2.1. Algae Are Harvested and Concentrated onto Amberlite Anion Exchange Resin
Amberlite CG-400, a divinylbenzene-based resin containing quaternary ammonium groups (3.8 mmol/g [
21]), has been previously shown to bind and concentrate two different species of green algae for removal from the water supply [
22]. Here, we used Amberlite to concentrate and dewater biomass from two potentially high oil-producing green algal species,
Neochloris oleoabundans [
23] and KAS 603 [
24]. For routine comparisons, algal suspension was passed through the column until saturation was achieved. Algae appeared to bind on contact, initially accumulating as a band at the top of the resin bed. As more algae were added, the upper green layer progressively expanded down to the bottom of the resin bed. Prior to the resin bed becoming solid green, the flow-through was clear and colorless. Once the resin bed became solid green, color quickly began to appear in the effluent and this was taken as the saturation point.
To determine the binding capacity of the resin for Neochloris and KAS 603, the OD680 of the algal suspension was measured before and after passing the algae through an Amberlite column. The concentration of algae in the initial suspension and the in flow-through were determined from algal OD680 absorbance versus dry cell weight (DCW) calibration curves generated for both types of algae (Supplementary Figure S1). The flow-through included the solution from the algae algal suspension that went through the resin and the subsequent wash to remove unbound algae. The total amount of algae bound to the resin was then determined by subtracting the amount of algae in the flow-through from the total that was added to the column.
For all the experiments algal binding to the resin was tested at pH 7, although there was no significant difference in binding over the pH range of 6–9 (Supplementary Figure S2). Since for Amberlite, algal binding decreases with increasing ionic strength, binding studies for both algae were tested under freshwater conditions (salinity 5 psu). The algal suspensions were used at 0.4 g/L, the value that we typically obtain in our simple airlift photobioreactors. When more dilute algal suspensions were tested, saturation of the resin was still achieved but, as would be expected, the volume of algal suspension and time required to achieve saturation increased. Since algae can be entrained in the resin beads, our protocol included a washing step between binding and elution to ensure only algae that were actually bound to the resin were counted.
Figure 1(a) gives a schematic for resin-binding and elution experiments shown in
Figure 1,
Figure 2 and
Figure 3. Algal binding capacity was determined for each cycle of algal binding. Reusability of the resin was assessed in terms of loss of binding capacity over multiple cycles of algal binding and elution. These experiments were carried out either using only fresh sulfuric acid/methanol reagent to elute the algae (Series A, “fresh”) or using sulfuric acid/methanol that was recycled after the first use (Series B, “used”).
Although the flow through approach in
Figure 1(a) gave repeatable values for saturation and was used for all experiments except that shown in
Figure 4, we later found that longer contact times, which involved stirring excess algae with resin for up to 15 min, gave somewhat larger binding capacities than those obtained using the flow through method. However, while the binding capacity numbers would be improved with longer contact times, the patterns remain the same.
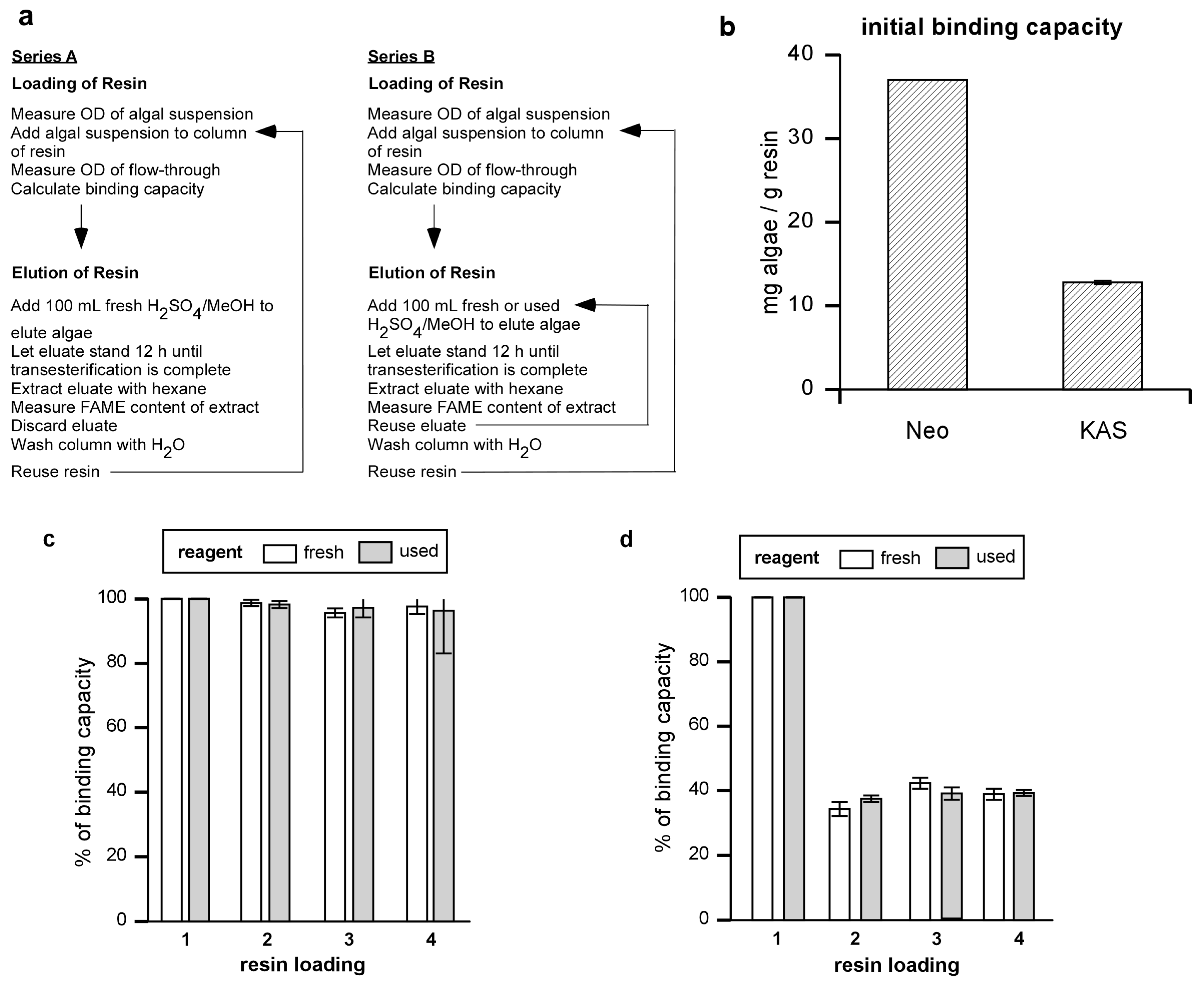
Figure 1.
Algal binding capacity of Amberlite and resin reuse. (a) Experiment series for determining binding capacity and reusability of resin and transesterification reagent. (b) Binding capacities of Amberlite (mg algal dry weight / gram resin) were determined for Neochloris and KAS 603. (c) Neochloris or (d) KAS 603 were loaded onto resin columns and eluted with 100 mL of 5% sulfuric acid/methanol reagent. After washing the column with distilled water, the operation was repeated for three more cycles, eluting with either fresh methanol sulfuric acid reagent (fresh) or reusing the previously used reagent (used). The binding capacity of the resin was determined for each cycle of algal loading onto the resin.
Figure 1.
Algal binding capacity of Amberlite and resin reuse. (a) Experiment series for determining binding capacity and reusability of resin and transesterification reagent. (b) Binding capacities of Amberlite (mg algal dry weight / gram resin) were determined for Neochloris and KAS 603. (c) Neochloris or (d) KAS 603 were loaded onto resin columns and eluted with 100 mL of 5% sulfuric acid/methanol reagent. After washing the column with distilled water, the operation was repeated for three more cycles, eluting with either fresh methanol sulfuric acid reagent (fresh) or reusing the previously used reagent (used). The binding capacity of the resin was determined for each cycle of algal loading onto the resin.
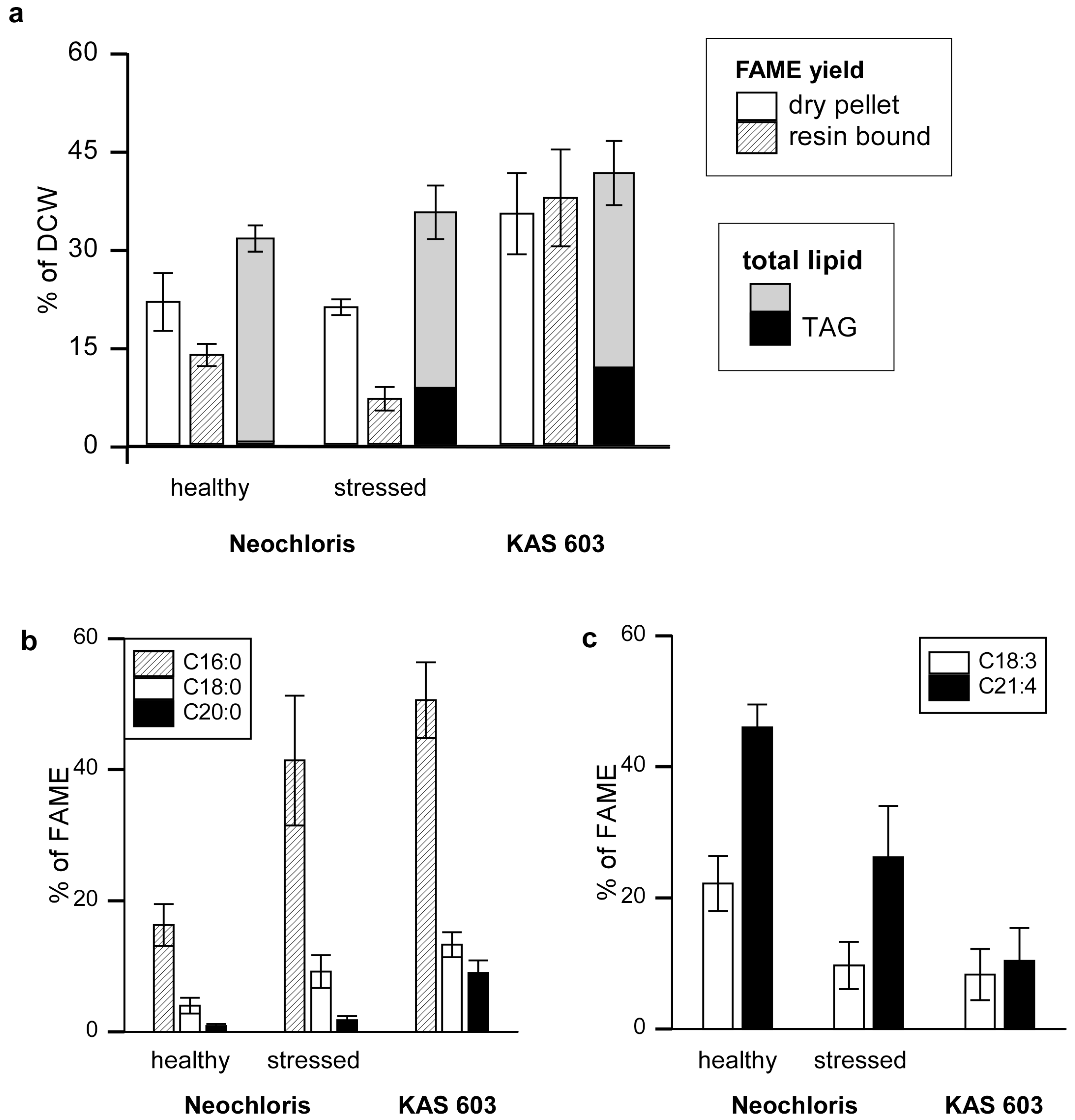
Figure 2.
FAME yield and characterization by resin-bound transesterification. (a) FAMEs from normal or stressed (nitrogen-starved) Neochloris and KAS 603 were generated either by elution of resin-bound algae with 5% sulfuric acid/methanol reagent or by subjecting dry algal pellets subjected to sequential base hydrolysis followed by treatment with sulfuric acid in methanol to esterify free fatty acids. The FAME yields were expressed as percent of dry cell weight. The weight of a crude lipid extract from parallel batches of algae and the TAG content those extracts (determined by HPLC) are given for comparison. The FAME prepared from resin-bound algae were analyzed by HPLC/MS to determine the abundance of (b) saturated C16:0, C18:0, and C20:0 and (c) unsaturated C18:3 and C21:4 acyl constituents relative to total FAME derived.
Figure 2.
FAME yield and characterization by resin-bound transesterification. (a) FAMEs from normal or stressed (nitrogen-starved) Neochloris and KAS 603 were generated either by elution of resin-bound algae with 5% sulfuric acid/methanol reagent or by subjecting dry algal pellets subjected to sequential base hydrolysis followed by treatment with sulfuric acid in methanol to esterify free fatty acids. The FAME yields were expressed as percent of dry cell weight. The weight of a crude lipid extract from parallel batches of algae and the TAG content those extracts (determined by HPLC) are given for comparison. The FAME prepared from resin-bound algae were analyzed by HPLC/MS to determine the abundance of (b) saturated C16:0, C18:0, and C20:0 and (c) unsaturated C18:3 and C21:4 acyl constituents relative to total FAME derived.
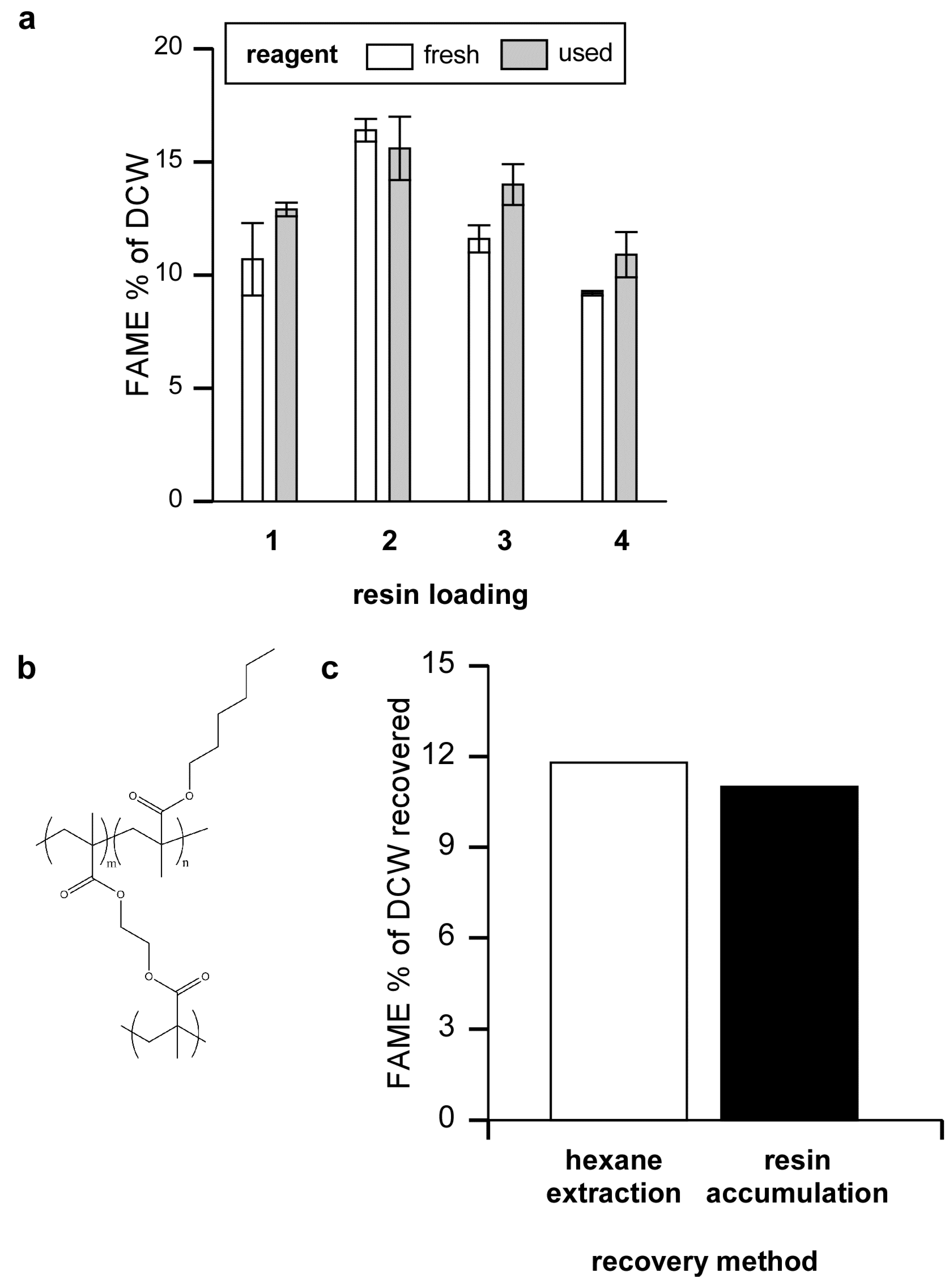
Figure 3.
Efficiency of FAME production using recycled reagent, and FAME removal. (a) Algal were loaded onto Amberlite and eluted with 5% sulfuric acid/methanol four times in succession using either fresh reagent or reusing the old reagent after the initial elution. Twelve h after each elution the FAME was extracted with hexane, solvent was removed and the amount of FAME determined as a percentage of algal dry cell weight; (b) The sulfuric acid/methanol reagent containing algal FAME was either extracted with hexane or, for comparison, passed over a hydrophobic resin column composed of 80% EGDMA and 20% HMA; (c) FAME relative to total dry algal weight obtained by hexane extraction or after eluting FAME bound to the hydrophobic column.
Figure 3.
Efficiency of FAME production using recycled reagent, and FAME removal. (a) Algal were loaded onto Amberlite and eluted with 5% sulfuric acid/methanol four times in succession using either fresh reagent or reusing the old reagent after the initial elution. Twelve h after each elution the FAME was extracted with hexane, solvent was removed and the amount of FAME determined as a percentage of algal dry cell weight; (b) The sulfuric acid/methanol reagent containing algal FAME was either extracted with hexane or, for comparison, passed over a hydrophobic resin column composed of 80% EGDMA and 20% HMA; (c) FAME relative to total dry algal weight obtained by hexane extraction or after eluting FAME bound to the hydrophobic column.
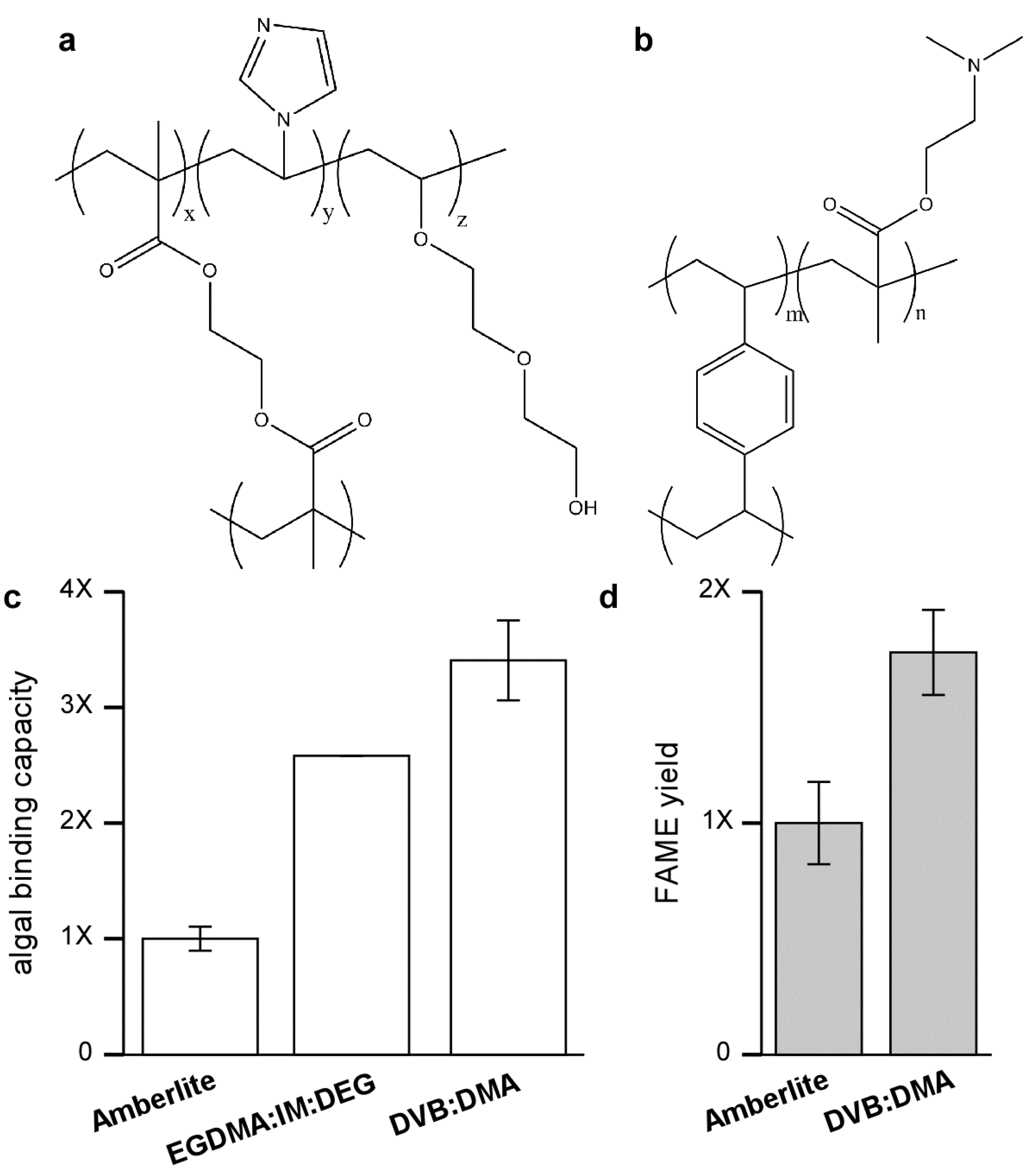
Figure 4.
Functionalized resins for improved binding of KAS603. The relative binding capacity of Amberlite for KAS 603 is compared to anion exchange resins composed of either (a) EGDMA-IM-DEG (60:30:10) or (b) DVB-DMA (60:40); (c) The results show that the binding capacity of Amberlite is low compared to the other resins; (d) In addition to binding more algae, subsequent elution of either Amberlite or DVB-DMA shows that greater amounts of FAME are produced from the DVB:DMA resin.
Figure 4.
Functionalized resins for improved binding of KAS603. The relative binding capacity of Amberlite for KAS 603 is compared to anion exchange resins composed of either (a) EGDMA-IM-DEG (60:30:10) or (b) DVB-DMA (60:40); (c) The results show that the binding capacity of Amberlite is low compared to the other resins; (d) In addition to binding more algae, subsequent elution of either Amberlite or DVB-DMA shows that greater amounts of FAME are produced from the DVB:DMA resin.
The results showed that the binding capacity for
Neochloris was 37.0 mg/g resin whereas that for KAS 603 was 12.8 mg/g resin [
Figure 1(b)]. In terms of efficiency of removal of algae from 1 L of 0.4 g/L suspension, 10 g of Amberlite will sequester 93% of the
Neochloris, whereas 30 g of Amberlite will sequester 96% of the KAS603 during a single pass through the column.
Although the difference in binding capacity could possibly be attributed to differences in surface charge density, studies to be detailed elsewhere show that the nature of the resin backbone, especially its hydrophobicity has a large impact on binding capacity [
25]. In resins based on a methacrylate backbone, both
Neochloris and KAS 603 showed similar binding capacities. Furthermore, binding capacity was greatly increased with the inclusion of glycol groups, which do not alter the charge characteristics of the resin but make it more hydrophilic.
After binding, algae were eluted with 100 mL of 5% sulfuric acid in methanol. This treatment visibly removed algae from the resin and regenerated the resin. It appears that most of the algae was dissolved by the sulfuric acid/methanol reagent as shown by filtering an eluate of Neochloris through a pre-weighed PTFE filter (Millipore Omnipore, pore size 0.1 μm). Only 6.1% of the original DCW was recovered on the filter.
In order to determine how completely the resin was regenerated, resin columns were loaded with
Neochloris [
Figure 1(c) “fresh”] or KAS 603 [
Figure 1(d) “fresh”] and eluted with fresh portions of sulfuric acid/methanol four times in succession. For comparison, parallel experiments were carried out where, after the initial binding and elution using fresh sulfuric acid/methanol solution, the reagent was then recycled for the three remaining cycles of algal binding and elution for both
Neochloris [
Figure 1(c) “used”] and KAS 603 [
Figure 1(d) “used”]. With each cycle, the amount of algae bound to the resin was determined based on the OD
680 as described above. Using fresh reagent,
Neochloris after the initial binding and elution, binding capacity dropped to 97% of its initial value and remained constant thereafter. Using fresh reagent with KAS 603, binding dropped to 39% of its initial value after the first cycle but remained constant thereafter. When the experiments were carried out using the same sulfuric acid/methanol reagent for each cycle, the results were comparable to those obtained using the fresh reagent [
Figure 1(c) and
Figure 1(d) “used”).
The results show that the sulfuric acid/methanol reagent can be used for multiple cycles before it is consumed or rendered ineffective. Eventually methanol will be consumed while products such as glycerol, FAME, and other molecules will build up in the recycled sulfuric acid/methanol reagent. Unused methanol, being quite volatile would be easy to remove from the mixture. FAME, as we detail below, can also be easily removed. It will be interesting to see if the recycled reagent can be further fractionated and if potentially high value compounds might also be isolated from the mixture.
The drop in binding capacity of Amberlite for KAS 603 is not understood. It is not due to the action of the sulfuric acid/methanol reagent alone since pretreatment of the resin with sulfuric acid/methanol prior to initial binding of algae does not lower the binding capacity. A similar drop in binding capacity is not seen with the high capacity anion exchange resins based on a more polar methacrylate backbone [
25]. Perhaps then the best explanation relates to the hydrophobicity of the divinylbenzene that interacts with hydrophobic components in the algae thereby either masking some of the charges on the resin or sterically interfering with binding.
2.2. Conversion of Algal Lipids to FAME
Since algae were eluted off the resin by 5% sulfuric acid in methanol, a reagent that catalyzes the transesterification of esterified fatty acid to FAMEs, tests were carried out to measure conversion of lipids in the eluate to FAME. To quantify FAME and other lipids, normal-phase HPLC was used in conjunction with an evaporative light scattering detector and mass spectrometry (HPLC-ELSD/MS; Supplementary Figure S3) [
24]. The advantage here is that one can rapidly measure the amount of FAME generated, its fatty acid composition, and the amount of residual triacylglycerol starting material present in the reaction product as well as in crude total lipid extracts (Supplementary Figure S4). In the reaction product, the presence of residual TAG is an indicator that the transesterification reaction did not reach completion. Preliminary tests carried out by extracting the sulfuric acid methanol eluate with hexane to obtain the products at various times after elution showed that 12 h at room temperature was sufficient to consume all the TAG. What remains in the extract are mainly saturated hydrocarbons, which have been characterized in more detail elsewhere [
24], and FAME (Supplementary Figure S4a).
As a reference, algal lipids were converted to FAME by a two step procedure that entailed treatment of dry algal pellets with base to hydrolyze fatty acid esters followed by re-esterification of free fatty acids in sulfuric acid and methanol [
26]. The results showed 21.7%, 20.9%, and 35.2% of dry weights were recovered as FAME for healthy
Neochloris, stressed
Neochloris, and KAS 603 respectively [
Figure 2(a)]. Acid-catalyzed transesterification of resin-bound algae resulted in 13.6%, 6.9%, and 37.6% of dry weight recovered as FAME for healthy
Neochloris, stressed
Neochloris, and KAS 603 respectively. For comparison, FAME synthesis yields are shown alongside total lipid extract amounts [
Figure 2(a)]. Crude lipid extract constituted 31.4% of total dry weight for healthy
Neochloris, 35.4% for stressed
Neochloris, and 41.3% for KAS 603. HPLC analysis of the crude lipid extract showed that TAG constituted 0.4%, 8.6%, and 11.7% of dry weight for healthy
Neochloris, stressed
Neochloris, and KAS 603, respectively.
For KAS 603 comparable yields of FAME were obtained using either method and the total FAME was close to the weight of total lipid. For Neochloris, both methods generated substantially less FAME than total lipid and the resin-bound algae yielded only 60% of the FAME generated from the dried pellet. Clearly, substantially more FAME can be generated by direct transesterification than can be accounted for by TAG alone. For healthy Neochloris, there was hardly any TAG present in the extracts yet 15%–20% of the DCW could be recovered as FAME. For KAS 603, 10% of the DCW was present as TAG but nearly 40% of the DCW was recovered as FAME. These data suggest that much of the FAME is derived from polar lipids such as glycolipids and phospholipids.
One of the surprising results of this study is the finding that
Neochloris accumulates high amounts of TAG when subjected to nitrogen deprivation [
23], yet with only a modest increase in total lipid. While TAG increased nearly ten-fold, total lipid still constituted approximately 20% of dry weight, and FAME yield from dried biomass was comparable between healthy and stressed
Neochloris. The most notable difference between FAME generated from healthy and stressed
Neochloris was found in the fatty acid composition. This can be seen by analyzing positive mode APCI mass spectra of the various FAME reactions. Mass signatures were determined based on the fragmentation behavior of FAME standards (Supplementary Figure S5). Fatty acyl groups in FAME were identified and quantified by positive mode APCI-MS, as shown in Supplementary Figure S6 and Supplementary Table S1.
Figure 2(b) and
Figure 2(c) indicate a trend towards a higher degree of fatty acid saturation with increased TAG content. For example, healthy
Neochloris, having little TAG content, yielded more C18:3 and C21:4 species and less C16:0, C18:0, and C20:0 than the other two algal groups. In contrast, stressed
Neochloris and KAS 603, having a higher TAG content, yielded more C16:0, C18:0, and C20:0, and less C18:3 and C21:4 than healthy
Neochloris. This shift in TAG fatty acid composition from unsaturated to saturated species with nitrogen starvation has been reported previously [
21].
2.6. Evaluation
While we are not equipped to do a formal life cycle analysis and feel it would be premature given the improvements needed in resin technology, nevertheless a comparison of the proposed resin-based processing to current approaches seems in order.
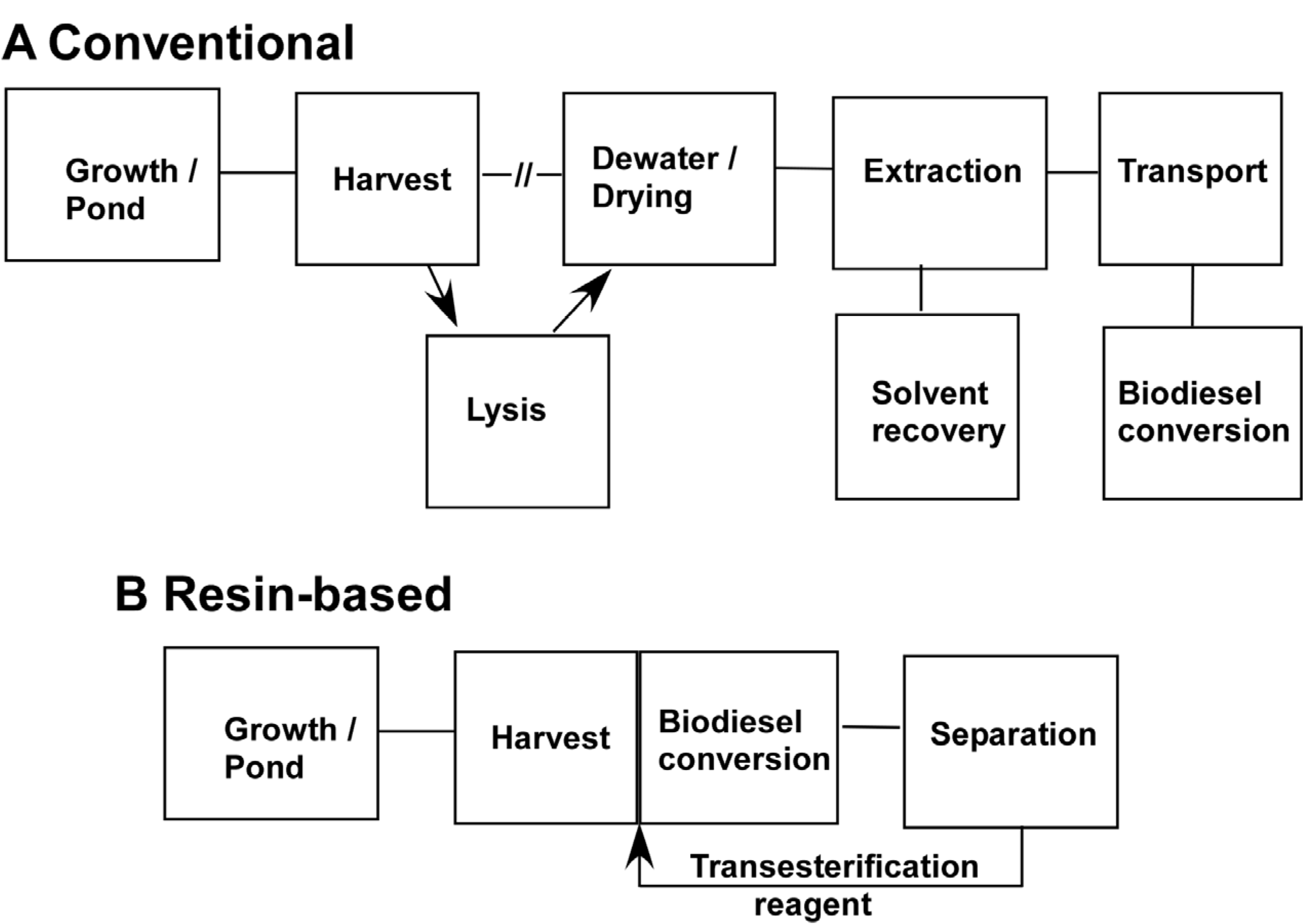
Figure 5 presents a general schematic for current algal processing schemes derived on published evaluations [
5,
29]. For the most part, the cost of growing algae would be the same. The use of resins could impact growth in terms of the need for nitrogen starvation or growth of monocultures as discussed below. Primarily, our one-step harvest to biodiesel approach would impact the most expensive steps in processing algae to biofuel, namely the harvesting and extraction steps.
Currently harvesting typically requires both pumping the algal suspension and some treatment such as centrifugation, flocculation or dissolved air flotation. Centrifugation and dissolved air flotation both have relatively large capital costs and substantial electricity. Where resins could make a difference is by eliminating the need for pumping water. While we have used resin beads for comparisons, we do not feel this is the best way to deploy them for harvesting. Resin beads are porous with a large internal volume that can trap water. The pores are typically 10–30 nm in diameter whereas the algae are on the order of 2–3 μm in diameter so they cannot enter the resin. Our measurements show that after the bulk water is removed, about 100 mg of water/gram resin is retained either inside the resin or entrained between the beads. A better alternative is to use thin films of resin where the internal volume is low compared to the surface area. We have proposed elsewhere a belt harvester type approach where a belt moves from the pond, where it picks up the algae to a vat which, in this case would contain sulfuric acid/methanol [
25]. In that study we estimated that a bristled belt 1 m wide × 7.5 m long could collect 3 kg algae per one complete turn of the belt. Other modes are possible such as mesh bags containing nonporous resin-coated particles that float or are semisubmerged.
Once the algae is harvested and eluted, the conversion to biodiesel is direct. There is no need for lysing, further drying and solvent extraction, steps that are considered quite expensive [
5]. Hexane extraction requires recovery of the hexane and a certain amount will be lost to the environment. Furthermore, hexane only recovers the neutral lipids (mainly TAG). Our experience at measuring TAG in pond-grown algae is that TAG levels rarely surpass 5% DCW and we have never seen them greater than 12% DCW. One of the advantages of this approach is that FAME is generated from both polar and neutral lipids thereby increasing the yield from the algae. Our data suggest improvements of up to 4-fold were possible with an alga (KAS 603) that made 10% TAG.
Figure 5.
Sequence of steps to obtain fuel from algae. (a) A conventional sequence of steps is given for the obtaining biodiesel from algae. (b) A sequence of processing steps using a resin-based approach. Both sequences are essentially the same in terms of growth. Conventional harvesting involves pumping of algal suspension and some other treatment such as centrifugation, dissolved air flotation or flocculation with chemicals. For the resin-based approach the resin will collect algae leaving most of the water behind. One possible mechanism is to use a belt harvester employing a resin- coated belt. For the conventional approach a possible lysis step between harvest and extraction has been included since it can improve extraction efficiency. For solvent extraction it is usually necessary to dry the algae. In the resin-based approach drying and conventional solvent extraction is eliminated. In this scenario, biodiesel would be produced on site so the cost of transportation of the extracted oil to a biodiesel plant would also be eliminated. Since biodiesel is generated with or without employing resins, the cost of that step would be similar in either scenario.
Figure 5.
Sequence of steps to obtain fuel from algae. (a) A conventional sequence of steps is given for the obtaining biodiesel from algae. (b) A sequence of processing steps using a resin-based approach. Both sequences are essentially the same in terms of growth. Conventional harvesting involves pumping of algal suspension and some other treatment such as centrifugation, dissolved air flotation or flocculation with chemicals. For the resin-based approach the resin will collect algae leaving most of the water behind. One possible mechanism is to use a belt harvester employing a resin- coated belt. For the conventional approach a possible lysis step between harvest and extraction has been included since it can improve extraction efficiency. For solvent extraction it is usually necessary to dry the algae. In the resin-based approach drying and conventional solvent extraction is eliminated. In this scenario, biodiesel would be produced on site so the cost of transportation of the extracted oil to a biodiesel plant would also be eliminated. Since biodiesel is generated with or without employing resins, the cost of that step would be similar in either scenario.
![Energies 05 02608 g005]()
The improved yield could affect several aspects of the algal growth process. Firstly, our data suggested that there was not so much to be gained by nitrogen starvation. Both starved and unstarved algae contained similar amounts of total lipid. Admittedly, the spectrum of fatty acids was different and this might be a factor. Secondly, resin-based conversion of total lipid to biodiesel might make it less important for growers to maintain a monoculture of high TAG-producing algae. Of course, high TAG production is a benefit but it is difficult to maintain monocultures in open ponds or in potentially other attractive scenarios where algae are grown in conjunction with wastewater treatment plants.
Finally production of biodiesel onsite eliminates the transportation cost of moving algal oil to a biodiesel plant. While the biodiesel must be recovered from the sulfuric acid methanol, we believe this can be done using a low solvent or even solventless hollow fiber extraction system. In commercial biodiesel plants, the glycerol separates from the biodiesel layer and the separation is facilitated by water. This may be possible as well but more study is needed to determine how best to fractionate the spent sulfuric acid/ methanol mixture. There will be many cellular components in the final sulfuric acid/methanol solution, some of which may be valuable as side products.