A Multi-Agent Closed-Loop Decision-Making Framework for Joint Forecasting and Bidding in Electricity Spot Markets
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Literature Review
1.3. Contributions
2. Materials and Methods
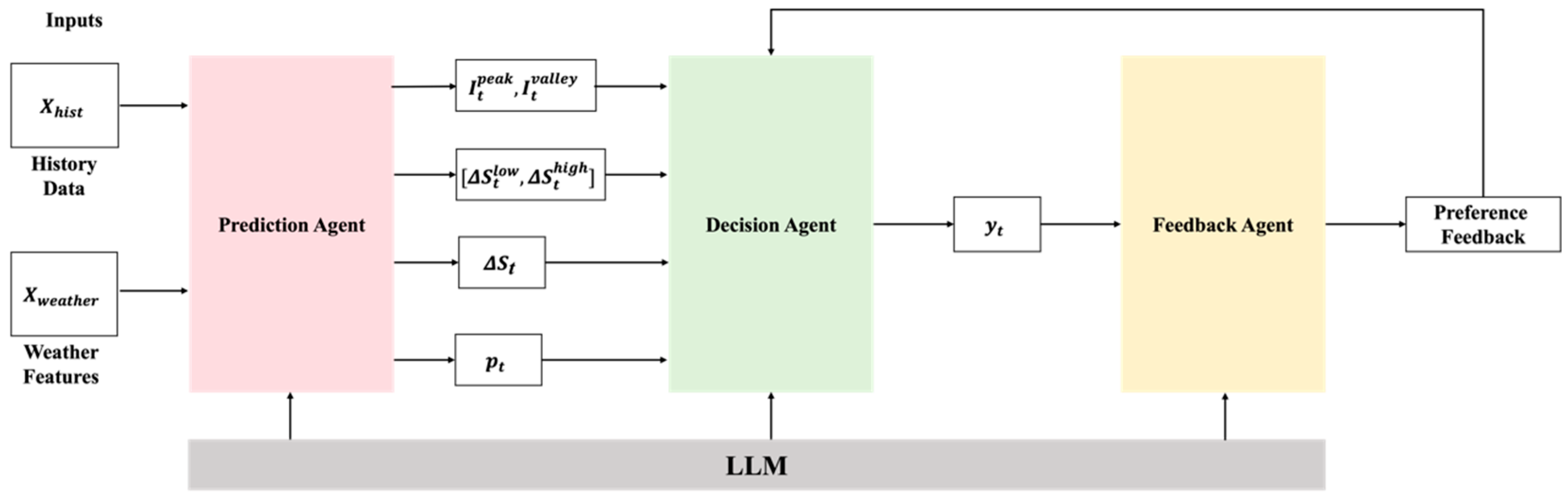
2.1. Technical Framework and Mathematical Modeling
2.1.1. Problem Formulation
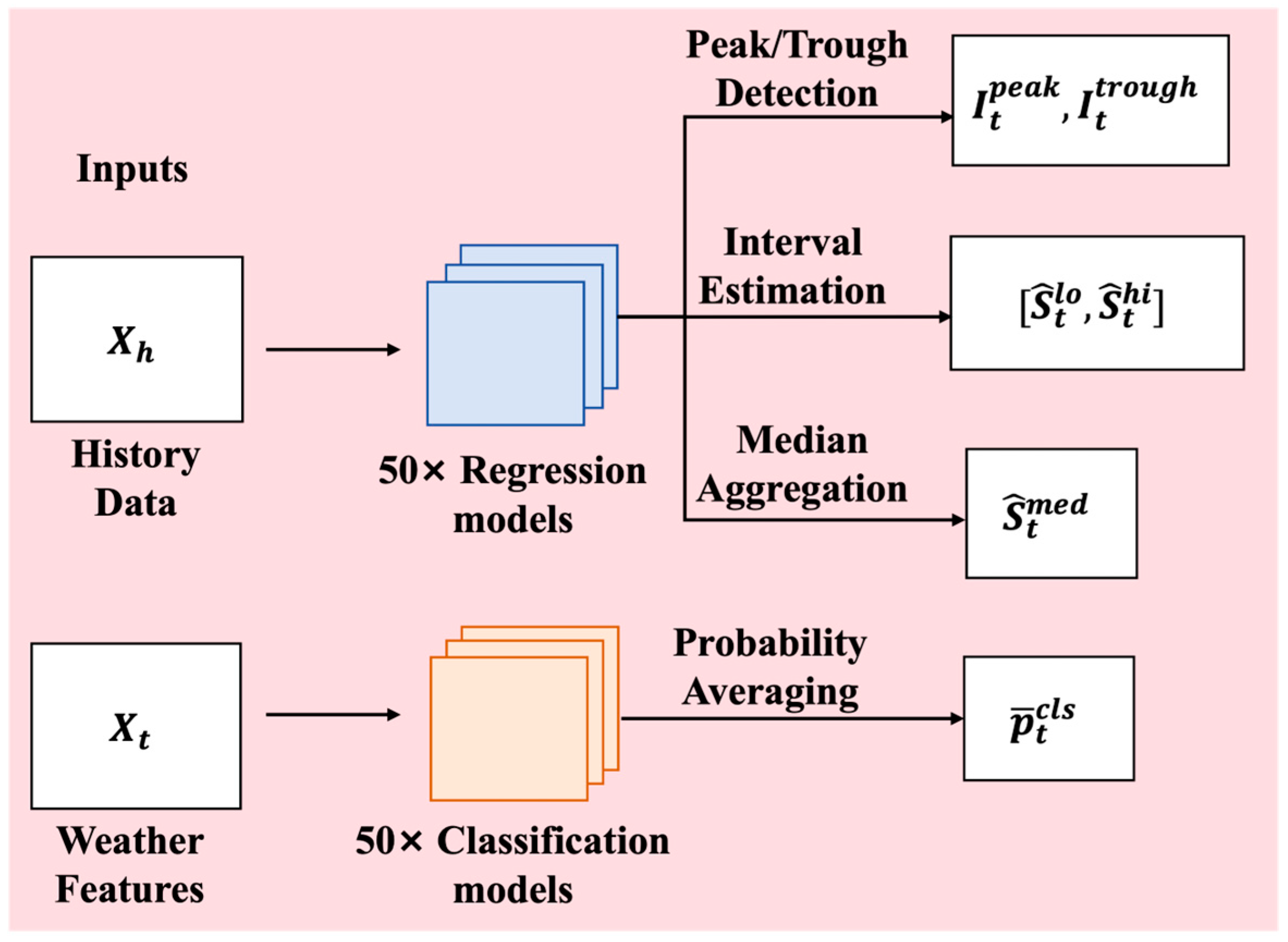
2.1.2. Forecasting Agent
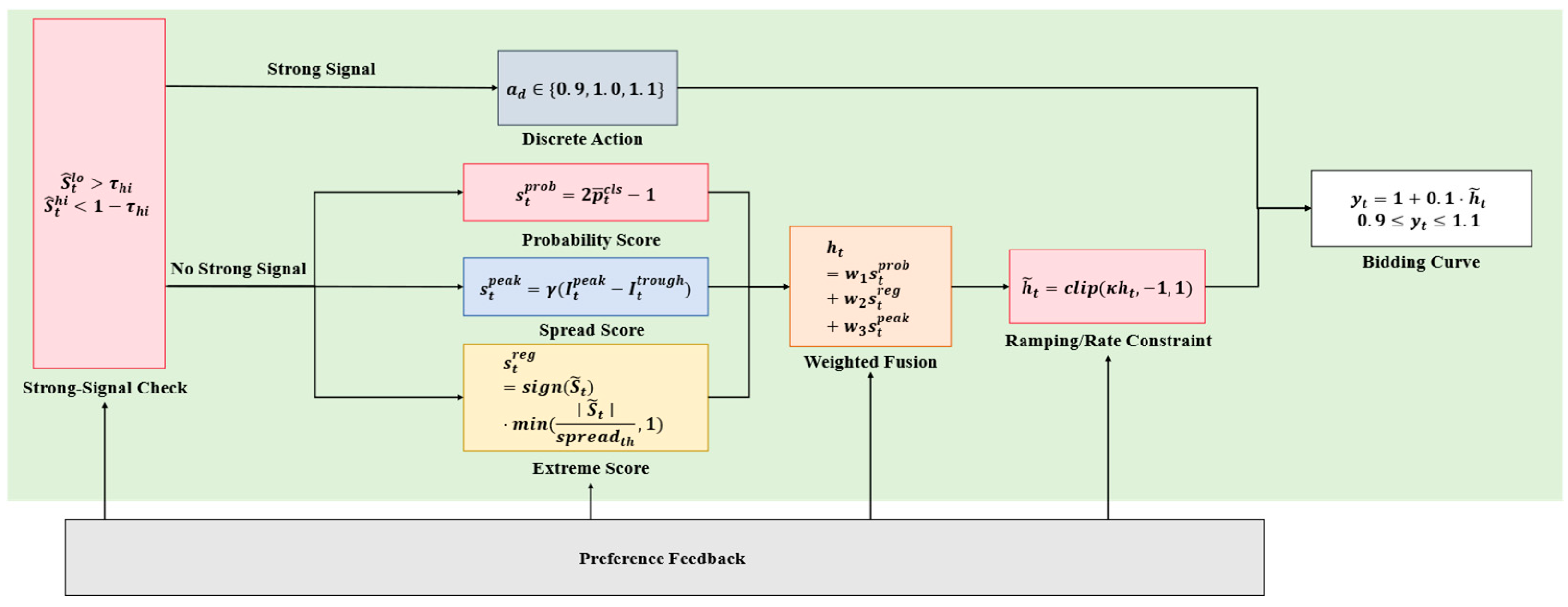
2.1.3. Strategy Agent
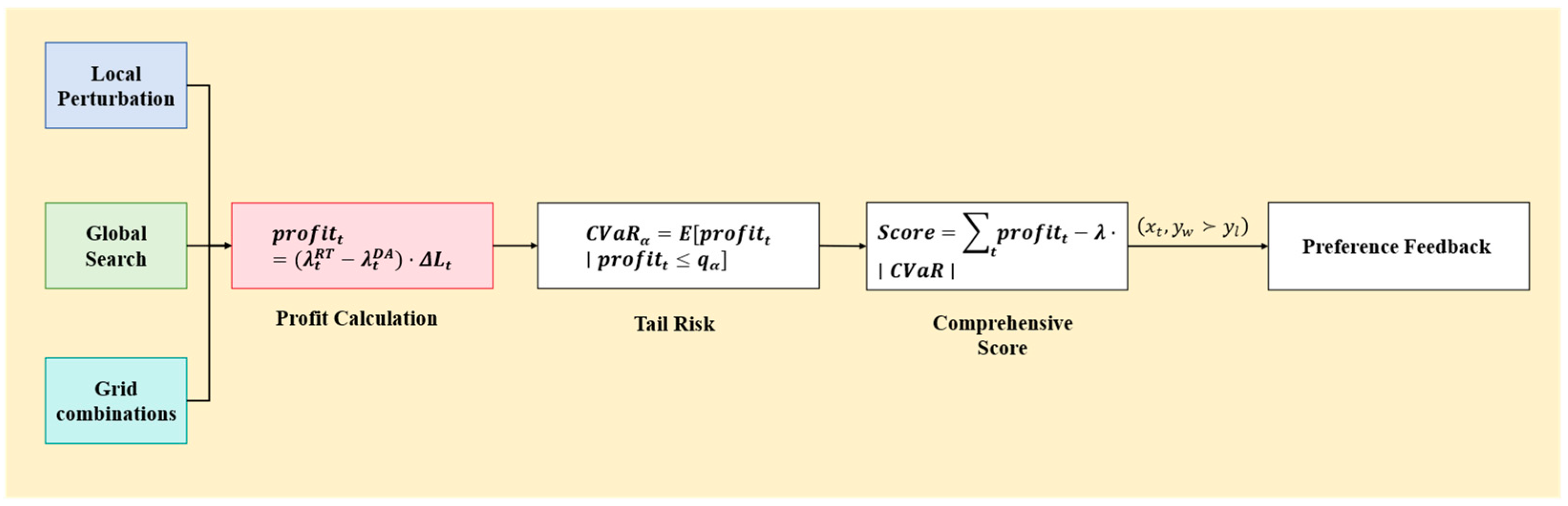
2.1.4. Feedback Agent
2.1.5. Joint Optimization of Forecasting and Strategy
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Data and Experimental Setup
2.2.2. Evaluation Metrics
2.2.3. Comparative Experiments
2.2.4. Ablation Study
3. Results
3.1. Comparative Experiment Results
3.2. Ablation Experiment Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Existing Research
4.2. Limitations
4.3. Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Florini, A. The International Energy Agency in global energy governance. Glob. Policy 2011, 2, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narajewski, M.; Ziel, F. Optimal bidding in hourly and quarter-hourly electricity price auctions: Trading large volumes of power with market impact and transaction costs. Energy Econ. 2022, 110, 105974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conejo, A.J.; Carrión, M.; Morales, J.M. Decision Making Under Uncertainty in Electricity Markets; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Weron, R. Electricity price forecasting: A review of the state-of-the-art with a look into the future. Int. J. Forecast. 2014, 30, 1030–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, T. Forecasting Nord Pool day-ahead prices with an autoregressive model. Energy Policy 2012, 49, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramchurn, S.D.; Vytelingum, P.; Rogers, A.; Jennings, N.R. Putting the ‘smarts’ into the smart grid: A grand challenge for artificial intelligence. Commun. ACM 2012, 55, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wei, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shang, S. Simulating financial market via large language model based agents. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.19966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, C.; Bahloul, M.; Prestwich, S.; Visentin, A. A Review of Electricity Price Forecasting Models in the Day-Ahead, Intra-Day, and Balancing Markets. Energies 2025, 18, 3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yin, Z.; Guo, X.; Ren, X. Day ahead electricity price forecasting based on the deep belief network. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 3960597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcjasz, G.; Narajewski, M.; Weron, R.; Ziel, F. Distributional neural networks for electricity price forecasting. Energy Econ. 2023, 125, 106843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.H.D.M.; Stefenon, S.F.; de Lima, J.D.; Nied, A.; Mariani, V.C.; Coelho, L.d.S. Electricity Price Forecasting Based on Self-Adaptive Decomposition and Heterogeneous Ensemble Learning. Energies 2020, 13, 5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y. A Stackelberg game-based approach to load aggregator bidding strategies in electricity spot markets. J. Energy Storage 2024, 95, 112509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhu, L.; Wang, B.; Fu, R.; Qi, L.; Jiang, X.; Sun, C. A Master–Slave Game-Based Strategy for Trading and Allocation of Virtual Power Plants in the Electricity Spot Market. Energies 2025, 18, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tian, C.; Li, Z.; Yin, S.; Xie, A.; Wang, P.; Ding, Y. The Impact of Participation Ratio and Bidding Strategies on New Energy’s Involvement in Electricity Spot Market Trading under Marketization Trends—An Empirical Analysis Based on Henan Province, China. Energies 2024, 17, 4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Liu, B.; Li, J. A Trading Model for the Electricity Spot Market That Takes into Account the Preference for Energy Storage Trading. Energies 2025, 18, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renshaw-Whitman, C.; Zobernig, V.; Cremer, J.L.; de Vries, L. Non-stationarity in multiagent reinforcement learning in electricity market simulation. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 235, 110712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Q.; Wang, B. A Bidding Strategy for Power Suppliers Based on Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning in Carbon–Electricity–Coal Coupling Market. Energies 2025, 18, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Yuan, W.; Li, L. MRL-Based Model for Diverse Bidding Decision-Makings of Power Retail Company in the Wholesale Electricity Market of China. Axioms 2023, 12, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowotarski, J.; Weron, R. Recent advances in electricity price forecasting: A review of probabilistic forecasting. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1548–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, K.; Li, X. Online Preference Alignment for Language Models via Count-based Exploration. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.12735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q. LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G. Box and Jenkins: Time Series Analysis, Forecasting and Control. In A Very British Affair: Six Britons and the Development of Time Series Analysis During the 20th Century; Palgrave Macmillan UK: London, UK, 2013; pp. 161–215. [Google Scholar]
| Method | Monthly Profit (×104 CNY) | SWA | Precision | Recall | AA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XGBoost | 140,801.04 | 57.36% | 50.88% | 62.95% | 58.27% |
| LightGBM | 105,464.19 | 54.60% | 49.18% | 51.73% | 55.02% |
| prophet | 8669.411 | 55.04% | 48.48% | 89.16% | 62.11% |
| ARIMA | −18,500.30 | 49.21% | 45.10% | 42.32% | 51.40% |
| Prediction Agent | 146,933.46 | 57.36% | 53.25% | 40.45% | 56.05% |
| Method | Monthly Profit (×104 CNY) |
|---|---|
| Joint | 157,746.64 |
| Joint-noCI | 149,763.89 |
| Joint-noPV | 123,559.44 |
| Joint-noCM | 146,616.57 |
| Joint-noFO | 146,933.46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Deng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, Z.; Guo, N.; Yu, J.; Wang, B.; Liao, M. A Multi-Agent Closed-Loop Decision-Making Framework for Joint Forecasting and Bidding in Electricity Spot Markets. Energies 2025, 18, 6486. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18246486
Zhang S, Deng W, Zhang Y, Jing Z, Guo N, Yu J, Wang B, Liao M. A Multi-Agent Closed-Loop Decision-Making Framework for Joint Forecasting and Bidding in Electricity Spot Markets. Energies. 2025; 18(24):6486. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18246486
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shicheng, Wangli Deng, Yuqin Zhang, Zhijun Jing, Ning Guo, Jianyu Yu, Bo Wang, and Mei Liao. 2025. "A Multi-Agent Closed-Loop Decision-Making Framework for Joint Forecasting and Bidding in Electricity Spot Markets" Energies 18, no. 24: 6486. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18246486
APA StyleZhang, S., Deng, W., Zhang, Y., Jing, Z., Guo, N., Yu, J., Wang, B., & Liao, M. (2025). A Multi-Agent Closed-Loop Decision-Making Framework for Joint Forecasting and Bidding in Electricity Spot Markets. Energies, 18(24), 6486. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18246486






