Physicochemical Properties and Low-Temperature Sulfur Fixation Patterns of Fly Ash from a Biomass Power Plant
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sampling and Testing of BA
2.1. Sampling of BA
2.2. Testing of BA
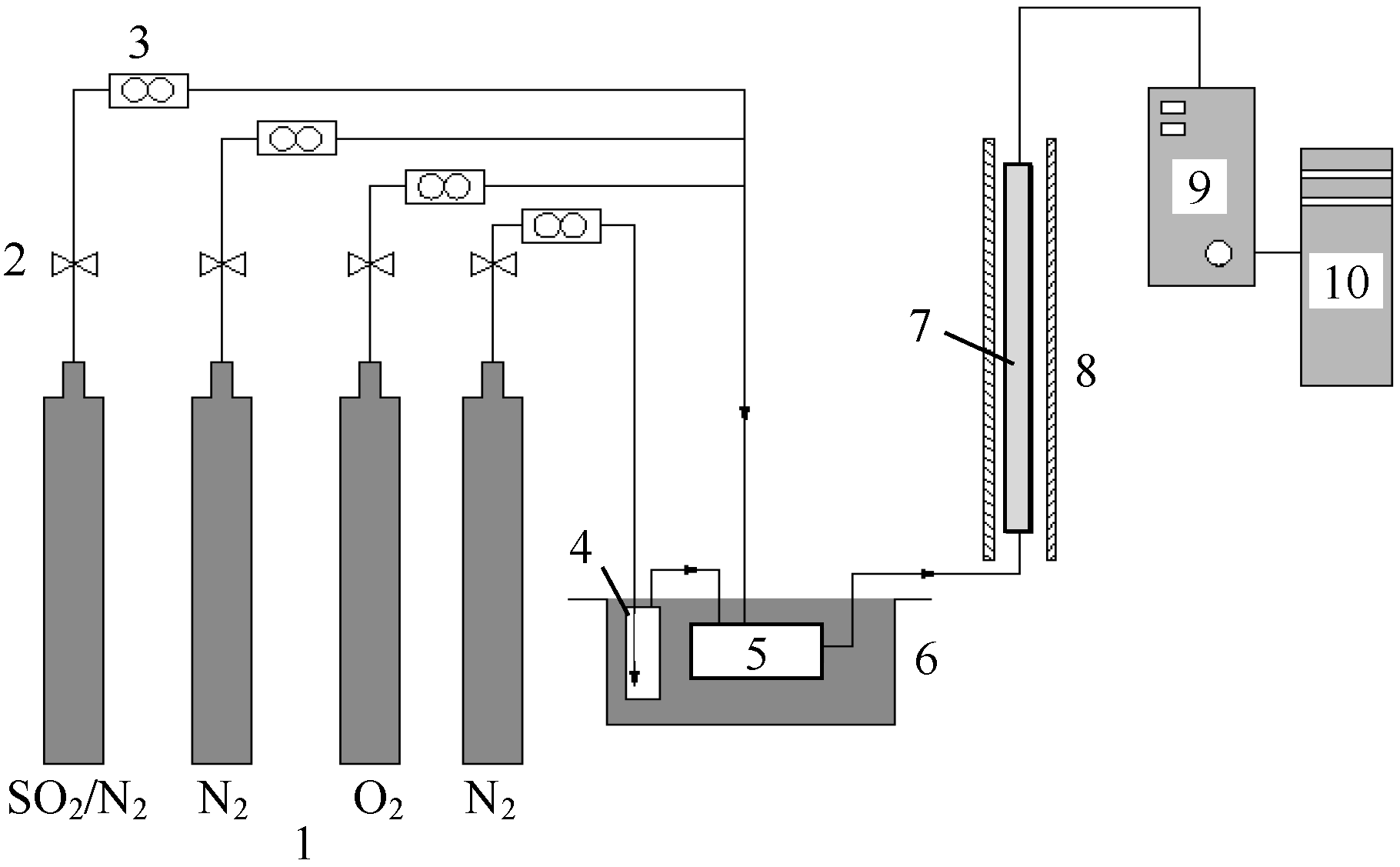
2.3. Experimental Device for Examining the Absorption of SO2 by BA
3. Analysis of the Physicochemical Properties of BA
3.1. Chemical Compositions of Biomass Analyzed by XRF and XRD
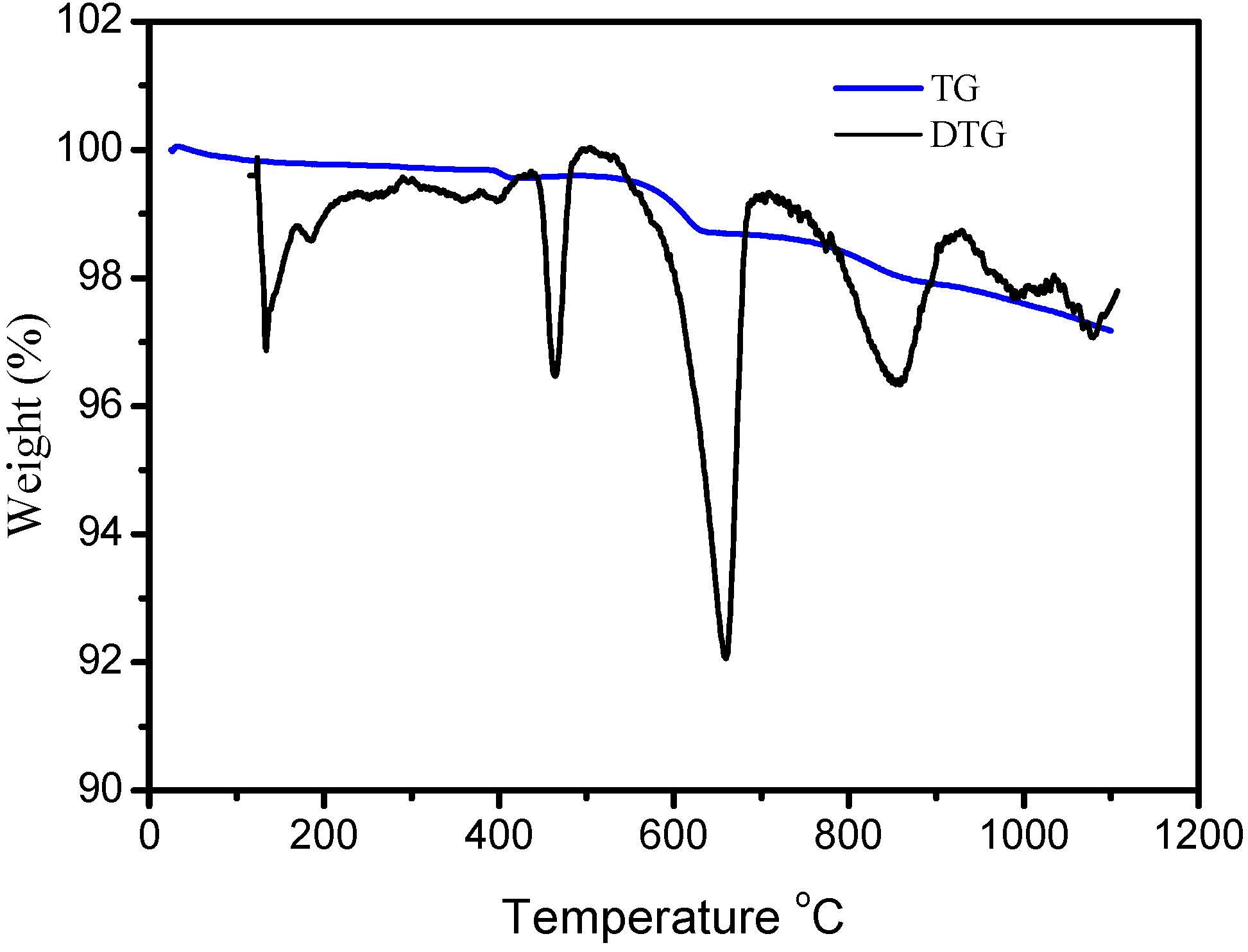
3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis of BA
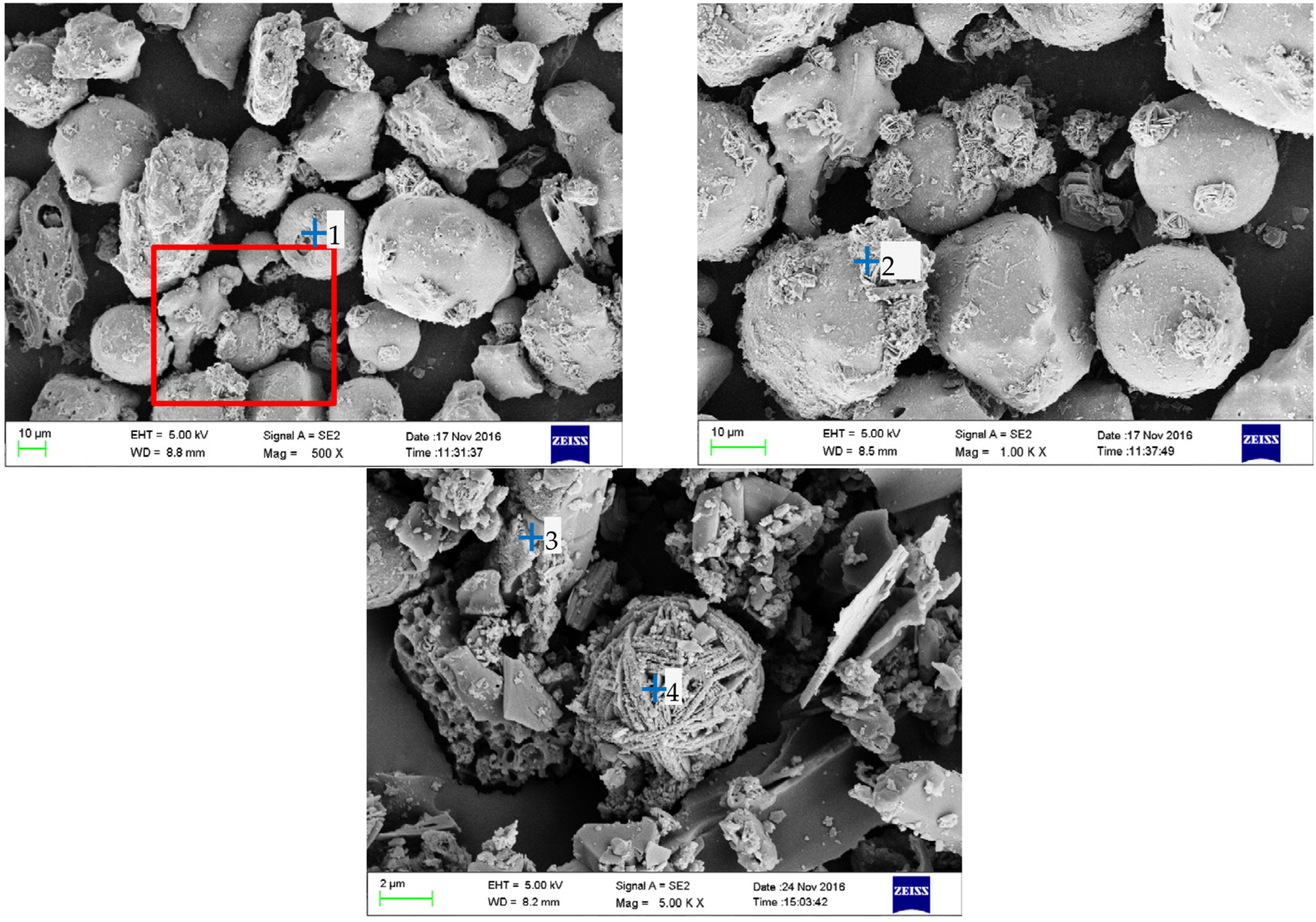
3.3. Microstructural Characteristics of the BA Particles
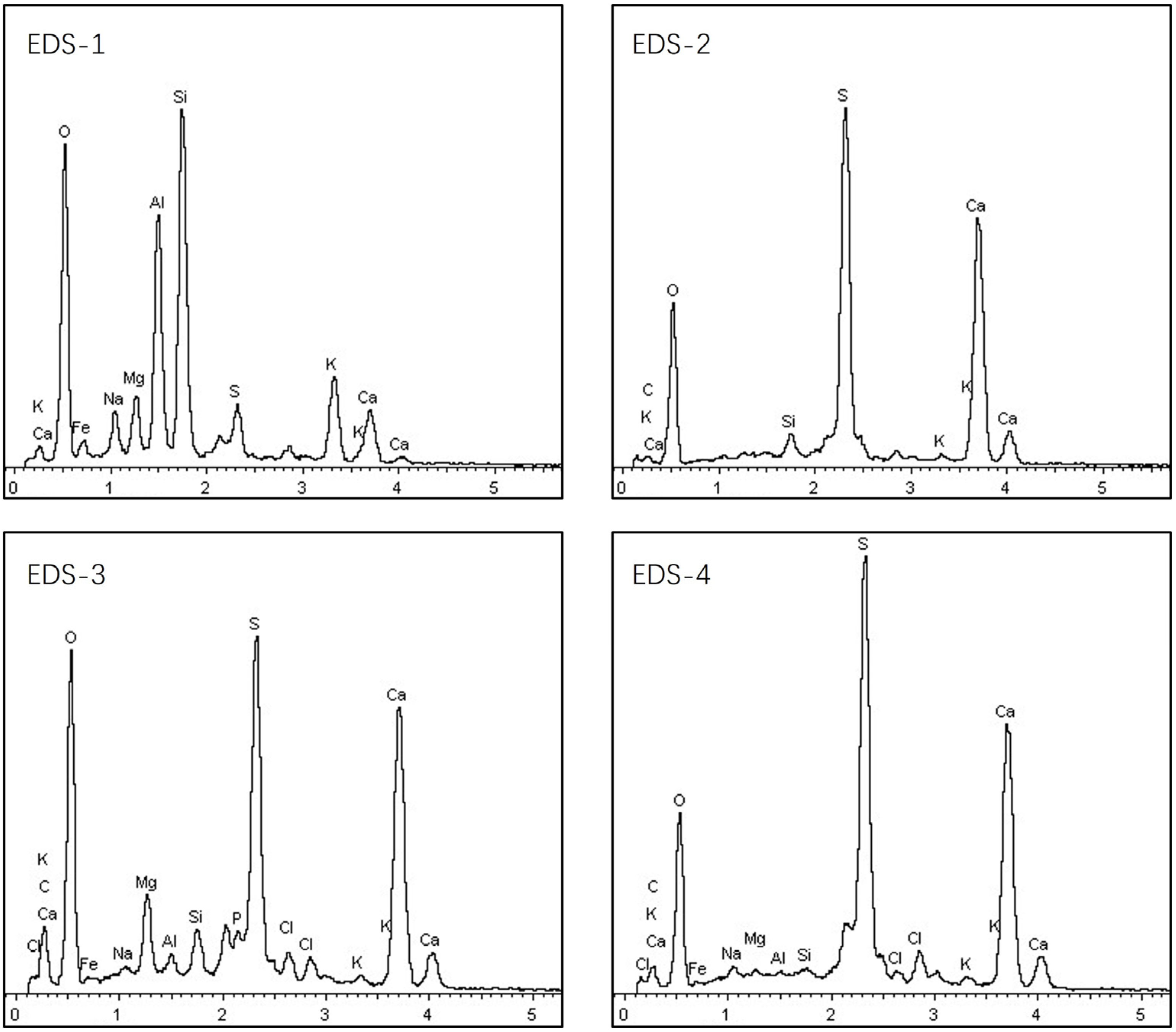
3.4. Biomass Particle Surface Analysis Using EDS
- (1)
- EDS analysis of angular particles
- (2)
- EDS analysis of spherical particles
- (3)
- Flocculent-shaped particles
4. SO2-Absorbing Property of the BA
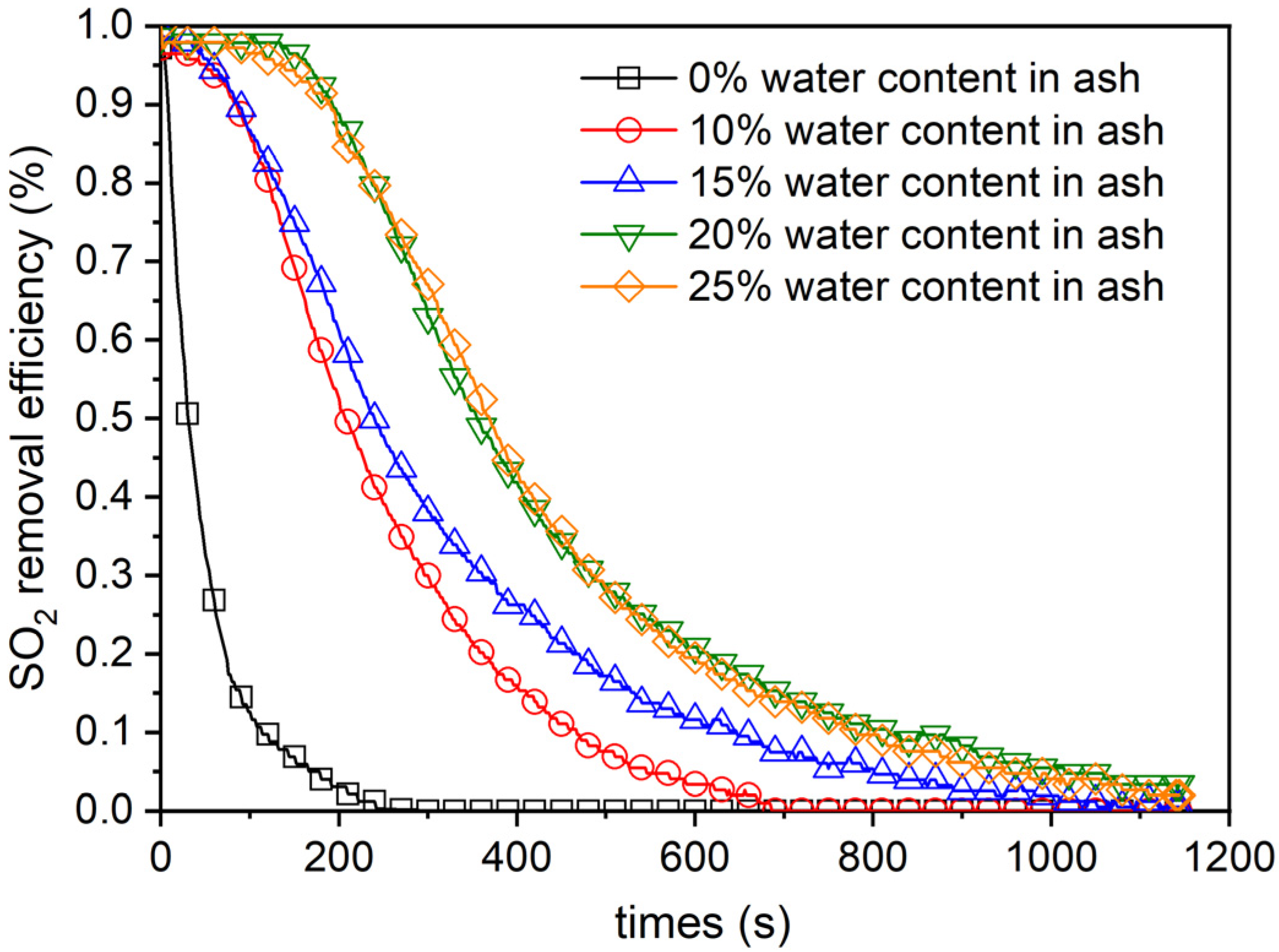
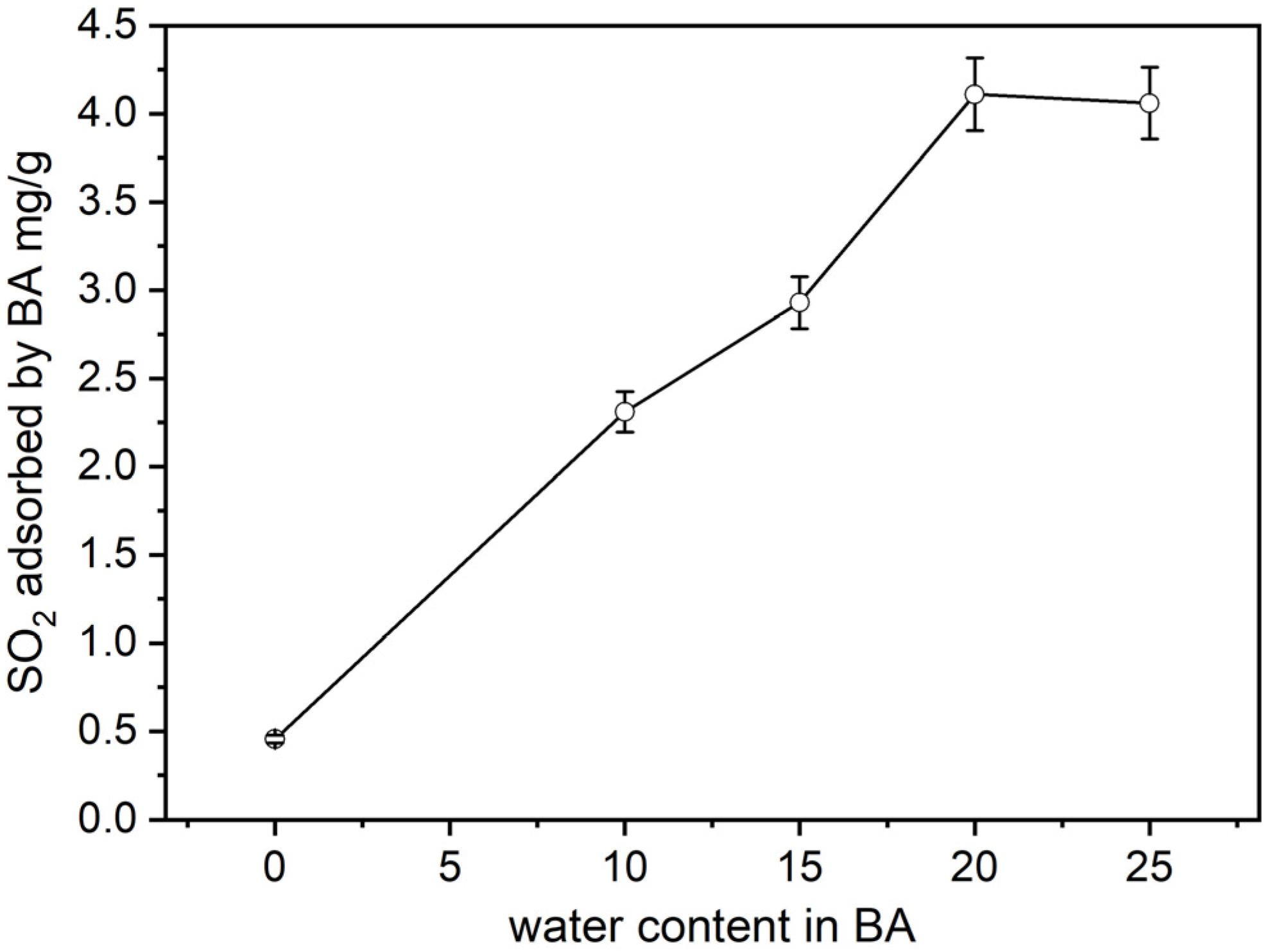
4.1. Effect of Water Content in the BA
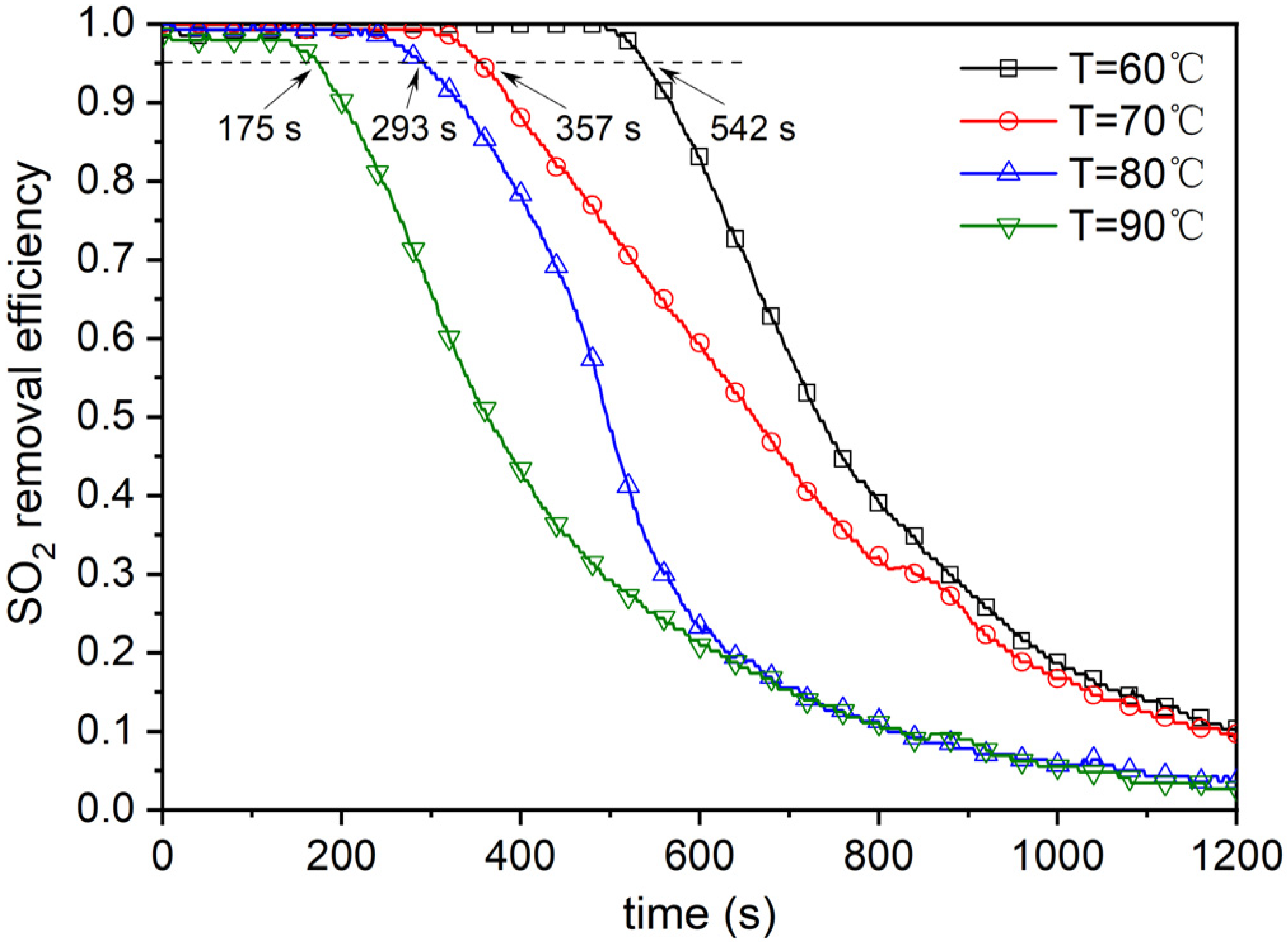
4.2. Effect of Reaction Temperature
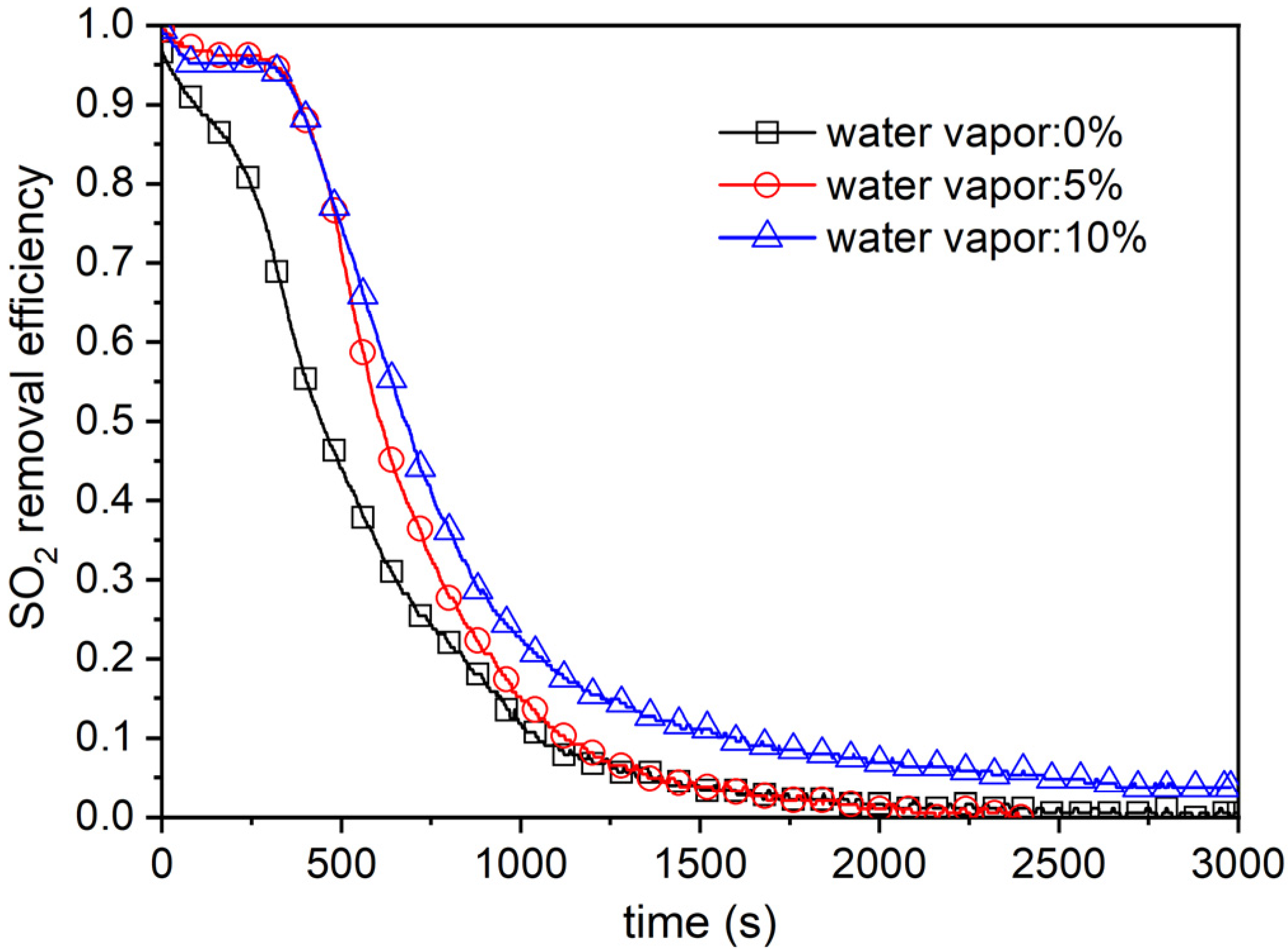
4.3. Effect of Moisture Content in Flue Gas
5. Characteristic Analysis of the Desulfurized BA
5.1. Chemical Composition Analyses of the Desulfurized BA Using XRF and XRD
5.2. SEM and EDS Analyses
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cornea, T.M.; Dima, M. Biomass energy—A way towards asustainable future. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2010, 9, 1341–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Grée, G.D.; Florea, M.V.A.; Keulen, A.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Contaminated biomass fly ashes—Characterization and treatment optimization for reuse as building materials. Waste Manag. 2016, 49, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarelho, L.A.C.; Teixeira, E.R.; Silva, D.F.R.; Modolo, R.C.E.; Labrincha, J.A.; Rocha, F.J.F.T. Characteristics of distinct ash flows in a biomass thermal power plant with bubbling fluidised bed combustor. Energy 2015, 90, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Song, W. Power Production from biomass in Denmark. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2005, 33, 650–655. [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev, S.V.; Baxter, D.; Andersen, L.K.; Vassileva, C.G. An overview of the composition and application of biomass ash.: Part 2. Potential utilisation, technological and ecological advantages and challenges. Fuel 2013, 105, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Jaturapitakkul, C.; Chalee, W.; Rattanasak, U. Comparative study on the characteristics of fly ash and bottom ash geopolymers. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, L.L.; Miles, T.R.; Miles, T.R., Jr.; Jenkins, B.M.; Milne, T.; Dayton, D.; Bryers, R.W.; Oden, L.L. The behavior of inorganicmaterial in biomass fired power boilers: Field and laboratoryexperiences. Fuel Process. Technol. 1998, 54, 47–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girón, R.P.; Ruiz, B.; Fuente, E.; Gil, R.R.; Suárez-Ruiz, I. Properties of fly ash from forest biomass combustion. Fuel 2013, 114, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, S.V.; Baxter, D.; Andersen, L.K.; Vassileva, C.G.; Morgan, T.J. An overview of the organic and inorganic phase composition of biomass. Fuel 2012, 94, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RenYong, S.; JiuYu, L.; Jun, J.; Mehmood, K.; Yuan, L.; RenKou, X.; Wei, Q. Characteristics of biomass ashes from different materials and their ameliorative effects on acid soils. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 55, 294–302. [Google Scholar]
- Dahl, O.; Nurmesniemi, H.; Poykio, R.; Watkins, G. Heavy metal concentrations in bottom ash and fly ash fractions from a large-sized (246 MW) fluidized bed boiler with respect to their Finnish forest fertilizer limit values. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 1634–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Han, Z.; Sheng, C. Feasibility evaluation of biomass fly ashes from power station using as fertilizer. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, E.R.; Mateus, R.; Camões, A.F.; Bragança, L.; Branco, F.G. Comparative environmental life-cycle analysis of concretes using biomass and coal fly ashes as partial cement replacement material. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 2221–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obernberger, I.; Supancic, K. Possibilities of ash utilisation from biomass combustion plants. In Proceedings of the 17th European Biomass Conference & Exhibition, Hamburg, Germany, 29 June–3 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Odzijewicz, J.I.; Wołejko, E.; Wydro, U.; Wasil, M.; Jabłońska-Trypuć, A. Utilization of Ashes from Biomass Combustion. Energies 2022, 15, 9653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, O.; Nurmesniemi, H.; Poykio, R.; Watkins, G. Comparison of the characteristics of bottom ash and fly ash from a medium-size (32 MW) municipal district heating plant incinerating forest residues and peat in a fluidized-bed boiler. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, P. Characterization of Typical Biomass Ashes and Study on Their Potential of CO2 Fixation. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 6047–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Combustion characteristics of different biomass fuels. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2004, 30, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Han, K.; Wang, Q.; Gao, J. Carbonization of biomass: Effect of additives on alkali metals residue, SO2 and NO emission of chars during combustion. Energy 2017, 130, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Hao, R.; He, H.; Yang, F.; Mao, X.; Mao, Y.; Zhao, P. Combustion behavior, emission characteristics of SO2, SO3 and NO, and in situ control of SO2 and NO during the cocombustion of anthracite and dried sawdust sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokni, E.; Ren, X.; Panahi, A.; Levendis, Y.A. Emissions of SO2, NOx, CO2, and HCl from Co-firing of coals with raw and torrefied biomass fuels. Fuel 2018, 211, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlan, I.; Lee, K.T.; Kamaruddin, A.H.; Mohamed, A.R. Rice Husk Ash/Calcium Oxide/Ceria Sorbent for Simultaneous Removal of Sulfur Dioxide and Nitric Oxide from Flue Gas at Low Temperature. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2009, 26, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlan, I.; Lee, K.T.; Kamaruddin, A.H.; Mohamed, A.R. Sorption of SO2 and NO from simulated flue gas over rice husk ash (RHA)/CaO/CeO2 sorbent: Evaluation of deactivation kinetic parameters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1609–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, L.C.; Lee, K.T.; Mohamed, A.R. Effect of operating conditions towards simultaneous removal of SO2 and NO using copper modified rice husk ash: Role as sorbent and catalyst. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Ma, Z. Preparation of CFB fly ash/sewage sludge ceramsite and the morphological transformation and release properties of sulfur. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 373, 130864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Dollimore, D.; Alexander, K.; Wilburn, F.W. The origin of the exothermic peak in the thermal decomposition of basic magnesium carbonate. Thermochim. Acta 2001, 367–368, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, J.M.; Jakobsen, J.G.; Frandsen, F.J.; Glarborg, P. Release of K, Cl, and S during Pyrolysis and Combustion of High-Chlorine Biomass. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 4961–4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benassi, L.; Dalipi, R.; Consigli, V.; Pasquali, M.; Borgese, L.; Depero, L.E.; Clegg, F.; Bingham, P.A.; Bontempi, E. Integrated management of ash from industrial and domestic combustion: A new sustainable approach for reducing greenhouse gas emissions from energy conversion. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 14834–14846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraber, A. Co-combustion and its impact on fly ash quality: Pilot-scale experiments. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 104, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutchko, B.G.; Kim, A.G. Fly ash characterization by SEM-EDS. Fuel 2006, 85, 2537–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhman, M.; Nordin, A.; Skrifvars, B.J.; Backman, R.; Hupa, M. Bed agglomeration char-acteristics during fluidized bed combustion of biomassfuels. Energy Fuels 2000, 14, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, L.C.; Lee, K.T.; Mohamed, A.R. Rice husk ash sorbent doped with copper for simultaneous removal of SO2 and NO: Optimization study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, F.F.; Zank, J. Flue gas desulphurization by spray dry absorption. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2000, 39, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Lu, J.; Ma, X. SO3/sulfuric acid mist removal in simulated flue gas: Multi-factor study based on two-film theory mass transfer process. Fuel 2024, 357, 129698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yang, S.; Wang, H. Slurry Droplet Dynamics and Absorption Reaction Characteristics in Industrial-Scale Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization Reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 17705–17722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Type | Cotton Stalks | Corn Stalks | Wheat Straws | Forestry Stalks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion | 30% | 25% | 15% | 30% |
| Component | SiO2 | CaO | Al2O3 | K2O | Fe2O3 | MgO | SO3 | P2O5 | Na2O | Cl | TiO2 | Others | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 54.89 | 10.52 | 9.93 | 7.57 | 5.76 | 4.52 | 1.6 | 1.54 | 1.47 | 1.18 | 0.693 | 0.327 | 100 |
| Sample | C | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | S | Cl | K | Ca | Fe | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDS-1 | 0 | 67.74 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31.91 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.35 | 0 | 100 |
| EDS-2 | 0 | 58.66 | 1.81 | 1.88 | 11.17 | 17.99 | 0 | 0.35 | 6.32 | 0.59 | 1.23 | 100 |
| EDS-3 | 1.07 | 60.83 | 0.65 | 0.66 | 1.34 | 9.92 | 0.32 | 1.72 | 1.63 | 21.4 | 0.46 | 100 |
| Component | SiO2 | CaO | Al2O3 | K2O | Fe2O3 | MgO | SO3 | P2O5 | Na2O | Cl | TiO2 | Others | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 47.07 | 12.58 | 12.89 | 6.4 | 7.43 | 2.04 | 9.14 | 0.85 | 0.32 | 0.218 | 0.822 | 0.24 | 100 |
| Sample | C | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | K | Ca | Fe | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDS-1 | 0 | 62.47 | 2.21 | 2.31 | 8.19 | 13.55 | 0 | 2.06 | 0 | 4.24 | 2.87 | 2.1 | 100 |
| EDS-2 | 0.37 | 64.87 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.96 | 0 | 16.73 | 0 | 0.32 | 16.75 | 0 | 100 |
| EDS-3 | 1.56 | 68.91 | 0.29 | 2.67 | 0.46 | 1.28 | 0.83 | 10.2 | 1.25 | 0.3 | 11.95 | 0.3 | 100 |
| EDS-4 | 0.66 | 62.84 | 0.7 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0 | 17.44 | 0.92 | 0.41 | 16.31 | 0.15 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, B.; Wei, A.; Zhang, L. Physicochemical Properties and Low-Temperature Sulfur Fixation Patterns of Fly Ash from a Biomass Power Plant. Energies 2025, 18, 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061466
Zhang J, Zhang P, Zhou J, Zhao B, Wei A, Zhang L. Physicochemical Properties and Low-Temperature Sulfur Fixation Patterns of Fly Ash from a Biomass Power Plant. Energies. 2025; 18(6):1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061466
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jun, Peng Zhang, Jie Zhou, Bo Zhao, Ansheng Wei, and Liqiang Zhang. 2025. "Physicochemical Properties and Low-Temperature Sulfur Fixation Patterns of Fly Ash from a Biomass Power Plant" Energies 18, no. 6: 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061466
APA StyleZhang, J., Zhang, P., Zhou, J., Zhao, B., Wei, A., & Zhang, L. (2025). Physicochemical Properties and Low-Temperature Sulfur Fixation Patterns of Fly Ash from a Biomass Power Plant. Energies, 18(6), 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061466





