Exergy Analysis of an Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell-Gas Turbine Hybrid System Fed with Ethanol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Systems Description
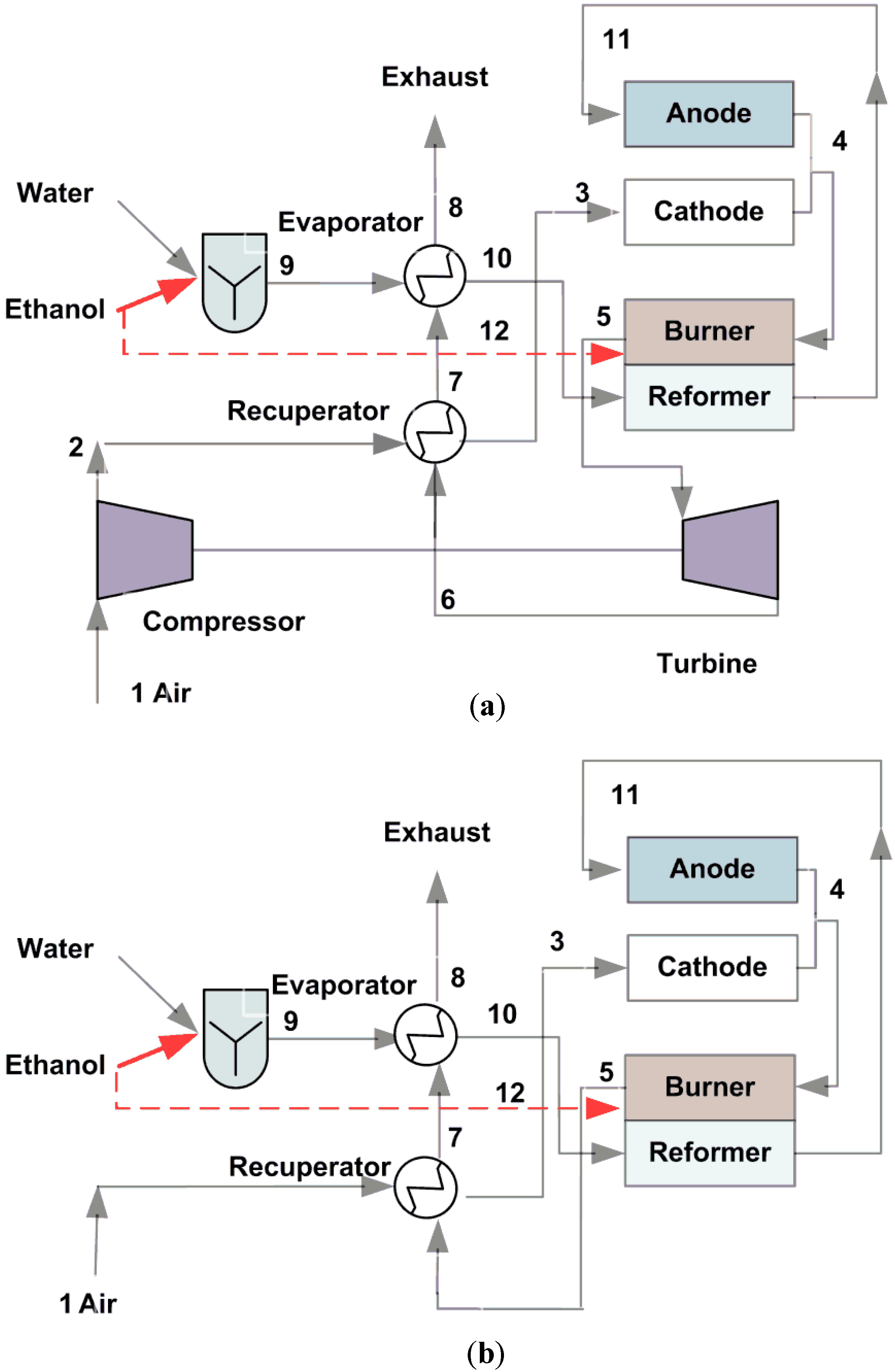
3. System Modeling
3.1. Solid Oxide Fuel Cell

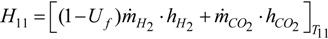

3.2. Burner-Reformer
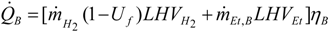
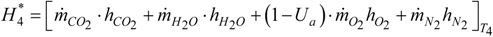
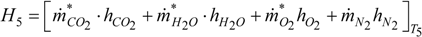
3.3. Compressor
3.4. Turbine
3.5. Recuperator
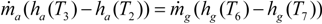
3.6. Evaporator
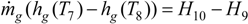
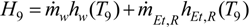

3.7. Simulation of the Systems


3.8. Exergy Analysis of the Systems

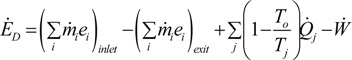

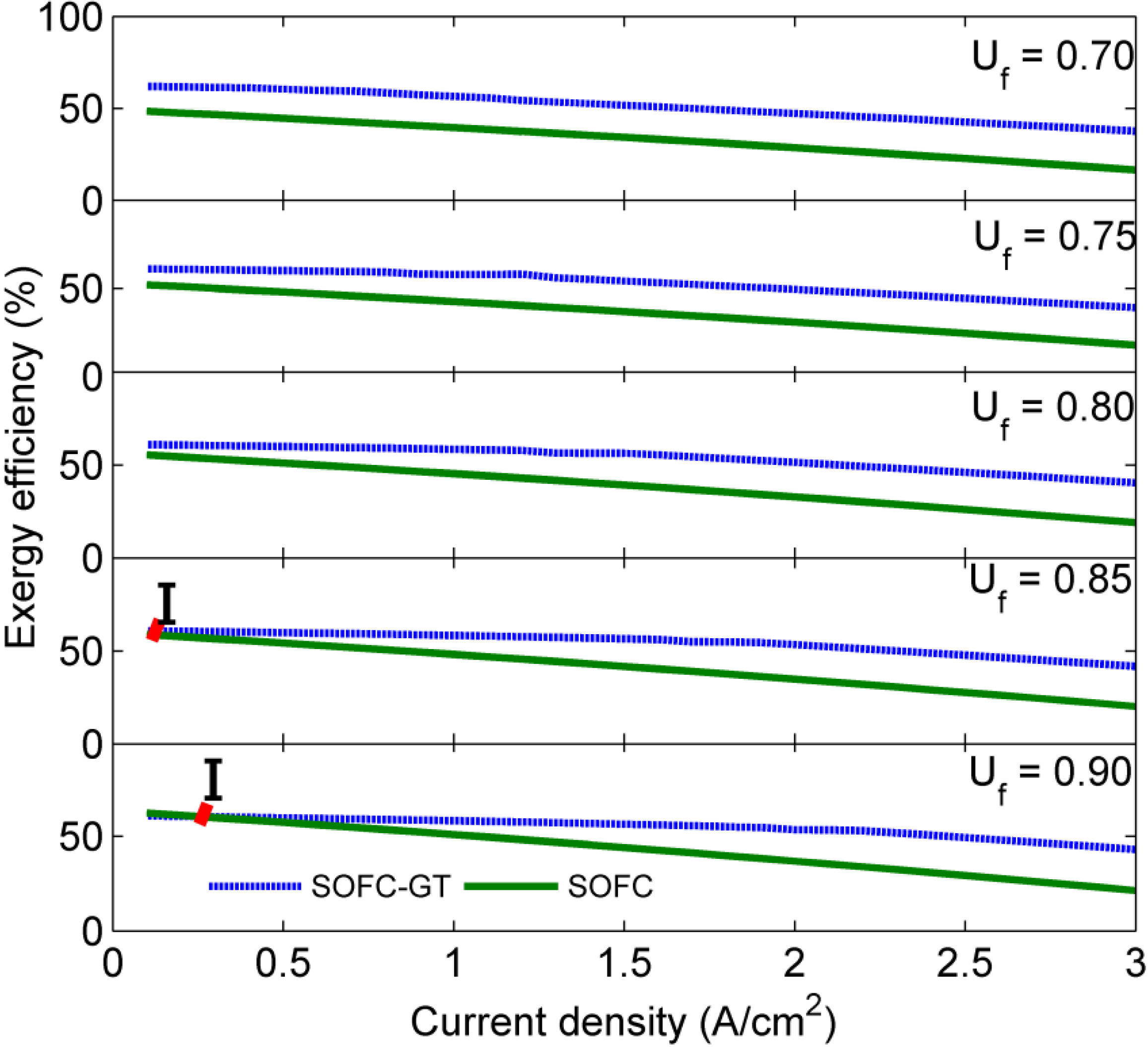
4. Results and Discussion
| Gas turbine cycle | |
| Compressor isentropic efficiency | 0.81 |
| Compressor pressure ratio | 4 |
| Turbine isentropic efficiency | 0.84 |
| AC generator efficiency | 0.95 |
| Burner-Reformer | |
| Ethanol Steam-to-Carbon Ratio | 1.5 |
| Burner efficiency | 0.98 |
| Pressure losses (%) | 5 |
| SOFC | |
| Air utilization factor (Ua) | 0.25 |
| Fuel utilization factor (Uf) | 0.85 |
| Pressure losses (%) | 4 |
| DC/AC conversion efficiency | 0.95 |
| Recuperator | |
| effectiveness | 0.85 |
| Pressure losses gas/air sides (%) | 4 |
| Ambient conditions | |
| Temperature (K) | 288 |
| Pressure (bar) | 1.013 |



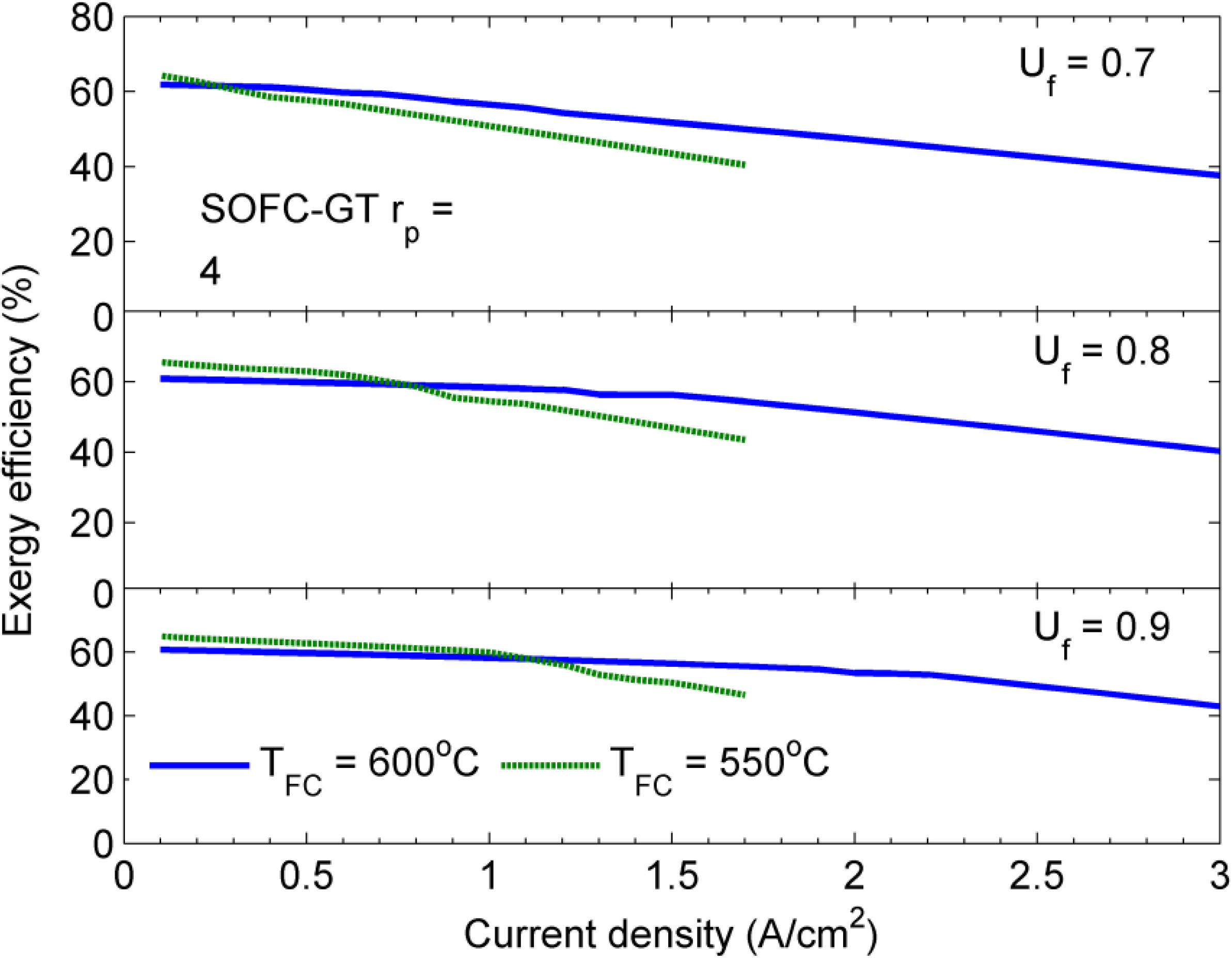
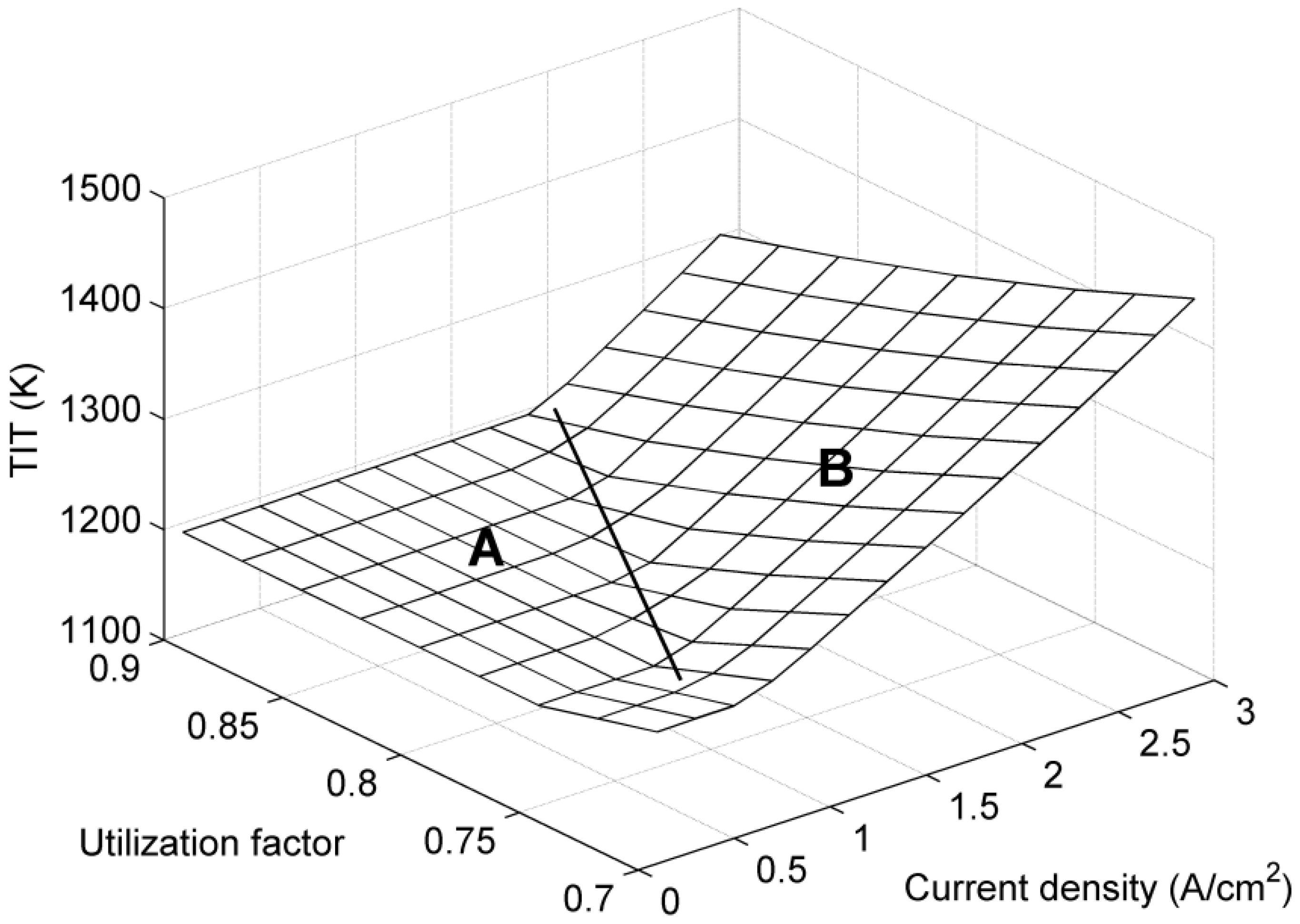
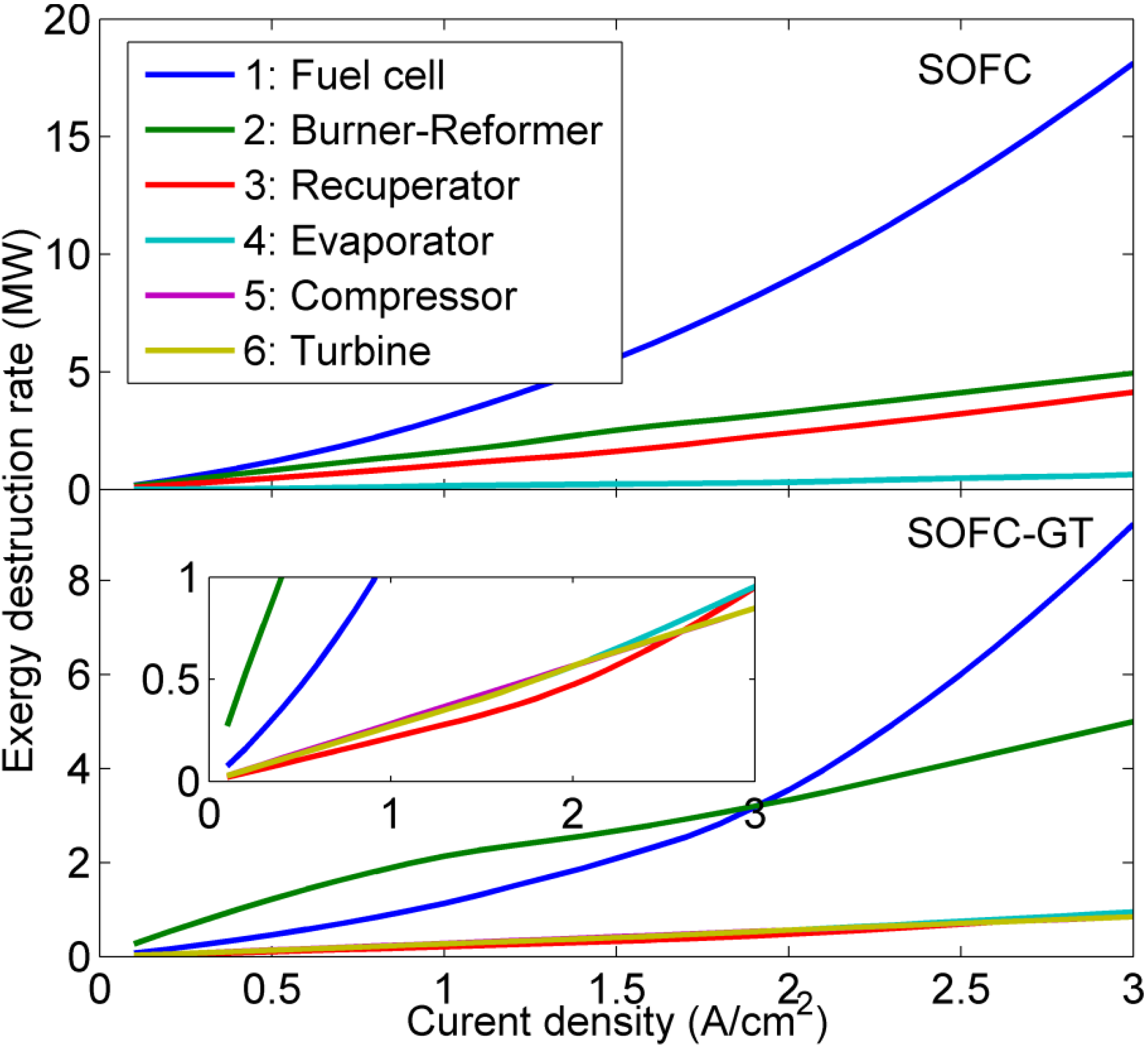
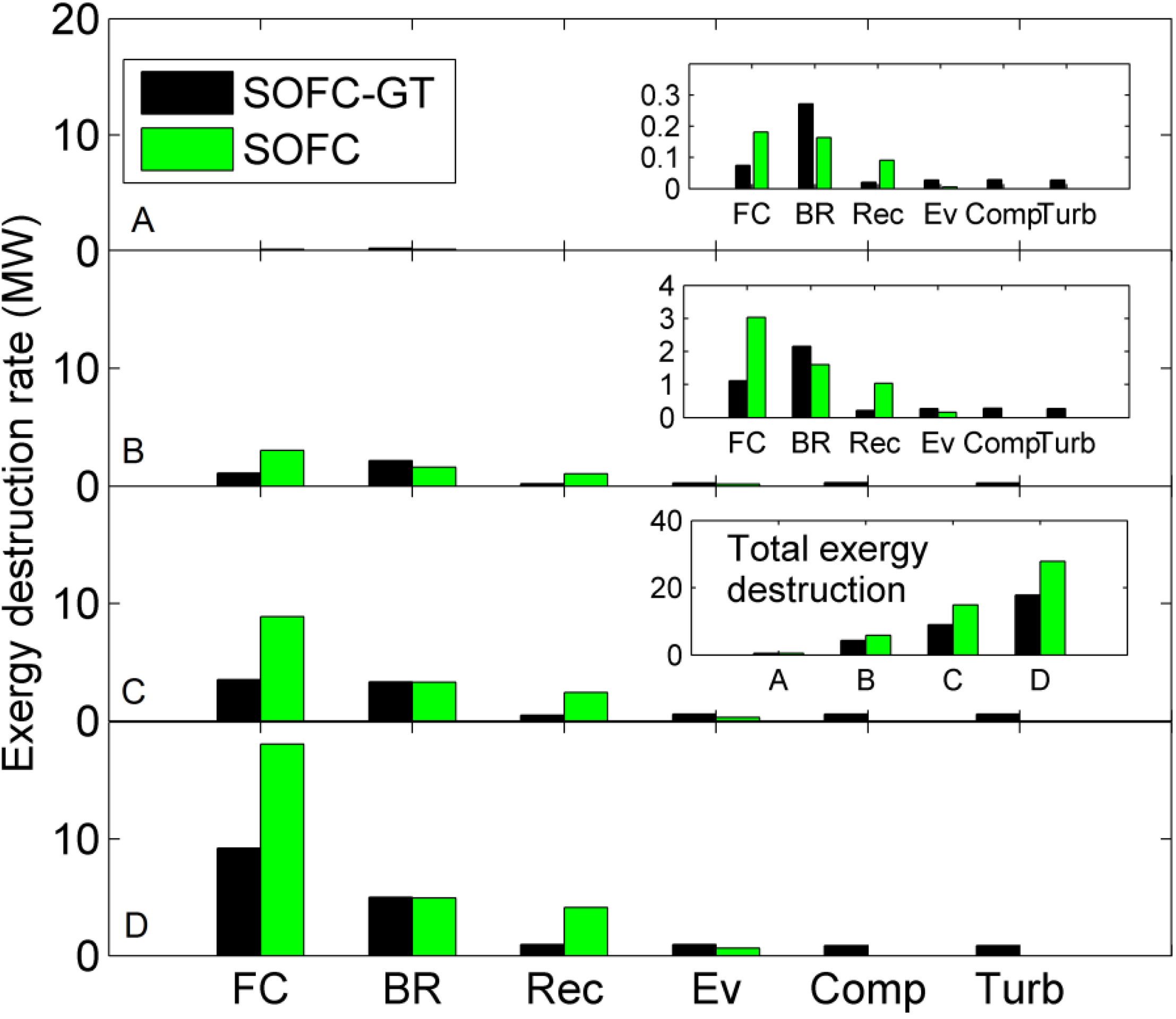

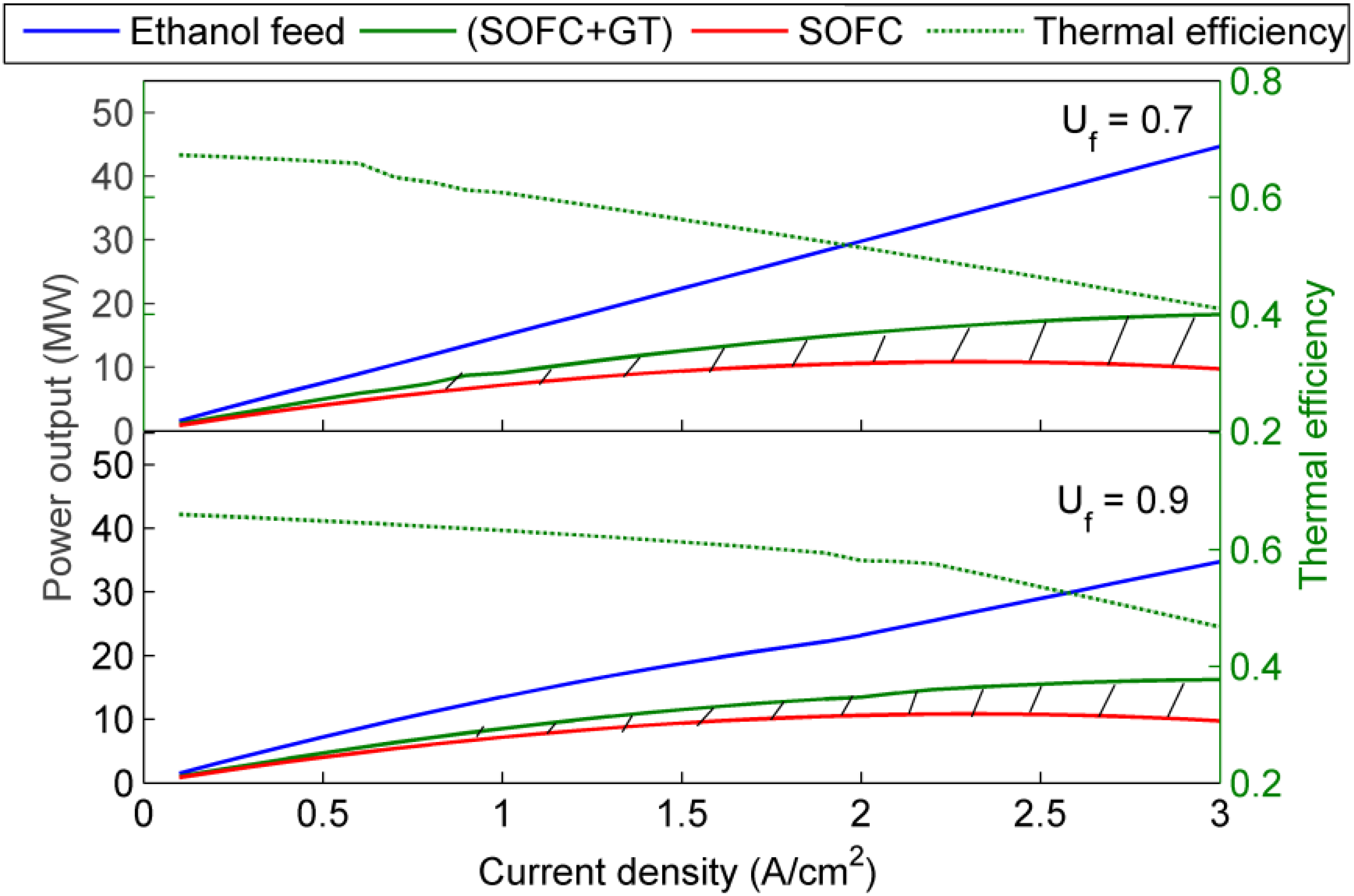
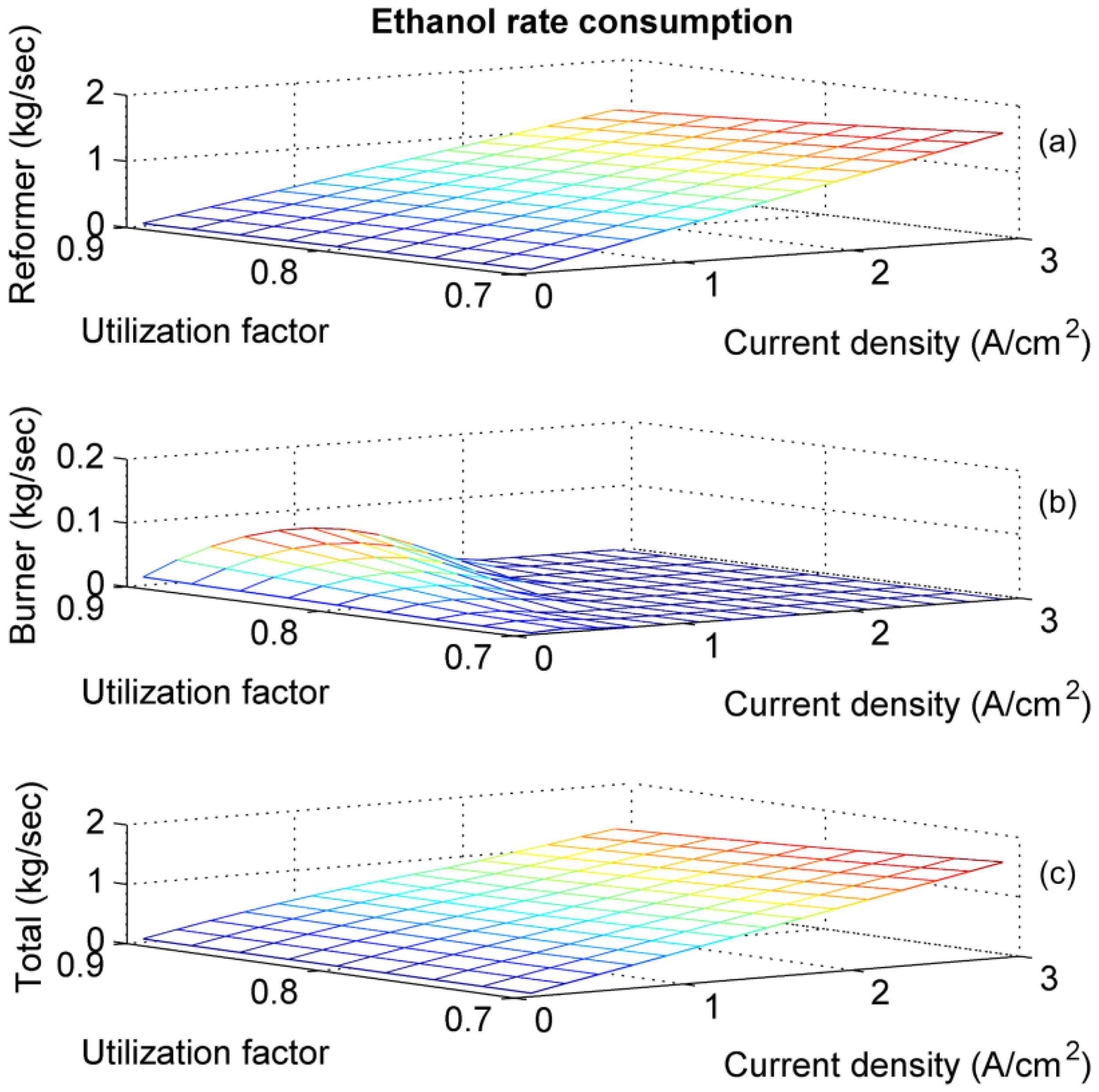
5. Conclusions
Nomenclature:
| Ac | Fuel cell stack area (m2) |
| e | Specific exergy (kJ/kg) |
| Ė | Exergy rate (kW) |
| h | Specific enthalpy (kJ/kg) |
| i | Current density (A/m2) |
| LHV | Lower heating value (kJ/kg) |
| ṁ | Mass flow rate (kg/s) |
Thermal energy (kW) | |
| rp | Pressure ratio |
| s | Specific entropy (kJ/kg·K) |
| T | Temperature (K) |
| U | Utilization factor |
| V | Voltage (V) |
| Ẇ | Power (kW) |
| x | Mole fraction |
| ε | Effectiveness |
| η | Isentropic efficiency |
| ηII | Exergy efficiency |
Subscripts
| 1...12 | Station numbering |
| a | Air |
| B | Burner |
| C | Compressor |
| D | Destruction |
| e | Exhaust |
| Et | Ethanol |
| Ev | Evaporator |
| f | Fuel |
| FC | Fuel cell |
| g | Exhaust gas |
| i | Inlet |
| o | Reference |
| R | Reformer |
| Rec | Recuperator |
| stoic | Stoichiometric |
| w | Water |
Acknowledgments
References
- Dunn, S. Hydrogen futures: Toward a sustainable energy system. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2002, 27, 235–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, R.S. A hydrogen utopia? Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2004, 29, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, J.L.; Braga, L.B.; de Souza, A.C.C.; Antunes, J.S.; Zanzi, R. The benefits of ethanol use for hydrogen production in urban transportation. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2009, 13, 2525–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douvartzides, S.; Coutelieris, F.; Tsiakaras, P. Exergy analysis of a solid oxide fuel cell power plant fed by either ethanol or methane. J. Power Sources 2004, 131, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recknagle, K.P.; Williford, R.E.; Chick, L.A.; Rector, D.R.; Khaleel, M.A. Three-dimensional thermo-fluid electrochemical modeling of planar SOFC stacks. J. Power Sources 2003, 113, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padullés, J.; Ault, G.W.; McDonald, J.R. An integrated SOFC plant dynamic model for power systems simulation. J. Power Sources 2000, 86, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanari, S.; Iora, P. Definition and sensitivity analysis of a finite volume SOFC model for a tubular cell geometry. J. Power Sources 2004, 132, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.H.; Ho, H.K.; Tian, Y. Multi-level modeling of SOFC–gas turbine hybrid system. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2003, 28, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandepu, R.; Imsland, L.; Foss, B.A.; Stiller, C.; Thorud, B.; Bolland, O. Modeling and control of a SOFC-GT-based autonomous power system. Energy 2007, 32, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.W.; Sohn, J.L.; Kim, T.S.; Ro, S.T. Performance characteristics of a MW-class SOFC/GT hybrid system based on a commercially available gas turbine. J. Power Sources 2006, 158, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Rao, A.D.; Brouwer, J.; Samuelsen, G.S. Analysis and optimization of a solid oxide fuel cell and intercooled gas turbine (SOFC–ICGT) hybrid cycle. J. Power Sources 2004, 132, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calise, F.; Palombo, A.; Vanoli, L. Design and partial load exergy analysis of hybrid SOFC–GT power plant. J. Power Sources 2006, 158, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseli, Y.; Dincer, I.; Naterer, G.F. Thermodynamic analysis of a combined gas turbine power system with a solid oxide fuel cell through exergy. Thermochim. Acta 2008, 480, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinni, C.; Stamatis, A.; Tsiakaras, P. An Exergetic Analysis of an Ethanol Fed SOFC-GT Hybrid System. In Proceedings of the 3rd European Fuel Cell Technology & Applications Conference—Piero Lunghi Conference (EFC), Rome, Italy, 15–18 December; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Massardo, A.F.; Lubelli, F. Internal reforming solid oxide fuel cell-gas turbine combined cycles (IRSOFC-GT): Part A—Cell model and cycle thermodynamic analysis. J. Eng. Gas. Turb. Power 2000, 122, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisiriwat, A. High Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Integrated with Autothermal Reformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2nd International Power and Energy Conference (PECon), Johor Bahru, Malaysia, 1–3 December 2008.
- Cocco, D.; Tola, V. Use of alternative hydrogen energy carriers in SOFC–MGT hybrid power plants. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douvartzides, S.L.; Coutelieris, F.A.; Tsiakaras, P.E. On the systematic optimization of ethanol fed SOFC-based electricity generating systems in terms of energy and exergy. J. Power Sources 2003, 114, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assabumrungrat, S.; Pavarajarn, V.; Charojrochkul, S.; Laosiripojana, N. Thermodynamic analysis for a solid oxide fuel cell with direct internal reforming fueled by ethanol. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 6015–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamsak, W.; Assabumrungrat, S.; Douglas, P.L.; Laosiripojana, N.; Suwanwarangkul, R.; Charojrochkul, S.; Croiset, E. Performance of ethanol-fuelled solid oxide fuel cells: Proton and oxygen ion conductors. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 133, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, Y.; Arteaga, L.E.; Morales, M.; Rosa, E.; Peralta, L.M.; Dewulf, J. Energy and exergy analysis of an ethanol fueled solid oxide fuel cell power plant. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhe, Y.; Qizhao, L.; Zhu, B. Thermodynamic analysis of ITSOFC co-generation system fueled by ethanol. Int. J. Energy Res. 2011, 35, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikalova, E.Y.; Maragou, V.I.; Demina, A.N.; Demin, A.K.; Tsiakaras, P.E. The effect of co-dopantaddition on the properties of Ln0.2Ce0.8O2−δ (Ln = Gd, Sm, La) solid-state electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2008, 181, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Haile, S.M. A high-performance cathode for the next generation of solid-oxide fuel cells. Nature 2004, 431, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cengel, Y.A.; Boles, A.M. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Akkaya, A.V.; Sahin, B.; Huseyin Erdem, H. Exergetic performance coefficient analysis of a simple fuel cell system. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2007, 32, 4600–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseli, Y.; Dincer, I.; Naterer, G.F. Thermodynamic modeling of a gas turbine cycle combined with a solid oxide fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 5811–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Oh, K.S.; Kim, T.S. Analysis of the design of a pressurized SOFC hybrid system using a fixed gas turbine design. J. Power Sources 2007, 170, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.M.; van Ness, H.C.; Abbot, M.M. Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, 6th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Larminie, J.; Dicks, A. Fuel Cells Systems Explained, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Sussex, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Cai, W.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Shen, W. Hydrogen production by steam reforming of ethanol over an Ir/CeO2 catalyst: Reaction mechanism and stability of the catalyst. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 4377–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, J.L.; Salmones, J.; García, L.A.; Ponce, A.; Zeifert, B.; Fuentes, G.A. Hydrogen production by ethanol steam reforming over co-hydrotalcites having basic sites. J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 2008, 11, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Ma, X. Hydrogen production from ethanol steam reforming over nickel based catalyst derived from Ni/Mg/Al hydrotalcite-like compounds. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 6699–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, R.; Huang, S.; Chen, W.; Shi, Q. Ni/Y2O3-Al2O3 catalysts for hydrogen production from steam reforming of ethanol at low temperature. J. Rare Earth. 2012, 30, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.J.; Díaz Alvarado, F.; Santos, J.C.; Gracia, F.; Cunha, A.F.; Rodrigues, A.E. Sorption-enhanced steam reforming of ethanol: Thermodynamic comparison of CO2 sorbents. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2012, 35, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotas, T.J. The Exergy Method of Thermal Plant Analysis; ButterWorth-Heinemann Ltd.: London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hotz, N.; Senn, S.M.; Poulikakos, D. Exergy analysis of a solid oxide fuel cell micropowerplant. J. Power Sources 2006, 158, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuel Cell Handbook, 5th ed.; EG&G Services Parsons, Inc., Science Applications International Corporation: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2000.
- Campanari, S. Thermodynamic model and parametric analysis of a tubular SOFC module. J. Power Sources 2001, 92, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Croiset, E.; Douglas, P.L.; Fowler, M.W.; Entchev, E. Simulation of a tubular solid oxide fuel cell stack using AspenPlusTM unit operation models. Energy Convers. Manag. 2005, 46, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Stamatis, A.; Vinni, C.; Bakalis, D.; Tzorbatzoglou, F.; Tsiakaras, P. Exergy Analysis of an Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell-Gas Turbine Hybrid System Fed with Ethanol. Energies 2012, 5, 4268-4287. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5114268
Stamatis A, Vinni C, Bakalis D, Tzorbatzoglou F, Tsiakaras P. Exergy Analysis of an Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell-Gas Turbine Hybrid System Fed with Ethanol. Energies. 2012; 5(11):4268-4287. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5114268
Chicago/Turabian StyleStamatis, Anastassios, Christina Vinni, Diamantis Bakalis, Fotini Tzorbatzoglou, and Panagiotis Tsiakaras. 2012. "Exergy Analysis of an Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell-Gas Turbine Hybrid System Fed with Ethanol" Energies 5, no. 11: 4268-4287. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5114268
APA StyleStamatis, A., Vinni, C., Bakalis, D., Tzorbatzoglou, F., & Tsiakaras, P. (2012). Exergy Analysis of an Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell-Gas Turbine Hybrid System Fed with Ethanol. Energies, 5(11), 4268-4287. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5114268






