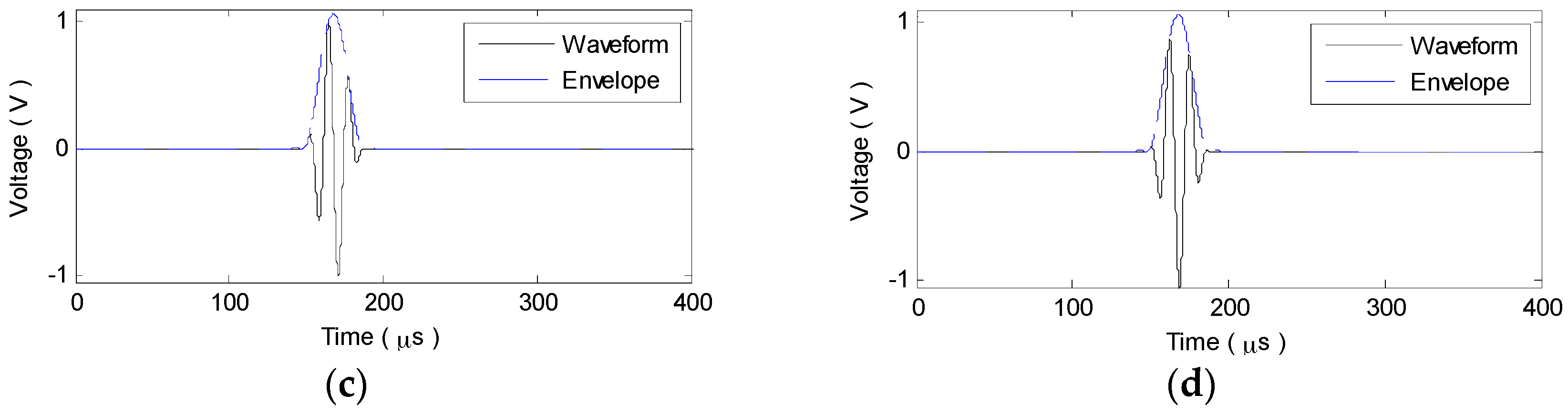
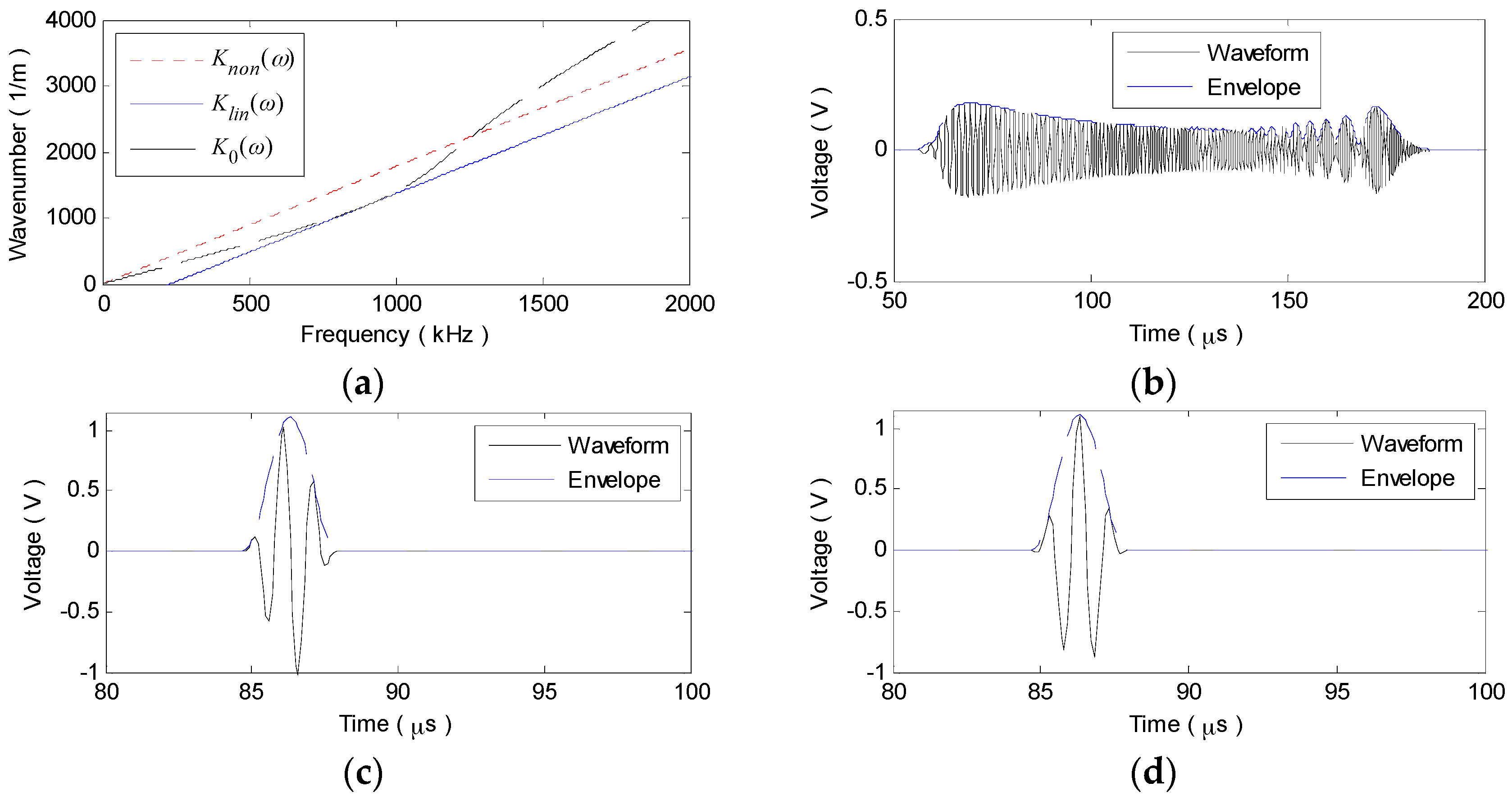
2.3. Numerical Simulation
3. Linearly-Dispersive or Non-Dispersive Signal Construction
3.1. Basic Principle of Signal Construction
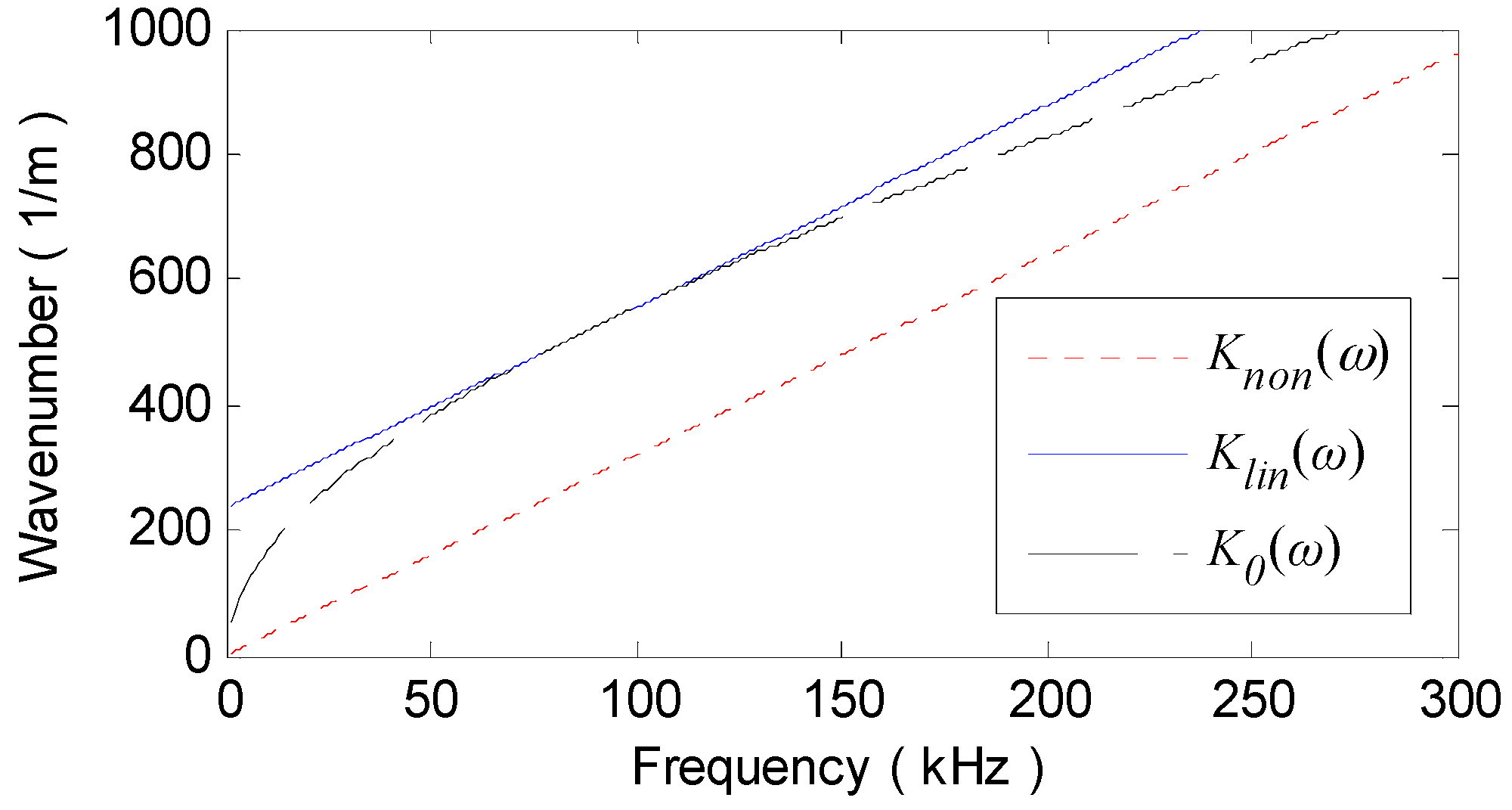
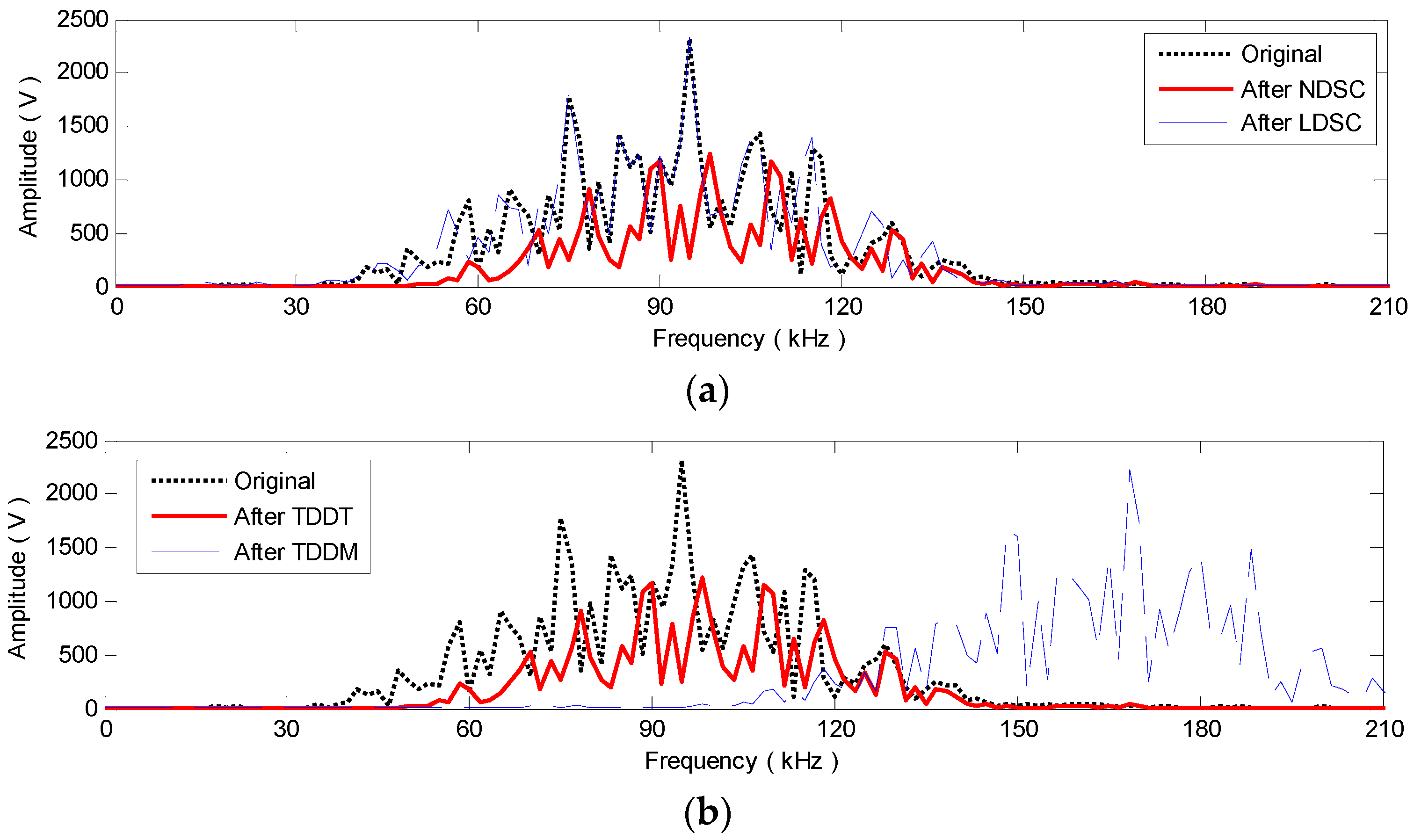
3.2. Numerical Realization of LDSC and NDSC
3.3. Comparison with TDDM and TDDT
4. High Spatial Resolution Imaging Based on LDSC or NDSC
5. Experimental and Numerical Validations
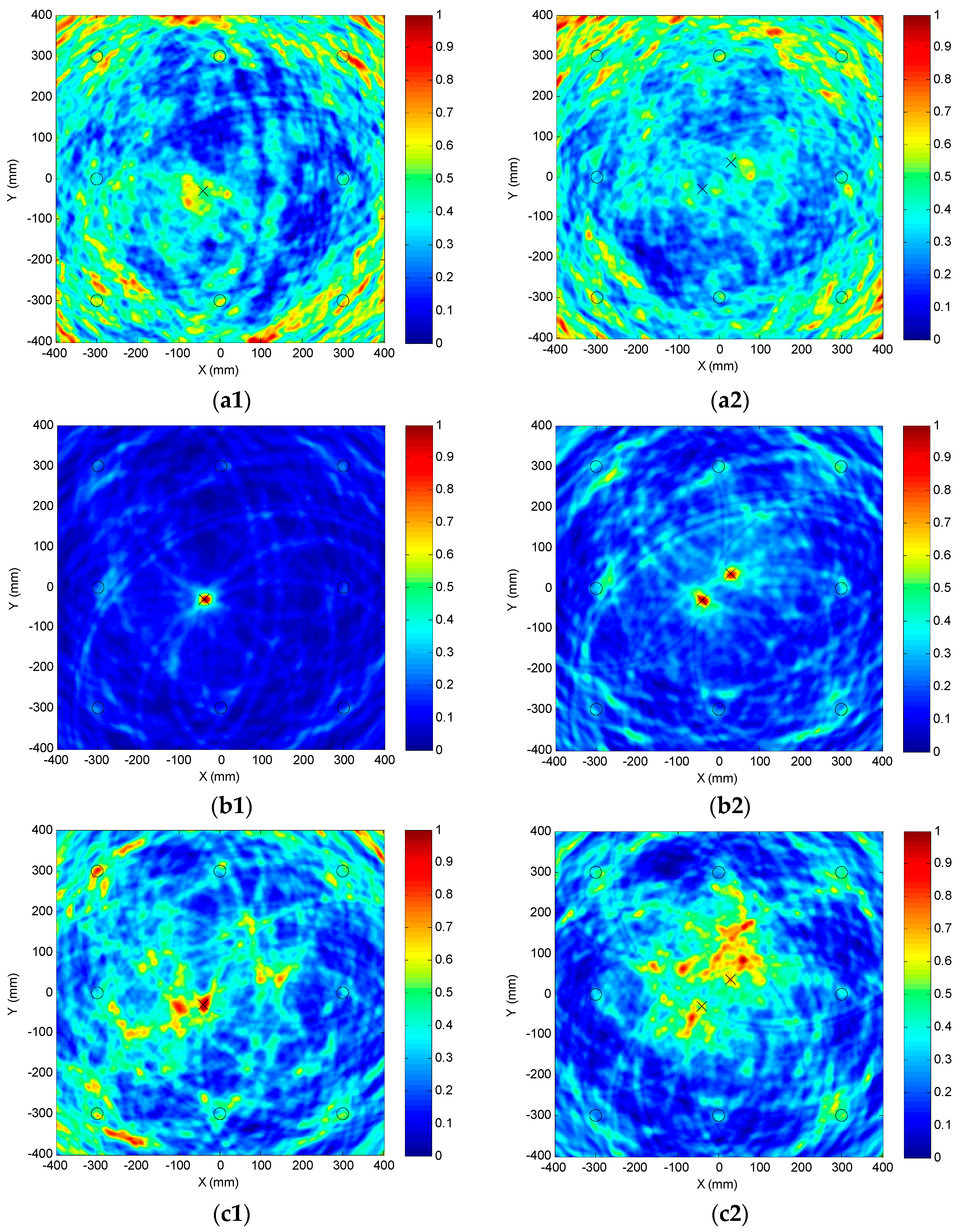
5.1. Imaging Experiment of Adjacent Dual Damages
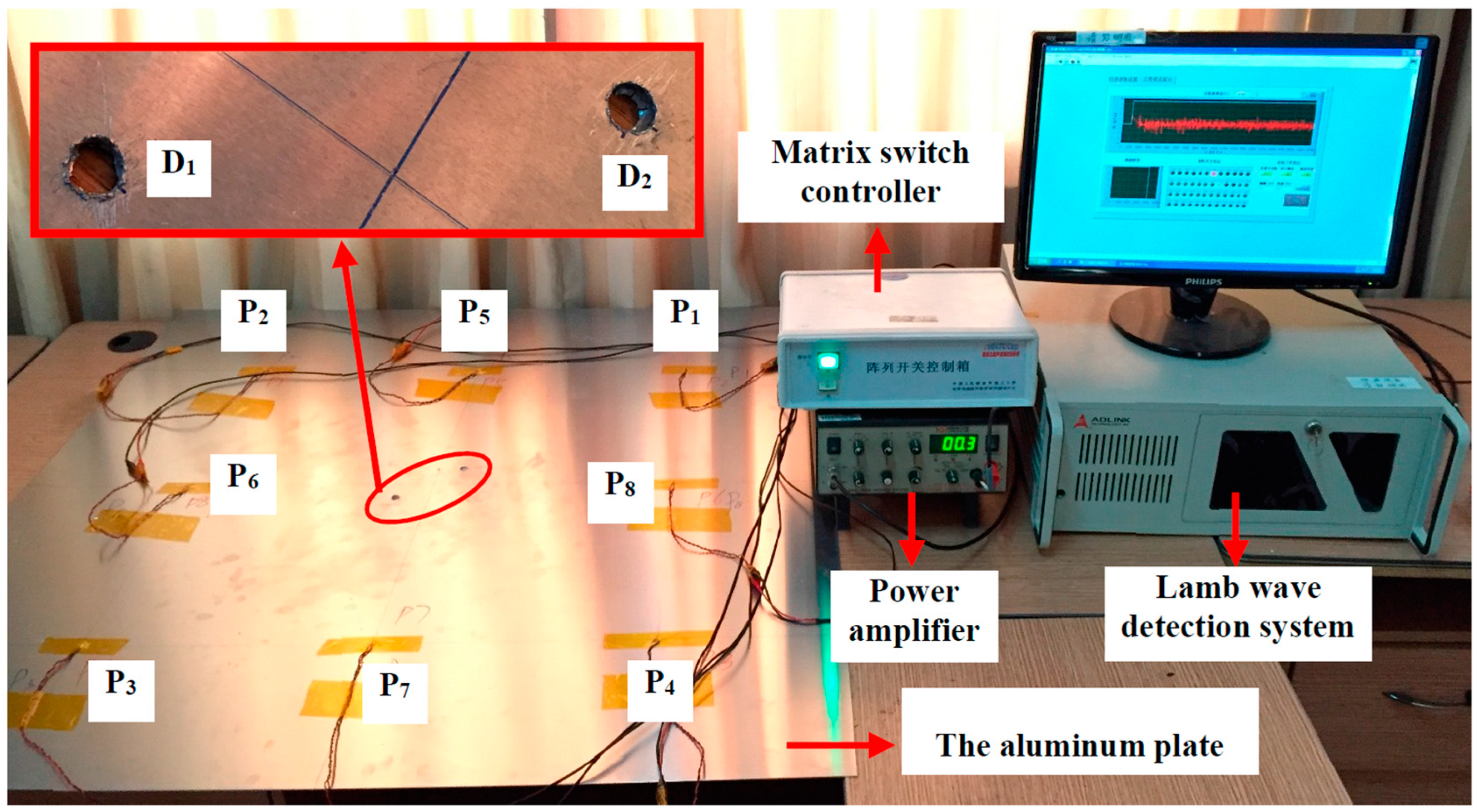
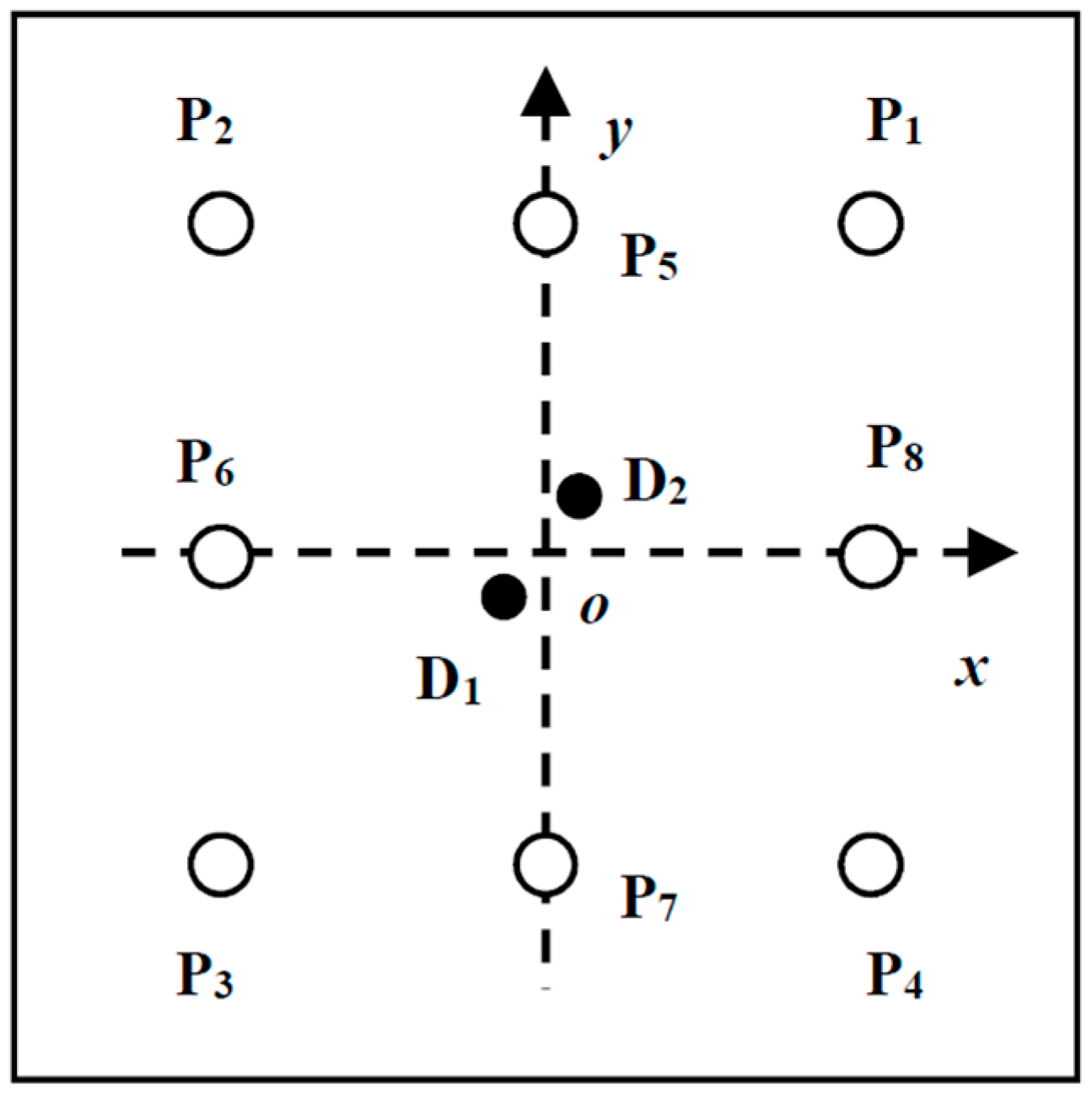
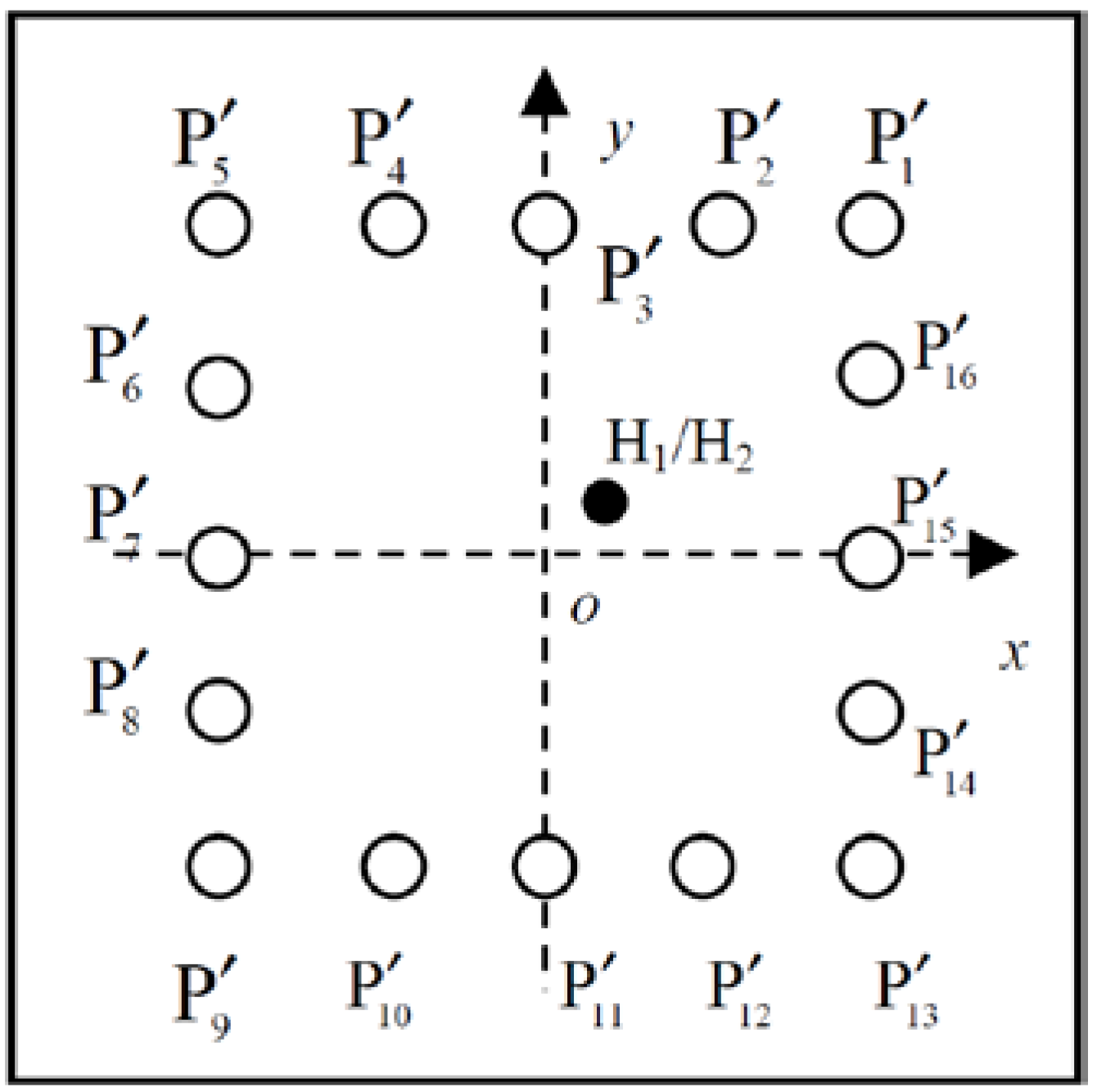
5.1.1. Experimental Setup
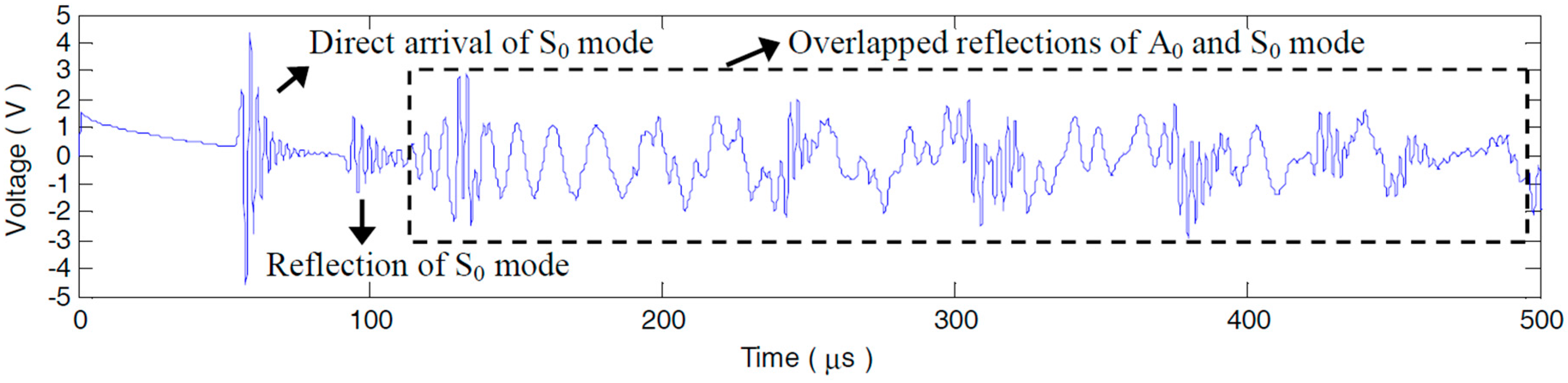
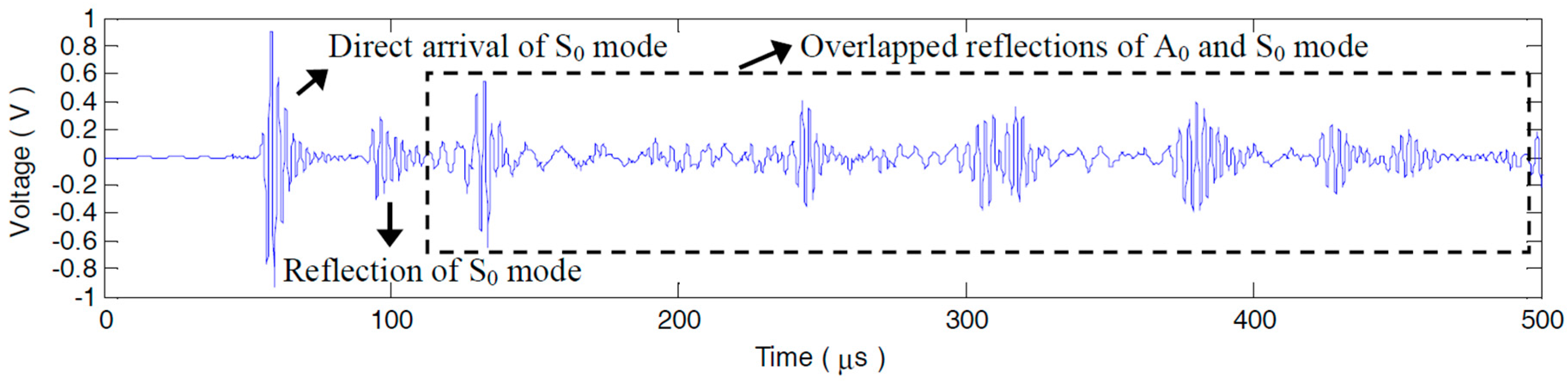
5.1.2. Compensation Effect on the Sensor Signals
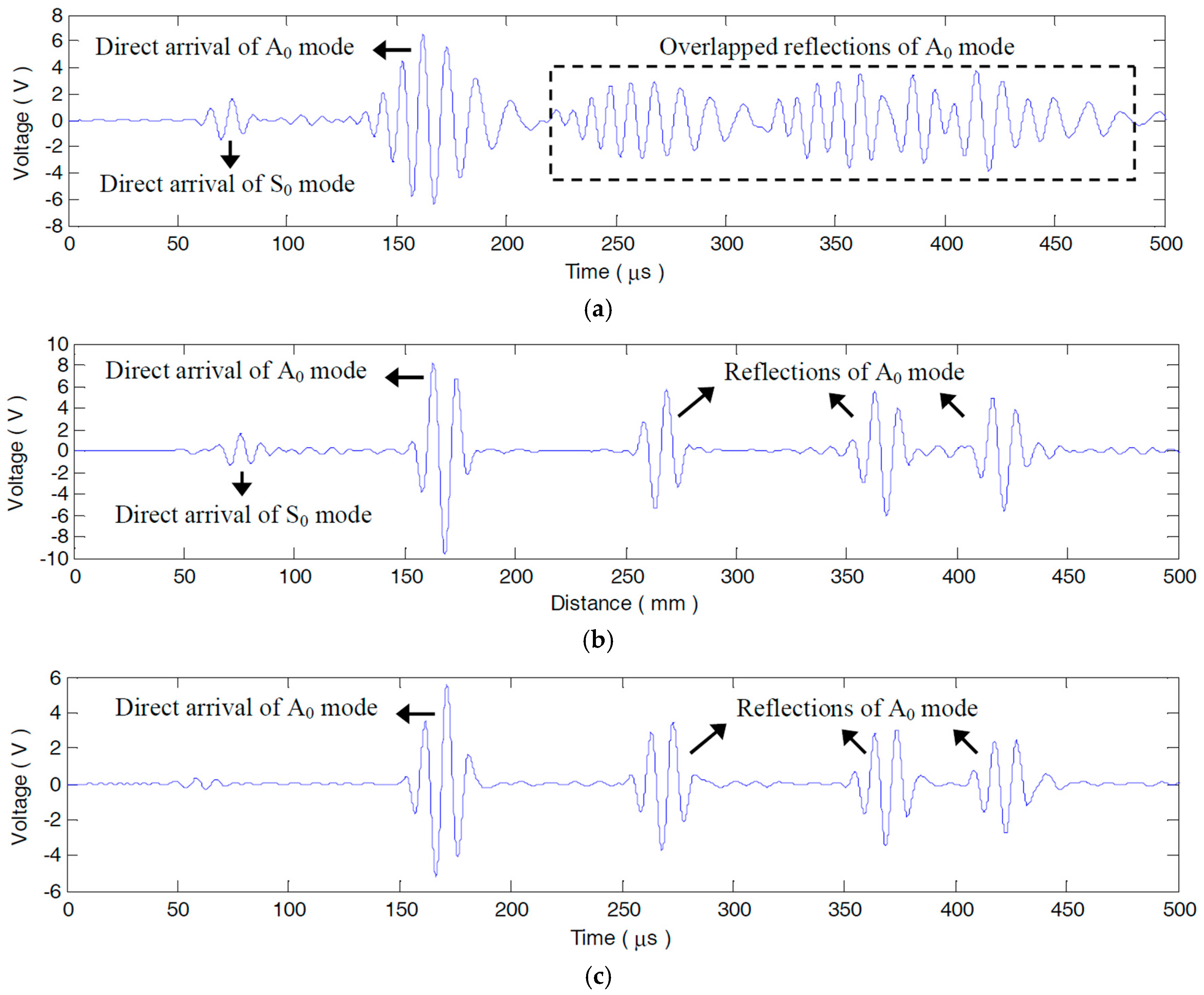
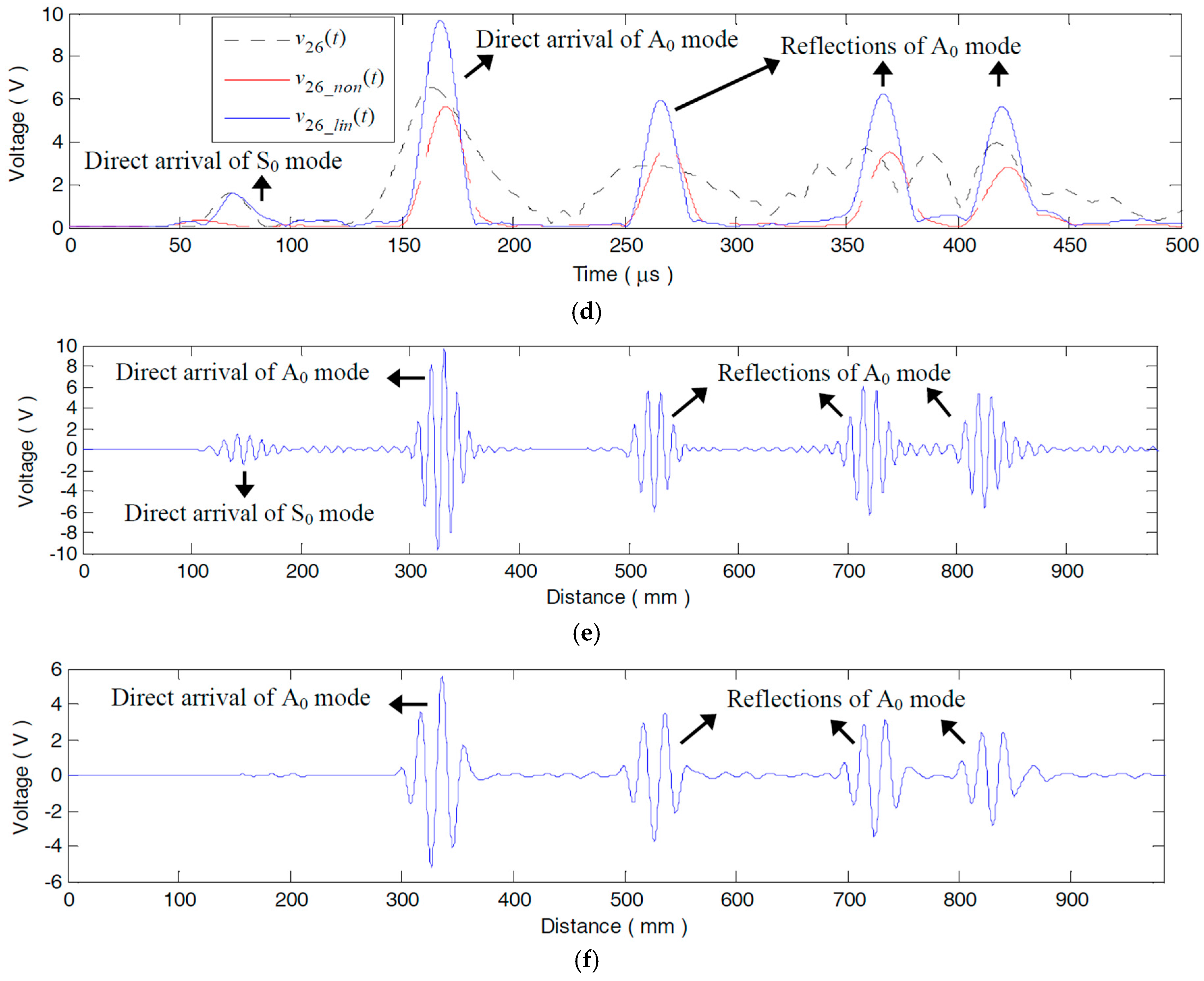
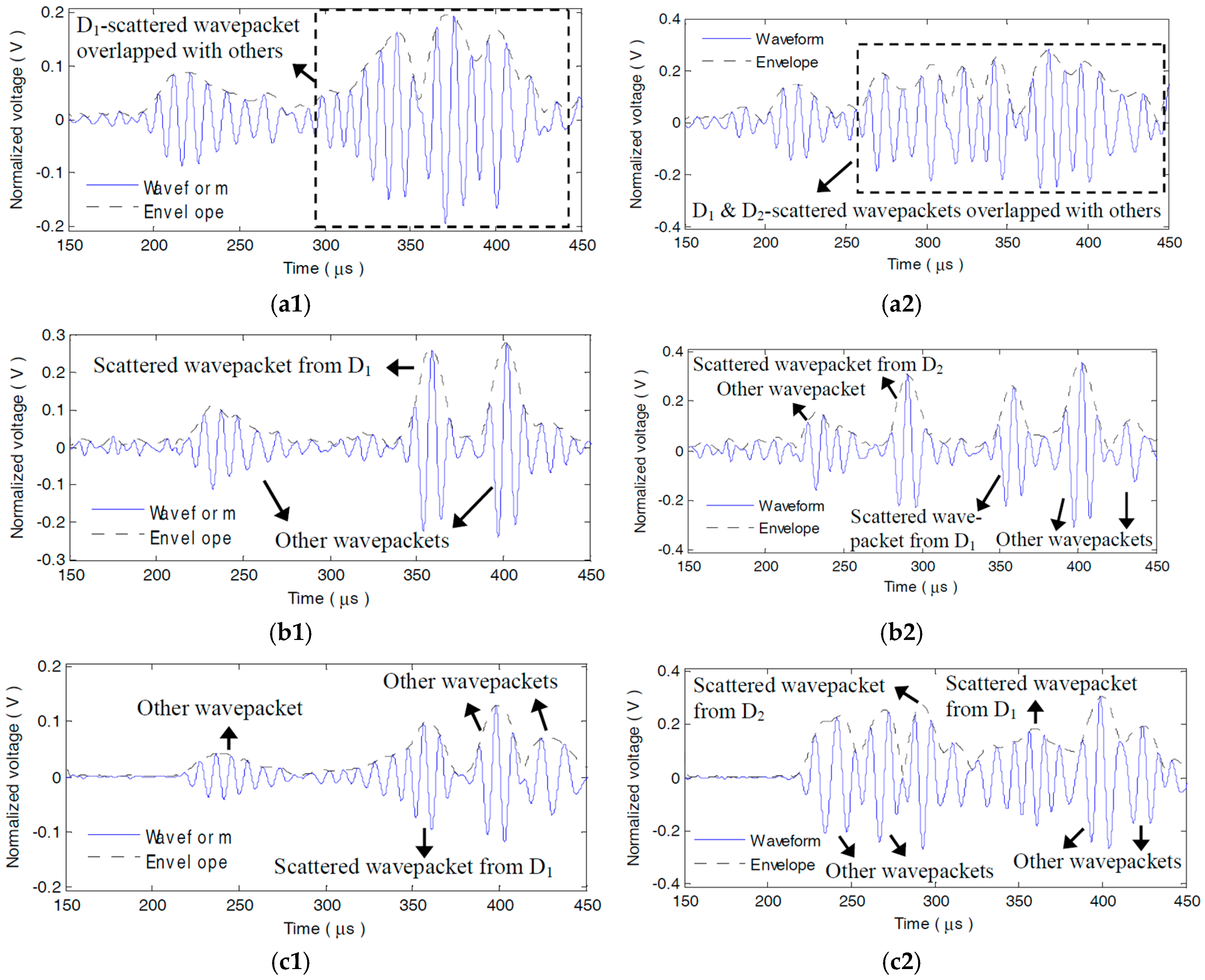
5.1.3. Compensation Effect on the Damage Scattered Signals
5.1.4. Damage Imaging Results
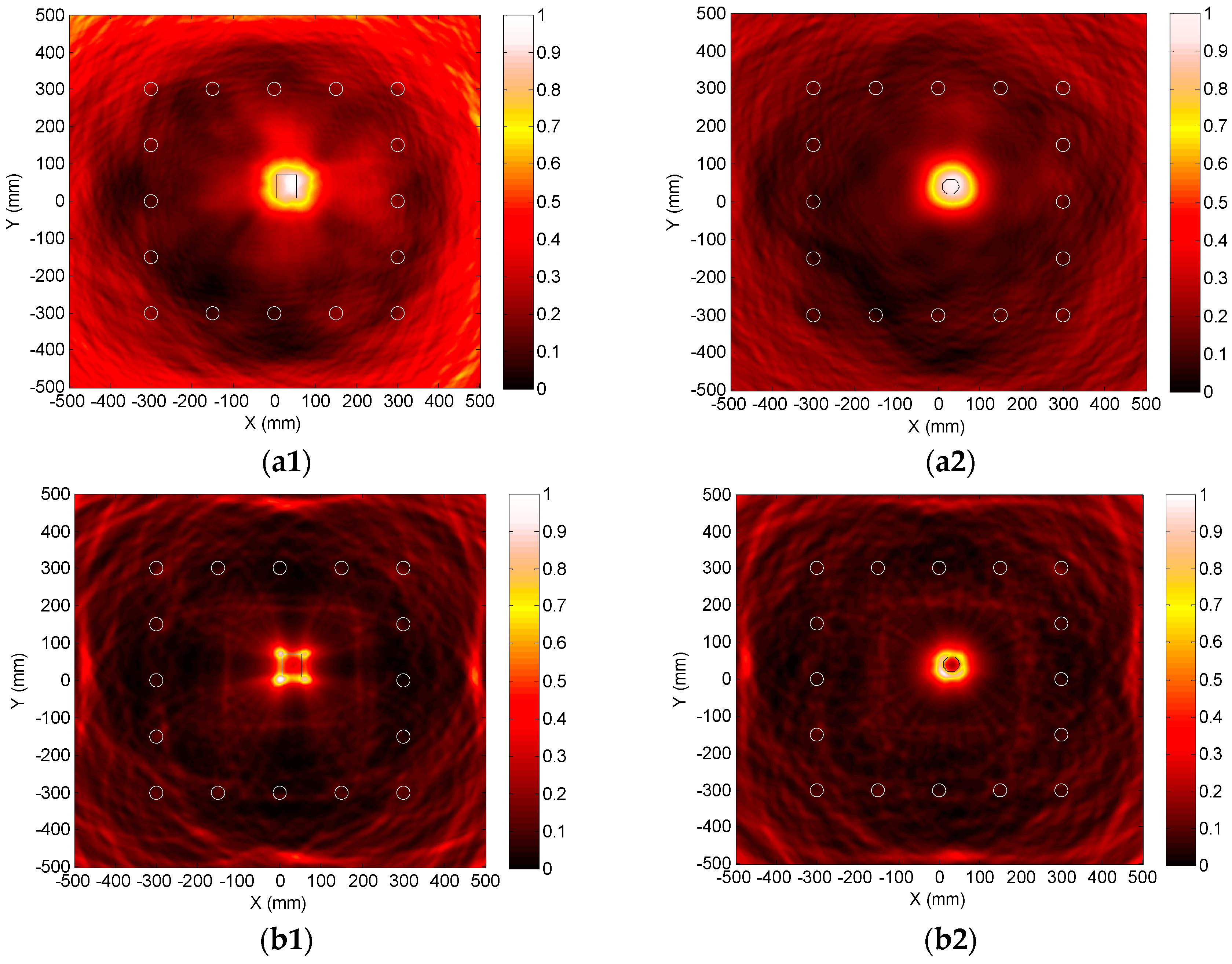
5.2. Numerical Simulation of Quantitative Imaging
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, S.F.; Liang, D.K.; Shi, L.H.; Zhao, X.; Wu, J.; Li, G.; Qiu, L. Recent progress on distributed structural health monitoring research at NUAA. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2008, 19, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, X.P.; Beard, S.J.; Kumar, A.; Ooi, T.K.; Chang, F.-K. Built-in sensor network for structural health monitoring of composite structure. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2007, 18, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihn, J.B.; Chang, F.-K. Pitch-catch active sensing methods in structural health monitoring for aircraft structures. Struct. Health Monit. 2008, 7, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.F.; Bao, Q.; Qiu, L. A single frequency component-based re-estimated MUSIC algorithm for impact localization on complex composite structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 105021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Wu, Z.J.; Rahim, G.; Bai, S.B. Design of a sensor network for structural health monitoring of a full-scale composite horizontal tail. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 055011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Giurgiutiu, V. In situ 2-D piezoelectric wafer active sensors arrays for guided wave damage detection. Ultrasonics 2008, 48, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, P.D. Omni-directional guided wave transducer arrays for the rapid inspection of large areas of plate structures. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2003, 50, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yuan, F.G. Damage identification in a composite plate using prestack reverse-time migration technique. Struct. Health Monit. 2005, 4, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Gao, H.; Zhang, G.; Ayhan, B.; Yan, F.; Kwan, C.; Rose, J.L. Active health monitoring of an aircraft wing with embedded piezoelectric sensor/actuator network: I. Defect detection, localization and growth monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Rose, J.T.; Chang, F.-K. A synthetic time-reversal imaging method for structural health monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2004, 13, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yuan, S.F. Baseline-free imaging method based on new PZT sensor arrangements. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2009, 20, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Yuan, S.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y. A time reversal focusing based impact imaging method and its evaluation on complex composite structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 105014–105024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, J.E. Detection, localization and characterization of damage in plates with an in situ array of spatially distributed ultrasonic sensors. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 17, 035035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Wang, X.; Cheng, L.; Yu, L.; Chen, Z. On selection of data fusion schemes for structural damage evaluation. Struct. Health Monit. 2009, 8, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleyne, D.N.; Cawley, P. Optimization of Lamb wave inspection techniques. NDT E Int. 1992, 25, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Giurgiutiu, V. Single mode tuning effects on Lamb wave time reversal with Piezoelectric wafer active sensors for structural health monitoring. J. Nondestr. Eval. 2007, 26, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, P.; Lowe, M.; Cawley, P. The effect of dispersion on long-range inspection using ultrasonic guided waves. NDT E Int. 2001, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ing, R.K.; Fink, M. Time reversed Lamb waves. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 1998, 45, 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.W.; Kim, S.B.; Sohn, H. Understanding a Time Reversal Process in Lamb Wave. Propagation. Wave Motion 2009, 46, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Shi, L.H.; Yuan, S.F.; Shao, Z.X. High spatial resolution imaging for structural health monitoring based on virtual time reversal. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 55018–55028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, R.; Goyette, J.; Zellouf, D. A numerical dispersion compensation technique for time recompression of Lamb wave signals. Ultrasonics 2002, 40, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, R.; Chahbaz, A.; Goyette, J. Guided Lamb waves and L-SAFT processing technique for enhanced detection and imaging of corrosion defects in plates with small depth-to wavelength ratio. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2004, 51, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, P.D. A Rapid signal processing technique to remove the effect of dispersion from Guided wave signals. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2003, 50, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, J.; Balasubramaniam, K.; Krishnamurthy, C.V. A phase reconstruction algorithm for Lamb wave based structural health monitoring of anisotropic multilayered composite plates. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.S.; Michaels, J.E. Adaptive dispersion compensation for guided wave imaging. AIP Conf. Proc. 2011, 1430, 623–630. [Google Scholar]
- Engholm, M.; Stepinski, T. Adaptive beamforming for array imaging of plate structures using lamb waves. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2010, 57, 2712–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradoa, V.T.; Higutia, R.T.; Kitanoa, C.; Martínez-Graullerab, Ó.; Adamowskic, J.C. Lamb mode diversity imaging for non-destructive testing of plate-like structures. NDT E Int. 2013, 59, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yuan, F.G. A linear mapping technique for dispersion removal of Lamb waves. Struct. Health Monit. 2010, 9, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.L.; Yu, L.Y.; Giurgiutiu, V. Lamb wave dispersion compensation in piezoelectric wafer active sensor phased-array applications. Proc. SPIE 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Shi, L.H.; Qing, X.P. A time-distance domain transform method for Lamb wave dispersion compensation considering signal waveform correction. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 105024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, L.D.; Marzani, A.; Speciale, N.; Viola, E. A passive monitoring technique based on dispersion compensation to locate impacts in plate-like structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 35021–35029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booer, A.K.; Chambers, J.; Mason, I.M. Fast numerical algorithm for the recompression of dispersed time signals. Electron. Lett. 1977, 13, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

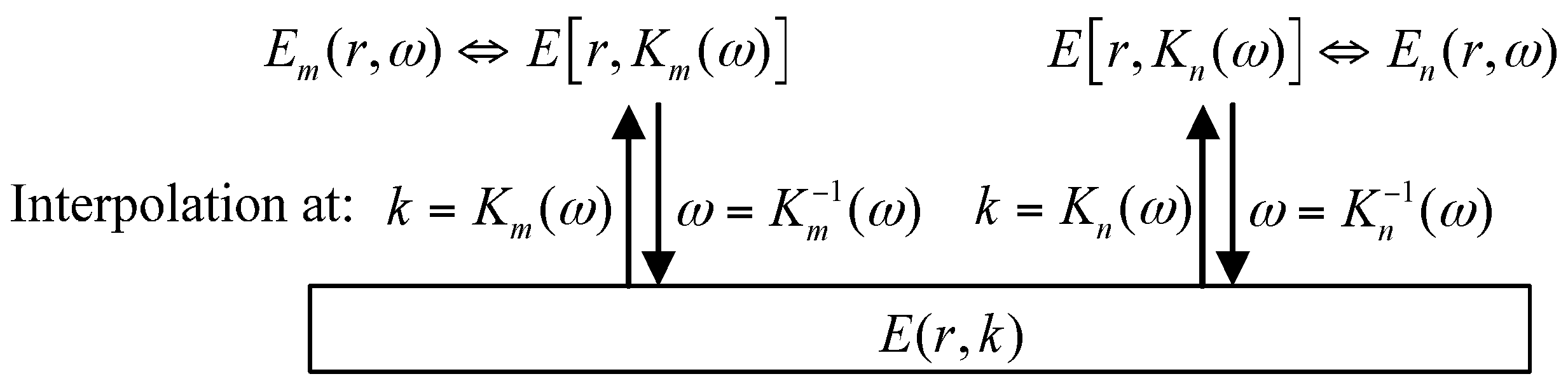

| Density ρ (kg·cm−3) | Poisson’s Ratio μ | Yong’s Modulus E (Gpa) |
|---|---|---|
| 2780 | 0.33 | 73.1 |
| PZTs | (x, y)/(mm) | PZTs | (x, y)/(mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | (300, 300) | P6 | (−300, 0) |
| P2 | (−300, 300) | P7 | (0, −300) |
| P3 | (−300, −300) | P8 | (300, 0) |
| P4 | (300, −300) | D1 | (−40, −30) |
| P5 | (0, 300) | D2 | (30, 35) |
| PZTs | (x, y)/(mm) | PZTs | (x, y)/(mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (300, 300) | (−150, −300) | ||
| (150, 300) | (0, −300) | ||
| (0, −300) | (150, −300) | ||
| (−150, −300) | (300, −300) | ||
| (−300, 300) | (300, −150) | ||
| (−300, 150) | (300, 0) | ||
| (−300, 0) | (300, 150) | ||
| (−300, −150) | H1 | (30, 40) | |
| (−300, −300) | H2 | (30, 40) |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, J.; Yuan, S.; Wang, T. Signal Construction-Based Dispersion Compensation of Lamb Waves Considering Signal Waveform and Amplitude Spectrum Preservation. Materials 2017, 10, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10010004
Cai J, Yuan S, Wang T. Signal Construction-Based Dispersion Compensation of Lamb Waves Considering Signal Waveform and Amplitude Spectrum Preservation. Materials. 2017; 10(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Jian, Shenfang Yuan, and Tongguang Wang. 2017. "Signal Construction-Based Dispersion Compensation of Lamb Waves Considering Signal Waveform and Amplitude Spectrum Preservation" Materials 10, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10010004
APA StyleCai, J., Yuan, S., & Wang, T. (2017). Signal Construction-Based Dispersion Compensation of Lamb Waves Considering Signal Waveform and Amplitude Spectrum Preservation. Materials, 10(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10010004






