Evaluation of CO2 Injectivity and Geological Storage Scenarios Using Nodal Analysis and Tubing Injectivity Index in a Depleted Gas Field in Malaysia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
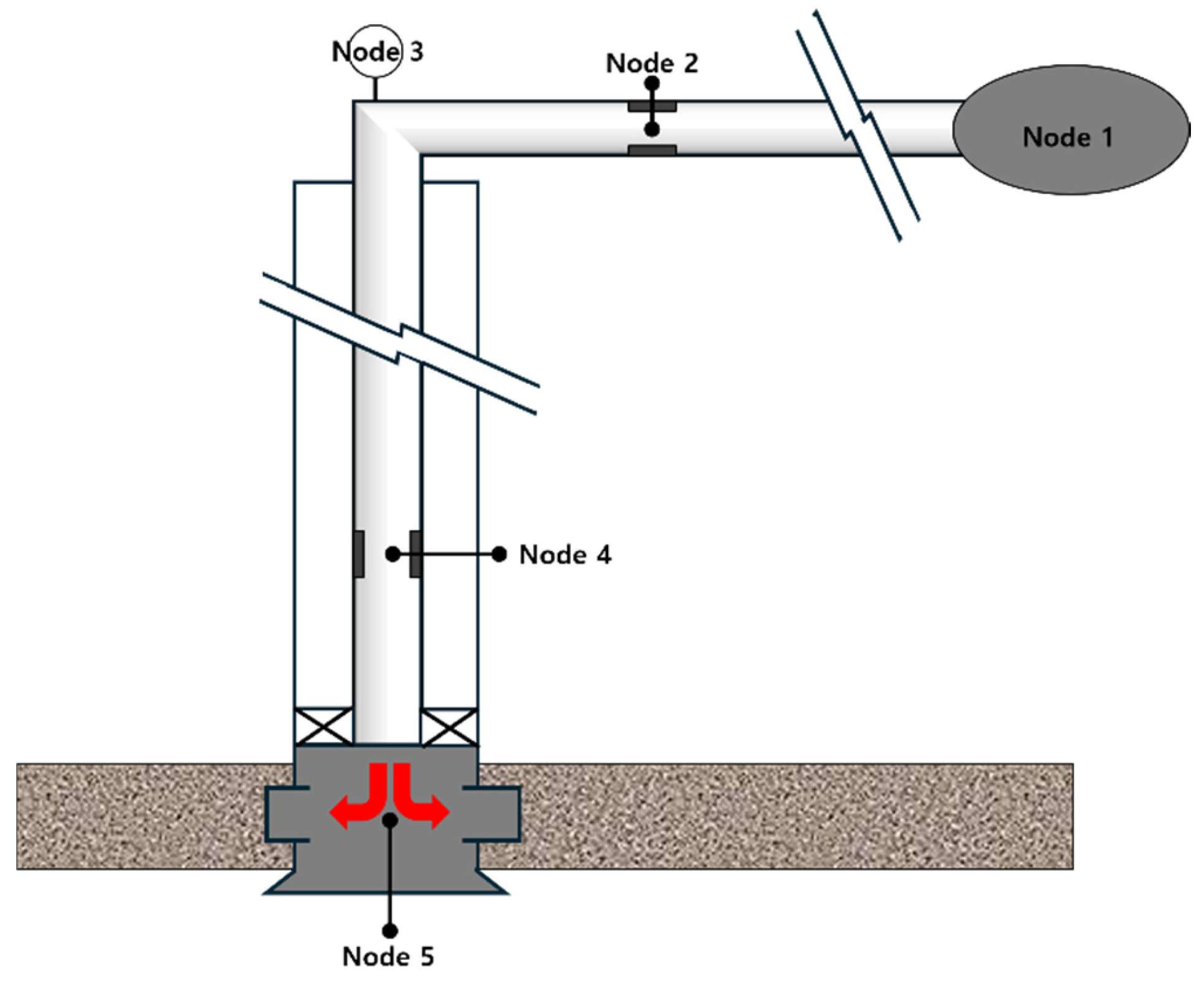
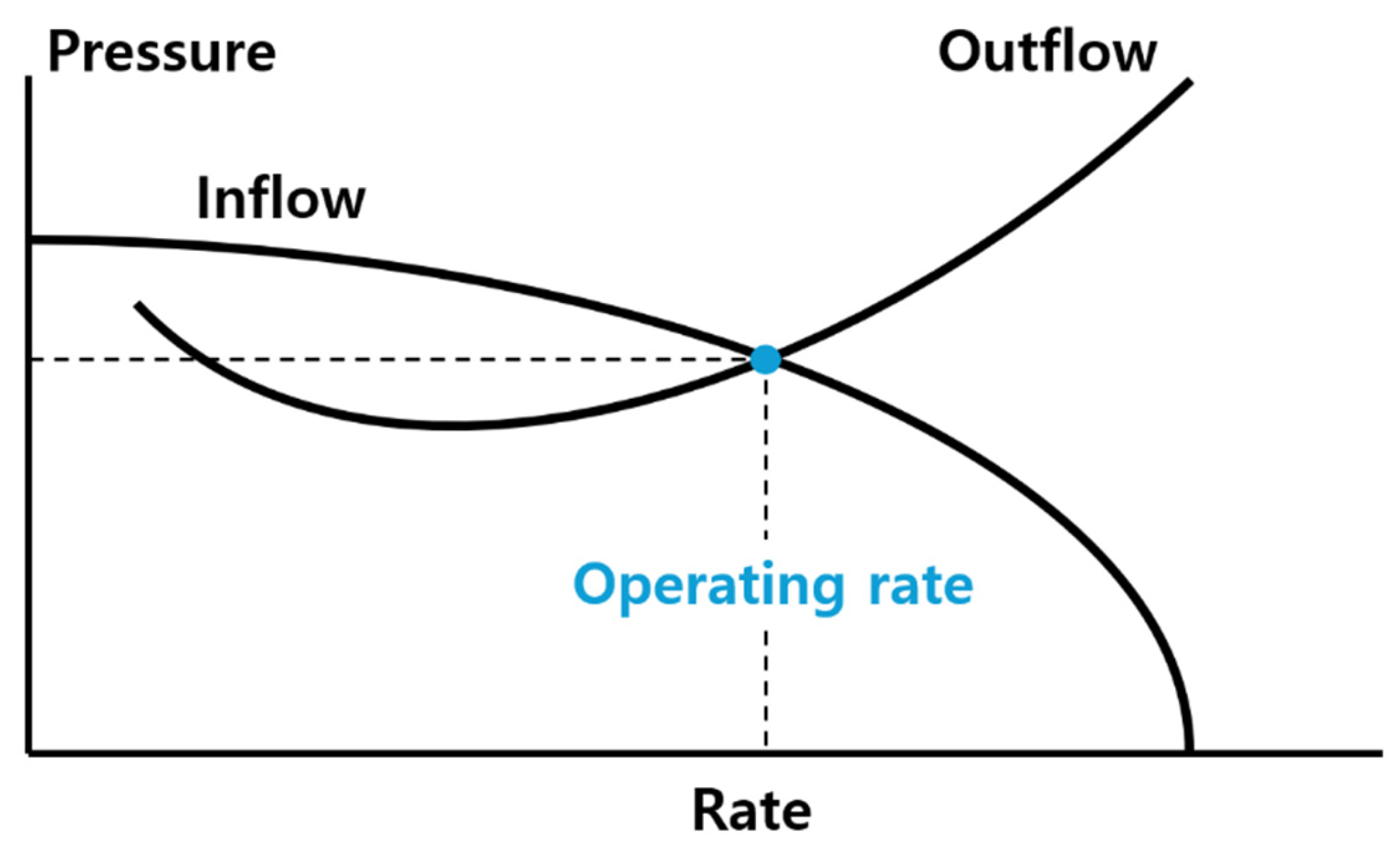
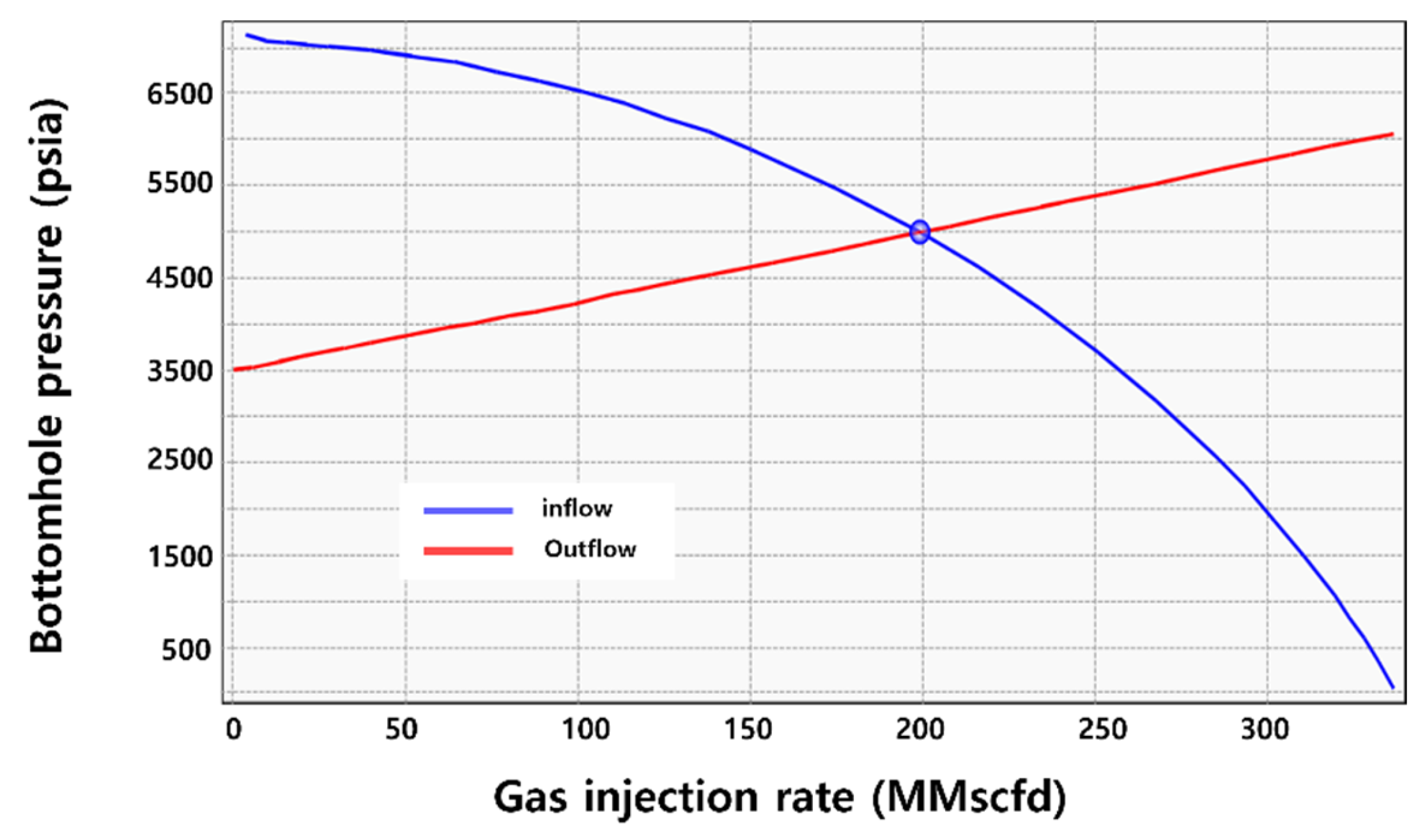
2.1. Nodal Analysis for CO2 Injection
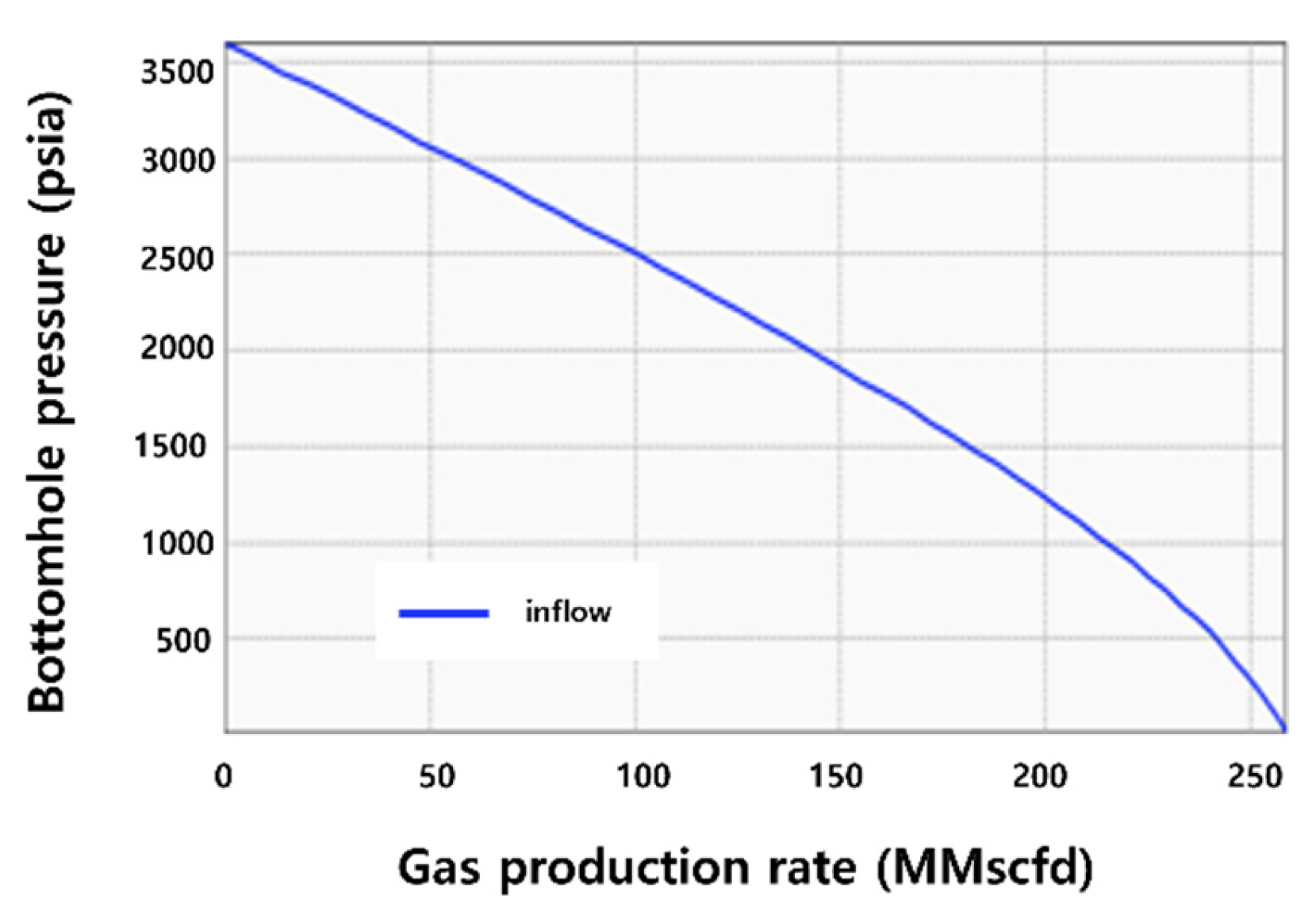
2.1.1. IPR Input Parameters
2.1.2. OPR Input Parameters
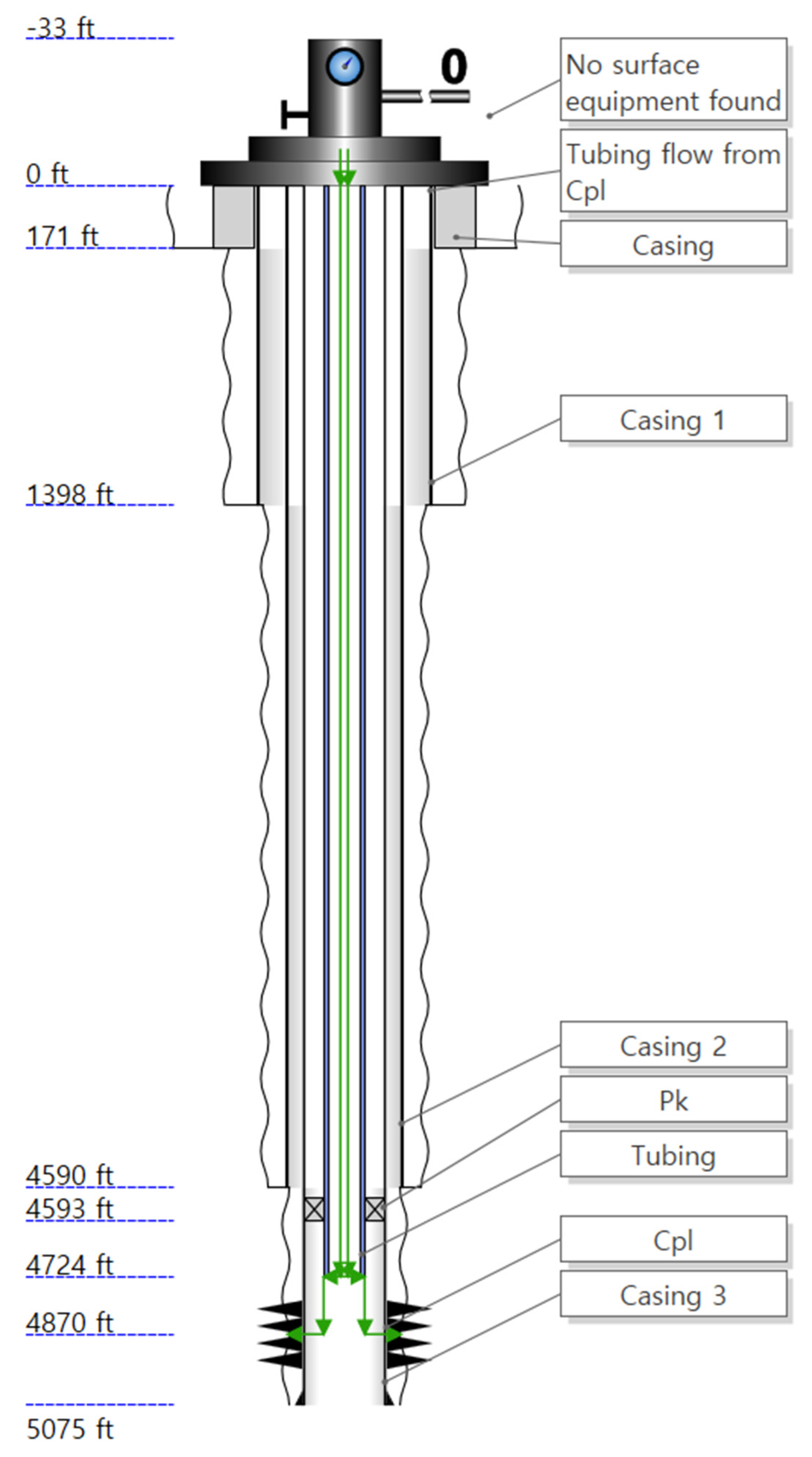
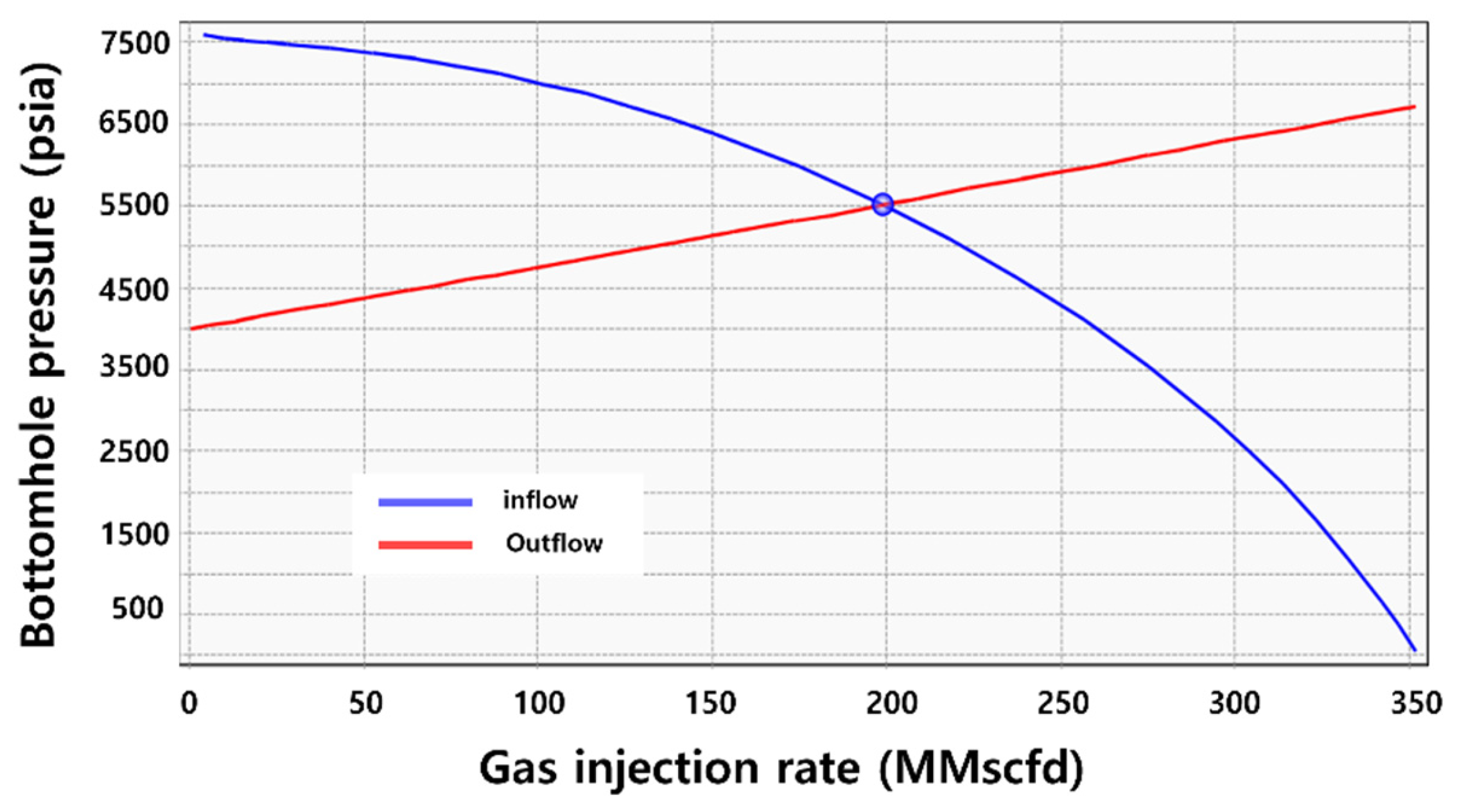
2.2. CO2 Injectivity Analysis of the Injection Well in Gas Field Z
- represents the hydrostatic pressure gradient,
- is the frictional pressure loss, and
- accounts for the acceleration term.
- is the mixture density (lbm/ft3),
- is the mixture velocity (ft/s),
- is the friction factor,
- is the inner diameter of the tubing (ft),
- is the deviation angle from the horizontal (°), and
- is the gravitational acceleration (32.174 ft/s2).
Sensitivity Parameters
2.3. CO2 Injection Scenario Design for Gas Field Z
3. Results
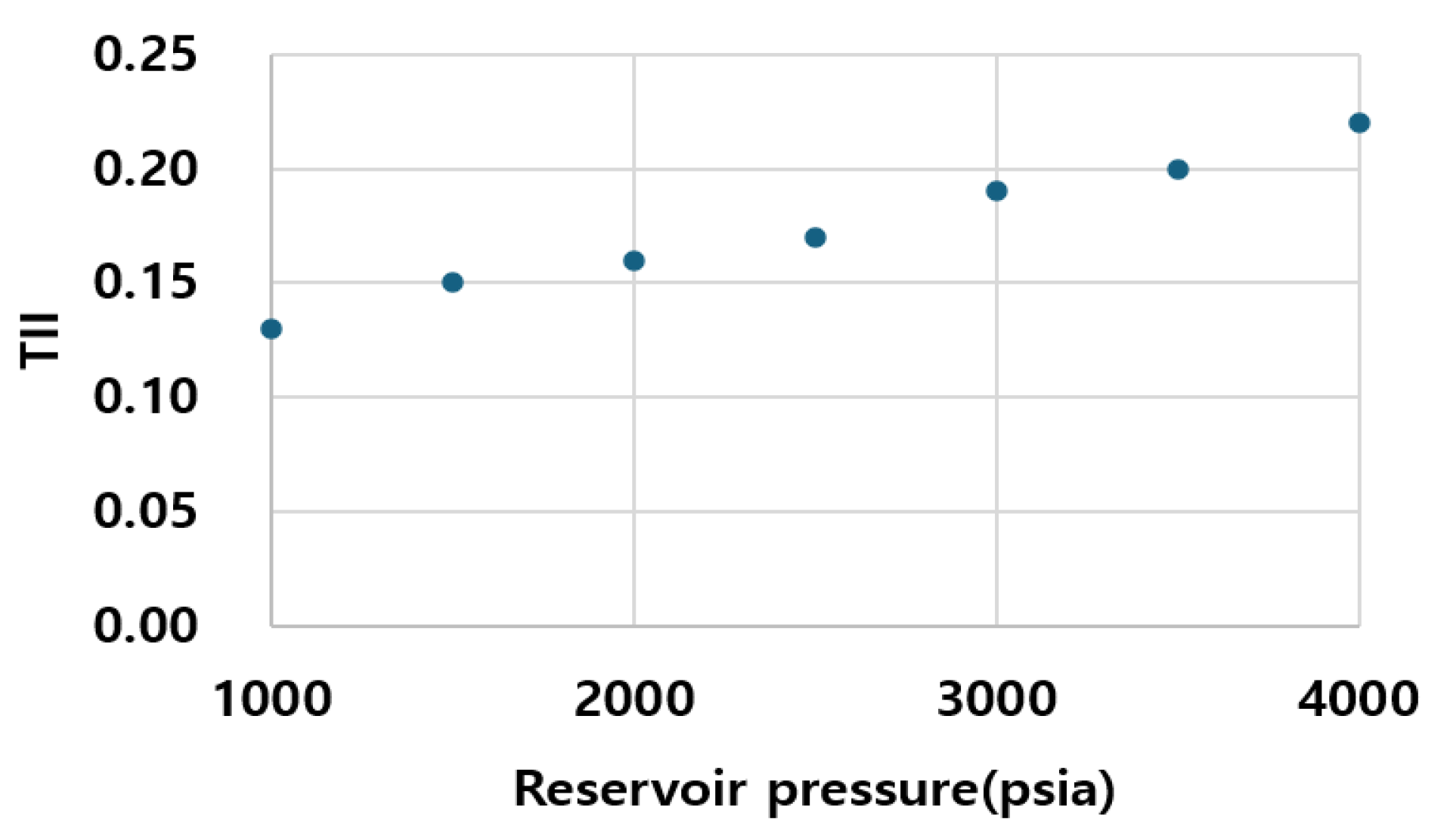
3.1. Sensitivity Analysis
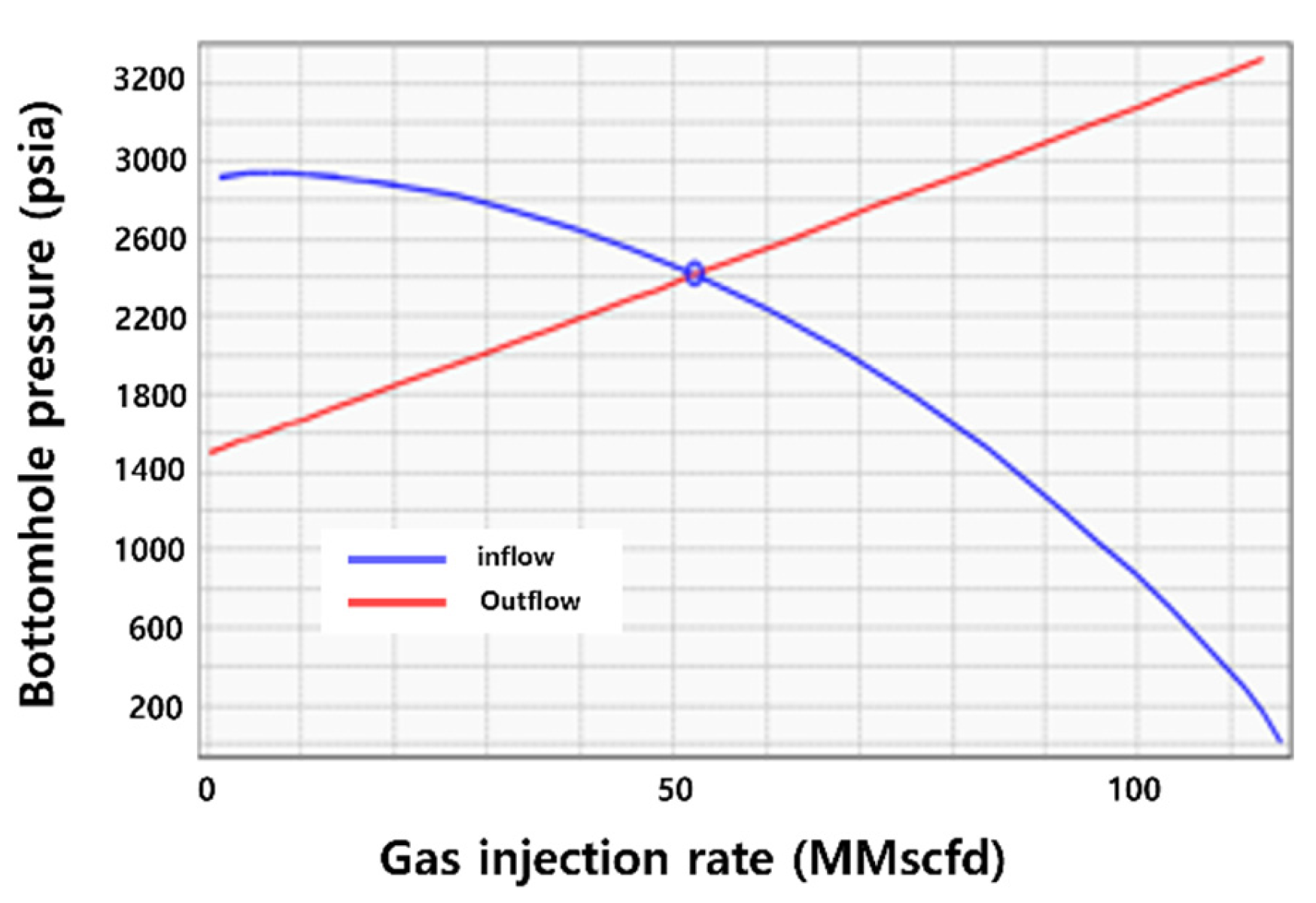
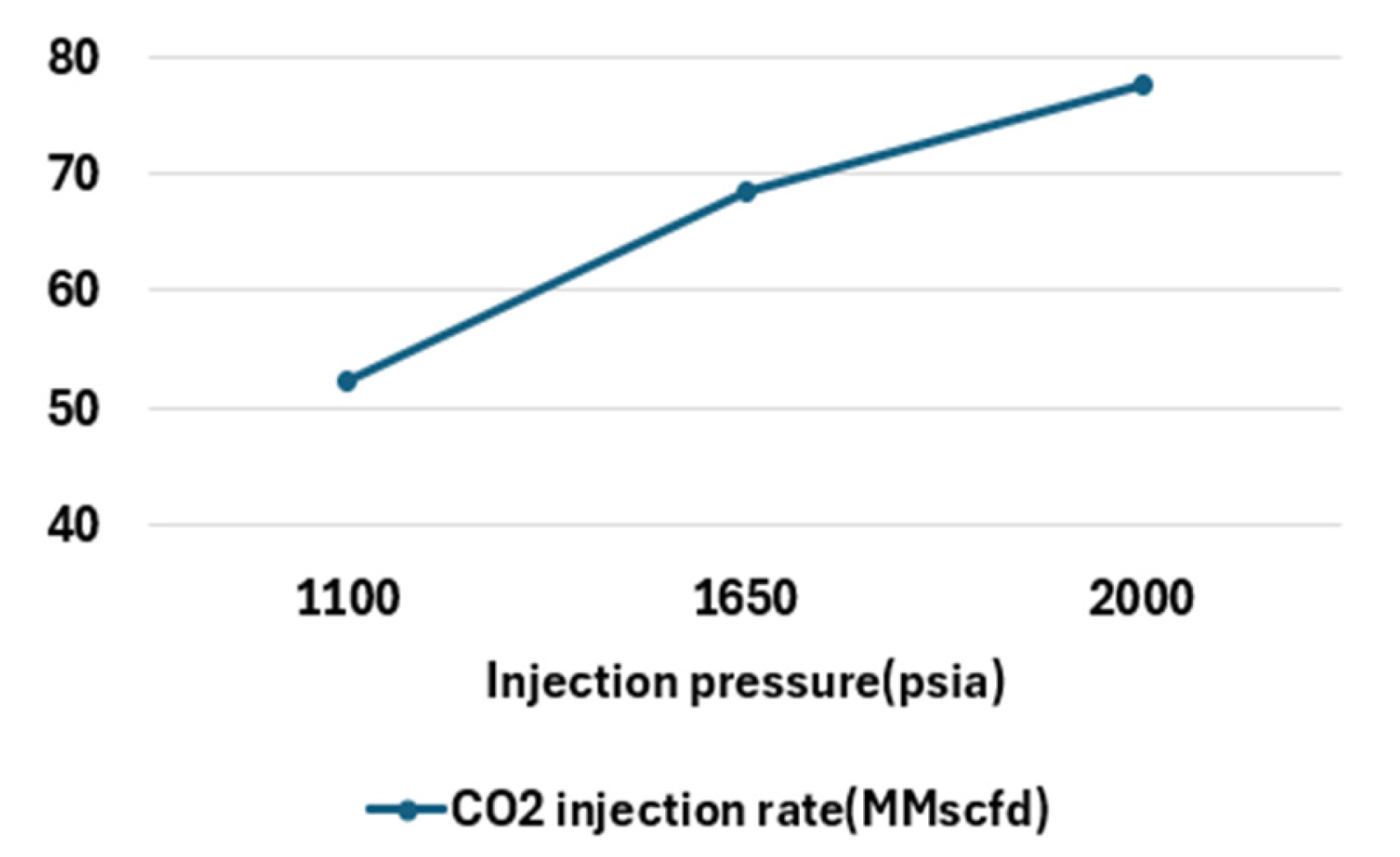
3.1.1. Injection Pressure
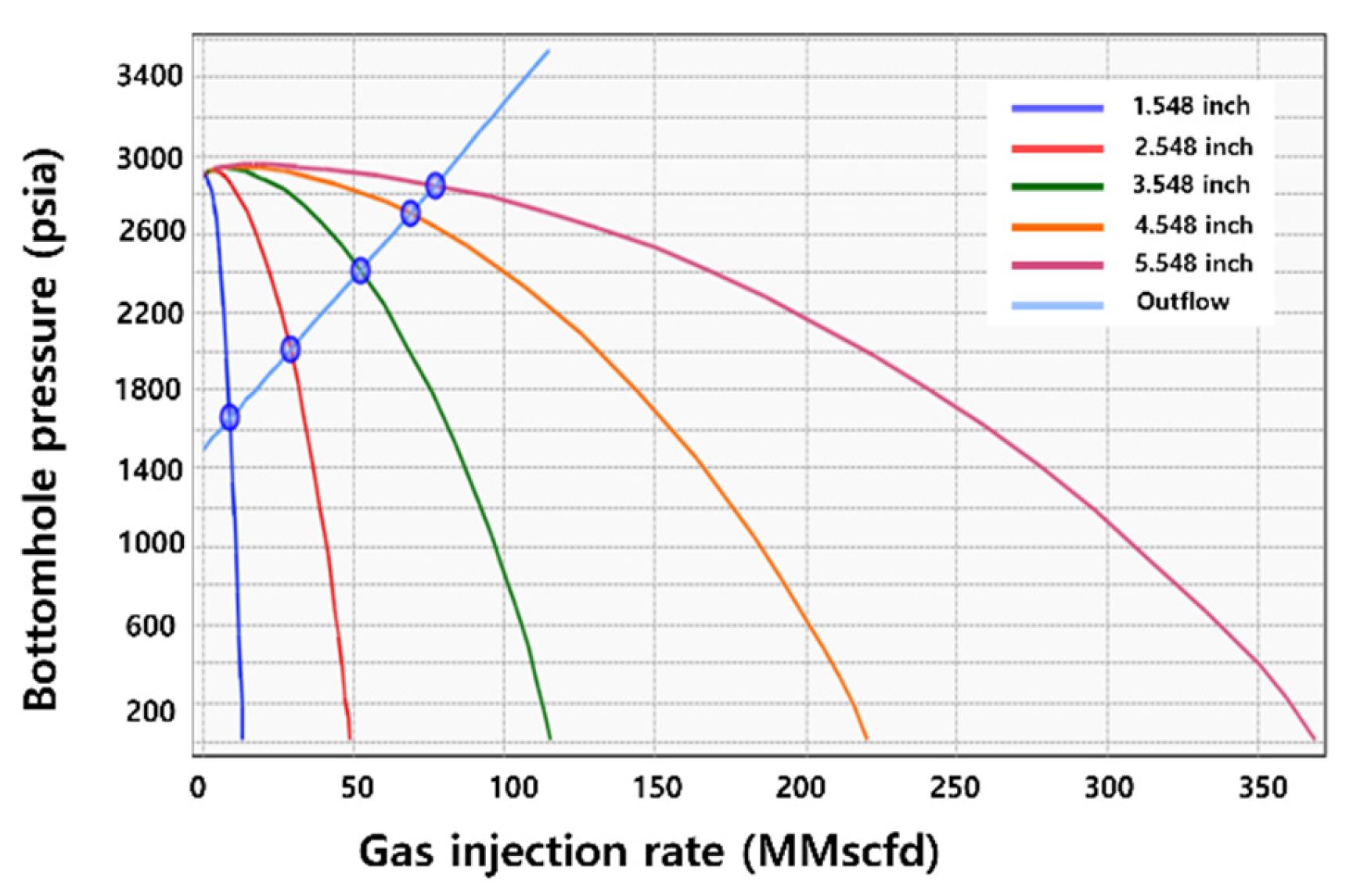
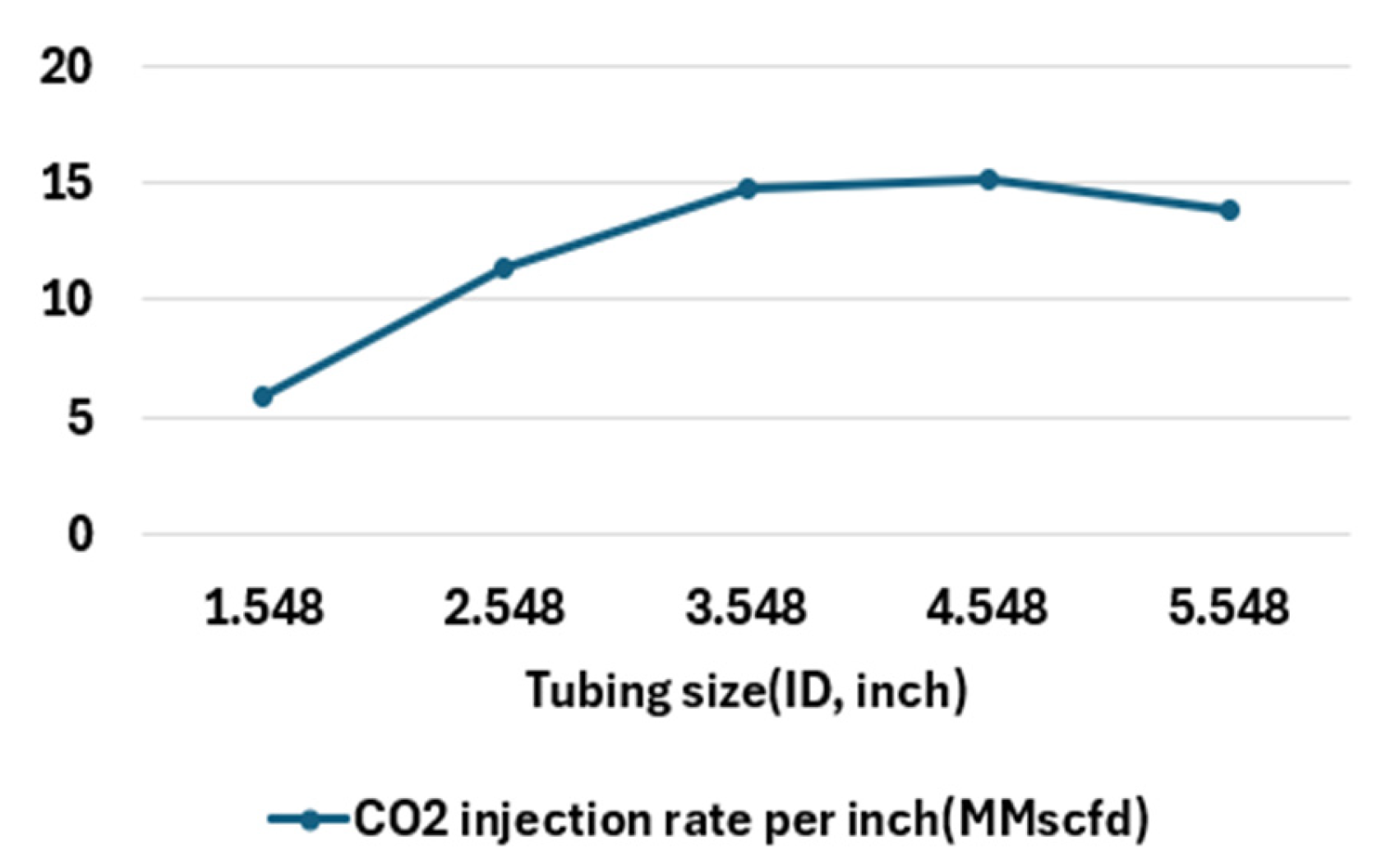
3.1.2. Tubing Size
3.1.3. Reservoir Pressure
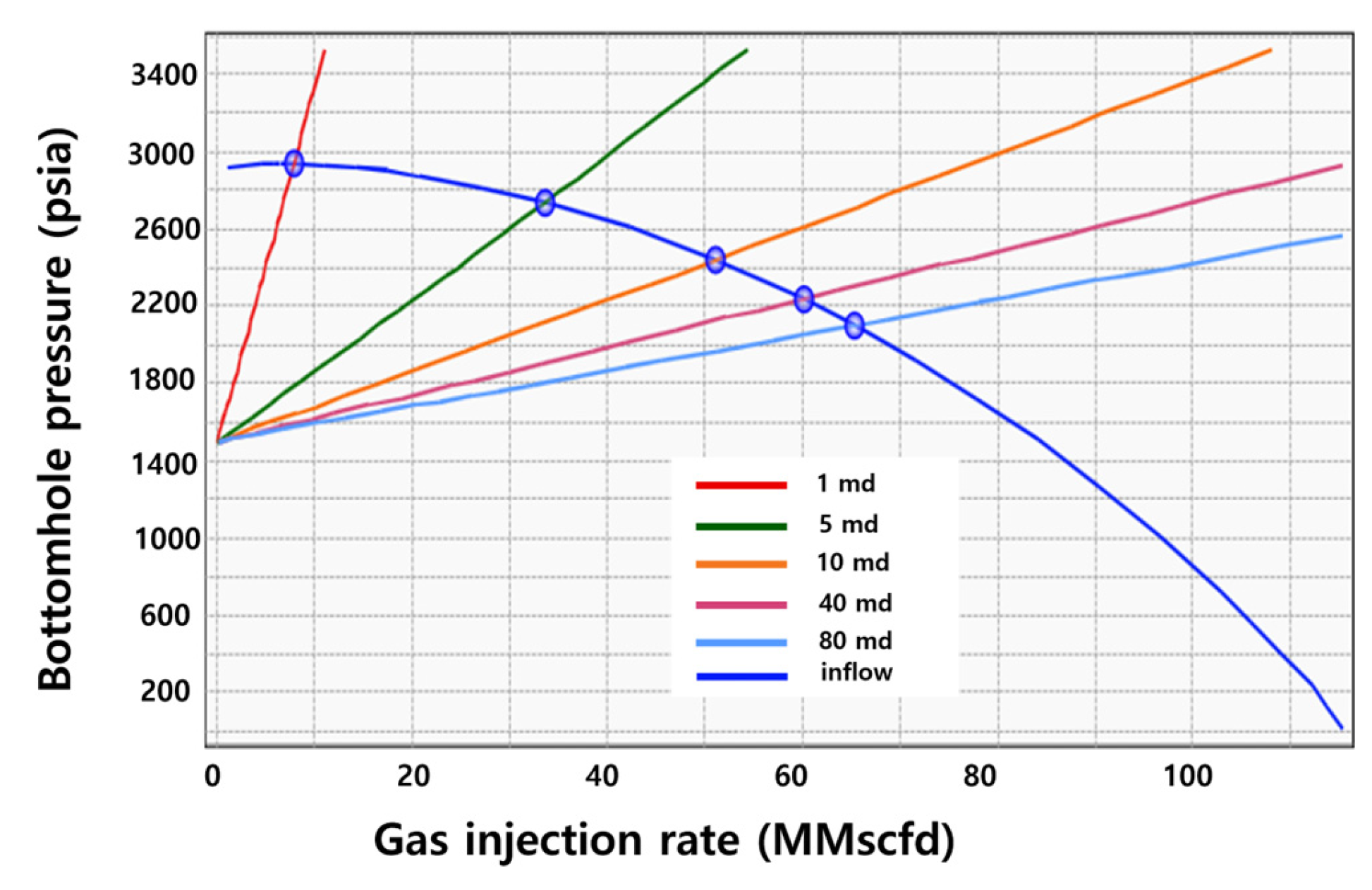
3.1.4. Reservoir Permeability
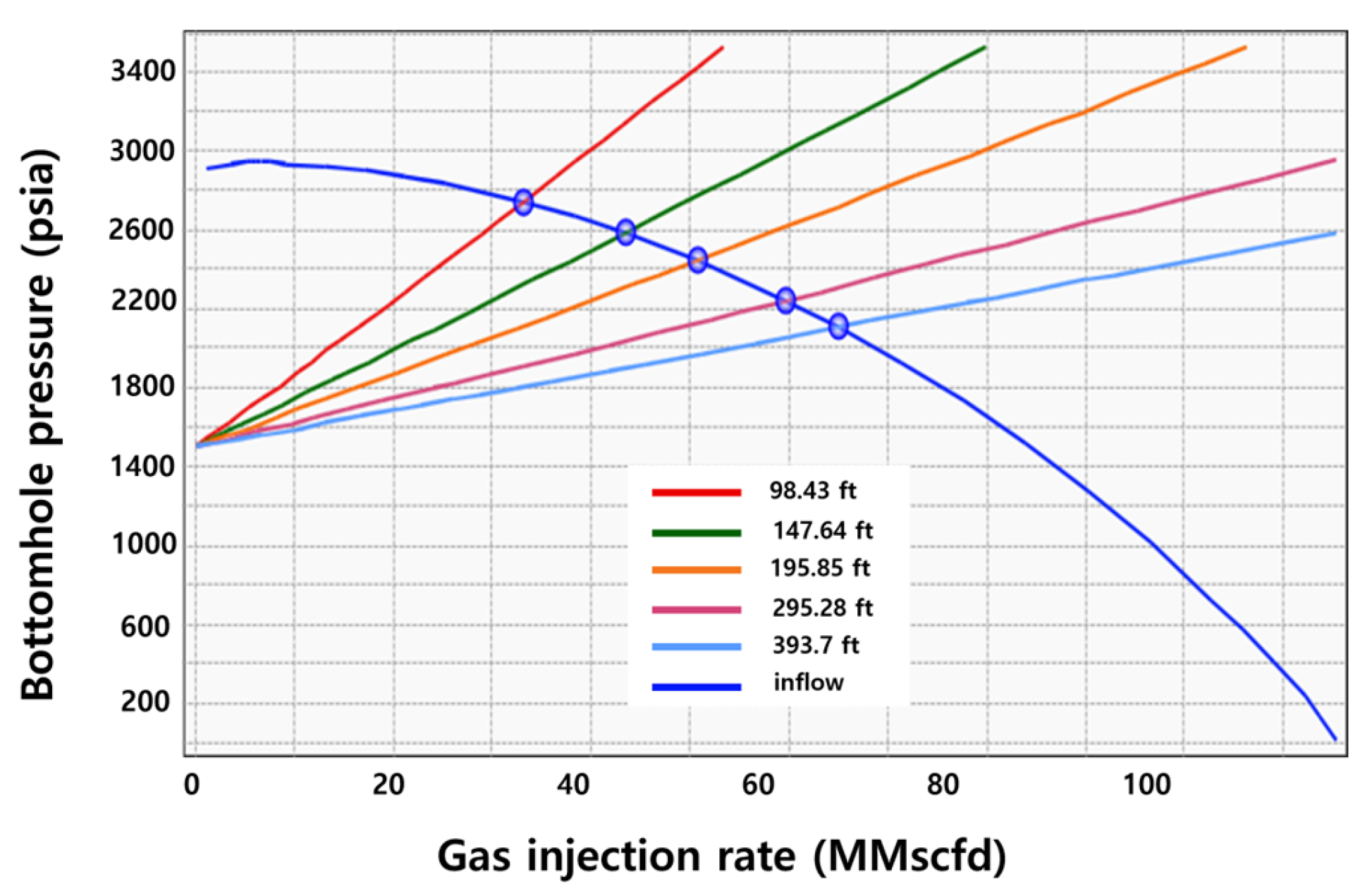
3.1.5. Reservoir Thickness
3.2. Results of CO2 Injection Scenario Design for Gas Field Z
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global CCS Institute. Global Status of CCS 2021—CCS Accelerating to Net Zero; Global CCS Institute: Melbourne, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Energy Technology Perspectives: Scenarios & Strategies to 2050; OECD/IEA: Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z. A Review of CO2 Storage in View of Safety and Cost-Effectiveness. Energies 2020, 13, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-G.; Song, Y.-H. R&D Trends and Future Utilization Plans of CO2 Geological Storage in Submarine Geological Structures. J. Korean Mar. Environ. Eng. 2008, 11, 24–34. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Korea Institute of Ocean Science and Technology (KIOST). CO2, the Main Cause of Climate Change, Is Stored in the Ocean Subsurface. Available online: https://www.kiost.ac.kr/cop/bbs/BBSMSTR_000000000011/selectBoardArticle.do?nttId=16853 (accessed on 22 September 2025). (In Korean).
- Kim, H.-M.; Park, E.-J.; Synn, J.H.; Park, Y.-C. Geological Storage of Greenhouse Gas (CO2) and Rock Engineering Aspects. Tunn. Undergr. Space (J. Korean Soc. Rock Mech.) 2008, 18, 175–184. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Asian Development Bank (ADB). Financial Report 2013: Management’s Discussion and Analysis and Annual Financial Statements; ADB: Manila, Philippines, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.-Y. Global CCS Trends and Policy Implications of Major Countries; POSRI Issue Report; POSCO Research Institute: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2023. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Afifi, M.; Ng, C.Y. Strategic Integration of Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS) Technologies in Malaysia: Leveraging Existing Infrastructure for Sustainable Decarbonisation. In Proceedings of the SPE Asia Pacific CCUS Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 26–27 August 2025; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA,, 2025. SPE-225913-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Jalil, M.A.; Chidambaram, P.; Yakup, M.H.; Affandi, R.A. CO2 Injection Strategies in a Depleted Multi-Stacked Clastic Gas Reservoirs: A Case Study of Carbon Capture and Storage Project Offshore Peninsular Malaysia. In Proceedings of the SPE Asia Pacific CCUS Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 26–27 August 2025; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA,, 2025. SPE-225914-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Putra, I.W.E.; Anuar, N.K.; Nesan, T.P.; Ahmad, W.Z.; Yunus, M.J.; Johar, J.M.; Sidek, A.M.M. Overcoming the Challenges of Developing High CO2 Gas Fields with Carbon Capture and Sequestration (CCS) in Malaysia. In Proceedings of the SPE Asia Pacific CCUS Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 26–27 August 2025; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA,, 2025. SPE-225836-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Offshore Energy. Malaysia: PETRONAS, Total to Study K5 Field Development—K5 Sour Gas up to ~70% CO2; Offshore Energy: Schiedam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- ERIA (Economic Research Institute for ASEAN and East Asia). Geological Storage Potential of CO2 in Southeast Asia—Malay, Sarawak, and Sabah Basins; ERIA Report; ERIA (Economic Research Institute for ASEAN and East Asia): Jakarta, Indonesia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Ansari, U. From CO2 Sequestration to Hydrogen Storage:Further Utilzation of Depleted Gas Reservoir. Reserv. Sci. 2025, 1, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Lv, M.; Li, C.; Sun, Q.; Wu, M.; Xu, C.; Dou, J. Effects of Crosslinking Agents and Rservoir Conditions on the Propagation of Fractures in Coal Reservoirs During Hydraulic Fracturing. Reserv. Sci. 2025, 1, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyushin, Y.; Nosova, V.; Krauze, A. Application of Systems Analysis Methods to Construct a Virtual Model of the Field. Energies 2025, 18, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggs, H.D. Production Optimization Using Nodal Analysis; OGCI Publications: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, T. Reservoir Engineering Handbook, 5th ed.; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. IPCC Special Report on Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y. A Study on CO2 Injectivity with Nodal Analysis in Depleted Oil and Gas Reservoirs. Master’s Thesis, Dong-A University, Busan, Republic of Korea, 2023. Available online: https://www.riss.kr/link?id=T16944284 (accessed on 10 October 2025). (In Korean).
- Lee, J.-H.; Park, Y.-C.; Kwon, S.-I.; Lee, Y.-S.; Wang, J.-H.; Jang, Y.-H.; Son, H.-A.; Jang, H.-C.; Sung, W.-M. CCS—Geological Storage Technology for Carbon Neutrality Era; CIR: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2022; ISBN 979-11-6856-069-7. Available online: https://product.kyobobook.co.kr/detail/S000061585389 (accessed on 12 October 2025). (In Korean)
- Al-Hussainy, R.; Ramey, H.J.; Crawford, P.B. The Flow of Real Gases Through Porous Media. J. Pet. Technol. 1966, 18, 624–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Lyons, W.C.; Ghalambor, A. Petroleum Production Engineering: A Computer-Assisted Approach; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hagedorn, A.R.; Brown, K.E. Experimental Study of Pressure Gradients Occurring During Continuous Two-Phase Flow in Small-Diameter Vertical Conduits. J. Pet. Technol. 1965, 17, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dake, H.P. Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, C. A Novel Approach to Production Allocation for Multi-Layer Commingled Tight Gas Wells: Insights from the Ordos Basin, NW China. Energies 2025, 18, 456. Available online: https://doi.org/10.3390/en18030456 (accessed on 10 November 2025). [CrossRef]
- Rutqvist, J. The Geomechanics of CO2 Storage in Deep Sedimentary Formations. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2012, 30, 525–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscheck, T.A.; Bielicki, J.M.; White, J.A.; Sun, Y.; Hao, Y.; Bourcier, W.L.; Carroll, S.A.; Aines, R.D. Pre-Injection Brine Production in CO2 Storage Reservoirs: An Approach to Augment the Development, Operation, and Performance of CCS While Generating Water. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2016, 54, 499–512. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijggc.2016.04.018 (accessed on 10 November 2025). [CrossRef]
- Michael, K.; Neal, P.R.; Allinson, G.; Ennis-King, J.; Hou, W.; Paterson, L.; Sharma, S.; Aiken, T. Injection Strategies for Large-Scale CO2 Storage Sites. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 4267–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachu, S. Review of CO2 Storage Efficiency in Deep Saline Aquifers. Int. J. Greenhouse Gas Control 2015, 40, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, S.M.; Cole, D.R. CO2 Sequestration in Deep Sedimentary Formations. Elements 2008, 4, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valluri, M.; Mishra, S.; Ravi Ganesh, P. Injectivity Index: A Powerful Tool for Characterizing CO2 Storage Reservoirs—A Technical Note. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, M.; De Gennaro, V.; Dumont, H.; Gisolf, A.; Dubost, F.-X. A New Method for CO2 Injectivity Evaluation: Feasibility Modeling and Sensitivity Analysis. In Proceedings of the GHGT-17, Calgary, AB, Canada, 20–24 October 2024; SSRN: Rochester, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]


| Input Variable | Input Value | Input Variable | Input Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reservoir depth (m) | 1611~1675 | Tubing size (inch) | 3.548 |
| Reservoir thickness (ft) | 209.97 | Borehole diameter (inch) | 12.5 |
| Initial reservoir pressure (psia) | 3600 | AOF (MMscfd) | 253 |
| Reservoir temperature (°F) | 230 | Reservoir permeability (md) | 10.5 |
| Input Variable | Input Value |
|---|---|
| Injection pressure (psia) | 1100/1650/2000 |
| Tubing size (ID, inch) | 1.548/2.548/3.548/4.548/5.548 |
| Reservoir pressure at injection (psia) | 1000/1250/1500/1750/2000 |
| Reservoir permeability (md) | 1/5/10/40/80/160 |
| Well 1 | Well 2 | Well 3 | Well 4 | Well 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reservoir depth (top, ft) | 4734.595 | 4764.602 | 4744.587 | 4719.587 | 4694.587 |
| Reservoir thickness (ft) | 150 | 209.97 | 250 | 300 | 350 |
| Permeability (md) | 25 | 10.5 | 20 | 15 | 5 |
| Flow efficiency (ft·md) | 3750 | 2204.69 | 5000 | 4500 | 1750 |
| Injection rate allocation (%) | 21.79 | 12.81 | 29.06 | 26.15 | 10.17 |
| Total Injection Rate (MMscfd) | Well 1 | Well 2 | Well 3 | Well 4 | Well 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1 (20 year) | 684.94 | 149.29 | 87.78 | 199.05 | 179.15 | 69.67 |
| Scenario 2 (15 year) | 913.23 | 199.05 | 117.03 | 265.4 | 238.86 | 92.89 |
| Scenario 3 (10 year) | 1369.87 | 298.58 | 175.54 | 398.11 | 358.3 | 139.34 |
| Scenario 4 (5 year) | 2739.73 | 597.16 | 351.08 | 796.22 | 716.59 | 278.68 |
| Injection Pressure (psia) | Tubing Size (ID, inch) | Reservoir Pressure at CO2 Injection (psia) | Reservoir Permeability (md) | Reservoir Thickness (ft) | Bottomhole Pressure (psia) | CO2 Injection Rate (MMscfd) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1100 | 3.548 | 1500 | 10 | 196.85 | 2147.13 | 52.30 |
| 1650 | 2716.59 | 68.50 | ||||
| 2000 | 2886.26 | 77.60 | ||||
| 1100 | 1.548 | 1500 | 10 | 196.85 | 1658.53 | 9.10 |
| 2.548 | 2005.61 | 28.92 | ||||
| 3.548 | 2417.13 | 52.30 | ||||
| 4.548 | 2708.16 | 68.73 | ||||
| 5.548 | 2852.08 | 76.90 | ||||
| 1100 | 3.548 | 1000 | 10 | 196.85 | 2122.73 | 64.54 |
| 1250 | 2273.78 | 58.59 | ||||
| 1500 | 2417.113 | 52.30 | ||||
| 1750 | 2551.42 | 45.46 | ||||
| 2000 | 2674.77 | 38.10 | ||||
| 1100 | 3.548 | 1500 | 1 | 196.85 | 2940.30 | 7.85 |
| 5 | 2739.08 | 33.60 | ||||
| 10 | 2441.87 | 51.08 | ||||
| 40 | 1841.34 | 74.24 | ||||
| 80 | 1681.83 | 79.13 | ||||
| 1100 | 3.548 | 1500 | 10 | 98.43 | 2744.36 | 33.20 |
| 147.64 | 2586.58 | 41.50 | ||||
| 196.85 | 2448.92 | 50.73 | ||||
| 295.28 | 2245.53 | 59.75 | ||||
| 393.7 | 2108.55 | 65.07 |
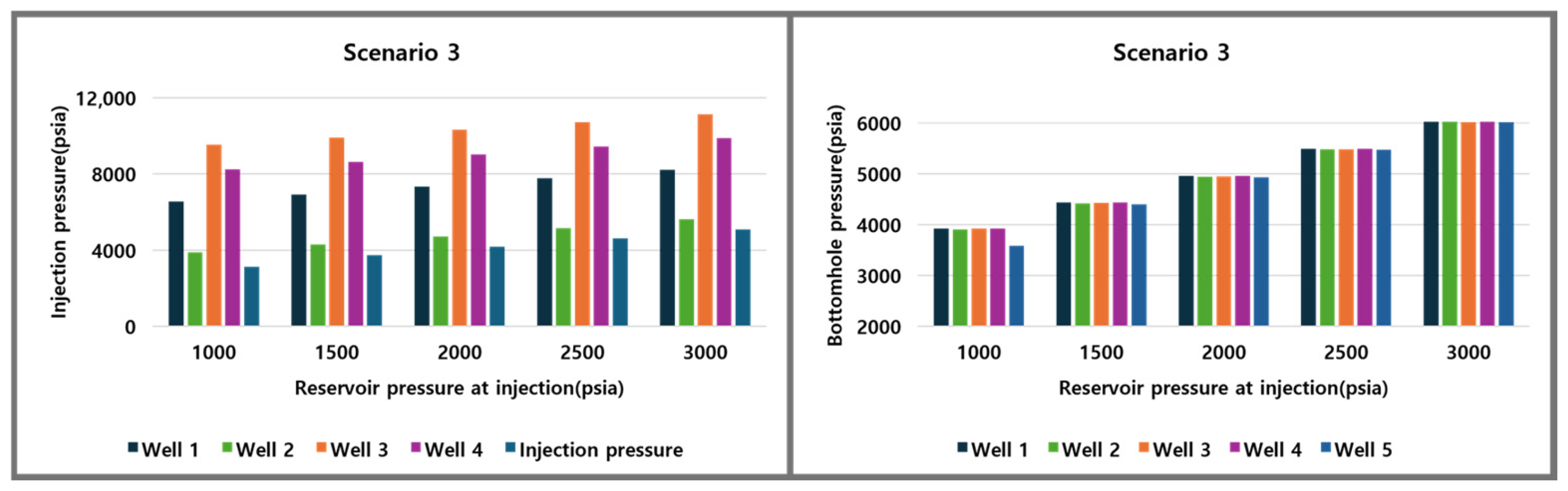
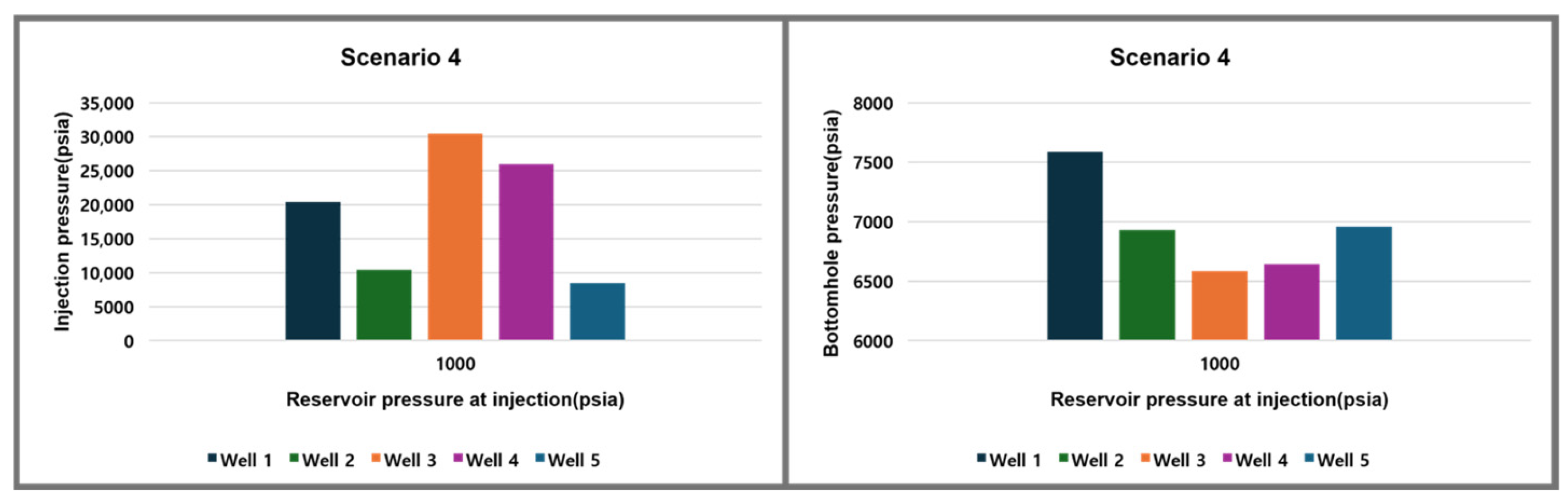
| Scenario | Well | Pres (psia) | Pi (psia) | Pwf (psia) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 1 | 1000 | 20,416.27 | 7586.24 |
| 2 | 1000 | 10,400.88 | 6931.76 | |
| 3 | 1000 | 30,503.19 | 6583.18 | |
| 4 | 1000 | 25,927.9 | 6644.86 | |
| 5 | 1000 | 8483.88 | 6956.55 |
| Scenario | Well | Pres (psia) | Pi (psia) | Pwf (psia) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
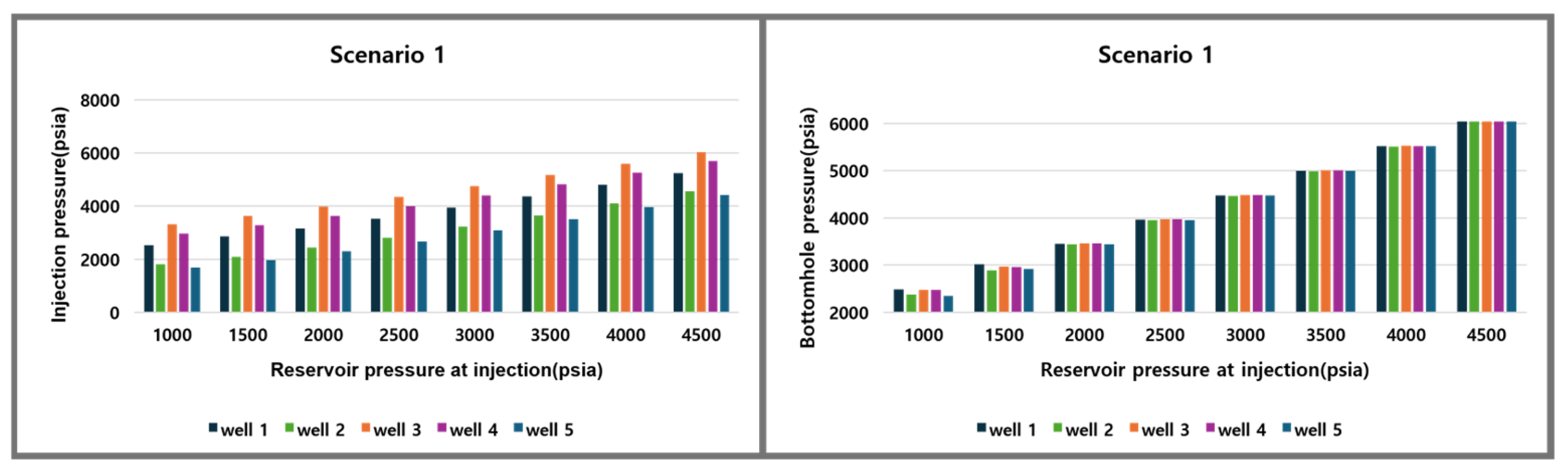
| 1 | 1 | 1000 | 2525.73 | 2486.13 |
| 1500 | 2856.59 | 3015.96 | ||
| 2000 | 3157.47 | 3452.20 | ||
| 2500 | 3534.20 | 3962.15 | ||
| 3000 | 3938.14 | 4478.74 | ||
| 3500 | 4360.35 | 4998.14 | ||
| 4000 | 4795.88 | 5519.12 | ||
| 4500 | 5241.81 | 6041.17 | ||
| 2 | 1000 | 1807.99 | 2374.76 | |
| 1500 | 2082.05 | 2891.40 | ||
| 2000 | 2439.40 | 3438.89 | ||
| 2500 | 2814.71 | 3950.75 | ||
| 3000 | 3222.51 | 4469.27 | ||
| 3500 | 3652.06 | 4990.82 | ||
| 4000 | 4097.52 | 5514.68 | ||
| 4500 | 4554.19 | 6038.96 | ||
| 3 | 1000 | 3309.73 | 2471.37 | |
| 1500 | 3628.89 | 2964.37 | ||
| 2000 | 3975.71 | 3460.57 | ||
| 2500 | 4355.01 | 3970.66 | ||
| 3000 | 4754 | 4486.85 | ||
| 3500 | 5169.52 | 5004.95 | ||
| 4000 | 5599.52 | 5525.45 | ||
| 4500 | 6035.08 | 6045.03 | ||
| 4 | 1000 | 2969.64 | 2478.27 | |
| 1500 | 3277.78 | 2959.89 | ||
| 2000 | 3624.27 | 3458.65 | ||
| 2500 | 4001.65 | 3968.99 | ||
| 3000 | 4403.76 | 4483.63 | ||
| 3500 | 4822.73 | 5003.06 | ||
| 4000 | 5252.06 | 5522.83 | ||
| 4500 | 5694.66 | 6043.93 | ||
| 5 | 1000 | 1678.05 | 2343.27 | |
| 1500 | 1962.88 | 2914.81 | ||
| 2000 | 2299.49 | 3442.34 | ||
| 2500 | 2647.05 | 3955.56 | ||
| 3000 | 3083.74 | 4474.92 | ||
| 3500 | 3516.13 | 4997.22 | ||
| 4000 | 3964.18 | 5520.73 | ||
| 4500 | 4424.48 | 6046.13 |
| Scenario | Well | Pres (psia) | Pi (psia) | Pwf (psia) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
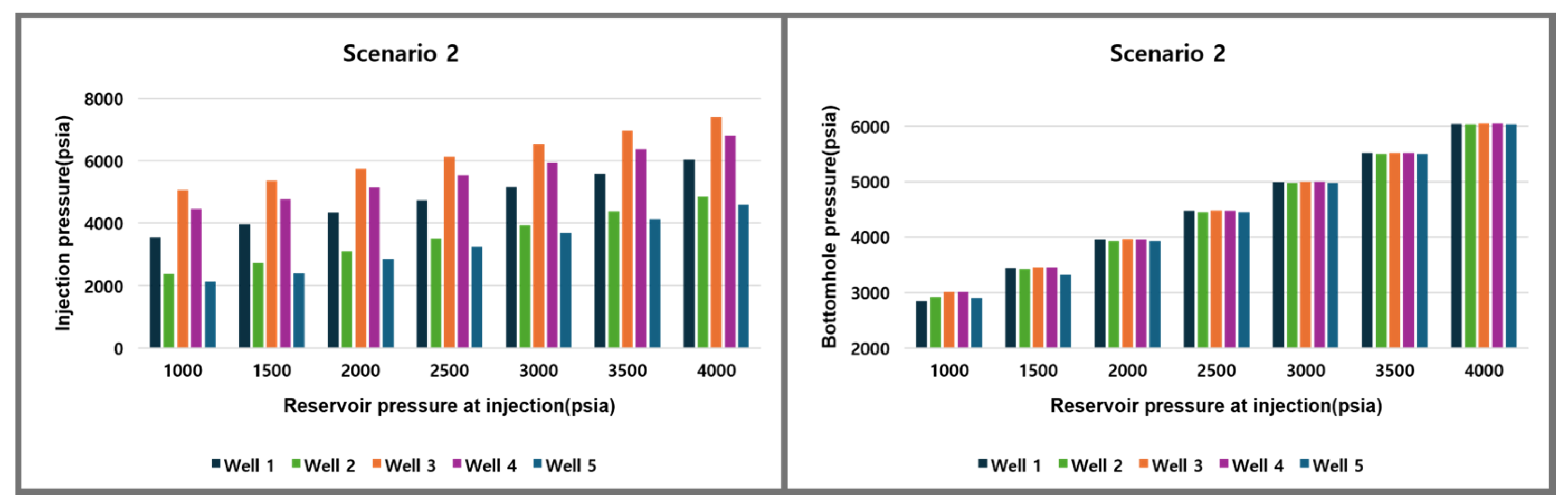
| 2 | 1 | 1000 | 3548.69 | 2845.85 |
| 1500 | 3963.45 | 3443.39 | ||
| 2000 | 4340.28 | 3951.30 | ||
| 2500 | 4741.16 | 4470.69 | ||
| 3000 | 5160.92 | 4994.26 | ||
| 3500 | 5593.98 | 5518.81 | ||
| 4000 | 6035.26 | 6045.24 | ||
| 2 | 1000 | 2387.96 | 2923.14 | |
| 1500 | 2722.16 | 3422.46 | ||
| 2000 | 3095.11 | 3930.35 | ||
| 2500 | 3503.17 | 4452.01 | ||
| 3000 | 3934.21 | 4978.78 | ||
| 3500 | 4380.77 | 5507.71 | ||
| 4000 | 4838.17 | 6037.09 | ||
| 3 | 1000 | 5064.04 | 3016.22 | |
| 1500 | 5371.51 | 3453.47 | ||
| 2000 | 5745.11 | 3961.22 | ||
| 2500 | 6139.08 | 4478.76 | ||
| 3000 | 6551.27 | 5001.31 | ||
| 3500 | 6973.09 | 5524.70 | ||
| 4000 | 7405.59 | 6048.59 | ||
| 4 | 1000 | 4460.45 | 3014.83 | |
| 1500 | 4767.52 | 3450.90 | ||
| 2000 | 5140.53 | 3957.20 | ||
| 2500 | 5539.45 | 4476.40 | ||
| 3000 | 5953.42 | 4999.29 | ||
| 3500 | 6380.46 | 5523.03 | ||
| 4000 | 6816.19 | 6047.82 | ||
| 5 | 1000 | 2139.33 | 2909.78 | |
| 1500 | 2407.61 | 3327.12 | ||
| 2000 | 2842.81 | 3926.53 | ||
| 2500 | 3251.49 | 4447.90 | ||
| 3000 | 3684.86 | 4975.41 | ||
| 3500 | 4135.41 | 5506.27 | ||
| 4000 | 4596.38 | 6036.73 |
| Scenario | Well | Pres (psia) | Pi (psia) | Pwf (psia) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 1 | 1000 | 6547.42 | 3926.08 |
| 1500 | 6929.89 | 4434.79 | ||
| 2000 | 7343 | 4963.72 | ||
| 2500 | 7767.11 | 5495.91 | ||
| 3000 | 8202.85 | 6029.78 | ||
| 2 | 1000 | 3895.68 | 3906.10 | |
| 1500 | 4290.83 | 4415.78 | ||
| 2000 | 4715.40 | 4944.95 | ||
| 2500 | 5160.15 | 5483.04 | ||
| 3000 | 5617.89 | 6022.21 | ||
| 3 | 1000 | 9535.76 | 3923.72 | |
| 1500 | 9909.90 | 4430.86 | ||
| 2000 | 10,306.14 | 4955.80 | ||
| 2500 | 10,715.36 | 5482.89 | ||
| 3000 | 11,132.72 | 6011.49 | ||
| 4 | 1000 | 8250.50 | 3926.60 | |
| 1500 | 8628.83 | 4434.27 | ||
| 2000 | 9031.30 | 4960.98 | ||
| 2500 | 9448.73 | 5491.75 | ||
| 3000 | 9872.61 | 6021.82 | ||
| 5 | 1000 | 3446.66 | 3586.78 | |
| 1500 | 3742.50 | 4404.27 | ||
| 2000 | 4171.61 | 4934.34 | ||
| 2500 | 4624.12 | 5476.20 | ||
| 3000 | 5088.10 | 6016.82 |
| Well 1 (psia) | Well 2 (psia) | Well 3 (psia) | Well 4 (psia) | Well 5 (psia) | Average (psia) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1 (20 year) | 4264.5 | 4239.5 | 4229.0 | 4231.0 | 4239.0 | 4240.6 |
| Scenario 2 (15 year) | 3732.5 | 3743.0 | 3727.5 | 3728.5 | 3746.0 | 3735.5 |
| Scenario 3 (10 year) | 2750.5 | 2763.0 | 2763.0 | 2755.5 | 2770.5 | 2760.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, Y.; Kwon, S. Evaluation of CO2 Injectivity and Geological Storage Scenarios Using Nodal Analysis and Tubing Injectivity Index in a Depleted Gas Field in Malaysia. Energies 2025, 18, 5983. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18225983
An Y, Kwon S. Evaluation of CO2 Injectivity and Geological Storage Scenarios Using Nodal Analysis and Tubing Injectivity Index in a Depleted Gas Field in Malaysia. Energies. 2025; 18(22):5983. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18225983
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Yubin, and Sunil Kwon. 2025. "Evaluation of CO2 Injectivity and Geological Storage Scenarios Using Nodal Analysis and Tubing Injectivity Index in a Depleted Gas Field in Malaysia" Energies 18, no. 22: 5983. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18225983
APA StyleAn, Y., & Kwon, S. (2025). Evaluation of CO2 Injectivity and Geological Storage Scenarios Using Nodal Analysis and Tubing Injectivity Index in a Depleted Gas Field in Malaysia. Energies, 18(22), 5983. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18225983






