Application of Carbon-Isotope-Logging Technology in High-Temperature and High-Pressure Wells: A Case Study of the Ledong Gas Field in the Yinggehai Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
3. Material and Methods
4. Result and Discussion
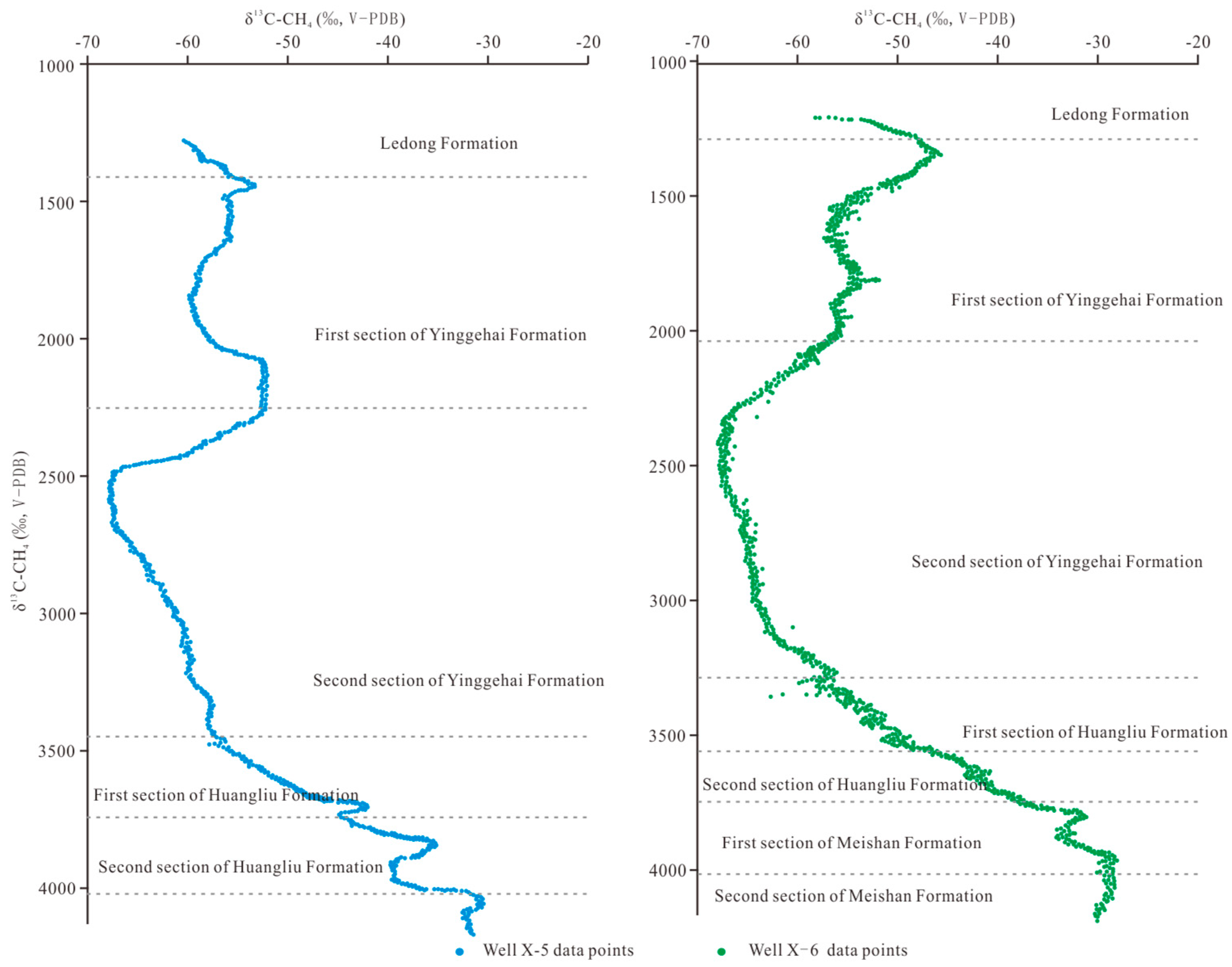
4.1. Gas Origin, Gas Source Type, and Source Rock Maturity of Oil and Gas Reservoir
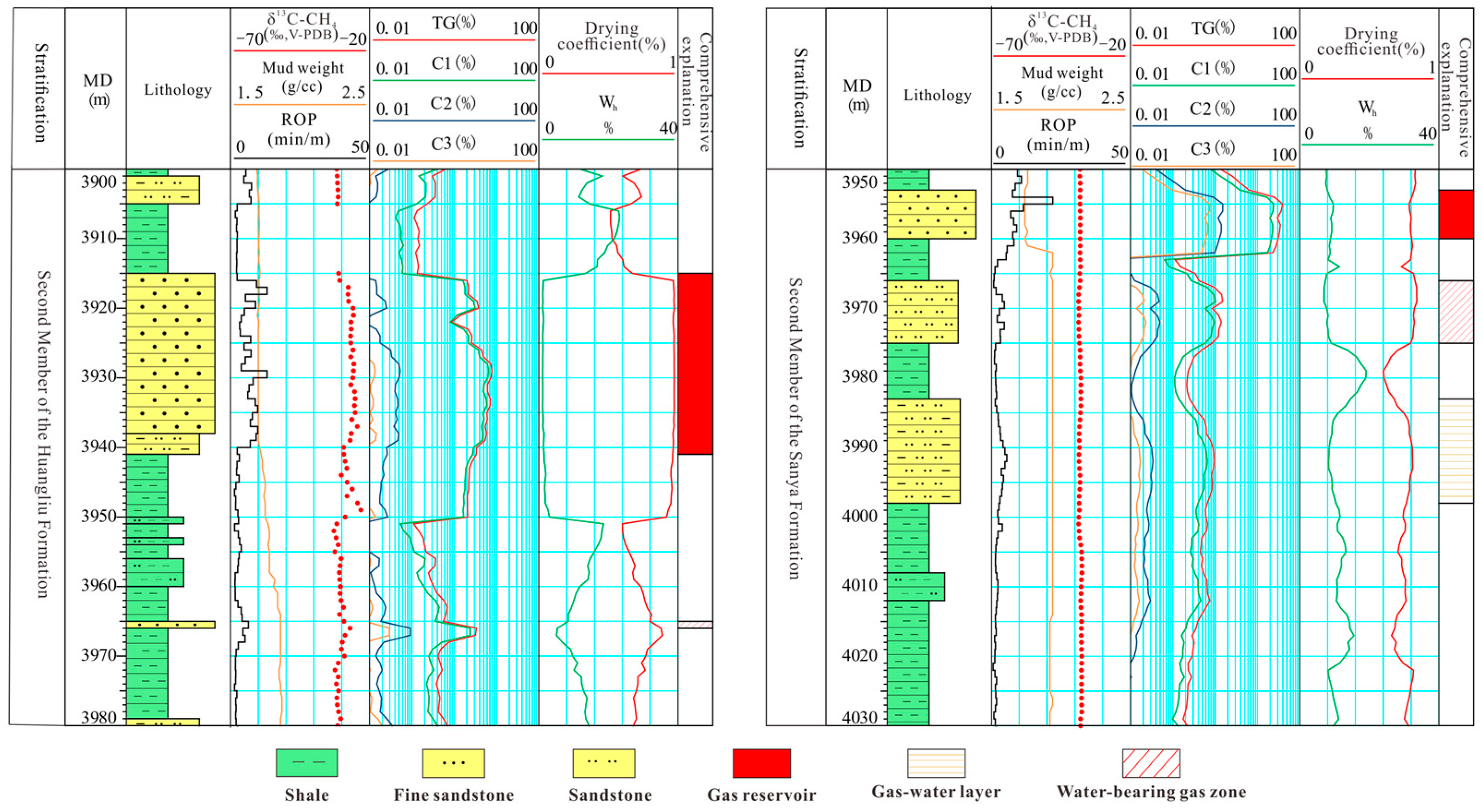
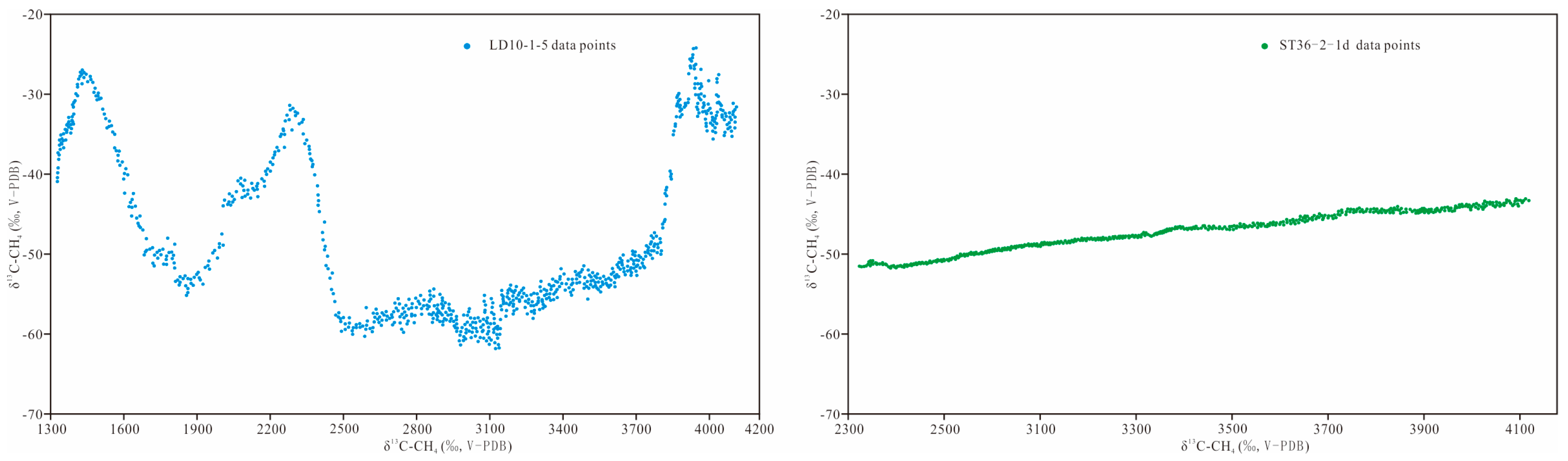
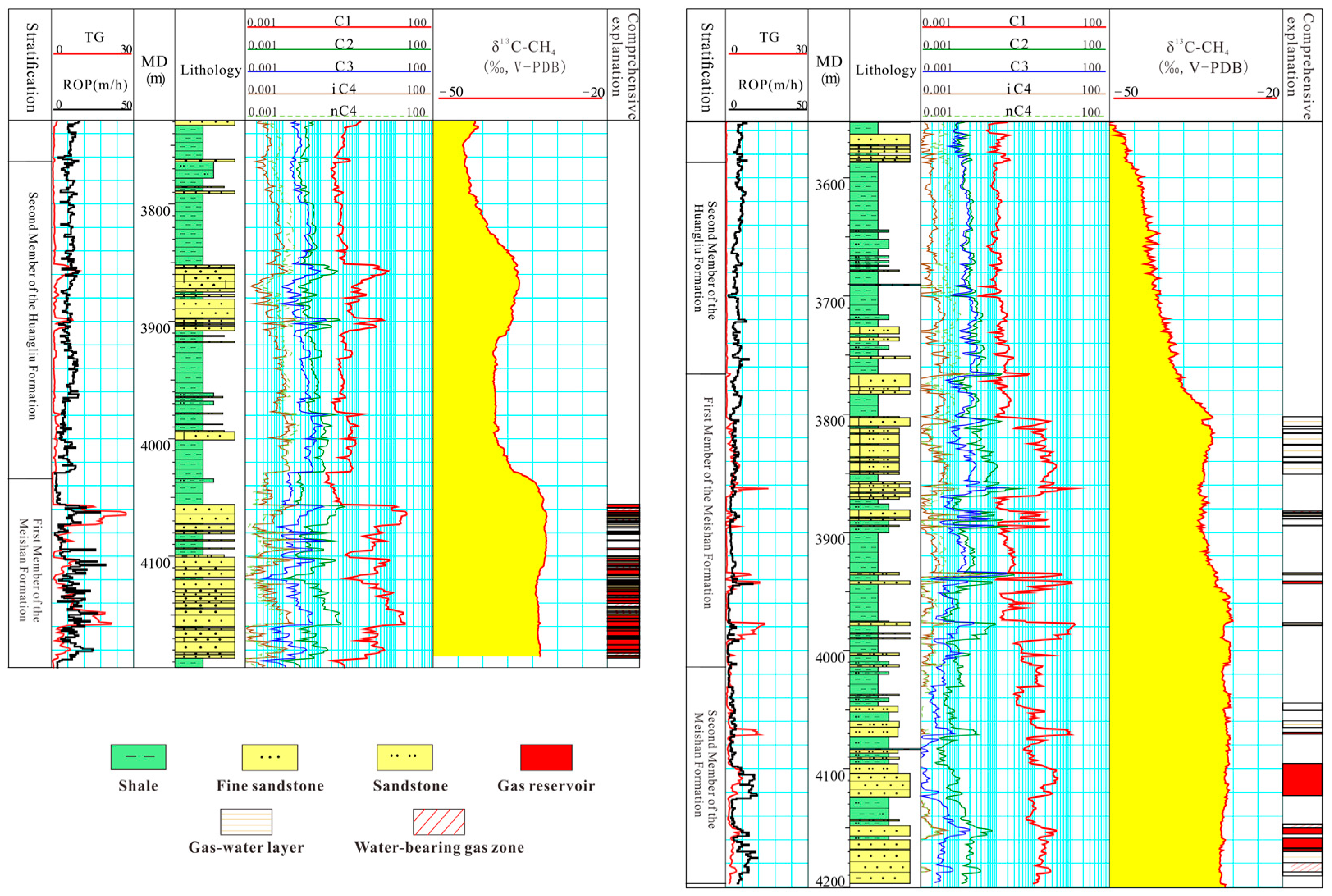
4.2. Identification of the Source of High Pressures via Isotope and Gas Logging
4.3. A Sharp Increase in Isotope Values Indicates Good Sealing Properties of the Cap Rock
4.4. Isotopic Trends Support Drilling Operations
5. Conclusions
- Real-time carbon isotope logging can quickly identify gas origin, maturity, and gas source type.
- Operational plans should be made before opening a sand body guided by real-time carbon isotopes of methane; the safety, quality, and efficiency of ultra-high-pressure formation operations should be ensured; and efforts should be made to help reduce costs and increase efficiency.
- According to the methane carbon isotope logging of the mudstone cover overlying a reservoir sand body, the sealing quality of the overlying mudstone cover can be employed to help make judgements so as to evaluate the gas abundance of the reservoir sand body as a new reference [8].
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.J. Application of methane carbon isotope in oil and gas geochemical exploration and the existing problems and countermeasures. Miner. Geol. 2003, 54–58. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=14CuGbpFC1CMYyXSk6b38ybiPOtzr1L1_kQxO4vpBs-od60BdAj5IwGQR_mtLKJZdOhd9ZSWiNng0fyR2bxeV7t0rRH6IYoAUf2e0hrP2tbhXoXNtmfOE7JQQeFddmMwVzjZvco--kKCpjjfO2kR334m58DjAOOgZ7LQrAOBcQ2ZHqP_xu6BJmmmE-M90Bn2&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Yi, R.; Jiang, F.; Wang, R.; Jiao, H. The Application of Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotope Geochemistryto the Study of Groundwater Circulation Conditionsin Karst Mountain Area—By the Example of Groundwater in the Zhenning Region. Acta Geol. Sichuan 2021, 41, 678–681+687. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; He, F.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Duan, X.; Zhao, H.; Han, H. Geochemical Characteristics of Natural Gas in the Shihexi Formation in Sulige Area. J. Oil Gas Technol. 2009, 31, 184–187+397. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=14CuGbpFC1BxiXn3PngnLbcAf7KUMT7RSr4gzn6-IPZjvGkrY5MDS4dyFj7egus1KxsKdBZWayqxj9KJiSgW5vYWYrFB7CHUh6NKzqDOAcf2Gzc0RBwmL7bcRxC0cuPPe-k2Fz-_IXoRS5TlZHNXNWTMfenB0VTTj_79-bZmqtvoyyEsWnIm_HAP6y-hBN6R&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Dai, J. Characteristics of Carbon and Hydrogen Isotopes of Natural Gas and Identification of Various Types of Natural Gas. Nat. Gas Geosci. 1993, 3, 1–40. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=14CuGbpFC1CD6Ib2OK06vrg9GNrJst0LxlAMpyvrIexdVtWuk5MMW7MmulPI4YZjAfm4JvKq9A5LYqtw395L9gAObjbUuvI805TbroKyl_mj93cRSs3Gw6HzA74KZwyM-St2PKGccToJhFrK3lrDQOSh3Ma4IBzweuIP7fvXz_uU1LODVnl9tbzCJh03Sgvr&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Geng, H.; Chen, P.; Chen, M. Application of Real-time Methane Carbon Isotope Logging in Well YC1-1-1 in the Western South China Sea. Mud Logging Eng. 2016, 27, 45–48+93–94. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, G.; Yang, S. Application of carbon isotope logging technology in shale oil of Gulong Qingshankou Fm: A case study of well GY 3. Mud Logging Eng. 2022, 33, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Cheng, T.; Tang, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhu, H. The Application of δ13C1 to Surface Geochemical Exploration and it Sexisting Problems. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2008, 32, 549–552. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=14CuGbpFC1AFTyJScSXLXIgBGKP3tWEs_0vLwSwv1hVe0UUTw1HbzkKHZrIToKHmEl_PFA7rpwtrBoQSaf4pc8H4P2pdI2bWffjpxhu7Xy4fUJOp44WrnSr7qAAMn4R0e6bgTVJhl6cHV7O-dTAlXn5J0uJnMgoBjbnBgRksX-YmoODaw6tM9GlZ1tZuPwks&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Niu, Q.; Qu, Y.Y.; Ci, X.H.; Zhou, W.Z.; Zhang, H.X. Development Status and Prospect of Carbon Isotope Logging Technology. Mud Logging Eng. 2019, 30, 8–15+184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, J.; Guo, J.; Ma, X. Characteristics of Fluid Inclusion and Periods of Hydrocarbon Accumulation ofthe Huangliu Formation in the Ledong10-1 Area, Yinggehai Basin. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2023, 23, 12382–12390. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=14CuGbpFC1AVJ7cr5vyvNbTnNslxAXpEQmxOhTmKOdjabps-P0vbJSYDS_WKB-VRN98ITFe5vR_nFVflbt30s9GWsY-3s9tWoXPsv4s6mH4t2Eq9Zp6URvMnhJC2EfZR-PC5xBYTPkkioteQe2qbQfbKWE0lkXxGRNIGjFr5uPQKSZawqa8IdX4R5exdWCQQvsPtihyCXqo=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Ni, P.; Mao, M.; Huang, X. Application of Real-time Isotope Logging in Prediction of Oil and Gas Reservoirs. J. Oil Gas Technol. 2017, 39, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, G.; Gan, J.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Geng, H.; Yu, L.; Guo, X. Application of real-time carbon isotope logging technology in genesis and reservoir formation of natural gas in Songtaouplift, Qiongdongnanbasin. China Offshore Oil Gas 2018, 30, 56–61. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.5339.TE.20180703.1656.014 (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Shui, L.; Guo, L.; Xu, X.; Huang, X.; Huang, H.; Chen, S.; Song, X. Characteristics of CO2 Inclusions and Fluid Injection History in Ledong 10 Area, Yinggehai Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2021, 43, 835–843. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=14CuGbpFC1Coad10YYhS_FnyLU6pV3qOzq-qKMe63I_YQqaTw0uhnM-LAruO58Q-DY6fLQUgkDSpb58lThw-9byFL4Q0EQTYjVhxKIosMAUWRg24UAzyGkNNbpyZ9uaeiIaT0RCvG3q8-tSidCRFajSeWlYfIYo0OvmVWIyGGjWUfmjtEwLFLknen1HRL6ILW7BJVgZtLt0=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Shi, X.; Kang, S.; Luo, C.; Wu, W.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Li, Y. Shale gas exploration potential and reservoir conditions of the Longmaxi Formation in the Changning area, Sichuan Basin, SW China: Evidence from mud gas isotope logging. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 233, 105239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. Drilling technology for HTHP exploration in South China Sea and its prospect. Oil Drill. Prod. Technol. 2016, 38, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakami, A.; Ellis, L.; Al-Ramadan, K.; Abdelbagi, S. Mud gas isotope logging application for sweet spot identification in an unconventional shale gas play: A case study from Jurassic carbonate source rocks in Jafurah Basin, Saudi Arabia. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 76, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yan, J.; Qiu, X.; Wang, M.; Geng, B.; Hu, Q. Characteristics and correlations of rock components, structure, and physical properties of deep clastic reservoirs in the LD-X area of Yinggehai basin, western South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 167, 106995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G. Application of Carbon Isotope Logging Technology in Sweet Spot Evaluation of Shale Gas Wells in Weiyuan Area, Southern Sichuan. Mud Logging Eng. 2022, 33, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Hu, Y.T.; Jiang, B. Application and understanding of real-time methane carbon isotope logging in drilling. J. Pet. Nat. Gas 2017, 39, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Pu, R.; Li, H.; Qu, H.; Ji, T.; Su, S.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, H. Distribution characteristics of delta reservoirs reshaped by bottom currents: A case study from the second member of the Yinggehai Formation in the DF1-1 gas field, Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2022, 41, 86–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, E. The application of Bernard diagram in natural gas genesis studies. In Management Theory and Practice, 6th ed.; Cole, G.A., Ed.; Thomson: London, UK, 1988; p. 186. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Huang, Z.; Fan, C.; Xu, M.; Hou, J. Diagenetic and hydrothermal fluid influence on tight sandstone reservoir quality: Gravity-flow deposits from the Huangliu Formation, Ledong area, Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 215, 110633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Pang, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; He, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, G. Anomalies of natural gas compositions and carbon isotope ratios caused by gas diffusion: A case from the Donghe Sandstone reservoir in the Hadexun Oilfield, Tarim Basin, northwest China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 156, 75–89. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Song, Y.; Cheng, K.; Hong, F.; Fan, G. Characteristics of Carbon Isotopes of Organic Alkane Gases in Petroliferous Basins of China. Acta Pet. Sin. 1993, 14, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Xie, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ma, J. Geochemical behaviors of HPHT gas reservoirs in the Yinggehai Basin and the efficient gas accumulation mode in its diapir flanks. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2015, 2, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Application of ultra-high temperature and high pressure coring technology in well LD13. Offshore Oil 2022, 42, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y. Accumulation mechanism and resource prospect of high-temperature and high-pressure natural gas in the western South China Sea: A case study of Yingqiong Basin. Oil Drill. Prod. Technol. 2016, 38, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liang, H.; Liao, G. Research and application of key technology of compound logging in deep-water area of Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Mud Logging Eng. 2019, 30, 16+132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P. The significance of hydrocarbon exploration indicated by carbon isotope logging data: A case study of well A1 in Wenchang B Sag. Petrochem. Ind. Technol. 2019, 31, 229–231. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=14CuGbpFC1B0XgDPaqv--jPQ2N9wp-mnPLmQJc9WmWgTGiyelz6bOvojjtbZ1yGFLRikhXknJN7mtNYgOG6AOezdb9Vv3T88UIykoPZXhfZrwWEJtVxIKIYxUERyXFlfCaqOeu9NF22_zooZcJBUgB4niJ-NGZzJDjuxwXy06lHlWh8TGjHVQZx4HQa-YX5S_9zLdG9NgBk=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Wu, S.; Tang, Y.C.; Lin, M.; Sneddon, A. Headspace isotope & compositional analysis for unconventional resources: Gas in place, permeability and porosity prediction and completions planning. Geosciences 2020, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.W.; Krooss, B.M. Experimental investigation on the carbon isotope fractionation of methane during gas migration by diffusion through sedimentary rocks at elevated temperature and pressure. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 2723–2742. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.C.; Ji, M.; Chen, Y.; Gan, J.; Wang, D.D.; Zhang, C.Y. Accumulation characteristics and exploration potentials of gas accumulation belt in Qiongdongnan Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2024, 45, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; He, S.; Yang, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhang, R.; Ren, S.; Zhao, X.; Yao, G. Diagenesis characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs with high temperature, overpressure and high CO2 content: A case study of Neogene Meishan-Huangliu Formation in LD10 area, Yinggehai Basin. Lithol. Reserv. 2019, 35, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Cao, J.; Luo, J.; Li, S.; Wu, S.; Da, L.; Ho, J.; Ma, Q. Heterogeneity and influencing factors of marine gravity flow tight sandstone underabnormally high pressure: A case study from the Miocene Huangliu Formationreservoirs in LD10 area, Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 903–915+949. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Fan, C.; Tuo, L.; Liu, F.; Hou, J. Origin and accumulation characteristics of natural gas in the middle and north section of eastern slope, Yinggehai sag. China Offshore Oil Gas 2022, 34, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P. The significance of oil and gas exploration indicated by carbon isotope logging data—Taking A1 well inWenchang B depression as an example. Petrochem. Ind. Technol. 2019, 31, 229–231. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=14CuGbpFC1DVJODJ2J1Hz2MU7oyACGDCrevrLjOrG3Y9Ag7uXO67dtrg7ziPf56-vvhnjbe7hQEFjolCRadumic9O2vKdlYshrBOTdouVh3QJTFNSHwDXhxhj0mdivdPkdx4_T7KTdeMDLB1RjDkY7_AtnddALQVFSn0VXmxjlunR1_6JttoMmbGL06FoM5drVLGOV37xdc=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Ma, J.; Zhao, J.; Guo, J. Reservoir fluid inclusion characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation periods of Huangliu Formation in Ledong 10-1 area, Yinggehai Basin. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2019, 23, 12382–12390. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Chen, D.X.; Zhang, J.C.; Lv, X.; Dang, W.; Liu, Y.; Liao, W.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F. Combining isotopic geochemical data and logging data to predict the range of the total gas content in shale: A case study from the Wufeng and Longmaxi shales in the Middle Yangtze area, south China. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 10487–10498. [Google Scholar]
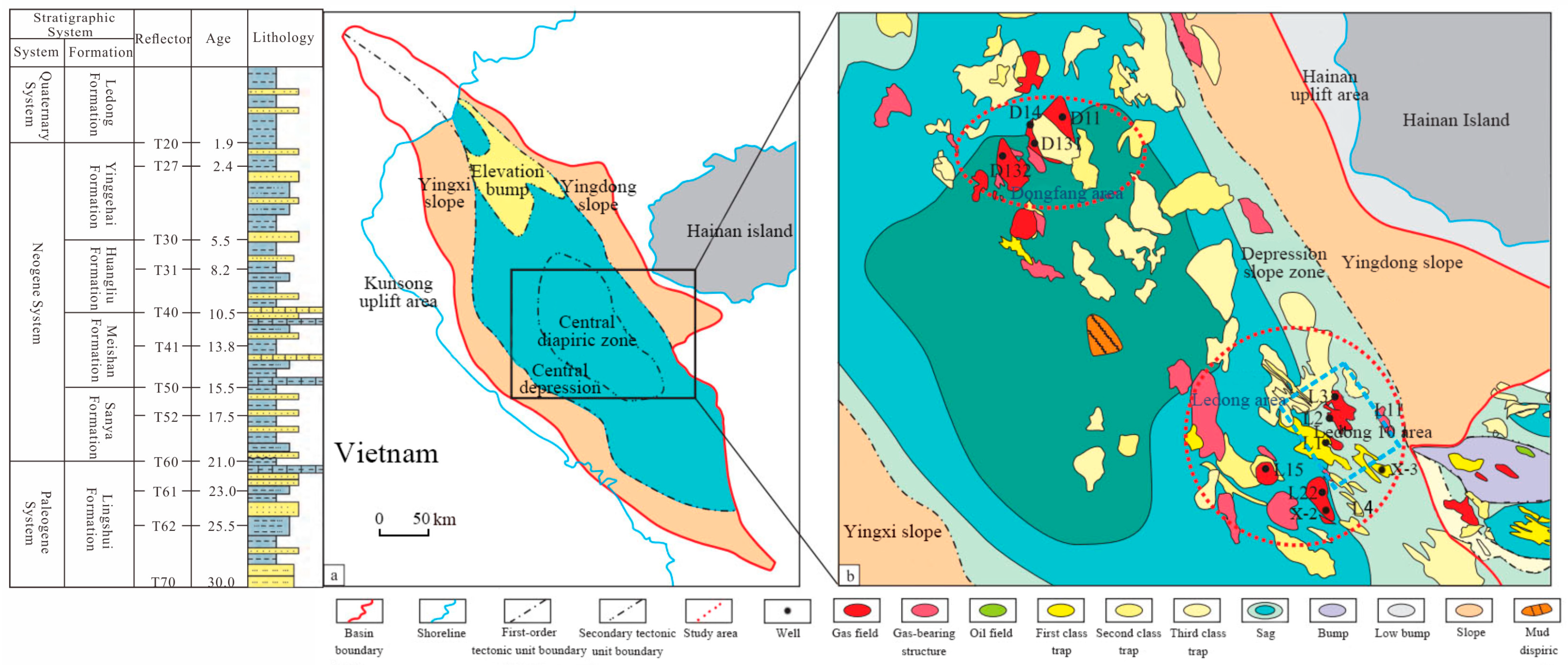
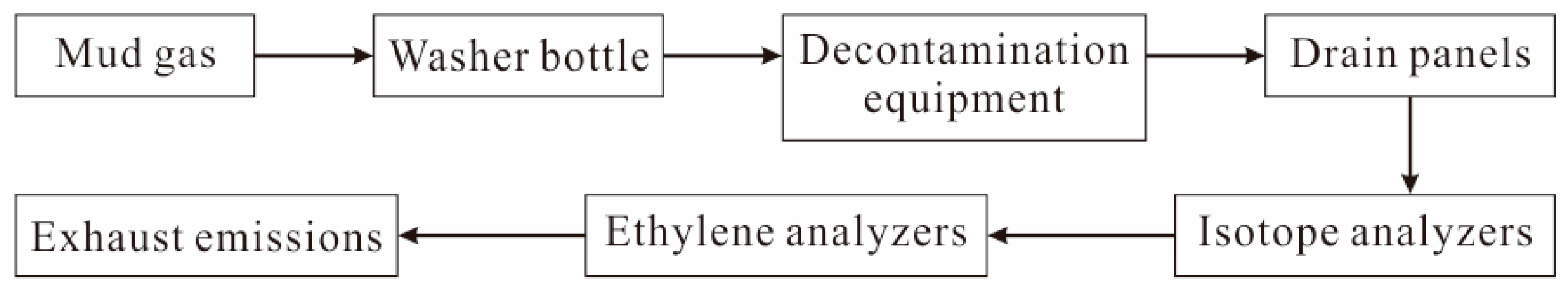
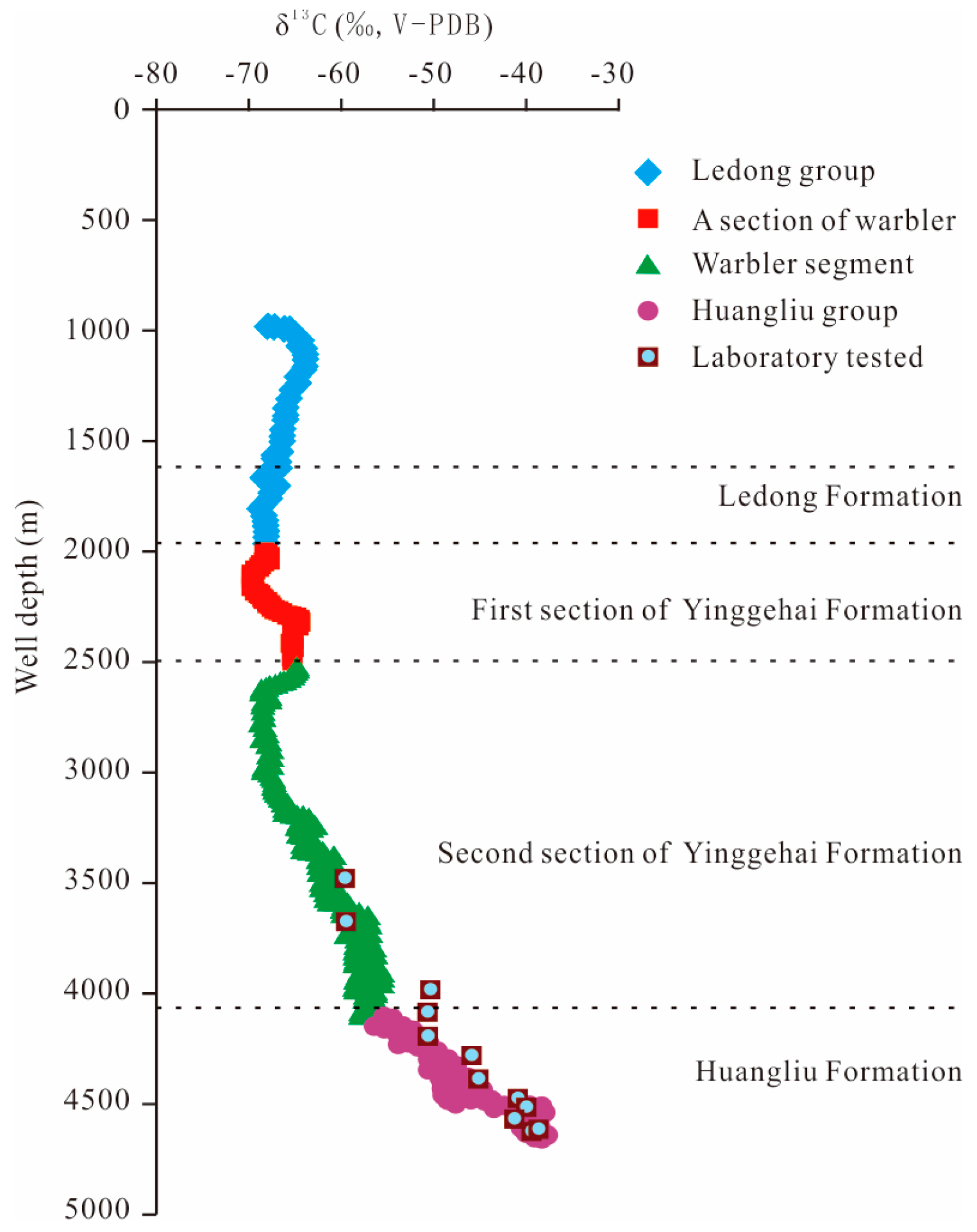
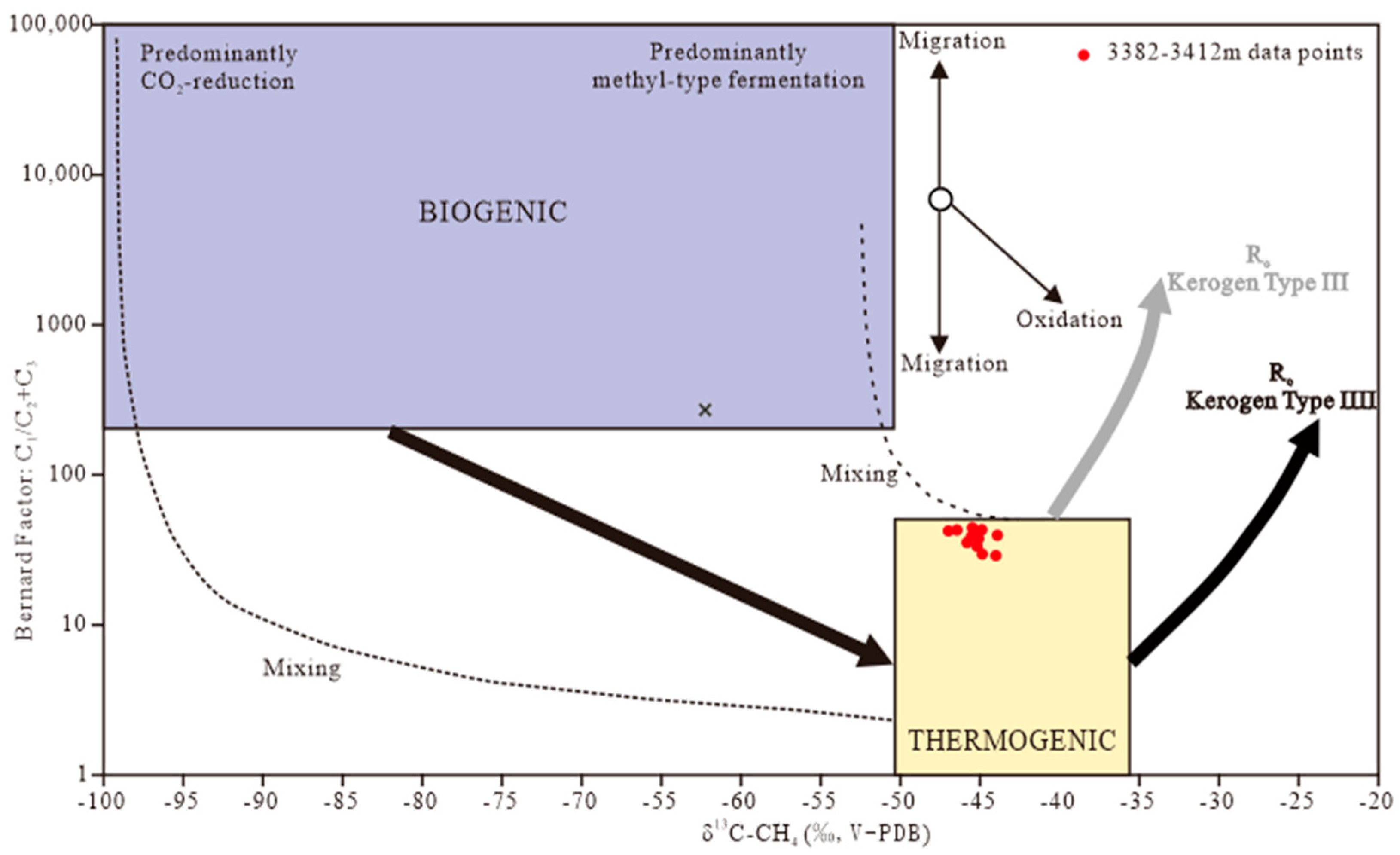
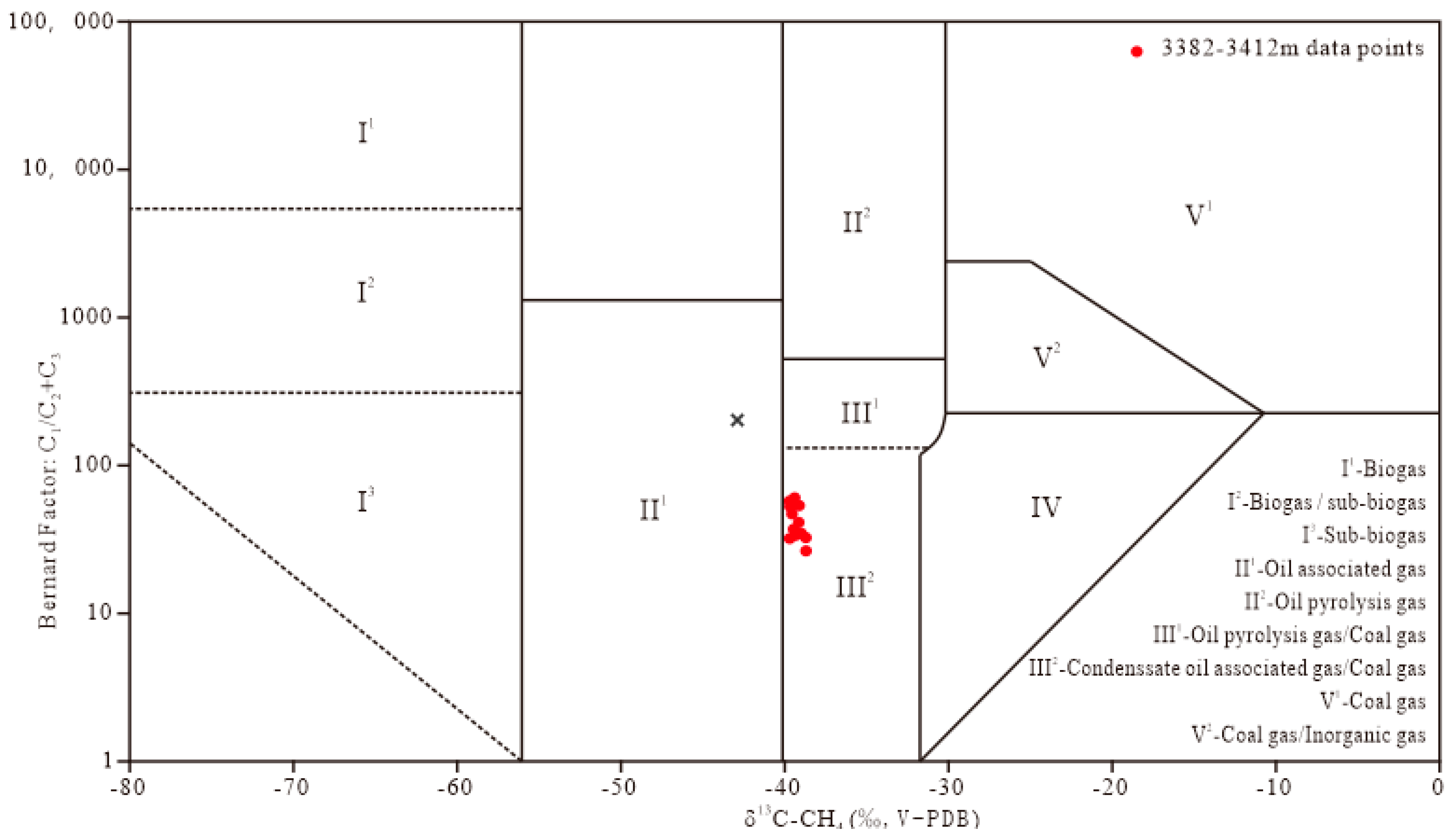
| Well Interval (m) | Variation Interval of δ13C-CH4 (‰, V-PDB) | δ13C-CH4 (‰, V-PDB) | Maturity (Ro) | Gas Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3382.00–3412.00 m | −39.72~−38.70 | −39.26 | 1.53 | Over-mature oil type gas-coal type gas |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, H.; Xin, X.; Cheng, L.; Su, J.; Hu, Y.; Song, T.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. Application of Carbon-Isotope-Logging Technology in High-Temperature and High-Pressure Wells: A Case Study of the Ledong Gas Field in the Yinggehai Basin. Energies 2025, 18, 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18071728
Geng H, Xin X, Cheng L, Su J, Hu Y, Song T, Wang R, Li Y. Application of Carbon-Isotope-Logging Technology in High-Temperature and High-Pressure Wells: A Case Study of the Ledong Gas Field in the Yinggehai Basin. Energies. 2025; 18(7):1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18071728
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Heng, Xiaojun Xin, Leli Cheng, Jiarong Su, Yitao Hu, Ting Song, Ruike Wang, and Yongkang Li. 2025. "Application of Carbon-Isotope-Logging Technology in High-Temperature and High-Pressure Wells: A Case Study of the Ledong Gas Field in the Yinggehai Basin" Energies 18, no. 7: 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18071728
APA StyleGeng, H., Xin, X., Cheng, L., Su, J., Hu, Y., Song, T., Wang, R., & Li, Y. (2025). Application of Carbon-Isotope-Logging Technology in High-Temperature and High-Pressure Wells: A Case Study of the Ledong Gas Field in the Yinggehai Basin. Energies, 18(7), 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18071728





