Fault Detection and Classification of Power Lines Based on Bayes–LSTM–Attention
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
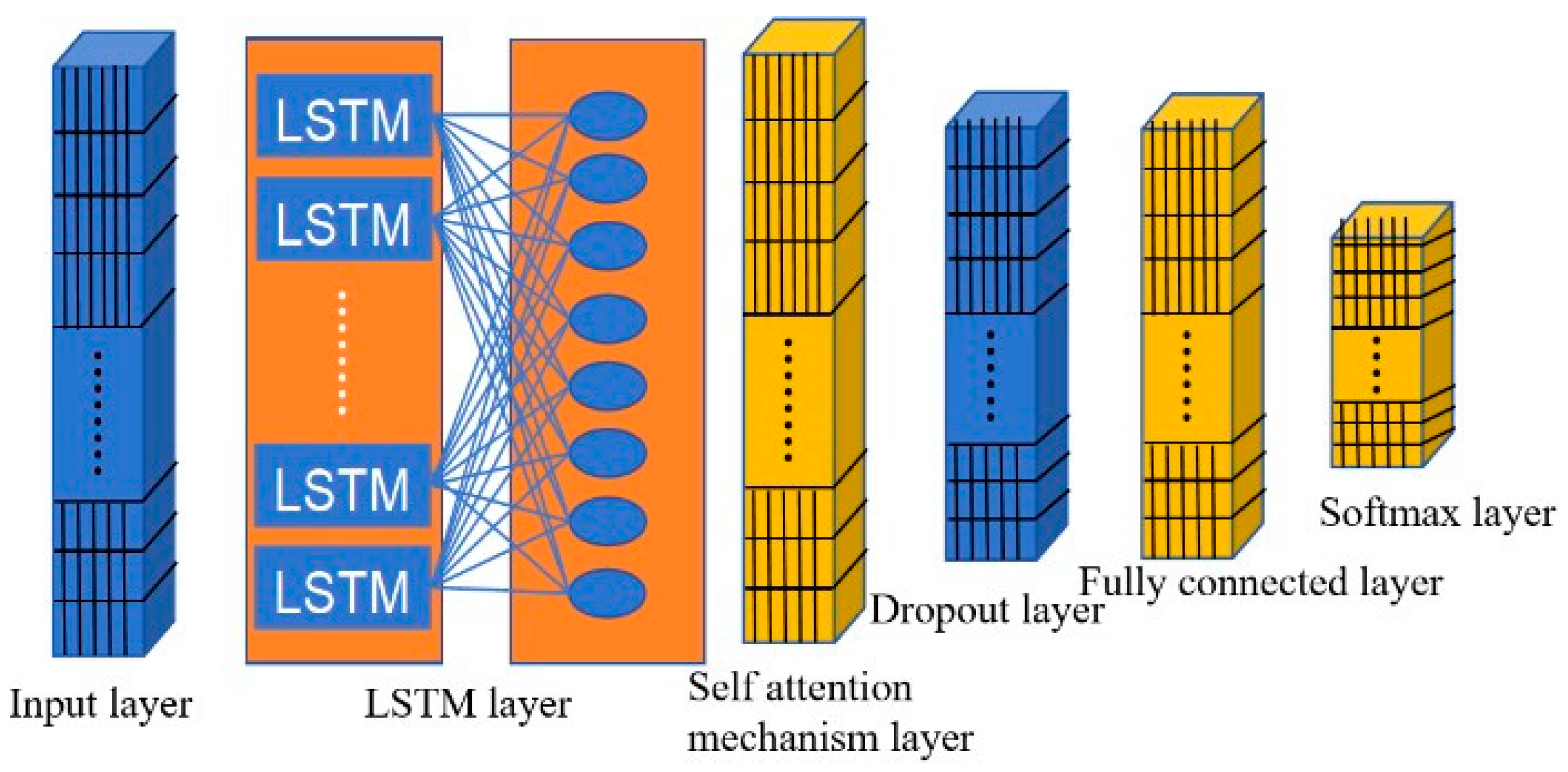
2.1. Bayes–LSTM–Attention-Based Model for Line Fault Classification
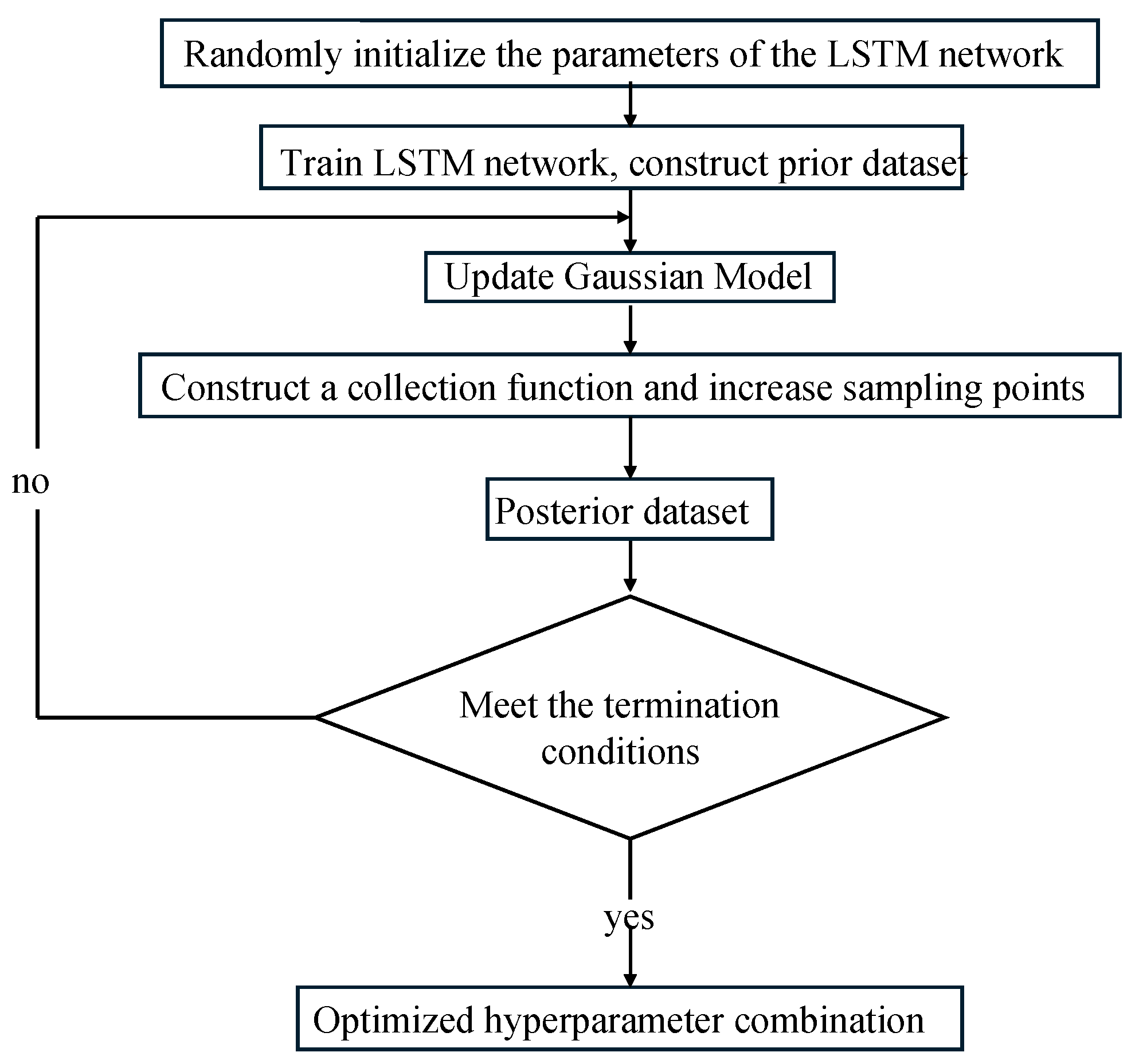
2.1.1. Bayesian Optimization
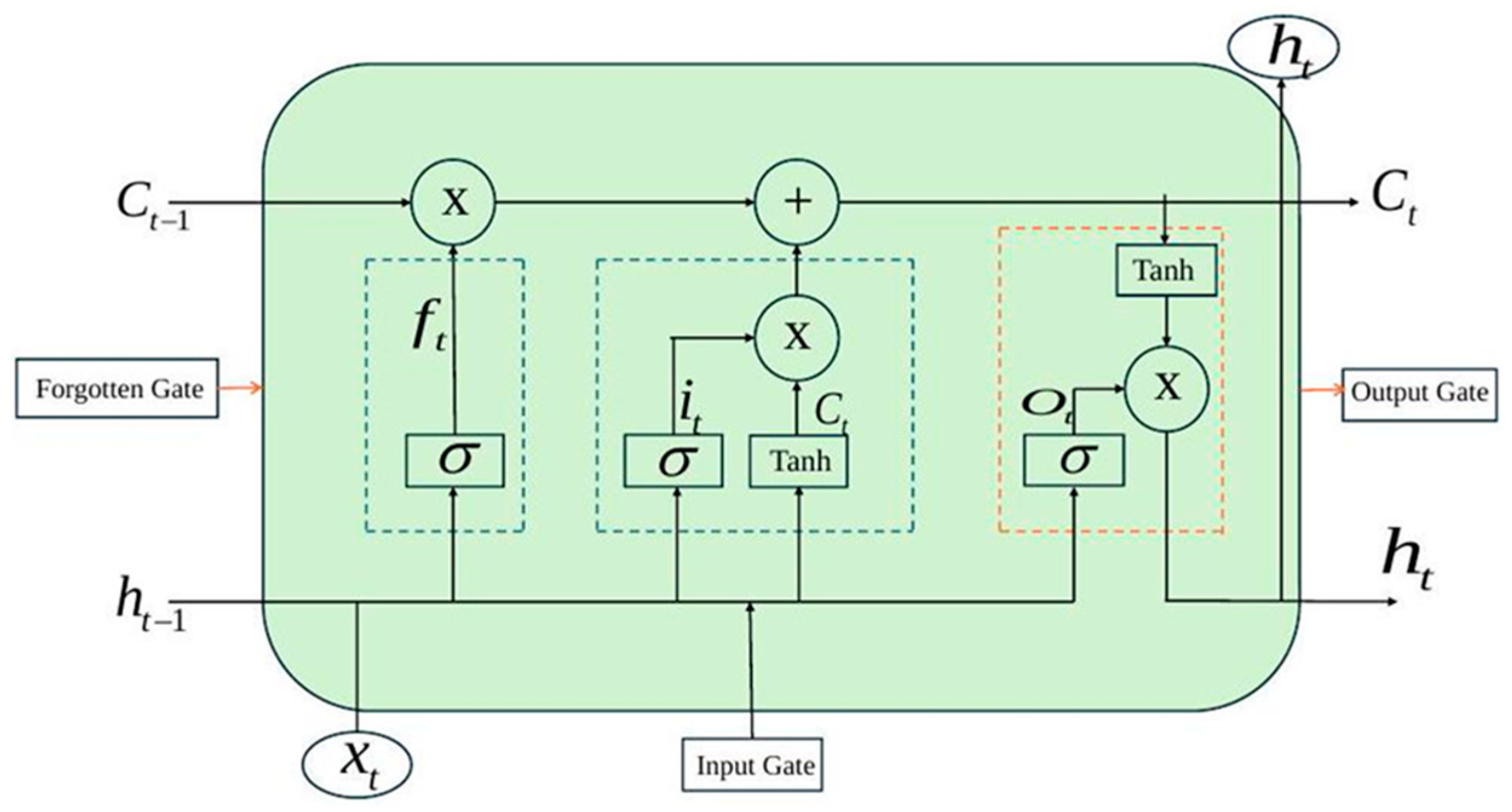
2.1.2. Long Short-Term Memory
2.1.3. Self-Attention Mechanism
- (1)
- Linear Transformation
- (2)
- Calculate Attention Weights
- (3)
- Calculate Weighted Value Vectors
2.1.4. Classification Evaluation Metrics
2.2. Fault Classification Process
3. Results
3.1. Input Data and Parameter Settings
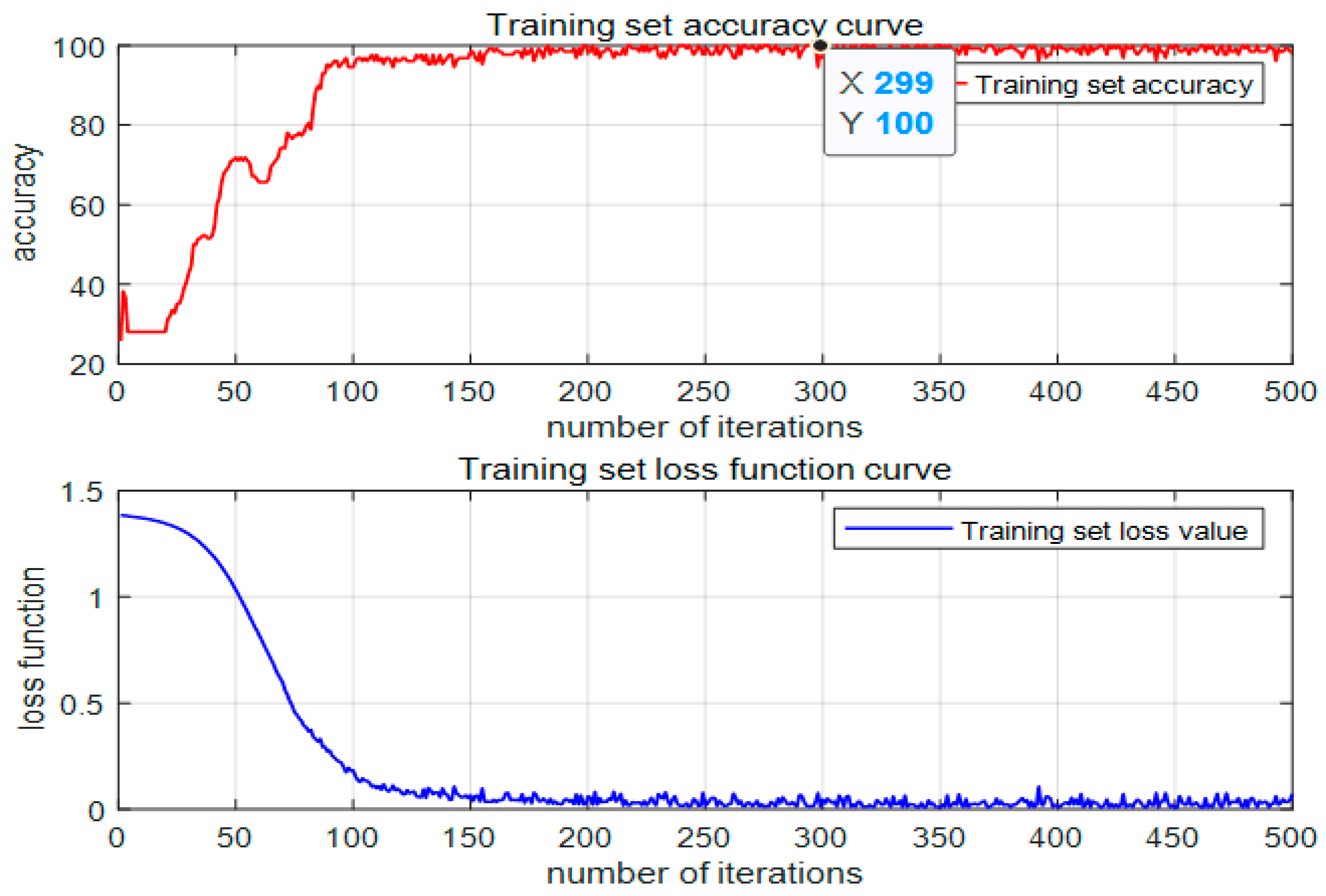
3.2. Classification Result Analysis
4. Discussion
- (1)
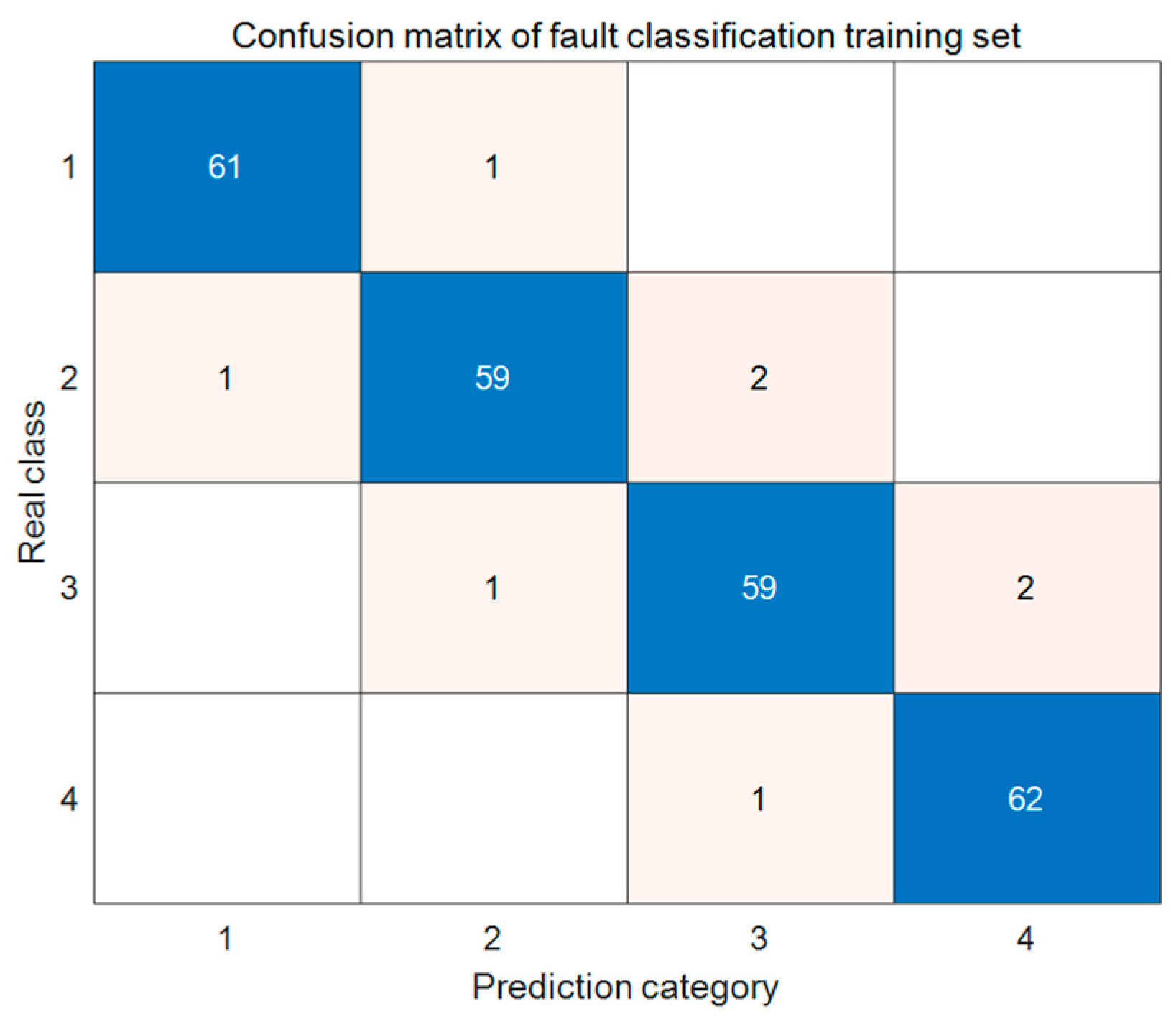
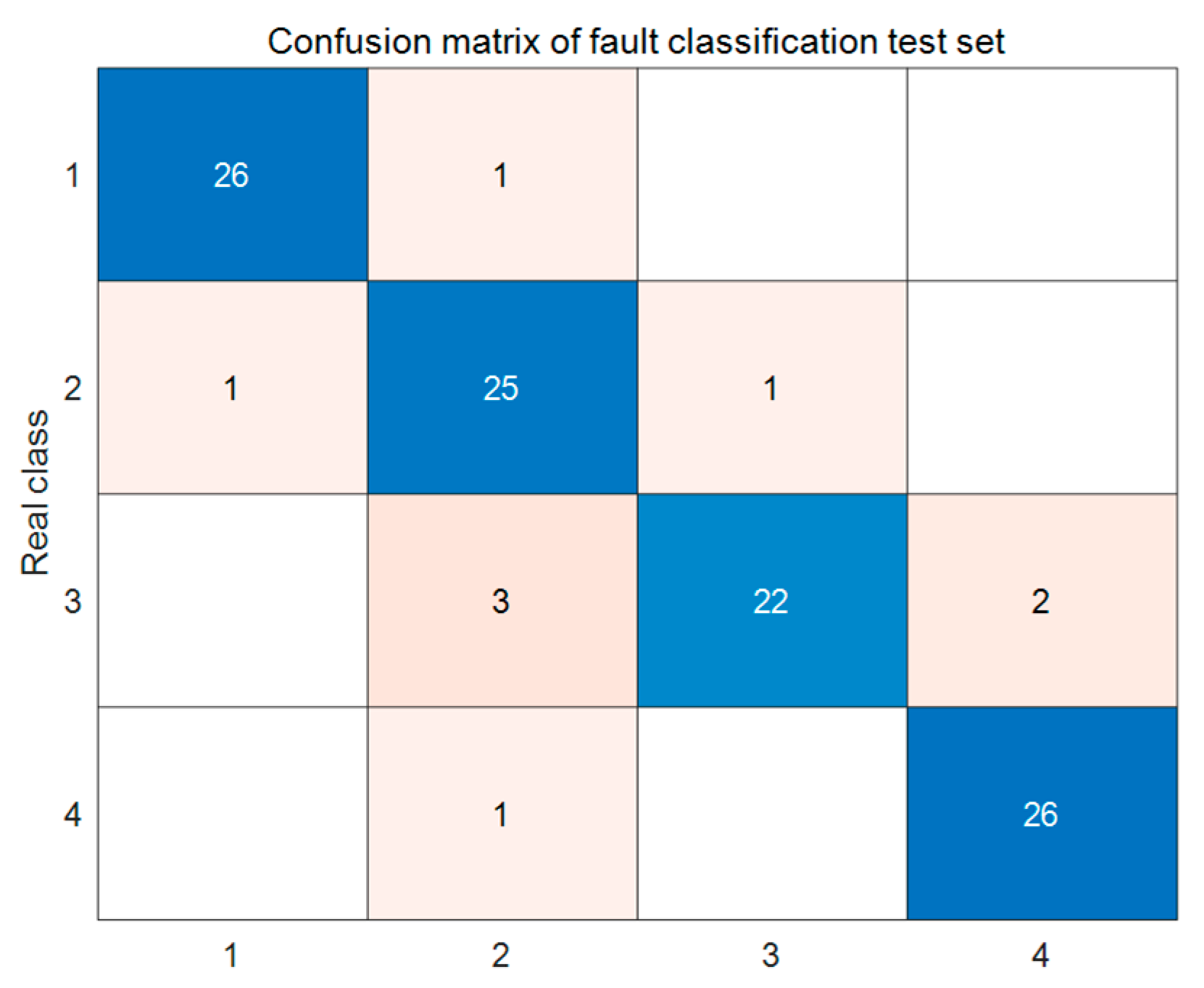
- By learning 12 distinct features of fault samples through the LSTM network, the proposed Bayes–LSTM–Attention model demonstrates superior accuracy in fault classification, with a prediction accuracy of 95.3% on the test set, demonstrating high classification precision and overall effectiveness.
- (2)
- A comparison of the true and predicted values for both the training and test sets reveals similar accuracy, indicating that the model exhibits strong generalization ability for various line fault types. Additionally, evaluation metrics generated using the polygon area method demonstrate the model’s high precision and stability in fault classification for transmission lines.
- (3)
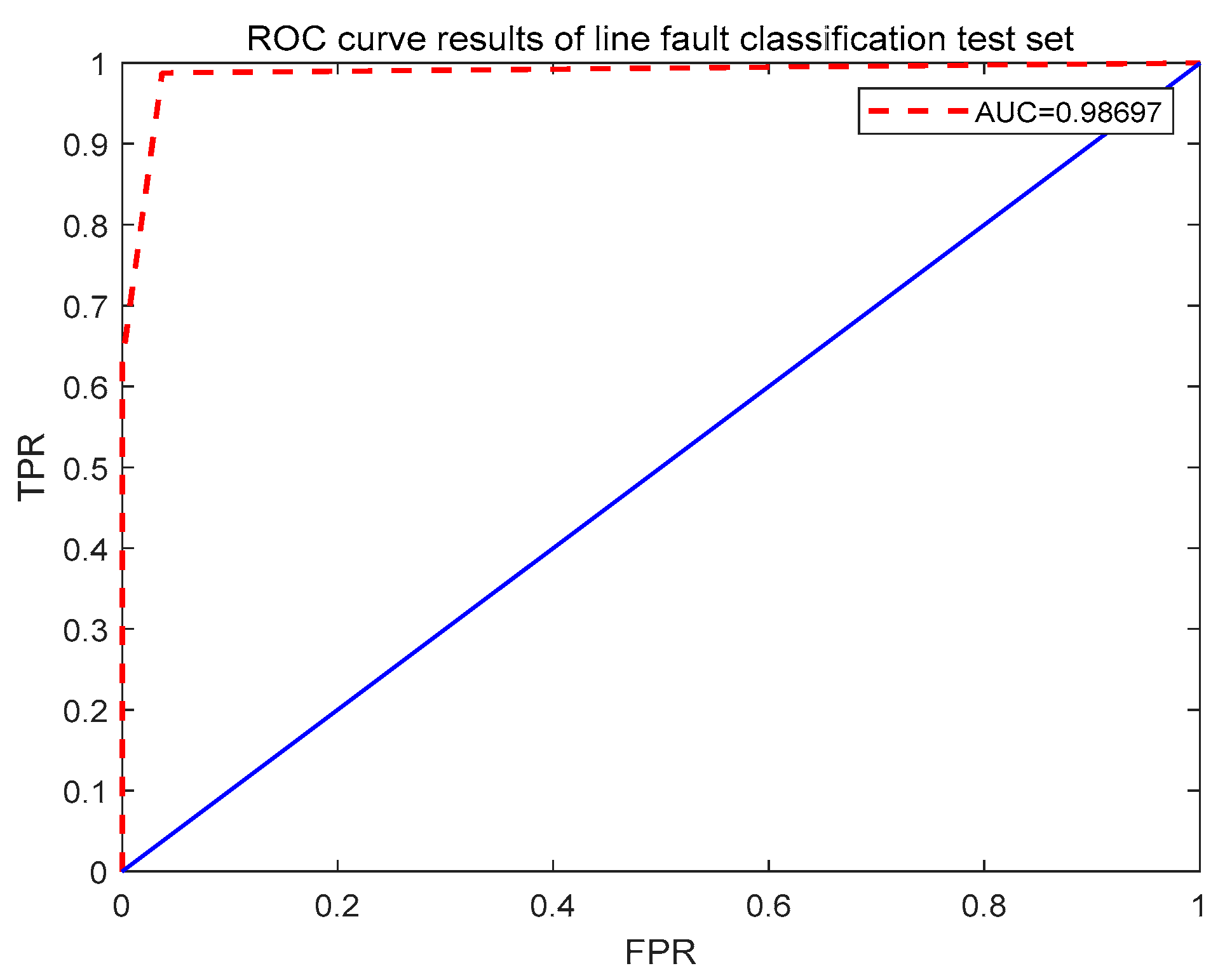
- By introducing the self-attention mechanism, the model is able to adaptively focus on the key information in the fault sequence, enhancing its ability to global dependencies. Combined with the analysis results of the Polygon Area Metric (PAM) and the ROC curve, the model exhibits high classification stability and robustness different thresholds, and can effectively respond to the complex and changeable fault scenarios in power systems, providing reliable technical support for practical applications.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, Z.R.; Niu, S.S.; Jin, N. Current situation and development trend of parameter measurement of AC lines. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2017, 41, 181–191. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, B.H.; Fan, X.K. A rapid protection scheme for overhead lines in flexible DC power grid. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2016, 40, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Luo, G.; He, Z. A fault classification method for high-voltage transmission lines based on wavelet entropy and support vector machine. Power Grid Technol. 2007, 23, 22–26+32. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Cao, W.; Wang, D.; Ding, M. A fault diagnosis method for transmission lines on multi-supportvect or machine models. High Volt. Technol. 2020, 46, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W. Research on Fault Classification and Fault lo Cation of MMC-HVDC Direct Current Line Based on VWAA-SVM. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University of Technology, Lanzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R. Fault Feature Extraction and Diagnosis of Transmission Line Based on Improved HHO Optimization VMD-SVM model. Master’s Thesis, Lia University of Technology, Fuxin, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J. Prediction Method for Ice Accretion and Galloping of Transmission Lines Based on FEM and Improved PSO-SVM Algorithm. Master’s Thesis, Three Gorges University, Yichang, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Gao, C.; Song, M.; Ming, H. Power line fault detection classification system based on HHO-SVM. Integr. Smart Energy 2023, 45, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H.; Song, J.; Liu, Y.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Song, L. A prediction mode l of transmission line icing galloping based on O-SVM algorithm. J. Vib. Shock 2023, 42, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ning, X.; Yin, C. Research on fault diagnosis of power lines on SVM-RF. Shandong Electr. Power Technol. 2022, 49, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J. Fault Diagnosis and Location of Active Distribution Networks Based on SVM. Master’s Thesis, North China Electric Power University, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.; Mishra, D.P.; Dey, K.; Mishra, P. Fault Detection and Classification of a Transmission Line Using Discrete Wavelet Transform & Artificial Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Information Technology (ICIT), Bhubaneswar, India, 27–29 December 2017; pp. 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.K.; Rao, H.; Xu, S.; Huang, R.; Wen, J. Fault detection method for overhead flexible DC grid based on artificial neural. Proc. Chin. Soc. Electr. Eng. 2019, 39, 4416–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Mishra, A.; Singhal, A.; Dahiya, V.; Gupta, M.; Gawre, S.K. Fault Detection in Transmission Line Using ANN. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Students’ Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Science (SCEECS), Bhopal, India, 18–19 February 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leh, N.A.M.; Zain, F.M.; Muhammad, Z.; Hamid, S.A.; Rosli, A.D. Fault Detection Method Using ANN for Power Transmission Line. In Proceedings of the 2020 10th IEEE International Conference on Control System, Computing and Engineering (ICCS CE), Penang, Malaysia, 21–22 August 2020; pp. 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Lu, X.; Sun, H.; Ye, Q. Research on fault location of power lines on signal analysis technol ogy and artificial intelligence algorithm. Energy Environ. Prot. 2022, 44, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, L.; Li, Y.; Li, B. A Double-ended Transmission Line Non-synchronous Fault Location Algorithm Based on Artifi cial Neural Network and Migration. Power Grid Technol. 2023, 47, 5169–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Qin, L.; Liu, D. A Comprehensive Fault Identification Method for Transmission Lines Base d on GMAPM and SOM-LVQ-ANN. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. (Eng. Ed.) 2019, 52, 1079–1090+1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Xu, D. A method for fault location of transmission lines based on neural network. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2004, 2, 50–53+83. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J. Research on a New Method of Fault Location in Transmission Lines Based on Artificial Neural Networks. Master’s Thesis, Sich University, Chengdu, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, H.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Sun, S.; Liu, K. single-ended traveling wave fault location method based on neural network. Proc. Chin. Soc. Electr. Eng. 2011, 31, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, M.M.; Sharma, M.; Ganguly, A. Detection and Classification of Transmission Line Faults using LSTM Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Industrial Electronics: Developments & Applications (ICIDeA), Imphal, India, 29–30 September 2023; pp. 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajashekar, J.; Yadav, A. Transmission lines Fault Detection and Classification Using Deep Learning Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 Second International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Computing, Communication and Sustainable Technologies (ICAECT), Bhilai, India, 21–22 April 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Jia, H.; Yang, Z.; Geng, W.; Wang, J. Research on fault diagnosis method of transmission line on CNN-LSTM. Power Grid Clean Energy 2023, 39, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Wu, H.; Chen, W. A method for identifying fault lines in AC and DC power grids based CNN-LS TM networks. J. Sichuan Univ. Sci. Eng. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 37, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y. Research on Guided Search of High-Voltage Line Cascading Failure Based on GCN-LSTM. Master’s Thesis, North China Electric Power University, Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Chen, S.; Bi, G.; Deng, X.; Niu, Y.; Yao, H. Research on fault location of UHV line based on hybrid LSTM deep learning. Electr. Power Sci. Eng. 2023, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, F. Research on intelligent diagnosis method of line fault based on LSTM. Large Mot. Technol. 2023, S2, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Chen, S.; Bi, G.; Gao, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, L. Fault diagnosis of weak receiving-end DC transmission system on par. Electr. Mach. Control Appl. 2022, 6, 49. [Google Scholar]



| Predicted as Positive Class | Predicted as Negative Class | |
|---|---|---|
| Actually classified as positive | True Positive (TP) | False Negative (FN) |
| Actually classified as negative | False Positive (FP) | True Negative (TN) |
| Fault Category | Number of Training Samples | Number of Testing Samples | Total Number of Samples | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | 62 | 27 | 89 | 24.93% |
| Type 2 | 62 | 27 | 89 | 24.93% |
| Type 3 | 62 | 27 | 89 | 24.93% |
| Type 4 | 63 | 27 | 90 | 25.21% |
| Total | 249 | 108 | 357 | 100% |
| Sample Category | Prediction Correct | Forecast Error | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | 239 | 10 | 95.9% |
| Test set | 103 | 5 | 95.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.; Li, H.; Zeng, W.; Fan, J.; Ren, Z. Fault Detection and Classification of Power Lines Based on Bayes–LSTM–Attention. Energies 2025, 18, 6483. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18246483
Yang C, Li H, Zeng W, Fan J, Ren Z. Fault Detection and Classification of Power Lines Based on Bayes–LSTM–Attention. Energies. 2025; 18(24):6483. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18246483
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Chen, Hao Li, Wenhui Zeng, Jiayuan Fan, and Zhichao Ren. 2025. "Fault Detection and Classification of Power Lines Based on Bayes–LSTM–Attention" Energies 18, no. 24: 6483. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18246483
APA StyleYang, C., Li, H., Zeng, W., Fan, J., & Ren, Z. (2025). Fault Detection and Classification of Power Lines Based on Bayes–LSTM–Attention. Energies, 18(24), 6483. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18246483





