Abstract
4LiF-MM’2O4 composites were synthesized via the mechanical milling of LiF and MM’2O4 (M = Mn, Mg, Zn; M’ = Mn Fe) for 72 h. In the obtained composites, the XRD peak broadened because of the milling, and the composites possessed a rock-salt-type structure. During charge–discharge measurements at 0.1 C, composites with spinel materials containing Mg showed particularly high discharge capacities; the discharge capacity of 4LiF-MMn2O4 and 4LiF-MFe2O4 was 310 mAh/g and 309 mAh/g, respectively. The discharge voltage was approximately 3.2 V for 4LiF-MgMn2O4 and approximately 2.8 V for 4LiF-MgFe2O4, and 4LiF-MgMn2O4 composites had the highest energy densities, exceeding 1000 Wh/kg. During cycle characteristic measurements with a cutoff voltage of 4.8 V and 4.4 V, the initial capacity retentions at the 100th cycle were 11% and 79%, respectively. The Coulombic efficiency was also better at a cutoff voltage of 4.4 V than that of 4.8 V, indicating that electrolyte decomposition has a significant influence on the cycle characteristics. Additionally, composites were synthesized via mechanical milling using various molar ratios of LiF and MgMn2O4. In xLiF-MgMn2O4 (x ≥ 3), the discharge potential was approximately 3.2 V, and the discharge capacity was higher than 250 mAh/g. The highest discharge capacity was observed for 4LiF-MgMn2O4 among xLiF-MgMn2O4 (x ≥ 3) composites.
1. Introduction
Recently, it has been reported that oxides containing Li and transition elements or composites obtained via the mechanical milling of LiF and an oxide containing a transition metal with a planetary ball mill can function as a positive electrode active material for Li-ion secondary batteries [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. Among oxide active materials, a sample obtained via milling LiF and LiMoO2 has been reported to possess a discharge capacity of over 300 mAh/g and exhibit excellent battery characteristics [9]. In previous studies, we have shown that a mixture of LiF and NiO transforms to a solid solution with a rock-salt-type crystal structure via mechanical milling, and a sample milled for 72 h shows a discharge capacity higher than 200 mAh/g [10]. Composites of LiF and MnO, CoO, or NiO-MnO solid solutions also exhibit similar charge–discharge characteristics [1,11]. In these active materials, Li ions are desorbed and inserted during the charge–discharge process, and it has been confirmed that the oxidation number of transition elements increases or decreases accordingly. Because these composites are oxyfluorides, they have lower electronic conductivity than pure oxides and must be composited with conductive carbon to obtain sufficient charge–discharge characteristics. When Li-doped NiO is used as a source material, the conductivity is improved, and sufficient charge–discharge properties can be obtained, even when electrodes are prepared using the same procedure as that used for conventional cathode active materials, such as LiCoO2. For a composite obtained from LiF and Li-doped NiO, a discharge capacity of 247 mAh/g, which is 95% of the theoretical capacity (252 mAh/g), has been obtained [12]. However, when NiMn2O4, which is a spinel compound, is used as the transition metal oxide, a composite obtained by milling LiF and NiMn2O4 at a molar ratio of 4:1 exhibits a maximum discharge capacity exceeding 300 mAh/g [13]. One of the source materials was spinel oxide, but after mechanical milling, the XRD peak from the spinel structure disappeared, and a diffraction peak derived from the rock-salt structure, as seen in LiF-MO, was observed. This structural change is considered to be important for the development of charge–discharge characteristics. The direct compositing of LiF with NiO and Mn2O3, which are the raw materials of NiMn2O4, also affords charge and discharge characteristics, but the discharge capacity obtained is smaller than that of LiF- NiMn2O4. Clearly, the properties after milling depend on the state of the raw materials. In this composite, changes in the oxidation numbers of Ni and Mn occur during the charge–discharge process. Because the change in the oxidation number of Ni occurs at a relatively high potential, the upper potential limit for charging is high, leading to the degradation of the battery characteristics. In this study, we synthesized composites from oxides in which Ni in NiMn2O4 was substituted with other elements and investigated the effects of the substitution of the constituent elements on the electrochemical properties. The rate and cycle characteristics were evaluated for batteries using the 4LiF-MgMn2O4 composite, which exhibited the highest energy density among the obtained composites. The charge compensation mechanism of 4LiF-MgMn2O4 during the charge–discharge process was also investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
MM’2O4 (M = Mg, Zn; M’ = Mn, Fe) was obtained by milling equal amounts of MO and M’2O3 and calcining at 1073 K for 96 h in air. 4LiF-MMn2O4 (M = Mg, Mn, Zn) and 4LiF-MFe2O4 (M = Mg, Zn) composites were synthesized via the mechanical milling of LiF and spinel oxides at a molar ratio of 4:1. Composites were fabricated with mixing ratios ranging from 1:1 to 5:1 with respect to LiF and MgMn2O4. A planetary ball mill device (P-7; Fritsch Japan Co., Ltd., Yokohama, Japan) was used for milling, which was performed in an Ar atmosphere for 72 h at a rotation speed of 650 rpm. A zirconia vessel (volume of 30 mL) with 60 zirconia balls (5 mm in diameter) and 10 g of zirconia balls (2 mm in diameter) was used to perform mechanical milling. The obtained samples were characterized via XRD analysis and SEM. Powder XRD patterns were recorded using a Rigaku Rad-B system with Cu-Kα radiation. SEM (S-3000E; Hitachi High-Technologies Co., Tokyo, Japan) imaging was performed to observe the morphology of the samples. To confirm the redox current, cyclic voltammetry measurements were performed in the range of 2.0 to 4.8 V at a sweep rate of 0.5 mV/s. The charge–discharge measurements were performed at rates of 0.1 C using a stainless-steel cell for voltages of 2.0–4.4 and 4.8 V (versus Li/Li+). The test cell consisted of a positive electrode sheet composed of the obtained composite, a piece of Li foil as the anode, and 1 M LiPF6-EC/DEC (1:1 volume ratio) as the electrolyte. A cathode sheet was prepared using the fabricated composite (60 wt.%), KETJENBLACK (30 wt.%), and PVDF (10 wt.%). To obtain a sufficient electronic conductivity, the composites and KETJENBLACK (Tokyo, Japan) were milled using a planetary ball mill at 300 rpm for 30 min. XPS was performed to examine the valence states of Mn and O; a Kratos AXIS ULTRA DLD system (Shimadzu Co., Kyoto, Japan) with a monochromatic Al Kα X-ray source was employed for this purpose.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRD Patterns and Crystal Structure
Figure 1 shows the XRD patterns of the synthesized spinel oxides MM’2O4 (M = Mg, Zn; M’ = Mn, Fe). The obtained compounds were objective spinel-type oxides [14,15,16,17,18]. A small diffraction peak from the source material Fe2O3 (indicated by “◆”) is observed in the pattern of MgFe2O4, and the peaks of Mg2MnO4 [19], which are indicated by the mark (▼) in the figure, are detected for MgMn2O4. Because a species with excess Mg was detected, composites were prepared with a reduced amount of Mg, and the peak of Mg2MnO4 was not observed for Mg:Mn = 0.78:2 (see Figure S1 in Supplementary Materials). However, in the following results, samples prepared with the original ratios were used to maintain the same elemental ratios as other spinels in the composite preparation process.
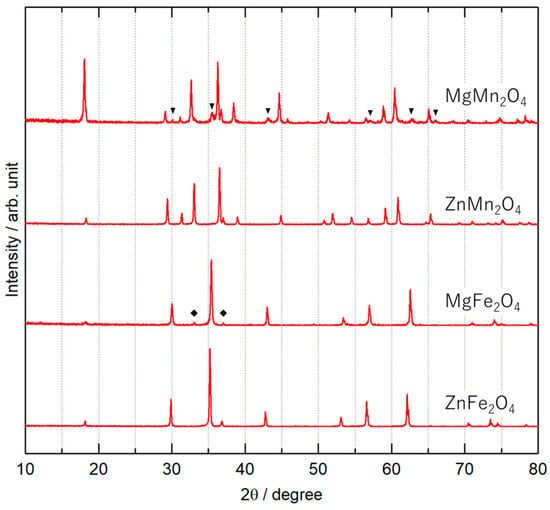
Figure 1.
XRD patterns of MM’2O4 (M = Mg, Zn; M’ = Mn, Fe).
Figure 2 shows the XRD patterns of the composites obtained by milling LiF and MM’2O4 (M = Mg, Zn, Mn; M’ = Mn, Fe) for 72 h. No peaks of LiF, which was the source material, were observed in the diffraction patterns of any of the obtained composites, and broad diffraction peaks were observed at approximately 2θ = 35° and 44°. These peaks are similar to those observed in composites, such as 4LiF-NiMn2O4, and can be regarded as the diffraction peaks of the obtained composites. The diffraction peaks of LiF-NiO also appear at similar angles and are attributed to the rock-salt-type material, suggesting that the obtained composites in this experiment also have a rock-salt-type structure. A small peak corresponding to MFe2O4 (M = Mg, Zn) was observed in the XRD pattern of the sample after milling with M’ = Fe. In our previous report on a 72 h-milled sample of 4LiF-NiMn2O4 (which showed good charge–discharge characteristics), diffraction peaks attributed to the source, i.e., NiMn2O4 were observed. It is likely that the composition of the sample obtained in this study is sufficiently advanced to the same magnitude as that of 4LiF-NiMn2O4. Considering the difference in M in 4LiF-MMn2O4, diffraction peaks are observed at the highest angle when M is Mn(II), suggesting that the unit cell is small. Next, the lattice is larger for Zn and Mg, wherein the lattice of Mg is larger than that of Zn, which is not consistent with the expected relationship between the lattice constants and ionic radii. For the 4LiF-MFe2O4, the lattice is also smaller in the M = Zn composite as shown in Figure 2, but the reasons for these trends are not clear. The XRD peaks characteristic of the composite were at 2θ = 35° and 44°. Simulations of the XRD patterns show that the ratio of the intensities of these peaks (I35/I44) is the largest for the M = Zn composites. The observed patterns were consistent with the simulation results, suggesting that the obtained composites had a rock-salt-type structure. The raw material transition metal oxides are spinel-type, but the anion arrangement of the spinel-type structure is the same as that of the rock-salt-type, with a cubic close-packed structure. It is likely that only the cation arrangement changed by the mechanical milling. Figure 3 shows SEM images of the calcined MgMn2O4 powder and 4LiF-MgMn2O4 composite after milling for 72 h. The MgMn2O4 particles were large as a result of the reaction and growth of the particles during the calcination process. In contrast, the composite exhibited smaller particles, with sizes ranging from 100 nm to 1 µm. The particle size also changed significantly with milling.

Figure 2.
XRD patterns of 4LiF-MMn2O4 (M = Mg, Zn, Mn) composites, 4LiF-MFe2O4 (M = Mg, Zn), and LiF.
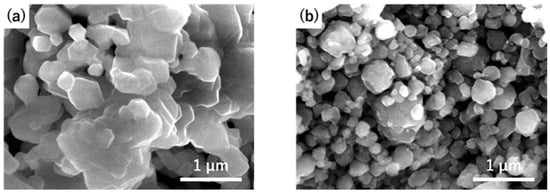
Figure 3.
SEM images of (a) MgMn2O4 obtained via calcination at 800 °C and (b) 4LiF-MgMn2O4 composites milled for 72 h.
3.2. Charge–Discharge and CV Measurements
The results of charge–discharge measurements for batteries using the synthesized composites, 4LiF-MMn2O4 (M = Mg, Mn, Zn) and 4LiF-MFe2O4 (M = Mg, Zn), as the cathode are shown in Figure 4, which shows the discharge curve for the 1st cycle at a rate of 0.1 C. Focusing on M, the discharge capacity in the M = Mg composite was large, exceeding 300 mAh/g, regardless of the central metal. The discharge capacities obtained for the M = Zn composite were relatively small, with values of 174 and 132 mAh/g for 4LiF-ZnMn2O4 and 4LiF-ZnFe2O4, respectively. Discharge capacities exceeding 200 mAh/g were obtained for the M = Mn composite (4LiF-Mn3O4). The 4LiF-Mn3O4 composite had a discharge capacity that is approximately 2/3 of the theoretical capacity, but 4LiF-MgMn2O4 had a discharge capacity that is 87% of the theoretical capacity, suggesting that the majority of the contained Li ions are desorbed and inserted through the charge–discharge reaction. As mentioned above, a discharge capacity exceeding 300 mAh/g was obtained for the M = Mg composites. Under the same measurement conditions, this value is the largest discharge capacity among a series of LiF and spinel oxide composites, including the previously reported M = Ni composite. One possible reason for this is that the discharge capacity per active material mass increases in composites with M = Mg, which is a lighter element, compared with M = Zn or Mn. Comparing Figure 4a,b, the voltage during discharge was generally higher when the trivalent metal in the obtained composites was Mn. This is due to the difference in the redox potential between Fe and Mn, as shown in the following cyclic voltammetry, where the composite with Mn as the transition metal species had the higher discharge voltage.
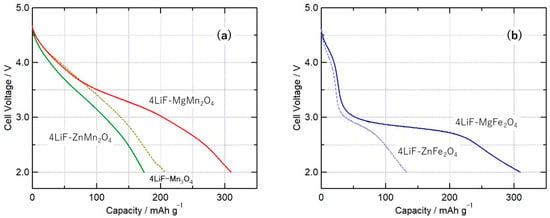
Figure 4.
Discharge curves of (a) 4LiF-MMn2O4 (M = Mg, Mn, Zn) and (b) 4LiF-MFe2O4 (M = Mg, Zn) composites milled for 72 h, at 0.1 C for the voltage range of 2.0–4.8 V.
Table 1 summarizes the average voltage, discharge capacity, and energy density (per cathode weight) observed during the discharge process for batteries using the composite cathode. The discharge capacities of 4LiF-MgMn2O4 and 4LiF-MgFe2O4 were approximately equal, and as a result of the difference in discharge potentials, 4LiF-MgMn2O4 had the highest energy density, with values exceeding 1000 Wh/kg. Figure 5 shows the cyclic voltammograms of 4LiF-MgMn2O4 and 4LiF-MgFe2O4. For 4LiF-MgFe2O4, a large reduction current peak was observed at 2.3 V, and for 4LiF-MgMn2O4, a reduction current peak was observed at approximately 3.1 V. This is consistent with the fact that the average discharge voltage of the battery with 4LiF-MgMn2O4 is higher than that of 4LiF-MgFe2O4. The reduction current peak changes abruptly in 4LiF-MgFe2O4, corresponding to a small voltage change during the discharge process for 4LiF-MgFe2O4. In 4LiF-MgFe2O4, oxidation current peaks were observed at 2.7 V and above 4.2 V, where the oxidation current at 2.7 V was small and the current above 4.2 V was large. An oxidation current above 4 V was also observed in previously reported compounds and is considered to indicate the hysteresis of the valence change of Fe [20]. In 4LiF-MgMn2O4, the oxidation current peak was at approximately 3.6 V, and the oxidation current was observed over a wide range; a relatively large oxidation current was observed at potentials higher than 4.5 V. This oxidation current at high potentials is considered to correspond to the decomposition of the electrolyte, as also observed in LiF-NiO and 4LiF-NiMn2O4. However, the charge–discharge capacity of 4LiF-MgMn2O4 cannot be explained only by the capacity resulting from the valence change of Mn, suggesting the possibility that the oxidation current resulting from the valence change of oxide ions is included, as previously reported for active materials containing Mn and others [21,22,23].

Table 1.
Discharge properties of batteries prepared with the obtained composites as the cathode. The capacity ratio is the percentage of the experimental discharge capacity (1st) relative to the theoretical capacity.
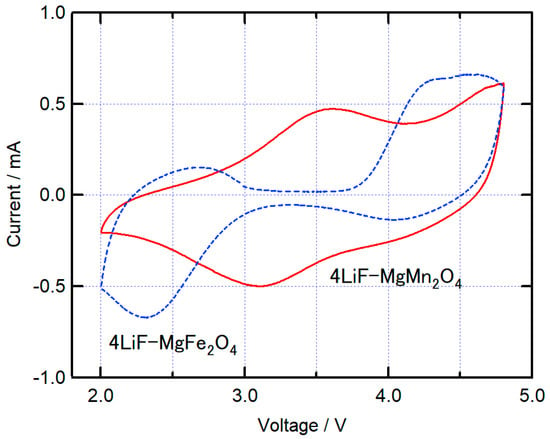
Figure 5.
Cyclic voltammograms of 4LiF-MgMn2O4 and 4LiF-MgFe2O4 composites at a scan rate of 0.5 mV s−1.
3.3. XPS Spectra
XPS measurements were performed to investigate the ionic state of the 4LiF-MgMn2O4 composite, which had the highest energy density during the charge–discharge process. The obtained spectra are shown in Figure 6. Figure 6a,b show the Mn 2p and Li 1s spectra, respectively. Figure 6a(i–v),b(i–v) show the charging and discharging states of the samples: (i) before charge/discharge measurement, (ii) after charging, (iii) after half discharge, (iv) after full discharge, and (v) after half-charge (2nd cycle) of the cathode sheets. As shown in spectrum (i) of Figure 6a, a peak is observed at 642 eV in the spectrum of Mn 2p before the charge–discharge measurement, confirming that the Mn ions in the composite are Mn3+ ions, as expected from the spinel, which is the source material of the composite. A shift in the peak to 643.1 eV is observed with charging, indicating the formation of Mn4+ (spectrum (ii)) [24,25]. For the cathode after the half-discharge process, the intensity of the spectrum corresponding to Mn3+ increased (spectrum (iii)), and after discharge (spectrum (iv)), a similar Mn3+ peak was observed before charge. When half-charged in the next charge process (spectrum (v)), a shift in the peak to a higher energy side can be observed, suggesting that Mn4+ was regenerated. In the Li 1s spectrum, a peak is observed at 56.1 eV as shown in (i) of Figure 6b, indicating the presence of Li ions [26]. Because Li ions are desorbed from the active material via charging, the peak intensity of Li decreases, and the spectrum is almost unidentifiable at full charge (ii). The intensity of the peak recovers with discharge (iii), and a spectrum similar to that before the charge–discharge measurement was obtained at the end of discharge (iv), as shown in Figure 6b. In the next charge process, a decrease in the Li 1s peak intensity was observed again (v). The O 1s spectrum is shown in Figure S2 in the Supplementary Materials, where a peak shift corresponding to the change in Mn oxidation state was observed. It was confirmed that the charge–discharge process of this composite proceeds with the valence of the transition metal species, Mn ions, through the desorption and insertion of Li ions, similar to that of the conventional cathode active materials of Li-ion secondary batteries and LiF-NiO composites.
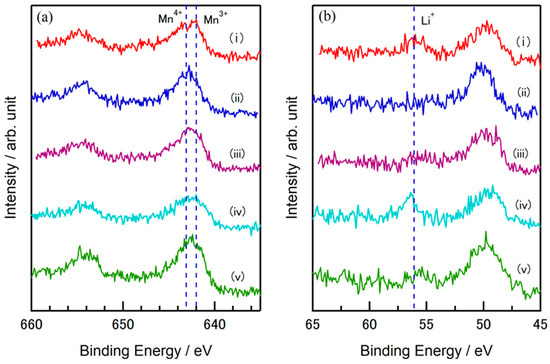
Figure 6.
(a) Mn 2p and (b) Li 1s XPS spectra of the 4LiF-MgMn2O4 composite obtained (i) before charge, (ii) after charge, (iii) after half discharge, (iv) after full discharge, and (v) after 2nd half charge processes.
3.4. Cycling Performance
Figure 7 shows the cycle characteristics of 4LiF-MgMn2O4 measured at different upper voltage limits. In the cycle characteristics with an upper cutoff limit of 4.8 V, shown in Figure 7a, the discharge capacity decreased significantly with the number of cycles, reaching 70% and 29% of the initial discharge capacity at the 20th and 50th cycles, respectively. The discharge capacity at the 100th cycle was very small compared with the initial capacity, i.e., 29.9 mAh/g, which was 11% of the initial capacity. The Coulombic efficiencies varied slightly but were generally between 95% and 100%. In contrast, the cycle characteristics with an upper cut-off voltage of 4.4 V, as shown in Figure 7b, maintained 96% and 92% of the initial discharge capacity at the 20th and 50th cycles, respectively, and the discharge capacity at the 100th cycle was 124 mAh/g (79% of the initial capacity). The Coulombic efficiencies for an upper cut-off voltage of 4.4 V were improved compared with those for the cutoff voltage of 4.8 V and were generally higher than 97%. During charge–discharge measurements at the upper cutoff limit of 4.8 V, the charge capacity increased, and the discharge capacity obtained was also large; however, similar to the LiF-NiO and 4LiF-NiMn2O4 composites, the decomposition of the electrolyte occurred simultaneously, and a decrease in the Coulombic efficiency and cycle characteristics was observed. Although the initial capacity was small to be 157 mAh/g with the upper cutoff voltage of 4.4 V, the cycle characteristics and Coulombic efficiency improved. Electrolyte decomposition is the main factor in cycle characteristic degradation, and the use of electrolytes with a wide potential window may improve the cycle characteristics while maintaining a high discharge capacity.
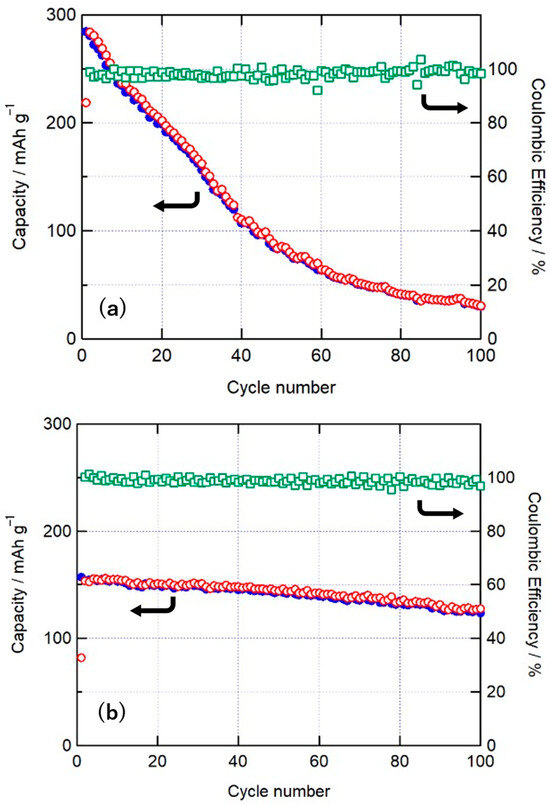
Figure 7.
Charge (○) and discharge (●) capacity and Coulombic efficiency (□) of the 4LiF-MgMn2O4 composites for voltages of (a) 2.0–4.8 V and (b) 2.0–4.4 V.
3.5. Molar Ratio of LiF and MgMn2O4
Figure 8 shows the XRD patterns of the xLiF-MgMn2O4 composites synthesized by varying the molar ratio of LiF to MgMn2O4 from 1:1 to 5:1. In LiF-MgMn2O4 (LiF:MgMn2O4 = 1:1) and 2LiF-MgMn2O4 (2:1), diffraction peaks of MgMn2O4 were observed, and diffraction peak of LiF at 5:1. The peaks of such unreacted materials, if observed, are very small, and broad diffraction peaks originating from the rock-salt-type structure are clearly observed for all composites with x = 1 to 5 compositions. The intensity ratios of the peaks observed at approximately 2θ = 35° and 44° depend on the ratio of the number of electrons in the cation and anion sites. For this variation in composition, a relative decrease in the peak intensity at 35° is observed for composites with a higher ratio of LiF, which is in good agreement with the simulation results of the XRD patterns of xLiF-MgMn2O4. The diffraction peaks shifted to higher angles with increasing LiF ratio, indicating that LiF and MgMn2O4 formed a rock-salt-type composite via milling in all the synthesized composites.
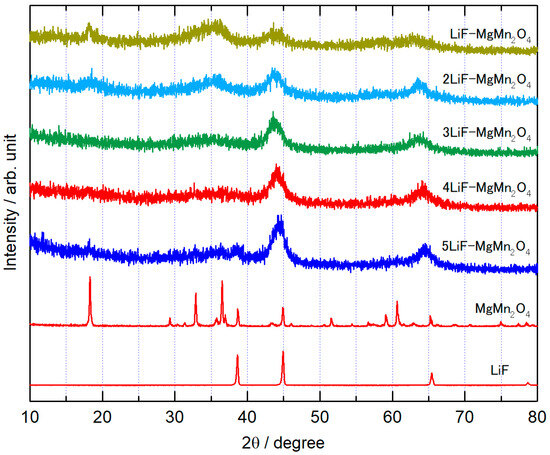
Figure 8.
XRD patterns of xLiF-MgMn2O4 composites (x = 1–5), LiF, and MgMn2O4.
Figure 9 shows the (a) cyclic voltammograms and (b) discharge curves of batteries prepared with xLiF-MgMn2O4 as the cathode. The oxidation and reduction current peaks shifted to higher potentials as x increased from 1 to 3, as shown in Figure 9a. This suggests that the redox potential increases because of the increase in the ratio of F− ions among the anions that constitute the composite. This tendency is consistent with that observed for other cathode active materials, such as LiVPO4F and Li2CoPO4F, and is attributed to the higher redox potential of transition metal ions during the charge–discharge process because of the larger electronegativity of the anions [27,28]. For composites with x = 1 or 2, a peak in oxidation current at approximately 3.0 to 3.3 V and a peak in reduction current below 2.7 V were observed, and the current was smaller than that of other compositions. The peak of oxidation current and reduction current was observed above 3.5 V and 3.1 V, respectively, when x was higher than 3. Although there was some shift with the changes in composition, the amount of shift was smaller than that for x between 1 and 3. During the charge–discharge measurements of batteries using these composites as cathodes, the discharge capacities for x = 1 and 2 were less than 250 mAh/g, as shown in Figure 9b. The discharge potential was lower than that of the composites with x higher than 3, which is consistent with the CV measurement results shown in Figure 9a. For composites with x ≥ 3, the discharge potential was approximately 3.2 V, and the discharge capacity was the highest at x = 4. For a series of composites, such as LiF-NiO and 4LiF-NiMn2O4, composites with equal amounts of O and F ions often show the highest discharge capacity, and the composites synthesized in this study showed similar results [8,10,13].
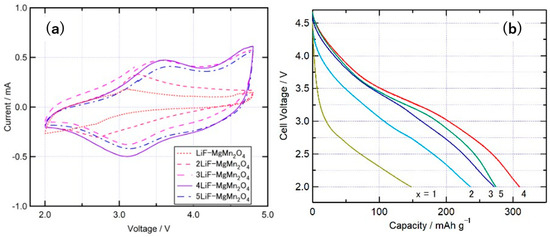
Figure 9.
(a) Cyclic voltammograms at a scan rate of 0.5 mV s–1, and (b) charge–discharge curves of xLiF-MgMn2O4 composites (x = 1–5).
4. Conclusions
Composite compounds were obtained by mechanical milling LiF and several spinel-type oxides. From XRD measurements, although the diffraction peaks were broadened via mechanical milling, all the obtained composites were found to possess a rock-salt-type structure. During the charge–discharge measurements of the composite, the discharge voltage was approximately 3.3 V for 4LiF-MMn2O4 and approximately 2.7 V for 4LiF-MFe2O4. Regarding the discharge capacity, a capacity exceeding 300 mAh/g was obtained for the M = Mg composite with the raw materials MMn2O4 and MFe2O4, and the capacity was lower for M = Zn. Therefore, the 4LiF-MgMn2O4 composite exhibited the highest energy density, exceeding 1000 Wh/kg. XPS measurement of 4LiF-MgMn2O4 confirmed that the valence change of the Mn ion and the desorption/insertion of Li ions occurred during the charge and discharge processes. During the measurement of cycle characteristics, when the upper limit voltage for charging was set at 4.8 V, although the discharge capacity was high for the first cycle, the initial capacity retention at the 100th cycle was 11%. In contrast, when the upper voltage limit was set to 4.4 V, the initial capacitance decreased to approximately 150 mAh/g, but the initial capacity retention improved to 79% at the 100th cycle. The Coulombic efficiency was also better at the upper cutoff limit of 4.4 V, indicating that electrolyte decomposition has a significant influence on the cycle characteristics. Furthermore, xLiF-MgMn2O4 composites were synthesized via mechanical milling with various molar ratios of LiF and MgMn2O4. In all composites, XRD peaks originating from the rock-salt-type structure were observed, as in the other composites. The continuous shift in the diffraction peaks with respect to the change in the ratio indicates that the composition of the source material corresponds to that of the composite. In xLiF-MgMn2O4, the discharge potential and discharge capacity were small at x = 1 and x = 2, respectively; the discharge potential was approximately 3.3 V, and the discharge capacity was over 250 mAh/g at x ≥ 3. The highest discharge capacity was found for 4LiF-MgMn2O4, and the same trend was observed for xLiF-MgMn2O4 composites. As in the previous series of composites, the highest discharge capacity was observed when the amounts of F and O ions, which are the anion species contained in the composite, were equal.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/en18215764/s1, Figure S1: XRD patterns of Mg0.78Mn2O4 and MgMn2O4; Figure S2: O 2p 1s XPS spectra of the 4LiF-MgMn2O4 composite.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Y.T.; methodology: Y.T. and Y.Y.; validation: Y.T., Y.Y. and Y.K.; formal analysis: Y.T. and Y.K.; investigation: Y.T., Y.Y. and Y.I.; data curation: Y.T., Y.Y. and Y.I.; writing—original draft preparation: Y.T.; writing—review and editing: Y.T. and Y.K.; visualization: Y.T. and Y.Y.; supervision: Y.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP26420722.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jung, S.-K.; Jung, S.-K.; Kim, H.; Cho, M.G.; Cho, S.-P.; Lee, B.; Kim, H.; Park, Y.-U.; Hong, J.; Park, K.-Y.; et al. Lithium-free transition metal monoxides for positive electrodes in lithium-ion batteries. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 16208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.Y.; Ren, S.H.; Knapp, M.; Wang, D.; Witter, R.; Fichtner, M.; Hahn, H. Disordered Lithium-Rich Oxyfluoride as a Stable Host for Enhanced Li+ Intercalation Storage. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1401814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, C.; Berg, E.; Tarascon, J.M. Triggering the In Situ Electrochemical Formation of High Capacity Cathode Material from MnO. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, C.; Källquist, I.; Chable, J.; Chang, J.H.; Johnsen, R.E.; Ruiz-Zepeda, F.; Mba, J.-M.A.; Naylor, A.J.; Garcia-Lastra, J.M.; Vegge, T.; et al. Improved cycling stability in high-capacity Li-rich vanadium containing disordered rock salt oxyfluoride cathodes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 21244–21253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitajou, A.; Kobayashi, E.; Okada, S. Electrochemical Performance of a Novel Cathode material “LiFeOF” for Li-ion Batteries. Electrochemistry 2015, 83, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kitajou, A.; Ishado, Y.; Inoishi, A.; Okada, S. Amorphous xLiF-FeSO4 (1 ≤ x ≤ 2) composites as a cathode material for lithium ion batteries. Solid State Ion. 2018, 326, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Liang, Z.; Chen, H.; Xu, G.; Song, H. V2O3–Li3PO4 Composite: A New Type of Cathodic Active Material for Li-Ion Batteries. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2101955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, A.; Ugata, Y.; Ikeuchi, I.; Hibino, M.; Nakura, K.; Miyaoka, Y.; Kawamura, I.; Shibata, D.; Ohta, T.; Yabuuchi, N. Durable Manganese-Based Li-Excess Electrode Material without Voltage Decay: Metastable and Nanosized Li2MnO1.5F1.5. ACS Energy Lett. 2023, 8, 2753–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, N.; Hoshino, S.; Xie, L.; Chen, S.; Ikeuchi, I.; Natsui, R.; Nakura, K.; Yabuuchi, N. Reversible Li storage for nanosize cation/anion-disordered rocksalt-type oxyfluorides: LiMoO2—x LiF (0 ≤ x ≤ 2) binary system. J. Power Sources 2017, 367, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y.; Nasu, H.; Izumi, Y.; Arai, J.; Otsuka, S.; Yamane, Y.; Yamada, K.; Kohno, Y.; Kobayashi, K. Synthesis and charge-discharge properties of LiF-NiO composite as a cathode material for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2016, 329, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y.; Kimura, N.; Nasu, H.; Kohno, Y. Fabrication and charge–discharge properties of composites of LiF and NixMn1−xO solid solution for cathode material of Li-ion secondary battery. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2020, 50, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y.; Kimura, N.; Nasu, H.; Izumi, Y.; Arai, J.; Yamane, Y.; Yamada, K.; Kohno, Y.; Kobayashi, K. Effects of Li-doped NiO on the charge–discharge properties of LiF–NiO composites used as cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2017, 47, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y.; Kimura, N.; Izumi, Y.; Arai, J.; Kohno, Y.; Kobayashi, K. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of 4LiF-NiMn2O4 composite as a cathode material for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2017, 354, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, K.S.; Sinha, A.P.B.; Biswas, A.B. Crystal distortion in spinels containing Mn3+ ions. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1960, 17, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, L.; Xiao, X.; Hu, Z.; Han, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D.F.; Liu, X.F. The effects of Co doping on the crystal structure and electrochemical performance of Mg(Mn2 − xCox)O4 negative materials for lithium ion battery. Solid State Sci. 2015, 39, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-D.; Wu, Z.-S.; Zang, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.-D. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline Zn–Mn spinel. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2007, 68, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidya, Y.S.; Manjunatha, H.C.; Sridhar, K.N. Comparative study of multi functional nanoferrites for radiation shielding, photoluminescence and antibacterial properties. Inorg. Chem. Com. 2022, 138, 109217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapat, P.; Dhaka, S.; Mund, H.S. Investigation of the influence of annealing temperature on the structural and magnetic properties of MgFe2O4. J. Electron. Mat. 2021, 50, 4671–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Ai, L.; Ding, J.; Zhu, P.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; Jiang, H.; Yu, F.; et al. Synthesis, Electronic Structure, and Electrochemical Properties of the Cubic Mg2MnO4 Spinel with Porous-Spongy Structure. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ji, P.; Han, X. Rheological phase synthesis of nanosized α-LiFeO2 with higher crystallinity degree for cathode material of lithium-ion batteries. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2016, 183, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabuuchi, N.; Takeuchi, M.; Komaba, S.; Ichikawa, S.; Ozaki, T.; Inamasu, T. Li1.3Nb0.3V0.4O2 as a positive electrode material for rechargeable lithium batteries. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 2051–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabuuchi, N.; Nakayama, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Komaba, S.; Hashimoto, Y.; Mukai, T.; Shiiba, H.; Sato, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nakao, A.; et al. Origin of stabilization and destabilization in solid-state redox reaction of oxide ions for lithium-ion batteries. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuma, R.; Harada, M.; Zhao, W.; Sawamura, M.; Noda, Y.; Nakayama, M.; Goto, M.; Kan, D.; Shimakawa, Y.; Yonemura, M.; et al. Unexpectedly Large Contribution of Oxygen to Charge Compensation Triggered by Structural Disordering: Detailed Experimental and Theoretical Study on a Li3NbO4–NiO Binary System. ACS Cent. Sci. 2022, 8, 775–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramana, C.V.; Massot, M.; Julien, C.M. XPS and Raman spectroscopic characterization of LiMn2O4 spinels. Surf. Interface Anal. 2005, 37, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Chu, B.; Wang, C.; Huang, T.; Yu, A. Dynamic evolution of Cathode−Electrolyte interface of LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 during the initial Charge−Discharge process. J. Power Sources 2019, 438, 226979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, R.; Lindgren, F.; Stokes-Rodriguez, K.; Buga, M.; Ungureanu, C.; Gouveia, T.; Christensen, I.; Pal, S.; Vlad, A.; Ladam, A.; et al. An XPS Study of Electrolytes for Li-Ion Batteries in Full Cell LNMO vs Si/Graphite. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 34266–34280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, S.; Ueno, M.; Uebou, Y.; Yamaki, J. Fluoride phosphate Li2CoPO4F as a high-voltage cathode in Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2005, 146, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.; Gover, R.K.B.; Burns, P.; Bryan, A.; Saidi, M.Y.; Swoyer, J.L. Structural and electrochemical properties of lithium vanadium fluorophosphate, LiVPO4F. J. Power Sources 2005, 146, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).