The Impact of Industrial Robots on Energy Efficiency: Evidence from Chinese Cities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background and Hypotheses
2.1. Literature Review
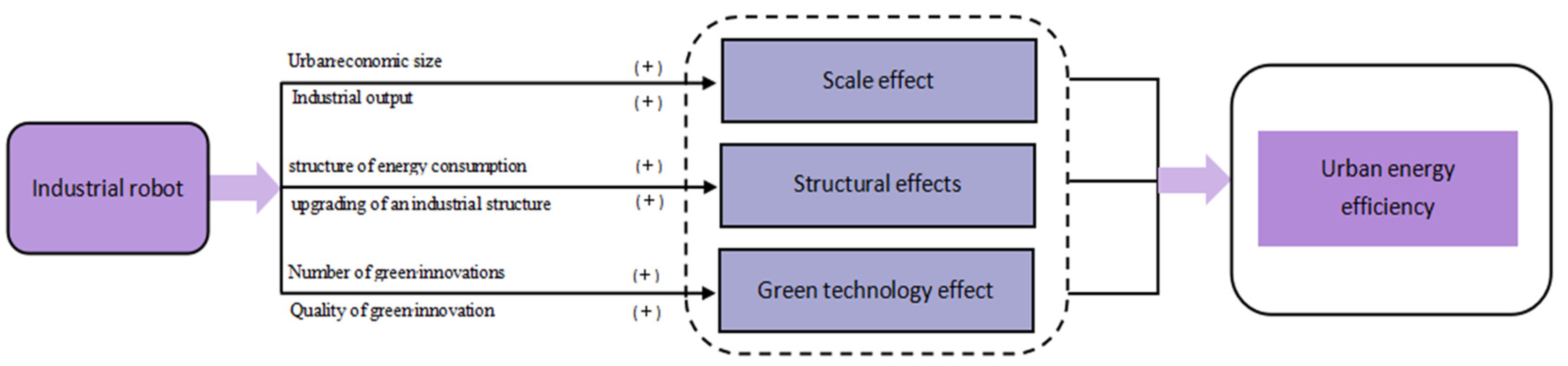
2.2. Research Hypothesis
3. Methodology and Data
3.1. Empirical Modeling
3.2. Variables
3.2.1. Dependent Variable
3.2.2. Independent Variable
- Stage 1: Baseline Employment Structure Calibration
- Stage 2: Industry-Adjusted Penetration Rate
- Stage 3: City-Level Stock Aggregation
3.2.3. Control Variables
3.3. Data Sources and Processing
4. Results
4.1. Baseline Regression Analysis
4.2. Robustness Checks
4.2.1. Replacement of Independent Variable Measures
4.2.2. Lagged One-Period Regression Treatment
4.2.3. Excluding Megacities
4.3. Endogeneity Test
4.4. Heterogeneity Analysis
4.4.1. Innovative Cities
4.4.2. Geographically Differentiated Development
4.4.3. Level of Human Capital
4.5. Analysis of Mechanisms
4.5.1. Scale Effect Test
4.5.2. Structural Effects
4.5.3. Green Technology Effect
5. Discussion
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Policy Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Index Code | Variable | Definition | Data Source | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable | ||||
| lnCCR | Total factor energy efficiency | The measurement was performed using the ultra-efficient CCR-DEA model | China Urban Statistical Yearbook, China Industrial Statistical Yearbook, China Environmental Statistical Yearbook, China Energy Statistical Yearbook | [29] |
| Independent variable | ||||
| lnRobot | Industrial robot penetration rate | Municipal per capita robot stock (per 100 people) | China Customs Database, Official Database of International Federation of Robotics (IFR) | [24] |
| Control variable | ||||
| lnGdp | Level of economic development | Per capita GDP | China Urban Statistical Yearbook | [67] |
| lnEdu | Educational status, education, or training received | The number of college students per 10,000 people | China Urban Statistical Yearbook | [56] |
| lnFdi | Actual use of foreign capital | The proportion of foreign capital actually used in GPT | China Urban Statistical Yearbook | [43] |
| lnPop | Population size | Total population of prefecture-level cities at the end of the year | China Urban Statistical Yearbook | [43] |
| lnGov | Extent of Government Intervention | Ratio of government budget expenditure to budget revenue | China Urban Statistical Yearbook | [45] |
| lnIS | Industrial structure | The proportion of added value of the secondary industry out of the total industrial added value | China Urban Statistical Yearbook, China Industrial Statistical Yearbook, Wind Database | [24] |
| Mechanism variable | ||||
| lnCapsto | Economies of scale | Stock of capital | China Urban Statistical Yearbook | [42] |
| lnIov | Industrial scale | Location entropy of total industrial output value in each region | China Urban Statistical Yearbook, China Industrial Statistical Yearbook | [33] |
| lnEcs | Energy structure | The proportion of clean energy consumption out of the total energy consumption | China Energy Statistical Yearbook, China Environmental Statistical Yearbook | [45,51] |
| lnAis | Quality structure | Upgrading of industrial structure | China Industrial Statistical Yearbook, China Urban Statistical Yearbook, Wind Database | [55] |
| lnGrepap | Number of green innovations | Green patent applications | China Urban Statistical Yearbook, National Intellectual Property Patent Database | [56] |
| lnGrepau | Quality of green innovation | Green patent authorization | China Urban Statistical Yearbook, National Intellectual Property Patent Database | [56] |
| Instrumental variable | ||||
| Five countries import | Five countries’ import of industrial robots | Computational aggregation of mean diffusion intensities from the predominant source countries | China Customs Database | [58] |
References
- BP. BP Statistical Review of World Energy 2019. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/business-sites/en/global/corporate/pdfs/energy-economics/statistical-review/bp-stats-review-2019-full-report.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwjz__HI1bmQAxXHrlYBHa43B2oQFnoECAwQAQ&usg=AOvVaw2-4FHh1TLr436eLRPP9jn7 (accessed on 3 March 2024).
- International Energy Agency (IEA). World Energy Statistics 2022; IEA: Paris, France, 2022. Available online: https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics (accessed on 8 March 2024).
- Acemoglu, D.; Restrepo, P. Robots and jobs: Evidence from US labour markets. J. Political Econ. 2020, 128, 2188–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhuang, Y.; Chen, Y. How does artificial intelligence affect pollutant emissions by improving energy efficiency and developing green technology. Energy Econ. 2024, 131, 107355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Council of the People’s Republic of China. The 13th Five-Year Plan for Economic and Social Development of the People’s Republic of China (2016–2020). Available online: https://en.ndrc.gov.cn/policies/202105/P020210527785800103339.pdf (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Liu, L.; Rasool, Z.; Ali, S.; Wang, C.; Nazar, R. Robots for sustainability: Evaluating ecological footprints in leading AI-driven industrial nations. Technol. Soc. 2024, 76, 102460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Teng, R.; Feng, D.; Gai, J. Industrial robots and pollution: Evidence from Chinese enterprises. Econ. Anal. Policy 2024, 82, 629–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Federation of Robotics (IFR). World Robotics 2024: Industrial Robots [and/or Service Robots]. Available online: https://ifr.org/ (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Shahbaz, M.; Siddiqui, A.; Ahmad, S.; Jiao, Z. Financial development as a new determinant of energy diversification: The role of natural capital and structural changes in Australia. Energy Econ. 2023, 126, 106926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomazzoli, C.; Scannapieco, S.; Cristani, M. Internet of things and artificial intelligence enable energy efficiency. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2023, 14, 4933–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, Y.; Fan, D.; Li, Y.; Shao, X.F.; Zheng, J. Alleviating corporate environmental pollution threats toward public health and safety: The role of smart city and artificial intelligence. Saf. Sci. 2021, 143, 105433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Wang, Y. Does energy-saving and emission reduction policy affects carbon reduction performance? A quasi-experimental evidence in China. Appl. Energy 2022, 324, 119758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sękala, A.; Blaszczyk, T.; Foit, K.; Kost, G. Selected issues, methods, and trends in the energy consumption of industrial robots. Energies 2024, 17, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhu, N.; Lv, J.; Luo, S. Industrial robot applications’ effects on consumption of energy and its spatial effects. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2025, 27, 14365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Qi, X.; Xu, M.; Su, J.; Wang, Z. Digital finance, industrial structure upgrading, and energy efficiency in China: A provincial-level empirical analysis. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2025, 12, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhong, N.; Tu, X.; Jia, J.; Wang, J. Tackling environmental challenges in pollution controls using artificial intelligence: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yan, J. A data-driven method for optimising the energy consumption of industrial robots. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, A.; Ahmad, K. A review on emerging artificial intelligence (AI) techniques for air pollution forecasting: Fundamentals, application and performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 322, 129072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Ma, D. Artificial intelligence and green development well-being: Effects and mechanisms in China. Energy Econ. 2025, 141, 108094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerkle, A.; Eaton, W.; Al-Yacoub, A.; Zimmer, M.; Kinnell, P.; Henshaw, M.; Lohse, N. Towards industrial robots as a service (IRaaS): Flexibility, usability, safety and business models. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2023, 81, 102484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, R.; Gunasekar, S.; Kaliyaperumal, D.; Nedungadi, P. Navigating the Nexus of Artificial Intelligence and Renewable Energy for the Advancement of Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merabet, G.H.; Essaaidi, M.; Haddou, M.B.; Qolomany, B.; Qadir, J.; Anan, M.; Benhaddou, D. Intelligent building control systems for thermal comfort and energy-efficiency: A systematic review of artificial intelligence-assisted techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 144, 110969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Zeng, C. Towards low-carbon development: The role of industrial robots in decarbonisation in Chinese cities. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xuan, Y. How does intelligence improve regional energy efficiency. Empirical test based on provincial panel data in China. Bus. Manag. J. 2022, 44, 27–46. [Google Scholar]
- Xuefei, H.; Li, L.; Jun, W. Spatial Spillover Effects of Innovation Drive on Economy-Energy-Environment Coupling Coordination Development—Based on Provincial Panel Data and Spatial Durbin Models. Manag. Rev. 2021, 33, 113. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Cifuentes-Faura, J.; Yang, X.; Pan, J. The green innovation effect of industrial robot applications: Evidence from Chinese manufacturing companies. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2025, 210, 123904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Kong, Z.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. Pathways to stable economic policy: The role of industrial robotics and energy transition. Renew. Energy 2025, 244, 122751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, A.; Han, M.; Veglianti, E. Carbon emission reduction effects of industrial robot applications: Heterogeneity characteristics and influencing mechanisms. Technol. Soc. 2022, 70, 102034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F.; Mohsin, M. Role of artificial intelligence on green economic development: Joint determinates of natural resources and green total factor productivity. Resour. Policy 2023, 82, 103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Jiang, H.; Adebayo, T.S.; Awosusi, A.A.; Razzaq, A. Asymmetric effects of high-tech industry and renewable energy on consumption-based carbon emissions in MINT countries. Renew. Energy 2022, 196, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, T.S.; Kartal, M.T.; Ullah, S. Role of hydroelectricity and natural gas consumption on environmental sustainability in the United States: Evidence from novel time-frequency. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 328, 116987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Lim, D.G. Industrial robots, employment growth, and labour cost: A simultaneous equation analysis. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 159, 120202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Ye, X.; Li, J.; Yang, J. How does artificial intelligence affect the transformation of China’s green economic growth? An analysis from internal-structure perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; He, L.Y.; Lin, X. Robot adoption and energy performance: Evidence from Chinese industrial firms. Energy Econ. 2022, 107, 105837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Lin, W. Does the application of industrial robots overcome the Solow paradox? Evidence from China. Technol. Soc. 2022, 68, 101932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Han, M.; Shen, Y. Technology-driven energy revolution: The impact of digital technology on energy efficiency and its mechanism. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1242580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzarovsky, R.; Horak, T.; Bocak, R. Evaluating Energy Efficiency and Optimal Positioning of Industrial Robots in Sustainable Manufacturing. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 8, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hu, Y.; Karuppiah, M.; Kumar, P.M. Artificial intelligence on economic evaluation of energy efficiency and renewable energy technologies. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 47, 101358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, L.; Lee, C.C. How does the use of industrial robots affect the ecological footprint? International evidence. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 198, 107483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.T.; Tan, Y.M.; Zhao, J.Y. Research on trajectory planning of robotic arm of hydraulic rock drilling robot. Chin. J. Constr. Mach. 2021, 19, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, K. Agglomeration economy, urban productivity and optimal scale. Stat. Decis. 2022, 38, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, R.R.; Xiao, X.T. The impact of industrial intelligence on urban green eco-efficiency: An empirical study based on industrial robot data. Contemp. Econ. Res. 2023, 338, 98–113. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J.; Huang, Q.; Su, T. How enterprise intelligence impacts green development efficiency–evidence from industrial robot applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 522, 146396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q. Analysis of the impact of factor agglomeration on urban energy efficiency from the perspective of industrial linkage. Low Carbon World 2024, 14, 166–168. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.C.; Qin, S.; Li, Y. Does industrial robot application promote green technology innovation in the manufacturing industry? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 183, 121893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wei, T.; Affuso, E. Credit constraints and energy efficiency: Evidence from manufacturing firms. Energy Effic. 2025, 18, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yong, S.K. Management practices and energy efficiency: Evidence from firms in China. J. Comp. Econ. 2024, 52, 848–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, S.; Shen, Z.; Song, M.; Zhu, Z. Impact of sulfur dioxide emissions trading pilot scheme on pollution emissions intensity: A study based on the synthetic control method. Energy Policy 2022, 161, 112730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, D.E.; Prettner, K.; Saadaoui, J.; Veruete, M. Artificial intelligence and the skill premium. Financ. Res. Lett. 2025, 81, 107401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Yang, L. The Impact of Public Data Openness on Urban Energy Efficiency: Evidence from Chinese Cities. J. Ind. Technol. Econ. 2025, 44, 66–76. [Google Scholar]
- Pengfei, Z.; Mengyu, H.; Yang, S. Impact of Intelligent Manufacturing on Total-Factor Energy Efficiency: Mechanism and Improvement Path. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hao, Y.; Ren, S. How do environmental regulation and environmental decentralization affect green total factor energy efficiency: Evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2020, 91, 104880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Ma, S.; Yao, S. How does artificial intelligence enhance carbon productivity?—Mechanism pathways and threshold effects from a multidimensional perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 13, 1603633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Han, X. Has digital technology innovation improved urban total factor energy efficiency?—Evidence from 282 prefecture-level cities in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 378, 124784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Liu, H. Global value chain embeddedness, industrial structure upgrading and urban carbon emission efficiency: Empirical evidence from prefecture-level cities in China. Technol. Econ. Manag. Res. 2023, 194, 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, B.; Gu, R.; Wang, P.; Hu, Y. How Does New Quality Productive Forces Affect Green Total Factor Energy Efficiency in China? Consider the Threshold Effect of Artificial Intelligence. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Huang, Z.; Wu, J.; Güneri, F.; Shen, Z.Y.; Yu, C. Harnessing the power of industrial robots for green development: Evidence from China’s manufacturing industry. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2025, 215, 124099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, Z.; Li, J. Research on the Environmental Effects and Mechanisms of Industrial Intelligent Transformation. Nankai Econ. Stud. 2023, 11, 186–209. [Google Scholar]
- Badareu, G.; Doran, M.D.; Firu, M.A.; Croitoru, I.M.; Doran, N.M. Exploring the Role of Robots and Artificial Intelligence in Advancing Renewable Energy Consumption. Energies 2024, 17, 4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency. World Energy Outlook 2022; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2022; Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-outlook-2022 (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Mohsin, J. Robots, Natives and Immigrants in US local labor markets. Labour Econ. 2023, 85, 102456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boqiang, L.; Chonghao, W. Does industrial relocation affect green total factor energy efficiency? Evidence from China’s high energy-consuming industries. Energy 2024, 289, 130002. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.L.; Liu, H.D.; Wang, R.Z.; Yan, S.Z.; Cui, L.Y. Comprehensive efficiency evaluation of integrated energy system based on cross-efficiency super-efficiency CCR model. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2020, 44, 78–86. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Yang, K.; Fujii, H.; Liu, J. Artificial intelligence and energy intensity in China’s industrial sector: Effect and transmission channel. Policy 2021, 70, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Y. Do industrial robots optimize the energy structure? Evidence from fossil energy consumption. Energy Econ. 2025, 148, 108638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Su, Z. The Application of Industrial Robot and the High-Quality Development of Manufacturing Industry: From a Sustainability Perspective. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendao, Y.; Yilan, Z. The dynamic impact of industrial robot penetration on chain resilience: City evidence from China. Systems 2025, 13, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Yu, D. How robot application empowers industrial low-carbon development: A study based on the perspective of carbon reduction and efficiency enhancement. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2025, 220, 124301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Su, S. Comparison of industrial structure optimization paths under environmental regulation: Efficiency improvement or structure improvement? Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2025, 102, 104297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fan, Z.; Yao, D. The impact of industrial robot on green total factor energy efficiency under the “resource curse” perspective: Evidence from cities in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 385, 125641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Ti, J.; Yang, F.; Chen, H.H. Blessing or Curse? The Impact of the Penetration of Industrial Robots on Green Sustainable Transformation in Chinese High-Energy-Consuming Industries. Energies 2025, 18, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.Z.; Lee, C.C.; Li, Y. Assessing the impact of industrial robots on manufacturing energy intensity in 38 countries. Energy Econ. 2022, 105, 105748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.J.; Wang, X.J.; He, Y.T. Industrial agglomeration and pollution emission intensity: A re-examination based on a fixed-effect threshold regression model. J. Ind. Technol. Econ. 2017, 36, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Said, R.; Ismail, N.W.; Haris, A.; Hamzah, H.Z. Impact of population ageing on the application of industrial robots: Evidence from China. J. Econ. Ageing 2024, 29, 100529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| VarName | Obs | Mean | SD | Min | Median | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnCCR | 3384 | 0.436 | 0.088 | 0.255 | 0.428 | 0.690 |
| lnRobot | 3384 | 0.261 | 0.809 | 0.001 | 0.092 | 24.162 |
| lnGdp | 3384 | 15.328 | 1.205 | 11.805 | 15.174 | 19.504 |
| lnEdu | 3384 | 5.809 | 0.996 | 0.400 | 5.909 | 8.027 |
| lnFdi | 3384 | 11.674 | 2.035 | 3.057 | 11.807 | 16.835 |
| lnPop | 3384 | 4.660 | 0.779 | 2.779 | 4.587 | 7.816 |
| lnGov | 3384 | 2.800 | 0.449 | 0.704 | 2.787 | 5.603 |
| lnIS | 3384 | 0.024 | 0.027 | 0.000 | 0.015 | 0.261 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnCCR | Installations | Lagging Quantity | Excluding Special Large Cities | Endogeneity Test | |
| lnRobot | 0.004 ** | 0.074 *** | 0.006 *** | 0.004 ** | 0.016 ** |
| (0.002) | (0.021) | (0.002) | (0.002) | (0.007) | |
| lnGdp | 0.045 *** | 0.041 *** | 0.046 *** | 0.045 *** | 0.063 *** |
| (0.008) | (0.008) | (0.008) | (0.008) | (0.013) | |
| lnEdu | −0.011 *** | −0.011 *** | −0.01 ** | −0.011 *** | −0.012 *** |
| (0.004) | (0.004) | (0.004) | (0.004) | (0.004) | |
| lnFdi | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | |
| lnPop | −0.054 *** | −0.052 *** | −0.056 *** | −0.054 *** | −0.063 *** |
| (0.008) | (0.008) | (0.008) | (0.008) | (0.009) | |
| lnGov | −0.003 | −0.001 | −0.004 | −0.003 | −0.004 |
| (0.004) | (0.004) | (0.004) | (0.004) | (0.004) | |
| lnIS | 0.641 *** | 0.676 *** | 0.584 *** | 0.641 *** | 0.662 *** |
| (0.119) | (0.121) | (0.133) | (0.119) | (0.115) | |
| constant | 0.000 | 0.001 | −0.029 | −0.04 | −0.244 |
| (0.154) | (0.105) | (0.109) | (0.100) | (0.154) | |
| Observations | 3168 | 3168 | 2904 | 3168 | 3168 |
| R-squared | 0.773 | 0.777 | 0.779 | 0.777 | 0.773 |
| KP rk LM statistic | / | / | / | / | 59.43 |
| p-value | / | / | / | / | 0.000 |
| KP rk Wald F stat | / | / | / | / | 62.73 |
| Hansen J statistic | / | / | / | / | 0.000 |
| city fe | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| year fe | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Innovative City = 0 | Innovative City = 1 | Midwest | East | Student Enrolment in Colleges = 0 | Student Enrolment in Colleges = 1 | |
| lnRobot | 0.005 *** | −0.068 *** | 0.006 *** | −0.001 | 0.005 ** | 0.001 |
| (0.002) | (0.017) | (0.002) | (0.013) | (0.002) | (0.008) | |
| lnGdp | 0.048 *** | 0.078 *** | 0.052 *** | 0.024 | 0.049 *** | 0.045 *** |
| (0.009) | (0.021) | (0.009) | (0.015) | (0.01) | (0.012) | |
| lnEdu | −0.006 | −0.079 *** | −0.008 * | −0.012 | 0.001 | −0.036 *** |
| (0.004) | (0.022) | (0.005) | (0.009) | (0.005) | (0.010) | |
| lnFdi | 0.000 | 0.001 | −0.002 | 0.011 *** | −0.001 | 0.005 ** |
| (0.001) | (0.003) | (0.001) | (0.002) | (0.002) | (0.002) | |
| lnPop | −0.051 *** | −0.133 *** | −0.06 *** | −0.044 *** | −0.055 *** | −0.077 *** |
| (0.008) | (0.028) | (0.009) | (0.015) | (0.011) | (0.013) | |
| lnGov | −0.001 | 0.01 | −0.001 | −0.011 * | 0.006 | −0.013 *** |
| (0.004) | (0.009) | (0.004) | (0.006) | (0.005) | (0.005) | |
| lnIS | 0.107 | −0.386 ** | 1.101 *** | −0.017 | 0.672 | 0.463 *** |
| (0.241) | (0.163) | (0.170) | (0.167) | (0.483) | (0.133) | |
| constant | −0.102 | 0.213 | −0.1 | 0.204 | −0.143 | 0.46 ** |
| (0.110) | (0.396) | (0.122) | (0.200) | (0.132) | (0.183) | |
| Observations | 2731 | 437 | 2256 | 912 | 1584 | 1584 |
| R-squared | 0.774 | 0.890 | 0.779 | 0.760 | 0.768 | 0.818 |
| city fe | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| year fe | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Scale Effects | Structural Effects | Green Technology Effects | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) |
| lnCapsto | lnIov | lnEcs | lnAis | lnGrepap | lnGrepau | |
| lnRobot | 0.012 * | 0.052 *** | 0.009 * | 0.041 ** | 0.182 *** | 0.17 *** |
| (0.007) | (0.014) | (0.005) | (0.018) | (0.045) | (0.044) | |
| lnGdp | 0.256 *** | 0.865 *** | −0.008 | −0.624 *** | 0.537 *** | 0.519 *** |
| (0.028) | (0.071) | (0.016) | (0.047) | (0.069) | (0.069) | |
| lnEdu | 0.018 | 0.047 | −0.015 ** | −0.064 *** | 0.282 *** | 0.143 *** |
| (0.017) | (0.029) | (0.008) | (0.018) | (0.052) | (0.051) | |
| lnFdi | 0.043 *** | 0.063 *** | 0.004 | −0.002 | 0.037 *** | 0.034 ** |
| (0.004) | (0.009) | (0.002) | (0.005) | (0.014) | (0.014) | |
| lnPop | −0.153 *** | −0.389 *** | 0.036 ** | 0.195 *** | 0.256 *** | 0.033 |
| (0.030) | (0.062) | (0.017) | (0.042) | (0.082) | (0.081) | |
| lnGov | −0.004 | 0.139 *** | 0.003 | −0.020 | 0.132 *** | 0.114 *** |
| (0.012) | (0.027) | (0.008) | (0.016) | (0.036) | (0.037) | |
| lnIS | −1.395 *** | 1.325 | −0.262 | −3.806 *** | 5.009 *** | 3.886 *** |
| (0.361) | (0.894) | (0.267) | (0.397) | (0.869) | (0.795) | |
| constant | 11.378 *** | 2.516 *** | 0.080 | 7.703 *** | −9.673 *** | −7.506 *** |
| (0.352) | (0.880) | (0.205) | (0.565) | (0.923) | (0.887) | |
| Observations | 3163 | 2348 | 3108 | 3166 | 2112 | 2112 |
| R-squared | 0.981 | 0.976 | 0.572 | 0.889 | 0.954 | 0.958 |
| city fe | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Year fe | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buliesibaike, K.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J. The Impact of Industrial Robots on Energy Efficiency: Evidence from Chinese Cities. Energies 2025, 18, 5669. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215669
Buliesibaike K, Zhao Y, Wang J. The Impact of Industrial Robots on Energy Efficiency: Evidence from Chinese Cities. Energies. 2025; 18(21):5669. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215669
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuliesibaike, Kalixia, Yuhuan Zhao, and Jiayang Wang. 2025. "The Impact of Industrial Robots on Energy Efficiency: Evidence from Chinese Cities" Energies 18, no. 21: 5669. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215669
APA StyleBuliesibaike, K., Zhao, Y., & Wang, J. (2025). The Impact of Industrial Robots on Energy Efficiency: Evidence from Chinese Cities. Energies, 18(21), 5669. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215669






