A Precision Monitoring Method and Control Strategy for a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell in the Power Generation System of the Antarctic Space Physics Observatory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. SPO Power Generation System
3. PEMFC Power Generation System
3.1. PEMFC Operation Mechanism
3.2. PEMFC Control System
3.2.1. PEMFC Monitoring Module
3.2.2. PEMFC Control Strategy
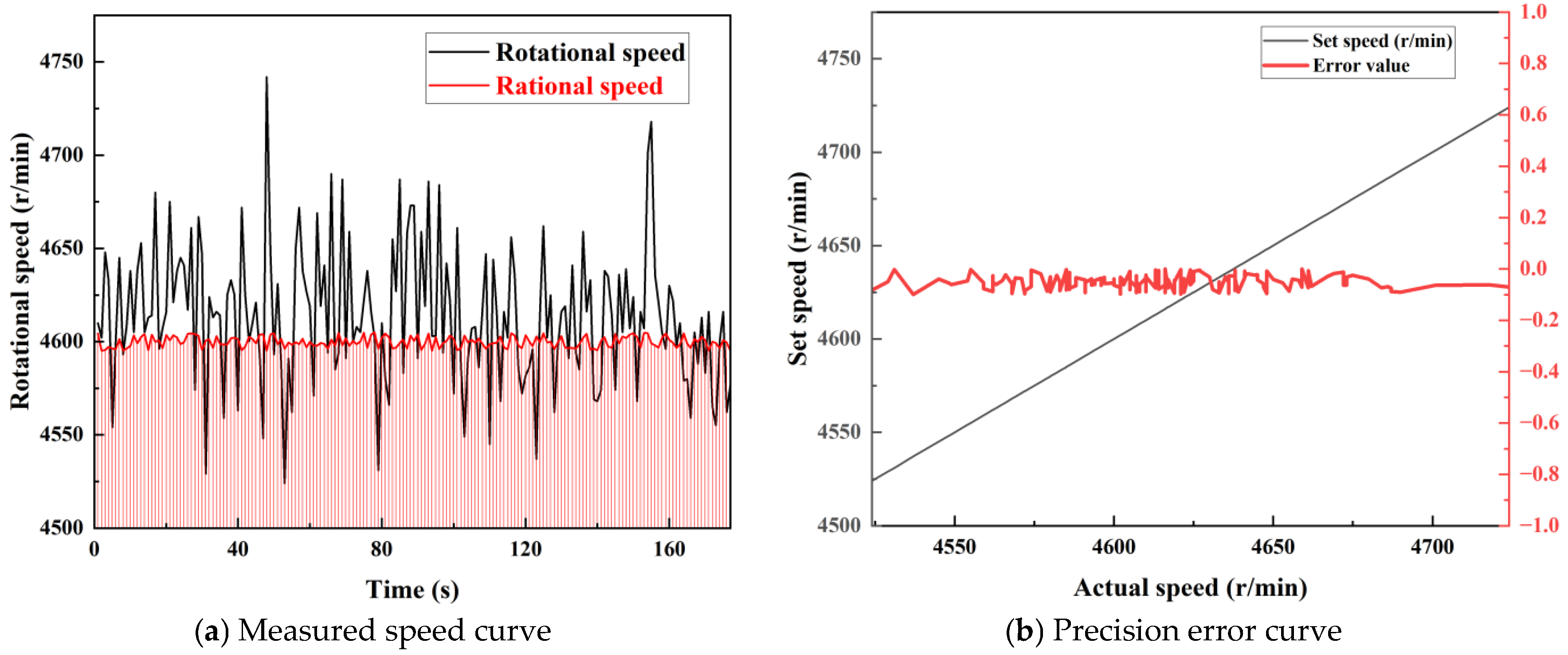
4. Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chundong, G.; Honglin, H. The development potential of field scientific observation and research stations should be highly valued. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2019, 34, 344–348. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, S.E.; Wahid, M.A. Hydrogen from solar energy, a clean energy carrier from a sustainable source of energy. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 4110–4131. [Google Scholar]
- Sharaf, O.Z.; Orhan, M.F. An overview of fuel cell technology: Fundamentals and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 32, 810–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, T.-C.; Xu, Y. Current situation and prospect of PEMFC hydrogen power generation system. Power China 2006, 39, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.J.; Wei, X.Z.; Ming, P.W.; Wang, X.; Jiang, S.; Dai, H. Order reduction, simplification and parameters identification for cold start model of PEM fuel cell. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 274, 116465. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, H.P.; Ji, C.W.; Wang, S.F.; Shi, M.; Zhang, H.; Liang, C. Analysis of the cold start behavior of a polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell in constant power start-up mode. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 19245–19264. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.L.; Li, G.N.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y. Optimization and parametric analysis of PEMFC based on an agglomerate model for catalyst layer. J. Energy Inst. 2014, 87, 163–174. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, X.; Bo, H.; Mingruo, H. Research on Mass Transfer Characteristics Based on semi-empirical Model of polarization Curve. Agric. Equip. Veh. Eng. 2023, 61, 166–168+172. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Lu, Y.; Yang, D. Simulation model and experimental study on performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cells under high temperature and pressure. Electr. Age 2023, S1, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Lan, F. Global Sensitivity Analysis of multi-scale parameter Double cost Function of Fuel cell Model. Automot. Eng. 2023, 45, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Yu, T. Distributed deep reinforcement learning for optimal voltage control of PEMFC. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2021, 15, 2778–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaarslan, I.; Kart, S.; Genc, N.; Uzmus, H. Design and application of PEM fuel cell- based cascade boost converter. Electr. Eng. 2019, 101, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Wang, C.Y. Analysis of cold start in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, B139–B142. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Analysis of the key parameters in the cold start of polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, B1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mukherjee, P.P.; Mishler, J.; Mukundan, R.; Borup, R.L. Cold start of polymer electrolyte fuel cells: Three-stage startup characterization. Electrochim. Acta. 2010, 55, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chena, J.; Wang, Y.; Mukherjee, P.P. One Dimensional Analysis of Subzero Start-Up for Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 16, 273–284. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.J.; Wang, S.X.; Yue, L.K.; Wang, G. Cold-start method for proton exchange membrane fuel cells based on locally heating the cathode. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113716. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.B.; Luo, Y.Q.; Yu, S.H.; Jiao, K. Modeling of cold start processes and performance optimization for proton exchange membrane fuel cell stacks. J. Power Sources 2014, 247, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.E.; Harel, F.; Jemeï, S.; Gouriveau, R.; Hissel, D.; Boulon, L.; Agbossou, K. Proton exchange membrane fuel cell operation and degradation in short-circuit. Fuel Cells 2014, 14, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G. Overview of cold start simulation for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Mar. Electr. Technol. 2014, 34, 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Deng, P.; Ma, J. Low temperature start-up process of fuel cell for catalytic combustion assisted heating. J. Tongji Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2013, 41, 910–914. [Google Scholar]
- Calderón, A.J.; González, I.; Calderón, M.; Segura, F.; Andújar, J.M. A New, Scalable and Low Cost Multi-Channel Monitoring System for Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. Sensors 2016, 16, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKahn, D.A.; Liu, X. Comparison of Two Models for Temperature Observation of Miniature PEM Fuel Cells Under Dry Conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 5283–5292. [Google Scholar]
- Kuan, Y.D.; Septiani, A.; Yuliane, A. Development of The Diagnostic System for Fuel Cell Vehicle using LabVIEW. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on System Science and Engineering (ICSSE), New Taipei City, Taiwan, 28–30 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dudek, M.; Raźniak, A.; Lis, B.; Siwek, T.; Adamczyk, B.; Uhl, D.; Kalawa, W.; Uhl, T. Monitoring of the Operating Parameters a Low-Temperature Fuel-Cell Stack for Applications in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles: Part II. In E3S Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2019; Volume 108, p. 01030. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Wang, Y. Water spatial distribution in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell: Convolutional neural network analysis of neutron radiography. Energy AI 2023, 14, 2666–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishler, J.; Wang, Y.; Mukundan, R.; Spendelow, J.; Hussey, D.S.; Jacobson, D.L.; Borup, R.L. Probing the water content in polymer electrolyte fuel cells using neutron radiography. Electrochim. Acta. 2012, 75, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mishlera, J.; Wanga, Y.; Mukundan, R.; Borup, R.L.; Hussey, D.S.; Jacobson, D. In Situ Investigation of Water Distribution in Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Using Neutron Radiography. ECS Trans. 2010, 33, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W. Fuel Cell Test System Based on AVR Single-chip Computer. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer Network, Electronic and Automation (ICCNEA), Xi’an, China, 23–25 September 2017; pp. 3146–3349. [Google Scholar]
- Strahl, S.; Husar, A.; Puleston, P.; Riera, J. Performance Improvement by Temperature Control of an Open-Cathode PEM Fuel Cell System. Fuel Cells 2014, 14, 466–478. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Dai, Z. Using Artificial Neural Network to Control the Temperature of Fuel Cell. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Communications, Circuits and Systems Proceedings, Guilin, China, 25–28 June 2006; pp. 2159–2162. [Google Scholar]
- O’Keefe, D.; El-Sharkh, M.Y.; Telotte, J.C.; Palanki, S. Temperature dynamics and control of a water-cooled fuel cell stack. J. Power Sources 2014, 256, 470–478. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Guangyi, C.; Xinjian, Z. Temperature model and fuzzy control for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Control. Theory Appl. 2011, 28, 1371–1376. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.; Li, Q.; Han, Y. Real-time optimal temperature adaptive inverse control for air cooled PEMFC power generation System. Chin. J. Sol. Energy 2017, 38, 2168–2175. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Qin, L.; Jiang, H.; Xun, L. A Device for Extending Low Temperature Storage Time of Fuel Cell Stack. China Patent 201758156, 9 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Li, X.; Liu, C. Self-starting fuel cell power generation System. Power Grid Clean Energy 2011, 27, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Hou, Z.; Wang, K.; Sun, D.; Liu, C. A Fuel Cell Thermal Insulation System. China Patent 201946691U, 24 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, W.; Dou, Y.; Zuo, G.; Fan, B.; Xing, Y. Improving Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Operational Reliability Through Cabin-Based Fuzzy Control in Costal Standalone Observation Systems in Antarctica. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birk, W. Fuel Cell System and Method for Starting a Fuel Cell System. U.S. Patent 6756143 B2, 29 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
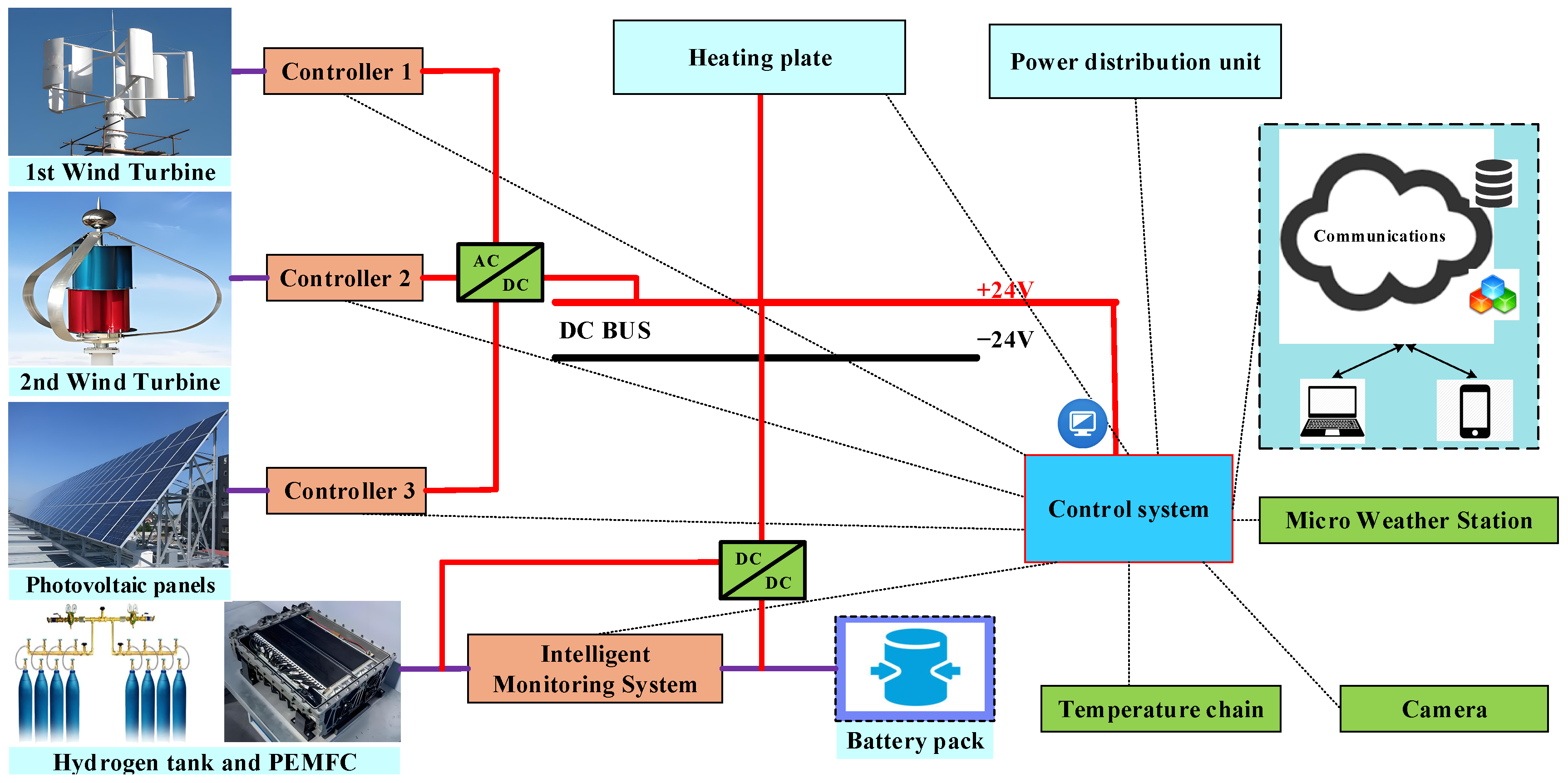

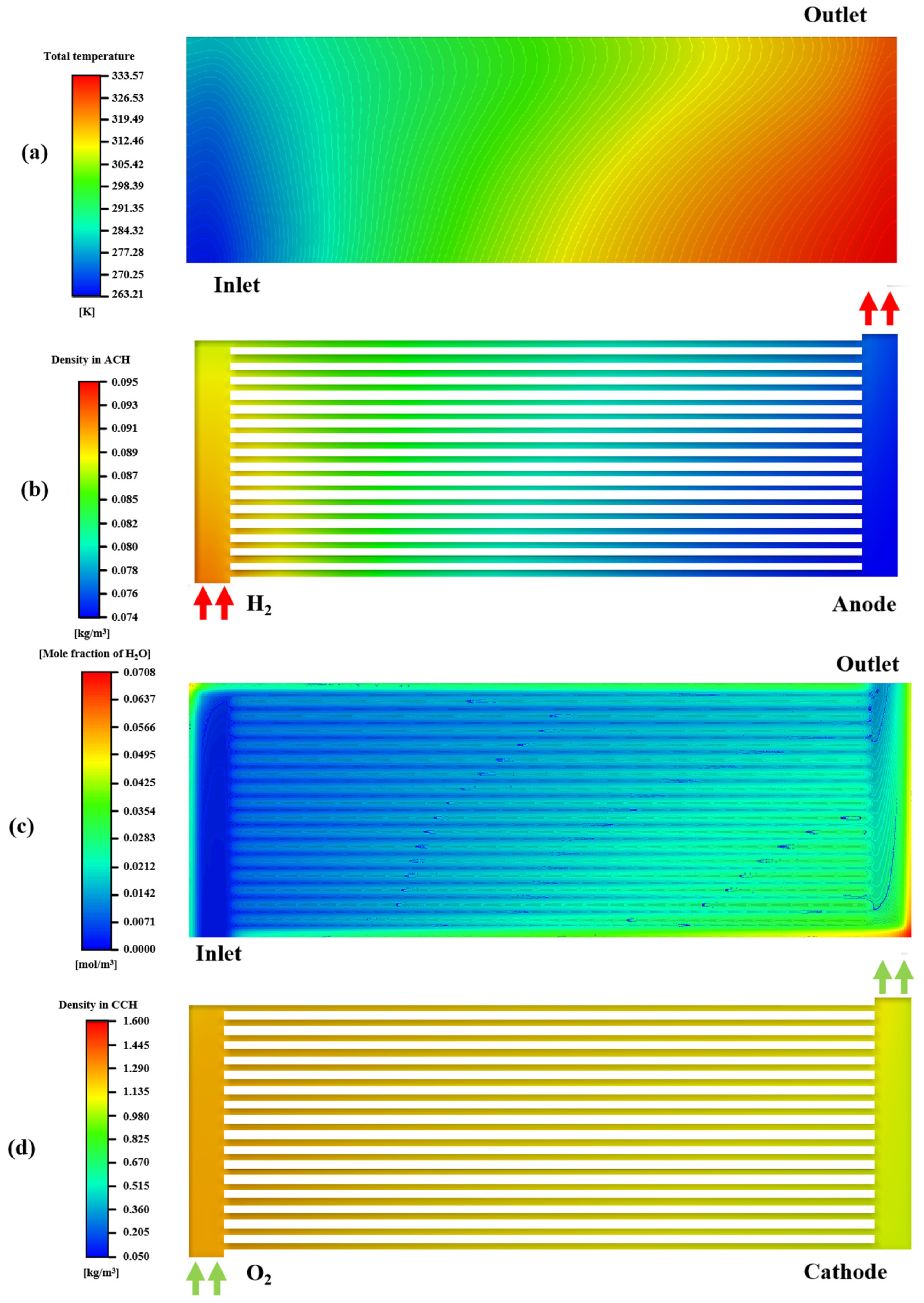
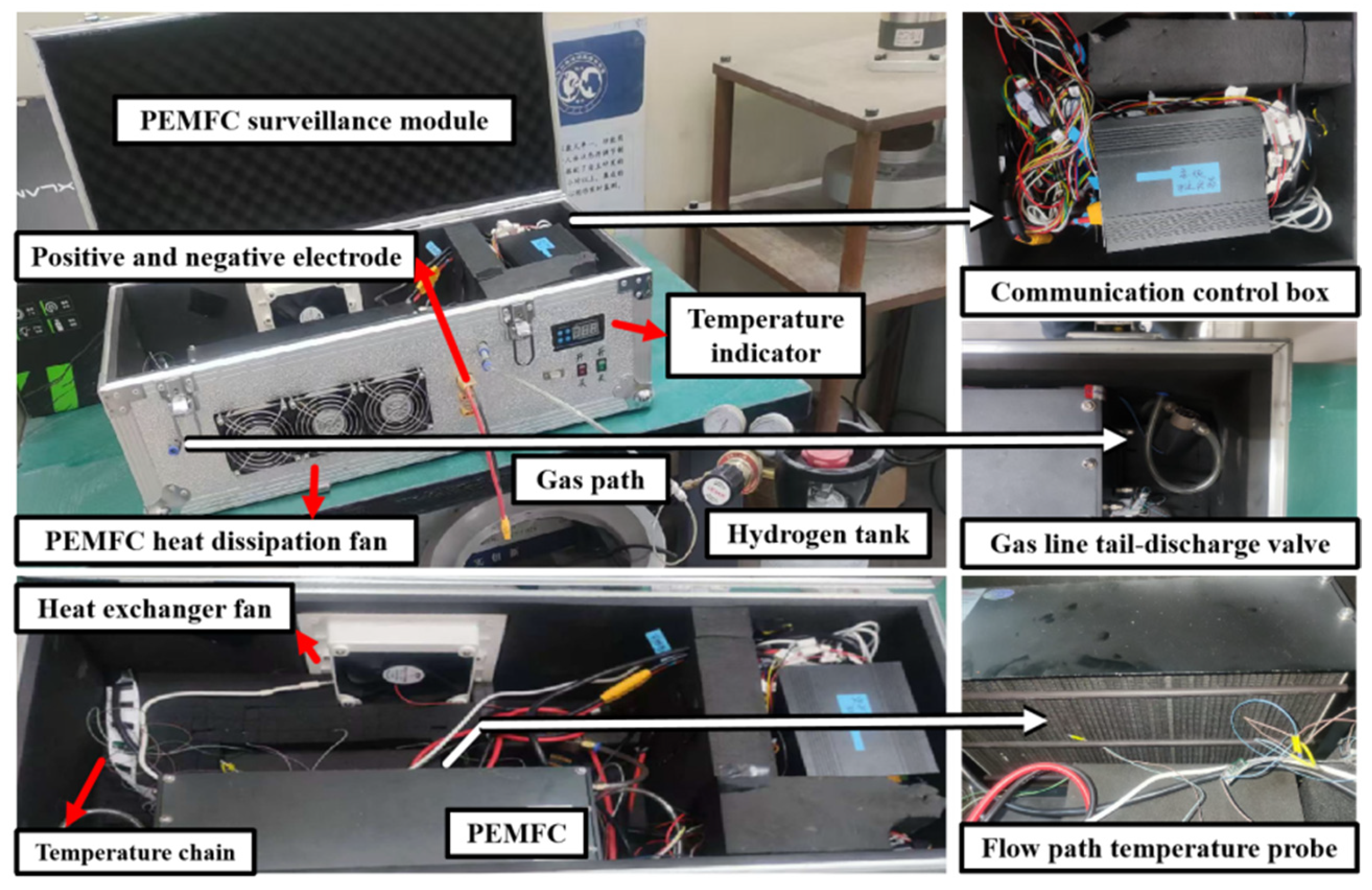


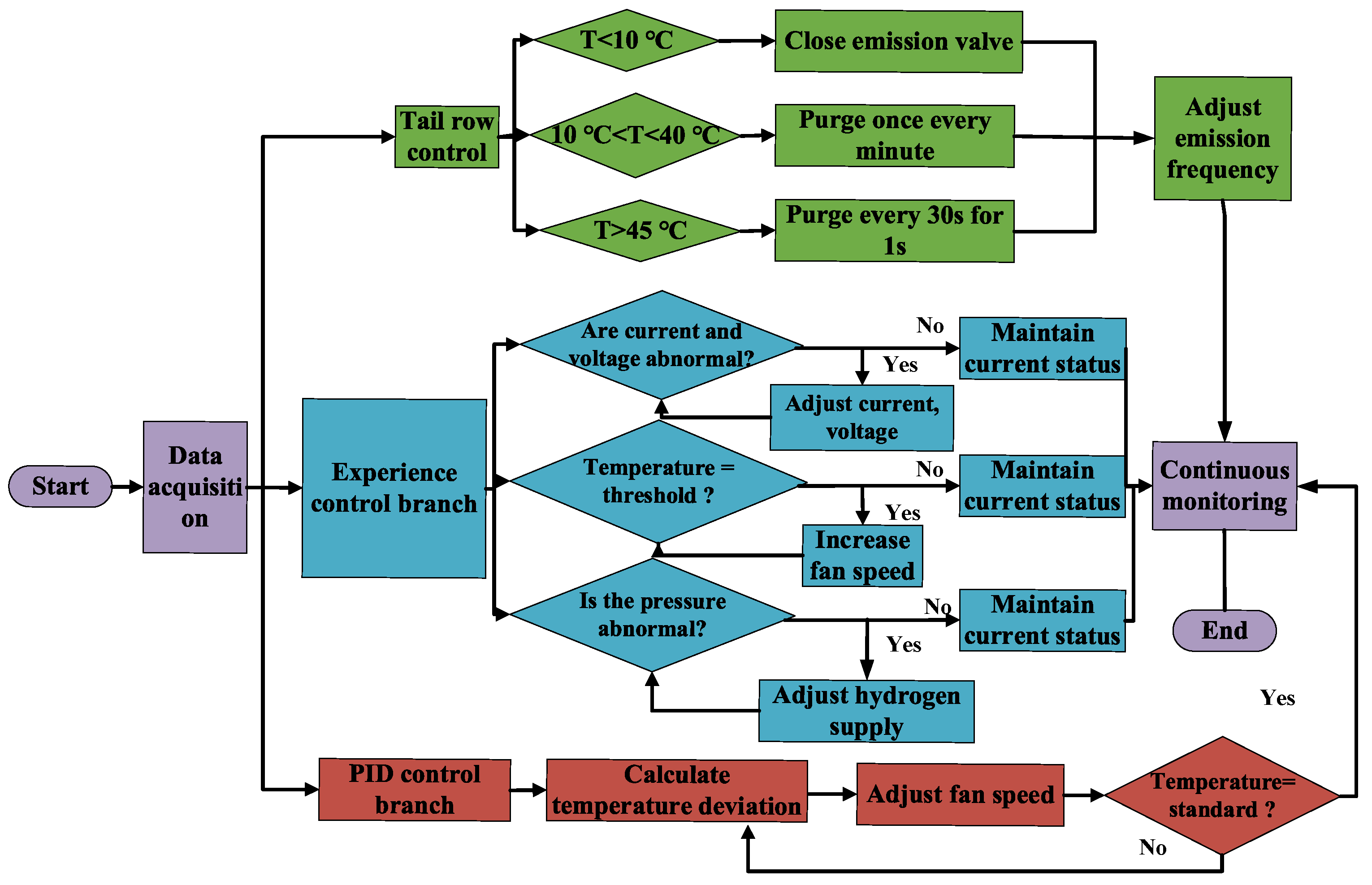


| Power Unit | Quantity (Units) | Type | Power (W) | Monitoring Unit | Power Consumption (W) | Quantity (Sets) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wind Turbine | 1 | Q-type | 1000 | Monitoring Unit | 100 | 1 |
| 1 | H-type | 1000 | ||||
| Photovoltaic Panel | 1 | Flexible | 800 | Control Module | 20 | 1 |
| Energy Storage Battery | 1 | Lead-acid battery | 1000 | Heater | 30 | 1 |
| Hydrogen Fuel Cell | 1 | PEMFC | 1000 | Communication Module | 10 | 2 |
| Hydrogen storage | 6 × 240 L × 13.5 Mpa | |||||
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Length and width | 100 mm; 35 mm |
| Thickness of anode and cathode (BP, CH, GDL, CL, MEM) | 2 mm; 1 mm; 0.2 mm; 0.03 mm; 0.01 mm; 0.03 mm |
| Width of CH | 1 mm |
| Pressure of CH outlets | 1 atm |
| Pore radii of CL and GDL [29] | 1.2 × 10−8 and 3.89 × 10−5 m |
| Equivalent weight of membrane (EW) | 1.1 kg/mol |
| R; F | 8.314 J/mol/K; 96,485 C/mol |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuo, G.; Ren, Y.; Wang, J.; Dou, Y. A Precision Monitoring Method and Control Strategy for a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell in the Power Generation System of the Antarctic Space Physics Observatory. Energies 2025, 18, 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18071693
Zuo G, Ren Y, Wang J, Dou Y. A Precision Monitoring Method and Control Strategy for a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell in the Power Generation System of the Antarctic Space Physics Observatory. Energies. 2025; 18(7):1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18071693
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuo, Guangyu, Yong Ren, Jin Wang, and Yinke Dou. 2025. "A Precision Monitoring Method and Control Strategy for a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell in the Power Generation System of the Antarctic Space Physics Observatory" Energies 18, no. 7: 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18071693
APA StyleZuo, G., Ren, Y., Wang, J., & Dou, Y. (2025). A Precision Monitoring Method and Control Strategy for a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell in the Power Generation System of the Antarctic Space Physics Observatory. Energies, 18(7), 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18071693





