Designing Structure-Dependent MPC-Based AGC Schemes Considering Network Topology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Generator and Power Network Dynamics
2.1. Generator Dynamic Model
2.2. Power Network Model
2.3. Generator and Network Coupling Model
2.4. Line Power Flow Model
3. MPC-Based AGC
3.1. Centralized MPC-Based AGC
3.2. Line Flow Control in Centralized Structure
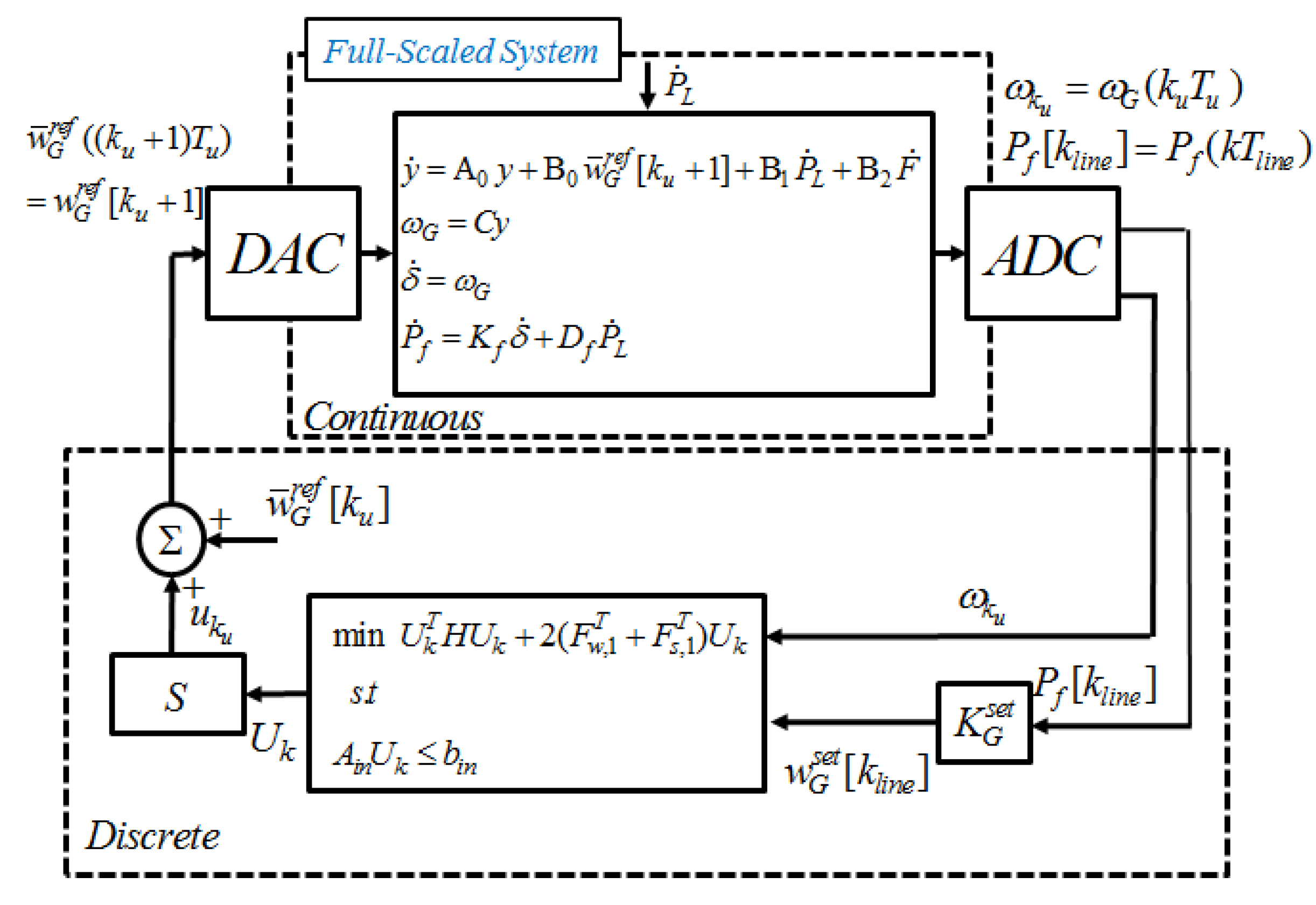
3.3. Distributed MPC-Based AGC
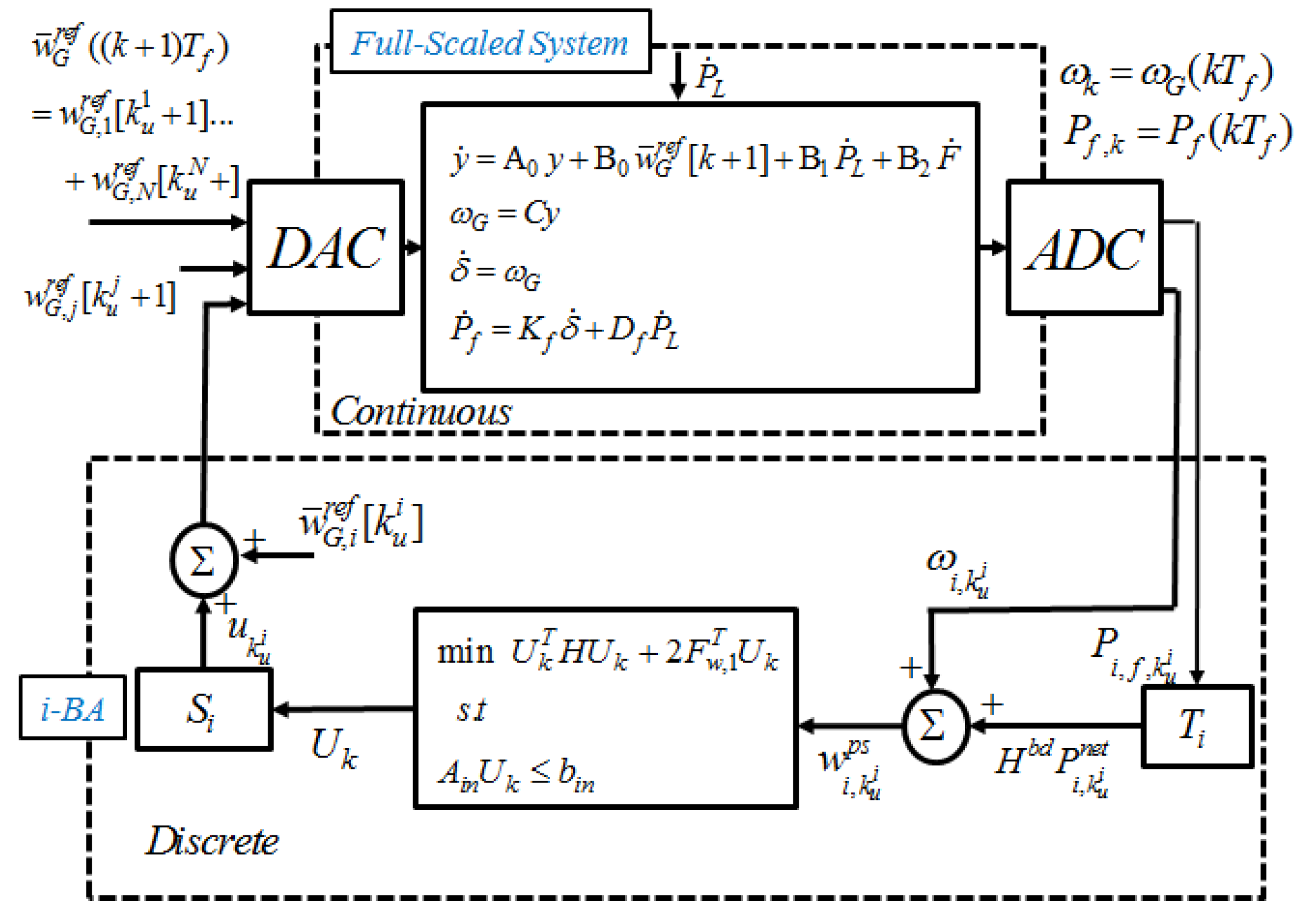
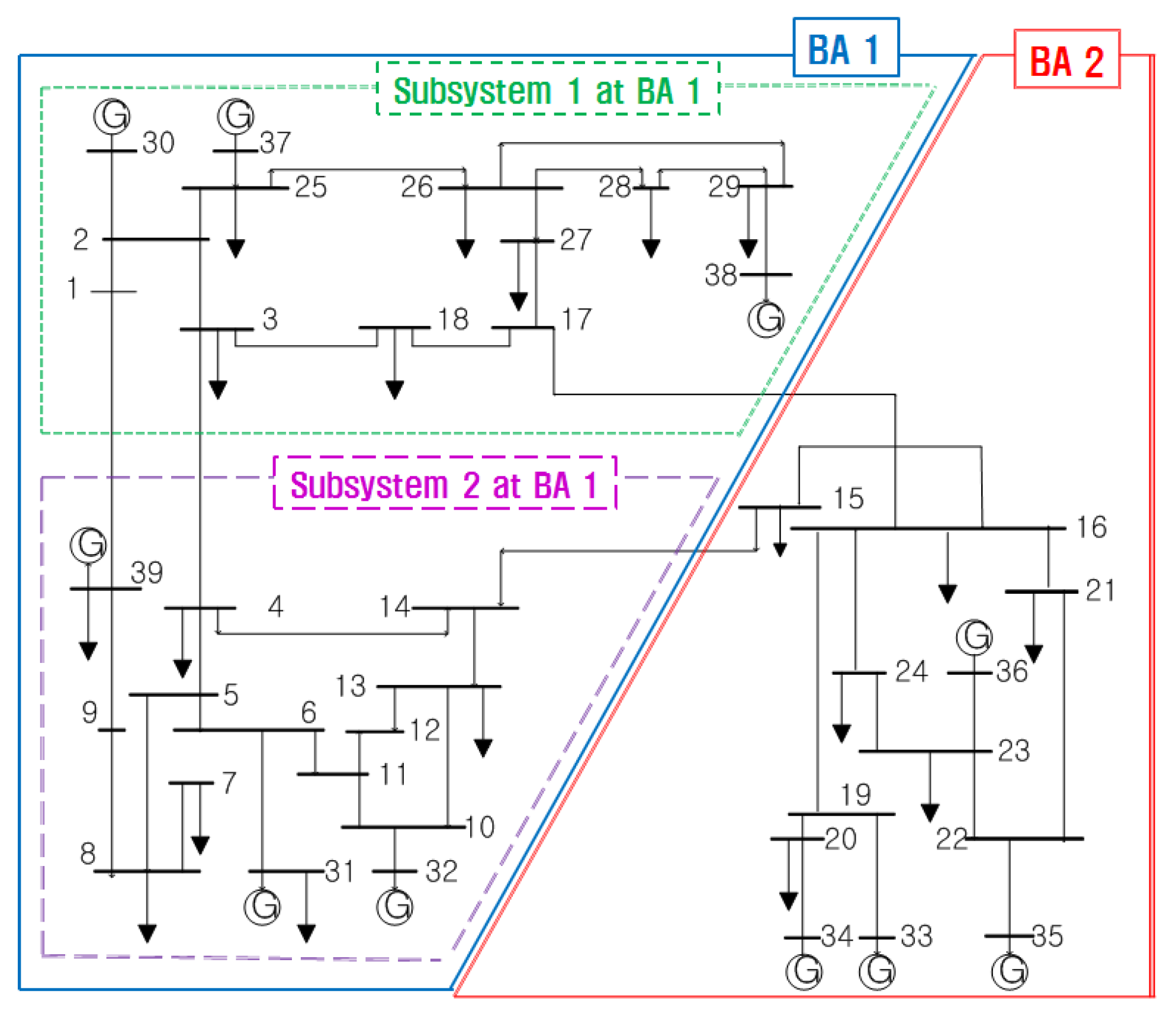
3.4. Bulk-Area Partitioning for MPC-Based AGC
4. Illustrative Example
| Generator Bus | M | D | Tg | Ta | Kt | r | () | () |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # 30 (Gen1) | 2 | 5 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 250 | 19 | 3 | −3 |
| # 31 (Gen2) | 3 | 5 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 250 | 19 | 3 | −3 |
| # 32 (Gen3) | 2 | 5 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 250 | 19 | 2 | −2 |
| # 33 (Gen4) | 2 | 5 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 250 | 19 | 2 | −2 |
| # 34 (Gen5) | 3 | 5 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 250 | 19 | 3 | −3 |
| # 35 (Gen6) | 2 | 5 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 250 | 19 | 3 | −3 |
| # 36 (Gen7) | 2 | 5 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 250 | 19 | 3 | −3 |
| # 37 (Gen8) | 2 | 5 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 250 | 19 | 3 | −3 |
| # 38 (Gen9) | 3 | 5 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 250 | 19 | 2 | −2 |
| # 39 (Gen10) | 2 | 5 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 250 | 19 | 2 | −2 |
| Event time [s] | Bus number | Magnitude [pu] |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 28 | 0.2 |
| 50 | 13 | -0.1 |
| 100 | 22 | 0.15 |
4.1. Centralized MPC-Based AGC Systems

| Description | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Discretized Minimum Step Time [s] | Tf | 1 |
| AGC Update Time [s] | Tu | 2 |
| Line Control Update Time [s] | Tline | 6 |
| Weighting Matrix | Q | 102I |
| QN | 102I | |
| R | I | |
| Qf | Iline | |
| Rf | I | |
| Prediction Horizon | N | 20 |
| Frequency Bias Factor | 200 |
4.2. Distributed MPC-based AGC Systems
| Description | Parameter | BA1 | BA2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discretized Minimum Step Time [s] | Tf | 1 | 1 |
| AGC Update Time [s] | Tu | 3 | 2 |
| Weighting Matrix | Q | 102I1 | 102 I2 |
| QN | 102 I1 | 102 I2 | |
| R | I1 | I2 | |
| Prediction Horizon | 20 | 20 | |
| Frequency Bias Factor | 120 | 80 |
| Description | Parameter | SB1 | SB2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical power sampling time [s] | Tm | 4 | |
| Q | 102Isb1 | 102 Isb2 | |
| Weighting Matrix | QN | 102 Isb1 | 102 Isb2 |
| R | Isb1 | Isb2 | |
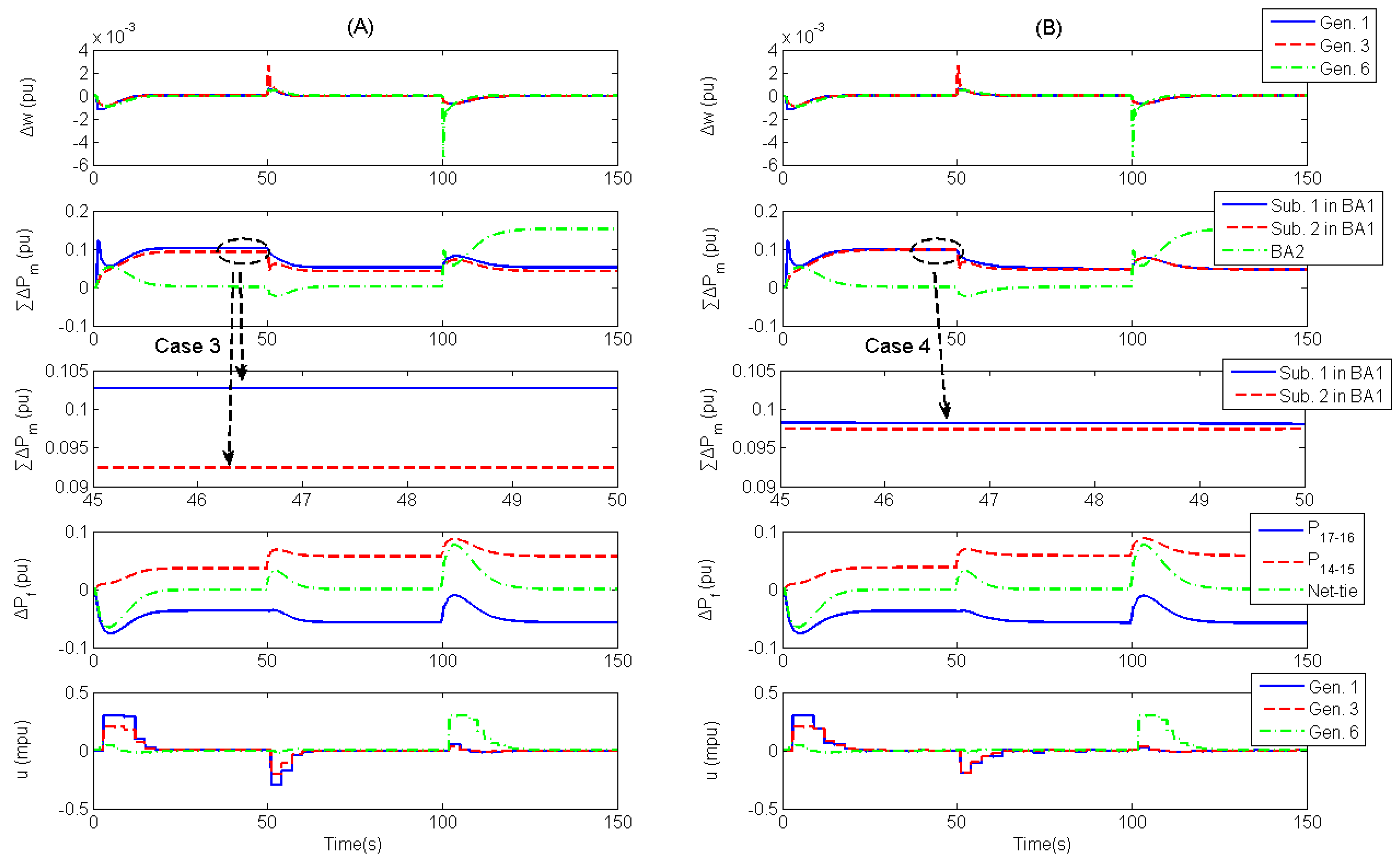
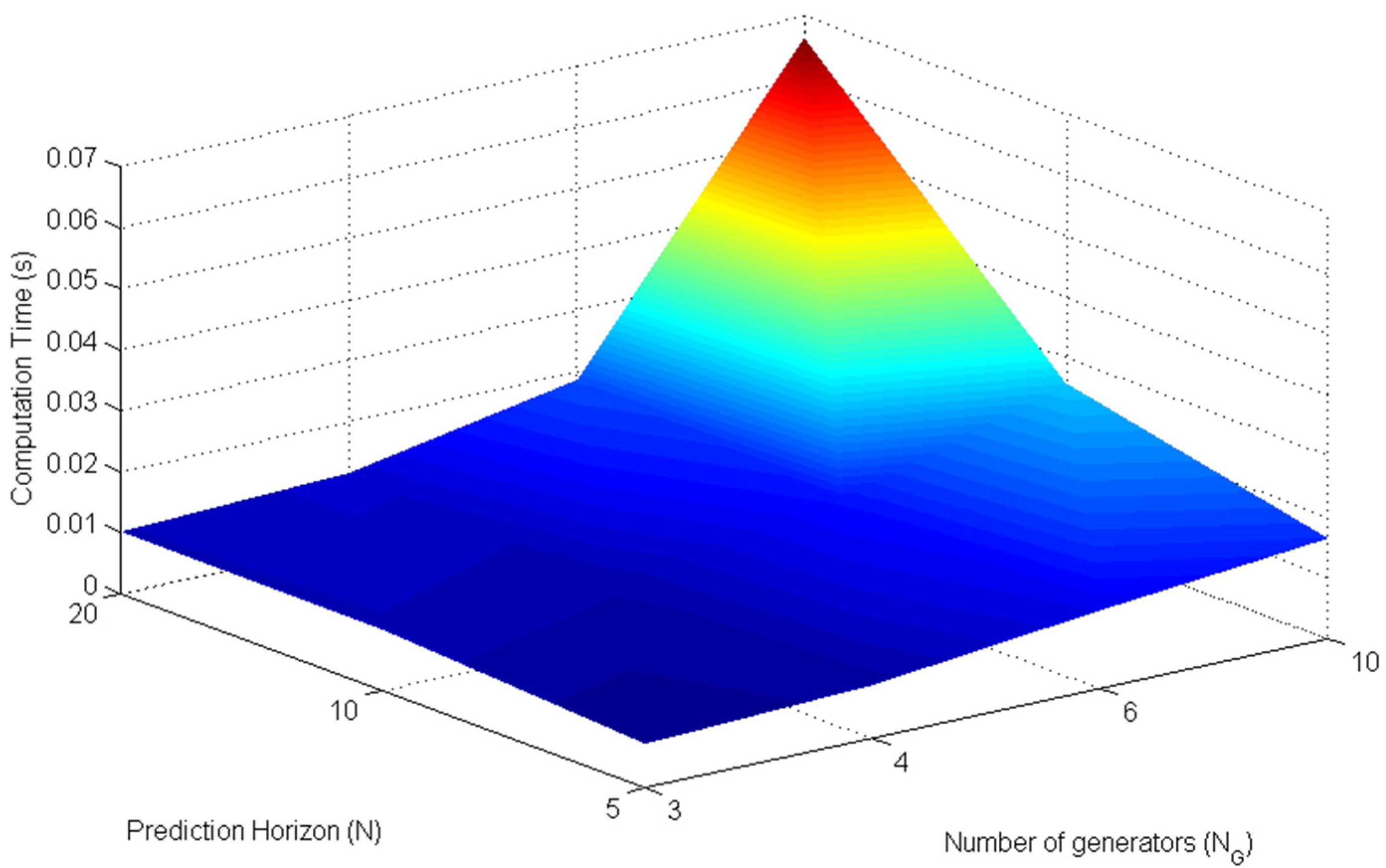
4.3. Discussion on Structure-Dependent AGC Scheme
| Considerations for implementation | Centralized structure | Distributed structure | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | Proposed | Original | Proposed | |
| Wheeling | Χ | Χ | Χ | |
| Computation Time | Χ | Χ | ∆ | |
| Practicality | Χ | Χ | ||
| Settling time (Tst) [s] | 7.60 | 24.60 | 15.05 | 16.01 |
5. Conclusions
Nomenclature
Constants:
| V | Bus voltage [pu] |
Bus voltage angle [radian] | |
| P | Initial bus power generation or demand [pu/100 MW] |
| Ta | Time constant of the turbine [s] |
| Tg | Time constant of governor [s] |
| Tf | Discretized minimum time step [s] |
| Tu | Discretized automatic generation control update time [s] |
| Tm | Discretized mechanical power sampling time step [s] |
| Tline | Discretized line power flow control update time step [s] |
| Tst | Frequency settling time [s] |
| D | Damping constant |
| M | Moment of inertia of the generator [s] |
| Kt | Parameter in linearization for turbine characteristics |
| r | Parameter in linearization for governor droop characteristics |
| J | Jacobian matrix of power evaluated at angle |
Frequency bias factor in i-balancing area | |
Maximum generation control ramp rate [pu/s] | |
Minimum generation control ramp rate [pu/s] |
Variables:
Load reference [pu] | |
Load frequency set point [pu] | |
Generator frequency [pu] | |
| Pm | Turbine mechanical power [pu] |
Governor-controlled valve opening [pu] | |
| F | Mapped injected-power [pu] |
| Pf | Tie-line power flow [pu] |
| y | Concatenated state variables in full-scale dynamic model |
Indices:
| k | Discretized minimum time step [k = kTf] |
| ku | Discretized frequency control update time step [ku = kuTu] |
| Kline | Discretized tie-line flow control update time step [kline = klineTline] |
| km | Discretized mechanical power sampling time step [km = kmTm] |
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, G. EPRI Power System Dynamics Tutorial; Report 1016042; Electric Power Research Institute: Palo Aoto, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rossiter, J.A. Model-Based Predictive Control: A Practical Approach; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, T.H.; Bevrani, H.; Hassan, A.A.; Hiyama, T. Model predictive based load frequency control design. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference of Electrical Engineering, Busan, Korea, 11–14 July 2010; pp. 1–6.
- Kong, L.F.; Xiao, L. A new model predictive control scheme-based load-frequency control. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation, Guangzhou, China, 30 May–1 June 2007; pp. 2514–2518.
- Yousef, A.M. Model predictive control approach based load frequency controller. WSEAS Trans. Syst. Cont. 2011, 6, 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- Camponogara, E.; Jia, D.; Krogh, B.H.; Talukdar, S. Distributed model predictive control. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2002, 22, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkat, A.; Hiskens, I.; Rawlings, J.; Wright, S. Distributed MPC strategies with application to power system automatic generation control. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2008, 16, 1192–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, H.; Liu, X. Nonlinear distributed MPC strategy with application to AGC of interconnected power system. In Proceedings of the Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Qingdao, China, 25–27 May 2013.
- Ma, M.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Allgöwer, F. Distributed model predictive load frequency control of multi-area interconnected power system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 62, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundur, P. Power System Stability and Control; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 581–613. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, T.H.; Bevrani, H.; Hassan, A.A.; Hiyama, T. Decentralized model predictive based load frequency control in an interconnected power system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, M.; Zaborszky, J. Dynamics and Control of Large Electric Power Systems, 1st ed.; John Willey and Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 352–370. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. Structure Modeling and Hierarchical Control of Large Scale Electric Power System. Ph.D. Dissertation, Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science—Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Eidson, B. Estimation and Hierarchical Control of Market-driven Electric Power Systems. Ph.D. Dissertation, Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science—Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Makarov, Y.V.; Ma, J.; Lu, S.; Nguyen, T.B. Assessing the Value of Regulation Resources Based on Their Time Response Characteristics; CERTS Report PNNL-17632; Pacific Northwest National Laboratory: Richland, WA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, A.J.; Wollenbergy, B.F. Power Generation, Operation, and Control; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, C.L.; Nagle, H.T. Digital Control System, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1990; pp. 356–372. [Google Scholar]
- Bertsekas, D.P. Dynamic Programming and Optimal Control, 1st ed.; Athena Scientific: Belmont, MA, USA, 1995; Volume 1, pp. 130–157. [Google Scholar]
- Pai, M.A. Energy Function Analysis for Power System Stability; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, R.D.; Murillo-Sanchez, C.E.; Gan, D. MATPOWER 5.0.0 User’s Manual. Available online: http://www.pserc.cornell.edu//matpower/ (accessed on 17 December 2014).
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, Y.-S.; Park, J.; Yoon, Y.T. Designing Structure-Dependent MPC-Based AGC Schemes Considering Network Topology. Energies 2015, 8, 3437-3454. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8053437
Jang Y-S, Park J, Yoon YT. Designing Structure-Dependent MPC-Based AGC Schemes Considering Network Topology. Energies. 2015; 8(5):3437-3454. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8053437
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Young-Sik, JoonHyung Park, and Yong Tae Yoon. 2015. "Designing Structure-Dependent MPC-Based AGC Schemes Considering Network Topology" Energies 8, no. 5: 3437-3454. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8053437
APA StyleJang, Y.-S., Park, J., & Yoon, Y. T. (2015). Designing Structure-Dependent MPC-Based AGC Schemes Considering Network Topology. Energies, 8(5), 3437-3454. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8053437






