Shell-Optimized Hybrid Generator for Ocean Wave Energy Harvesting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Fabrication of Hybrid Generator Unit
2.2. ATS-HG and the Control Group Fabrication
2.3. Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
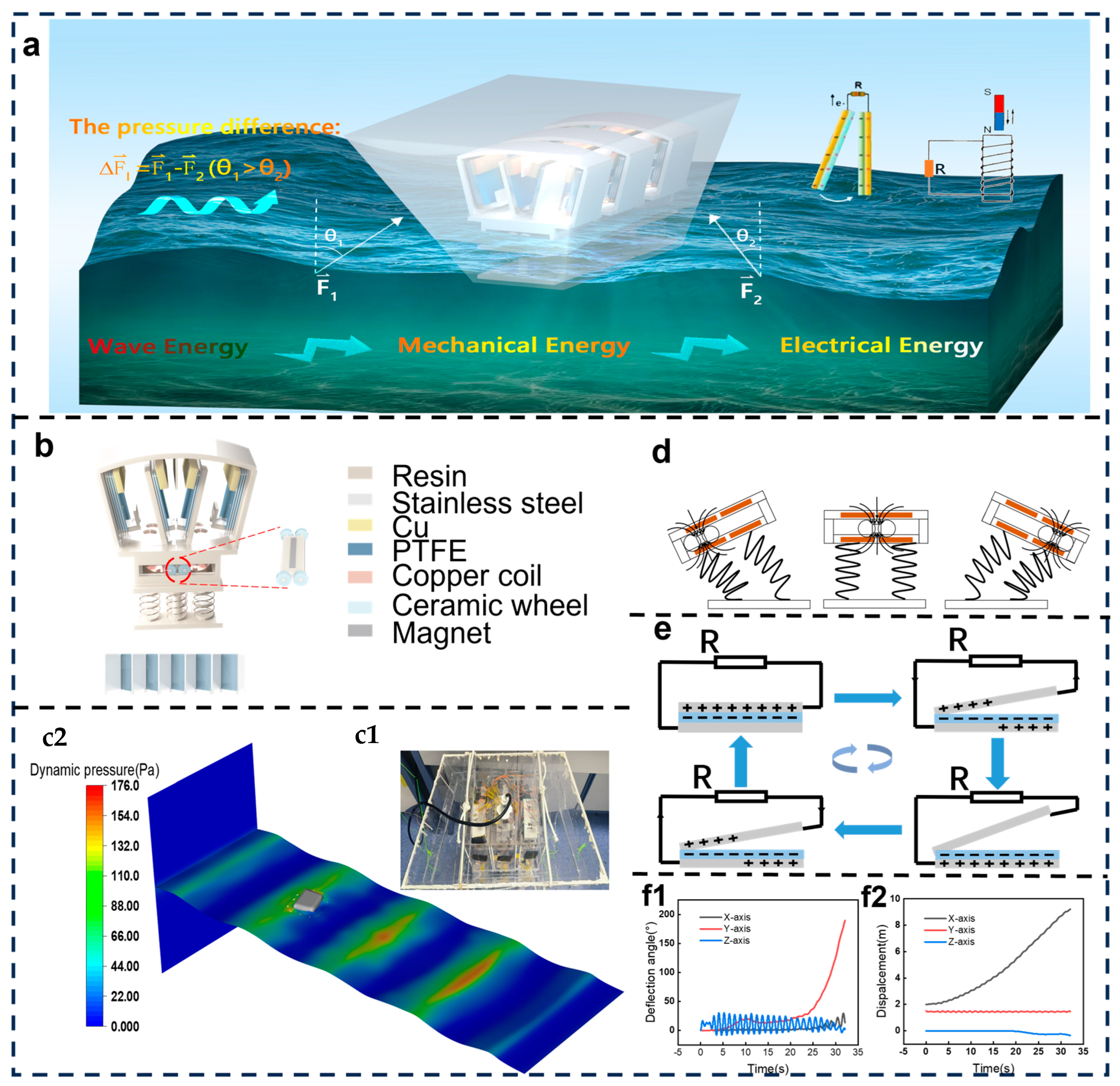
3.1. Structural Design and Working Mechanism
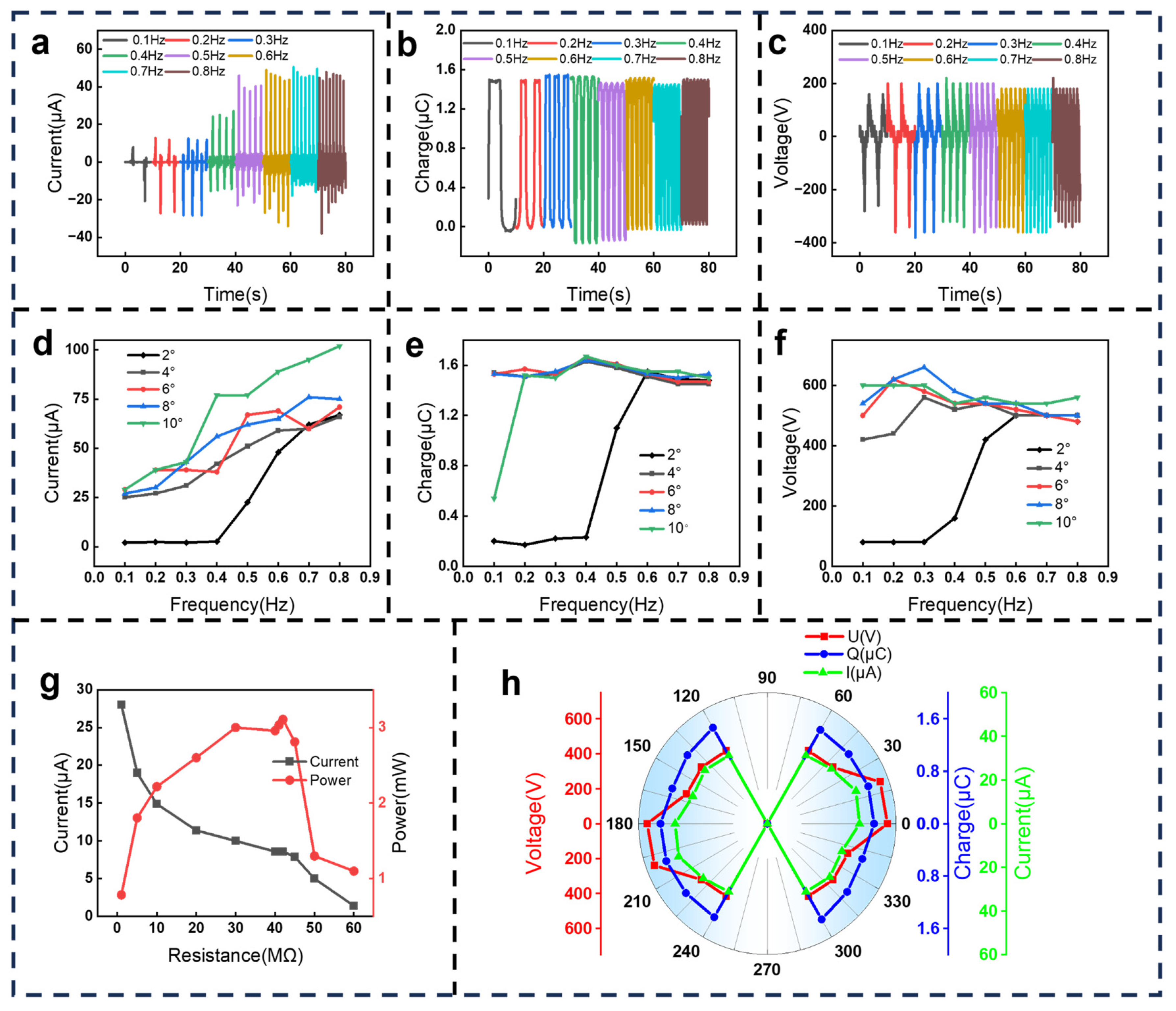
3.2. The Structural Optimization
3.3. Performance on 6-DoF Platform Simulating Seesaw Motions
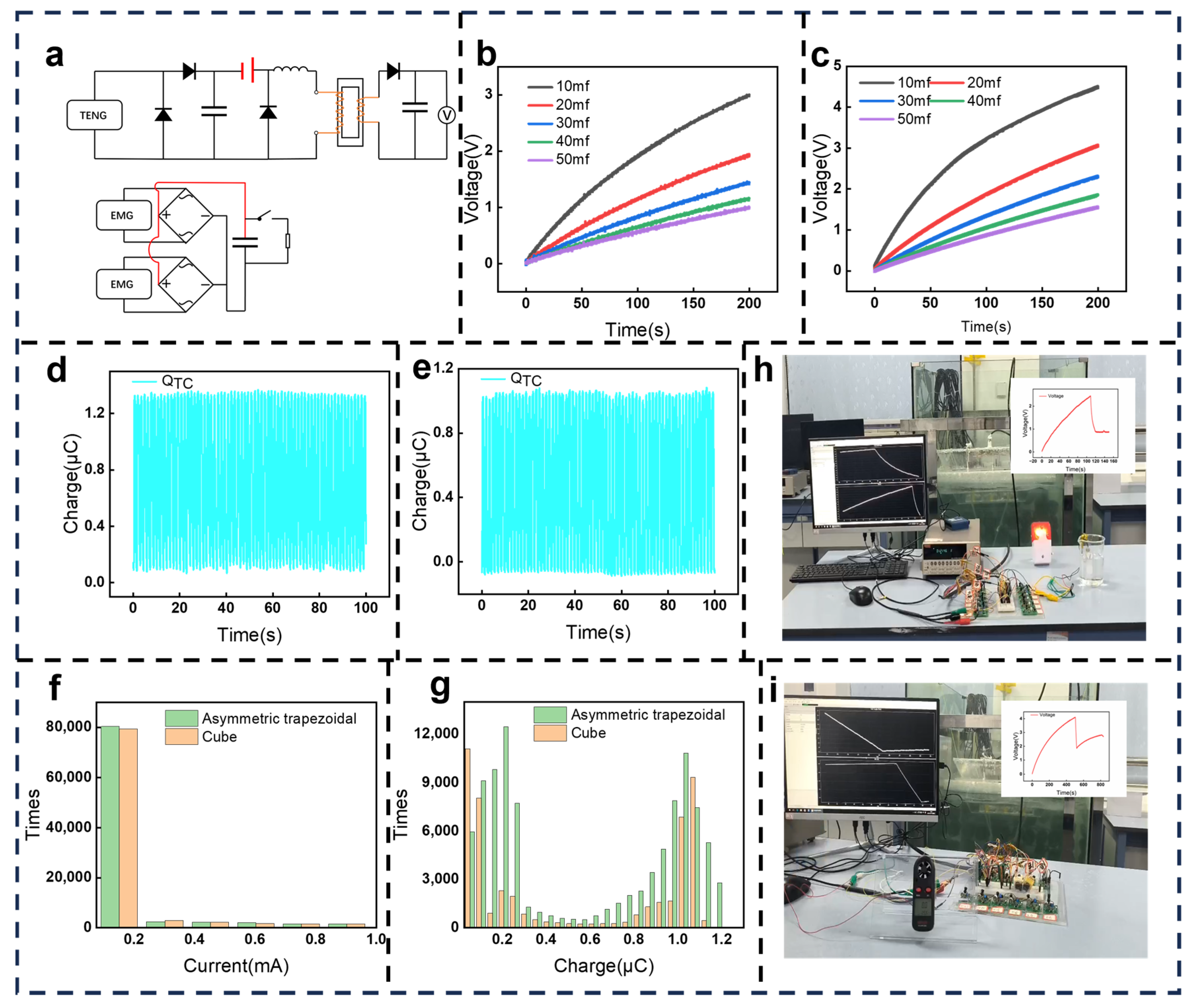
3.4. Power Management and Performance Comparison in Simulated Water Waves
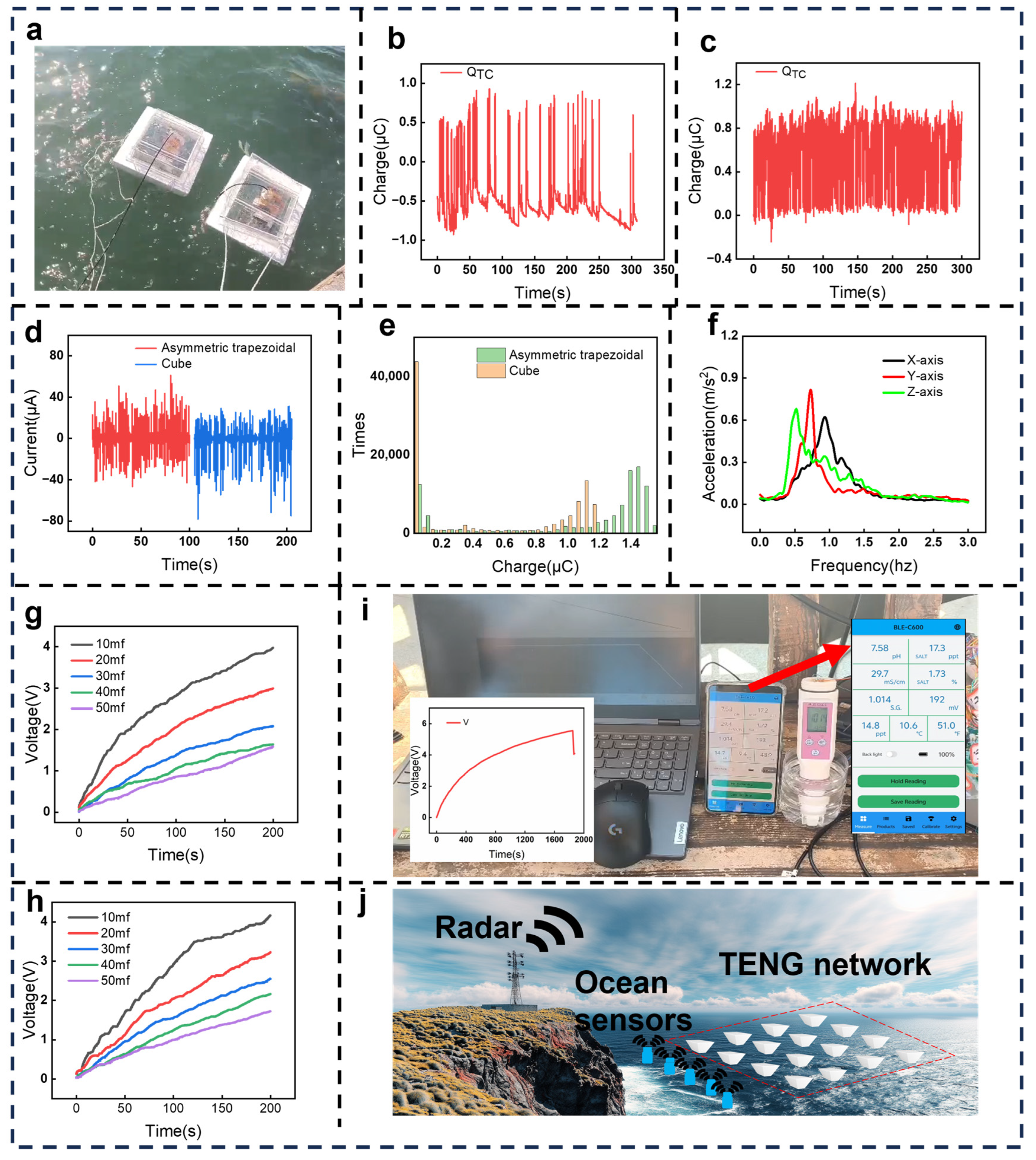
3.5. Acceleration Analysis and Integration of the Device in Simulated Water Waves
3.6. Performance Comparison, Statistical Analysis, and Integration of the Device in the Real Ocean
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, C.; Shao, L.; Shi, W.; Su, Q.; Lin, G.; Li, X.; Chen, X. An assessment of global ocean wave energy resources over the last 45 a. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2014, 33, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yu, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, B.; Yin, L. Characterization of Wave Power Resources off the Coast of Guangdong. Processes 2023, 11, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthwick, A.G.L. Marine Renewable Energy Seascape. Engineering 2016, 2, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwasilu, F.; Jung, J.-W. Potential for power generation from ocean wave renewable energy source: A comprehensive review on state-of-the-art technology and future prospects. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2019, 13, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumara, K.D.R.J. On the placement of a wave manipulator suitable for energy harnessing in the Nearshore. Cogent Eng. 2022, 9, 2124636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Gao, D.; Hua, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z. An Improved Approach to Wave Energy Resource Characterization for Sea States with Multiple Wave Systems. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, F. Type synthesis of parallel mechanisms capturing wave energy. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C-J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2019, 233, 6689–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Mei, N.; Zhang, D.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, C. Review of wave power system development and research on triboelectric nano power systems. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 966567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.; Sorokin, V.; Aw, K. Systematic literature review of wave energy harvesting using triboelectric nanogenerator. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 201, 114626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, X.; Jiang, T.; Liu, G.; Xiao, T.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Xi, F.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Networks Integrated with Power Management Module for Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807241. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.L.; Jiang, T.; Xu, L. Toward the blue energy dream by triboelectric nanogenerator networks. Nano Energy 2017, 39, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as new energy technology and self-powered sensors—Principles, problems and perspectives. Faraday Discuss. 2014, 176, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ni, Y.; Zi, Y.; Cui, H.; Li, X. Enhanced triboelectric nanogenerators in saline environments and their applications in the ocean. Nano Energy 2024, 126, 109636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.J.; Wang, H.L.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, J. Nanocomposite Electret Layer Improved Long-Term Stable Solid-Liquid Contact Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Small 2024, 20, 2310023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Guo, W.; Dong, S.; Liu, A.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Lin, C.; Zhang, J. A hybrid triboelectric nanogenerator for enhancing corrosion prevention of metal in marine environment. npj Mater. Degrad. 2022, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Shang, C.; Ma, H.; Li, C.; Xue, L.; Xu, Q.; Wei, Z.; Li, W.; Yalikun, Y.; Lai, Y.-C.; et al. A tube-shaped solid–liquid-interfaced triboelectric–electromagnetic hybrid nanogenerator for efficient ocean wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2022, 100, 107540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Dong, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B. Multi-Physics Coupling Modeling Method for the Rolling-Spherical Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Tribology 2020, 40, 680–686. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Jiang, T.; Liu, G.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Spherical triboelectric nanogenerator integrated with power management module for harvesting multidirectional water wave energy. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Shao, J.; Sagoe-Crentsil, K.; Duan, W. Investigation on energy efficiency of rolling triboelectric nanogenerator using cylinder-cylindrical shell dynamic model. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Chen, T.; Yang, J.; Hu, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, D.; Liu, F.; Liu, L.; Wu, H. Omnidirectional water wave energy harvesting by a spherical triboelectric nanogenerator with sliced-pizza-shaped electrodes. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2024, 5, 101933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, B.; Yang, J.; Hu, Y.; He, L.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, J. A Rotating Triboelectric Nanogenerator Driven by Bidirectional Swing for Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Small 2023, 19, 2304412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Shi, Q.; Lee, C. A novel hybridized blue energy harvester aiming at all-weather IoT applications. Nano Energy 2020, 76, 105052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, B.; Guo, H.; Wu, Z.; Zou, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Super-robust and frequency-multiplied triboelectric nanogenerator for efficient harvesting water and wind energy. Nano Energy 2019, 64, 103908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Han, J.; Chen, P.; Hong, Z.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Durable Roller-Based Swing-Structured Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Small 2023, 20, 2307288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jing, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Yu, X.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, T.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.L. Soft-bionic-fishtail structured triboelectric nanogenerator driven by flow-induced vibration for low-velocity water flow energy harvesting. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Wang, X.; Cheng, T.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.L. 3D fully-enclosed triboelectric nanogenerator with bionic fish-like structure for harvesting hydrokinetic energy. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 5098–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tao, K.; Ren, C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yi, H. A sea snake structure wave power generator for efficiently harvesting ocean wave energy with flexible structure. In Proceedings of the 46th Annual Conference of the IEEE-Industrial-Electronics-Society (IECON), Singapore, 18–21 October 2020; pp. 3489–3492. [Google Scholar]
- Yar, A. High performance of multi-layered triboelectric nanogenerators for mechanical energy harvesting. Energy 2021, 222, 119949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huo, D.; Su, J.; He, Z. Portable Multi-Layer Capsule-Shaped Triboelectric Generator for Human Motion Energy Harvesting. Micromachines 2024, 15, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yang, P.; Qiao, W.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Multi-layered triboelectric nanogenerator incorporated with self-charge excitation for efficient water wave energy harvesting. Appl. Energy 2023, 336, 120792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, C.; Guo, D.; Liu, H.; Ning, H.; Liu, G.; Wan, L. Highly Sensitive Hybrid Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Ferris-Wheel-Like Structure for Ocean Wave Energy Harvesting. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2024, 8, 2400310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, W.; Tuo, L.; Qu, H.; Zhai, L.; Wan, L.; et al. Enhanced hybrid generator with spring coupling effect for low-grade water wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2025, 133, 110488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Lee, J.-w.; Kim, K.; Yoo, D.; Kim, D.S.; Hwang, W.; Song, I.; Sim, J.-Y. A Spherical Hybrid Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Enhanced Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Micromachines 2018, 9, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatnia, Z.; Asadi, E.; Askari, H.; Zu, J.; Esmailzadeh, E. Modeling and performance analysis of duck-shaped triboelectric and electromagnetic generators for water wave energy harvesting. Int. J. Energy Res. 2017, 41, 2392–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Yoon, H.J.; Kim, S.W. Hybrid Energy Harvesters: Toward Sustainable Energy Harvesting. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1802898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, Q.; Ding, Z.; Li, Z.; Zheng, H.; Fu, J.; Diao, C.; Zhang, X.; Tian, J.; Zi, Y. A fully-packaged ship-shaped hybrid nanogenerator for blue energy harvesting toward seawater self-desalination and self-powered positioning. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Wen, H.; Cao, S.; Yao, H.; Wan, L.; Wang, Z.L. Interaction between Water Wave and Geometrical Structures of Floating Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2103408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Wen, H.; Liu, H.; Guo, D.; Liu, G.; Qu, H.; Wan, L.; Yao, H.; Zhai, J. High-sensitivity blue-energy-shuttle and in-situ electrical behaviors in ocean. Nano Energy 2024, 125, 109546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Zhai, L.; Li, S.; He, S.; Feng, J.; Wan, L.; Liu, G.; Zhai, J. Structural Quality Factor of Flo-TENG under Stochastic Wave Excitation. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2405165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, J.; Su, E.; Li, C.; Tang, W.; Liu, G.; Cao, L.N.Y.; Wang, Z.L. Dynamic behavior and energy flow of floating triboelectric nanogenerators. Appl. Energy 2024, 367, 123468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; He, W.; Guo, H.; Long, L.; Xi, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, A.; Hu, C. Ultrahigh Electricity Generation from Low-Frequency Mechanical Energy by Efficient Energy Management. Joule 2021, 5, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, W.; Bamgboje, D.; Guo, H.; Hu, T.; Wang, Z.L. Self-driven power management system for triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2020, 71, 104642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holthuijsen, L.H. Waves in Oceanic and Coastal Waters; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; p. 70. ISBN 978-0-521-86028-4. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Guo, D.; Zhu, H.; Wen, H.; Li, J.; Wan, L. Shell-Optimized Hybrid Generator for Ocean Wave Energy Harvesting. Energies 2025, 18, 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061502
Liu H, Guo D, Zhu H, Wen H, Li J, Wan L. Shell-Optimized Hybrid Generator for Ocean Wave Energy Harvesting. Energies. 2025; 18(6):1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061502
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Heng, Dongxin Guo, Hengda Zhu, Honggui Wen, Jiawei Li, and Lingyu Wan. 2025. "Shell-Optimized Hybrid Generator for Ocean Wave Energy Harvesting" Energies 18, no. 6: 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061502
APA StyleLiu, H., Guo, D., Zhu, H., Wen, H., Li, J., & Wan, L. (2025). Shell-Optimized Hybrid Generator for Ocean Wave Energy Harvesting. Energies, 18(6), 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061502





