Optimal Power Flow-Assisted Unit Commitment with Multi-Level Load Variation Analysis in Renewable-Based Power Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. System Model
3. Problem Mathematical Modeling
3.1. Unit Commitment Formulation (MINLP)
- Objective Function of Unit Commitment
- a.
- Fuel Cost Function of Thermal Generators
- b.
- Startup Cost Model of Thermal Generators
- c.
- Shutdown Cost Model of Thermal Generators
- d.
- Operational Cost Model of PHS
- 2.
- Unit Commitment Constraint Model
- a.
- Power Balance Constraint Model
- b.
- Thermal Generator Power Output Constraint
- c.
- Thermal Generator Minimum Up-Time Constraint
- d.
- Thermal Generator Minimum Down-Time Constraint
- e.
- PHS Capacity Constraint Model
3.2. Power Flow Constraint
- a.
- Power Balance Constraints
- b.
- Bus Voltage Limits
- c.
- Generator Reactive Power Limits
4. Integrated MINLP–PSO Framework for Unit Commitment and Optimal Power Flow
4.1. MINLP Optimization with SCIP
4.2. PSO-Assisted Optimal Power Flow Under UC Constraints
4.3. Integrated MINLP–PSO Optimization Flow
4.4. SCIP and PSO Parameters Setting
5. Results
5.1. UC with Load Flow Scheduling Results
5.2. OPF Dispatch Results
5.3. Voltage Profile
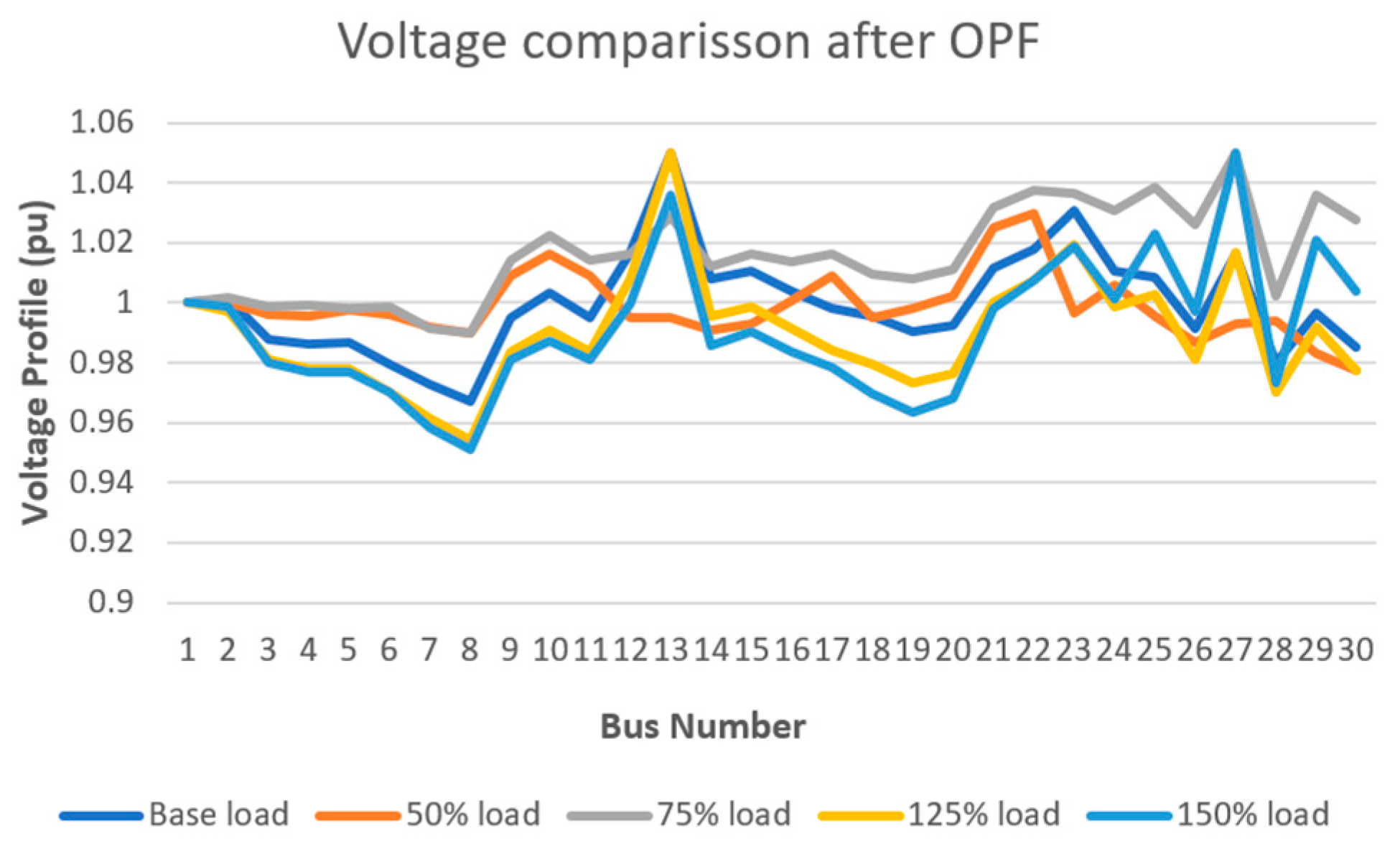
5.4. Multi-Scenario Analysis
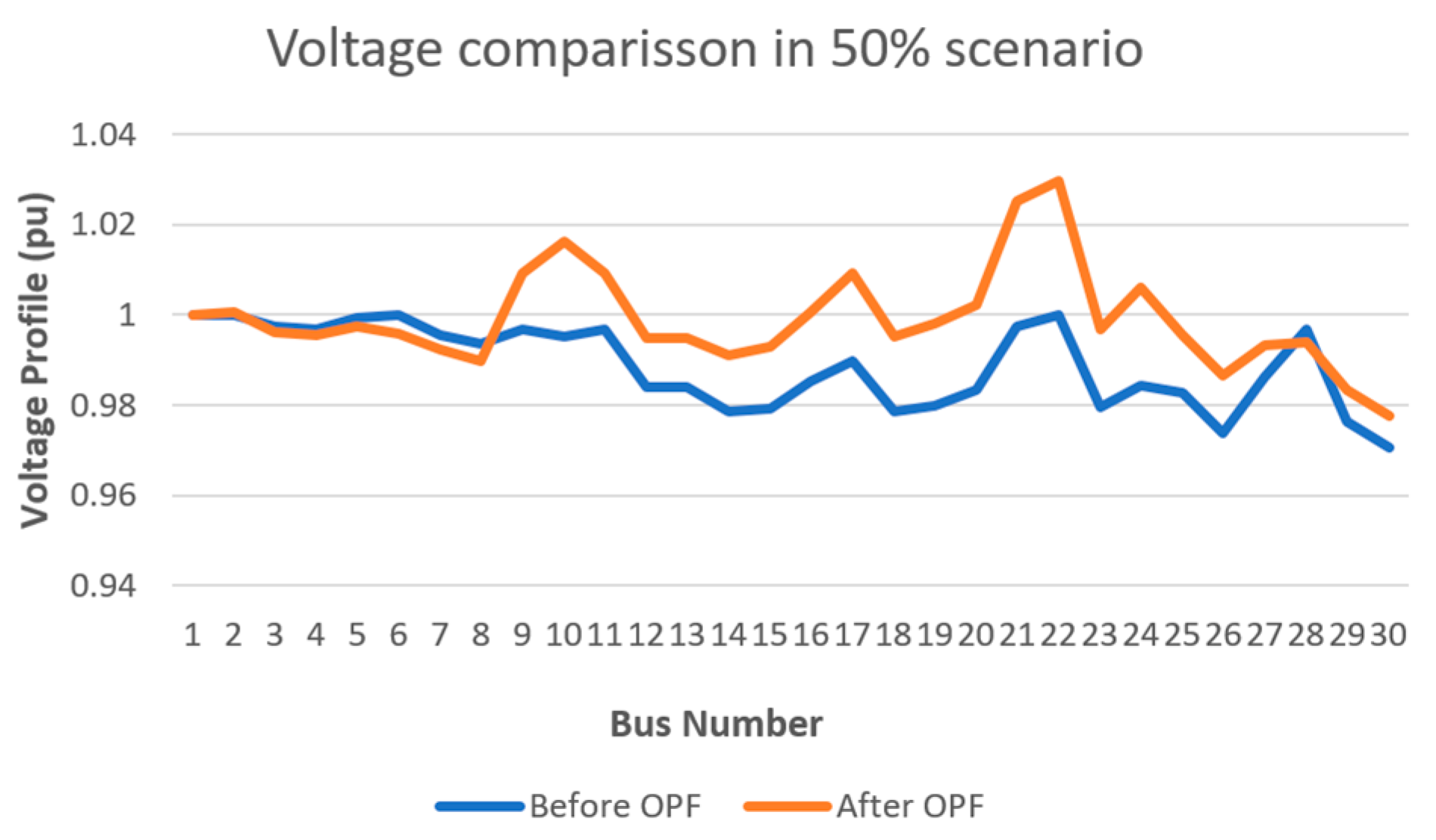
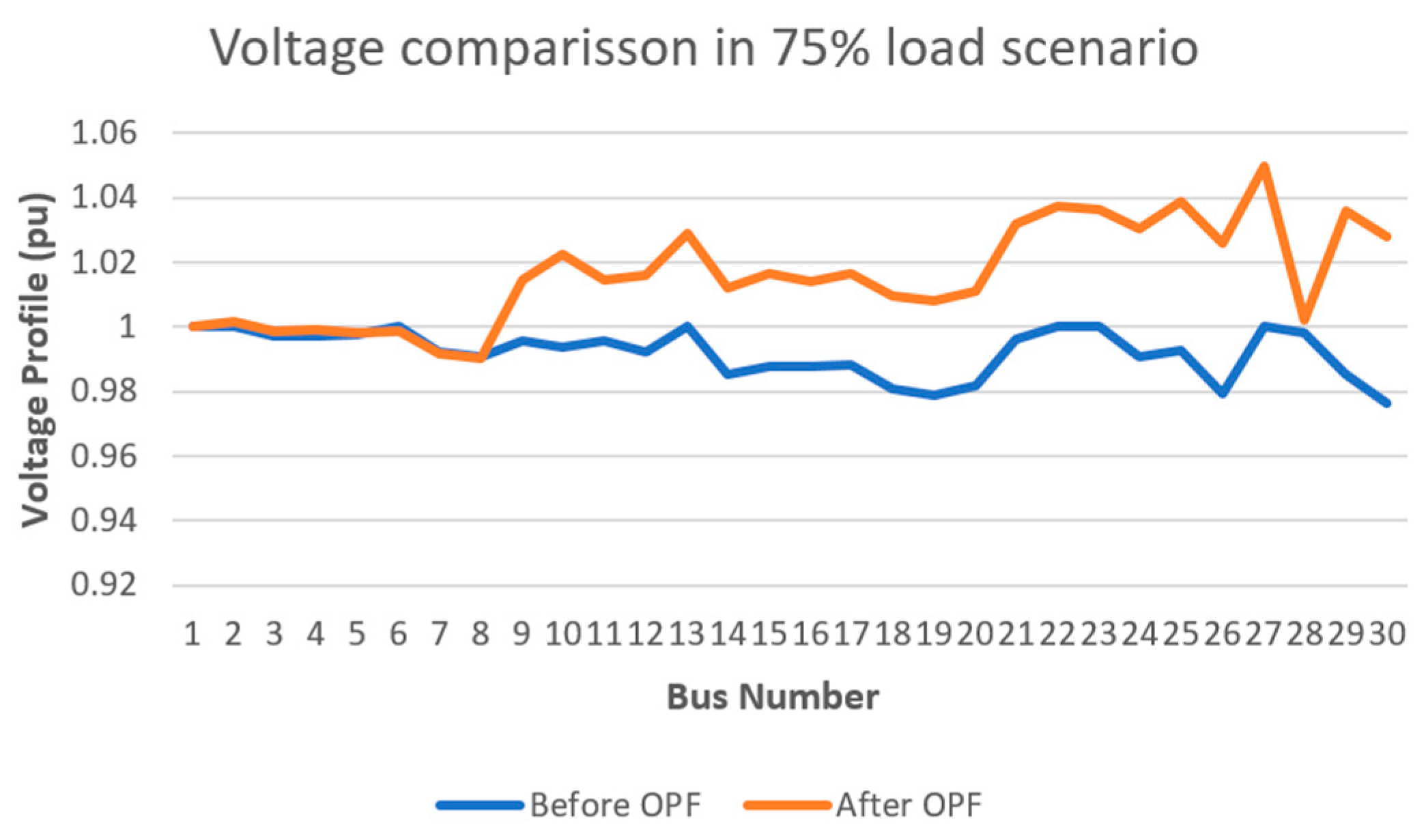
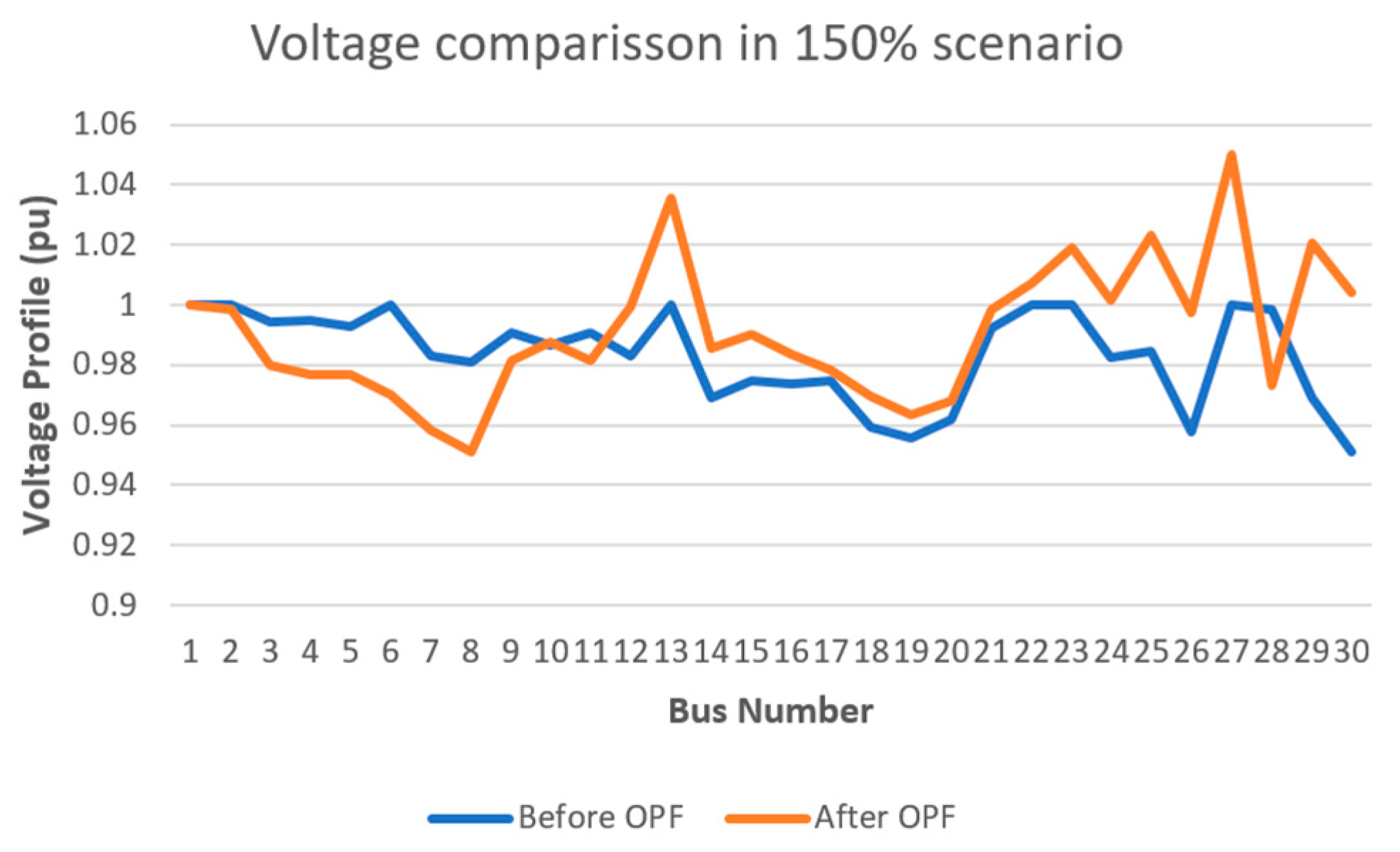
- Voltage Comparison Before and After OPF
- b.
- Power Loss Comparison
- c.
- PHS impact on power system price
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elomari, Y.; Norouzi, M.; Marín-Genescà, M.; Fernández, A.; Boer, D. Integration of Solar Photovoltaic Systems into Power Networks: A Scientific Evolution Analysis. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwaigwe, K.N.; Mutabilwa, P.; Dintwa, E. An overview of solar power (PV systems) integration into electricity grids. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2019, 2, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.I.; Go, Y.I. Power management scheme development for large-scale solar grid integration. J. Electr. Syst. Inf. Technol. 2023, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeyi, M.J.B.; Olanrewaju, O.A. Sustainable Energy Transition for Renewable and Low Carbon Grid Electricity Generation and Supply. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 9, 743114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.I.; Chen, L.; Yang, M.; Msigwa, G.; Farghali, M.; Fawzy, S.; Rooney, D.W.; Yap, P.-S. Cost, environmental impact, and resilience of renewable energy under a changing climate: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 741–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada, M.; Popoola, P. Recent advances in solar photovoltaic materials and systems for energy storage applications: A review. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2023, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NREL. Best Research-Cell Efficiency Chart. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cell-efficiency (accessed on 17 November 2025).
- Parthiban, R.; Ponnambalam, P. An Enhancement of the Solar Panel Efficiency: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 937155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, X.-P.; Sterling, M. Solar power generation intermittency and aggregation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leo, P.; Ciocia, A.; Malgaroli, G.; Spertino, F. Advancements and Challenges in Photovoltaic Power Forecasting: A Comprehensive Review. Energies 2025, 18, 2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesseh, P.K.; Chen, J.; Lin, B. Electricity price modeling from the perspective of start-up costs: Incorporating renewable resources in non-convex markets. Front. Sustain. Energy Policy 2023, 2, 1204650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harker Steele, A.J.; Burnett, J.W.; Bergstrom, J.C. The impact of variable renewable energy resources on power system reliability. Energy Policy 2021, 151, 111947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.B.; Kazmi, S.A.A.; Khan, Z.A.; Altamimi, A.; Alghassab, M.A.; Alojaiman, B. Voltage Profile Improvement by Integrating Renewable Resources with Utility Grid. Energies 2022, 15, 8561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, H.; Won, D. Operation Strategy of Shared ESS Based on Power Sensitivity Analysis to Minimize PV Curtailment and Maximize Profit. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 197097–197110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, M.; Giraldez, J.; Gotseff, P.; Hoke, A. Estimation of solar photovoltaic energy curtailment due to volt–watt control. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2020, 14, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Son, B.; Kim, S.H. Operation Planing and Capacity Calculation of Energy Storage Systems Considering Curtailment of Renewable Energy. J. Korean Sol. Energy Soc. 2023, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyinka, A.M.; Esan, O.C.; Ijaola, A.O.; Farayibi, P.K. Advancements in hybrid energy storage systems for enhancing renewable energy-to-grid integration. Sustain. Energy Res. 2024, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalović, Z.; Haas, R.; Ajanović, A.; Sayer, M. Prospects of electricity storage. Renew. Energy Environ. Sustain. 2023, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Knueven, B.; Watson, J.-P. Modeling flexible generator operating regions via chance-constrained stochastic unit commitment. Comput. Manag. Sci. 2020, 17, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiyullah, S.F.S.; Bharathidasan, S.G. Profit Based Unit Commitment of Thermal Units with Renewable Energy and Electric Vehicles in Power Market. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2021, 16, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuijts, R.H.; van den Akker, M.; van den Broek, M. Effect of modelling choices in the unit commitment problem. Energy Syst. 2024, 15, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yin, H.; Wang, P.; Gu, C.; Wang, K.; Hu, Y. A fast linearized AC power flow-constrained robust unit commitment approach with customized redundant constraint identification method. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1218461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H. A Unit Commitment Model Considering Feasibility of Operating Reserves under Stochastic Optimization Framework. Energies 2022, 15, 6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncer, D.; Kocuk, B. An MISOCP-Based Decomposition Approach for the Unit Commitment Problem with AC Power Flows. In IEEE Transactions on Power Systems; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Bui, V.-H.; Su, W.; Wang, B. Surrogate Modeling for Solving OPF: A Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risi, B.-G.; Riganti-Fulginei, F.; Laudani, A. Modern Techniques for the Optimal Power Flow Problem: State of the Art. Energies 2022, 15, 6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabo, A.; Ibrahim Kanya, K.; Shu’aibu, N.; Onyema, C.; Aliyu, A.; Tanko, H.; Kwasau, S. A Review of State-of-the-Art Techniques for Power Flow Analysis. J. Sci. Technol. Eng. Res. 2023, 4, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, L.; Bello, A.; Reneses, J. A Review on the Unit Commitment Problem: Approaches, Techniques, and Resolution Methods. Energies 2022, 15, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacci, T.; Frangioni, A.; Gentile, C.; Tavlaridis-Gyparakis, K. New Mixed-Integer Nonlinear Programming Formulations for the Unit Commitment Problems with Ramping Constraints. Oper. Res. 2024, 72, 2153–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaari, G.; Tekbiyik-Ersoy, N.; Dagbasi, M. The State of Art in Particle Swarm Optimization Based Unit Commitment: A Review. Processes 2019, 7, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, E.S.; Nunes, M.V.A.; Nascimento, M.H.R.; Leite, J.C. Rational Application of Electric Power Production Optimization through Metaheuristics Algorithm. Energies 2022, 15, 3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-S. Nature-inspired optimization algorithms: Challenges and open problems. J. Comput. Sci. 2020, 46, 101104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, A.G. Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm and Its Applications: A Systematic Review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 2531–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, R.; Godoy, M.; Catalán, C.; Viveros, P.; Zio, E. Multi-objective two-stage stochastic unit commitment model for wind-integrated power systems: A compromise programming approach. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 152, 109214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, B.M.; Jaber, A.S. Unit commitment based on modified firefly algorithm. Meas. Control 2020, 53, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, A.; Gioffrè, D.; Francesco Castelli, A.; Bovo, C.; Martelli, E. A multi-stage stochastic programming model for the unit commitment of conventional and virtual power plants bidding in the day-ahead and ancillary services markets. Appl. Energy 2023, 336, 120739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Lai, H.; Zhang, Y. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Optimal Power Flow with Renewables Using Graph Information. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.11461. [Google Scholar]
- Gholami Trojani, A.; Samiei Moghaddam, M.; Mohamadi Baigi, J. Stochastic Security-constrained Unit Commitment Considering Electric Vehicles, Energy Storage Systems, and Flexible Loads with Renewable Energy Resources. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2023, 11, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.; Hanif, A.; Hussain, S.J.; Memon, M.I.; Ali, M.U.; Zafar, A. An optimization-based strategy for solving optimal power flow problems in a power system integrated with stochastic solar and wind power energy. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Roomi, A.R. 30-Bus System (IEEE Test Case). Available online: https://al-roomi.org/power-flow (accessed on 10 September 2025).
- Howlader, H.O.R.; Sediqi, M.M.; Ibrahimi, A.M.; Senjyu, T. Optimal thermal unit commitment for solving duck curve problem by introducing csp, psh and demand response. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 4834–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achterberg, T. SCIP: Solving constraint integer programs. Math. Program. Comput. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestuzheva, K.; Chmiela, A.; Müller, B.; Serrano, F.; Vigerske, S.; Wegscheider, F. Global optimization of mixed-integer nonlinear programs with SCIP 8. J. Glob. Optim. 2023, 91, 287–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolusani, S.; Besançon, M.; Bestuzheva, K.; Chmiela, A.; Dionísio, J.; Donkiewicz, T.; van Doornmalen, J.; Eifler, L.; Ghannam, M.; Gleixner, A.; et al. The SCIP Optimization Suite 9.0. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.17702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, D.; Lopes, L.G.; Morgado-Dias, F. Particle Swarm Optimisation: A historical review up to the current developments. Entropy 2020, 22, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavuz, A.; Celik, N.; Chen, C.-H.; Xu, J. A Sequential Sampling-based Particle Swarm Optimization to Control Droop Coefficients of Distributed Generation Units in Microgrid Clusters. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 216, 109074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, N.; Mishra, A. A discourse on metaheuristics techniques for solving clustering and semisupervised learning models. In Cognitive Big Data Intelligence with a Metaheuristic Approach; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Generator | Fuel Cost Function ($) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | |
| Slack | 0.02000 | 2.00000 | 0 |
| Thermal 1 | 0.01750 | 1.75000 | 0 |
| Thermal 2 | 0.06250 | 1.00000 | 0 |
| Thermal 3 | 0.00834 | 3.25000 | 0 |
| Thermal 4 | 0.02500 | 3.00000 | 0 |
| Thermal 5 | 0.02500 | 3.00000 | 0 |
| Generator | Bus | Active Power Limit (MW) | Reactive Power Limit (Mvar) | Voltage Limit (pu) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | ||
| Slack | 0 | 80 | 0.0 | 150 | −20 | 1.05 | 0.95 |
| Thermal 1 | 1 | 80 | 0.0 | 60 | −20 | 1.1 | 0.95 |
| Thermal 2 | 20 | 50 | 0.0 | 62.5 | −15 | 1.1 | 0.95 |
| Thermal 3 | 22 | 55 | 0.0 | 48.7 | −15 | 1.1 | 0.95 |
| Thermal 4 | 21 | 30 | 0.0 | 40 | −10 | 1.1 | 0.95 |
| Thermal 5 | 26 | 30 | 0.0 | 40 | −10 | 1.1 | 0.95 |
| Unit | Pmax (MW) | Pmin (MW) | Minimum Up Time | Minimum Down Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 162 | 25 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| 2 | 55 | 10 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 3 | 55 | 10 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| 4 | 55 | 10 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| 5 | 85 | 25 | 2.00 | 1.00 |
| 6 | 130 | 20 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Parameter | PHS 1 |
|---|---|
| PHS Maximum Power Output (MW) | 60 |
| PHS Maximum Capacity (MWh) | 518 |
| Efficiency (%) | 85 |
| Minimum Down Time (jam) | 1 |
| Minimum Up Time (jam) | 1 |
| Operational Cost ($) | 5.5 |
| Hour | Load (MW) | PV Output (MW) | Hour | Load (MW) | PV Output (MW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 135.4 | 0.0 | 13 | 186.5 | 77.3 |
| 2 | 128.3 | 0.0 | 14 | 190.0 | 85.9 |
| 3 | 125.6 | 0.0 | 15 | 186.5 | 64.9 |
| 4 | 126.4 | 0.0 | 16 | 183.4 | 51.4 |
| 5 | 129.4 | 0.0 | 17 | 177.4 | 29.7 |
| 6 | 114.9 | 0.0 | 18 | 180.2 | 19.2 |
| 7 | 102.6 | 2.4 | 19 | 185.6 | 5.9 |
| 8 | 107.3 | 8.2 | 20 | 186.5 | 0.0 |
| 9 | 126.7 | 26.1 | 21 | 178.8 | 0.0 |
| 10 | 148.8 | 41.8 | 22 | 169.3 | 0.0 |
| 11 | 165.2 | 54.2 | 23 | 160.2 | 0.0 |
| 12 | 175.3 | 57.7 | 24 | 147.7 | 0.0 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of particles | 300–900 |
| PSO Maximum iteration | 10–15 |
| NR maximum iteration | 7 |
| Inertia weight (ω) | 0.7 |
| Cognitive coefficient (c1) | 1.5 |
| Social coefficient (c2) | 1.5 |
| Penalty Type | Penalty Weight |
|---|---|
| Voltage Deviation Penalty (pV) | 10,000 |
| Active Power Generation Penalty (pP) | 1000 |
| Reactive Power Generation Penalty (pQ) | 1000 |
| Ramping Rate Violation Penalty (pRamp) | 1000 |
| Newton–Raphson Convergence Tolerance Penalty (pNR) | 1,000,000 |
| Generator (Bus) | PV (MW) | PHS (MW) | Total Load (MW) | Cost ($) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slack | 1 | 12 | 21 | 22 | 26 | ||||
| 36.4 | 48.75 | 9.12 | 19.65 | 9.12 | 12.36 | 135.40 | 411.31 | ||
| 35.3 | 47.49 | 8.24 | 19.3 | 8.24 | 9.72 | 128.30 | 345.94 | ||
| 34.88 | 47.01 | 7.91 | 19.16 | 7.91 | 8.71 | 125.57 | 336.65 | ||
| 35.01 | 47.15 | 8.01 | 19.2 | 8.01 | 9.01 | 126.39 | 339.43 | ||
| 35.47 | 47.68 | 8.38 | 19.35 | 8.38 | 10.13 | 129.40 | 349.67 | ||
| 33.23 | 45.13 | 6.59 | 18.64 | 6.59 | 4.76 | 114.93 | 300.85 | ||
| 30.76 | 42.3 | 4.61 | 17.84 | 4.61 | 0.1 | 2.4 | 102.64 | 252.53 | |
| 30.48 | 41.98 | 4.39 | 17.75 | 4.39 | 0.1 | 8.2 | 107.28 | 248.93 | |
| 30.86 | 42.41 | 4.68 | 17.87 | 4.68 | 0.1 | 26.1 | 126.67 | 253.81 | |
| 32.01 | 43.73 | 5.61 | 18.24 | 5.61 | 1.82 | 41.8 | 148.78 | 274.71 | |
| 32.62 | 44.42 | 6.1 | 18.44 | 6.1 | 3.28 | 54.2 | 165.16 | 287.68 | |
| 33.64 | 45.59 | 6.91 | 18.76 | 6.91 | 5.73 | 57.7 | 175.26 | 309.59 | |
| 32.35 | 44.11 | 5.88 | 18.35 | 5.88 | 2.63 | 77.3 | 186.45 | 281.89 | |
| 31.56 | 43.21 | 5.25 | 18.1 | 5.25 | 0.74 | 85.9 | 190.00 | 265.20 | |
| 34.25 | 46.29 | 7.4 | 18.96 | 7.4 | 7.21 | 64.9 | 186.45 | 322.94 | |
| 35.88 | 48.15 | 8.7 | 19.48 | 8.7 | 11.1 | 51.4 | 183.45 | 358.67 | |
| 38.31 | 50.93 | 10.65 | 20.26 | 10.65 | 16.93 | 29.7 | 177.44 | 413.39 | |
| 40.36 | 53.27 | 12.29 | 20.92 | 12.29 | 21.85 | 19.2 | 180.17 | 460.75 | |
| 43.26 | 56.59 | 14.61 | 21.84 | 14.61 | 28.81 | 185.63 | 529.60 | ||
| 43.47 | 56.83 | 14.78 | 21.91 | 14.78 | 29.31 | 6.32 | 186.45 | 534.64 | |
| 43.12 | 56.42 | 14.5 | 21.8 | 14.5 | 28.47 | 178.81 | 526.16 | ||
| 41.64 | 54.73 | 13.31 | 21.33 | 13.31 | 24.92 | 169.25 | 490.85 | ||
| 40.25 | 53.14 | 12.2 | 20.88 | 12.2 | 21.58 | 160.24 | 458.08 | ||
| 38.3 | 50.92 | 10.64 | 20.26 | 10.64 | 16.92 | 147.69 | 413.24 | ||
| Total | 3717.8 | 8771.14 | |||||||
| Generator (Bus) | PV (MW) | PHS (MW) | Total Load (MW) | Cost ($) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slack | 1 | 12 | 21 | 22 | 26 | ||||
| 38.03 | 48.75 | 9.12 | 19.65 | 9.12 | 12.36 | 137.03 | 420.98 | ||
| 36.81 | 47.49 | 8.24 | 19.30 | 8.24 | 9.72 | 129.81 | 351.11 | ||
| 36.33 | 47.01 | 7.91 | 19.16 | 7.91 | 8.71 | 127.03 | 341.63 | ||
| 36.48 | 47.15 | 8.01 | 19.20 | 8.01 | 9.01 | 127.86 | 344.47 | ||
| 36.99 | 47.68 | 8.38 | 19.35 | 8.38 | 10.13 | 130.92 | 354.91 | ||
| 34.52 | 45.13 | 6.59 | 18.64 | 6.59 | 4.76 | 116.23 | 305.21 | ||
| 31.85 | 42.30 | 4.61 | 17.84 | 4.61 | 0.10 | 2.43 | 103.75 | 256.12 | |
| 31.61 | 41.98 | 4.39 | 17.75 | 4.39 | 0.10 | 8.19 | 108.41 | 252.57 | |
| 32.67 | 42.41 | 4.68 | 17.87 | 4.68 | 0.10 | 26.06 | 128.47 | 259.72 | |
| 35.16 | 43.73 | 5.61 | 18.24 | 5.61 | 1.82 | 41.76 | 151.93 | 285.24 | |
| 37.26 | 44.42 | 6.10 | 18.44 | 6.10 | 3.28 | 54.19 | 169.79 | 303.45 | |
| 38.94 | 45.59 | 6.91 | 18.76 | 6.91 | 5.73 | 57.70 | 180.55 | 327.87 | |
| 40.43 | 44.11 | 5.88 | 18.35 | 5.88 | 2.63 | 77.25 | 194.53 | 309.81 | |
| 41.06 | 43.21 | 5.25 | 18.10 | 5.25 | 0.74 | 85.89 | 199.50 | 297.99 | |
| 40.73 | 46.29 | 7.40 | 18.96 | 7.40 | 7.21 | 64.93 | 192.92 | 345.58 | |
| 40.82 | 48.15 | 8.70 | 19.48 | 8.70 | 11.10 | 51.42 | 188.37 | 376.08 | |
| 41.47 | 50.93 | 10.65 | 20.26 | 10.65 | 16.93 | 29.71 | 180.61 | 424.77 | |
| 43.20 | 53.27 | 12.29 | 20.92 | 12.29 | 21.85 | 19.19 | 183.01 | 471.17 | |
| 46.09 | 56.59 | 14.61 | 21.84 | 14.61 | 28.81 | 188.45 | 540.28 | ||
| 45.10 | 56.83 | 14.78 | 21.91 | 14.78 | 29.31 | 6.32 | 189.03 | 540.79 | |
| 45.78 | 56.42 | 14.50 | 21.80 | 14.50 | 28.47 | 181.48 | 536.24 | ||
| 44.05 | 54.73 | 13.31 | 21.33 | 13.31 | 24.92 | 171.65 | 499.75 | ||
| 42.40 | 53.14 | 12.20 | 20.88 | 12.20 | 21.58 | 162.41 | 465.98 | ||
| 40.18 | 50.92 | 10.64 | 20.26 | 10.64 | 16.92 | 149.56 | 419.92 | ||
| Total | 3793.7 | 9031.64 | |||||||
| Hours | pV | pQ | pP | pRamp | pNR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 3 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 4 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 5 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 6 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 7 | - | [24, 0.21] | - | - | - |
| 8 | - | - | [24, 7.32 × 10−5] | - | - |
| 9 | - | - | [24, 0.001027] | - | - |
| 10 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 11 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 12 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 13 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 14 | - | - | [24, 0.001] | - | - |
| 15 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 16 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 17 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 18 | - | - | [24, 0.00219] | - | - |
| 19 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 20 | - | [5, 56.2] | - | - | - |
| 21 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 22 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 23 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 24 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Generator (Bus) | PV (MW) | PHS (MW) | Total Load (MW) | Cost ($) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slack | 1 | 12 | 21 | 22 | 26 | ||||
| 34.37 | 49.14 | 9.14 | 19.74 | 10.47 | 14.05 | 137.03 | 420.98 | ||
| 33.00 | 46.44 | 10.41 | 19.20 | 8.10 | 12.50 | 129.81 | 351.11 | ||
| 34.63 | 45.08 | 8.50 | 18.90 | 8.59 | 11.24 | 127.03 | 341.63 | ||
| 32.54 | 46.04 | 10.15 | 19.09 | 7.99 | 11.89 | 127.86 | 344.47 | ||
| 33.25 | 46.67 | 10.57 | 19.26 | 8.17 | 12.85 | 130.92 | 354.91 | ||
| 31.09 | 45.44 | 6.80 | 18.97 | 7.68 | 6.12 | 116.23 | 305.21 | ||
| 28.77 | 42.61 | 2.35 | 16.78 | 4.55 | 6.28 | 2.38 | 103.75 | 256.12 | |
| 31.61 | 41.98 | 4.39 | 17.75 | 4.39 | 0.10 | 8.19 | 108.41 | 252.57 | |
| 32.67 | 42.41 | 4.68 | 17.87 | 4.68 | 0.10 | 26.06 | 128.47 | 259.72 | |
| 33.27 | 43.90 | 4.94 | 18.16 | 7.81 | 2.05 | 41.71 | 151.93 | 285.24 | |
| 35.28 | 43.76 | 4.73 | 18.85 | 7.67 | 4.73 | 54.19 | 169.79 | 303.45 | |
| 37.63 | 44.98 | 5.60 | 19.14 | 7.88 | 7.01 | 57.70 | 180.55 | 327.87 | |
| 31.55 | 48.13 | 5.22 | 19.41 | 7.78 | 4.26 | 77.13 | 194.53 | 309.81 | |
| 33.22 | 47.06 | 8.23 | 18.07 | 3.76 | 1.93 | 85.69 | 199.50 | 297.99 | |
| 38.17 | 48.55 | 12.08 | 18.60 | 8.35 | 1.16 | 64.90 | 192.92 | 345.58 | |
| 37.70 | 47.39 | 9.14 | 18.87 | 8.35 | 14.96 | 51.41 | 188.37 | 376.08 | |
| 39.82 | 49.62 | 10.70 | 20.26 | 10.26 | 20.05 | 29.71 | 180.61 | 424.77 | |
| 43.16 | 53.06 | 12.32 | 20.92 | 12.29 | 21.98 | 19.19 | 183.01 | 471.17 | |
| 44.63 | 56.72 | 16.87 | 22.18 | 15.40 | 26.60 | 188.45 | 540.28 | ||
| 50.05 | 63.08 | 21.65 | 23.63 | 18.29 | 6.32 | 6.32 | 189.03 | 540.79 | |
| 44.01 | 55.33 | 15.58 | 22.13 | 14.68 | 29.58 | 181.48 | 536.24 | ||
| 39.13 | 52.90 | 14.86 | 22.56 | 14.63 | 27.31 | 171.65 | 499.75 | ||
| 39.42 | 52.52 | 12.88 | 21.15 | 12.43 | 23.88 | 162.41 | 465.98 | ||
| 36.40 | 51.82 | 10.57 | 20.97 | 11.04 | 18.63 | 149.56 | 419.92 | ||
| Total | 3786 | 9016.05 | |||||||
| Hours | pV | pQ | pP | pRamp | pNR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 3 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 4 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 5 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 6 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 7 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 8 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 9 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 10 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 11 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 12 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 13 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 14 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 15 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 16 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 17 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 18 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 19 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 21 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 22 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 23 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 24 | - | - | - | - | - |
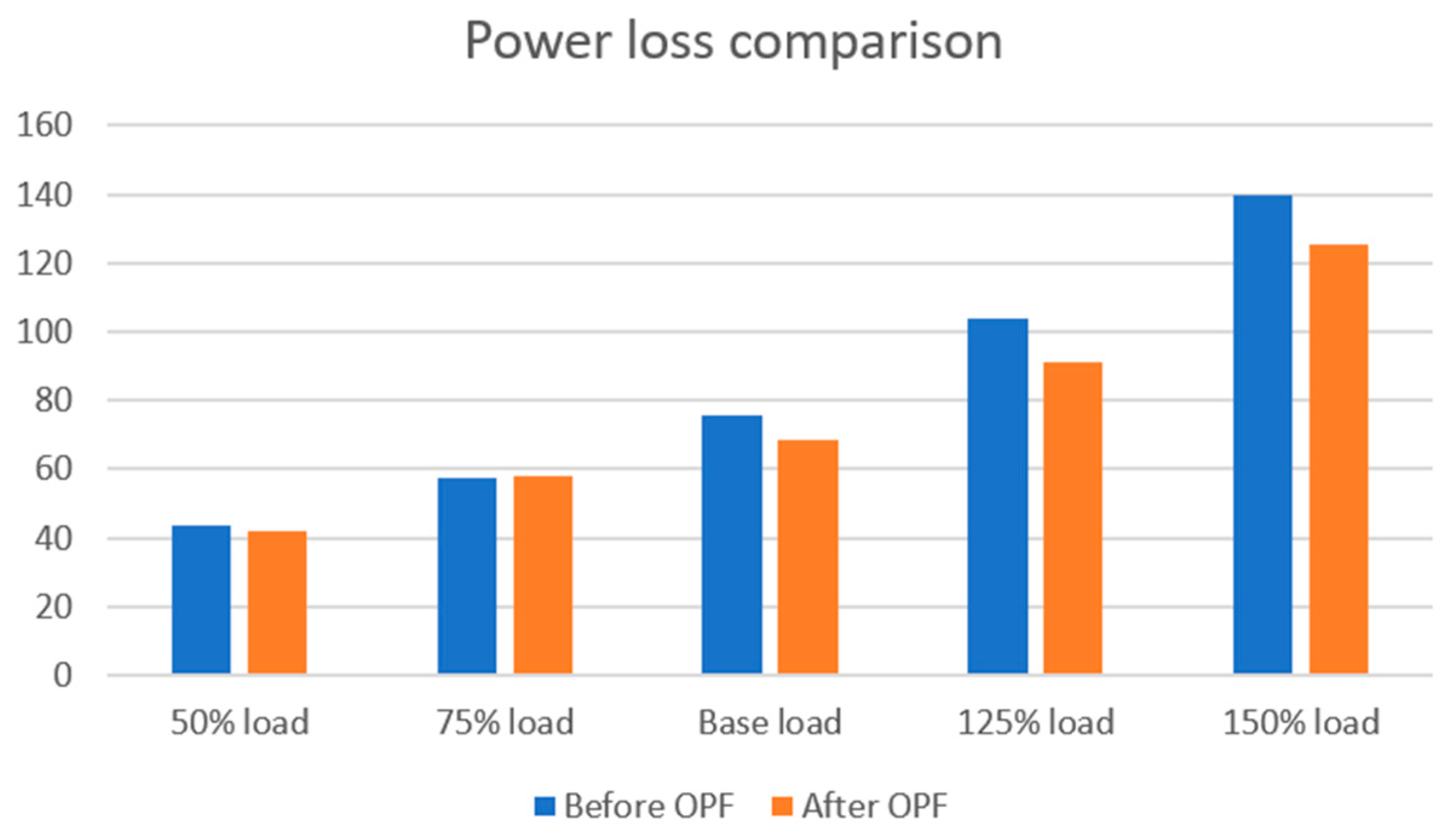
| Load Scenario | Before OPF | After OPF |
|---|---|---|
| Base load | 75.42 | 68.22 |
| 50% load | 43.74 | 41.74 |
| 75% load | 57.61 | 57.90 |
| 125% load | 103.94 | 91.05 |
| 150% load | 139.87 | 125.45 |
| Load Scale | With PHS ($) | Without PHS ($) | Price Difference ($) | Relative Difference to the Initial Price (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5× | 2982.37 | 3021.36 | 38.99 | 1.29 |
| 0.75× | 5697.31 | 5716.12 | 18.81 | 0.33 |
| 1.00× | 8771.14 | 8790.68 | 19.54 | 0.22 |
| 1.25× | 12,097.18 | 12,118.27 | 21.09 | 0.17 |
| 1.50× | 15,660.12 | 15,684.64 | 24.52 | 0.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siregar, R.H.; Akhyar, A.; Lubis, R.S.; Hadi, M.N. Optimal Power Flow-Assisted Unit Commitment with Multi-Level Load Variation Analysis in Renewable-Based Power Systems. Energies 2025, 18, 6340. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18236340
Siregar RH, Akhyar A, Lubis RS, Hadi MN. Optimal Power Flow-Assisted Unit Commitment with Multi-Level Load Variation Analysis in Renewable-Based Power Systems. Energies. 2025; 18(23):6340. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18236340
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiregar, Ramdhan Halid, Akhyar Akhyar, Rakhmad Syafutra Lubis, and Muhammad Nurul Hadi. 2025. "Optimal Power Flow-Assisted Unit Commitment with Multi-Level Load Variation Analysis in Renewable-Based Power Systems" Energies 18, no. 23: 6340. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18236340
APA StyleSiregar, R. H., Akhyar, A., Lubis, R. S., & Hadi, M. N. (2025). Optimal Power Flow-Assisted Unit Commitment with Multi-Level Load Variation Analysis in Renewable-Based Power Systems. Energies, 18(23), 6340. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18236340






