Distributed Model Predictive Load Frequency Control for Virtual Power Plants with Novel Event-Based Low-Delay Technique Under Cloud-Edge-Terminal Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
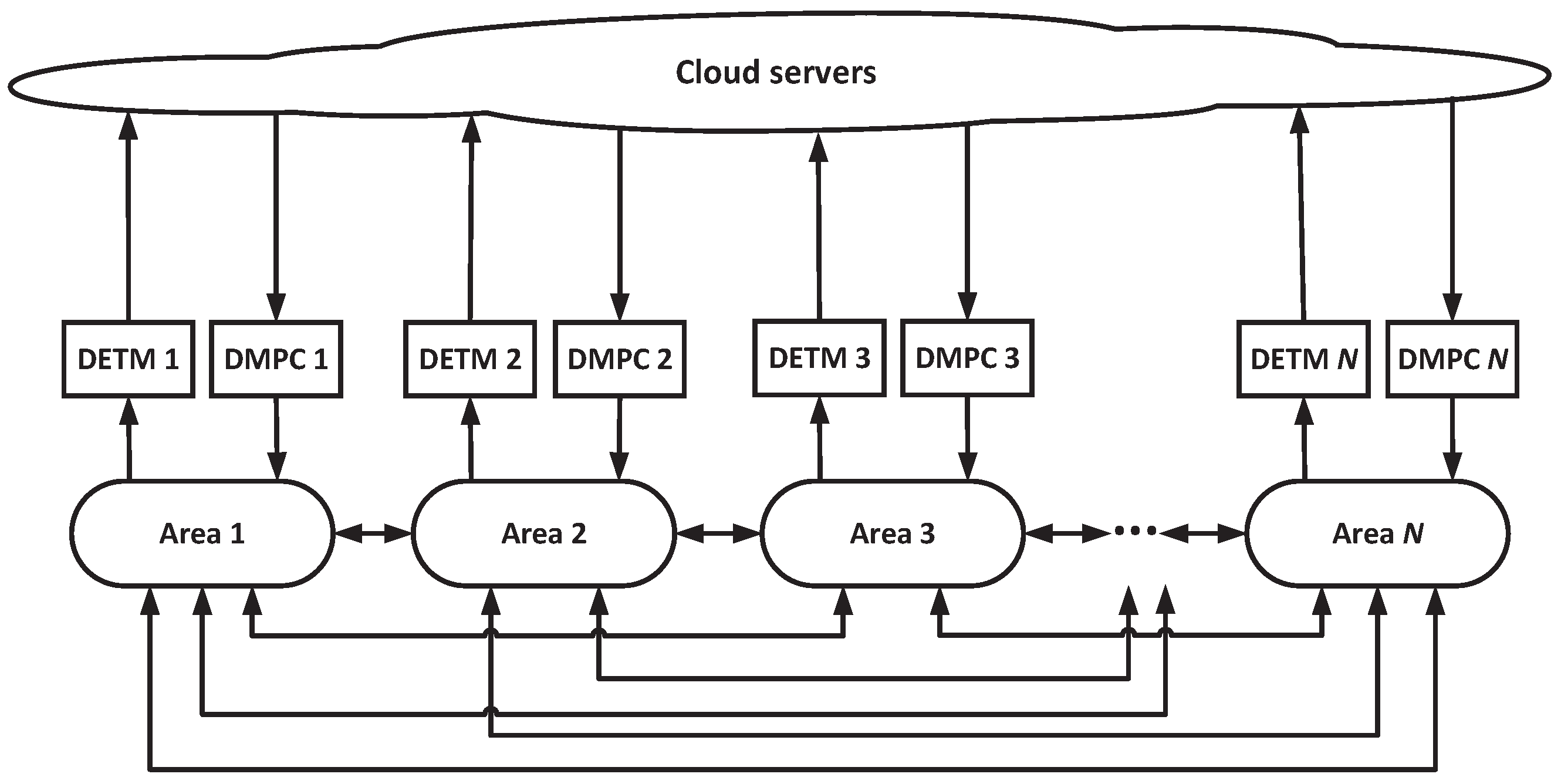
2.1. General Structure of VPP
2.2. Wind Storage System Frequency Modulation Model
2.3. Electric Vehicle Frequency Modulation Model
2.4. Distributed Predictive LFC Model with VPP
3. Main Results
3.1. LMI-Based Auxiliary of
3.2. Sufficient Conditions for PIS
| Algorithm 1 DETM-based DMPC for System (14) |
Step 1. At , set the initial state , the matrices and , and set the scalars , , , , , , , , , , , and . Step 2. If the error between and meets the event-triggered condition in DETM (8), then update by ; otherwise, implement on the controller. |
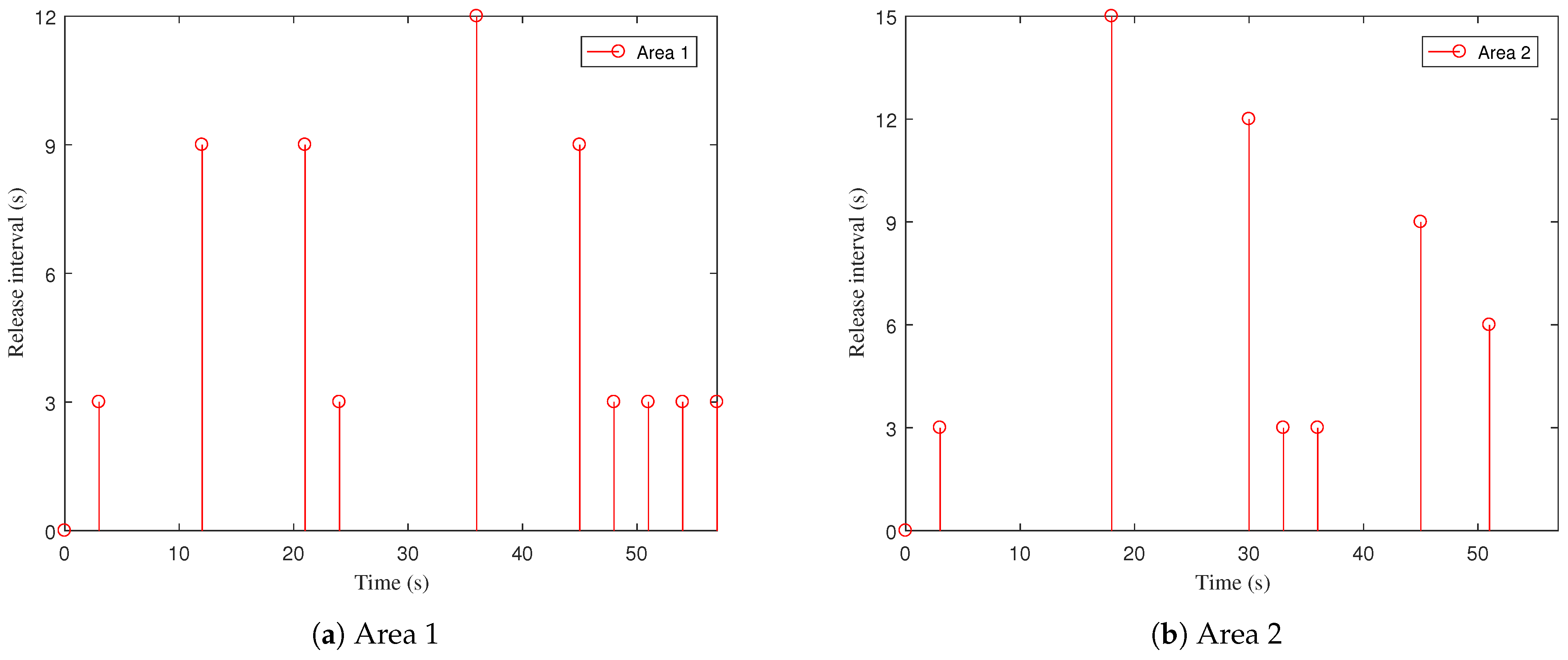
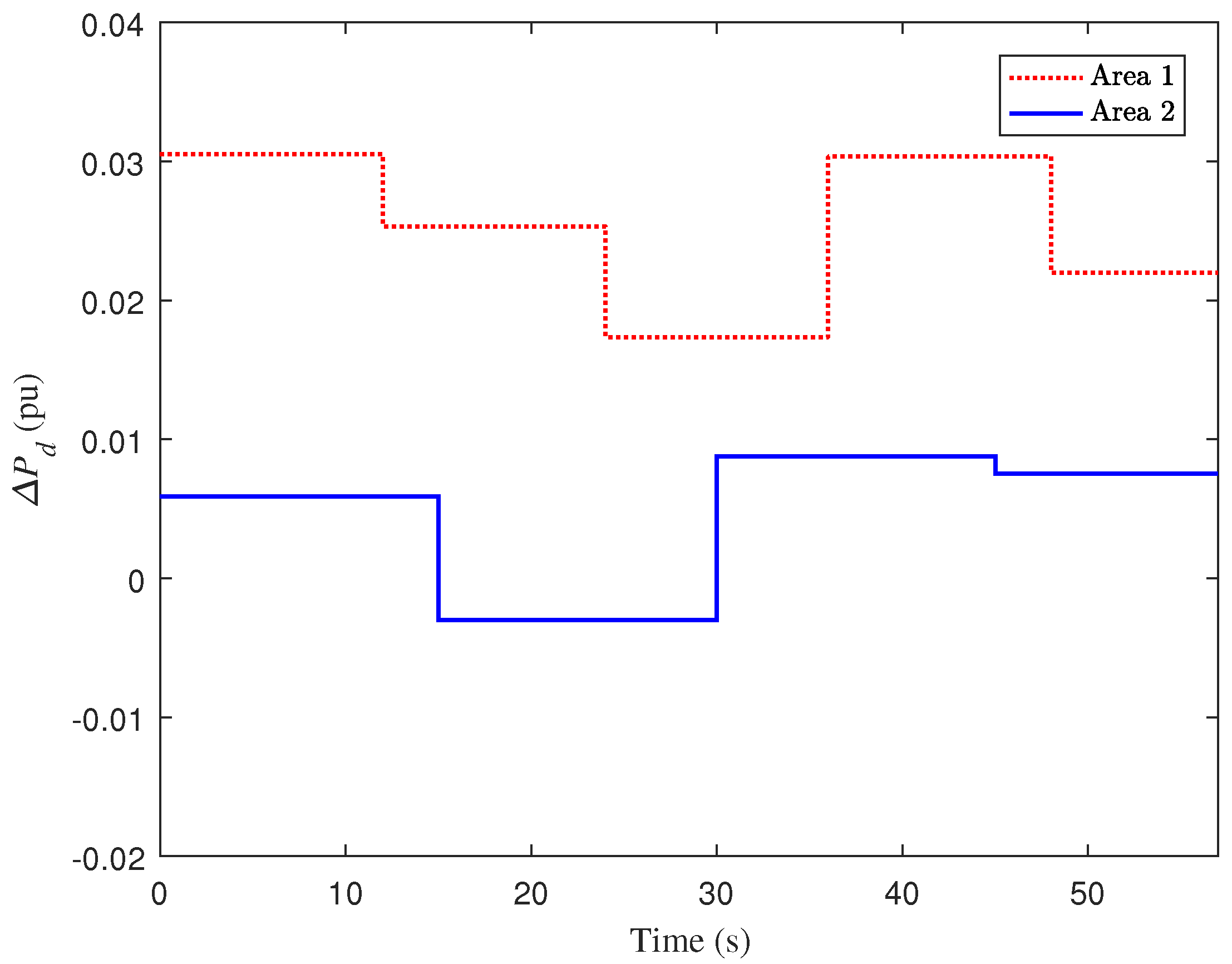
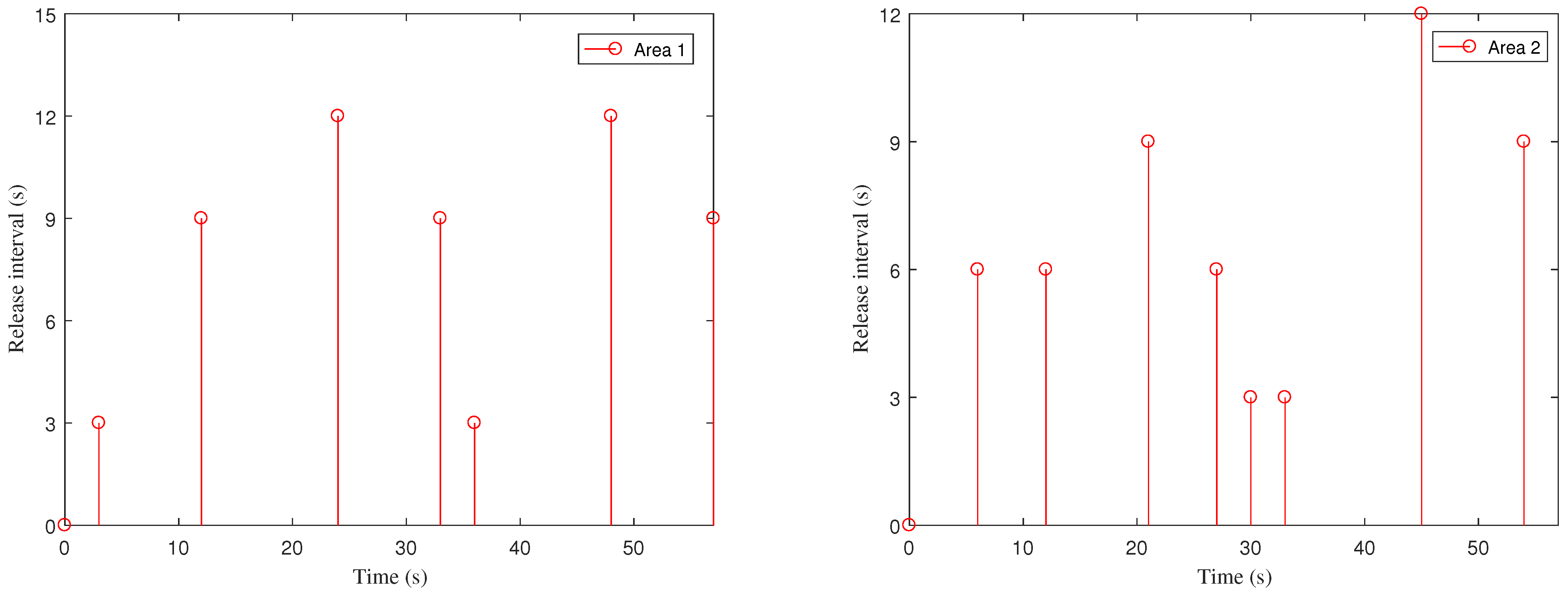
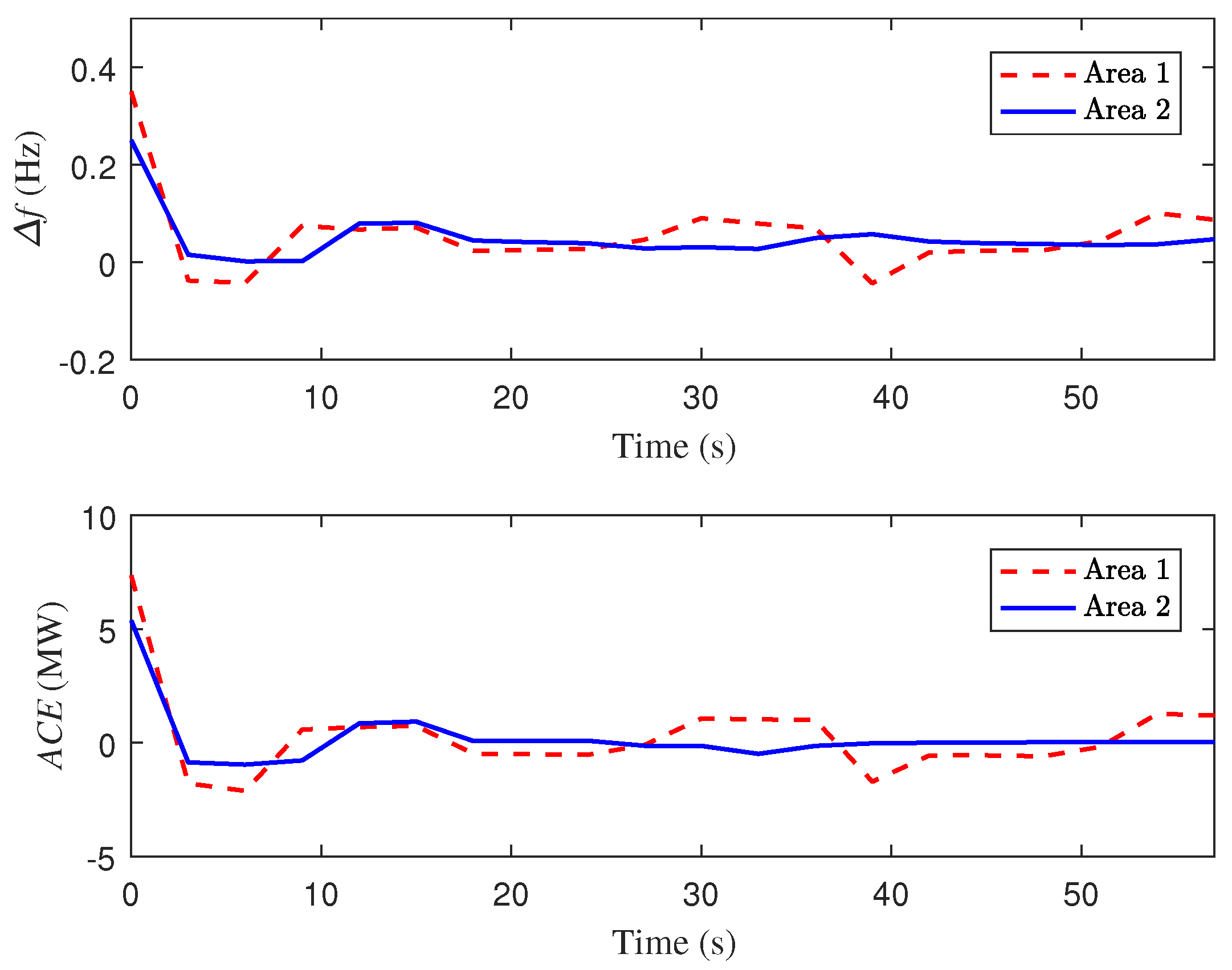
4. Case Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VPP | virtual power plant |
| LFC | load frequency control |
| DMPC | distributed model predictive control |
| CMPC | centralized model predictive control |
| DETM | dynamic event-triggered mechanism |
| OP | optimization problem |
| DV | dynamic variable |
| AAV | adaptive adjustment variable |
References
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.; Terzija, V. Review on deep learning applications in frequency analysis and control of modern power system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 136, 107744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Illindala, M.S. Robust distributed load frequency control for multi-area power systems with photovoltaic and battery energy storage system. Energies 2024, 17, 5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, X.C.; Zhang, C.K.; He, Y.; Jin, L.; Jiang, L.; Spencer, J.W.; Wu, M. Robust load frequency control for power system considering transmission delay and sampling period. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 17, 5292–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qu, G.; Tang, Y.; Low, S.; Li, N. Reinforcement learning for selective key applications in power systems: Recent advances and future challenges. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13, 2935–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, M.; Milano, F. Aggregated model of virtual power plants for transient frequency and voltage stability analysis. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2021, 36, 4366–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xie, L.; Pang, D.; Shi, H.; Zheng, H. Load frequency control of multiarea power systems with virtual power plants. Energies 2024, 17, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, G.; Dong, Z.Y. Two-stage community energy trading under end-edge-cloud orchestration. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 1961–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.T.; Chen, G.; Zhou, X. Distributed carbon-aware energy trading of virtual power plant under denial of service attacks: A passivity-based neurodynamic approach. Energy 2022, 257, 124751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, M.; Hao, J. Event-triggered communication network with limited-bandwidth constraint for multi-agent reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 3966–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Yu, W.; Cui, L.; Hou, Z.; Chen, Z. Event-triggered data-driven load frequency control for multiarea power systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 5982–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Chen, J. Periodic event-eriggered MPC for continuous-time nonlinear systems with bounded disturbances. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2023, 68, 8036–8043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Wei, F.; Zhang, C.K.; Wu, M. Networked output-feedback MPC: A bounded dynamic variable and time-varying threshold-dependent event-based approach. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 2308–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Shi, P.; Chambers, J. Dynamic event-triggered model predictive control under channel fading and denial-of-service attacks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 21, 6448–6459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Han, T.; An, J.; Wu, M. Fault diagnosis for networked switched systems: An improved dynamic event-based scheme. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 8376–8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Dong, S.; Shi, P.; Chen, G.; Guan, X. Distributed observer-based event-triggered load frequency control of multiarea power systems under cyber attacks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2023, 20, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Xu, M.; Fan, Y. SOC-SOH estimation and balance control based on event-triggered distributed optimal kalman consensus filter. Energies 2024, 17, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Wang, D.; Park, J.H.; Sreeram, V.; Wang, J. Switching-like event-triggered sliding mode load frequency control for networked power systems under energy-limited DoS attacks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2024, 54, 1589–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Chen, G.; Guo, M.; Chen, T.; Luo, L.; Sun, L. Model predictive hybrid PID control and energy-saving performance analysis of supercritical unit. Energies 2024, 17, 6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Song, Y. Model-predictive control for Markovian jump systems under asynchronous scenario: An optimizing prediction dynamics approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 67, 4900–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Wu, Y.; Wen, Y. Adaptive event-triggered model predictive load frequency control for power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2023, 38, 4003–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzoni, A.; Parisio, A.; Todd, R.; Forsyth, A.J. Optimal virtual power plant management for multiple grid support services. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 1479–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, P.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y. Secondary frequency control considering optimized power support from virtual power plant containing aluminum smelter loads through VSC-HVDC link. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2023, 11, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Lee, K.Y. Two-layer robust distributed predictive control for load frequency control of a power system under wind power fluctuation. Energies 2023, 16, 4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Hu, Z.; Song, Y. A Reinforcement learning based coordinated but differentiated load frequency control method with heterogeneous frequency regulation resources. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 2239–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, G.; Wang, P. H∞ load frequency control of power system integrated with EVs under DoS attacks: Non-fragile output sliding mode control approach. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 4565–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zhang, J.; Yan, H. Adaptive event-triggering H∞ load frequency control for network-based power systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | R | D | M | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area 1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 1.0 | 21.0 | 10 |
| Area 2 | 0.4 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 1.5 | 21.5 | 12 |
| = = 0.1986 | ||||||
| Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Area 1 | 1 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
| Area 2 | 1.2 | 0.15 | 0.06 |
| Performance Criteria | SAE | SSE | STSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| DMPC under DETM in [13] | 1.3671 | 0.1162 | 0.0887 |
| DMPC under DETM (8) | 1.5217 | 0.1184 | 0.1269 |
| CMPC under DETM (8) | 1.4762 | 0.1195 | 0.1295 |
| Method | DMPC | CMPC |
|---|---|---|
| Times (s) | 1.3087 | 2.2116 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, K.; Shi, N.; Cai, S.; Zhang, L.; Shao, X.; Cao, H.; Fei, M.; Zhou, S.; Wan, X. Distributed Model Predictive Load Frequency Control for Virtual Power Plants with Novel Event-Based Low-Delay Technique Under Cloud-Edge-Terminal Framework. Energies 2025, 18, 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061380
Kang K, Shi N, Cai S, Zhang L, Shao X, Cao H, Fei M, Zhou S, Wan X. Distributed Model Predictive Load Frequency Control for Virtual Power Plants with Novel Event-Based Low-Delay Technique Under Cloud-Edge-Terminal Framework. Energies. 2025; 18(6):1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061380
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Kai, Nian Shi, Si Cai, Liang Zhang, Xinan Shao, Haohao Cao, Mingjin Fei, Shisen Zhou, and Xiongbo Wan. 2025. "Distributed Model Predictive Load Frequency Control for Virtual Power Plants with Novel Event-Based Low-Delay Technique Under Cloud-Edge-Terminal Framework" Energies 18, no. 6: 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061380
APA StyleKang, K., Shi, N., Cai, S., Zhang, L., Shao, X., Cao, H., Fei, M., Zhou, S., & Wan, X. (2025). Distributed Model Predictive Load Frequency Control for Virtual Power Plants with Novel Event-Based Low-Delay Technique Under Cloud-Edge-Terminal Framework. Energies, 18(6), 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061380







